Effects of Static Magnetic Field on Compression Properties of Mg-Al-Gd Alloys Containing Gd-Rich Ferromagnetic Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
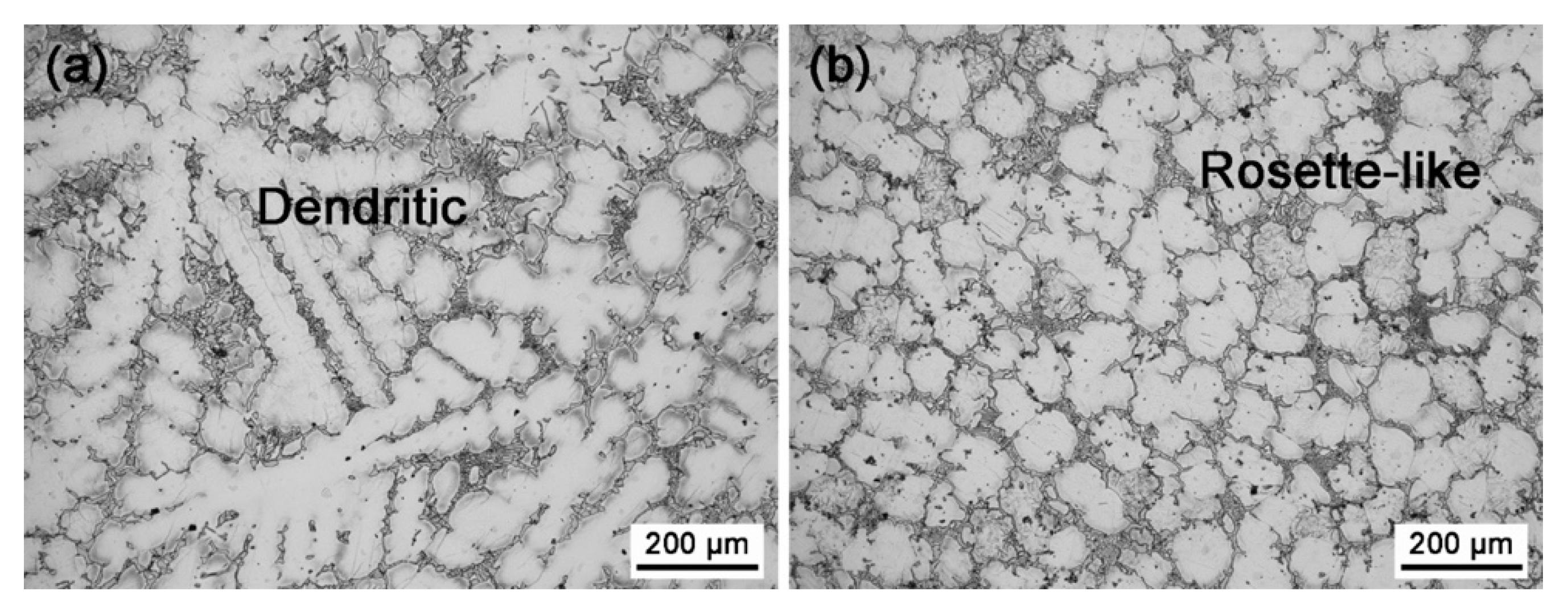
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
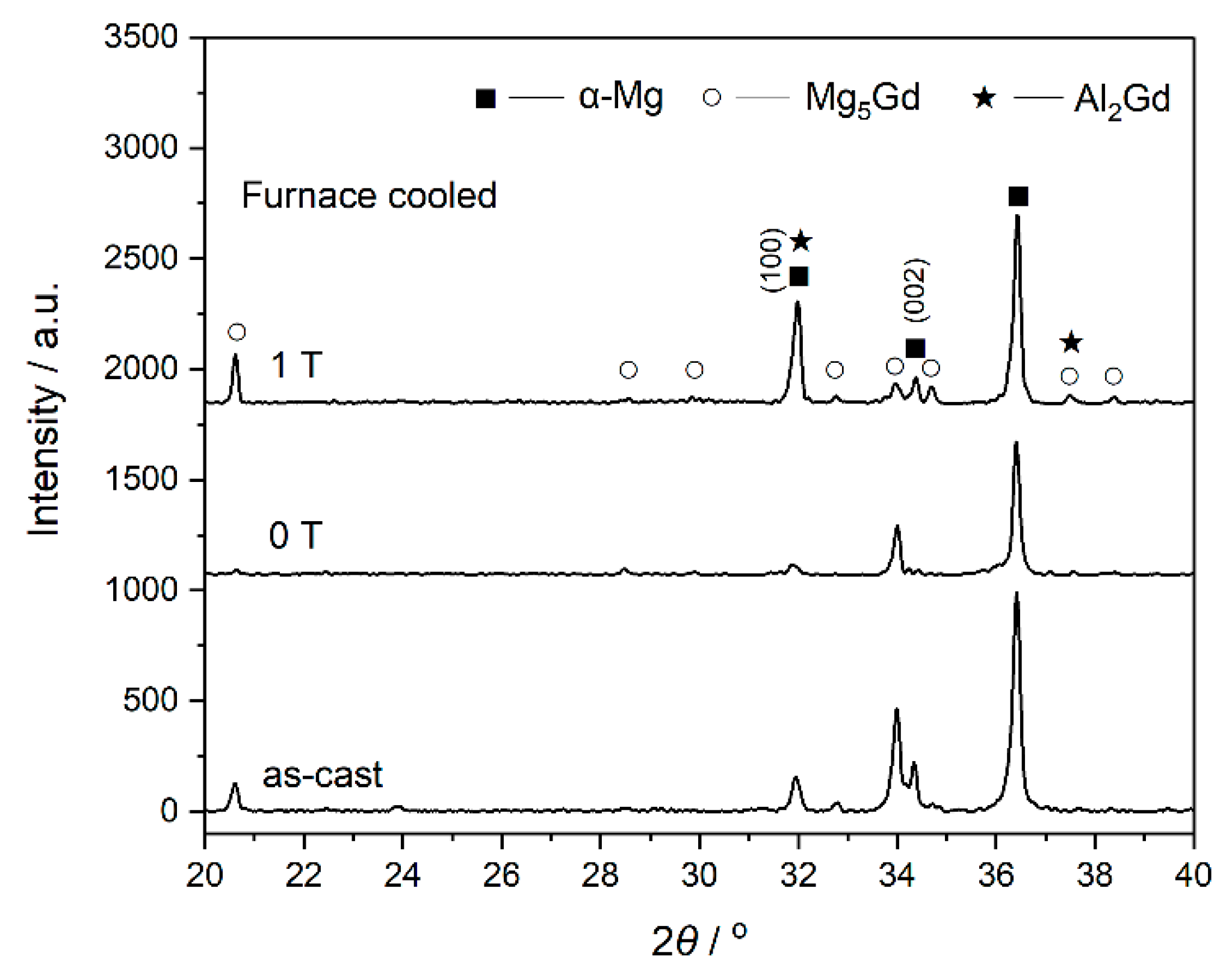
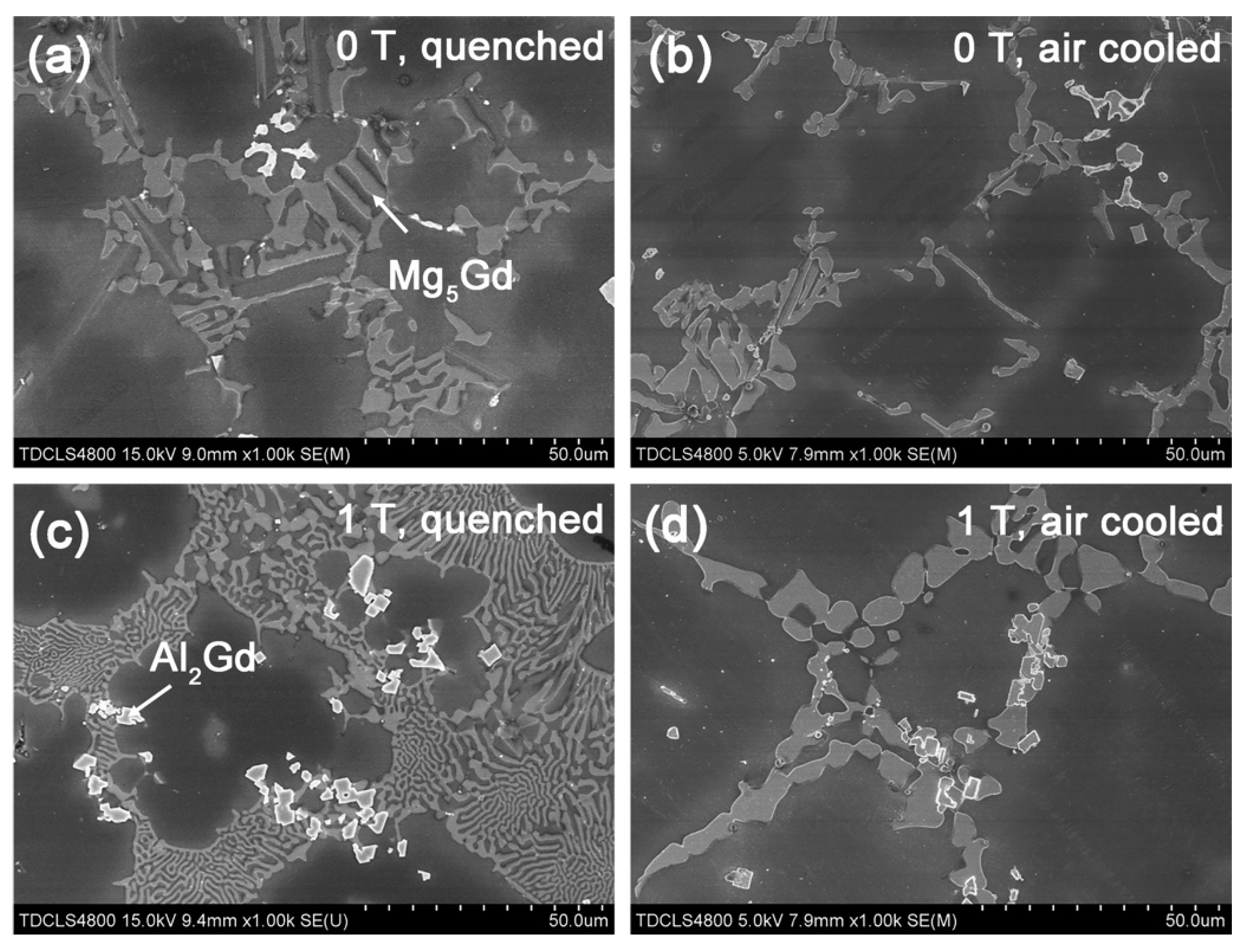
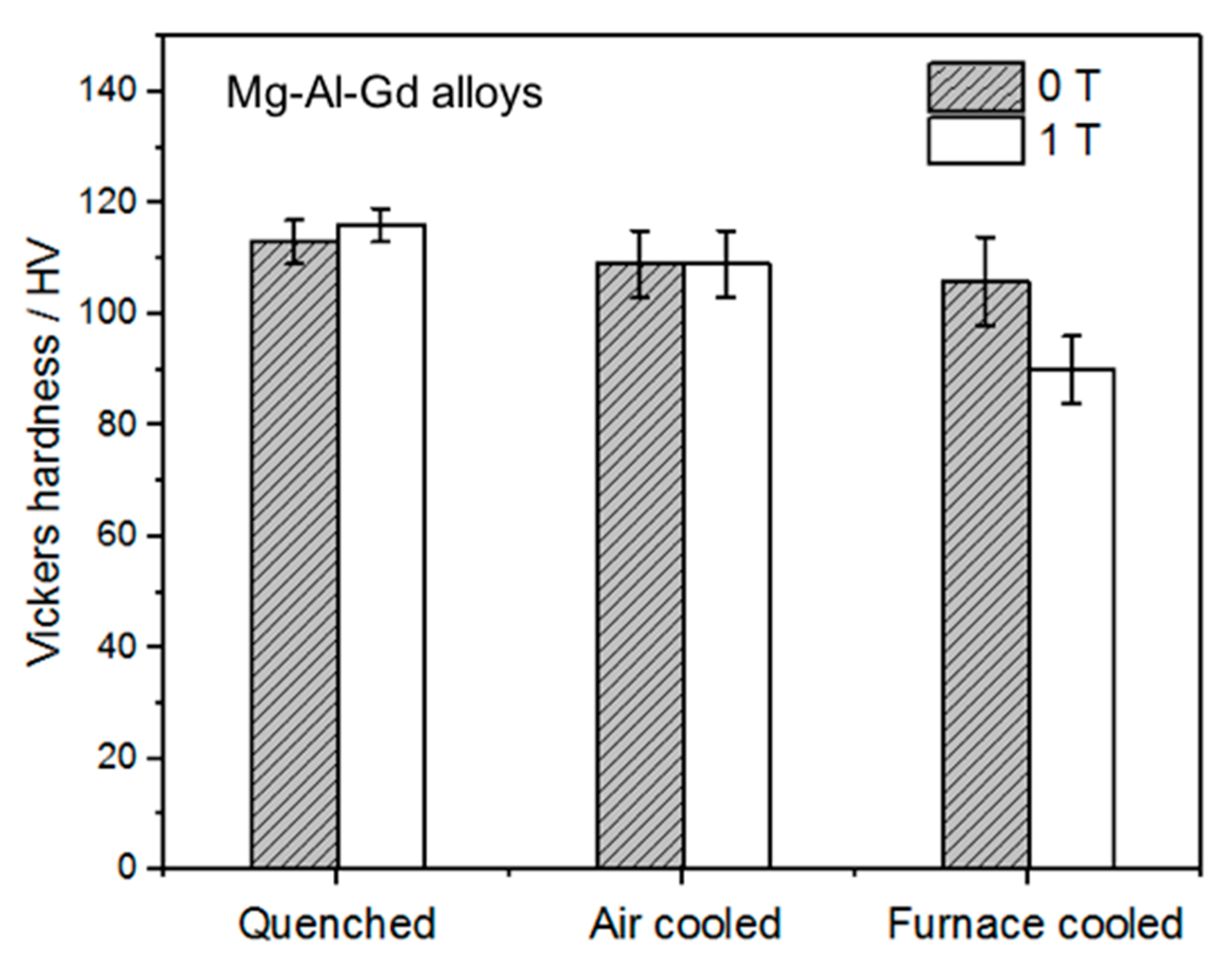
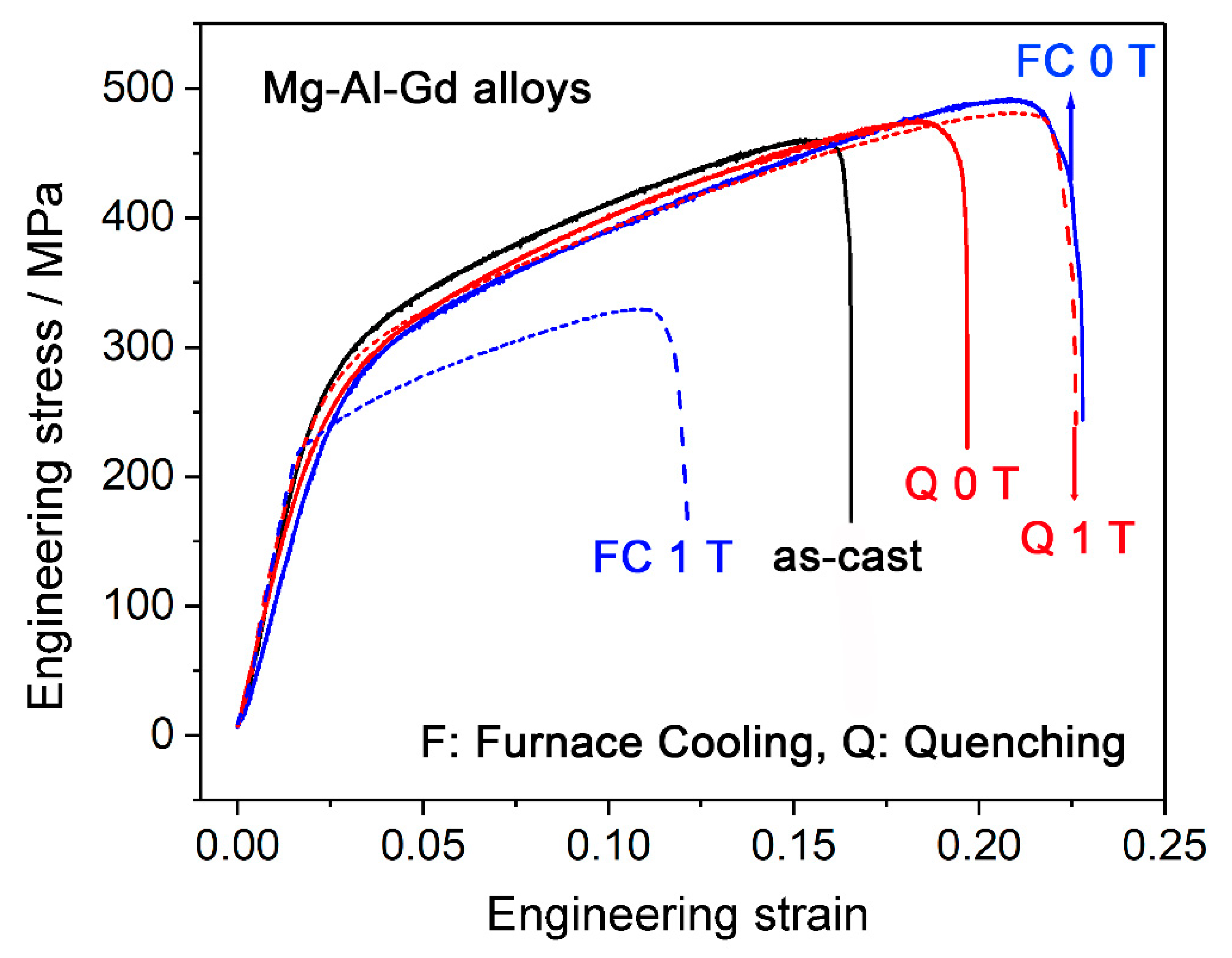
- By comparing the furnace-cooled alloys under 0 T and 1 T, it was found that the magnetic field resulted in the orientation of the (100) crystal faces instead of the (200) faces for the α-Mg grains, which led to the decrease of the hardness for the furnace-cooled alloy. The magnetic field accelerated the precipitation of the Mg5Gd phase upon cooling, and in return inhibited the precipitation of the Al2Gd phase. Although the Al2Gd particles were refined, the remained Al2Gd particles were driven to precipitate at the grain boundaries of the α-Mg phase by the magnetic field. Therefore, the precipitation strengthening was suppressed, and the mechanical properties of the furnace-cooled Mg–Al–Gd alloys under the magnetic field were decreased.
- (2)
- For the quenched alloys after homogenization under the magnetic field, no orientation of the α-Mg phase was identified. Although the content of the Mg5Gd phase was hardly changed in the alloys, the eutectic Mg5Gd laths were significantly refined by the magnetic field. In addition, the contents of the Al2Gd and GdH2 strengthening phases were increased in the alloy treated under 1 T, and the Al2Gd and GdH2 particles were still located within the α-Mg grains. Therefore, the hardness, compression strength, and ductility of the Mg–Al–Gd alloys were improved under the magnetic field, in contrast with the as-cast alloy, as well as the one without magnetic treatment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frankel, G.S. Magnesium alloys: Ready for the road. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1189–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, S.L.; Elsayed, A.; Ravindran, C. Inclusions in magnesium and its alloys: A review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.Y.; Shi, Z.M.; Song, G.-L.; Liu, M.; Atrens, A. Corrosion behaviour in salt spray and in 3.5% NaCl solution saturated with Mg(OH)2 of as-cast and solution heat-treated binary Mg-X alloys: X = Mn, Sn, Ca, Zn, Al, Zr, Si, Sr. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 60–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Meng, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, R. Development of Hot-Extruded Mg–RE–Zn Alloy Bar with High Mechanical Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Qi, W.; Wang, J.; Ju, P.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F. Influence of Rare Earth Element (Y) on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Hot Extrusion AZ91 Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, A.; Azzeddine, H.; Lachhab, R.; Baudin, T.; Helbert, A.-L.; Brisset, F.; Huang, Y.; Bradai, D.; Langdon, T.G. Evaluating the textural and mechanical properties of an Mg-Dy alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 778, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Zha, M.; Liu, S.; Yan, R.-F.; Wang, C. Effect of Ce Addition on Modifying the Microstructure and Achieving a High Elongation with a Relatively High Strength of As-Extruded AZ80 Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2018, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.; Grzybowska, A. Influence of phase composition on microstructure and properties of Mg-5Al-0.4Mn-xRE (x = 0, 3 and 5wt.%) alloys. Mater. Charact. 2016, 115, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Dai, J.; Guo, G.; Liu, Z. Effect of Ca and Sr on microstructure and compressive creep property of Mg–4Al–RE alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 610, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzychoń, T.; Kiełbus, A.; Lityńska-Dobrzyńska, L. Microstructure, microstructural stability and mechanical properties of sand-cast Mg–4Al–4RE alloy. Mater. Charact. 2013, 83, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yin, D.; Ye, B.; Jiang, H.; Ding, W. Microstructure refinement of Mg-Al-RE alloy by Gd addition. Mater. Lett. 2019, 246, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbahari, B.; Mirzadeh, H.; Emamy, M. Toward unraveling the effects of intermetallic compounds on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Gd–Al–Zn magnesium alloys in the as-cast, homogenized, and extruded conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbahari, B.; Mirzadeh, H.; Emamy, M. Elucidating the effect of intermetallic compounds on the behavior of Mg–Gd–Al–Zn magnesium alloys at elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 4186–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokobayashi, H.; Kishida, K.; Inui, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y. Enrichment of Gd and Al atoms in the quadruple close packed planes and their in-plane long-range ordering in the long period stacking-ordered phase in the Mg–Al–Gd system. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 7287–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Yokobayashi, H.; Inui, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y. The crystal structure of the LPSO phase of the 14H-type in the Mg–Al–Gd alloy system. Intermetallics 2012, 31, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Zhu, S.; Easton, M.A.; Xu, W.; Wu, G.; Ding, W. Precipitation process in a Mg–Gd–Y alloy grain-refined by Al addition. Mater. Charact. 2014, 88, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, S. Recent development and prospect of electromagnetic processing of materials. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2000, 1, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fautrelle, Y.; Ren, Z. Influence of thermoelectric effects on the solid–liquid interface shape and cellular morphology in the mushy zone during the directional solidification of Al–Cu alloys under a magnetic field. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3803–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, F.; Zhan, W.; Hu, P.H.; Zhou, Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloy under a steady magnetic field. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, G.; Ding, W. Preparation of an Mg–Gd–Zn alloy semisolid slurry by low frequency electro-magnetic stirring. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Q. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y alloy containing icosahedral quasicrystals phase treated by pulsed magnetic field. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 688, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Zhai, C.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Li, Q. Effects of magnetic field on the microstructure and mechanical property of Mg-Al-Gd alloys. Mater. Charact. 2019, 154, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z. Effect of gadolinium on microstructure and rolling capability of AZ31 alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 475, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbahari, B.; Emamy, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Synergistic effect of Al and Gd on enhancement of mechanical properties of magnesium alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2017, 27, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uporova, N.; Uporov, S.A.; Sidorov, V.E. Magnetic susceptibility and parameters of electronic structure of Al2REM (Gd, Dy, and Ho) intermetallic compounds at high temperatures. Russ. Phys. J. 2011, 54, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, L.P.; Xiao, C.B.; Tang, X. Effect of DC magnetic field on solidified structure, crystal texture and mechanical properties of Mg97Y2Cu1 alloy. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2016, 45, 933–938. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Fu, P.; Qian, S.; Fu, P.; Ding, W. Effects of intermediate frequency magnetic field on the solution treatment of Mg–Gd alloy. Mater. Lett. 2014, 123, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Olson, G.; Cohen, M. Homogeneous martensitic nucleation in Fe Co precipitates formed in a Cu matrix. Acta Met. Mater. 1993, 41, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde, P.; Hänzi, A.; Sologubenko, A.S.; Uggowitzer, P.J. High-strength magnesium alloys for degradable implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Kainer, K.U. Strain induced GdH2 precipitate in Mg–Gd based alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlček, M.; Čížek, J.; Lukáč, F.; Hruška, P.; Smola, B.; Stulíková, I.; Kudrnova, H.; Minarik, P.; Kmječ, T.; Vlasák, T. Hydrogen absorption in Mg-Gd alloy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 22598–22604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Li, X.-G.; Hirata, T.; Matsubara, E.; Waseda, Y.; Masumoto, T. A correlation between stability of compounds and structure of hydrogen-induced amorphous alloys in GdM2 (M = Fe, Co, Ni). Acta Met. Mater. 1993, 41, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Sabat, R.K.; Panda, S.; Mishra, S.C.; Suwas, S. Mechanical Property of Pure Magnesium: From Orientation Perspective Pertaining to Deviation from Basal Orientation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, V.; Stulikova, I.; Smola, B.; Mordike, B.L.; Vlach, M.; Bakkar, A.; Pelcova, J. Thermal stability and corrosion behaviour of Mg-Y-Nd and Mg-Tb-Nd alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 462, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H. Effect of Gd–Ca combined additions on the microstructure and creep properties of Mg–7Al–1Si alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 620, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





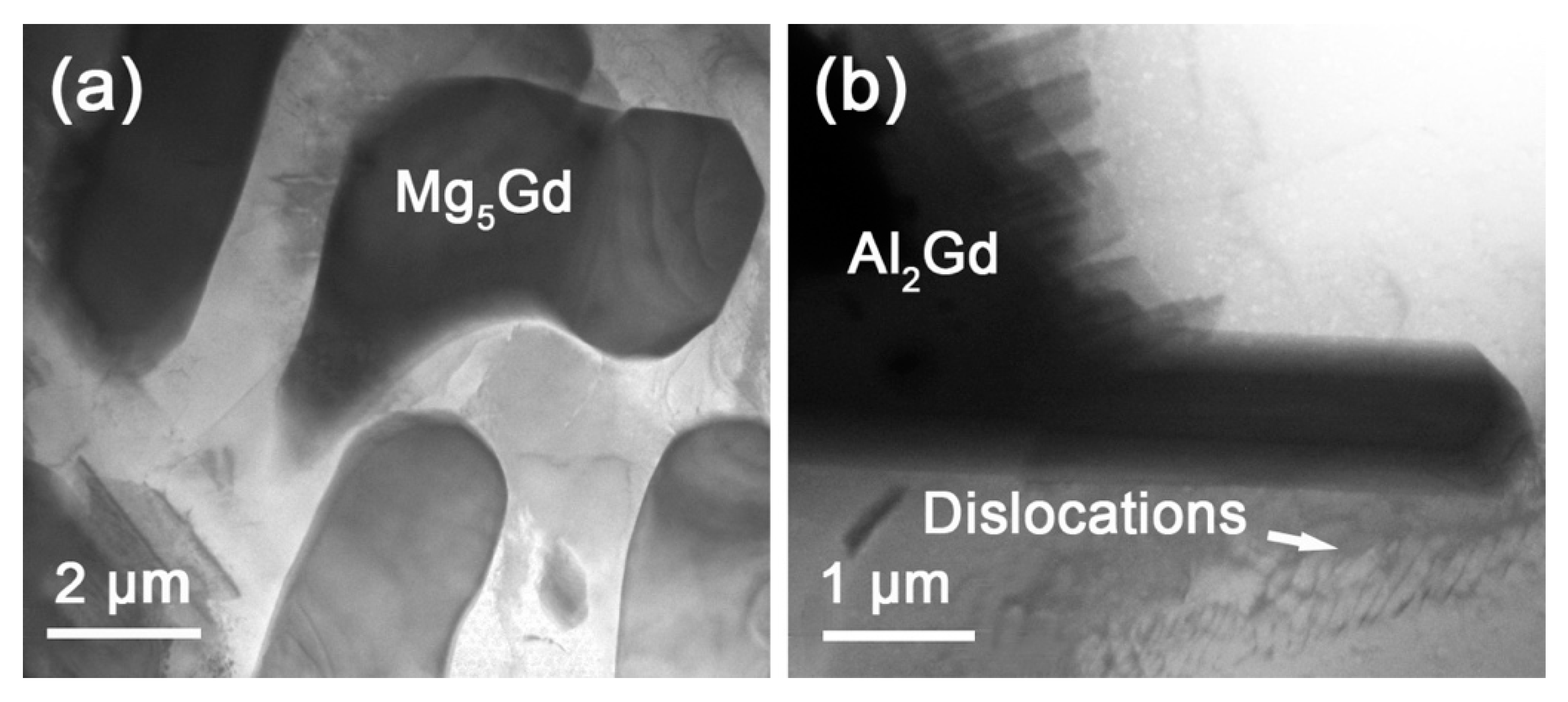
| Magnetic Field/T | Phase Content/wt.% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Mg | Mg5Gd | Al2Gd | GdH2 | |||
| As-cast | N/A | N/A | 73.26 | 24.23 | 2.51 | / |
| 620 °C, 20 min | Furnace cooled | 0 | 93.02 | 4.10 | 2.19 | / |
| 1 | 85.28 | 12.17 | 1.44 | / | ||
| Quenched | 0 | 82.82 | 9.34 | 0.77 | 7.07 | |
| 1 | 79.82 | 9.41 | 1.21 | 9.56 | ||
| Air cooled | 0 | 73.75 | 23.16 | 1.27 | 1.83 | |
| 1 | 79.35 | 8.69 | 2.96 | 9.01 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Q.; Li, X.; Li, S.; He, C.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. Effects of Static Magnetic Field on Compression Properties of Mg-Al-Gd Alloys Containing Gd-Rich Ferromagnetic Phase. Materials 2020, 13, 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214957
Cai Q, Li X, Li S, He C, Liu X, Feng X. Effects of Static Magnetic Field on Compression Properties of Mg-Al-Gd Alloys Containing Gd-Rich Ferromagnetic Phase. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214957
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Qi, Xinyao Li, Shukui Li, Chuan He, Xingwei Liu, and Xinya Feng. 2020. "Effects of Static Magnetic Field on Compression Properties of Mg-Al-Gd Alloys Containing Gd-Rich Ferromagnetic Phase" Materials 13, no. 21: 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214957
APA StyleCai, Q., Li, X., Li, S., He, C., Liu, X., & Feng, X. (2020). Effects of Static Magnetic Field on Compression Properties of Mg-Al-Gd Alloys Containing Gd-Rich Ferromagnetic Phase. Materials, 13(21), 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214957





