Fatigue of Narrow Dental Implants: Influence of the Hardening Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dental Implants.
2.2. Mechanical Properties
2.3. Residual Stress
2.4. Statistical Analysis
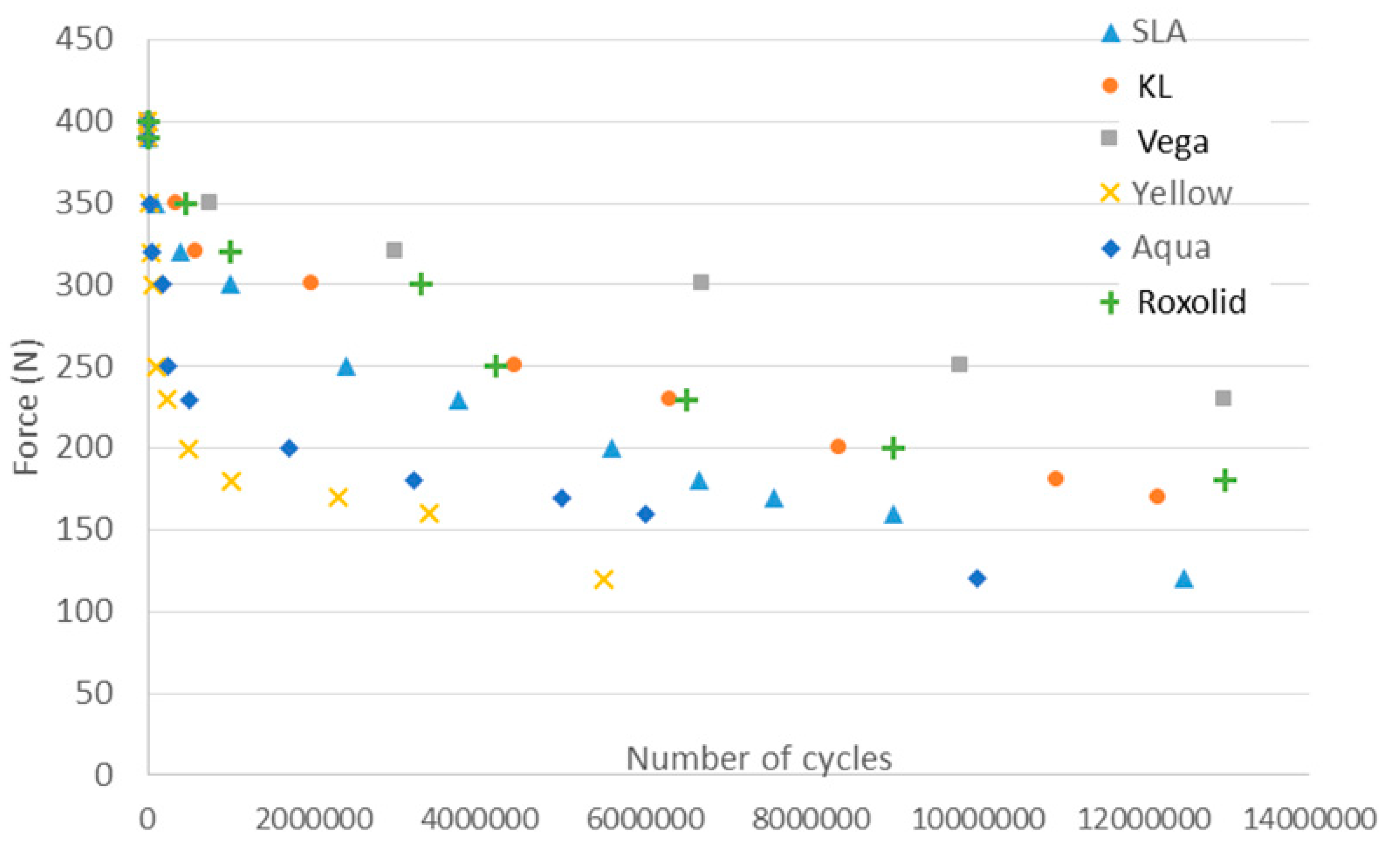
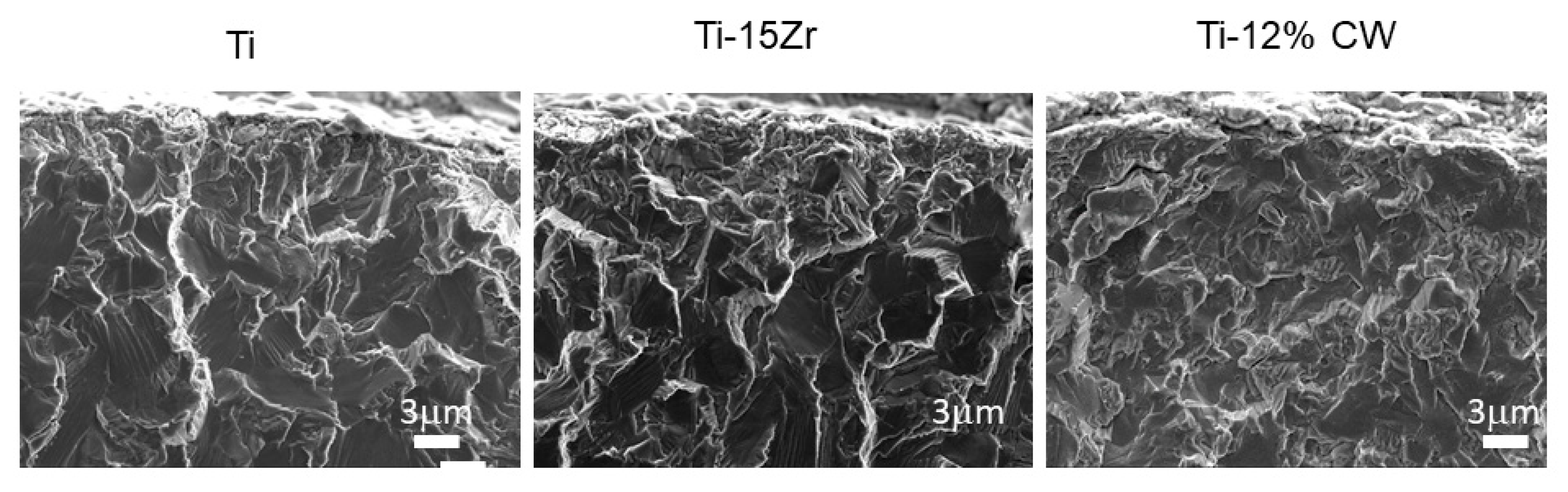
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical approval
References
- Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P.; Zaniboni, M. Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 237–259. [Google Scholar]
- Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P.; Zaniboni, M.; Corsi, E.; Anello, T. Titanium-zirconium alloy narrow diameter implants for the rehabilitation of horizontally deficient edentulous ridges; prospective study on 18 consecutive patients. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunder, U.; Gracis, S.; Capelli, M. Influence of the 3-D bone-to-implant relationship on esthetics. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2005, 25, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gargallo, J.; Satorres, M.; Puyuelo, J.L.; Sánchez-Garcés, M.A.; Pi-Urgell, J.; Gay-Escoda, C. Endosseous dental implant fractures an analysis of 21 cases. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cirugía Bucal 2008, 13, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Goonarwardhana, D.; Judge, R.; Palamara, J.; Abduo, J. Effect of implant diameter and alloy on peri-implant strain: An in vitro quantitative strain analysis. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Dent. 2016, 24, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Imam, A.; Moshaverinia, A.; McGlumphy, A. Implant abutment interface: A comparison of the ultimate force to failure among narrow-diameter implant systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, D. Fixed partial dentures and crows supported by small diameter dental implants in compromised sites. Implant Dent. 2008, 17, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, D.; Witek, L.; Fardin, V.B.; Bonfante, E.A.; Coelho, P.G. Fatigue Failure of narrow implants with different implant-abutment connection designs. J. Prosthodont. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Padrós, A. Fracture and fatigue behaviour of shot blasted titanium dental implants. Implant. Dent. 2002, 11, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Sevilla, P. Fatigue life of bioactive titanium dental implants treated by means of Grit Blasting and Thermo-Chemical treatment. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, P.; Sandino, C.; Arciniegas, M.; Martínez-Gomis, J.; Peraire, M.; Gil, F.J. Evaluating mechanical properties and degradation of YTZP dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Lázaro, P.; Rios, J.V. Implant–abutment connections: Influence of the design on the microgap and their fatigue and fracture behavior of dental implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, M.; Krafft, T.; Kelly, J.R. Fracture of a narrow-diameter roxolid implant: Clinical and fractographic considerations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolentino, L.; Sukekava, F.; Seabra, M.; Lima, L.A.; Garcez-Filho, J.; Araujo, M.G. Success and survival rates of narrow diameter implants made of titanium-zirconium alloy in the posterior region o. the jaws-results from a 1 year follow-up. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoofi, S.; Khademi, M.; Amid, R.; Kadkhodazadeh, M.; Moyahhedi, M.R. Comparison of the effect of three abutment-implant connections on stress distribution the internal surface on dental implants: A Finite element Analyis. J. Dent. Res. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2013, 7, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Alemida, E.O.; Freitas Ac Bonfante, E.A. Mechanical testing of implant supported anterior crowns with different implant/abutment connections. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.W.; Yang, B.E. Long-term cumulative survival and mechanical complications of single tooth Ankylos Implants: Focus on the abutment neck fractures. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Rodriguez, D.; Haapasalo, M. Antibacterial Coatings on Titanium Surfaces: A Comparison Study Between in Vitro Single-Species and Multispecies Biofilm. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5992–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Rodriguez, D.; Gil, F.J. Variation of roughness and adhesion strength of deposited apatite layers on titanium dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Planel, J.A.; Padros, A.; Aparicio, C. The effect of shot blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Altuna, P.; Lucas- Taulé, E.; Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Figueras-Alvarez, O.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Nart, J. Clinical evidence on titanium-zirconium dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohan, D.; Vazquez, L.; Park, Y.; Sammartino, G.; Bernard, J.P. Identification card and codification of the chemical and morphological characteristics of 14 dental implant surfaces. J. Oral Implant. 2011, 37, 525–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Taylor, T.D.; Zabler, S.; Wiest, W.; Fretwurst, T. The impact of force transmission on narrow-body dental implants made of commercially pure titanium and titanium zirconia alloy with a conical implant-abutment connection: An experimental pilot study. Int. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Takada, Y. Mechanical properties and microstructures of dental cast Ti-6Nb-4Cu, Ti-18Nb-2Cu, and Ti-24Nb-1Cu alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, R.; Bonfante, E.; Machado, L.; Tovar, N.; Coelho, P.G. Mechanical evaluation of four narrow-diameter implant systems. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2014, 27, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Binon, P.P.; Curtis, D.A. A classification system to measure the implant-abutment microgap. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 879–885. [Google Scholar]
- Pegueroles, M.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Planell, J.A.; Gil, F.J.; Aparicio, C. Adsorption of fibronectin, fibrinongen, and albumin on TiO2: Time-Resolved Kinetics, Structural Changes, and Competition Study. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Padros, E.; Planell, J.A. Applications of environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) in biomaterials field. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allum, S.R.; Tomlinson, R.A.; Joshi, R. The impact of loads on standard diameter, small diameter and mini implants: A comparative laboratory study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 9, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Silvente, A.I.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-García, I.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Gil, F.J.; Jimenez-Guerra, A. Influence of the Titanium implants surface treatment on the surface roughness and chemical composition. Materials 2020, 13, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Flichy-Fernández, A.; Punset, M.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J. Fracture and Fatigue of Titanium Narrow Dental Implants: New Trends in Order to Improve the Mechanical Response. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
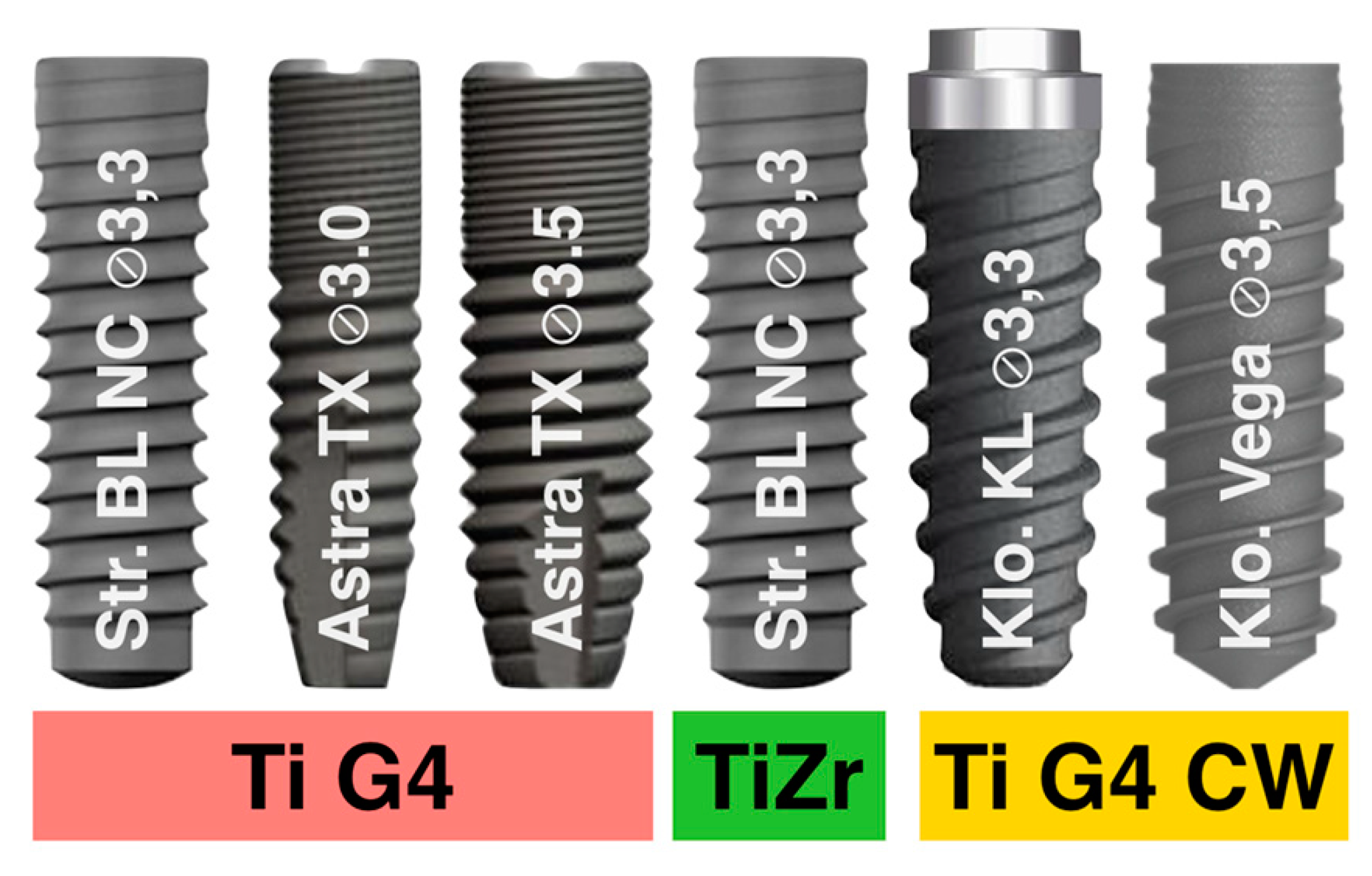
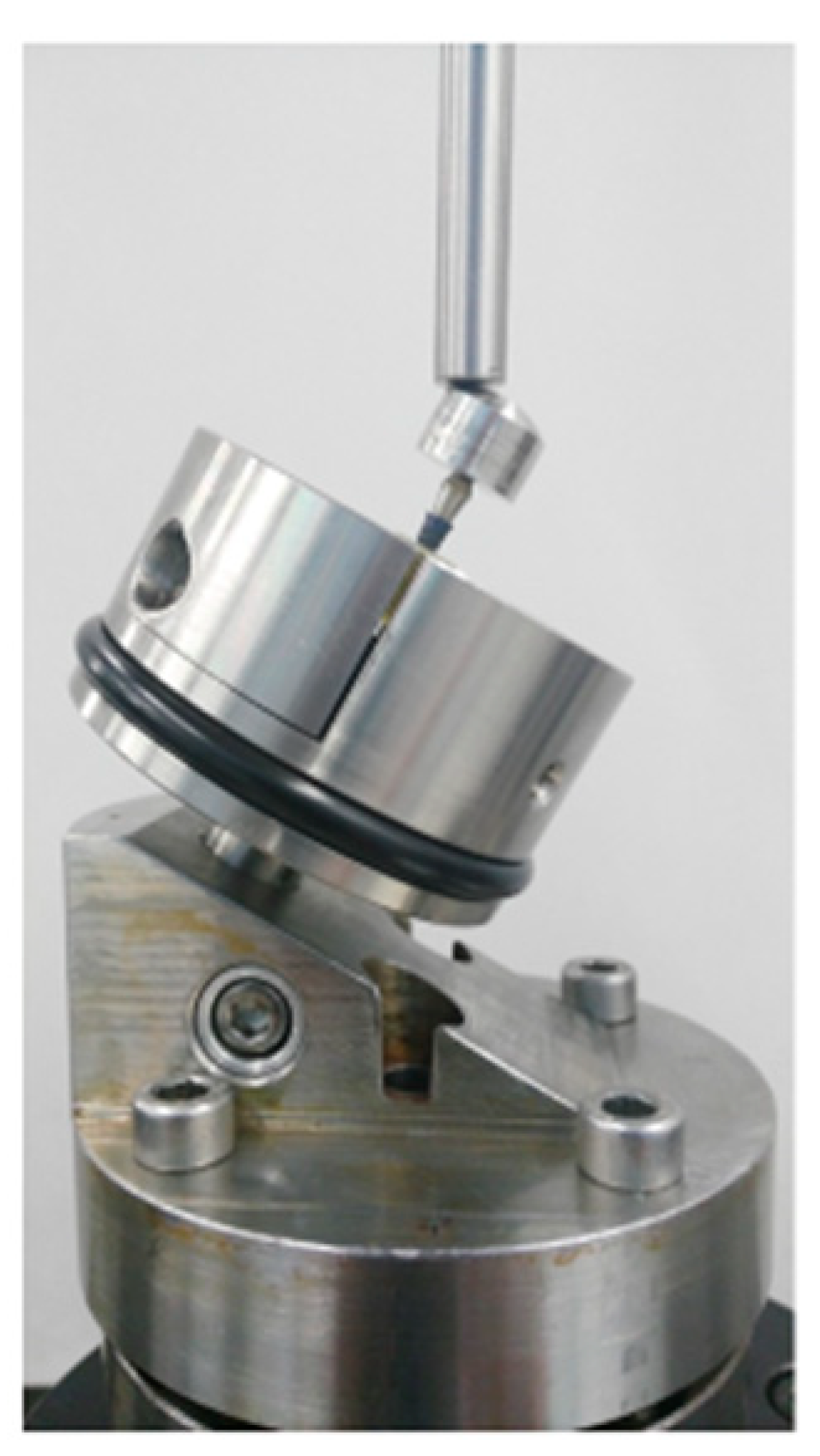




| Group | Group 1 Commercially Pure-Grade 4 Ti | Group 2 Ti Alloyed with 15% Zr | Group 3 Commercially Pure-Grade 4 Titanium Hardened by 12% Cold Worked |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implant Type | Bone level SLA (3.3 mm, h = 8 mm) (Straumann AGR, Basel, Switzerland) (n = 25) Bone level Osseospeed TX Yellow (3.0 mm, h =11 mm) (Astra Tech, Dentsply, Charlotte, NC, USA) (n = 25) Bone level Osseospeed TX Aqua (5 mm, h = 8 mm) (Astra Tech, Dentsply, Charlotte, North Carolina, US) (n = 25) | Bone level Roxolid (3.3 mm, h = 8 mm) (Straumann AGR, Basel, Switzerland) (n = 25) | KL (3.3 mm, h = 8 mm) with regular hexagon external connection (Klockner, Madrid. Spain) (n = 25). Bone Level Vega (3.5 mm, h = 8 mm) (Klockner, Madrid. Spain) (n = 25). |
| Connection Type | Conical internal | Cross-fit internal | Hexagon external/internal |
| Implant | Maximum Strength (MPa) | Yield Stress 0.2% (MPa) | Ductility (%) | Hardness (HV) | Residual Stress (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | SLA | 520 (21) | 443 (23) | 16 (7) | 109 (10) | −70 (6) |
| Yellow | 470 (40) | 375 (12) | 16 (5) | 102 (10) | −54 (13) | |
| Aqua | 480 (39) | 368 (25) | 19 (4) | 103 (11) | −45 (12) | |
| Group 2 | Roxolid | 887 (34) | 689 (23) | 24 (3) | 197 (13) | −55 (17) |
| Group 3 | KL | 1032 (41) | 783 (15) | 6 (2) | 356 (22) | −375 (43) |
| Vega | 1090 (37) | 750 (21) | 7 (3) | 378 (26) | −398 (34) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez, R.A.; Gargallo, J.; Altuna, P.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Gil, F.J. Fatigue of Narrow Dental Implants: Influence of the Hardening Method. Materials 2020, 13, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061429
Pérez RA, Gargallo J, Altuna P, Herrero-Climent M, Gil FJ. Fatigue of Narrow Dental Implants: Influence of the Hardening Method. Materials. 2020; 13(6):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061429
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez, R.A., J. Gargallo, P. Altuna, M. Herrero-Climent, and F.J. Gil. 2020. "Fatigue of Narrow Dental Implants: Influence of the Hardening Method" Materials 13, no. 6: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061429
APA StylePérez, R. A., Gargallo, J., Altuna, P., Herrero-Climent, M., & Gil, F. J. (2020). Fatigue of Narrow Dental Implants: Influence of the Hardening Method. Materials, 13(6), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061429







