Experimental Investigation and Analytical Modeling of Chloride Diffusivity of Fly Ash Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chloride Diffusion Test of Fly Ash Concrete
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Experimental Results and Discussions
3. Chloride Diffusivity of Fly Ash Concrete
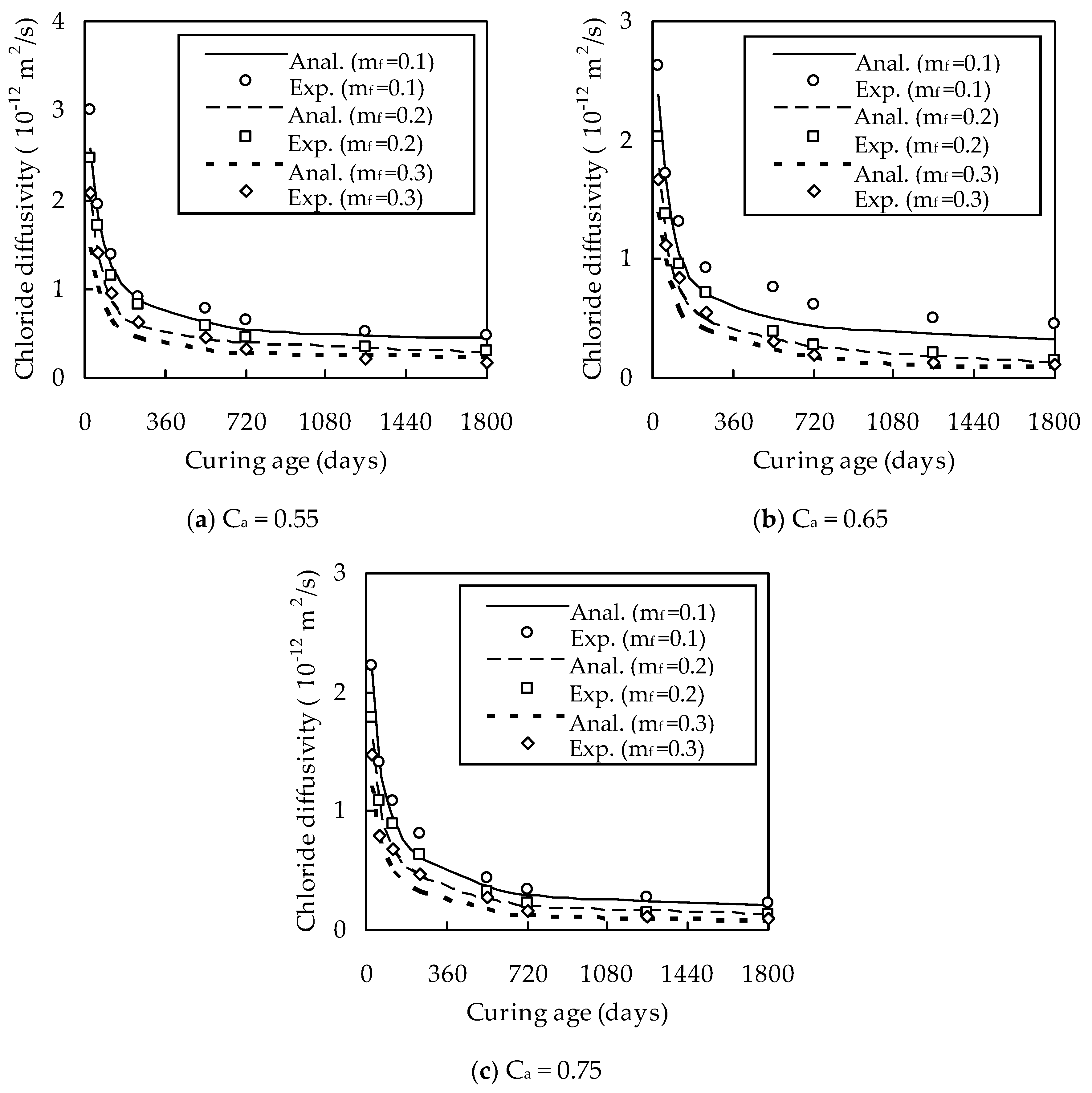
4. Experimental Verification and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurumisawa, K.; Nawa, T.; Owada, H. Prediction of the diffusivity of cement-based materials using a three-dimensional spatial distribution model. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Wang, X.R. A numerical method for predicting the chloride diffusivity of mature cement paste. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, V.G. Effect of fly ash on Portland cement systems: Part I. low-calcium fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, V.G. Effect of fly ash on Portland cement systems: Part II, high-calcium fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Lam, L.; Wong, Y.L. Study on high strength concrete prepared with large volumes of low calcium fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, L.; Wong, Y.L.; Poon, C.S. Degree of hydration and gel/space ratio of high-volume fly ash/cement systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.L.; Ortega, J.M.; Flor, M.; López, M.P.; Sánchez, I.; Climent, M.A. Microstructure and durability of fly ash cement grouts for micropiles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 117, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yio, M.H.N.; Wong, H.S.; Buenfeld, N. 3D pore structure and mass transport properties of blended cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 117, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Coffetti, D.; Crotti, E. Plain and ultrafine fly ashes mortars for environmentally friendly construction materials. Sustainability 2018, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog. Energ. Combust. 2010, 36, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.D.A.; Shehata, M.H.; Shashiprakash, S.G.; Hopkins, D.S.; Cail, K. Use of ternary cementitious systems containing silica fume and fly ash in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.J. Experimental investigation and theoretical estimate of the chloride diffusion coefficient of mature fly ash cement paste. Materials 2019, 12, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.H.; Jang, S.Y. Prediction of diffusivity of concrete based on simple analytic equations. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Ye, G. New perspective of service life prediction of fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradllo, M.K.; Hu, Q.N.; Ley, M.T. Using X-ray imaging to investigate in-situ ion diffusion in cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalee, W.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Chindaprasirt, P. Predicting the chloride penetration of fly ash concrete in seawater. Mar. Struct. 2009, 22, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damrongwiriyanupap, N.; Scheiner, S.; Pichler, B.; Hellmich, C. Self-consistent channel approach for upscaling chloride diffusivity in cement pastes. Transp. Porous Med. 2017, 118, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.P.; Ye, G.; Wang, Q.N.; Sun, W. Modeling of the chloride diffusivity of ultra-high performance concrete with a multi-scale scheme. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 27, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; De Schutter, G.; Jiang, Z.W.; Chen, Q. Multi-level diffusion model for manufactured sand mortar considering particle shape and limestone powder effects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Song, W.B. A numerical algorithm for evaluating the chloride diffusion coefficient of concrete with crushed aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Xing, H.Y.; Jin, X.Y. Differential effective medium theory for the chloride diffusivity of concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2015, 112, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.F.; Easterbrook, D.; Yang, J.; Li, L.Y. A three-phase, multi-component ionic transport model for simulation of chloride penetration in concrete. Eng. Struct. 2015, 86, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Zhang, Y.R.; Gao, Y.H. Chloride transport in concrete under flexural loads in a tidal environment. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Cheng, L.; Gao, Z.M.; Guo, S.Y. Effects of different mineral admixtures on carbonation resistance of lightweight aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y. Application of the Nernst-Einstein equation to concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caré, S. Influence of aggregates on chloride diffusion coefficient into mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, G.Y.; Leung, C.K.Y. Hydration and physical characteristics of ultrahigh-volume fly ash-cement systems with low water/binder ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijen, J. Benefits of slag and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 1996, 10, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivonka, P.; Hellmich, C.; Smith, D. Microscopic effects on chloride diffusivity of cement pastes—A scale-transition analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2251–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.K.; Dawson, A.R.; Thom, N.H. Macro/micro-pore structure characteristics and the chloride penetration of self-compacting concrete incorporating different types of filler and mineral admixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 72, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nežerka, V.; Bílý, P.; Hrbek, V.; Fládr, J. Impact of silica fume, fly ash, and metakaolin on the thickness and strength of the ITZ in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Nemati, K.M. The percolation of pore space in the cement paste/aggregate interfacial zone of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.J.; Guo, Z.Q.; Huang, X.F.; Stroeven, P.; Sluys, L.J. ITZ volume fraction in concrete with spheroidal aggregate particles and application: Part II, prediction of the chloride diffusivity of concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2011, 63, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.L.; Torquato, S. Nearest-surface distribution functions for polydispersed particle system. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 5530–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torquato, S. Random Heterogenerous Materials: Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.X.; Ba, M.F.; Guo, X.G.; Han, X.Y. Evaluation of sub-microstructure in concrete with low water-binder ratio by SEM-BSE image analysis. J. Wuhan Univ. Tenol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2010, 25, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudoos, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Kim, H.G.; Ryou, J.S. Influence of the surface roughness of crushed natural aggregates on the microhardness of the interfacial transition zone of concrete with mineral admixtures and polymer latex. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, J.L.; Epps, R.; Kosson, D.S. The impact of carbonation on bulk and ITZ porosity in microconcrete materials with fly ash replacement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.J.; Li, C.Q.; Zhou, X.Z. Thickness of interfacial transition zone and cement content profiles around aggregates. Mag. Concr. Res. 2005, 57, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, D.P. Influence of silica fume on diffusivity in cement-based materials: II, multi-scale modeling of concrete diffusivity. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Su, J.K. Approximate migration coefficient of interfacial transition zone and the effect of aggregate content on the migration coefficient of mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material | CaO (%) | SiO2 (%) | Al2O3 (%) | Fe2O3 (%) | MgO (%) | SO3 (%) | K2O (%) | Na2O (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | 5.40 | 47.00 | 26.37 | 5.23 | 0.38 | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.61 |
| Cement | 65.31 | 21.21 | 3.88 | 3.25 | 1.12 | 0.98 | 0.57 | 0.12 |
| w/b | Dosage of Material (kg/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly Ash | Cement | Water | Aggregate | |
| 0.4 | 61.7 | 555.3 | 246.8 | 1474.1 |
| 0.4 | 121.5 | 485.9 | 242.9 | 1474.0 |
| 0.4 | 179.4 | 418.6 | 239.2 | 1473.9 |
| 0.4 | 48.0 | 432.0 | 192.0 | 1742.0 |
| 0.4 | 91.9 | 367.6 | 183.8 | 1742.1 |
| 0.4 | 132.3 | 308.6 | 176.3 | 1742.0 |
| 0.4 | 34.3 | 308.5 | 137.1 | 2010.0 |
| 0.4 | 67.5 | 269.9 | 135.0 | 2010.0 |
| 0.4 | 99.7 | 232.5 | 132.9 | 2010.0 |
| 0.5 | 54.3 | 488.4 | 271.4 | 1474.0 |
| 0.5 | 107.0 | 428.1 | 267.6 | 1473.9 |
| 0.5 | 158.3 | 369.4 | 263.9 | 1474.0 |
| 0.5 | 42.2 | 379.9 | 211.0 | 1742.0 |
| 0.5 | 83.2 | 333.0 | 208.1 | 1741.9 |
| 0.5 | 123.1 | 287.3 | 205.2 | 1742.0 |
| 0.5 | 30.1 | 271.3 | 150.7 | 2010.0 |
| 0.5 | 59.5 | 237.8 | 148.6 | 2010.0 |
| 0.5 | 88.0 | 205.2 | 146.6 | 2010.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.-Z.; Zheng, J.-J.; Ye, H.-L.; Yang, J. Experimental Investigation and Analytical Modeling of Chloride Diffusivity of Fly Ash Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040862
Zhang J, Zhou X-Z, Zheng J-J, Ye H-L, Yang J. Experimental Investigation and Analytical Modeling of Chloride Diffusivity of Fly Ash Concrete. Materials. 2020; 13(4):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040862
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jian, Xin-Zhu Zhou, Jian-Jun Zheng, Hai-Long Ye, and Jin Yang. 2020. "Experimental Investigation and Analytical Modeling of Chloride Diffusivity of Fly Ash Concrete" Materials 13, no. 4: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040862
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhou, X.-Z., Zheng, J.-J., Ye, H.-L., & Yang, J. (2020). Experimental Investigation and Analytical Modeling of Chloride Diffusivity of Fly Ash Concrete. Materials, 13(4), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040862





