Characterization of W–Cr Metal Matrix Composite Coatings Reinforced with WC Particles Produced on Low-Carbon Steel Using Laser Processing of Precoat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
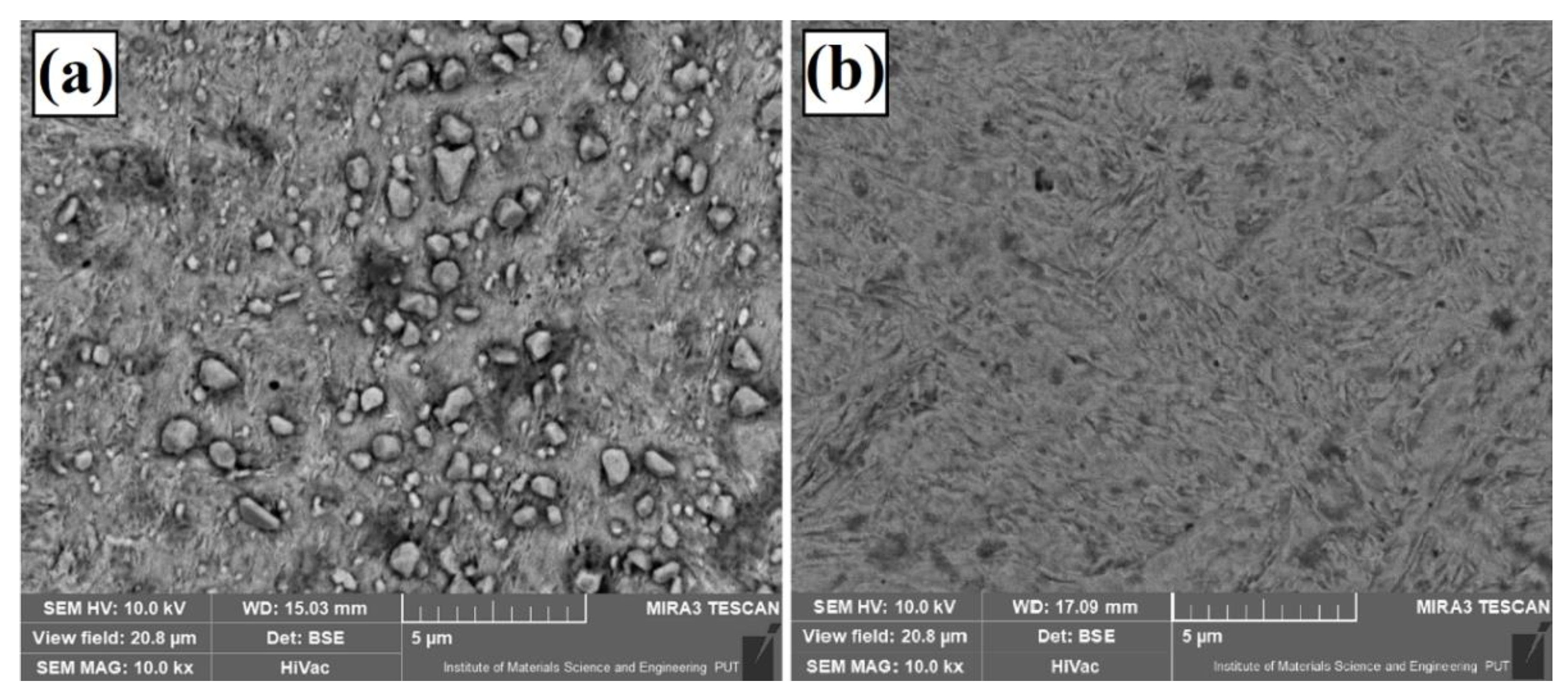
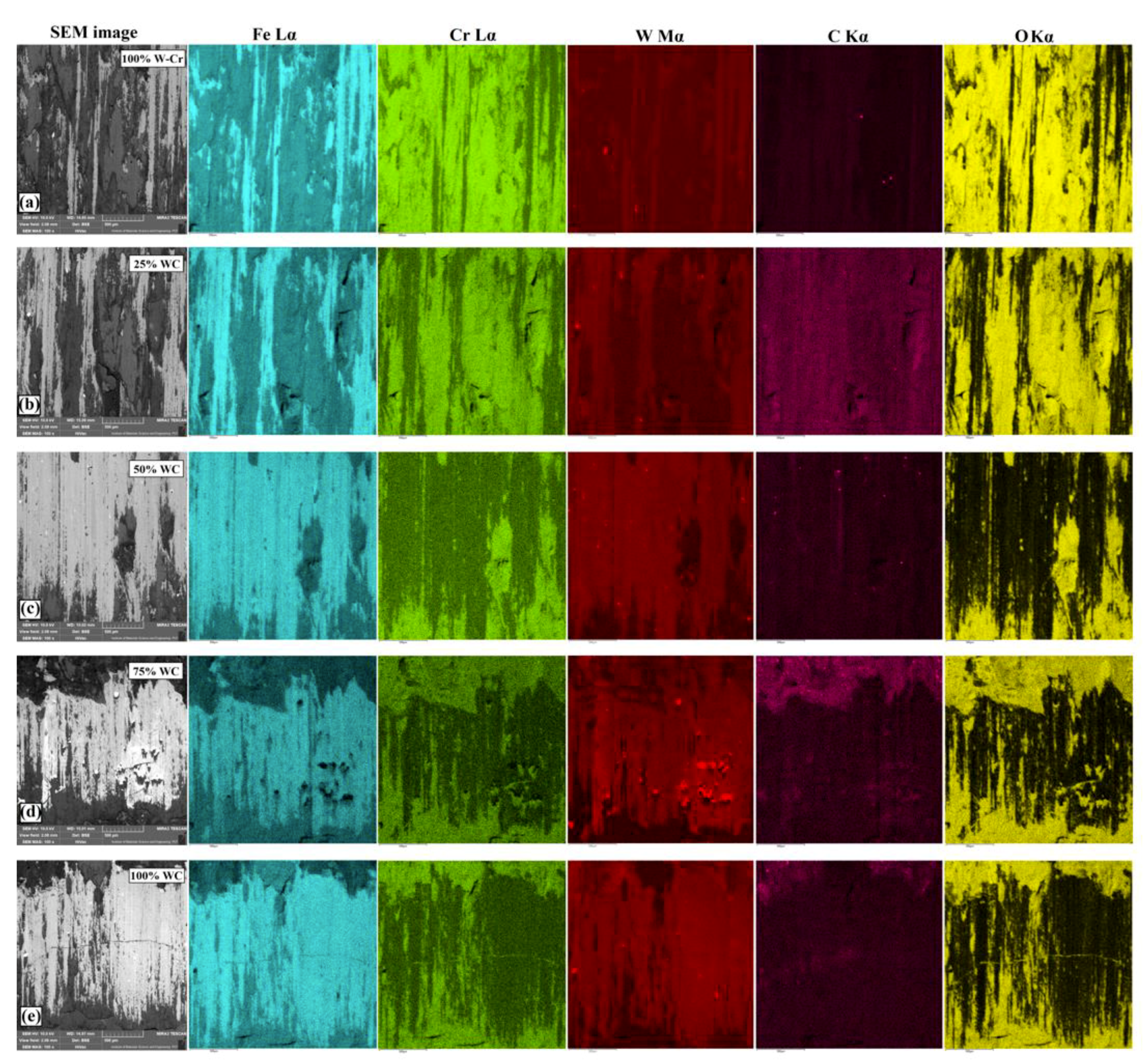
3.1. Microstructure, Chemical, and Phase Analysis
3.2. Microhardness Results
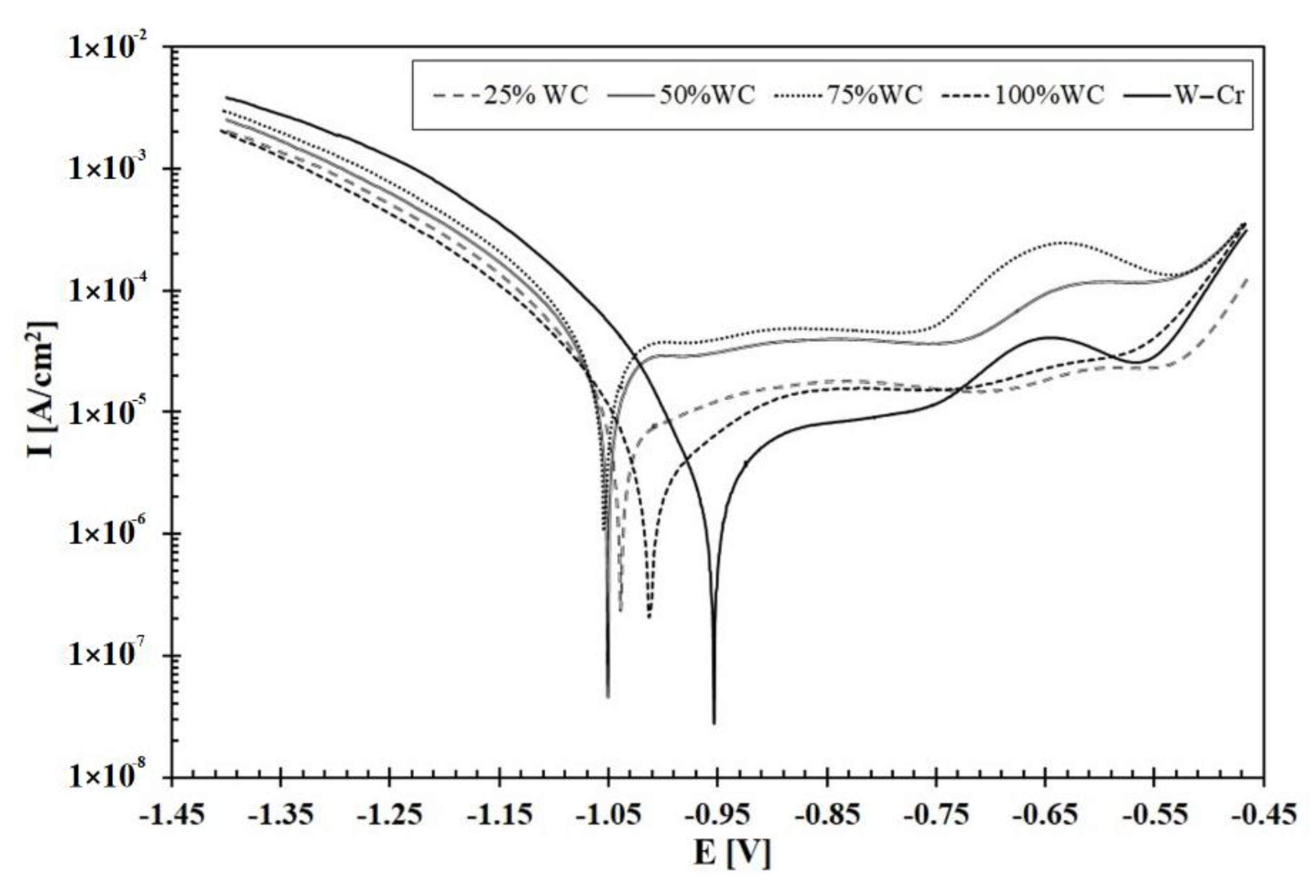
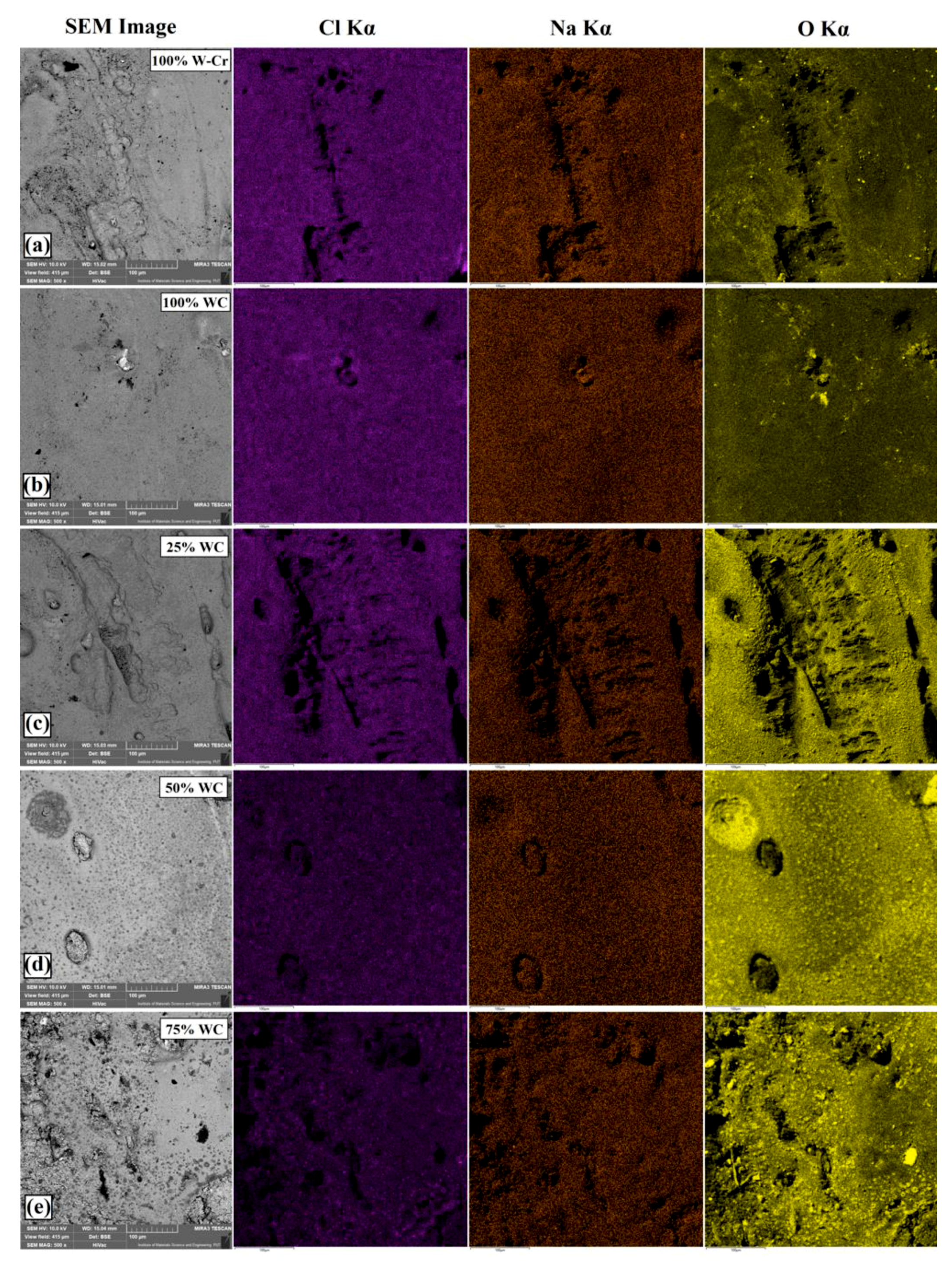
3.3. Corrosion Resistance
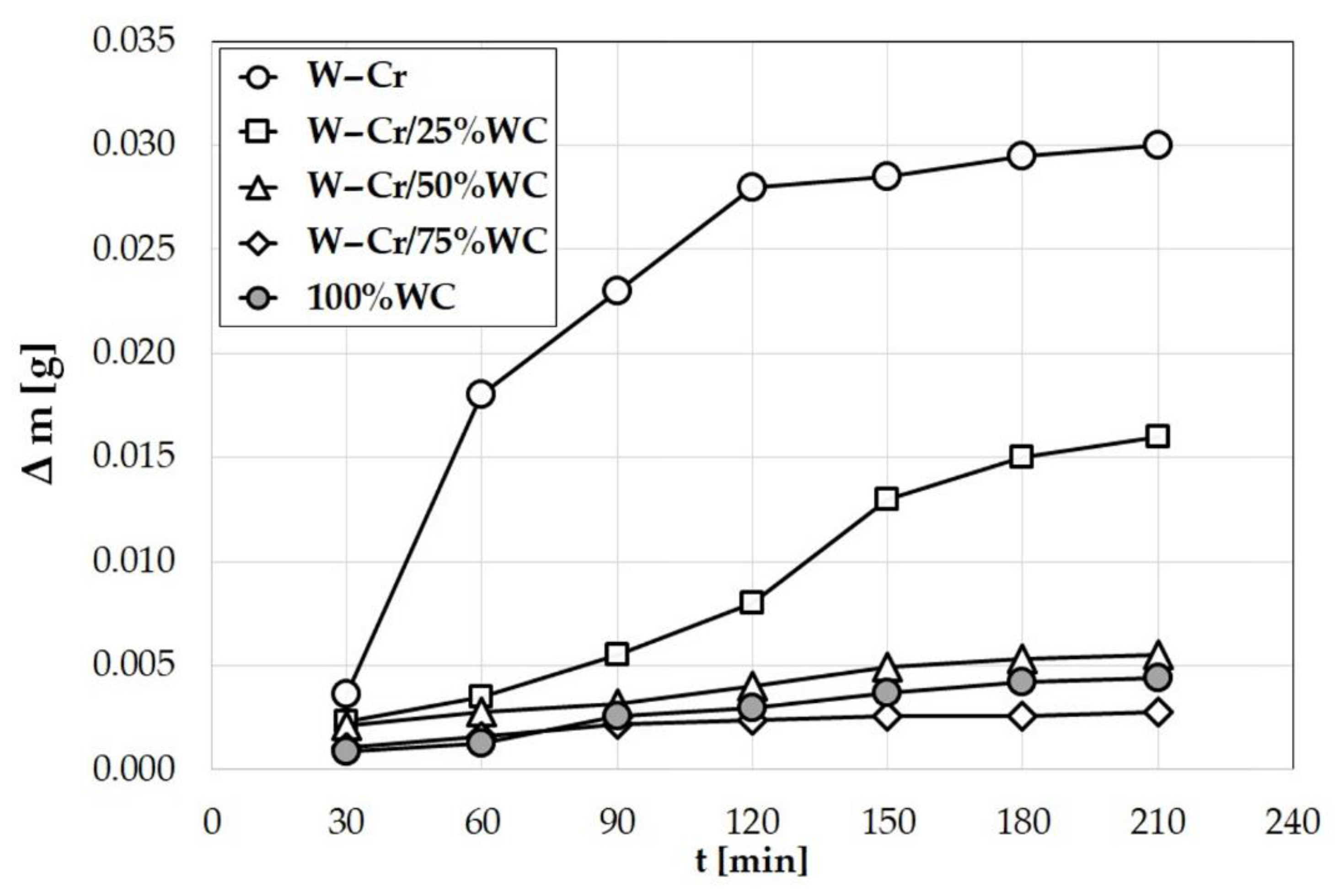
3.4. Wear Resistance
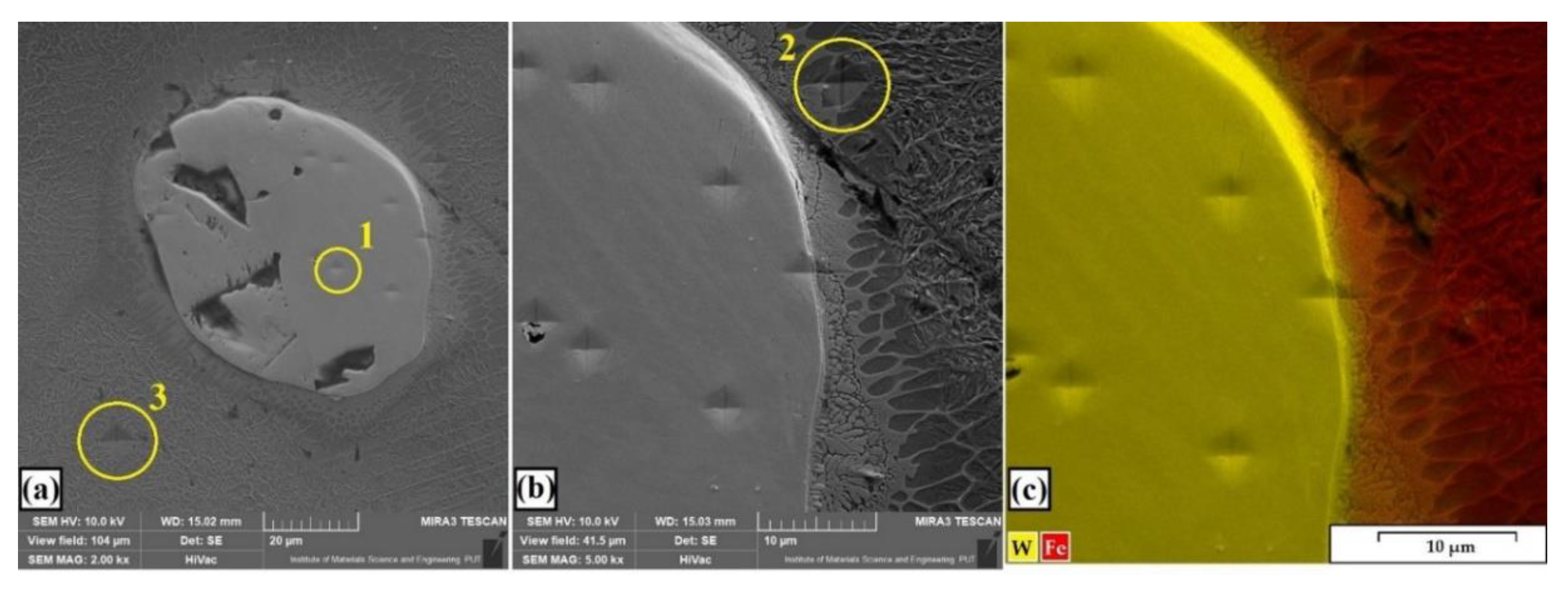
3.5. Instrumented Indentation Test
4. Conclusions
- −
- increasing the content of WC particles reduces the thickness of the W–Cr/WC coatings;
- −
- increasing the content of WC particles contributes to increasing the microhardness of the produced W–Cr metal matrix composite coatings;
- −
- increasing the content of WC particles in the W–Cr metal matrix composite coatings contributes to increasing wear resistance;
- −
- on the surface of the coating containing 100% WC, cracks were observed after a wear test. These cracks were probably formed during the friction process, because no cracks were observed during microstructure observation. These cracks led to reducing the wear resistance. Despite this, the wear resistance of 100% WC coatings was quite high;
- −
- increasing the amount of WC as the reinforcing phase in the W–Cr composite coating reduced corrosion resistance. This was due to an increase in the number of corrosion cells in the entire coating;
- −
- as a result of laser processing of precoats consisting of W, Cr, and WC particles, newly formed coatings rich in primary and secondary tungsten carbides (WC, W2C, M7C3) were obtained. These were carbide phases characterized by high microhardness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czerwinski, F. (Ed.) Thermochemical treatment of metals. In Heat Treatment—Conventional and Novel Application; InTech Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.R. Surface Engineering for Corrosion and Wear Resistance; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- St-Georges, L. Development and characterization of composite Ni–Cr +WC laser cladding. Wear 2007, 263, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Deng, P.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, P.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Microstructure and wear behaviors of WC-Ni coatings fabricated by laser cladding under high frequency micro-vibration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M.; Grech, M.; Betts, J.C. The in-flight temperature variation and dissolution of WC powder particles producing an Fe–Cr–W–C system by direct laser deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 207, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Cao, J.; Lu, H.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Luoa, K.Y. Wear properties and microstructural analyses of Fe-based coatings with various WC contents on H13 die steel by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 369, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Dai, X.; Zheng, H. Microstructure and wear resistance of Fe-based WC coating by multi-track overlapping laser induction hybrid rapid cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2012, 44, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.M.; Zhang, Y.D. The microstructure and wear-resistant properties of laser cladding Ni-based WC alloy on Q345 steel surface. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 556–562, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H. High temperature wear resistance of laser cladding NiCrBSi and NiCrBSi/WC-Ni composite coatings. Wear 2011, 270, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, J.W.; Costello, A. Laser powder deposition of WC materials for improved wear resistance. In Advances in Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials-2007, Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, PowderMet 2007, Denver, CO, USA, 13–16 May 2007; Metal Powder Industries Federation: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwimp, J.; Rombouts, M.; Geerinck, E.; Motmans, F. Applications of laser cladded WC-based wear resistant coatings. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Du, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Bai, H.L.; Jiang, E.Y. Influence of WC particle behavior on the wear resistance properties of Ni–WC composite coatings. Wear 2004, 257, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; West, D.R.F. Laser surface cladding of stellite and stellite-SiC composite deposits for enhanced hardness and wear. Wear 1991, 143, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; West, D.R.F.; Steen, W.M. Wear studies of variable composition stellite-SiC laser clad deposits. Key Eng. Mater. 1990, 46, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, J.; Näkki, J.; Vuoristo, P. Microstructure and properties of hard and wear resistant MMC coatings deposited by laser cladding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2009, 27, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A. Wear resistance in the soil of Stellite-6/WC coatings produced using laser cladding method. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 64, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chatha, S.S.; Sidhu, B.S. Effect of alloying elements in Fe-based hardfacings to improve the abrasive wear behavior of ploughshares. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 4737–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chatha, S.S.; Sidhu, B.S. Abrasive wear characteristics and microstructure of Fe-based overlaid ploughshares in different field conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Fujita, H.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ohta, Y. Diffusion carbide coatings formed in molten borax systems. J. Mater. Eng. 1987, 9, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowska, A.; Swadźba, R.; Popławski, M.; Bartkowski, D. Microstructure, microhardness, phase analysis and chemical composition of laser remelted FeB-Fe2B surface layers produced on Vanadis-6 steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 86, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Ajmal, M.; Nusair Khan, A.; Hussain, A.; Akhter, R. Surface modification of air plasma spraying WC–12%Co cermet coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 56, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajkowski, J.; Popielarski, P.; Ignaszak, Z. Cellular automaton finite element method applied for microstructure prediction of aluminium casting treated by laser beam. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2019, 19, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowski, S.; Przestacki, D.; Chwalczuk, T. The evaluation of surface integrity during machining of Inconel 718 with various laser assistance strategies. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 136, 01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwalczuk, T.; Przestacki, D.; Szablewski, P.; Felusiak, A. Microstructure characterisation of Inconel 718 after laser assisted turning. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 188, 01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidridge, T.; Poling, G.; Foroozmehr, E.; Kadekar, V.; Gupta, M.C. Laser cladding of Inconel 690 on Inconel 600 superalloy for corrosion protection in nuclear applications. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yao, C.; Li, D.; Dai, Z. In situ synthesized high volume fraction WC reinforced Ni-based coating by laser cladding. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Liao, B.; Sun, Y.; Dai, X.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. Effect of laser remelting on microstructure and properties of WC reinforced Fe-based amorphous composite coatings by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 103, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, W.; Yao, K.; Goussain, J.-C.; Mayer, C.; Becker, A. Microstructural evolution in high power laser cladding of Stellite 6+WC layers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 157, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zeng, X. Growth characteristics and mechanism of carbides precipitated in WC–Fe composite coatings by laser induction hybrid rapid cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 505, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X. A study of Ni-based WC composite coatings by laser induction hybrid rapid cladding with elliptical spot. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 3110–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, E.; Amado, J.M.; Montero, J.; Tobar, M.J.; Yáñez, A. Comparative study of Co-based alloys in repairing low Cr-Mo steel components by laser cladding. Phys. Procedia 2012, 39, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnia, A.; Malek Ghaini, F.; Ocelík, V.; De Hosson, J.T.M. Microstructural characterization of Co-based coating deposited by low power pulse laser cladding. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Chen, C. Characteristics of thin surface layers of cobalt-based alloys deposited by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 4557–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Y. Laser cladding Ni–Co duplex coating on copper substrate. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelík, V.; de Oliveira, U.; de Boer, M.; de Hosson, J.T.M. Thick Co-based coating on cast iron by side laser cladding: Analysis of processing conditions and coating properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5875–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiß, S.; Bischoff, E.; Grünenwald, B. Metallographic characterisation of stellite/WC composite layers produced by laser cladding. Pract. Metallogr. 1996, 33, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. High Power Direct Diode Laser cladding of Stellite 6 + WC coatings. Mach. Technol. Mater. 2012, 7, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, M.-J.; Niu, X.; Yuan, B.; Liang, E.-J.; Wang, D.-S. Preparation and characterization of in situ synthesized B4C particulate reinforced nickel composite coatings by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.H.; Geng, L.; Xu, B.; Li, J. Laser cladding NiCrBSi+2%B4C coating on Ti-6Al-4V. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 79–82, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Młynarczak, A.; Piasecki, A.; Dudziak, B.; Gościański, M.; Bartkowska, A. Microstructure, microhardness and corrosion resistance of Stellite-6 coatings reinforced with WC particles using laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 68, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A.; Popławski, M.; Przestacki, D. Microstructure, microhardness, corrosion and wear resistance of B, Si and B–Si coatings produced on C45 steel using laser processing. Metals 2020, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, J.; Caecel, B.; Ramos, A.; Amigó, V. Laser Cladding of TiC for Better Titanium Components. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14577-1:2015. Metallic Materials—Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters—Part 1: Test Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
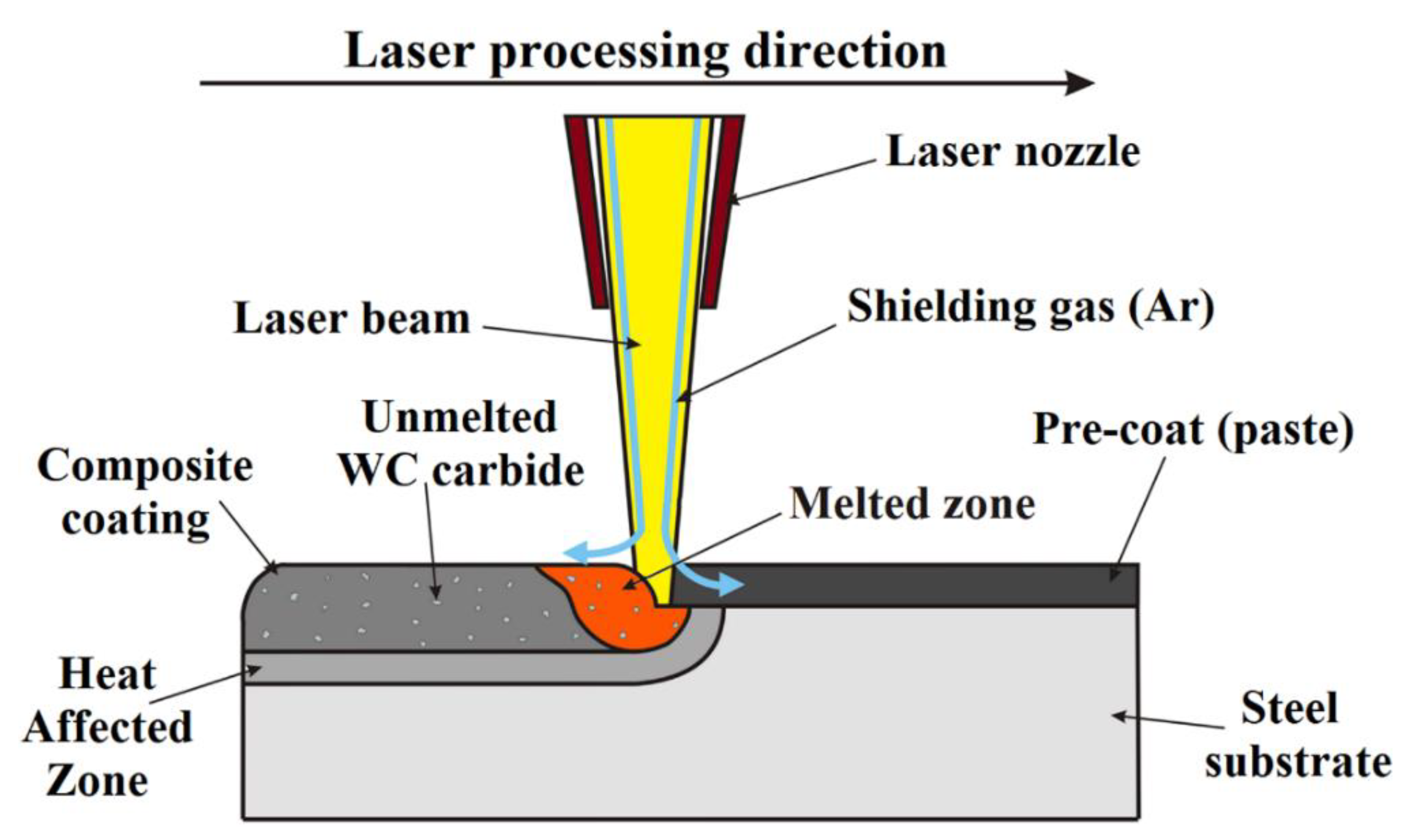
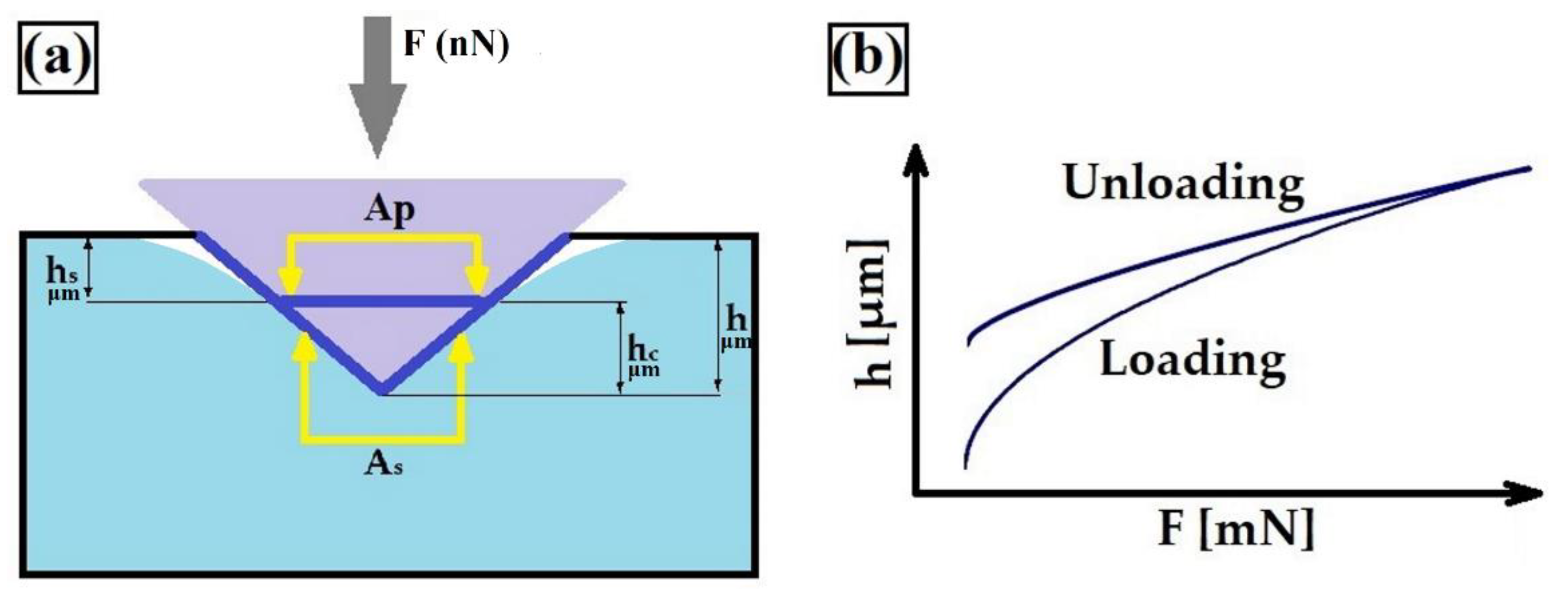


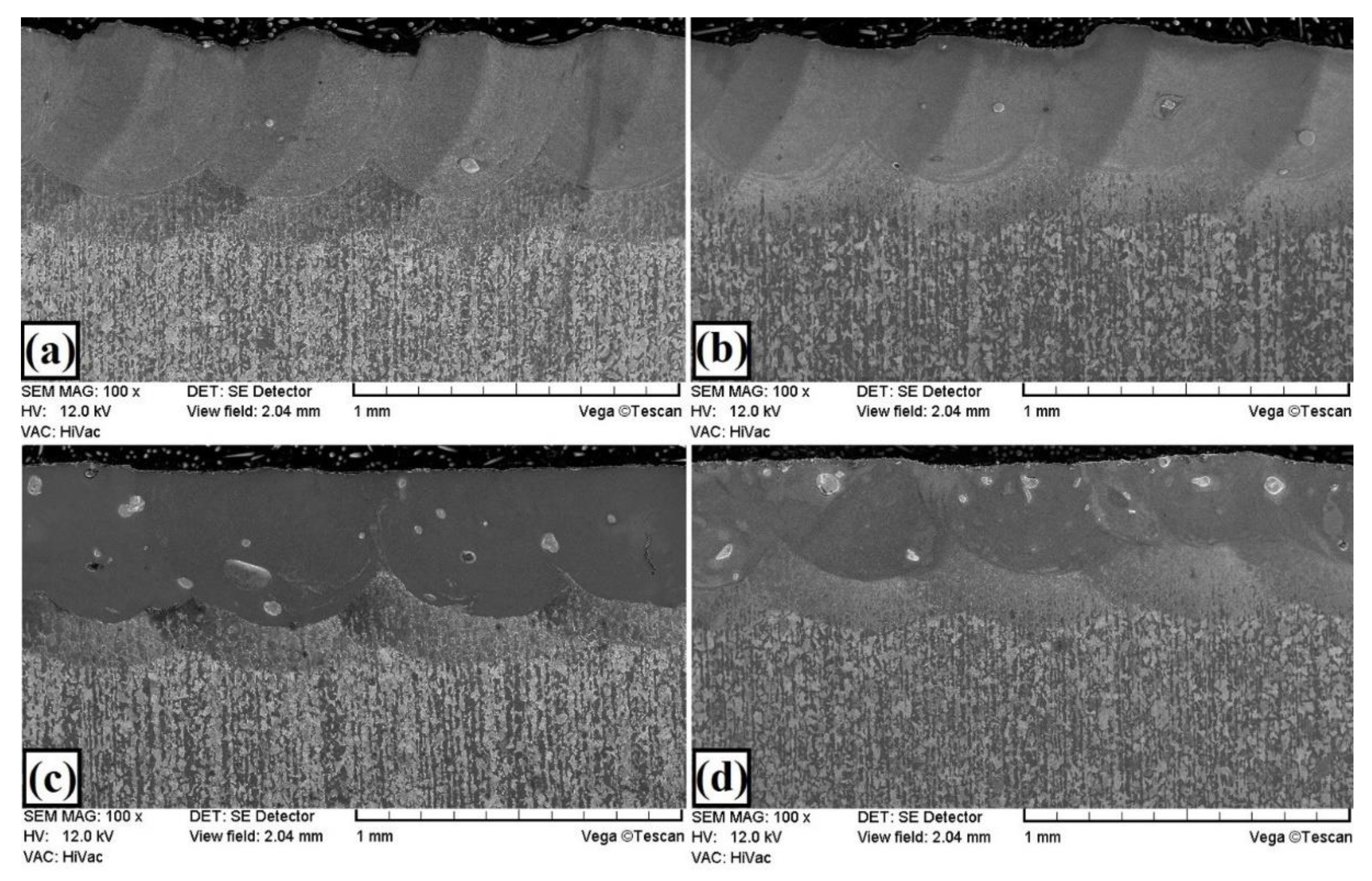
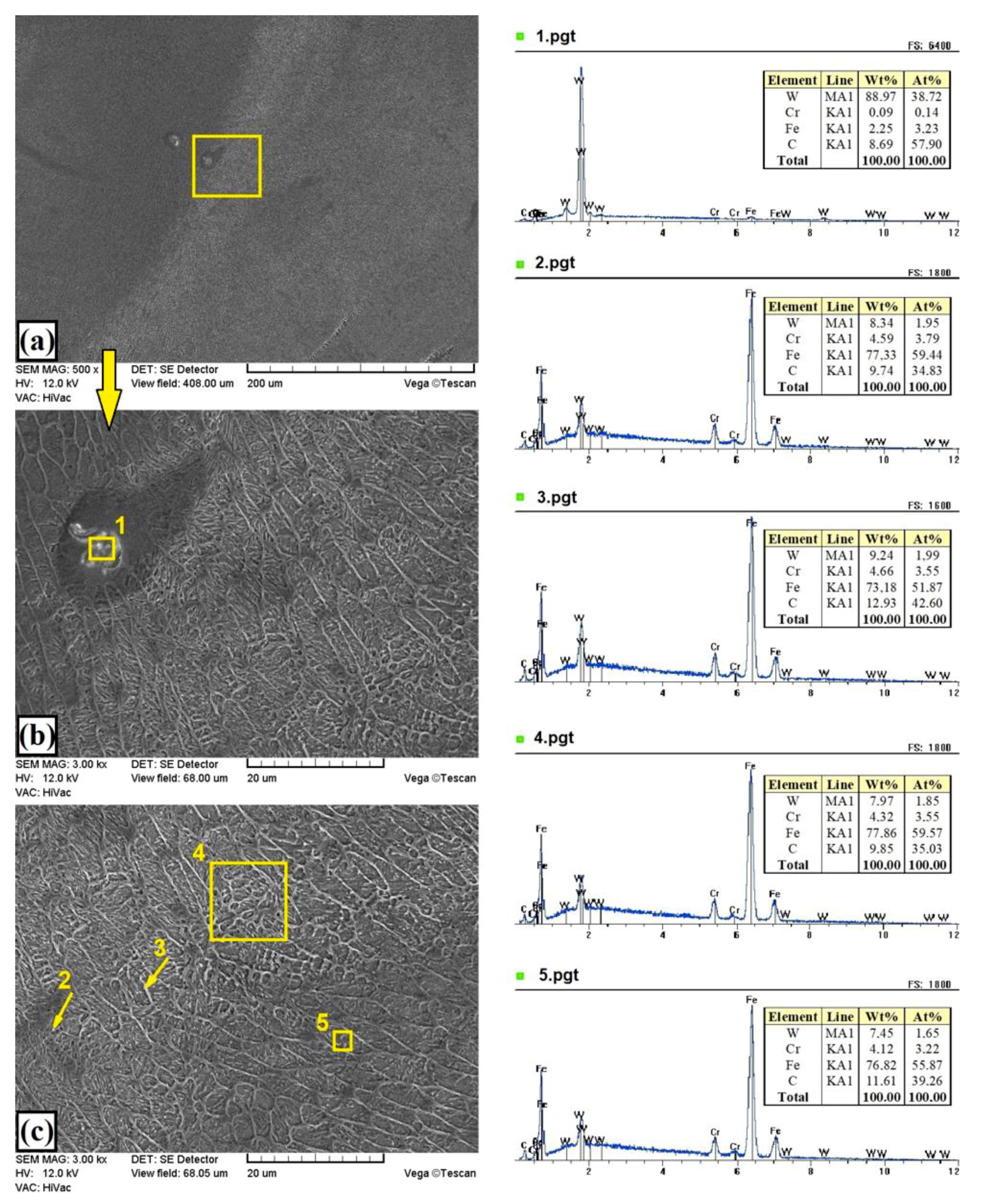
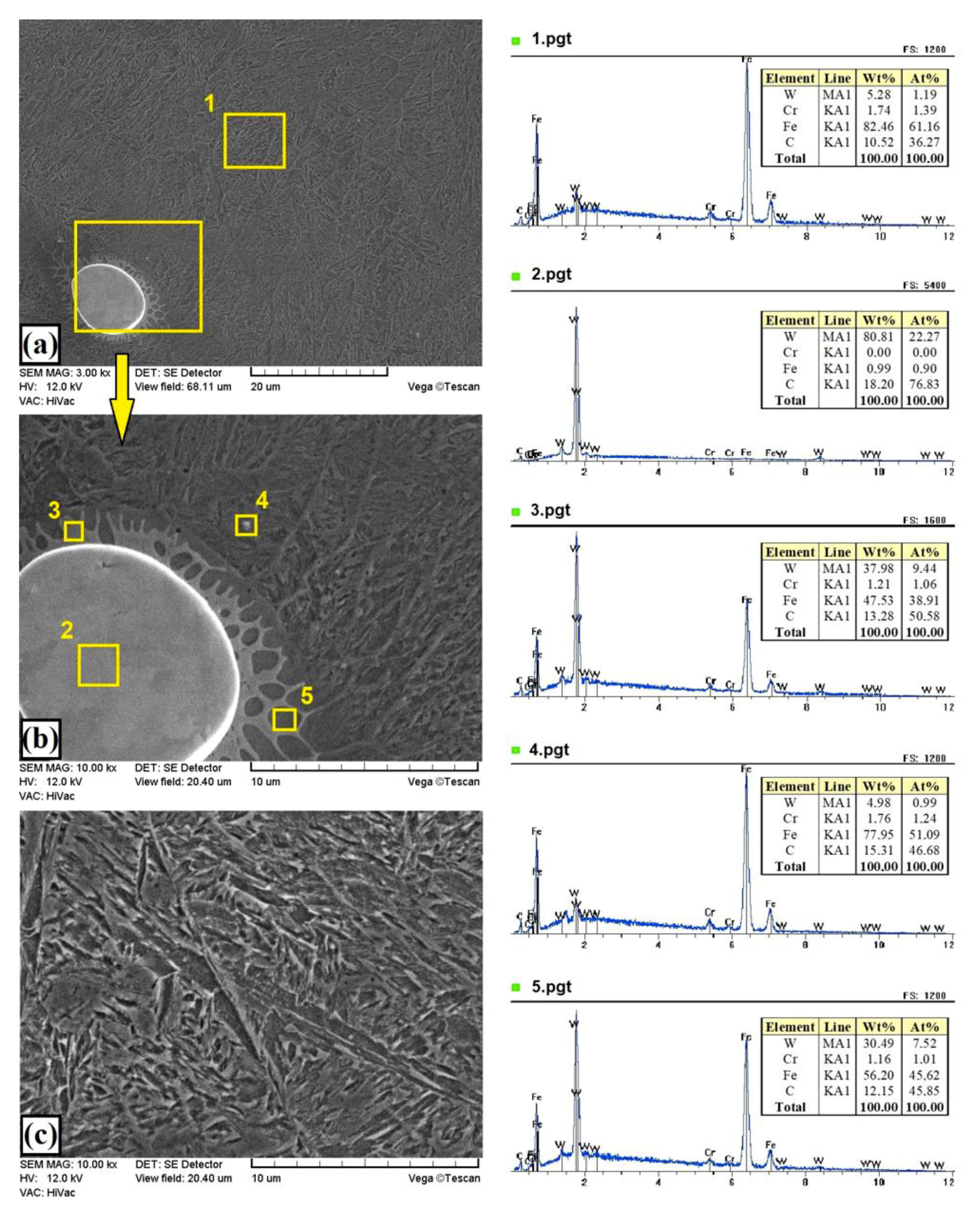

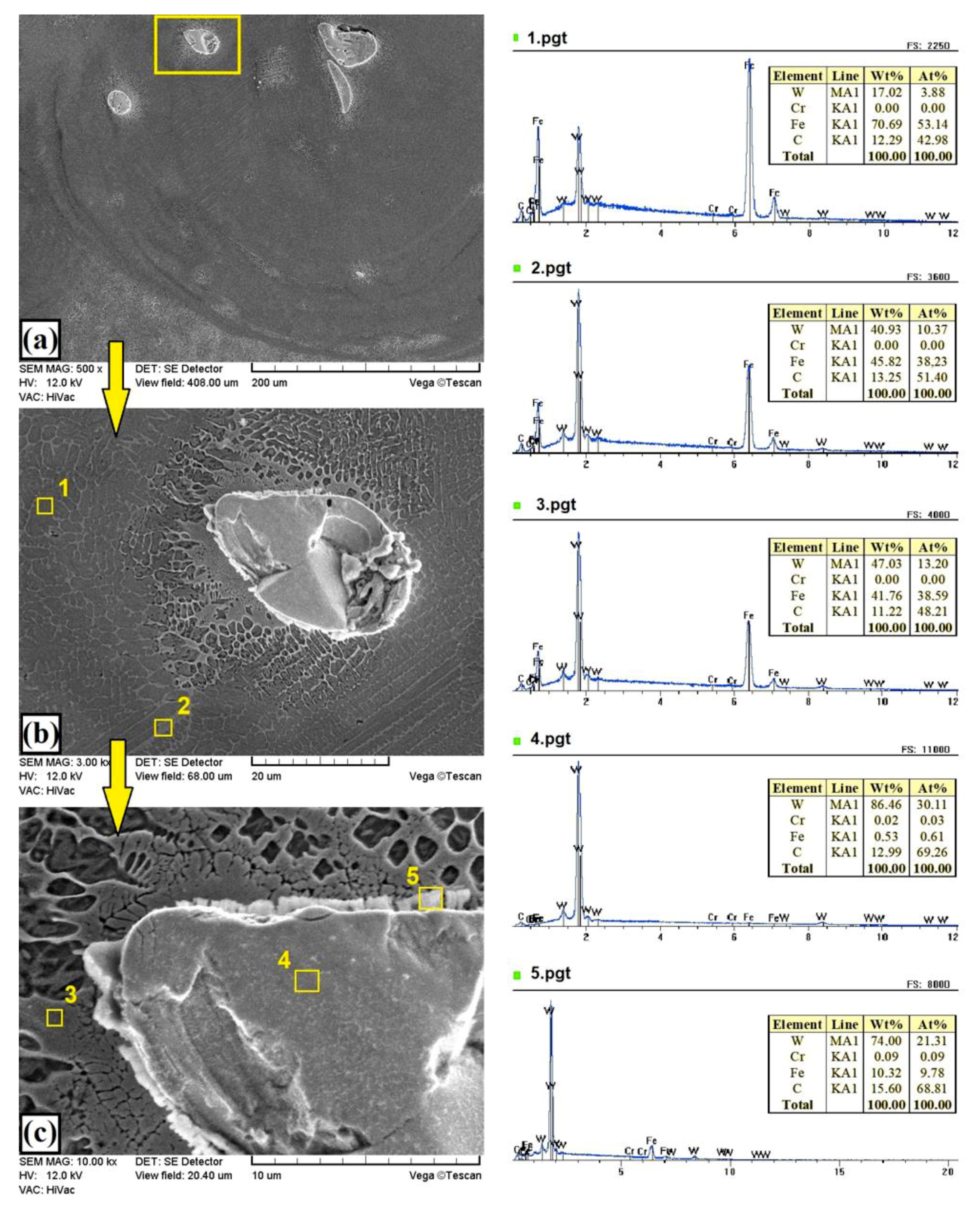
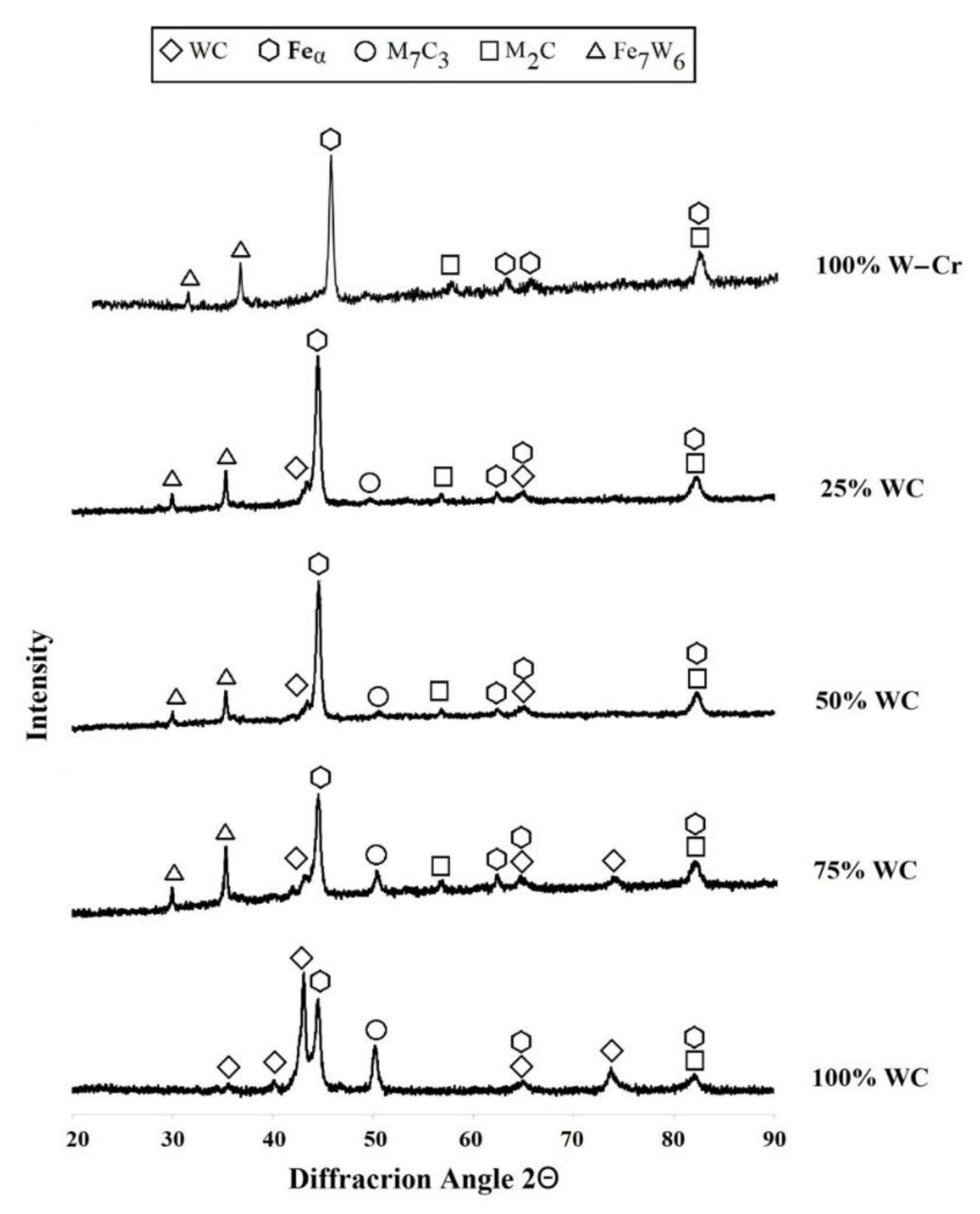
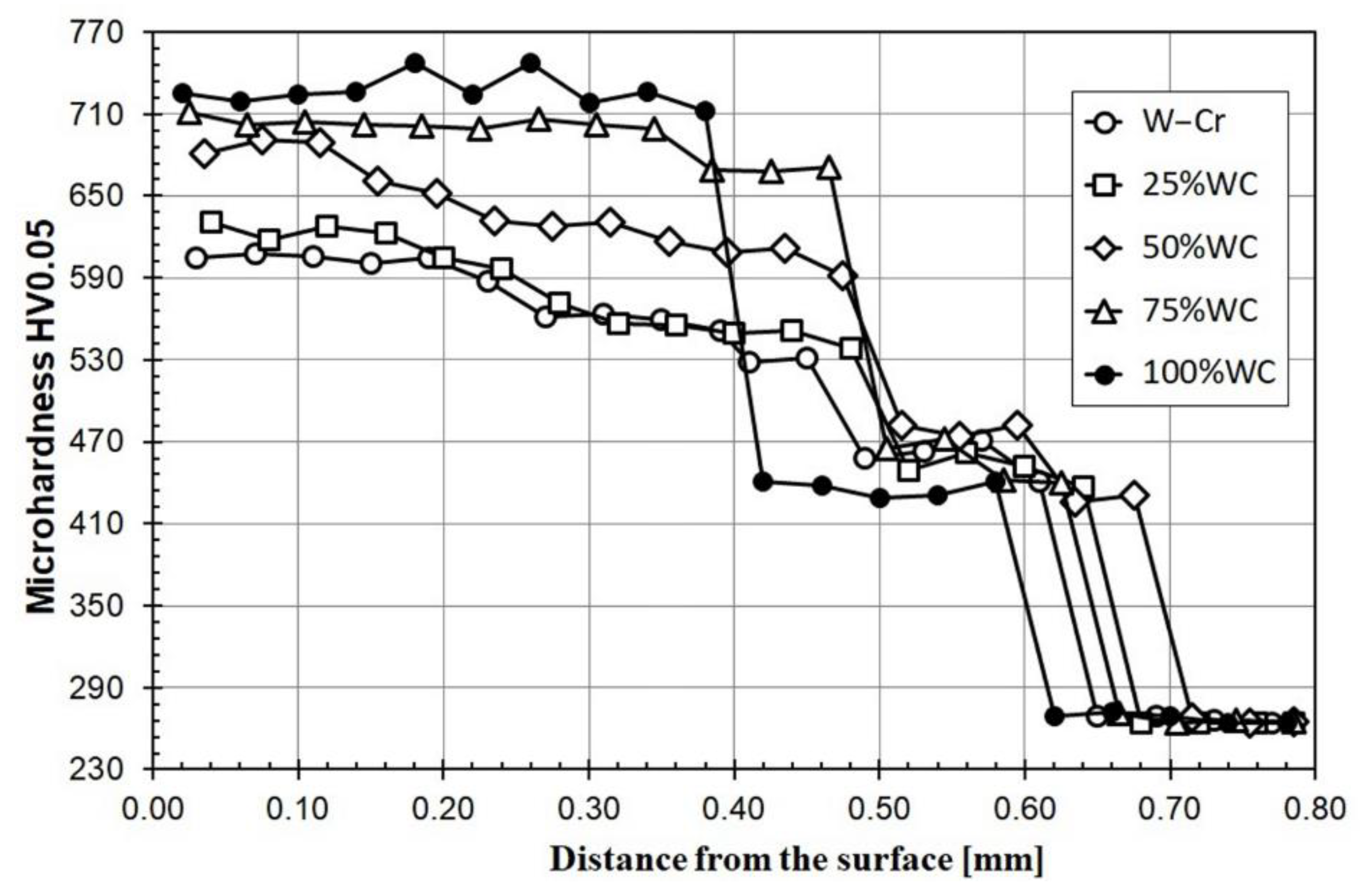


| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.32 | 0.63 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.07 | base |
| Composition of Powder Mixture | Parameters of Laser Beam | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| W–Cr (%) | WC (%) | Power of Laser Beam (W) | Scanning Rate of Laser Beam (mm/min) |
| 100 | 0 | 600 | 400 |
| 75 | 25 | 600 | 400 |
| 50 | 50 | 600 | 400 |
| 25 | 75 | 600 | 400 |
| 0 | 100 | 600 | 400 |
| Coating Type | Current Icorr (A·cm2) | Potential Ecorr (V) |
|---|---|---|
| W–Cr | 2.72 × 10−6 | −0.953 |
| W–Cr/25% WC | 5.68 × 10−6 | −1.04 |
| W–Cr/50% WC | 1.74 × 10−5 | −1.05 |
| W–Cr/75% WC | 2.22 × 10−5 | −1.05 |
| WC | 2.31 × 10−6 | −1.01 |
| Type of Coating | Designation | Martens Hardness (HM), N/mm2 | Vickers Hardness HV | Young’s Modulus (E), GPa | Plastic Deformation ηplast, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% W–Cr | Matrix | 2154 | 256 | 186 | 85.5 |
| W–Cr/25% WC | Carbide–boundary matrix | 13,502 4889 4300 | 1967 643 520 | 556 242 276 | 62.9 76.3 84.4 |
| W–Cr/50% WC | Carbide–boundary matrix | 14,048 5506 4453 | 2164 748 525 | 527 247 316 | 59.1 72.3 85.5 |
| W–Cr/75% WC | Carbide–boundary matrix | 14,692 5775 4756 | 2259 807 589 | 582 232 285 | 59.6 70.2 79.6 |
| 100% WC | Carbide–boundary matrix | 15,342 6349 6027 | 2385 930 857 | 602 225 229 | 60.4 63.1 67.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A.; Popielarski, P.; Hajkowski, J.; Piasecki, A. Characterization of W–Cr Metal Matrix Composite Coatings Reinforced with WC Particles Produced on Low-Carbon Steel Using Laser Processing of Precoat. Materials 2020, 13, 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225272
Bartkowski D, Bartkowska A, Popielarski P, Hajkowski J, Piasecki A. Characterization of W–Cr Metal Matrix Composite Coatings Reinforced with WC Particles Produced on Low-Carbon Steel Using Laser Processing of Precoat. Materials. 2020; 13(22):5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225272
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartkowski, Dariusz, Aneta Bartkowska, Paweł Popielarski, Jakub Hajkowski, and Adam Piasecki. 2020. "Characterization of W–Cr Metal Matrix Composite Coatings Reinforced with WC Particles Produced on Low-Carbon Steel Using Laser Processing of Precoat" Materials 13, no. 22: 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225272
APA StyleBartkowski, D., Bartkowska, A., Popielarski, P., Hajkowski, J., & Piasecki, A. (2020). Characterization of W–Cr Metal Matrix Composite Coatings Reinforced with WC Particles Produced on Low-Carbon Steel Using Laser Processing of Precoat. Materials, 13(22), 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225272









