Abstract
The main objective of the presented preliminary study was the identification of iron-containing phases. Iron-containing phases had accumulated in organic topsoil horizons collected from an area that has long been affected by the steel industry and emissions from power plants. X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy methods were used for the determination of the iron-containing mineral phases in topsoil subsamples which, after two-staged separation, varied in terms of magnetic susceptibility and granulometry. The Mössbauer spectra were recorded using paramagnetic and magnetic components, although the latter occurred only in the strongly magnetic fraction. The central part of spectra was fitted by two doublets (D1 and D2), which were identified as aluminosilicates. Simultaneously, the experimental spectra were described using several Zeeman sextets (Z1, Z2, and Z3) corresponding to the occurrence of hematite and magnetite-like phases with iron in tetrahedral and octahedral sites. Identification of magnetic phases in the tested material, including hematite, led to the conclusion that soil contamination in the studied area was presumably caused by emissions from a nearby power plant. Magnetite-like phases with a different iron content detected in topsoil samples could be related to metallurgical and coking processes, reflecting the specificity of the industrial area from which the samples were taken. The specific composition of the iron-containing aluminosilicates also illustrated the intense and long-lasting impact of the steel and coking industries on the studied area.
1. Introduction
Intensive industrialization and urbanization are the main reasons for environmental pollution, which has had a serious impact on human health. It is necessary to assess and monitor the environmental hazards caused by industrial emissions as well as to identify contaminants [1,2]. Urban, industrial, and traffic-related emissions are the main source of iron mineral-rich dust, which are byproducts of fossil-fuel combustion and high-temperature technological processes [3,4]. Due to how soils contaminated by the above-mentioned dust and various types of soil sediments are characterized by specific magnetic properties, Mössbauer spectroscopy is needed for a deeper analysis of the impact of anthropogenic pollution on the environment.
Paramagnetic iron minerals are naturally occurring components of soil, rocks, sediments, coal, and other raw materials used in industry. They acquire ferrimagnetic properties as a result of thermal transformations during high-temperature industrial processes. These iron compounds include oxides, sulfides, and hydroxides [5]. The chemical composition of dust from various industries differs depending on the type of fuel used in the production process and the kind of technology used. Iron compounds of industrial dusts are often referred to as technogenic magnetic particles (TMPs). These particles are carriers of metals and metalloids which can be adsorbed onto their surface or incorporated into crystal lattices [6]. Due to the presence of iron compounds in industrial dust, it is possible to determine their presence in the environment with the use of 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy [7].
Deposition and accumulation of atmospheric particles on different surfaces has been examined by analyzing the various components of the ecosystem (snow [8], street dust [9], industrial dust [10], tree leaves [11]). As opposed to the periodically variable elements of the ecosystem where harmful substances are dispersed, these substances accumulate in the soil [12,13]. Many authors have indicated that the organic layer is the main soil horizon of anthropogenic particle accumulation [14]. Taking into account the long-term impact of human activities on the environment, it is necessary to determine the accumulation of TMP in soils exposed to urban, road-traffic, and industrial emissions.
The main objective of this preliminary study was to determine iron-containing phases, which are accumulated in organic horizons of topsoil collected from an area subjected to the long-term effects of the steel industry and emissions from power plants. In the Upper Silesia agglomeration, there are many areas under strong anthropopressure. The studies presented in this article, which describe the accumulated pollutants in the upper soil layer, are a continuation of our research presented in reference [4], on using Mössbauer spectroscopy to analyze the composition of iron-containing phases in industrial soils (urban soils) exposed to the impact of power plants and coking plants. Many iron-containing phases such as aluminosilicates with Fe3+, hydroxide aluminosilicates with Fe2+, as well as magnetic phases (magnetite and pyrrhotite) have been identified [4]. Pyrrhotite has been recognized as a characteristic ferromagnetic mineral that is formed during high-temperature pyrolysis of coking coal [5,15]. It is important to continue study aimed at understanding and explaining the mechanism of accumulation of pollution in industrial and post-industrial regions. Therefore, the identification of phases related to the emissions from a steelworks and a power plant will be the goal of this research. Moreover, before the main analysis, an innovative manner of soil separation (two-stage: granulometric and magnetic) was tested in order to obtain extremely different fractions.
2. Materials and Methods
The research was carried out in the central part of the Upper Silesian conurbation (southern Poland), the most urbanized, industrialized, and most polluted region of Poland [16]. There were numerous concentrated mines, steelworks, and coke and power plants, which are currently closed for the most part. They, however, have transformed the landscape and produced a lot of waste heaps, related to historical coal and ore mining and processing. Nowadays, it is nearly impossible to find an area in this region that has not been transformed by human activity. As such, soils in this area have been strongly transformed and contaminated [17,18,19,20].
First of all, before soil sampling, magnetic screening using Bartington MS2D susceptibility equipment (Bartington Instruments Ltd., Witney, UK) [21,22] was carried out in the area surrounding a steelworks and a power plant, which are located within ~7 km of each other. On the basis of spatial distribution of magnetic susceptibility (ĸ expressed in 10−5 SI units), hotspots (sites with the highest ĸ values) were chosen as the sites for soil collection in the amount of 1–1.5 kg, and the average field-wet bulk topsoil sample was taken from an area of approximately 2 m2.
After homogenization, root removal, and exsiccation in the air, samples were grounded and sieved through a 2-mm mesh. Afterwards, each sample was subjected to a two-stage separation: sieve separation and magnetic separation. After the first step, two granulometric fractions, with different grain sizes, I (Ø = 0.05–0.10 mm) and II (Ø = 0.25–0.50 mm), were attained. Both of them were then subjected to magnetic separation with a Frantz isodynamic magnetic separator, which consists of a vibrating chute mounted centrally between the pole pieces of an electromagnet. The chute may be inclined in any direction and the electromagnet current is continuously adjustable from 0 to 1.7 A. The separator divides a sample into two fractions. The strongly magnetic fraction consists of particles, each having a specific susceptibility above a value determined by the settings. The weakly magnetic fraction consists of particles of susceptibility below this value [23]. Two extreme currents, 0.2 A (strongly magnetic fraction denoted as A) and 1.6 A (weakly magnetic fraction denoted as B), were selected for the purpose of this study. As a result, four different fractions (subsamples) were obtained from one topsoil sample.
The subsamples placed in 1 cm3 plastic vials were weighed and subjected to volumetric magnetic susceptibility (ĸ) survey. The MFK1 Kappabridge device (Agico Advanced Geoscience Instruments Co., Brno, Czech Republic) was used, and low frequency (976 Hz) and low field intensity (200 A/m) were chosen for standard ĸ measurements at room temperature. Each sample was measured at least five times, and then the mean value was calculated. Afterwards, on the basis of the mean ĸ value and taking into account the weight of the samples, the mass-specific magnetic susceptibility (χ, m3/kg) was computed.
Each subsample was subjected to phase composition analysis using the X-ray diffraction method (XRD). Measurements were carried out using an X’Pert Pro Model 3040/60 (Phillips, Eindhoven, Holland) X-ray diffractometer with a copper anode (CuKα − λ = 1.54178 Ǻ) powered by an electric current of 30 mA, voltage of 40 kV, and a curved graphite monochromator to determine the wavelength emitted by the Cu anode. The diffraction patterns were recorded by “step scanning” of 0.04° 2θ steps in the angular range 2θ = 10 ÷ 140°.
Afterwards, the Mössbauer spectroscopy method was used for identification of iron-containing phases in the studied material. A conventional spectrometer working at room temperature with constant acceleration with 57Co:Rh source (activity ~50 mCi) in transmission geometry was used for recording the Mössbauer spectra. Metallic iron powder (α-Fe) absorbent was used for velocity and isomer shift calibration of the Mössbauer spectrometer. Samples for Mössbauer analysis were prepared as the absorbents of pressed soil separates without the use of a binder, which could have further disturbed the registration process. Due to the relatively low iron content in the tested material, the spectral registration process was carried out for about 5 days. After each recording of the experimental spectrum, a calibration measurement was performed. The process of deconvolution of experimental spectra was carried out using a dedicated PMOS numerical program [24] with implemented models, allowing for a discrete analysis of experimental spectra and an analysis using the distribution of magnetic fields H (T) and G—full width at a half maximum. The analysis process was carried out in two stages. In the first stage, each spectrum was analyzed separately, while in the second stage, the analysis covered individual series of spectra with common parameters. Numerical analysis included the characteristics of the middle part of the spectrum with the use of paramagnetic components, while the magnetic components were identified on the basis of the Zeeman sextet distribution. As a result of this analysis, a set of components describing the experimental spectra was obtained. The quality parameter of their fit (χ2) did not exceed 2, and there were no differences between the curve illustrating the differences in the model and the experimental description, proving the presence of additional components. The mineralogical identification of hyperfine parameters was based on the Mössbauer Mineral Handbook [25].
3. Results and Discussion
As expected, the mass-specific magnetic susceptibility varied widely, from 3.6 to 247.6 × 10−8 m3/kg (Table 1), with the highest values for the finest (Ø = 0.05–0.1 mm) and strongly magnetic (0.2 A) fraction (IA), while the lowest χ was noticed for subsample IB (Ø = 0.05–0.1 mm, 1.6 A), although the value was almost equal to the χ of IIB subsample (χ = 4.0 × 10−8 m3/kg).

Table 1.
Mass-specific magnetic susceptibility (χ) of topsoil subsamples after sieve and magnetic separation.
Theoretically, the lowest χ should have the coarser subsample (IIB), but probably the factors other than grain size influenced χ of this topsoil sample, as magnetic properties depend not only on the grain size of magnetic particles but also on their mineralogy and elemental concentration [26,27,28]. The influence of grain size on magnetic susceptibility was evidenced by the almost twice as high value of χ in the case of the finer IA subsample.
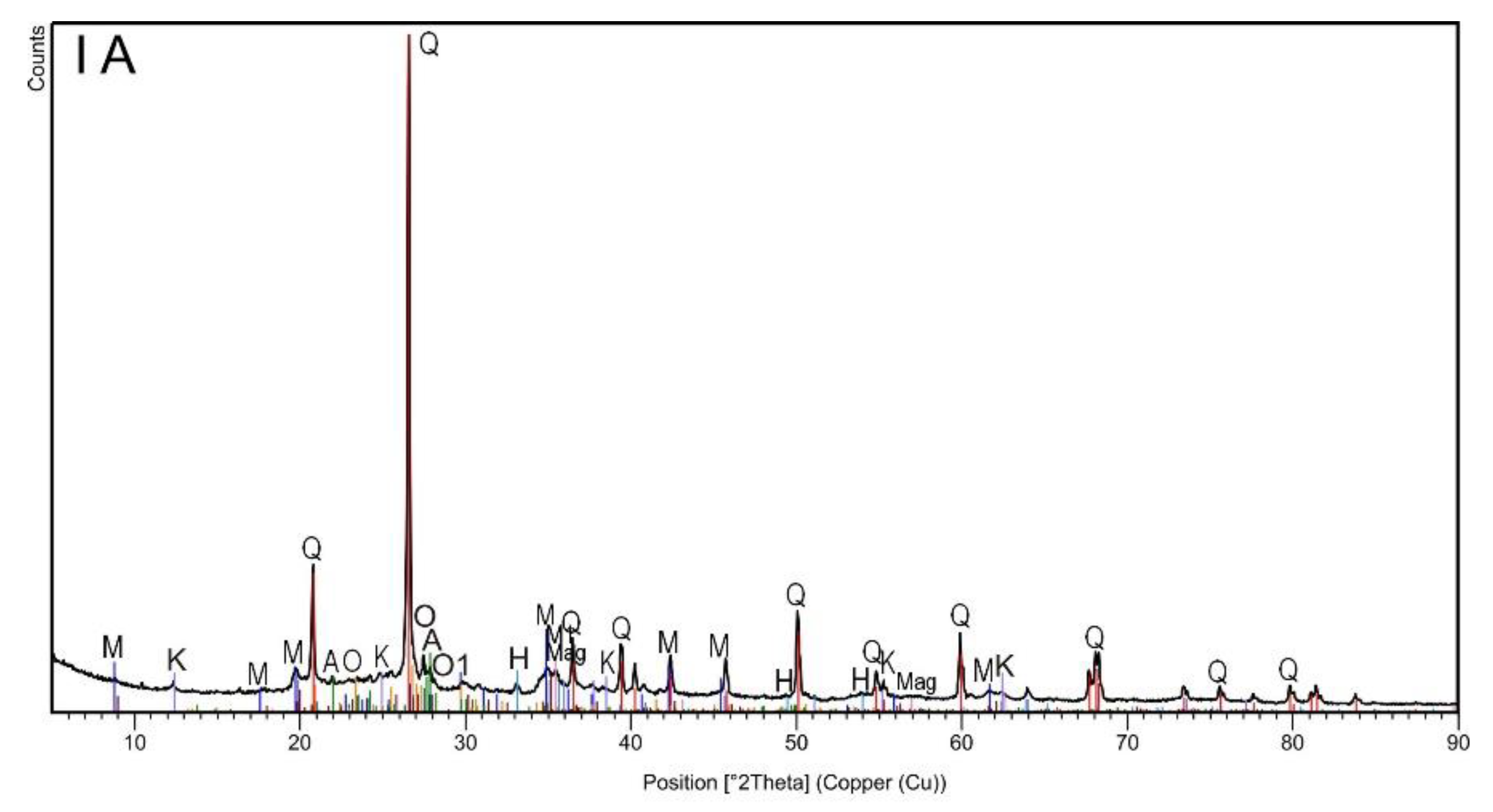
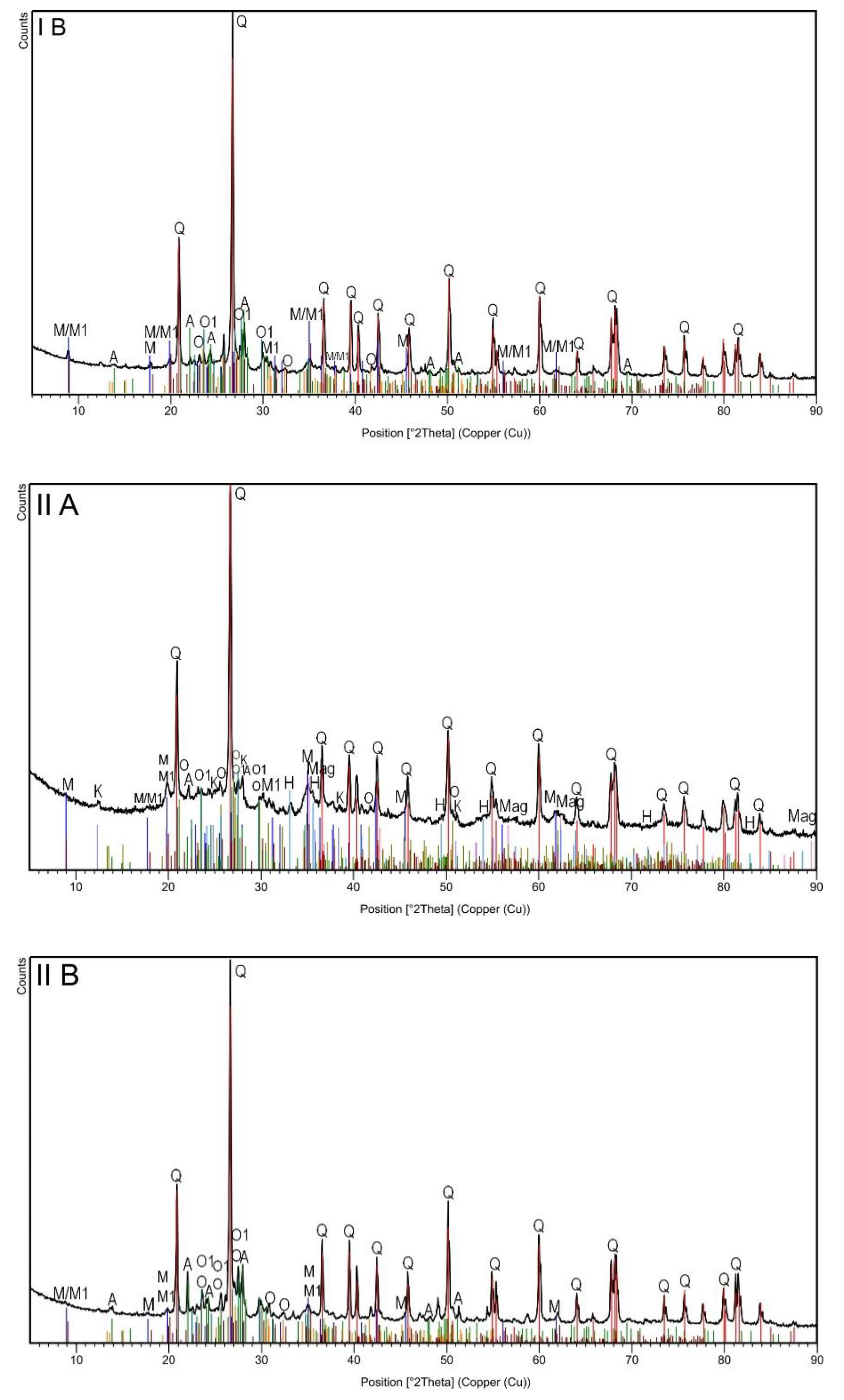
The XRD analysis (Figure 1, Table 2) revealed the multiphase composition of the studied materials of all analyzed samples. In general, six phases (quartz; two types of muscovite; albite and orthoclase with and without Fe) were common for all samples irrespective of the magnetic and grain fraction (Table 2). Since quartz is one of the most common components of rocks and soils, its highest proportion was found in all samples. XRD diffractograms showed major peaks of quartz SiO2 (Q: 2θ = 20.8°, 26.7°, 36.5°, 45.8°, 50.3°, 60.1°, 68.2°) [29]. The next quantitative phase was muscovite, which belongs to the minerals from the mica group. Typical muscovite impurities are Fe, Ge, Ti, Li, Na, Ca, Mg, and Fe, which can appear in the crystal structure. Minor modifications to the composition and crystal structure cannot be clearly noticed by phase analysis alone. Several polytypes of this mineral are generally known [30]. In the studied topsoil samples, muscovite was observed in two forms: muscovite-2M1 with additional elements such as Na, Mg, Ti, and Fe (Table 2), and albite-sodium aluminosilicate with an ordered Al-Si distribution. Ca, K, and Mg are the typical impurities of albite, but in the studied samples, such impurities occurred in a rather pure form. The next identified phase was orthoclase, which had epitaxial relationships with albite. Typical orthoclase impurities are Na, Fe, Ba, and Ca, but in this case, only iron was detected. In the case of samples separated by lower current (0.2 A), i.e., strongly magnetic subsamples in both granulometric fractions, the analysis revealed the presence of three additional phases (kaolinite, magnetite, and hematite). The peak at 12.4°, attributed to aluminosilicate plates, corresponds to the basal spacing of kaolinite Si2Al2O5(OH)4. Other diffraction peaks could be found at 2θ = 24.9°, 38.7°, and 62.5° [31]. The observed kaolinite was in a 1Md type of structure. Finally, iron oxides (hematite and magnetite) were detected in both strongly magnetic subsamples (IA and IIA). The presence of these iron oxides seemed obvious, especially considering the very high magnetic susceptibility of these subsamples. The broad diffraction peaks at 33.3° in IA and IIA subsamples (Figure 1) could have originated from hematite Fe2O3, while the peak at 30.0 and 35.8° could have originated from magnetite Fe3O4 [29].
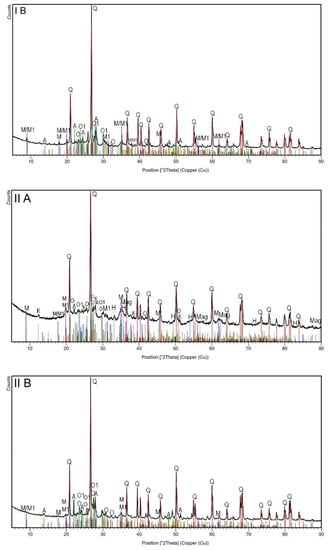
Figure 1.
The X-ray diffraction patterns of topsoil subsamples IA, IB, IIA and IIB.

Table 2.
The identified phases in topsoil subsamples after sieve and magnetic separation (presence of particulate phases in sample was marked as “x”).
Summarizing the results of the XRD analysis, it can be stated that only magnetic separation influenced the differentiation of the mineral phases of the studied soils, while grain size did not affect their mineral composition.
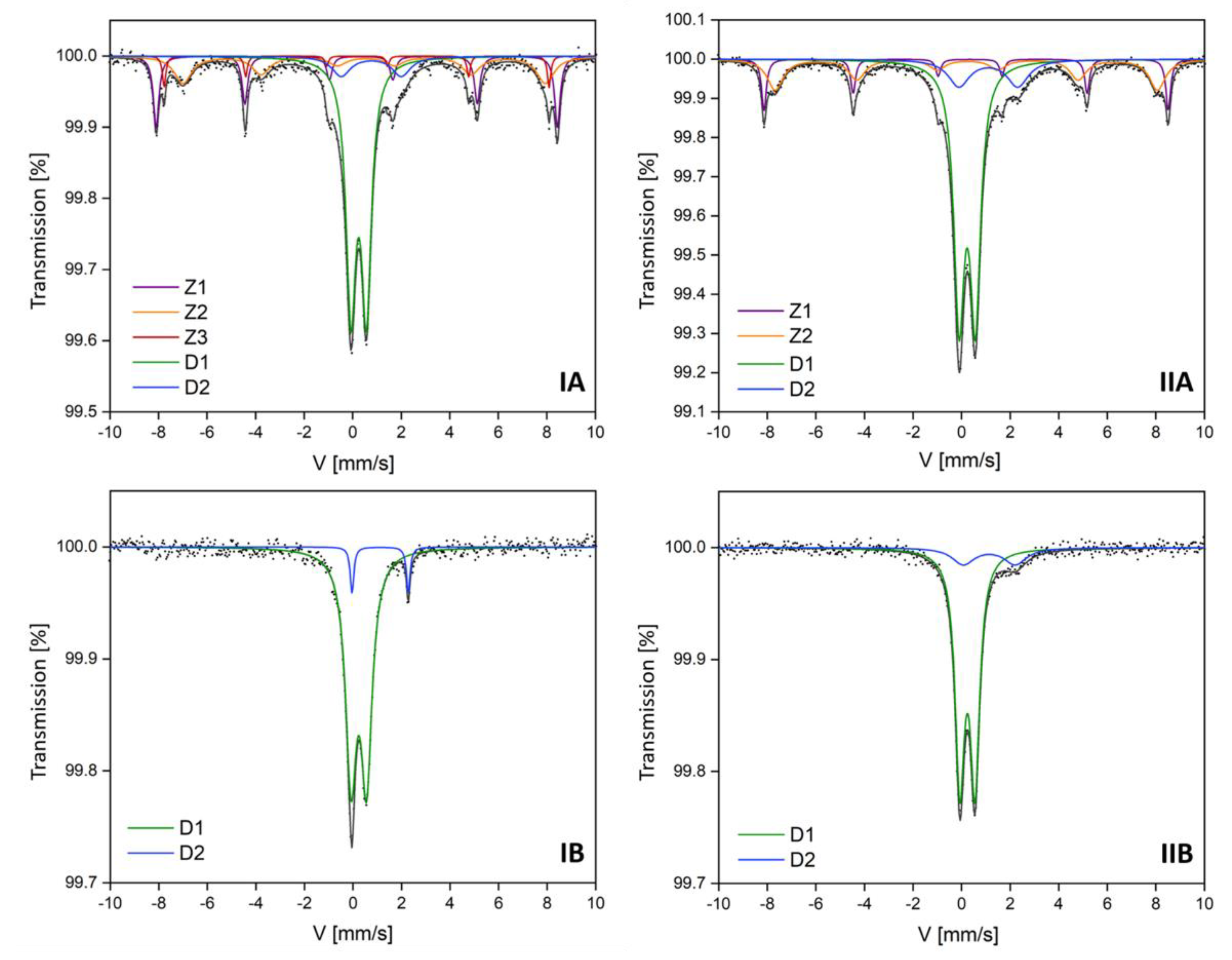
Mössbauer parameters of the hyperfine interactions are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4. In the central part of the experimental spectra of all subsamples (Figure 2), the presence of paramagnetic components marked as D1 and D2 was found. These paramagnetic components were identified as aluminosilicates with different Fe content. The presence of such components is consistent with the phase identification obtained by the XRD method. D1 doublets were identified as Fe3+ aluminosilicates, and D2 doublets were identified as Fe2+ aluminum silicate hydroxides [32]. Their percentage contribution was variable. The weakly magnetic subsamples (separated at 1.6 A current) exhibited a higher amount of Fe3+ aluminosilicates at 85 and 93% in IB and IIB samples, respectively (Table 4), while the strongly magnetic subsamples IA and IIA (separated at 0.2 A current) contained exactly 51% of Fe3+ aluminosilicates (Table 3).

Table 3.
Fitted Mössbauer parameters for spectra of samples IA and IIA. IS—isomer shift (with reference to metallic iron), QS—quadrupole splitting, H—magnetic hyperfine filed, A—relative area fraction with respect to whole fitted spectrum. Doublet compounds have been described as D1 and D2 and sexted compounds have been described as Z1, Z2, and Z3.

Table 4.
Fitted Mössbauer parameters for spectra of samples IB and IIB, where doublet compounds have been described as D1 and D2. IS—isomer shift (with reference to metallic iron), QS—quadrupole splitting, A—relative area fraction with respect to whole fitted spectrum.
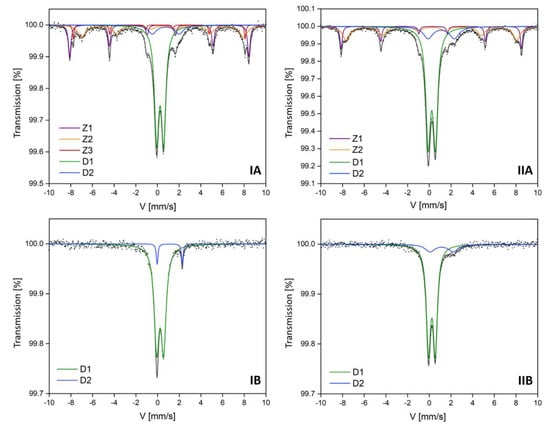
Figure 2.
The room temperature Mössbauer spectra of the topsoil subsamples (IA, IIA, IB, IIB). Fitted components are presented on the figure as D1, D2, Z1, Z2, Z3. The x-axis of these charts represents velocity (V), while the y-axis represents transmission (%). G—full width at half maximum = (0.35–0.40) mm/s.
Hyperfine parameters for D1 components may be disturbed by the overlapping of parameters characteristic for magnetite and maghemite nanoparticles, ferrihydrite, or pyrite, the presence of which was not found in the XRD analysis. However, their presence cannot be excluded by analyzing the results contained in the paper of Stevens et al. [25]. The differences between hyperfine parameters for the identified aluminosilicates can also be related to the differences in the chemical composition (iron content, as confirmed by chemical analysis carried out with the SEM-EDS method) of the identified components, which were determined by the ionic forms of iron in these compounds. The spectra of IB and IIB subsamples do not have a magnetic component (no sextet) [33]. This is in agreement with the X-ray diffraction results that revealed the presence of muscovite (M1) and orthoclase (O1), which presumably correspond to aluminosilicates identified by Mössbauer spectra. The proportion of aluminosilicate hydroxide with Fe2+ doublet (D2) revealed various dependencies. The magnetic fraction did not influence its content in investigated samples, but the share of D2 component in the coarse granulometric fraction was twice as high as in the smaller one. The percentage of D2 component in iron-containing phase composition of IA and IB (0.05–0.10 mm) was up to 8%, while for IIA and IIB (0.25–0.50 mm) it was up to 15%.
The experimental spectra of strongly magnetic subsamples (IA and IIA) were fitted by Zeeman sextets (Z1, Z2, and Z3). The Z1 component with a hyperfine magnetic field value of 51 T was identified as hematite with a stable share in the sample (19%). Similar results of Mössbauer spectroscopy were obtained for fly and bottom ashes generated in fluidized bed boilers in a Silesian power plant [34]. In fly ash samples, Waanders et al. found the presence of hematite and compounds with Fe3+ ions, as well as amorphous Fe3+, in glass and muscovite [35]. The similarities in hyperfine parameters with results obtained in the presented work suggest that fly ashes may be a source of pollution in the studied soils. Hematite could be the product of oxidative pyrolysis of the Fe-sulphates and carbonates, but also it can arise during the dehydroxylation of goethite and lepidocrocite [36].
In both magnetic subsamples IA and IIA, which are characterized by high magnetic susceptibility values, the presence of the Z2 component characterized by a hyperfine magnetic field with a value of about 46 T was observed, which can be assigned to the magnetite-like phase (mixed octahedral Fe3+ and Fe2+). On the other hand, the additional Z3 component, which was only present for the finest fractions (IA) at H = 49 T, could also be identified as magnetite, but with tetrahedral Fe3+ [37,38]. Their contribution is rather low (Z2: 16–20%; Z3: only 4%). In the works devoted to the study of metallurgical and coking dusts, similar results of the hyperfine field values were obtained, and it was suggested that the possible occurrence of magnesium ferrite, as the corresponding hyperfine field values for this spinel, is very similar to that of magnetite [3,39]. The results obtained in this study concerning the magnetite-like phase should be discussed in terms of the applied sieve separation used. In finer granulation (IA) magnetite with Fe2+/3+ as well as Fe3+ was identified, while in larger granulation (IIA) magnetite, only Fe2+/3+ was found. Magnetite in mineral form would be fitted with two Zeeman sextets, as confirmed in sample IA, due to the coexistence of Fe2+ and Fe3+ in the following chemical formula: Fe2+Fe3+2O4. Doriguetto et al. [39] established that at 300 K, natural magnetite is represented by two Zeeman sextets. The first sextet with H = 49 T was identified as magnetite with Fe3+, while the second sextet with H = 46 T was described as magnetite with Fe3+/2+ [9]. Combustion processes used by various industries (including but not limited to the power, fossil-fuel, transport, and coking industries, metallurgy, etc.) may have been the source of magnetite in the topsoil samples.
A greater share of magnetic components was observed in the spectra of subsample IA (41%) in comparison to that of subsample IIA (35%). This difference is not significant, but it corresponds well with the magnetic susceptibility value (χ), which was higher for IA (247.6 × 10−8 m3/kg) than for the IIA subsample (139.4 × 10−8 m3/kg). This confirms the assumption that the higher the content of magnetic iron components, the higher the value of soil magnetic susceptibility.
4. Summary
Results of the topsoil samples taken from an industrial area revealed their complex phase composition and an occurrence of iron-containing compounds. Subsamples diversified in terms of their magnetic susceptibility and grain size were characterized by different values of hyperfine parameters and thus diversity in characteristic iron-containing phases. Values of magnetic susceptibility corresponded well with the results of Mössbauer spectroscopy analysis. Weakly magnetic subsamples IIA and IIB (separated at 1.6 A current) exhibited larger amounts of paramagnetic components, i.e. aluminosilicates with Fe3+ (85–93%), while the strongly magnetic subsamples IA and IIA (separated at 0.2 A current) contained exactly 51% of aluminosilicates with Fe3+. The share of aluminosilicates with Fe2+ doublet (D2 component) in the coarse granulometric fraction (IIA and IIB: 0.25–0.5 mm) was twice as high as in the finer topsoil subsamples (IA and IB: 0.05–0.1 mm). Magnetic components (Z1, Z2, and Z3) were identified as hematite and magnetite, with iron in tetrahedral as well as octahedral sites, but only for strongly magnetic separates (IA and IIA). The identification of hematite in Mössbauer spectra analysis led to the conclusion that soil contamination in the studied area could be caused by emissions from power plants, while occurrence of magnetite-like phases in topsoil samples could be related to metallurgical and coking processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.K., A.H.-K., M.R.; methodology, P.K., A.H.-K., M.R. and I.M.; software, P.K., R.M.; validation, P.K., M.R., A.H.-K. and I.M.; formal analysis, P.K., A.H.-K., M.R. and I.M.; investigation, A.H.-K., P.K., M.R., I.M. and R.M.; resources, P.K., A.H.-K. and M.R.; data curation, P.K., A.H.-K. and M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, P.K., A.H.-K. and M.R.; writing—review and editing, P.K., A.H.-K. and M.R.; visualization, P.K., A.H.-K., M.R. and I.M.; supervision, P.K., A.H.-K. and M.R.; project administration, M.R.; funding acquisition, M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Science Centre of Poland on the basis of the decision number DEC-2013/09/B/ST10/02227.
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledges Sławomir Ilnicki and Witold Matyszczak from the Institute of Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Petrology, Faculty of Geology, Warsaw University for enabling magnetic separation of soil samples. We thank the Reviewers for their constructive comments that have improved the quality of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References and Note
- Sims, I.; Crane, M.; Johonson, I.; Credland, P. Biomonitoring the environmental impact of atmospheric emission from the Avonmouth zinc smelter, United Kingdon. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.F.; Allen, D.T. Hydrocarbon emissions from industrial release events in the Houston-Galveston area and their impact on ozone formation. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3785–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumiata, T.; Rachwał, M.; Magiera, T.; Brzózka, K.; Gzik-Szumiata, M.; Gawroński, M.; Górka, B.; Kyzioł-Komisińska, J. Iron-containing phases in metallurgical and coke dust as well as in bog iron ore. Nukleonika 2017, 62, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierlik, P.; Hanc-Kuczkowska, A.; Męczyński, R.; Matuła, I.; Dercz, G. Phase composition of urban soils by x-ray diffraction and mössbauer spectroscopy analysis. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2019, 64, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Rachwał, M.; Magiera, T.; Wawer, M. Coke industry and steel metallurgy as the source of sil contamination by technogenic magnetic particles, heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukouzas, N.; Hämäläinen, J.; Papanikolaou, A.; Tourunen, T.; Jäntii, T. Mineralogical and elemental composition of fly ash from pilot scale fluidized bed combustion of lignite, bituminous coal, wood chips and their blends. Fuel 2007, 86, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, A.; Gomes, C. Integration of magnetic measurements, chemical and statistical analysis in characterizing agricultural soils (central Portugal). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bućko, M.; Magiera, T.; Johanson, B.; Petrovsky, E.; Pesonen, L. Identification of magnetic particulates in road dust accumulated on roadside snow using magnetic, geochemical and micro-morphological analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeleńska, M.; Górka-Kostrubiec, B.; Werner, T.; Kądziałko-Hofmokl, M.; Szczepaniak-Wnuk, I.; Gonet, T.; Szwarczewski, P. Evaluatin of indoor/outdoor urban air pollution by magnetic, chemical and microscopic studies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiera, T.; Parzentny, H.; Róg, L.; Chybiorz, R.; Wawer, M. Spatial variation of soil magnetic susceptibility in relation to different emission sources in southern Poland. Geoderma 2015, 255, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.; Lavornia, J.; Chaparro, M.; Sinito, A. Biomonitors of urban air pollution: Magnetic studies and SEM observations of corticolous foliose and microfoliose lichens and their suitability for magnetic monitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, S.; Christensen, J.; Brown, S.; Vancuren, R.; Cliff, S.; Depaolo, D. Pb isotopes as ndicator of the Asian contribution to particulate air pollution in ueban California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 891–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunindi, M.; Tasdemir, Y. Atmospheric polychlorinated biphentyl (pcb) inputs to coastal city near the marmara sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 215, 427–439. [Google Scholar]
- Jordanova, D.; Goddu, S.; Kotsev, T.; Jordanova, N. Industrial contaminaion of alluvial soils near Fe-Pb mining site revealed by magnetic and geochemical studies. Geoderma 2013, 192, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Dubikova, M.; French, D.; Sahajwalla, V. Characterization of the origin and distribution of the minerals and phases in metallurgical cokes. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziubanek, G.; Spychała, A.; Marchwińska-Wyrwał, E.; Rusin, M.; Hajok, I.; Ćwieląg-Drabek, M.; Piekut, A. Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and the relationship with life expectancy in cohort of 3.5 million people in Silesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Fabijańczyk, P.; Magiera, T.; Rachwał, M. Micro-scale spatial correlation of magnetic susceptibility in soil profile in forest located in an industrial area. Geoderma 2015, 249–250, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasik, A.; Gruba, P.; Magiera, T. Application of magnetometry to assess distribution of dust pollution in topsoil of under-crown area of Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Catena 2017, 150, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachwał, M.; Wawer, M.; Magiera, T.; Steinnes, E. Integration of soil magnetometry and geochemistry for assessment of human health risk from metallurgical slag dumps. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26410–26423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawer, M.; Rachwał, M.; Kowalska, J. Impact of noise barriers on the dispersal of solid pollutants from car emissions and their deposition in soil. Soil Sci. Annu. 2017, 68, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoanet, H.; Leveque, F.; Segura, S. Magnetic susceptibility in environmental applications: Comparison of field probes. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1999, 115, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21226:2019—International ISO Standard: Soil Quality—Guideline for the Screening of Soil Polluted with Toxic Elements Using Soil Magnetometry, 1st ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- McAndrew, J. Calibration of a Frantz isodynamic separator and its application to mineral separation. Proc. Aust. Inst. Min. Metall. 1957, 181, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- PMOS—The specialized program for experimental Mössbauer spectra analysis designed by J. Żukrowski for the needs of University of Silesia employees.
- Stevens, J.G.; Khansanov, A.M.; Miller, J.W.; Pollak, H.; Li, Z. Mössbauer Mineral Handbook, Mössbauer Effect Data Center, 3rd ed.; The University of North Carolina: Asheville, NC, USA, 2005; pp. 1–636. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, R.; Maher, B. Fingerprinting upland sediment sources: Particle size specific magnetic linkages between soils, lake sediments and suspended sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, F.; Hao, Q.; Bloemendal, J.; Gibbs-Eggar, Z.; Patil, S.; Guo, Z. Links between particle size and magnetic grain size: General observations and some implications for Chinese loess studies. Sedimentology 2009, 56, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razik, S.; Dekkers, M.; Dobeneck, T. How environmental magnetism can enhance the interpretational value of grain-size analysis: A time-slice study on sediment export to the NW African margin in Heinrich Stadial and Mid Holocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 406, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Brindley, G.W. X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Clay Mineral Identification. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification; Brindley, G.W., Brown, G., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: London, UK, 1980; pp. 305–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, B.; Schweda, P. Kinetics of muscovite, phlogopite, and biotite dissolution and alteration at pH 1,4, room temperaturę. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W. Structures of Layer Silicates. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification; Brindley, G.W., Brown, G., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: London, UK, 1980; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kopcewicz, B.; Kopcewicz, M.; Jelenska, M.; Hasso-Agopsowicz, A. Mössbauer study of chemical transformations in soil samples during thermomagnetic measurements. Hyperfine Interact. 2005, 166, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Verma, N.; Prasad, R. Structural and catalytic properties of Zn1–xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 1833–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kądziołka-Gaweł, M.; Smolka-Danielowska, D. 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy investigations of iron phase cmposition in fluidized beds from the ELCHO power plant in Chorzów, Poland. Nukleonika 2017, 62, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waanders, F.; Vinken, E.; Mans, A.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A. Iron minerals in coal, weathered coal and coal ash—SEM and Mössbauer results. Hyperfine Interact. 2003, 148–149, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumiata, T.; Gawroński, M.; Górka, B.; Brzózka, K.; Świetlik, R.; Trojanowska, M.; Strzelecka, M. Chemical, magnetic and Mössbauer effect analysis of road dust from expressway. Nukleonika 2013, 58, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, G.; Almeida, F.; Ferreira, A.; Ciminelli, V. Preparation and Application of a Magnetic Composite (Mn3O4/Fe3O4) for Removal of As(III) from Aqueous Solutions. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, M.; Elbadawi, A.; Yassin, O. Synthesis and structural properties of MgFe2O4 ferrite nano-particles. J. Appl. Ind. Sci. 2013, 1, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Doriguetto, A.; Fernandes, N.; Persiano, A.; Nunes Filho, E.; Greneche, J.; Fabris, J. Characterization of natural magnetite. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2003, 30, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).