Experimental Study of Utilizing Recycled Fine Aggregate for the Preparation of High Ductility Cementitious Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportion and Preparation of Specimens
2.3. Test Method
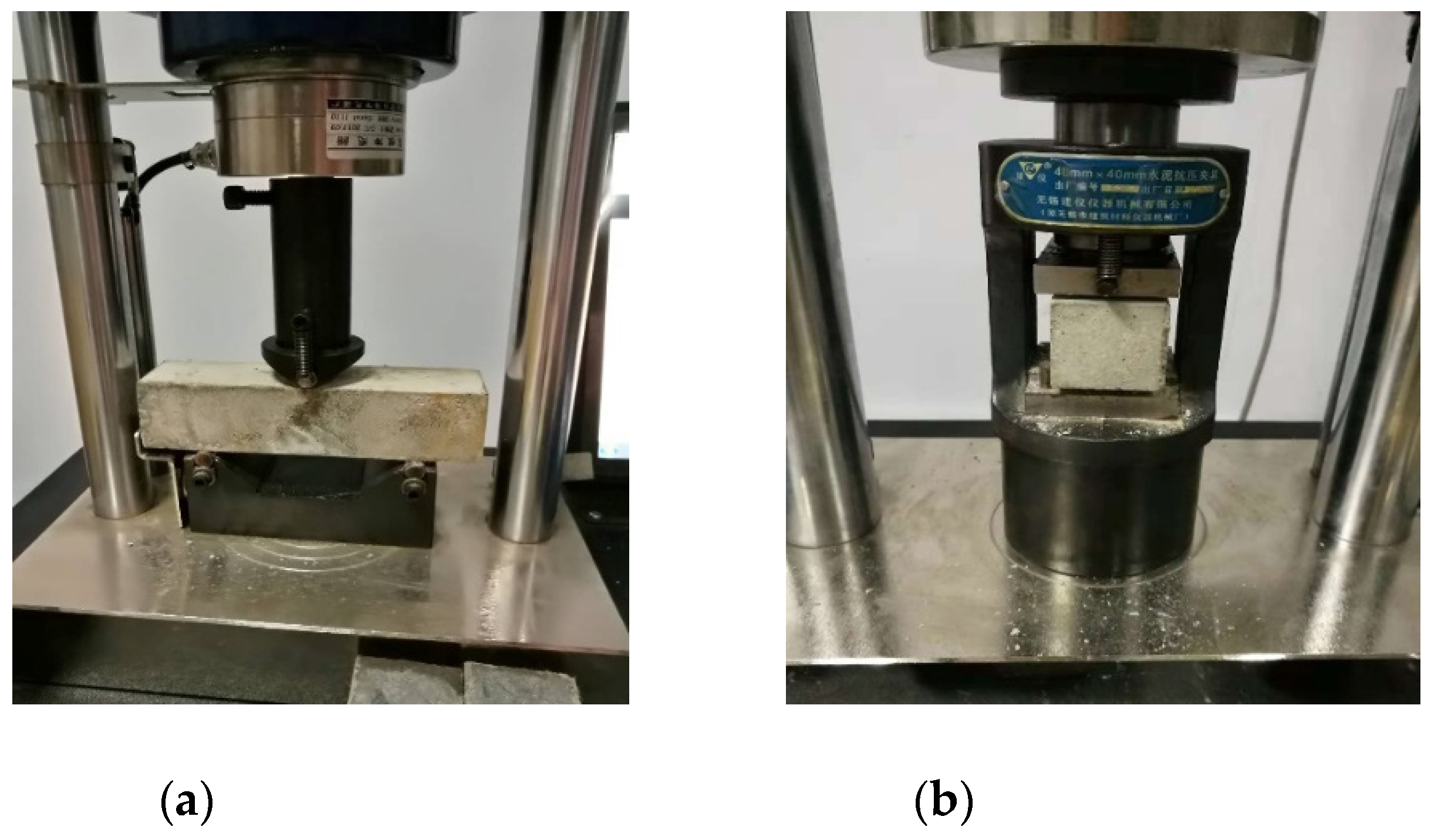
2.3.1. Flexural and Compressive Strength Test
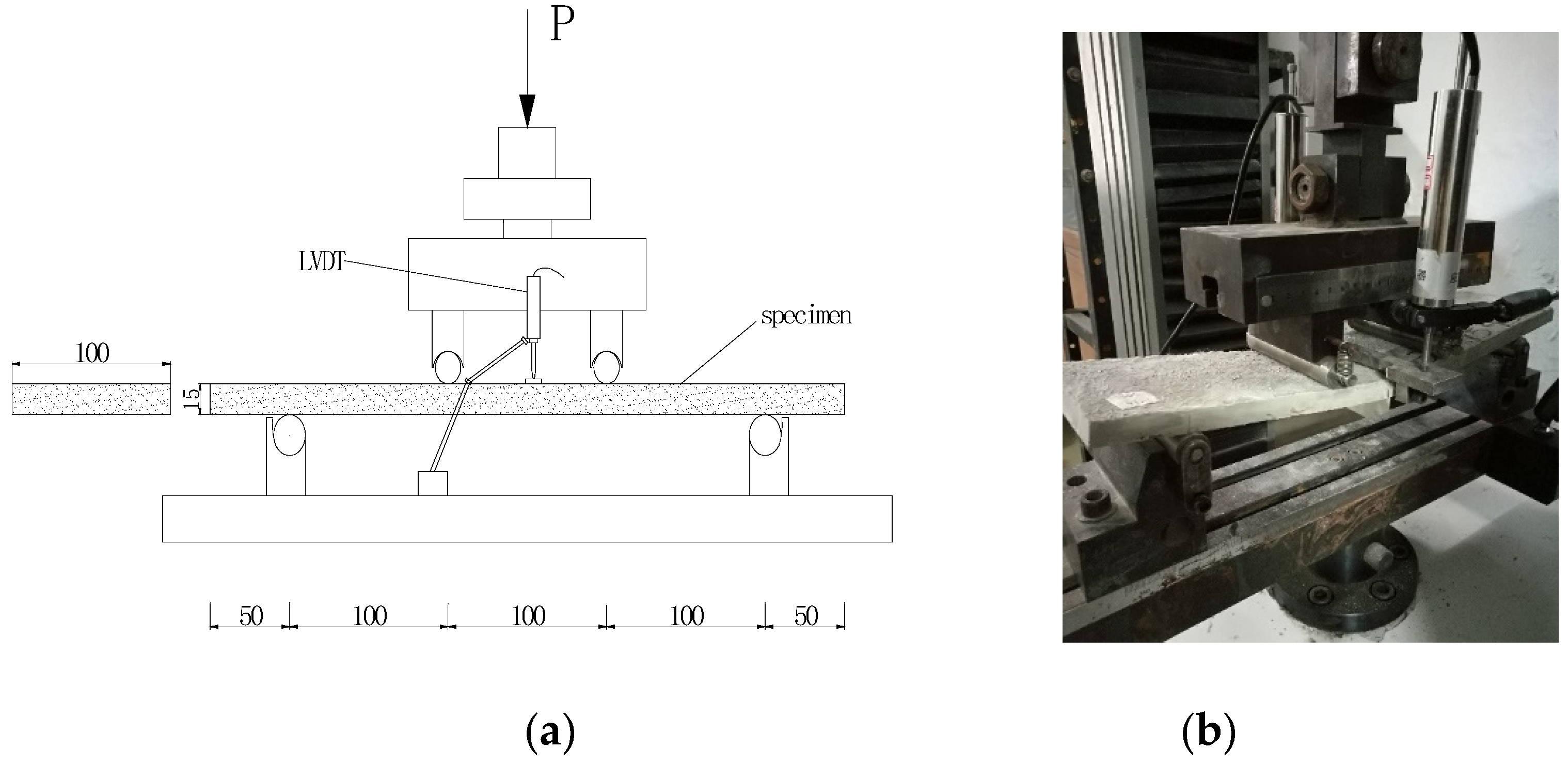
2.3.2. Four-Point Bending Test
2.3.3. Axial Tensile Test
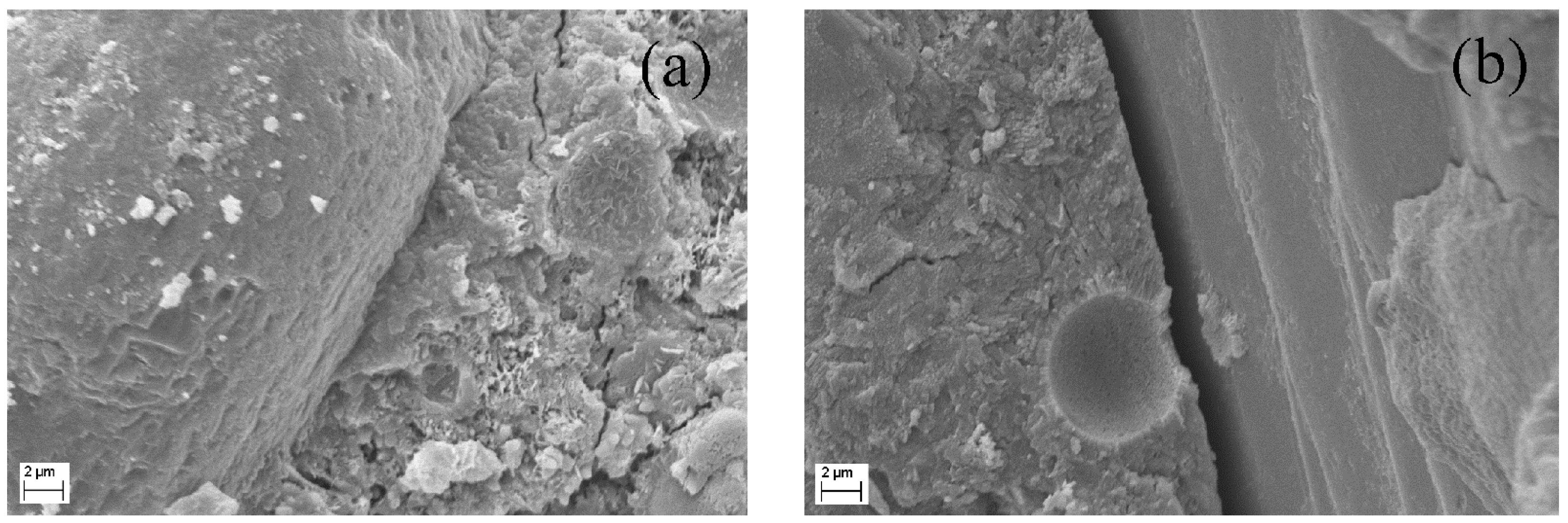
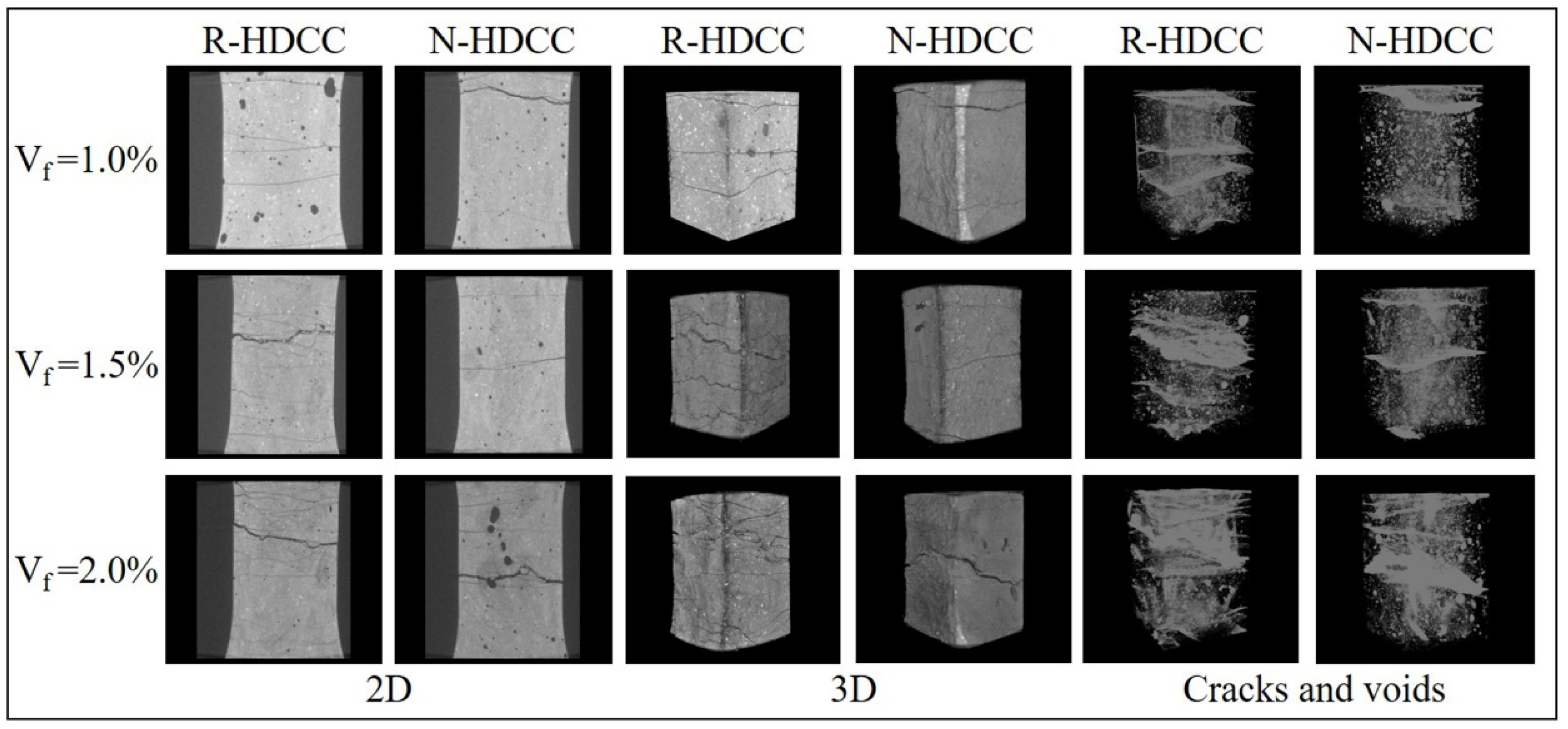
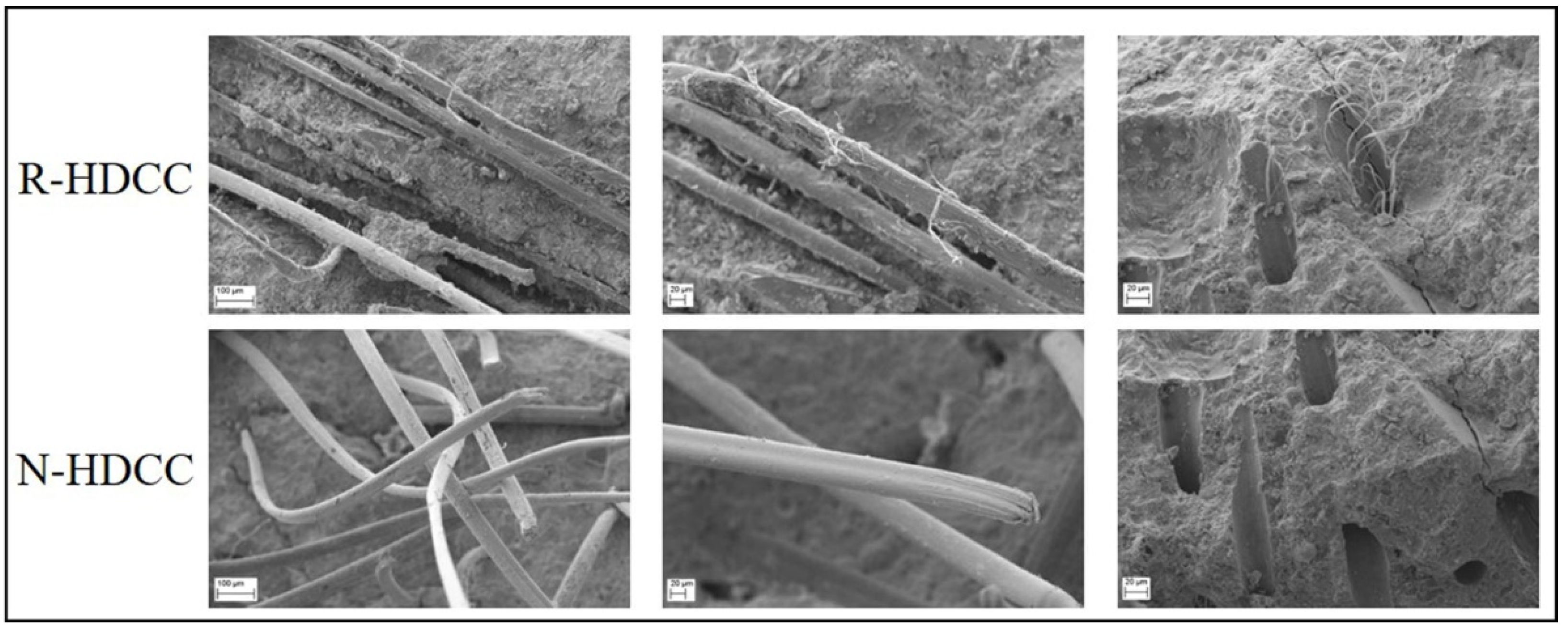
2.3.4. Microstructure Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
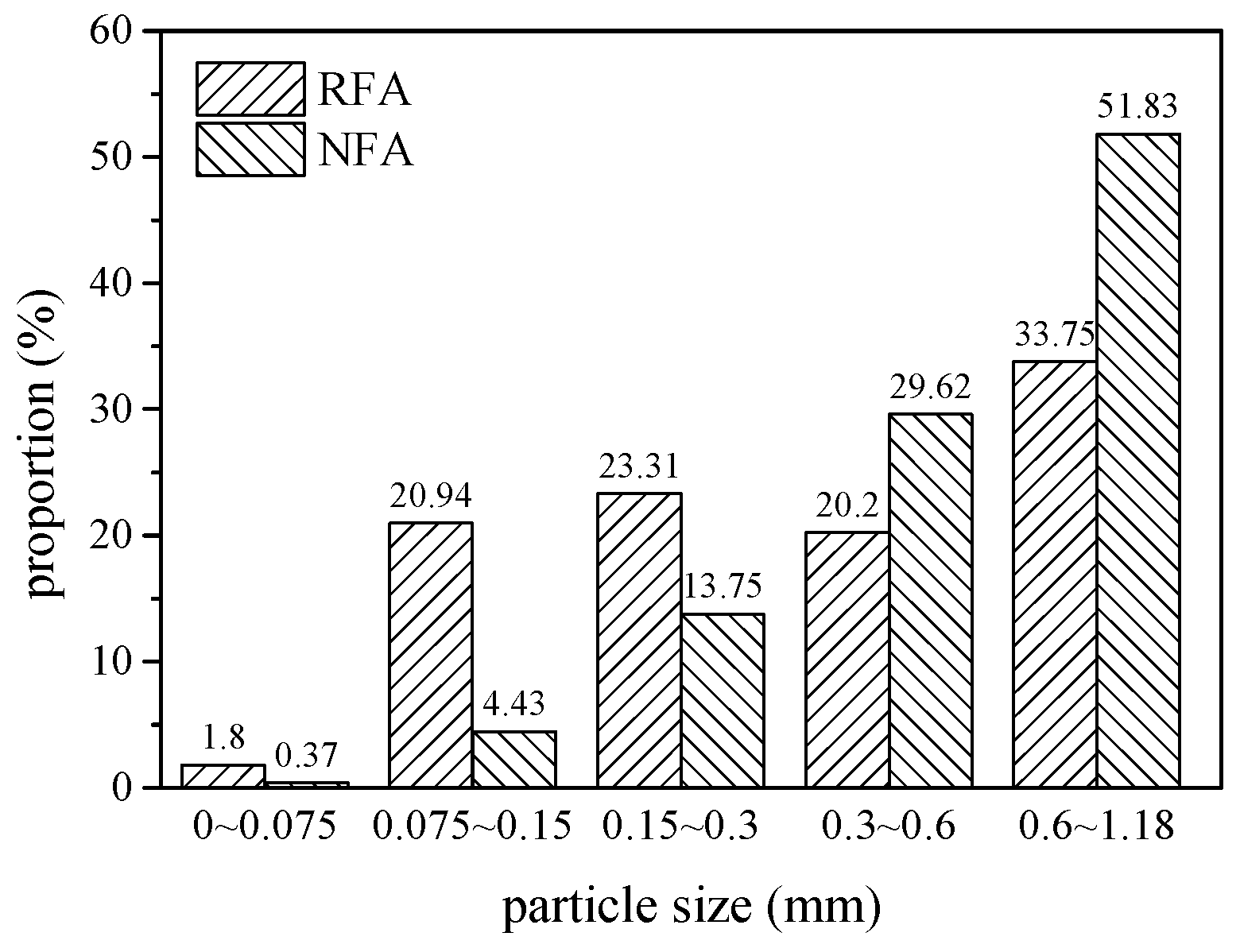
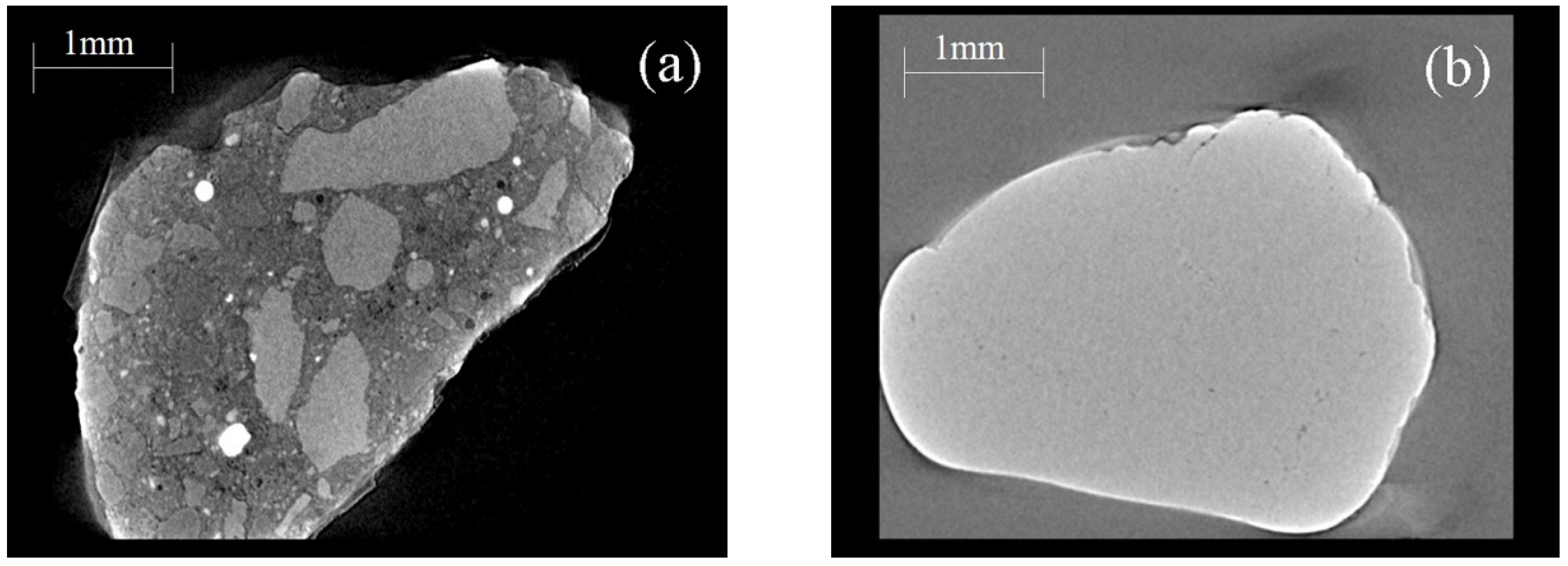
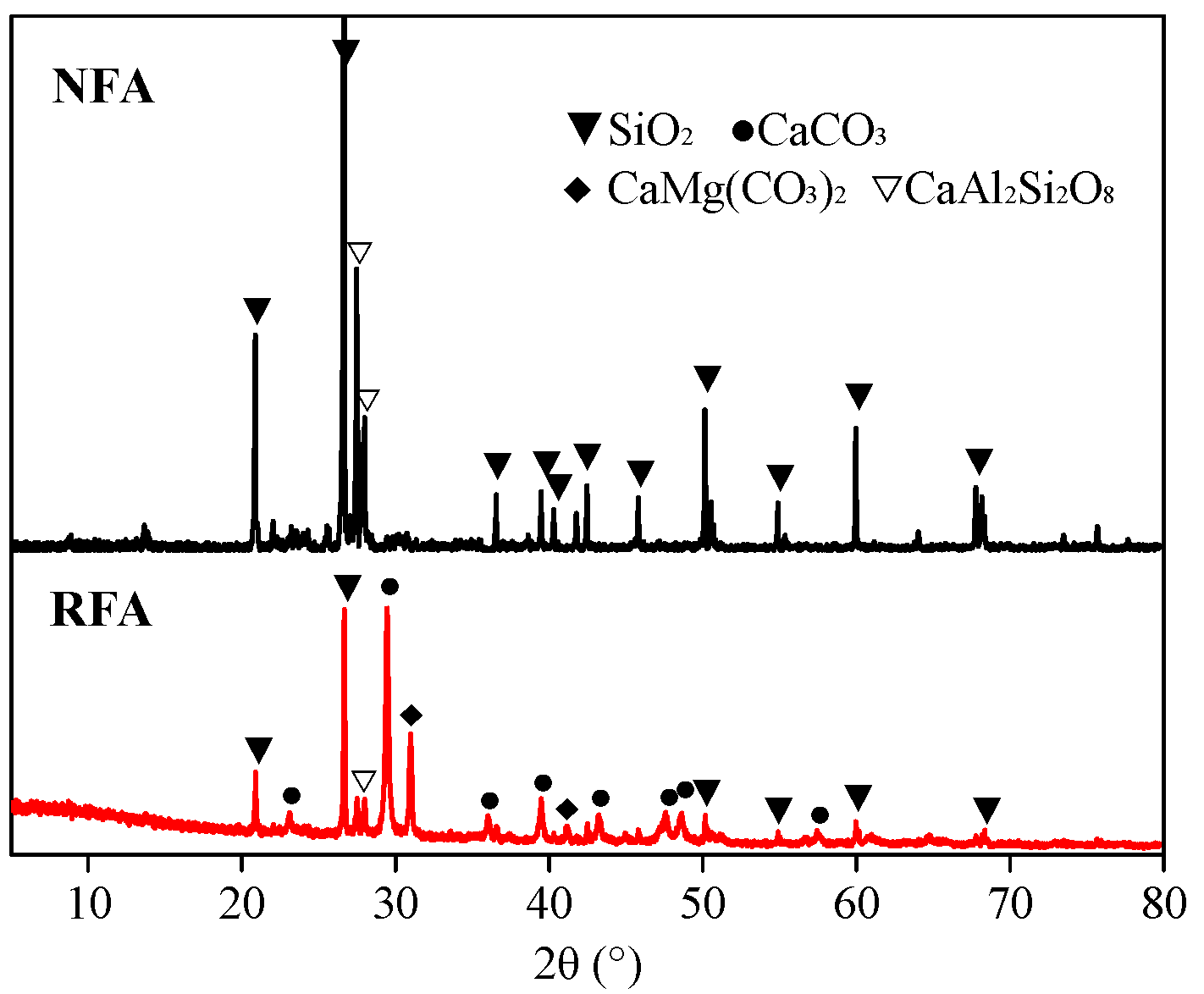
3.1. Properties of RFA and NFA
3.2. Compressive and Flexural Strength
3.3. Bending Stress-Deflection Curves
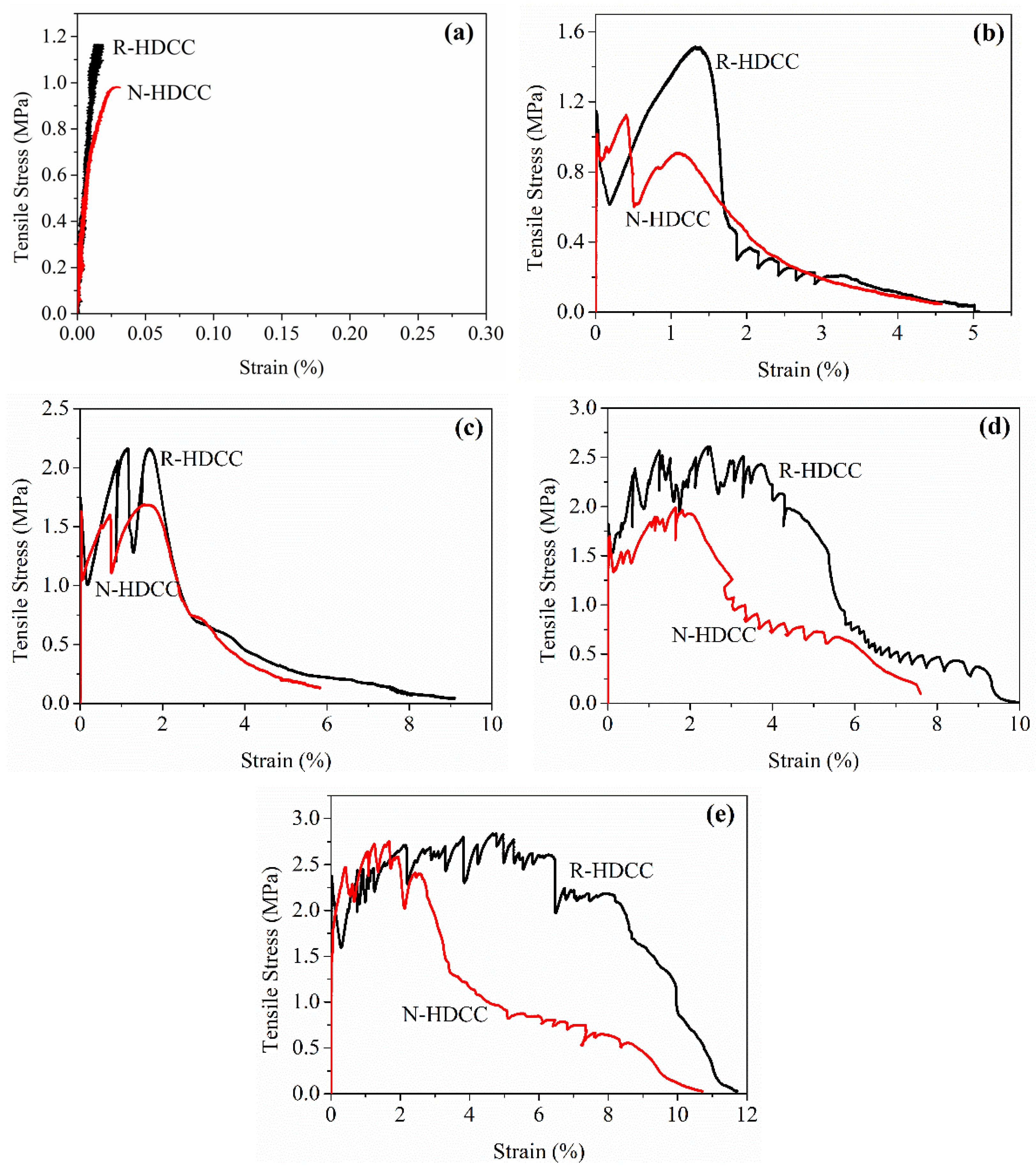
3.4. Axial Tensile Stress-Strain Curves
4. Prediction of Mechanical Properties
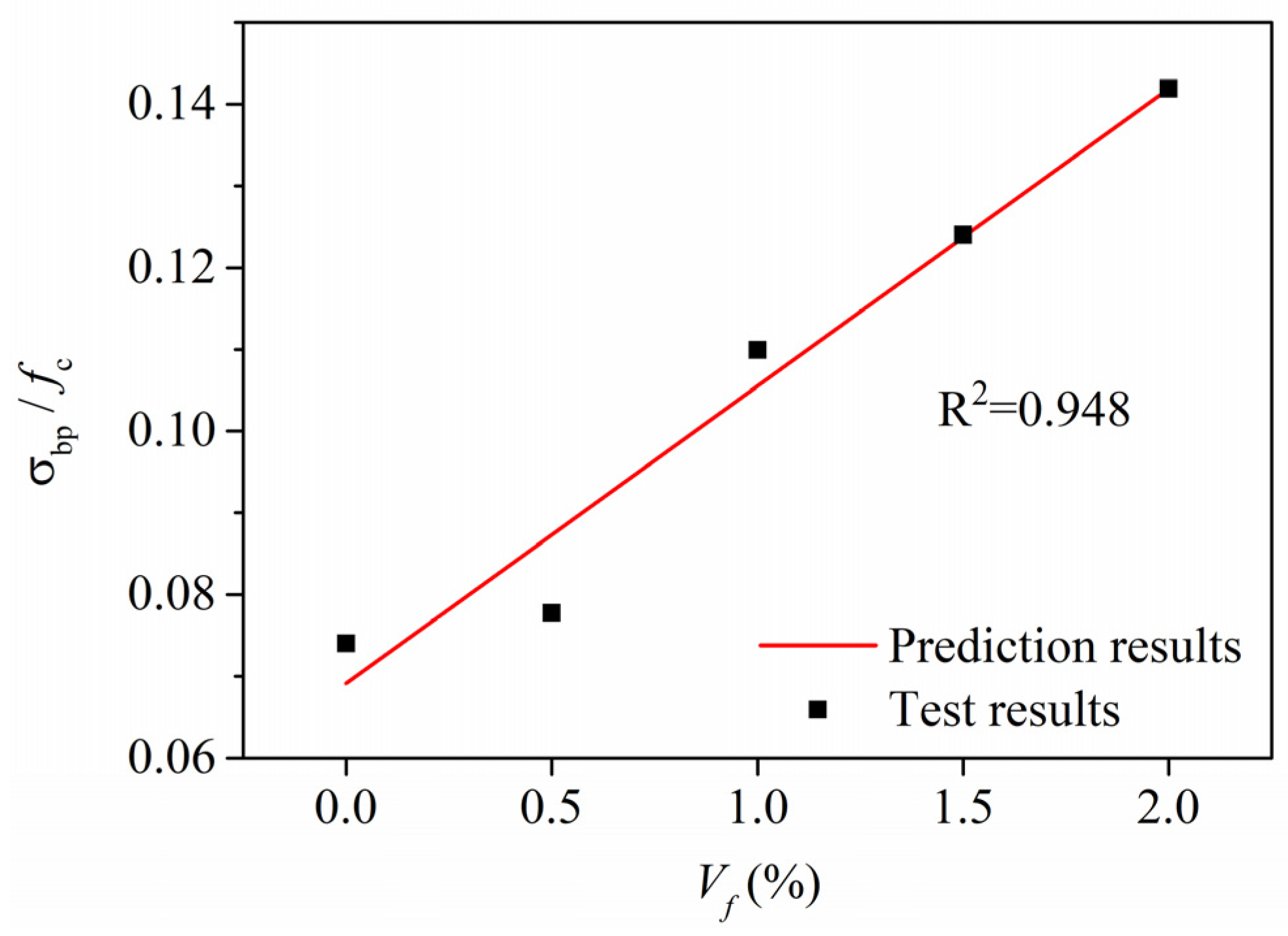
4.1. Bending Peak Strength
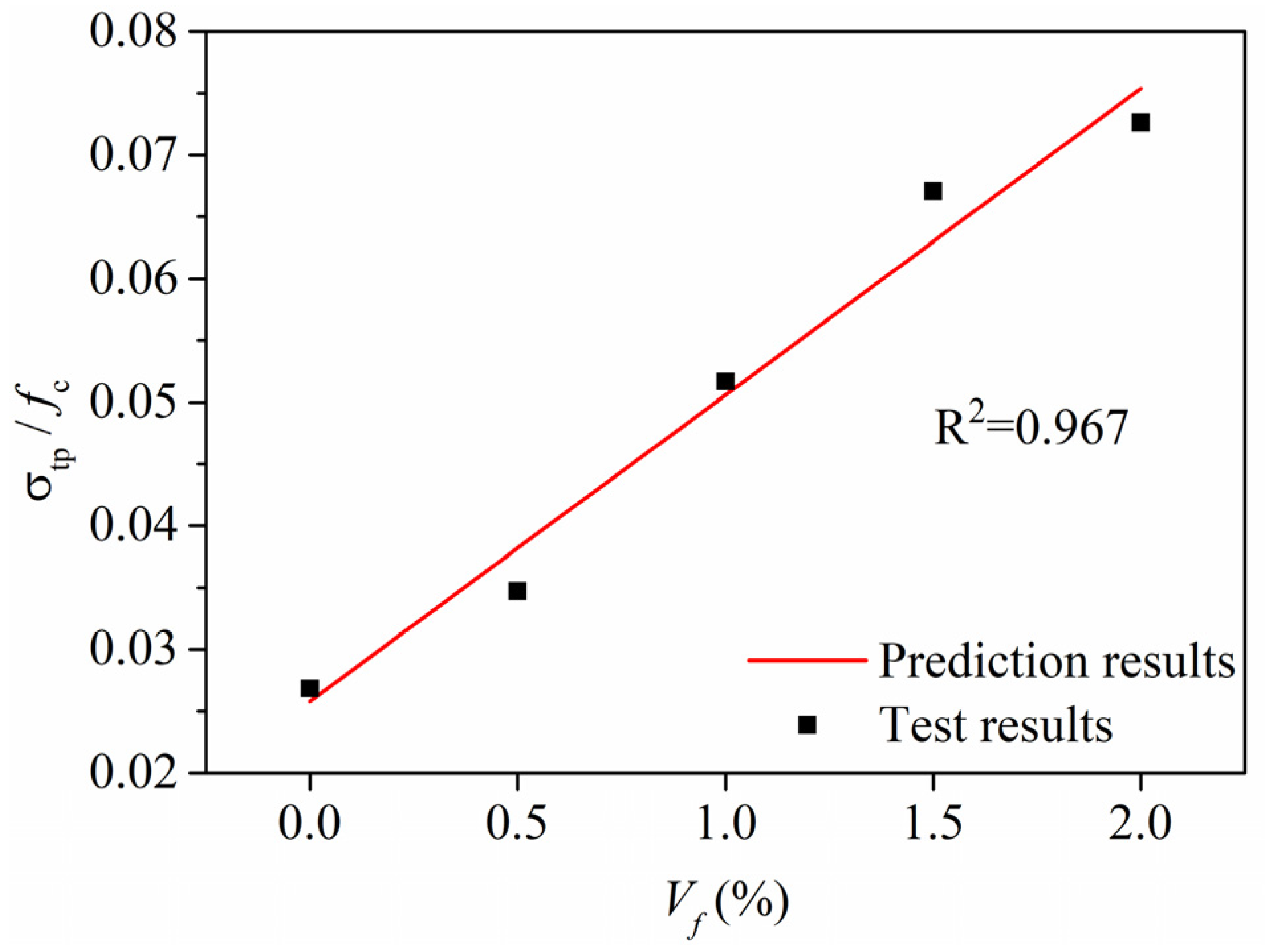
4.2. Tensile Peak Strength
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- RFA with original particle size distribution contains 4.86 times as much concrete crush dust as natural fine aggregate. The dust supplies a certain activity and a good filling effect in matrix. Coupled with the higher water absorption rate of RFA, HDCC with RFA forms a denser matrix. Thus, HDCC with RFA exhibits a higher compressive strength than HDCC with NFA.
- (2)
- Because of the denser matrix, HDCC with RFA has a higher bond between fiber and matrix than HDCC with NFA. This can be proved by the scanning electron microscope observations that fibers pulled out from HDCC with RFA were seriously damaged while fibers pulled out from HDCC with NFA were only slightly abraded. As a result, HDCC with RFA exhibits higher bending and tensile strength than HDCC with NFA.
- (3)
- The higher bond between fiber and matrix of HDCC with RFA and the finer particle sizes of RFA can greatly promote the development of multiple cracking. Thus, HDCC with RFA presents more remarkable stain hardening and exhibits 182.73% higher peak deflection in the bending and 183.33% higher peak strain in tension than HDCC with NFA.
- (4)
- The values of σbp/fc and σtp/fc of HDCC with RFA linearly increase with the increase of Vf, and the relationships are modelled by a linear equation, respectively. Additionally, there is also a good linear relationship between the values of σbp/fc and σtp/fc of HDCC with RFA.
- (5)
- HDCC with RFA exhibits better mechanical properties than HDCC with NFA. Therefore, the application of RFA in the preparation of HDCC can obtain significant social and economic benefits.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| RFA | recycled fine aggregate; |
| NFA | natural fine aggregate; |
| HDCC | high ductility cementitious composite; |
| R-HDCC | high ductility cementitious composite prepared with recycled fine aggregate; |
| N-HDCC | high ductility cementitious composite prepared with natural fine aggregate. |
References
- USEPA. Advancing Sustainable Materials Management: 2015 Fact Sheet; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Bostanci, S.C.; Limbachiya, M.; Kew, H. Use of recycled aggregates for low carbon and cost effective concrete construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, S.R.; Andrade, J.J.D.O. Investigation of mechanical properties and carbonation of concretes with construction and demolition waste and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A.C.J. A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000–2017). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P. Environmental Pollution Hazards of Urban Construction Wastes and Related Resource Recycling Measures: A Case Study in Central China. Nat. Envir. Pollut. Technol. 2018, 17, 777–782. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.C.; Kosmatka, S.H.; Voigt, G.F. Integrated Materials and Construction Practices for Concrete Pavement: A State of the Practice Manual; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Freedonia. World Construction Aggregates to 2015—Industry Study 2838; The Freedonia Group: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Verian, K.P.; Ashraf, W.; Cao, Y. Properties of recycled concrete aggregate and their influence in new concrete production. Resour. Conservat. Recycl. 2018, 133, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayasundara, M.; Mendis, P.; Crawford, R.H. Net incremental indirect external benefit of manufacturing recycled aggregate concrete. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Toward the Development of Sustainable Concretes with Recycled Concrete Aggregates: Comprehensive Review of Studies on Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arel, H.Ş.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Semi-green cementitious materials from waste granite by considering the environmental, economic, and health impacts: A review. Struct. Concr. 2019, 20, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Long, C.; Wu, C.; Duan, W.H.; Shah, S.P. Effects of nanoparticle on the dynamic behaviors of recycled aggregate concrete under impact loading. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, L.; Nokken, M. Mechanical behavior of recycled coarse aggregate concrete reinforced with steel fibers under direct shear. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Fonteboa, B.; Seara-Paz, S.; De Brito, J.; González-Taboada, I.; Martínez-Abella, F.; Vasco-Silva, R. Recycled concrete with coarse recycled aggregate. An overview and analysis. Materiales Construcción 2018, 68, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Shi, C.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ling, T.-C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete – A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Feng, J.; Hu, K. Mechanical Properties and ITZ Microstructure of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using Carbonated Recycled Coarse Aggregate. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2018, 33, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, M.V.A.; Brouwers, H.J.H. In Recycled concrete fines and aggregates: the composition of various size fractions related to crushing history. In Proceedings of the international conference on building materials (IBAUSIL), Weimar, Germany, 12–15 September 2012; pp. 1034–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zilin, Z.; Wenying, G.; Haoxuan, L. Research on production of recycled total-fine aggregate and its influence on concrete performance. J. Funct. Mater. 2016, 4, 4157–4163. [Google Scholar]
- Lederer, C.; Altstadt, S.; Andriamonje, S.; Andrzejewski, J.; Audouin, L.; Barbagallo, M.; Bécares, V.; Becvár, F.; Belloni, F.; Berthier, B.; et al. Effect of powder in recycled fine aggregate on compressive strength of recycled mortar. In Proceedings of the 6th American Nuclear Society International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Plant Instrumentation, Control, and Human-Machine Interface Technologies 2009, Knoxville, TN, USA, 5–9 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nili, M.; Sasanipour, H.; Aslani, F. The Effect of Fine and Coarse Recycled Aggregates on Fresh and Mechanical Properties of Self-Compacting Concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.-F.; Wang, E.; Zhou, X.; Le, Q.-L. Influence of high temperature on mechanical properties of concrete containing recycled fine aggregate. Comput. Concr. 2018, 21, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. Mechanical behaviour of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C. A simplified micromechanical model of compressive strength of fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1992, 14, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, V.C.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Ogawa, A.; Saito, T. Interface tailoring for strain-hardening polyvinyl alcohol-engineered cementitious composite (PVA-ECC). Mater. J. 2002, 99, 463–472. [Google Scholar]
- Manvi, N.G.; Kumar, A.A. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Engineered Cementitious Composite (HECC). Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 9856–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Ma, G.; Luo, H. Hybrid effects of steel fibers, basalt fibers and calcium sulfate on mechanical performance of PVA-ECC containing high-volume fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 97, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, S. Experimental Research on Ultra High Toughness Cementitious Composites; Dalian University of Technology: Dalian, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Said, S.H.; Razak, H.A.; Othman, I. Flexural behavior of engineered cementitious composite (ECC) slabs with polyvinyl alcohol fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.; Soliman, A.; Nehdi, M. Hybrid-fiber reinforced engineered cementitious composite under tensile and impact loading. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.U.; Mihashi, H.; Shaikh, F. A review on durability properties of strain hardening fibre reinforced cementitious composites (SHFRCC). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şahmaran, M.; Li, V.C. De-icing salt scaling resistance of mechanically loaded engineered cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jansen, D.C.; Shah, S.P.; Karr, A.F. Permeability study of cracked concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepech, M.; Li, V.C. Water Permeability of Cracked Cementitious Composites; Advanced Civil Engineering Materials Research Laboratory, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, E.-H. Macroscopic and microstructural properties of engineered cementitious composites incorporating recycled concrete fines. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 78, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, T.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Z.; Lin, X.; Liang, Y. Mechanical behavior of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) using recycled fine aggregate cured under different conditions and the mechanism based on integrated microstructural parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-Q.; Zhu, W.-J.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Z.-D.; Yu, J.-T.; Xiao, J.-Z. Micro-structural and mechanical properties of ultra-high performance engineered cementitious composites (UHP-ECC) incorporation of recycled fine powder (RFP). Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard, A. C1018. Standard Test Method for Flexural Toughness and First-Crack Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam with Third-Point Loading); American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Standard, A. C78. Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third Point Loading); American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, V.C.; Wang, S.; Wu, C. Tensile strain-hardening behavior of polyvinyl alcohol engineered cementitious composite (PVA-ECC). ACI Mater. J. Am. Concr. Inst. 2001, 98, 483–492. [Google Scholar]









| Chemical Composition | Cement (%) | Fly Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CaO | 63.42 | 4.2 |
| SiO2 | 18.77 | 54.45 |
| Al2O3 | 4.85 | 28.37 |
| MgO | 4.17 | 0.85 |
| SO3 | 3.53 | 0.85 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.15 | 6.03 |
| K2O | 1.2 | 2.29 |
| TiO2 | 0.255 | 1.25 |
| Na2O | 0.243 | 0.94 |
| loss of ignition | 3.08 | 3.17 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Elongation (%) | Length (mm) | Diameter (μm) | Density (g/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥1250 | >30 | ≥6 | 12 | 40 | 1.3 |
| Group | Parameters | Mix Proportion (kg/m3) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W/B | Vf (%) | R/B | VFA (%) | Aggregate Type | Cement | Fly Ash | Fine Aggregate | Fiber | Water | Water Reducer | |
| 25R00 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 0 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25R05 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 6.5 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25R10 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 13 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25R15 | 0.25 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 19.5 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25R20 | 0.25 | 2 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 26 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25N00 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 0 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25N05 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 6.5 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25N10 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 13 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25N15 | 0.25 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 19.5 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 25N20 | 0.25 | 2 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 831.6 | 356.4 | 475.2 | 26 | 297 | 12.1 |
| 45R00 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 0 | 403 | 0 |
| 45R05 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 6.5 | 403 | 0 |
| 45R10 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 13 | 403 | 0 |
| 45R15 | 0.45 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 19.5 | 403 | 0 |
| 45R20 | 0.45 | 2 | 0.4 | 30 | RFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 26 | 403 | 0 |
| 45N00 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 0 | 403 | 0 |
| 45N05 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 6.5 | 403 | 0 |
| 45N10 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 13 | 403 | 0 |
| 45N15 | 0.45 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 19.5 | 403 | 0 |
| 45N20 | 0.45 | 2 | 0.4 | 30 | NFA | 626.9 | 268.6 | 358.2 | 26 | 403 | 0 |
| Aggregate Type | Apparent Density (kg/m3) | Bulky Density (kg/m3) | Water Absorption (%) | Crushing Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFA | 2536 | 1309 | 6.72 | 18.3 |
| NFA | 2593 | 1460 | 1.18 | 12.8 |
| Group | σbc (MPa) | δbc (mm) | σbp (MPa) | δbp (mm) | δbu (mm) | Gb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25R00 | 6.19 | 0.09 | / | / | / | 35.20 |
| 25N00 | 4.87 | 0.10 | / | / | / | 35.01 |
| 25R05 | 6.25 | 0.11 | 6.47 | 0.12 | 1.76 | 373.17 |
| 25N05 | 4.78 | 0.21 | 4.84 | 0.22 | 5.30 | 720.10 |
| 25R10 | 6.57 | 0.20 | 9.33 | 6.22 | 8.17 | 4308.87 |
| 25N10 | 5.58 | 0.08 | 6.54 | 2.20 | 7.86 | 2562.66 |
| 25R15 | 6.78 | 0.23 | 10.43 | 7.58 | 10.53 | 6738.25 |
| 25N15 | 6.06 | 0.18 | 7.02 | 4.90 | 9.81 | 3451.62 |
| 25R20 | 8.11 | 0.42 | 11.89 | 7.67 | 17.26 | 10090.39 |
| 25N20 | 7.97 | 0.21 | 9.41 | 5.12 | 11.28 | 5403.01 |
| Group | σtc (MPa) | εtc (%) | σtp (MPa) | εtp (%) | εtu (%) | Et (GPa) | Gt | νt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45R00 | 1.15 | 0.02 | \ | \ | \ | 11.49 | 12.54 | 0.18 |
| 45N00 | 0.98 | 0.03 | \ | \ | \ | 6.49 | 18.47 | 0.12 |
| 45R05 | 1.14 | 0.01 | 1.51 | 1.32 | 5.08 | 12.82 | 2033.34 | 0.16 |
| 45N05 | 1.02 | 0.02 | 1.12 | 0.41 | 4.58 | 7.76 | 1634.00 | 0.30 |
| 45R10 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 2.16 | 1.69 | 9.10 | 13.29 | 4796.38 | 0.10 |
| 45N10 | 1.63 | 0.01 | 1.69 | 1.54 | 5.83 | 10.66 | 3872.03 | 0.14 |
| 45R15 | 1.82 | 0.02 | 2.61 | 2.48 | 10.02 | 16.01 | 11002.04 | 0.21 |
| 45N15 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 1.99 | 1.64 | 7.60 | 11.38 | 6263.50 | 0.13 |
| 45R20 | 2.38 | 0.02 | 2.84 | 4.76 | 11.73 | 20.35 | 18805.06 | 0.13 |
| 45N20 | 1.57 | 0.05 | 2.75 | 1.68 | 10.72 | 12.97 | 10143.70 | 0.15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, D.Y.; Lv, M.; Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, G.; Meng, Y. Experimental Study of Utilizing Recycled Fine Aggregate for the Preparation of High Ductility Cementitious Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030679
Gao DY, Lv M, Yang L, Tang J, Chen G, Meng Y. Experimental Study of Utilizing Recycled Fine Aggregate for the Preparation of High Ductility Cementitious Composites. Materials. 2020; 13(3):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030679
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Dan Ying, Mingyan Lv, Lin Yang, Jiyu Tang, Gang Chen, and Yang Meng. 2020. "Experimental Study of Utilizing Recycled Fine Aggregate for the Preparation of High Ductility Cementitious Composites" Materials 13, no. 3: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030679





