Evaluation of Milled Titanium versus Laser Sintered Co-Cr Abutments on the Marginal Misfit in Internal Implant-Abutment Connection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Specimens
2.2. Fit Evaluation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gracis, S.; Michalakis, K.; Vigolo, P.; Vult von Steyern, P.; Zwahlen, M.; Sailer, I. Internal vs. external connections for abutments/reconstructions: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S6), 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraschini, V.; Poubel, L.A.; Ferreira, V.F.; Barboza Edos, S. Evaluation of survival and success rates of dental implants reported in longitudinal studies with a follow-up period of at least 10 years: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Guisado-Moya, B. Retrospective long-term evaluation of dental implants in totally and partially edentulous patients. Part I: Survival and marginal bone loss. Implant Dent. 2014, 23, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobilio, N.; Fasiol, A.; Franceschetti, G.; Catapano, S. Marginal vertical fit along the implant-abutment interface: A microscope qualitative analysis. Dent. J. 2016, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butignon, L.E.; de Almeida Basilio, M.; Sgavioli Santo, J.; Arioli Filho, J.N. Vertical misfit of single-implant abutments made from different materials under cycling loading. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Cehreli, M.C. The significance of passive framework fit in implant prosthodontics: Current status. Implant Dent. 2001, 10, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggini, N.; McManus, L.M.; Hermann, J.S.; Medina, R.U.; Oates, T.W.; Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D.; Meolloning, J.T.; Cochran, D.L. Persistent acute inflammation at the implant-abutment interface. J. Dent. Res. 2003, 82, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggini, N.; McManus, L.M.; Hermann, J.S.; Medina, R.; Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D.; Cochran, D.L. Peri-implant inflammation defined by the implant-abutment interface. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N.; Serment, I.B.; Gürler, N. Sealing capability and marginal fit of titanium versus zirconia abutments with different connection designs. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2019, 11, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Chowdhary, R.; Kumari, S. Microleakage at the different implant abutment interface: A systematic review. J. Clin. Diag. Res. 2017, 11, ZE10–ZE15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, M.; van Steenberghe, D. Bacterial colonization of the internal part of two-stage implants. An in vivo study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1993, 4, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, C.D.; Pita, M.S.; Santos Ede, S.; Monesi, N.; Pedrazzi, V.; Albuquerque Junior, R.F.; Ribeiro, R.F. Microbiome of titanium and zirconia dental implants abutments. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Haddad, E.; Gianni, A.B.; Mancini, G.E.; Cura, F.; Carinci, F. Implant-abutment leaking of replace conical connection Nobel Biocare® implant system. An in vitro study of the microbiological penetration from external environment to implant abutment space. Oral Implantol. 2016, 9, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jemt, T. Failures and complications in 391 consecutively inserted fixed prostheses supported by Brånemark implants in edentulous jaws: A study of treatment from the time of prosthesis placement to the first annual checkup. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1991, 3, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Goodacre, C.J.; Kan, J.Y.; Rungcharassaeng, K. Clinical complications of osseointegrated implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 8, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricasulo, R.; Malchiodi, L.; Ghensi, P.; Fantozzi, G.; Cucchi, A. The influence of implant-abutment connection to peri-implant bone loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofron, M.D.; Carstens, M.; Fu, C.; Wen, H.B. In vitro assessment of connection strength and stability of internal implant-abutment connections. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 65, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siadat, H.; Beyabanaki, E.; Mousavi, N.; Alikhasi, M. Comparison of fit accuracy and torque maintenance of zirconia and titanium abutments for internal tri-channel and external-hex implant connections. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumcu, E.; Erdinç, G. Implant abutment selection criteria. Acta Sci. Dent. Sci. 2018, 8, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Spinato, S.; Stacchi, C.; Lombardi, T.; Bernardello, F.; Messina, M.; Dovigo, S.; Zaffe, D. Influence of abutment height and vertical mucosal thickness on early marginal bone loss around implants. A randomized clinical trial with an 18-month post-loading clinical and radiographic evaluation. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2020, 13, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Spinato, S.; Stacchi, C.; Lombardi, T.; Bernardello, F.; Massina, M.; Zaffe, D. Biological width establishment around dental implants is influenced by abutment height irrespective of vertical mucosal thickness: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, K.; Vidyasshree, V. Direct metal laser sintering: A digitised metal casting technology. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2013, 13, 389–392. [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman, S.H.; Vult von Steyern, P. Fracture strength of porcelain fused to metal crowns made of cast, milled or laser-sintered cocal-chromium. Acta Odont. Scand. 2013, 71, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçin, E.T.; Güncü, M.B.; Aktas, G.; Aslan, Y. Effect of manufacturing techniques on the marginal and internal fit of cobalt-chromium implant-supperted multiunit frameworks. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revilla-León, M.; Sánchez-Rubio, J.L.; Pérez-López, J.; Rubenstein, J.; Özcan, M. Discrepancy at the implant abutment-prosthesis interface of complete-arch cobalt-chromium implant frameworks fabricated by additive and subtractive technologies before and after ceramic veneering. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikeli, A.; Walter, M.H. Impact of bruxism on ceramic defects in implant-borne fixed dental prostheses: A retrospective study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manfredini, D.; Ephraim Winocur, E.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Paesani, D.; Lobbezoo, F. Epidemiology of bruxism in adults: A systematic review of the literature. J. Orofac. Pain. 2013, 27, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo Kinalskia, M.; Gonzalez Cadermatoria, M.; Lessa Hortab, B.; Britto Correaa, M.; Fernando Demarcoa, F.; Pereira-Cencia, T. Common mental disorders and bruxism in adults: A birth cohort study. J. Dent. 2019, 83, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsü, S.S.; Aksan, M.E.; Bulut, A.C. Fracture resistance of titanium, zirconia, and ceramic-reinforced polyetheretherketone implant abutments supporting CAD/CAM monolithic lithium disilicate ceramic crowns after aging. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Rus, F.; Alberto Ferreiroa, A.; Mutlu Özcan, M.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Guillermo Pradíes, G. Fracture resistance of crowns cemented on titanium and zirconia implant abutments: A comparison of monolithic versus manually veneered all-ceramic systems. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.I.; Brewer, J.D.; Monaco, E.A., Jr. Comparison of fracture resistance of pressable metal ceramic custom implant abutments with CAD/CAM commercially fabricated zirconia implant abutments. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 101, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adell, R.; Lekholm, U.; Brånemark, P.I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1981, 10, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.E.; Zembic, A.; Pjetursson, B.; Zwahlen, M.; Thoma, D.S. Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical, and aesthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.K.; Heo, S.J.; Koak, J.Y. Marginal accuracy and internal fit of 3-D Printing laser-sintered Co-Cr alloy copings. Materials 2017, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, T.; Hagiwara, Y.; Matsumura, H. Marginal fit and microgaps of implant abutment interface with internal anti-rotation configuration. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De França, D.G.; Morais, M.H. Influence of CAD/CAM on the fit accuracy of implant-supported zirconia and cobalt-chromium fixed dental prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, J.; Peláez, J.; López-Suárez, C.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Tobar, C.; Suárez, M.J. Influence of implant connection, abutment design and screw insertion torque on implant-abutment misfit. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Torres, E.M.; Rodrigues, R.C.; de Mattos, M.G.; Ribeiro, R.F. The effect of commercially pure titanium and alternative dental alloys on the marginal fit of one-piece cast implant frameworks. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrucea Verdugo, C.; Jaramillo Nunez, G.; Acevedo Avila, A.; Larrucea San Martin, C. Microleakage of the prosthetic abutment/implant interface with internal and external connection: In vitro study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Pérez, R.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Ferreiroa, A.; Salido, M.P.; Pradíes, G. Evaluation of the mechanical behavior and marginal accuracy of stock and laser-sintered implant abutments. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, E.; Suarez, M.J.; Serrano, B.; Lozano, J.F. Comparative analysis of two measurement methods for marginal fit in metal-ceramic and zirconia posterior FDPs. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2009, 22, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abduo, J.; Lyons, K.; Bennani, V.; Waddell, N.; Swain, M. Fit of screw-retained fixed implant frameworks fabricated by different methods: A systematic review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 24, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kano, S.C.; Binon, P.P.; Curtis, D.A. A classification system to measure the implant-abutment microgap. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2007, 22, 879–885. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, N.A.; Turkyilmaz, I. Evaluation of the sealing capability of implants to titanium and zirconia abutments against Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, and Fusobacterium nucleatum under different screw torque values. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo, E.; Suarez, M.J.; Serrano, B.; Lozano, J.F. A comparison of the marginal vertical discrepancies of zirconium and metal ceramic posterior fixed dental prostheses before and after cementation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 102, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.R.; Bayne, S.C.; Holland, G.A.; Sulik, W.D. Considerations in measurement of margin fit. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawafleh, N.A.; Mack, F.; Evans, J.; Hatamleh, M.M. Accuracy and reliability of methods to measure marginal adaptation of crowns and FDPs: A literature review. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 22, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassino, G.; Barone Monfrin, S.; Scanu, M.; Spina, G.; Preti, G. Marginal adaptation of fixed prosthodontics: A new in vitro 360-degree external examination procedure. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Groten, M.; Axmann, D.; Pröbster, L.; Weber, H. Determination of the minimum number of marginal gap measurements required for practical in vitro testing. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 83, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarri, M.; Hjerppe, J.; Romeo, D.; Fickl, S.; Thompson, V.P.; Stappert, C.F.J. Marginal accuracy of three implant-ceramic abutment configurations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, M.; Delgado, L.; Molmeneu, M.; Garcia, D.; Rodriguez, D. Analysis of the misfit of dental implant-supported prostheses made with three manufacturing processes. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 111, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Han, C.; Wei, Q.; Wen, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y. Differences in microstructure and properties between selective laser melting and traditional manufacturing for fabrication of metal parts: A review. Front. Mech. Eng. 2015, 10, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Dong, Z.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Loh, L.E.; Sing, S.L. Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, L.; Ortorp, A.; Smedberg, J.I.; Jemt, T. Precision of fit to implants: A comparison of Cresco and Procera(R) implant bridge frameworks. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2010, 12, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
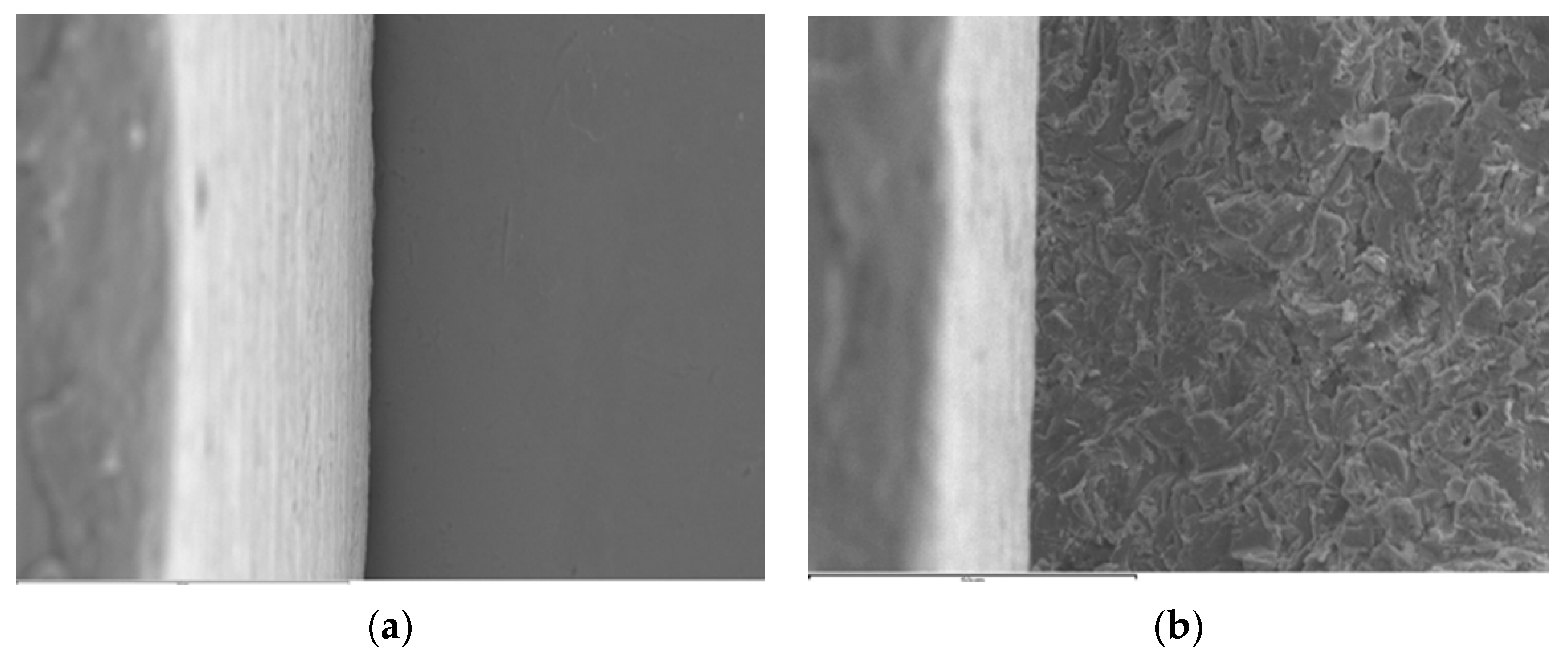
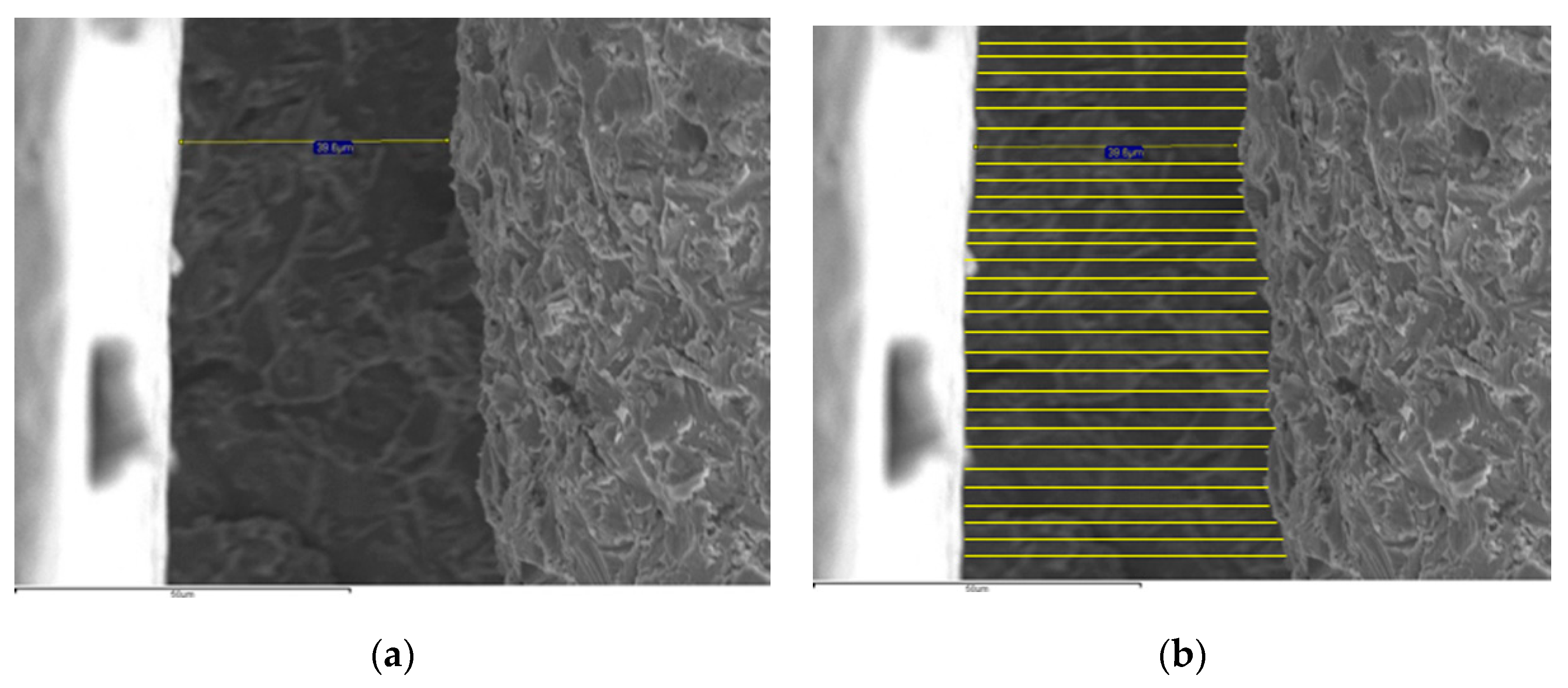

| Test Group | Implants | Implant Material | Connection Design | Implant Diameter × Length (mm) | Platform (mm) | Abutments | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM | Ocean IC STD | Ti grade V ELI | Internal hexagon | 4.5 × 11.5 (Ref.1592) | 4.1 | Aesthetic abutment 4.5 × 1 mm 1724 | Avinent Implant System SLU, Santpedor, Spain. |
| AS | Ocean IC STD | Ti grade V ELI | Internal hexagon | 4.5 × 11.5 (Ref.1592) | 4.1 | Scan abutment 2801 | Avinent Implant System SLU, Santpedor, Spain. |
| GM | HXI Tapered II | Ti grade IV | Internal hexagon | 4.5 × 12 (Ref.D11417) | 4.1 | Straight abutment 4.5 × 1.5 mm G100010 | GT Medical SL, Madrid, Spain. |
| GS | HXI Tapered II | Ti grade IV | Internal hexagon | 4.5 × 12 (Ref.D11417) | 4.1 | Scan Body E004409 | GT Medical SL, Madrid, Spain. |
| MM | InHex STD | Ti grade IV CP | Internal hexagon Internal morse connection | 3.75 × 11.5 (Ref.23203711) | 2.8 | STD Inhex prepable 4 × 1 mm 23207010 | Mozo Grau SA, Valladolid, Spain. |
| MS | InHex STD | Ti grade IV CP | Internal hexagon Internal morse connection | 3.75 × 11.5 (Ref.23203711) | 2.8 | Scanbody Inhex STD c/t 41236002 | Mozo Grau SA, Valladolid, Spain. |
| PM | TSADV S4 | Ti grade IV | Internal hexagon | 4.2 × 11.5 (Ref.04.115) | 4.7 | TSA S4 3.0 mm Abutment post 038.4030 | Phibo Group, Senmenant, Spain. |
| PS | TSADV S4 | Ti grade IV | Internal hexagon | 4.2 × 11.5 (Ref.04.115) | 4.7 | Scanbody 002-TSA34 | Phibo Group, Senmenant, Spain. |
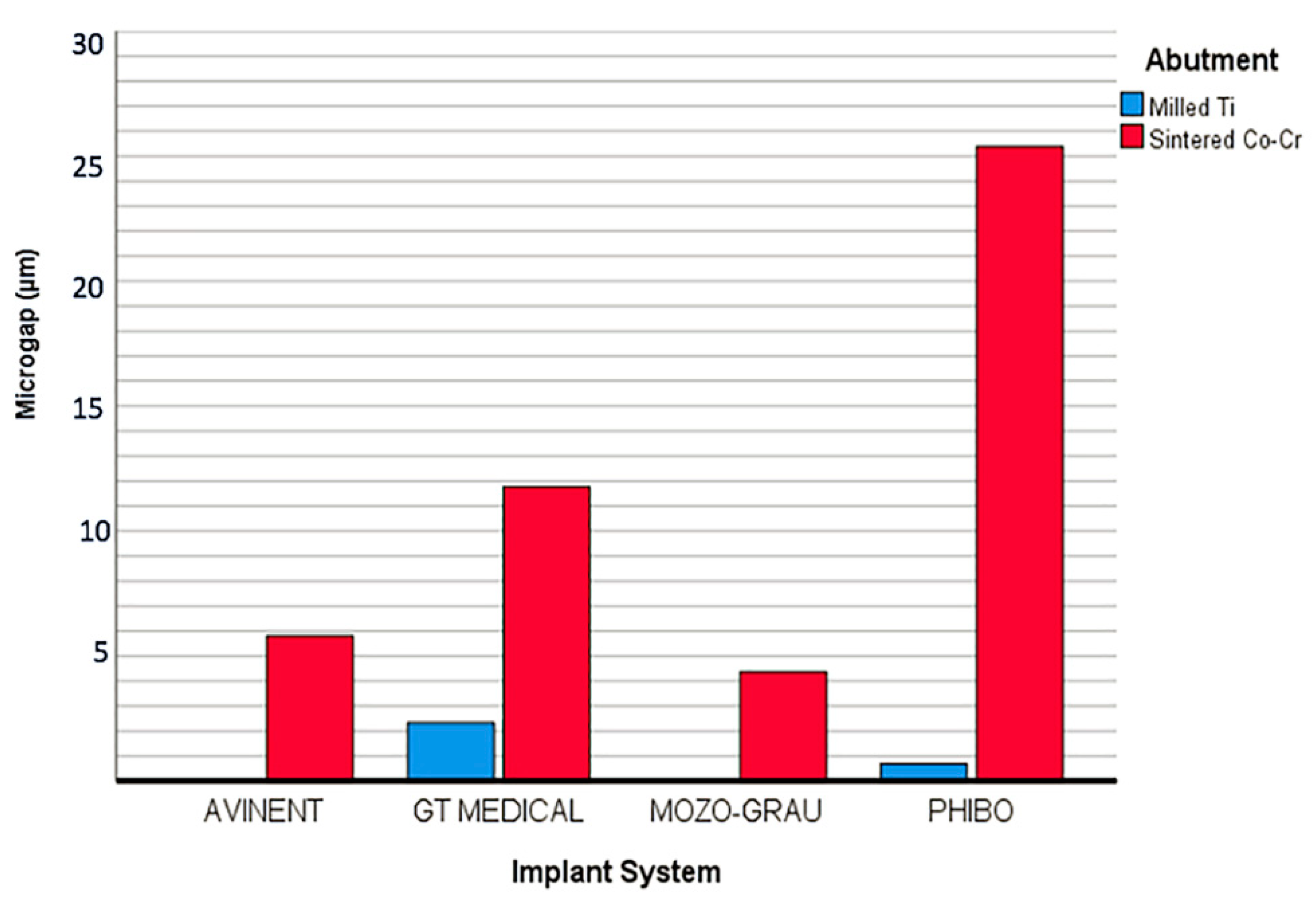
| Test Group | n | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVINENT (A) Santpedor, Spain | AM | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| AS | 10 | 5.81 | 10.29 | |
| GT MEDICAL (G) Madrid, Spain. | GM | 10 | 2.32 | 1.70 |
| GS | 10 | 11.77 | 12.41 | |
| MOZO GRAU (M) Valladolid, Spain. | MM | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | 10 | 4.36 | 6.29 | |
| PHIBO (P) Senmenant, Spain. | PM | 10 | 0.68 | 0.31 |
| PS | 10 | 25.38 | 12.27 | |
| x | Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances | t-Test for Equality of Means | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Sig. | f | df | Sig. (2-Tailed) | Mean Difference | Std. Error Difference | Lower | Upper | ||
| Marginal misfit | Equal variances assumed | 92.32 | 0.000 | 5.278 | 78 | 0.000 | 11.08050 | 2.0992937 | 6.9011273 | 15.2598727 |
| Equal variances not assumed | 5.278 | 39.724 | 0.000 | 11.08050 | 2.0992937 | 6.8367501 | 15.3242499 | |||
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected Model | 5249.839 a | 7 | 749.977 | 13.233 | 0.000 |
| Intercept | 3166.638 | 1 | 3166.638 | 55.872 | 0.000 |
| Abutment | 2455.550 | 1 | 2455.550 | 43.326 | 0.000 |
| Implant System | 1487.988 | 3 | 495.996 | 8.751 | 0.000 |
| Abutment-I mplant System | 1306.302 | 3 | 435.434 | 7.683 | 0.000 |
| Error | 4040.683 | 72 | 56.676 | – | – |
| Total | 12,497.160 | 80 | – | – | – |
| Corrected Total | 9330.523 | 79 | – | – | – |
| Dependent Variable: Marginal Discrepancy | 95% Confidence Interval for Difference b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abutment | Implant System (I) | Implant System (J) | Mean Difference (I−J) | Std. Error | Sig.b | Lower Bound | Upper Bound |
| Milled Ti | A | G | −2.325 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −11.459 | 6.809 |
| M | −3.553 × 10−15 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −9.134 | 9.134 | ||
| P | −0.680 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −9.814 | 8.454 | ||
| G | A | 2.325 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −6.809 | 11.459 | |
| G | 2.325 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −6.809 | 11.459 | ||
| M | 1.645 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −7.489 | 10.779 | ||
| M | A | −3.553 × 10−15 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −9.134 | 9.134 | |
| G | −2.325 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −11.459 | 6.809 | ||
| P | −0.680 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −9.814 | 8.454 | ||
| P | A | 0.680 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −8.454 | 9.814 | |
| G | −1.645 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −10.779 | 7.489 | ||
| M | 0.680 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −8.454 | 9.814 | ||
| Laser Sintered | A | G | −5.968 | 3.367 | 0.483 | −15.102 | 3.166 |
| M | 1.447 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −7.687 | 10.581 | ||
| P | −19.578 * | 3.367 | 0.000 | −28.712 | −10.444 | ||
| G | A | 5.968 | 3.367 | 0.483 | −3.166 | 15.102 | |
| M | 7.415 | 3.367 | 0.185 | −1.719 | 16.549 | ||
| P | −13.610 * | 3.367 | 0.001 | −22.744 | −4.476 | ||
| M | A | −1.447 | 3.367 | 1.000 | −10.581 | 7.687 | |
| G | −7.415 | 3.367 | 0.185 | −16.549 | 1.719 | ||
| P | −21.025 * | 3.367 | 0.000 | −30.159 | −11.891 | ||
| P | A | 19.578 * | 3.367 | 0.000 | 10.444 | 28.712 | |
| G | 13.610 * | 3.367 | 0.001 | 4.476 | 22.744 | ||
| M | 21.025 * | 3.367 | 0.000 | 11.891 | 30.159 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalo, E.; Vizoso, B.; Lopez-Suarez, C.; Diaz, P.; Pelaez, J.; Suarez, M.J. Evaluation of Milled Titanium versus Laser Sintered Co-Cr Abutments on the Marginal Misfit in Internal Implant-Abutment Connection. Materials 2020, 13, 4873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214873
Gonzalo E, Vizoso B, Lopez-Suarez C, Diaz P, Pelaez J, Suarez MJ. Evaluation of Milled Titanium versus Laser Sintered Co-Cr Abutments on the Marginal Misfit in Internal Implant-Abutment Connection. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214873
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalo, Esther, Beatriz Vizoso, Carlos Lopez-Suarez, Pedro Diaz, Jesus Pelaez, and Maria J. Suarez. 2020. "Evaluation of Milled Titanium versus Laser Sintered Co-Cr Abutments on the Marginal Misfit in Internal Implant-Abutment Connection" Materials 13, no. 21: 4873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214873
APA StyleGonzalo, E., Vizoso, B., Lopez-Suarez, C., Diaz, P., Pelaez, J., & Suarez, M. J. (2020). Evaluation of Milled Titanium versus Laser Sintered Co-Cr Abutments on the Marginal Misfit in Internal Implant-Abutment Connection. Materials, 13(21), 4873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214873







