Abstract
Herein, we report the surface functionalization of carbon nano-onions (CNOs) through an amidation reaction that occurs between the oxidized CNOs and 4-(pyren-4-yl)butanehydrazide. Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy methods were used to confirm the covalent functionalization. The percentage or number of groups in the outer shell was estimated with thermal gravimetric analysis. Finally, the potential applications of the functionalized CNOs as electrode materials in supercapacitors were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Functionalization increased the specific capacitance by approximately 138% in comparison to that of the pristine CNOs, while acid-mediated oxidation reduced the specific capacitance of the nanomaterial by 24%.
1. Introduction
The use of carbon nanomaterials (CNs) has been quite popular for the construction of supercapacitors (SCs) [1,2,3,4,5], specifically in electrochemical double-layer capacitors (EDCLs) [6,7]. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene shells are frequently used for energy storage, commonly as a hybrid metal type material [8,9,10]. The energy storage mechanism is based on the adsorption of electrolyte ions over a large specific surface area of electrically conductive porous electrodes [11,12]. Therefore, properties such as high conductivity, large surface area, corrosion resistance, temperature stability, and porosity are considered key characteristics for the development of these devices [13] Active and porous carbon compounds, such as carbide-derived carbons, templated carbons, graphene nanotubes, and carbon nanotubes, are the most commonly investigated materials for energy storage applications [14]. Likewise, multilayer concentric fullerenes, denoted as carbon nano-onions (CNOs), which were discovered by Iijima in 1980 [15], are promising CNs for SC applications because of their intrinsic properties of high mesoporosities and large surface areas [11,16,17,18,19]. It is well-known that the functionalization of the outer surface by different routes improves the process in which CNOs interact with electrolytes [20,21,22,23,24,25]. In this regard, the capacitive power of an SC is largely associated with an optimal electrode/electrolyte interface, where changes in morphology (rugosity, porosity, channels, etc.) are due to intermolecular forces and/or intra-interclusters, which play a major role [26,27,28,29,30]. Functionalizing with the correct structures that can enhance power density by means of interactions with electrolytes or even between nanoparticles is a challenge in this field [29]. Condensed benzene ring molecules can create π–π stacking interactions that could improve the performance of CNOs in two ways: (i) by using non-aqueous electrolytes, such as planar ionic liquids, which can work in a wide operating voltage window; and (ii) by favoring a regular porosity with narrow pore size distributions. The latter, according to Konrad and coworkers, who studied the concept of the “best porous size,” is considered the most important characteristic in the mechanistic process of charging and discharging in SCs [31].
In contrast with the investigation done by Giordani et al., who applied non-covalent functionalization to pyrene-BODIPY (boron-dipyrromethene) dyads for biological imaging [32], herein, we report the first covalent functionalization of CNOs with hydrazyl pyrene groups to modify the morphology of the CNO surfaces and therefore analyze the effect of functionalization on the specific capacitance. This study demonstrates that functionalization with pyrene moieties, such as the model of condensed rings, is an effective method for improving the capacitance of CNO electrodes when compared to the capacitance of pristine CNOs (p-CNOs).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of p-CNOs
Ultradispersed carbon nanodiamonds (NDs) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) with 10 nm average diameters were annealed in a Nabertherm LHT 02/18 oven (Lilienthal, Germany) at 1600 °C for 2 h under an inert atmosphere of nitrogen. The final temperature was maintained for 1 h, and then the material was slowly cooled to room temperature over a period of 1 h. Then, the residual amorphous carbon was eliminated by heating at 400 °C under air for 2 h. The final product was the pristine CNOs.
2.2. Functionalization of the p-CNOs
First, 40 mg of the p-CNOs were oxidized with a mixture of HNO3/H2SO4 (1:3) (15 mL under reflux) for 1 h. Afterward, 1 M NaOH was used to neutralize the solution. The precipitate was washed with water and methanol by centrifugation. The solid was vacuum dried for 12 h at 60 °C to yield the oxidized carbon nano-onions (ox-CNOs). Thereafter, 20 mg of the ox-CNOs were dispersed under sonication in chloroform (10 min), and then 500 mg of 4-(pyrene-4-yl)butanehydrazide, which was previously dissolved in chloroform, and 500 µL of triethylamine (TEA) (used as a base catalyst in the amidation process) were mixed and refluxed for 5 days. The carbon nano-onions that were functionalized with the pyrene derivatives (pyr-CNOs) were washed by centrifugation with chloroform, methanol, and water and then dried for 24 h in a vacuum oven at 60 °C.
2.3. Methods
The p-CNOs were examined with a Libra 120 high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) system (Zeiss, Germany). The accelerating voltage of the electron beam was 20–30 keV. A Shimadzu IR Affinity-1 instrument that was equipped with attenuated total reflectance (ATR) and a ThermoScientific DXR Smart Raman instrument (Waltham, MA, USA) that was equipped with a 532 nm laser beam were used for the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and the Raman analysis, respectively. The morphologies without any coatings were studied by using a JEOL JCM-5000 NeoScope scanning electron microscopy (SEM) system (Tokyo, Japan). The carbon powder was deposited on a carbon film. A high vacuum and source power between 10 and 15 kW were used. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) were carried out by using a TGA/DSC Mettler Toledo system (Columbus, OH, USA) by heating in air from 100 to 900 °C with a rate of 10 °C/min.
A three-electrode system was used for the cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments, which used a Pt mesh as the counter electrode, Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode, a glassy carbon (GC) disk with a 3 mm diameter as the working electrode, and a 1 M Na2SO4 solution as the electrolyte. The carbon nanostructures were sonicated in methanol (1 mg/mL). A 10–20 μL drop of the solution that contained the dispersed functionalized or non-functionalized CNs was then deposited on the GC electrode surface. After the solvent evaporated, the electrode was introduced into the solution electrolyte. CV was performed with scan rates of 20, 30, 40, 50, 100, 200 and 500 mV/s in an electrochemical window of -30 to 800 mV vs. Ag/AgCl. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) spectra were obtained in a range from 100 mHz to 10 kHz, with 5 mV as the voltage amplitude.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the CNOs
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) showed the formation of spherical concentric shells, a characteristic feature of p-CNOs (Figure 1). The diameter of the carbon nanoparticles ranged from 5.0 to 30.0 nm. These nanostructures consisted of approximately six-to-ten graphenic shells with interlayer distances of 0.34 nm (based on the diffraction patterns), which was approximately equal to the distance between two graphitic planes (0.334 nm) [33]. The surface of p-CNOs is mainly composed of hexagonal rings that are similar to graphene layers but include some pentagonal rings, defects, and holes [34,35]. The structural defects and high sphericity lead to the relatively high chemical reactivity of p-CNOs.
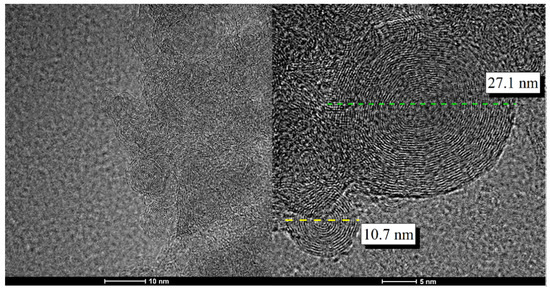
Figure 1.
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) images of the pristine carbon nano-onions (p-CNOs) that were obtained by annealing of ultradispersed carbon nanodiamonds under a nitrogen atmosphere at 1600 °C.
The p-CNOs underwent an acid treatment (HNO3/H2SO4; v/v = 1/3) to yield the ox-CNOs. Then, the reaction of the ox-CNOs with 4-(pyrene-4-yl)butanehydrazide yielded pyr-CNOs (Scheme 1). As a first qualitative observation, the oxidation of the p-CNOs resulted in a marked improvement in their ability to disperse in water, suggesting the presence of carboxylic groups on the surface of the CNOs. Likewise, aqueous dispersions of pyr-CNOs were very stable (no sedimentation was observed), even for weeks (Figure 2), indicating their potential for use as electrode materials, since homogeneity is an important factor when constructing SCs [36].
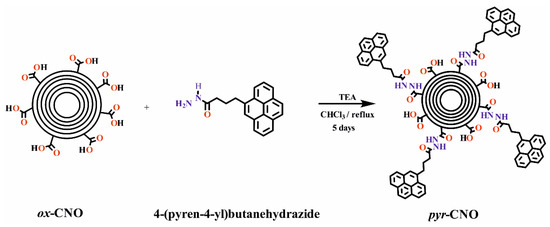
Scheme 1.
Functionalization of oxidized-CNOs (ox-CNOs) through amidation with pyrene hydrazide.

Figure 2.
Dispersions of CNOs that were functionalized with the pyrene (pyr-CNOs) in water.
The Fourier transform infrared spectra (FT-IR) showed the presence of carboxylic and pyrene groups on the functionalized CNOs (Figure 3). Based on IR spectroscopy, a broad absorption band that extended from 2800 to 3200 cm−1 indicated the presence of carboxylic groups (stretching vibrations of O–H) [37]. The intense absorption bands at 1390 and 1570 cm−1 were due to the in-plane bending vibrations of O–H and the stretching vibrations of C–O, confirming the oxidation of p-CNOs to ox-CNOs (Figure 3b), which is similar to other studies [37,38]. The spectral features between 1540 and 1590 cm−1 may have also been related to carboxyl and carbonyl groups [39]. The stretching of the C=O and N–H bonds at 1625 and 3315 cm−1, respectively, proved the presence of pyrenic moieties on the CNO surface (Figure 3c). Other bands with lower intensities are observed at between 2800 and 2940 cm−1. These less intense bands are associated with the symmetric and asymmetric stretching of C–H bonds.
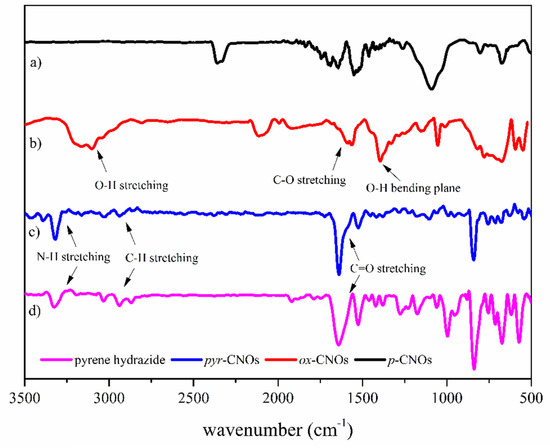
Figure 3.
FT-IR spectra of (a) p-CNOs, (b) ox-CNOs, (c) pyr-CNOs, (d) pyrene hydrazide.
The Raman spectra (Figure 4) show the characteristic G and D bands of the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs. These bands were related to the graphitization degree or C atoms with sp2 hybridization (G band) and the disorder degree or C atoms with sp3 hybridization (D band). Likewise, a second-order band, 2D or G’, was also observed [40]. The ratio of the intensities of the D and G bands (ID/IG) confirmed the covalent functionalization process (Table 1). Additionally, the D and G lines were intense and broad, and the D band was more intense than the G band. In this respect, our spectra were similar to those of strongly disordered graphene [41].
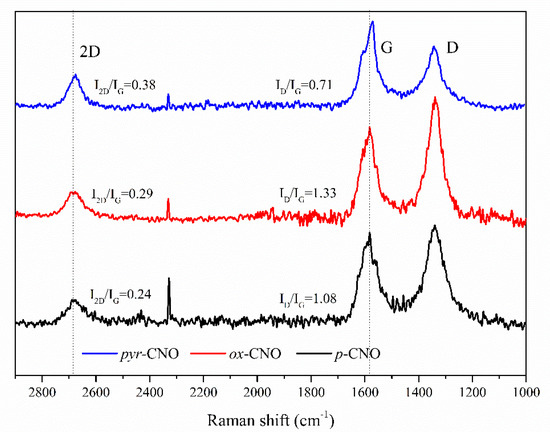
Figure 4.
Raman spectra of the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs, as obtained with 532 nm laser excitation.

Table 1.
D and G band intensity ratios of the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs.
Increases in the D band intensity in the Raman spectrum and in the ID/IG ratio of p-CNOs and ox-CNOs were observed. Oxidation with strong acids caused the outer shell to rupture, and therefore, the hybridization of the C atoms changed to sp3, which was confirmed by the presence of oxygen groups (carboxylic, hydroxylic and carbonyl groups) [37]. The general equation reported by Cançado et al. was used to determine the crystallite size (La) by Raman spectroscopy [42]:
where λ is the wavelength of the laser in nanometers (532 nm).
The intensity of the D band depends on the wavelength of the excitation light, which is due to the resonance Raman effect [43]. For our investigated materials, the TEM images showed that the smallest indivisible unit was the CNOs with diameters of approximately 5 nm (six-shell CNOs). Moreover, the spherical nanoparticles could easily aggregate. In the case of the CNOs, the ID/IG ratio may provide information about the size and edges of the aggregates (crystallite sizes) [41]. In our investigations, we estimated the value defined in the literature as the average crystallite size La, which was ca. 17.8 nm for the p-CNOs. After strong oxidation, the size decreased to approximately 14.5 nm. Taking into account all the known facts from the literature and our experimental data [37,44,45,46,47], we concluded that one aggregate could be formed with two or three CNO nanostructures.
The G band of the pyr-CNO spectrum increased with respect to one of the ox-CNOs, showing an unusual and opposite behavior. This band is associated with the phonon E2g, which corresponds to the lateral vibration of the hexagonal condensed rings in the graphenic layers [48,49,50]. It is possible that this vibration was given by the pyrene structure; if so, the confirmation of covalent functionalization by using the ratio ID/IG could not be conclusive. However, the G band in the pyr-CNOs spectrum exhibites a large full width at half maximum (FWHM) value. Additionally, the same spectrum shows an apparent shoulder that corresponds to the D’ band at ~1614 cm−1 (Figure 5). The latter is produced by the process of double resonance, which could be activated by the crystalline defects and could be associated with covalent functionalization [48].
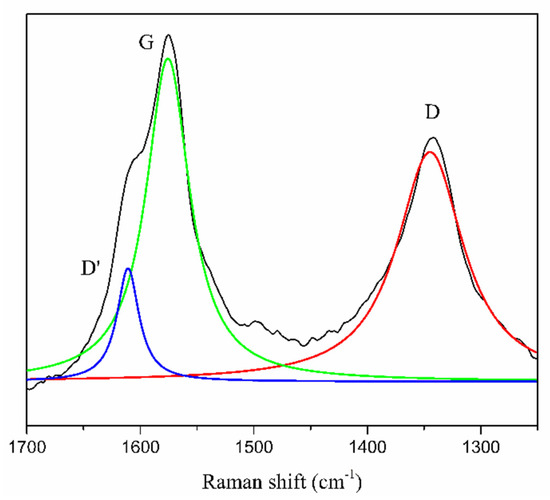
Figure 5.
Deconvolution of the G and D bands in the pyr-CNOs Raman spectrum.
On the other hand, the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) (Figure 6) showed that the p-CNOs (701 °C) had a higher decomposition temperature than the ox-CNOs (515 °C). This behavior can be attributed to the outer shell rupturing upon oxidation. The 20% loss of weight at 257 °C corresponded to the carboxylic fragments degrading in air. The TGA curve of the pyr-CNOs showed three decomposition temperatures that could correspond to: (i) non-amidized carboxylic groups at ~218 °C; (ii) covalent pyrene moieties that were functionalized at ~356 °C; and (iii) the carbon structure with a decomposition temperature of 495 °C.
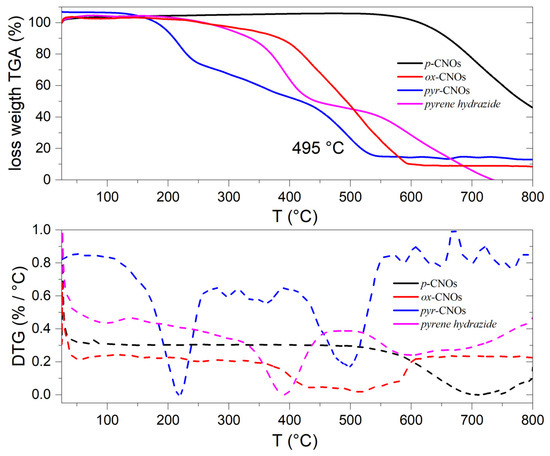
Figure 6.
TGA curves of the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs (top) and pyrene hydrazide under an air atmosphere. The first derivative of the corresponding TGA curve (bottom).
By considering the average of eight fullerenic concentric layers (HR-TEM images) and employing an approximation that was previously used by Cioffi and coworkers [51], the number of groups attached to the outer shell was estimated. In this regard, the ox-CNOs contained ≈362 carboxylic fragments or 1 per every 10 carbons in the outer shell. On the other hand, the pyr-CNOs contained ≈306 pyrene moieties or 1 per every 13 carbons in the outer shell.
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) studies of the three carbon nanomaterials are shown in Figure 7. The pristine and functionalized CNO surfaces exhibited a rough texture and porous morphologies, with many channels and three-dimensional aggregates, which may have contributed to improving the capacitive properties of the CNOs through the storage of the charge mechanism.

Figure 7.
SEM images of the (a) p-CNOs, (b) ox-CNOs and (c) pyr-CNOs.
3.2. Electrochemical Properties of the CNOs and their Derivatives
The cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves (Figure 8) show the characteristic pseudo-rectangular profiles of non-faradaic capacitive materials [52]. Therefore, the specific capacitance (CS) was determined based on Equation (1):
where v is the scan rate, the numerator corresponds to the total charge obtained by the integration of the instant current with a scan rate v, E2 and E1 are the potentials of the electrochemical window, and m is the mass of the active material. The film exhibited a stable behavior under cyclic voltammetric conditions. No changes in the current were observed after prolonged potential cycling in the potential range from −0.30 to +0.80 V vs. Ag/AgCl. Our results showed that the acid-mediated oxidation of the CNOs decreased the capacitance, which was likely due to the decrease in the conductivity as a consequence of structural damage on the surface. On the other hand, the CV curve of the pyr-CNOs had a larger area, indicating an increase in the capacitance. This fact was explained by the larger porosity, which was due to the organized CNO agglomerates on the GC surface [53,54].
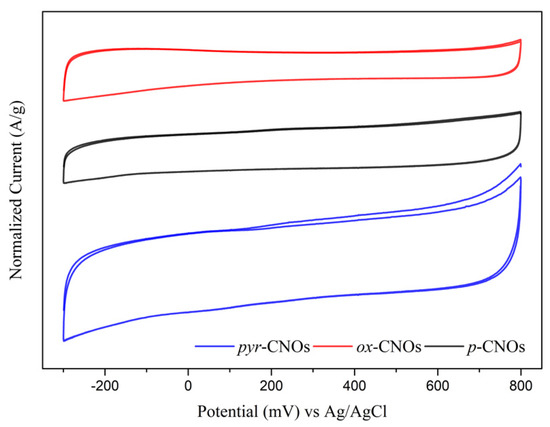
Figure 8.
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves of the glassy carbon electrode that was covered with the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs in 1.0 M Na2SO4, obtained with a sweep rate of 30 mV/s.
Table 2 summarizes the specific capacitances that were obtained for the p-CNOs, ox-CNOs and pyr-CNOs, which were calculated with a scan rate of 30 mV/s. The specific capacitance could also be calculated from Equation (2):
where ic is the capacitive current, v is the scan rate, and m is the mass of the deposited material on the electrode.

Table 2.
The specific capacitance of the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs based on the CV curve.
Given the existence of a linear correlation between the current peak and the scan rate, the specific capacitance could be calculated from the slope of the linear fit [55]. Figure 9 shows the CV curves that were obtained for each nanomaterial at 20, 30, 40, 50, 100, 200 and 500 mV/s, showing an increase in the current peak with increasing v. A linear relation between the capacitive current, ic, and the sweep rate, v, was observed (Figure 9d). From the slope of the ic – v function, the specific capacitance of the p-CNOs, ox-CNOs and pyr-CNOs was found (Table 2). Despite the faradaic component, the film that contained the ox-CNOs showed a much lower capacitance than p-CNOs. Strong oxidation caused damage to the carbon structure, which affected the intrinsic properties of the CNOs [56]. Table 2 compares the specific capacitance values that were obtained by both methods. The pyr-CNOs had the highest specific capacitance value, which as equal to 62.2 F/g.
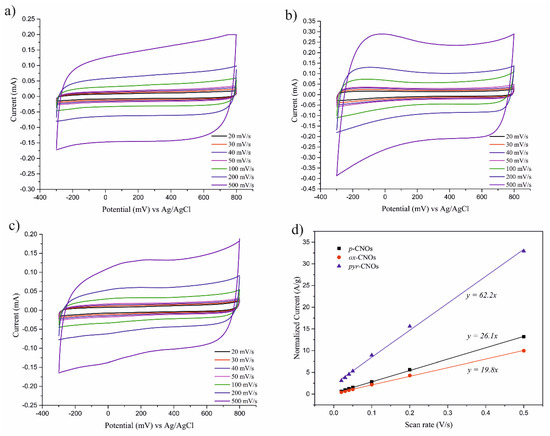
Figure 9.
Dependence of the CV curves on the scan rate in the (a) p-CNOs, (b) ox-CNOs, and (c) pyr-CNOs. (d) Linear regression of the current density against the scan rate.
Table 3 summarizes some of the specific capacitance values of the CNO materials, as reported by other authors. As can be observed, CNOs have mainly been studied in composites with electroactive materials, such as metal cations, C60, polyaniline (PANI) and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS), in which some of them reported larger values than our study. Nevertheless, pyr-CNOs are a non-hybrid material that exhibits a high-intermediate value, which opens the door for its use in composites.

Table 3.
Specific capacitance values obtained for the CNO materials.
The long cycling stability performance (the mechanical and electrochemical stability) of an SC is a fundamental requirement for materials with applications in energy storage devices. It was found that the CVs for pyr-CNOs were stable in the 1 M Na2SO4 solution at 100 mV/s (Figure 10). Tests were conducted by using 1000 cycles, and the resulting capacitive currents as a function of cycling numbers are shown in Figure 10c. The pyr-CNO electrodes exhibited a long-term cycling stability, retaining approximately 99% of their initial capacitive current after 1000 cycles. Figure 10a,b shows the first and the last eight cycles of the CV measurements, respectively. The normalized current decreased from 3.7 to 2.9 A/g between the first and the last cycle.
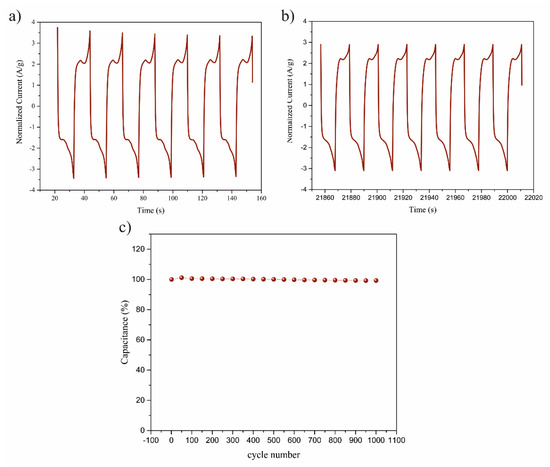
Figure 10.
Stability studies of pyr-CNOs based on the CV measurements (1000 cycles): (a) the first 8 cycles, (b) the last 8 cycles, and (c) capacitive current values as a function of cycling numbers.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is a technique that can provide information about the kinetics process of the electrolyte diffusing into the pores of the CNs, the effect of the resistance on the electron transfer and the contribution of each type of capacitance (EDLC or pseudocapacitance) [66]. The Nyquist plot and the Bode plot explain these results graphically, showing the relationship between the imaginary (Z’’) and the real (Z’) components of the impedance shown in the Nyquist plot, and the angle phase (ϕ) or impedance (Z) is plotted against the frequency in the Bode plot.
Figure 11a shows the EIS results that were obtained for the pristine and functionalized CNOs. The impedance spectra of the CN exhibited the shape that was expected for double-layer charging porous electrodes [13]. It is possible to identify two regions in the Nyquist plot: (i) the Knee frequency, which corresponds to the high-frequency region and is related to the beginning of the diffusion or charge-transfer process of the electrolyte at the electrode–electrolyte interface, and (ii) the Warburg finite-length diffusion at a low frequency, which is responsible for diffusion within the electrode [66,67]. The absence of a pronounced loop and the almost vertical line observed in the Nyquist plot at high and low frequencies, respectively, were useful to propose the equivalent circuit that describes the electrochemical behavior (Scheme 2).
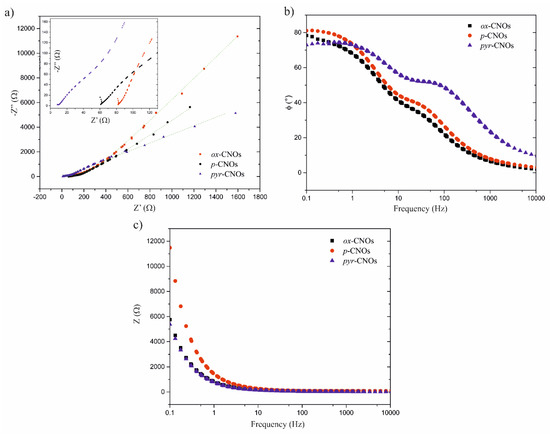
Figure 11.
(a) Nyquist plot (Z’’ vs. Z’). (b) Bode plot (ϕ vs. f). (c) Bode plot (Z vs. f) obtained for the GCE that was modified with the CNOs.
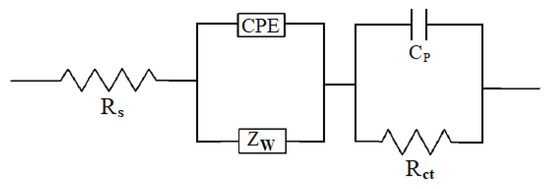
Scheme 2.
Equivalent electrical circuit representing the behavior of the CNOs in an aqueous electrolyte solution.
The green line in Figure 11a shows a good fit between the experimental results and the proposed equivalent circuit. This equivalent circuit consists of a solution resistance (Rs), the constant phase element (CPE) (which is related to the double-layer capacitance (Cdl)), the pseudocapacitance (Cp), the resistance at the electrode/nanomaterial interface (Rct), and the Warburg impedance (Zw). The latter represents the transport of counterions through the film during charging and is therefore evidence of the dependence on diffusion [68]. The electrical impedance is calculated by , where Y0 is a constant related to the admittance and has dimensions of F. The n parameter can take values between 1 and 0, exhibiting an ideal capacitor behavior when n = 1 and a resistor behavior when n = 0. The parameters of each equivalent circuit component were obtained by the fitting procedure (see Table 4). In this sense, the lower Rs, Rct and Zw values of the pyr-CNOs explained the increase in the specific capacitance upon functionalization and, therefore, the greater capacity to store energy. Even though the contribution of Cdl was lower for the pyr-CNOs than for the p-CNOs, it was compensated for by the Cp contribution. The n values that were obtained for our compounds were close to unity, indicating an almost ideal capacitive behavior.

Table 4.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) parameters that were determined for the GCE electrode that was modified with the functionalized and non-functionalized CNOs.
The Bode plot of the phase angles vs. frequencies (Figure 11b) shows that the observed phase angles (ϕ) at a low frequency were 80.6°, 77.9° and 73.2° for the p-CNOs, ox-CNOs and pyr-CNOs, respectively. All the CNOs deviated from the ideal value of 90° at low frequencies, indicating the faradaic contributions to the charge storage mechanism [13]. In this regard, the electron density of the aromatic rings could lead to greater faradaic contributions and, consequently, a larger deviation in ϕ (73.2° vs. 90°) [69,70]. The Bode plot of the impedance vs. frequency (Figure 11c) also shows that the pyr-CNOs possessed a lower impedance than the ox-CNOs, including that the functionalization process that was performed with the pyrene groups could restore the intrinsic properties of the nanomaterial, despite the previous oxidation process.
The capacitance C(ω) can also be written in its complex form [71]:
where:
and:
The dependence of the real and the imaginary capacitance on the frequency is shown in Figure 12a,b, respectively. The largest value of the real capacitance was obtained at low frequencies for the pyr-CNOs, which agreed with the CV measurements. In the C’’ vs. log f plot, a maximum was observed, denoted as the relaxation frequency, fR, which is related to the time constant, τR, indicating the time that was required to charge the capacitor through the resistor from an initial charge voltage of zero to approximately 63.2% of the value of an applied voltage [72]. The τR values of each nanomaterial are indicated in Table 4, showing that the film charging process was relatively fast compared to the charging process of a traditional aluminum electrolytic capacitor and a carbon–carbon supercapacitor, which have τR values of 126 and 7.94 µs [73], respectively, and Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCT)-based capacitors, with a relaxation time of ~0.1 s [74]. This indicates that the CNOs in this study are the type that can be used for high power over short-period designs.
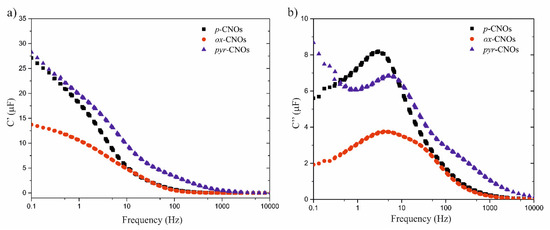
Figure 12.
Dependence of the (a) real part of the capacitance and the (b) imaginary part of the capacitance on the frequency of the CNOs.
4. Conclusions
The functionalization of CNOs with pyrene moieties increases the stability of the resulting dispersions in methanol to more than two weeks, and this stability enhances the potential of using CNOs as a capacitor material. The porous morphology of the nanomaterials was corroborated by SEM. Though the strong oxidation of the p-CNOs, yielding ox-CNOs, decreased the ability of the CNOs to act as supercapacitor materials, subsequent amidation with pyrene hydrazide was effective, increasing the specific capacitance by 138% with respect to that of the pristine CNs. The EIS experiments suggest reducing both the resistance to the solution and the charge transfer in the functionalized nanostructure. This fact could be associated with the aggregation of pyrene groups, which could contribute to the formation of porous inter- and/or intraclusters. On the other hand, the faradaic reactions of the pyr-CNOs could also contribute to the specific capacitance through pseudocapacitive storage. The latter was corroborated by the deviation from the 90° pure-capacitor angle phase in the pyr-CNOs. These results indicate that π–π stacking functionalization is a good strategy for improving power characteristics for the development of electronic devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, M.N.C.; performing the experiments, M.N.C., and J.D.V.; TEM measurements, M.E.P.-B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N.C., and J.D.V.; writing—review and editing, M.E.P.-B. and M.T.; funding acquisition, M.N.C., and M.E.P.-B. All authors approved the final version for submission. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge our profound gratitude for the economic support from Vicerrectoría de Investigaciones (CI 71065, 71155) and the Centro de Excelencia en Nuevos Materiales (CENM) from the Universidad del Valle. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Science Centre, Poland (grant #2017/25/B/ST5/01414) and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, Poland (SUB/2/DN/19/001/2204) to M.E.P.-B.
Acknowledgments
The authors also acknowledge the Tecnoparque SENA - NODO Cali for providing the Raman, SEM and TGA equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fic, K.; Platek, A.; Piwek, J.; Frackowiak, E. Sustainable materials for electrochemical capacitors. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slesinski, A.; Fic, K.; Frackowiak, E. New Trends in Electrochemical Capacitors. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 72, 247–286. [Google Scholar]
- Piwek, J.; Platek, A.; Fic, K.; Frackowiak, E. Carbon-based electrochemical capacitors with acetate aqueous electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 215, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hong, F.; Yan, X.; Su, X. Novel Synthesis of Nitrogen-Containing Bio-Phenol Resin and Its Molten Salt Activation of Porous Carbon for Supercapacitor Electrode. Materials 2019, 12, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shimizu, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Preparation and Carbon-Dependent Supercapacitive Behaviour of Nanohybrid Materials between Polyoxometalate and Porous Carbon Derived from Zeolitic Templates. Materials 2019, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís-Fernández, P.; Bissett, M.; Ago, H. Synthesis, structure and applications of graphene-based 2D heterostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4572–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Yushin, G. Review of nanostructured carbon materials for electrochemical capacitor applications: Advantages and limitations of activated carbon, carbide-derived carbon, zeolite-templated carbon, carbon aerogels, carbon nanotubes, onion-like carbon, and graphene. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2014, 3, 424–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H. Triple Layer Tungsten Trioxide, Graphene, and Polyaniline Composite Films for Combined Energy Storage and Electrochromic Applications. Polymers 2019, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Wang, H.; Jing, Y.; Peng, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; He, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X. Advanced asymmetric supercapacitors based on CNT@Ni(OH)2 core–shell composites and 3D graphene networks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19545–19555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Wang, H.; Jing, Y.; Peng, T.; Wang, X. Asymmetric supercapacitors based on carbon nanotubes@NiO ultrathin nanosheets core-shell composites and MOF-derived porous carbon polyhedrons with super-long cycle life. J. Power Sources 2015, 285, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Gogotsi, Y. Charge storage mechanism in nanoporous carbons and its consequence for electrical double layer capacitors. Philos. Transact. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 3457–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Largeot, C.; Portet, C.; Chmiola, J.; Taberna, P.-L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Simon, P. Relation between the Ion Size and Pore Size for an Electric Double-Layer Capacitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2730–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kötz, R.; Carlen, M. Principles and applications of electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2483–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, A.G.; Hollenkamp, A.F. Carbon properties and their role in supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2006, 157, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Direct observation of the tetrahedral bonding in graphitized carbon black by high resolution electron microscopy. J. Cryst. Growth 1980, 50, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Presser, V. Carbon Nanomaterials, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780849393860. [Google Scholar]
- Borgohain, R.; Yang, J.; Selegue, J.P.; Kim, D.Y. Controlled synthesis, efficient purification, and electrochemical characterization of arc-discharge carbon nano-onions. Carbon 2014, 66, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Mendez, U.; Kharissova, O.V.; Kharisov, B.I. CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Nanotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781466580893. [Google Scholar]
- McDonough, J.K.; Frolov, A.I.; Presser, V.; Niu, J.; Miller, C.H.; Ubieto, T.; Fedorov, M.V.; Gogotsi, Y. Influence of the structure of carbon onions on their electrochemical performance in supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 2012, 50, 3298–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Qian, M.; He, X.N.; Redepenning, J.; Goodman, P.; Li, H.M.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.F. Chemical activation of carbon nano-onions for high-rate supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 2013, 51, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniraj, V.K.A.; Kamaja, C.K.; Shelke, M.V. RuO2·nH2O Nanoparticles Anchored on Carbon Nano-onions: An Efficient Electrode for Solid State Flexible Electrochemical Supercapacitor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2528–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Ontoria, A.; Chaur, M.N.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Echegoyen, L. Preparation and characterization of soluble carbon nano-onions by covalent functionalization, employing a Na–K alloy. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2406–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegoyen, L.; Ortiz, A.L.; Chaur, M.N.; Palkar, A. Carbon Nano Onions. In Chemistry of Nanocarbons; Nagase, S., Wudl, F., Akasaka, T., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2010; pp. 464–481. ISBN 9780470721957. [Google Scholar]
- Palkar, A.; Melin, F.; Cardona, C.M.; Elliott, B.; Naskar, A.K.; Edie, D.D.; Kumbhar, A.; Echegoyen, L. Reactivity differences between carbon nano onions (CNOs) prepared by different methods. Chem. Asian J. 2007, 2, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echegoyen, L.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Carbon nano-onions for supercapacitor electrodes: Recent developments and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2010, 4, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Mykhailiv, O.; Zubyk, H.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Carbon nano-onions: Unique carbon nanostructures with fascinating properties and their potential applications. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2017, 468, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Taberna, P.-L.; Fantini, S.; Presser, V.; Pérez, C.R.; Malbosc, F.; Rupesinghe, N.L.; Teo, K.B.K.; Gogotsi, Y.; Simon, P. Capacitive Energy Storage from −50 to 100 °C Using an Ionic Liquid Electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 2396–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, J.; Gogotsi, Y. Carbon Onions: Synthesis and Electrochemical Applications. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2013, 22, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, M.; Jäckel, N.; Mochalin, V.N.; Presser, V. Review: Carbon onions for electrochemical energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3172–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelmess, J.; Giordani, S. Carbon nano-onions (multi-layer fullerenes): Chemistry and applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1980–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrat, S.; Pérez, C.R.; Presser, V.; Gogotsi, Y.; Kornyshev, A.A. Effect of pore size and its dispersity on the energy storage in nanoporous supercapacitors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelmess, J.; Frasconi, M.; Balakrishnan, P.B.; Signorelli, A.; Echegoyen, L.; Pellegrino, T.; Giordani, S. Non-covalent functionalization of carbon nano-onions with pyrene–BODIPY dyads for biological imaging. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 50253–50258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, R. Growth, Structure, and Properties of Graphite Whiskers. J. Appl. Phys. 1960, 31, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, K.R.; Scuseria, G.E. Why are buckyonions round? Theor. Chem. Acc. Theory Comput. Model. Theor. Chim. Acta 1998, 99, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxby, J.D.; Chatfield, S.P.; Palmisano, A.J.; Vassallo, A.M.; Wilson, M.A.; Pang, L.S.K. Thermogravimetric analysis of buckminsterfullerene and related materials in air. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.N.; Tiwari, R.N.; Kim, K.S. Zero-dimensional, one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional nanostructured materials for advanced electrochemical energy devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 724–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Dubis, A.T.; Lapinski, A.; Villalta-Cerdas, A.; Echegoyen, L. Electrochemical properties of oxidized carbon nano-onions: DRIFTS-FTIR and raman spectroscopic analyses. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2011, 12, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande Tovar, C.D.; Castro, J.I.; Valencia, C.H.; Navia Porras, D.P.; Mina Hernandez, J.H.; Valencia, M.E.; Velásquez, J.D.; Chaur, M.N. Preparation of Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanocomposite Films Incorporated with Oxidized Carbon Nano-Onions (Multi-Layer Fullerenes) for Tissue-Engineering Applications. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osswald, S.; Havel, M.; Gogotsi, Y. Monitoring oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Chhowalla, M.; Wang, H.; Sano, N.; Alexandrou, I.; Clyne, T.W.; Amaratunga, G.A.J. Characterisation of carbon nano-onions using Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 373, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, M.M.; Stavale, F.; Ferreira, E.H.M.; Vilani, C.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Capaz, R.B.; Achete, C.A.; Jorio, A. Quantifying ion-induced defects and Raman relaxation length in graphene. Carbon 2010, 48, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cançado, L.G.; Takai, K.; Enoki, T.; Endo, M.; Kim, Y.A.; Mizusaki, H.; Jorio, A.; Coelho, L.N.; Magalhães-Paniago, R.; Pimenta, M.A. General equation for the determination of the crystallite size La of nanographite by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 163106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, M.A.; Gomes, A.P.; Fantini, C.; Cançado, L.G.; Araujo, P.T.; Maciel, I.O.; Santos, A.P.; Furtado, C.A.; Peressinotto, V.S.T.; Plentz, F.; et al. Optical studies of carbon nanotubes and nanographites. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2007, 37, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldan, M.R.; Almeida, E.C.; Azevedo, A.F.; Gonçalves, E.S.; Rezende, M.C.; Ferreira, N.G. Raman validity for crystallite size La determination on reticulated vitreous carbon with different graphitization index. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 254, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, S.; Bekyarova, E.; Itkis, M.E.; Zhang, H.; Shepperd, K.; Hicks, J.; Sprinkle, M.; Berger, C.; Lau, C.N.; deHeer, W.A.; et al. Spectroscopy of Covalently Functionalized Graphene. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4061–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Hofmann, M. The big picture of Raman scattering in carbon nanotubes. Vib. Spectrosc. 2007, 45, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Lapinski, A.; Wilczewska, A.Z.; Dubis, A.T.; Villalta-Cerdas, A.; Winkler, K.; Echegoyen, L. The synthesis and characterization of carbon nano-onions produced by solution ozonolysis. Carbon 2011, 49, 5079–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, L.M.; Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Raman spectroscopy in graphene. Phys. Rep. 2009, 473, 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Basko, D.M. Raman spectroscopy as a versatile tool for studying the properties of graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C. Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: Disorder, electron-phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 2007, 143, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, C.T.; Palkar, A.; Melin, F.; Kumbhar, A.; Echegoyen, L.; Melle-Franco, M.; Zerbetto, F.; Rahman, G.M.A.; Ehli, C.; Sgobba, V.; et al. A Carbon Nano-Onion-Ferrocene Donor-Acceptor System: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 4419–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.E.; Pell, W.G. Power limitations of supercapacitor operation associated with resistance and capacitance distribution in porous electrode devices. J. Power Sources 2002, 105, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, G.; Ghimbeu, C.M.; Taberna, P.-L.; Simon, P.; Vix-Guterl, C. Relationship between the carbon nano-onions (CNOs) surface chemistry/defects and their capacitance in aqueous and organic electrolytes. Carbon 2016, 105, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béguin, F.; Presser, V.; Balducci, A.; Frackowiak, E. Carbons and electrolytes for advanced supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2219–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasibi, M.; Golozar, M.A.; Rashed, G. Nano zirconium oxide/carbon black as a new electrode material for electrochemical double layer capacitors. J. Power Sources 2012, 206, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Palkar, A.; Winkler, K.; Echegoyen, L. Electrochemical Properties of Small Carbon Nano-Onion Films. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2010, 13, K35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breczko, J.; Winkler, K.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Villalta-Cerdas, A.; Echegoyen, L. Electrochemical properties of composites containing small carbon nano-onions and solid polyelectrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7761–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Lewandowski, M.; Błaszyk, M.; Molina-Ontoria, A.; Luciński, T.; Echegoyen, L. Preparation and characterization of carbon nano-onion/PEDOT:PSS composites. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 4134–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kim, D.Y. Enhancement of Capacitance by Electrochemical Oxidation of Nanodiamond Derived Carbon Nano-Onions. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 139, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gra̧dzka, E.; Winkler, K.; Borowska, M.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Echegoyen, L. Comparison of the electrochemical properties of thin films of MWCNTs/C 60-Pd, SWCNTs/C60-Pd and ox-CNOs/C60-Pd. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 96, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailiv, O.; Imierska, M.; Petelczyc, M.; Echegoyen, L.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Chemical versus Electrochemical Synthesis of Carbon Nano-onion/Polypyrrole Composites for Supercapacitor Electrodes. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 5783–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Brus, D.M.; Molina-Ontoria, A.; Echegoyen, L. Synthesis of carbon nano-onion and nickel hydroxide/oxide composites as supercapacitor electrodes. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25891–25901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Muhammad, O.; Sayed, M.S.; Parida, S.; Shim, J.-J. In situ nitrogen-doped carbon nano-onions for ultrahigh-rate asymmetric supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Parida, S.; Badrayyana, S.; Singh, B.K. High performance flexible asymmetric CNO-ZnO//ZnO supercapacitor with an operating voltage of 1.8 V in aqueous medium. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozoemena, K.I.; Raju, K.; Ejikeme, P.M.; Ozoemena, K.I. High-performance Mn3O4/onion-like carbon (OLC) nanohybrid pseudocapacitor: Unravelling the intrinsic properties of OLC against other carbon supports. Carbon 2017, 117, 20–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gamby, J.; Taberna, P.L.; Simon, P.; Fauvarque, J.F.; Chesneau, M. Studies and characterisations of various activated carbons used for carbon/carbon supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2001, 101, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevnov, D.A.; Olson, T.S. Double-layer capacitors composed of interconnected silver particles and with a high-frequency response. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, W.; Yokoshima, K.; Murakami, Y.; Takasu, Y. Charge storage mechanism of nanostructured anhydrous and hydrous ruthenium-based oxides. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robat Sarpoushi, M.; Nasibi, M.; Moshrefifar, M.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Reza Riazi, H. Electrochemical investigation of graphene/nanoporous carbon black for supercapacitors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 33, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Saha, U.; Goswami, T.H.; Srivastava, A.; Prasad, N.E. ‘Pillar effect’ of chemically bonded fullerene in enhancing supercapacitance performances of partially reduced fullerenol graphene oxide hybrid electrode material. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberna, P.L.; Simon, P.; Fauvarque, J.F. Electrochemical Characteristics and Impedance Spectroscopy Studies of Carbon-Carbon Supercapacitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chandra, A. Significant Performance Enhancement in Asymmetric Supercapacitors based on Metal Oxides, Carbon nanotubes and Neutral Aqueous Electrolyte. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberna, P.L.; Portet, C.; Simon, P. Electrode surface treatment and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study on carbon/carbon supercapacitors. Appl. Phys. Mater. Sci. Process. 2006, 82, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portet, C.; Yushin, G.; Gogotsi, Y. Electrochemical performance of carbon onions, nanodiamonds, carbon black and multiwalled nanotubes in electrical double layer capacitors. Carbon 2007, 45, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).