Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Ni-TiC Composites Processed via Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mechanical Alloying
2.2. Spark Plasma Sintering
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-ray Diffraction
2.4. Microhardness, Compression, and Tribological Testings
3. Results and Discussion
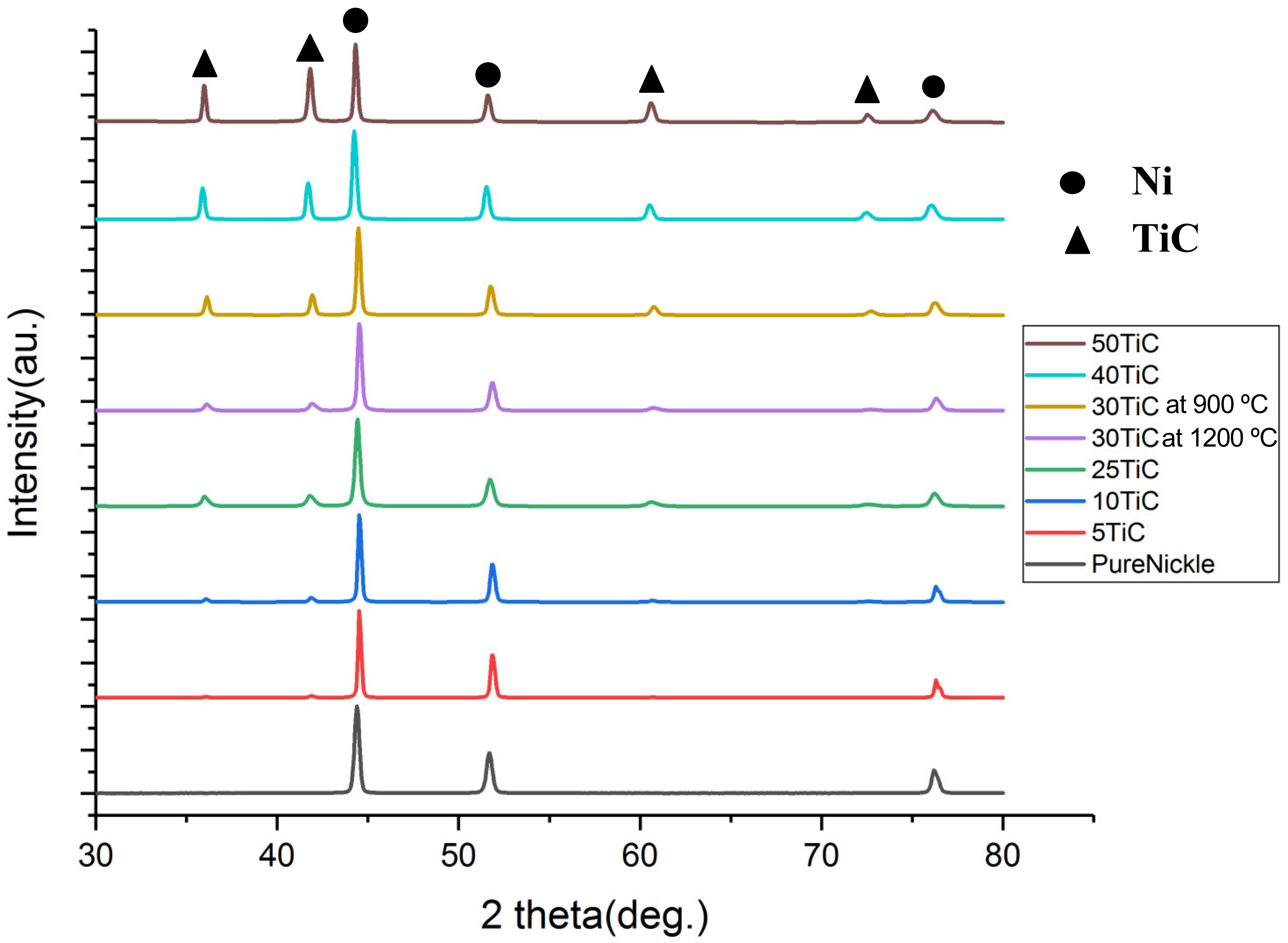
3.1. XRD Testing
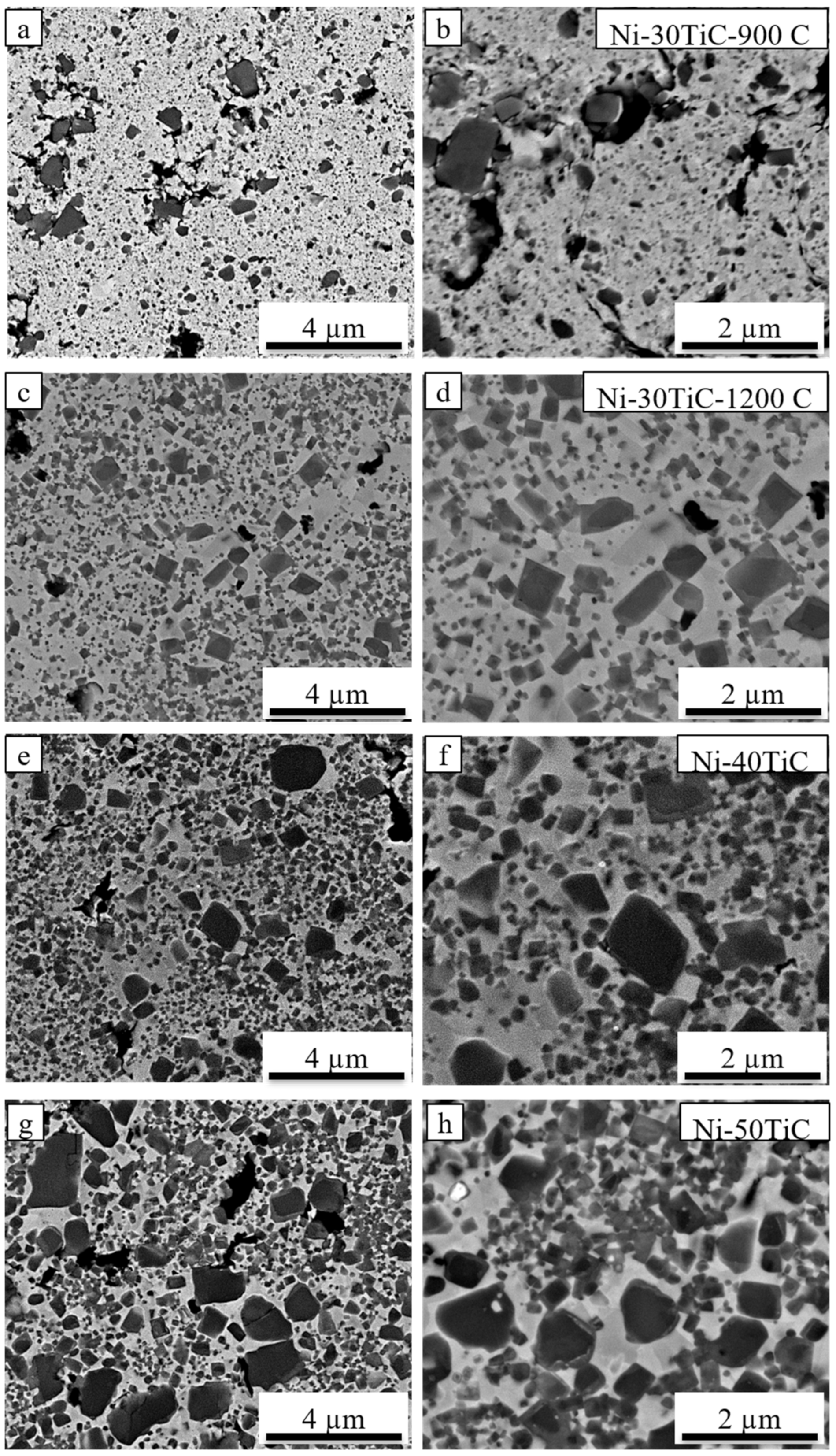
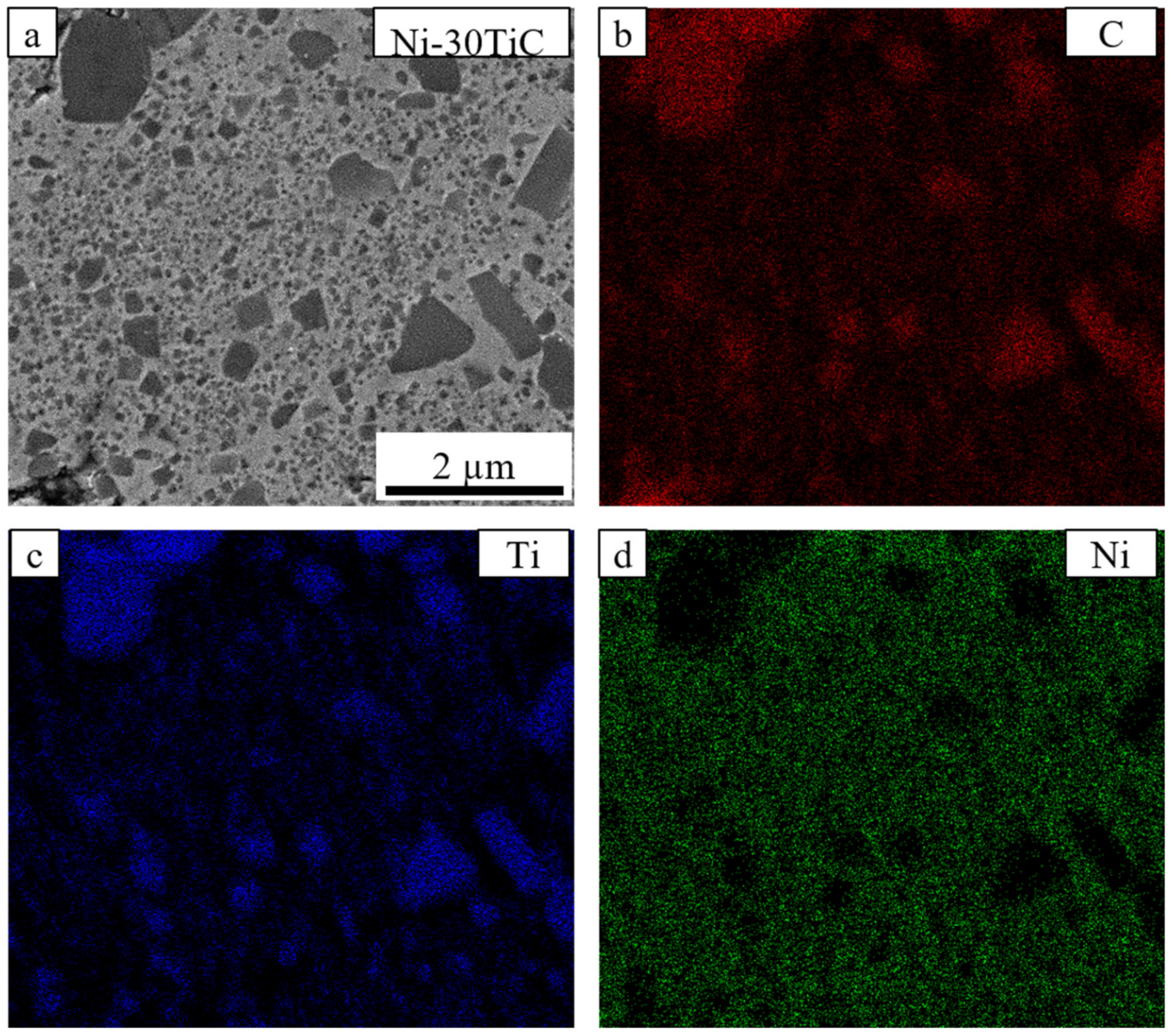
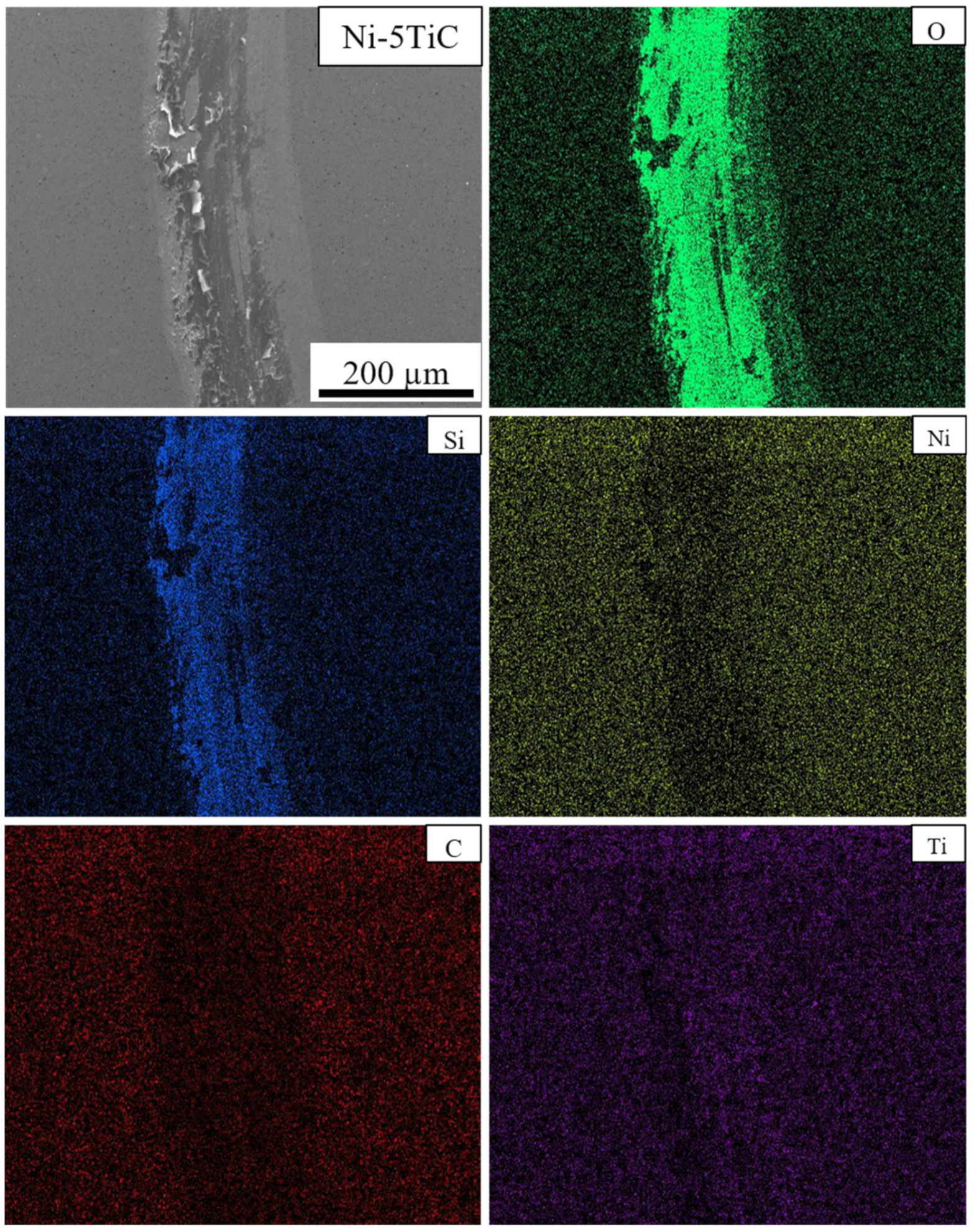
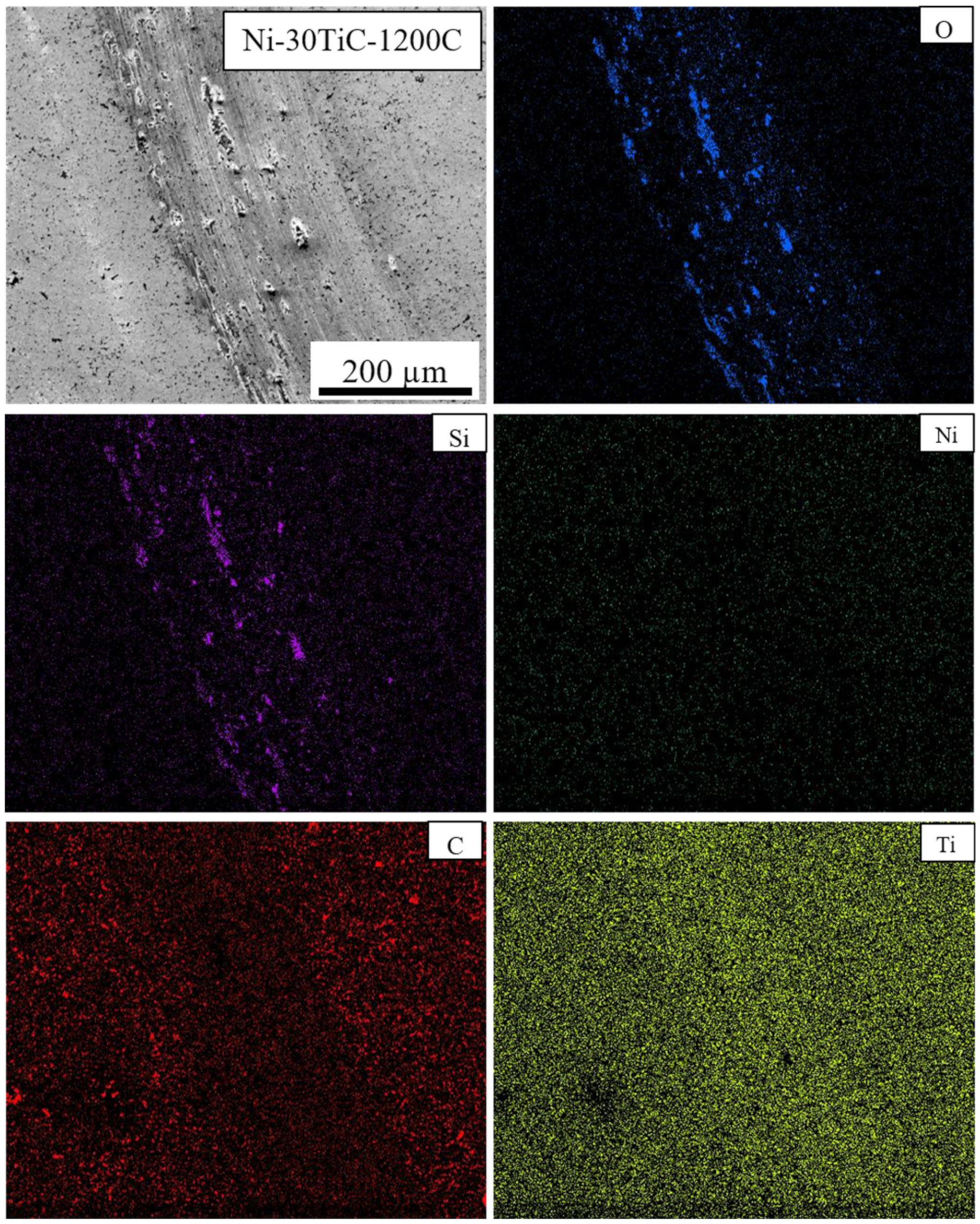
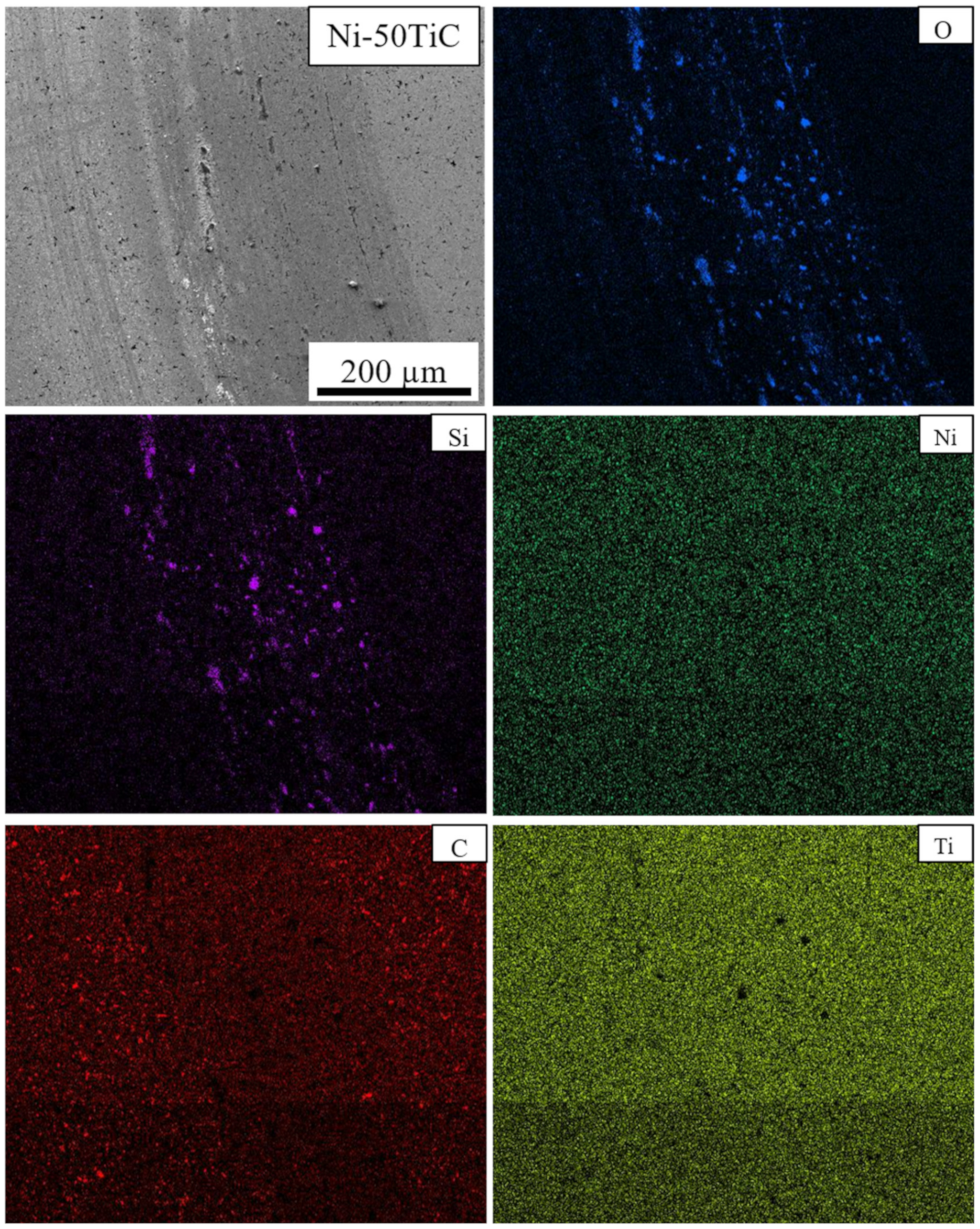
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis and Relative Density
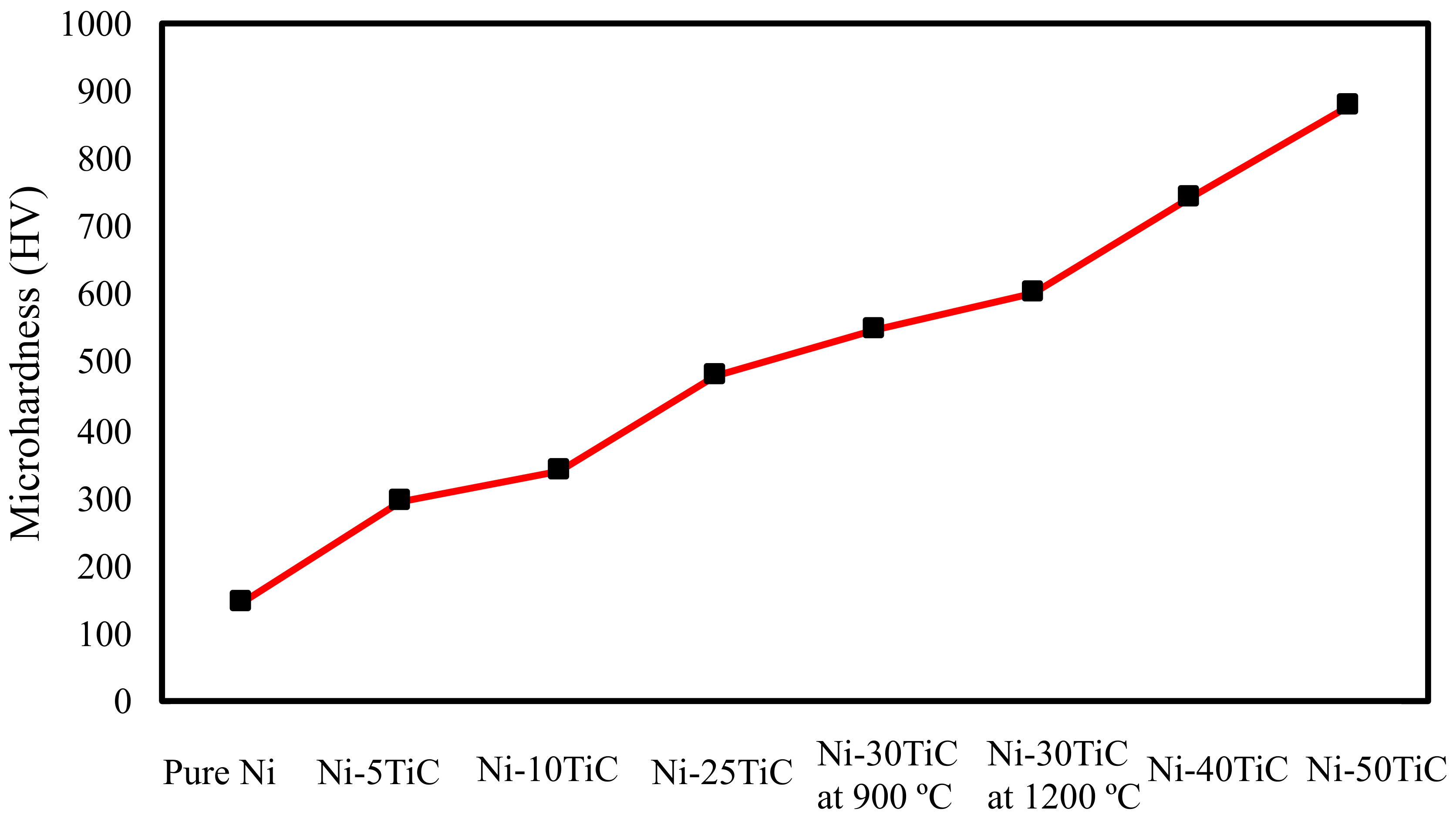
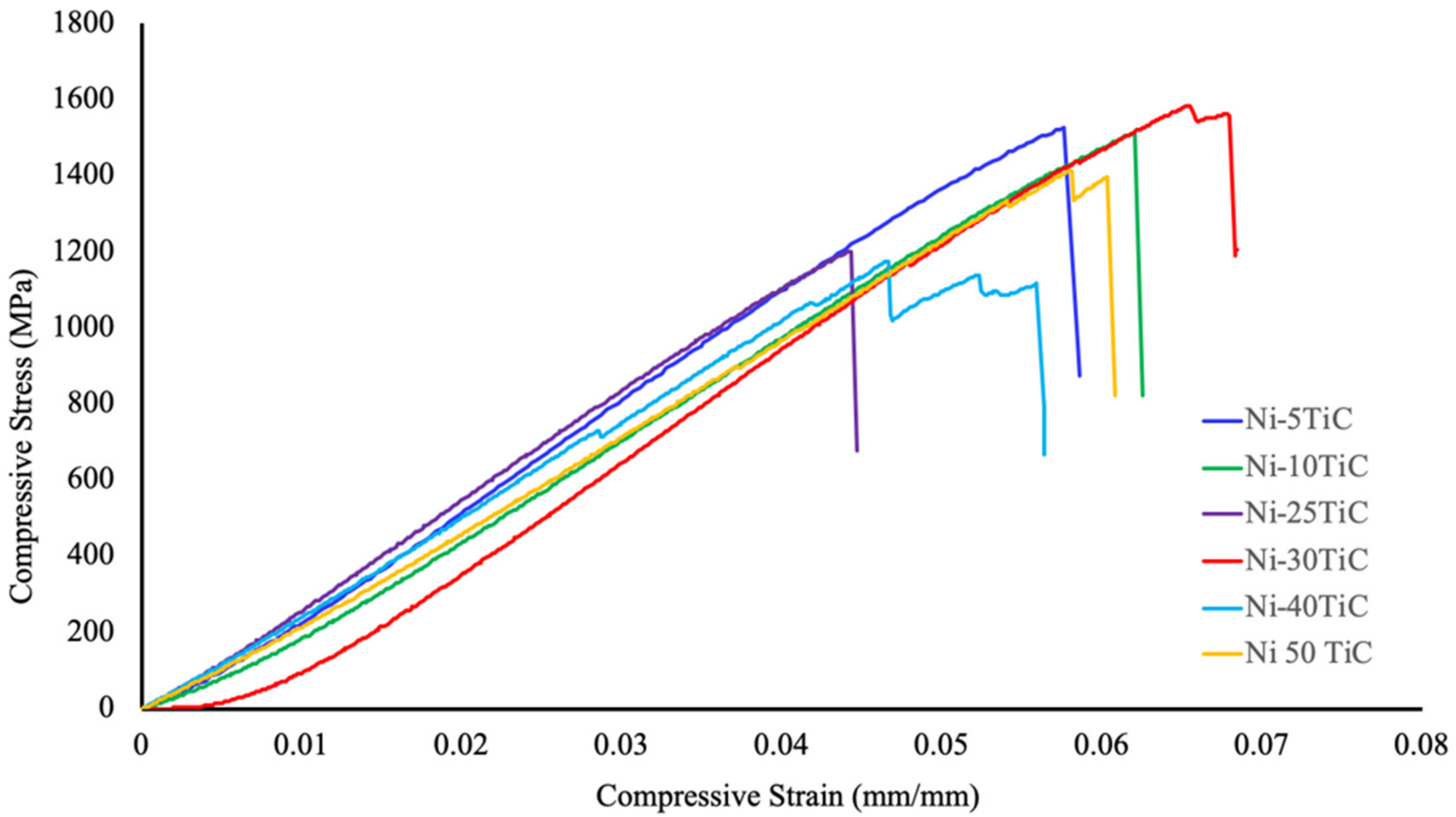
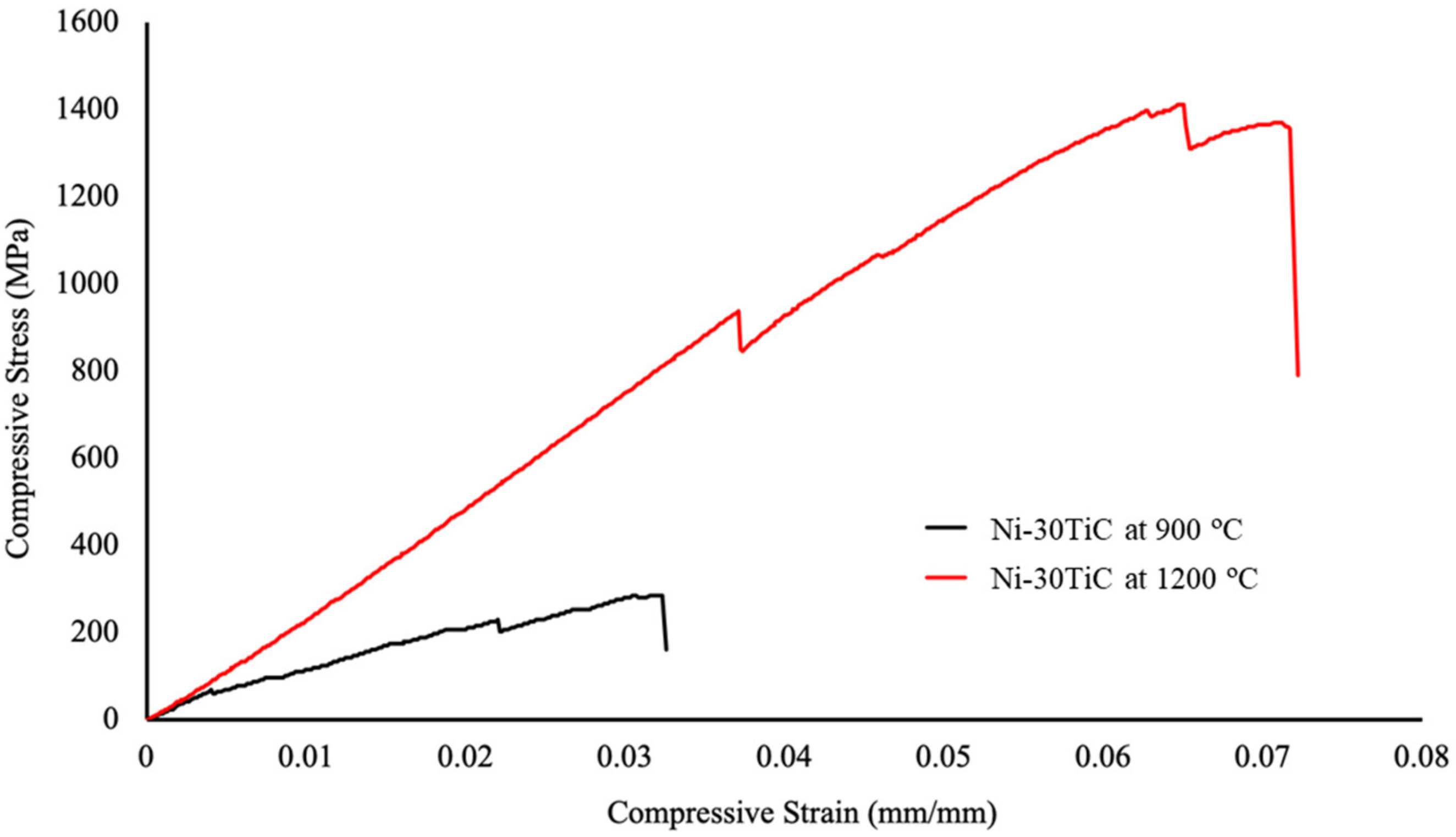
3.3. Mechanical Properties
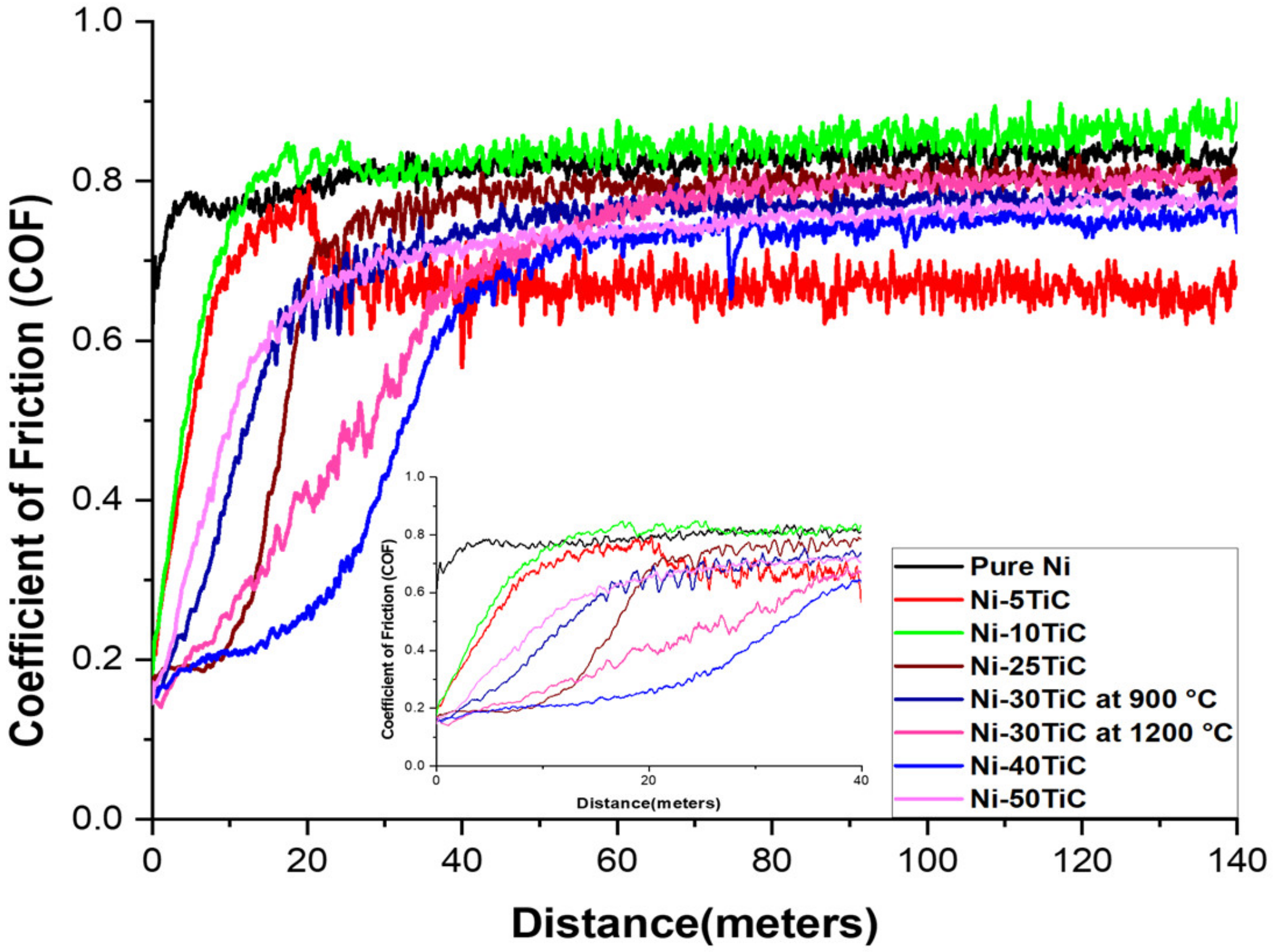
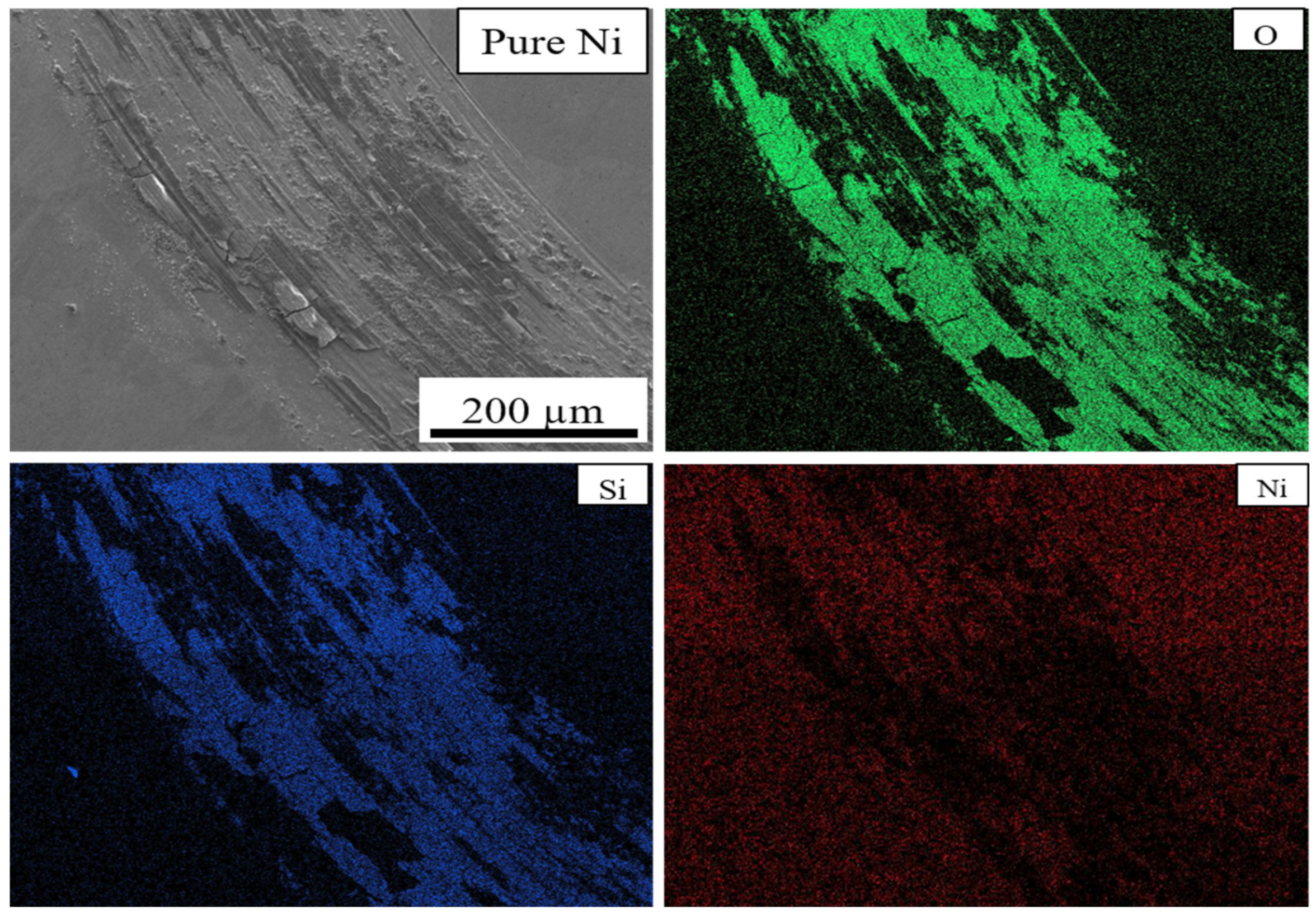
3.4. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miracle, D.B. Metal matrix composites—From science to technological significance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Mohamed, F.A.; Lavernia, E.J. Particulate reinforced metal matrix composites—A review. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkar, T.; Mohseni, H.; Hwang, J.; Scharf, T.W.; Tiley, J.S.; Hong, S.H.; Banerjee, R. Excellent strength-ductility combination in nickel-graphite nanoplatelet (GNP/Ni) nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 646, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhong, M.; Liu, W. TiC particulate composite coating produced in situ by laser cladding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 343, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doǧan, Ö.; Hawk, J.; Tylczak, J.; Wilson, R.; Govier, R. Wear of titanium carbide reinforced metal matrix composites. Wear 1999, 225–229, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, P.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Guo, Z. Effect of TiC content on Ni/TiC composites by direct laser fabrication. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohari, S.; Sadeghian, Z.; Lotfi, B.; Broeckmann, C. Application of spark plasma sintering (SPS) for the fabrication of in situ Ni–TiC nanocomposite clad layer. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 633, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, L. The historical development of mechanochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buie—2011—Evolution of Laboratory Mills and Grinders. Available online: https://www.labmanager.com/lab-product/evolution-of-laboratory-mills-and-grinders-18766 (accessed on 6 April 2011).
- Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Xie, R.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Ye, X.; Xu, H. The key role of ball milling time in the microstructure and mechanical property of ni-ticnp composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 5280–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheb, N.; Iqbal, Z.; Khalil, A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Al Aqeeli, N.; Laoui, T.; Al-Qutub, A.; Kirchner, R. Spark plasma sintering of metals and metal matrix nanocomposites: A review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, F.H.; Suryanarayana, C.; Russell, K.; Li, C.-G. Synthesis of intermetallics by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 192–193, 612–623. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanko, M.; Maruyama, T.; Tomino, H. Neck growth on initial stage of pulse current pressure sintering for coarse atomized powder made of cast-iron. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1999, 63, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hulbert, D.M.; Anders, A.; Dudina, D.V.; Andersson, J.; Jiang, D.; Unuvar, C.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Lavernia, E.J.; Mukherjee, A.K. The absence of plasma in ‘spark plasma sintering. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 33305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Shikatani, N.; Kawakami, Y.; Enjoji, T.; Ohtsu, Y.; Fujita, H. Observation of internal pulsed current flow through the ZnO specimen in the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Shikatani, N.; Kawakami, Y.; Enjoji, T.; Ohtsu, Y. Influence of internal pulsed current on the sintering behavior of pulsed current sintering process. THERMEC 2009 2010, 638, 2109–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M. Development of Advanced Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Systems and its Industrial Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Tokita, M. Mechanism of spark plasma sintering. Int. Symp. Funct. Graded Mater. 1994, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, R.; Licheri, R.; Locci, A.M.; Cincotti, A.; Cao, G. Consolidation/synthesis of materials by electric current activated/assisted sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 63, 127–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Gennari, S.; Garay, J.E.; Munir, Z.A. Fundamental investigations on the spark plasma sintering/synthesis process: II. Modeling of current and temperature distributions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 394, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International, A. G99-17: Standard test method for wear testing with a pin-on-disk apparatus. Annu. B ASTM Stand. 2017, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Borkar, T.; Banerjee, R. Influence of spark plasma sintering (SPS) processing parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, H.; Schoenstein, F.; Abdellaoui, M.; Jouini, N. Spark plasma sintering consolidation of nanostructured TiC prepared by mechanical alloying. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-eskandarany, M.S. Structure and properties of nanocrystalline TiC full-density bulk alloy consolidated from mechanically reacted powders. J. Alloy. Compd. 2000, 305, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teber, A.; Schoenstein, F.; Têtard, F.; Abdellaoui, M.; Jouini, N. Effect of SPS process sintering on the microstructure and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline TiC for tools application. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 30, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wong, L.N.Y. Loading rate effects on cracking behavior of flaw-contained specimens under uniaxial compression. Int. J. Fract. 2013, 180, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.P.; Guo, J.T.; Han, Y.F.; Yu, L.G. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of the NiAl-TiC in situ composite. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1997, 28, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigney, J.D.; Lewandowski, J.J. Effects of reinforcement size and distribution on fracture toughness of composite nickel aluminide intermetallics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 158, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaire, S.; Cliche, G. Tribological properties of TiC-Fe coatings obtained by plasma spraying reactive powders. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 1993, 2, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, P.; Torrance, A.A. The calculation of wear coefficients for plastic contacts. In Wear; Elsevier Sequoia S.A.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1991; Volume 145, pp. 367–383. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.M.; Qu, S.Y.; Zou, Z.D. Microstructure and wear properties of TiC/FeCrBSi surface composite coating prepared by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Walunj, G.; Torgerson, T.B.; Koricherla, M.V.; Khan, M.U.; Scharf, T.W.; Gupta, R.; Borkar, T. Tribological behavior of in situ processed NI-Ti-C nanocomposites. Tribol. Trans. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.C.D. The wear of metals by relatively soft abrasives. In Wear; Elsevier Sequoia S.A.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1968; Volume 11, pp. 245–275. [Google Scholar]

| No. | Specimen ID | Max. Temperature (°C) | Holding Time (min) | Pressure (MPa) | Grain Size Ni | Relative Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pure Ni | 900 | 5 | 65 | 33.67 μm | 98.20% |
| 2 | Ni-5TiC | 900 | 5 | 65 | 0.43 μm | 96.02% |
| 3 | Ni-10TiC | 900 | 5 | 65 | 0.36 μm | 93.39% |
| 4 | Ni-25TiC | 900 | 5 | 65 | 0.12 μm | 86.01% |
| 5 | Ni-30TiC | 900 | 5 | 65 | 0.11 μm | 84.01% |
| 6 | Ni-30TiC | 1200 | 5 | 65 | 0.21 μm | 98.27% |
| 7 | Ni-40TiC | 1200 | 5 | 65 | 0.20 μm | 94.46% |
| 8 | Ni-50TiC | 1200 | 5 | 65 | 0.19 μm | 91.77% |
| Samples and Sintering Temperature | Yield Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strain (%) | Hardness (HV) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-5TiC-900 °C | 1393.72 | 1414.01 | 4.93 | 294.7 | 29,735.41 |
| Ni-10TiC-900 °C | 1492.54 | 1511.27 | 5.79 | 338.4 | 27,351.03 |
| Ni-25TiC-900 °C | 1199.5 | 1202.52 | 4.14 | 483.1 | 29,287.06 |
| Ni-30TiC-900 °C | 97.55 | 288.02 | 2.99 | 549 | 17,573.48 |
| Ni-30TiC-1200 °C | 1436 | 1585.26 | 6.10 | 601.4 | 29,914.28 |
| Ni-40TiC-1200 °C | 1166.18 | 1175.44 | 4.35 | 743.9 | 26,993.81 |
| Ni-50TiC-1200 °C | 1390.06 | 1413.21 | 5.42 | 877.8 | 26,360.78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walunj, G.; Bearden, A.; Patil, A.; Larimian, T.; Christudasjustus, J.; Gupta, R.K.; Borkar, T. Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Ni-TiC Composites Processed via Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2020, 13, 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225306
Walunj G, Bearden A, Patil A, Larimian T, Christudasjustus J, Gupta RK, Borkar T. Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Ni-TiC Composites Processed via Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials. 2020; 13(22):5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225306
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalunj, Ganesh, Anthony Bearden, Amit Patil, Taban Larimian, Jijo Christudasjustus, Rajeev Kumar Gupta, and Tushar Borkar. 2020. "Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Ni-TiC Composites Processed via Spark Plasma Sintering" Materials 13, no. 22: 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225306
APA StyleWalunj, G., Bearden, A., Patil, A., Larimian, T., Christudasjustus, J., Gupta, R. K., & Borkar, T. (2020). Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Ni-TiC Composites Processed via Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials, 13(22), 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225306








