Tackling Complex Analytical Tasks: An ISO/TS-Based Validation Approach for Hydrodynamic Chromatography Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Performance and Quality Criteria for spICP-MS
2.4. Data Analysis Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
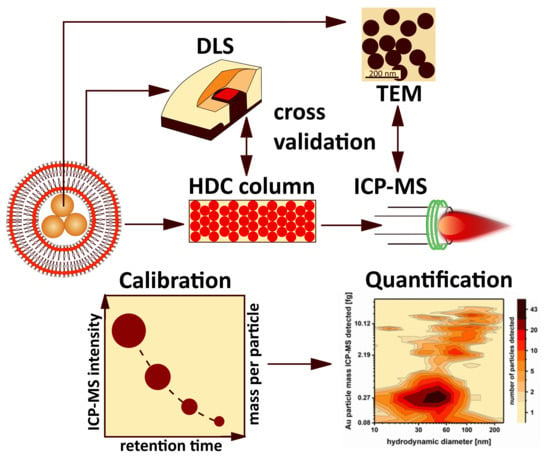
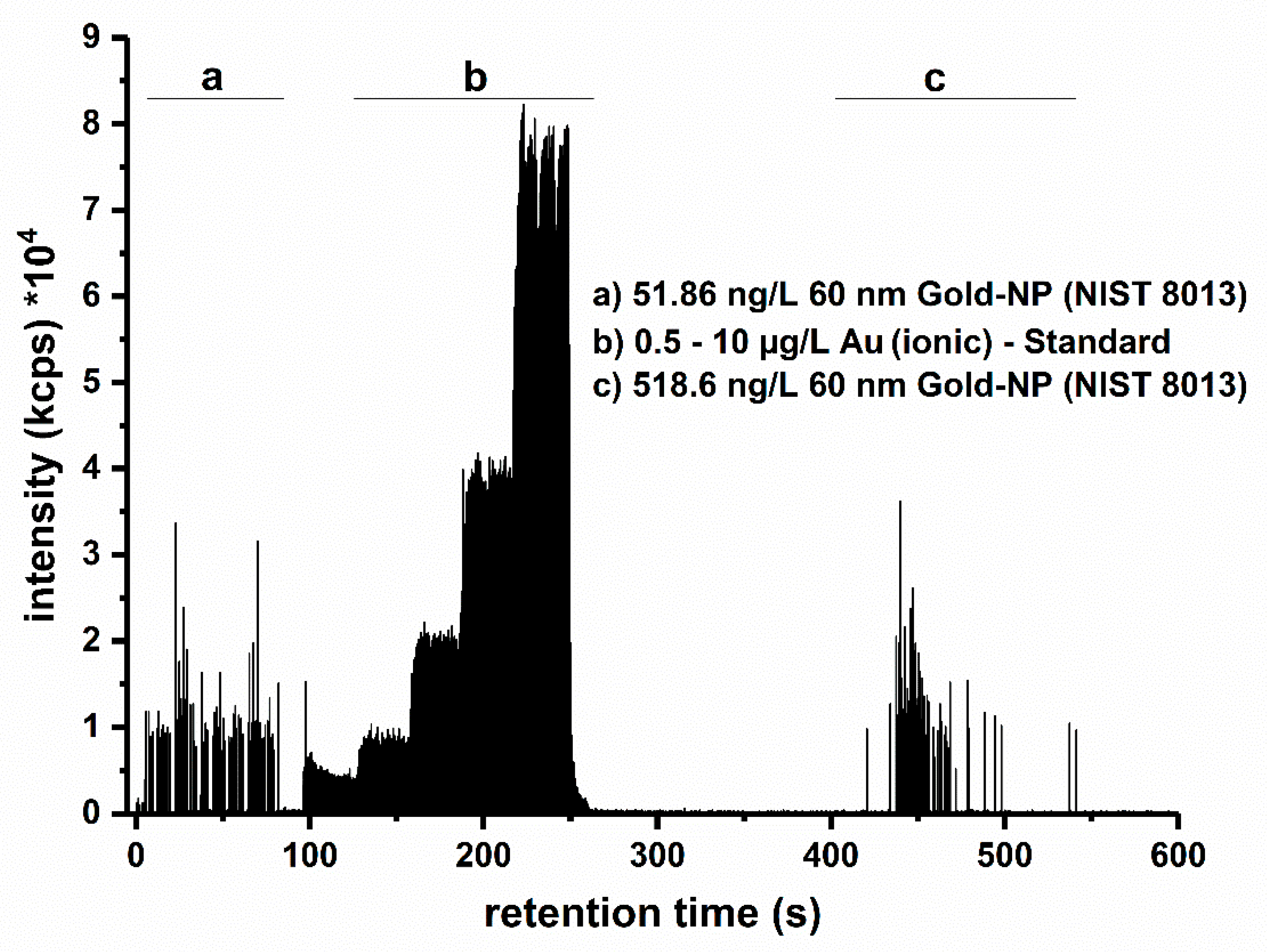
3.1. HDC-spICP-MS Setup and Calibration Approach
3.2. Determination of Quality Criteria Based on the Technical Specification (TS)
3.3. Determination of Quality Criteria (QC) for Nanoparticle Solutions Based on the Technical Specification (TS)
3.4. Additional Validation for Multidimensional Coupled Techniques
3.4.1. Modified Transport Efficiency
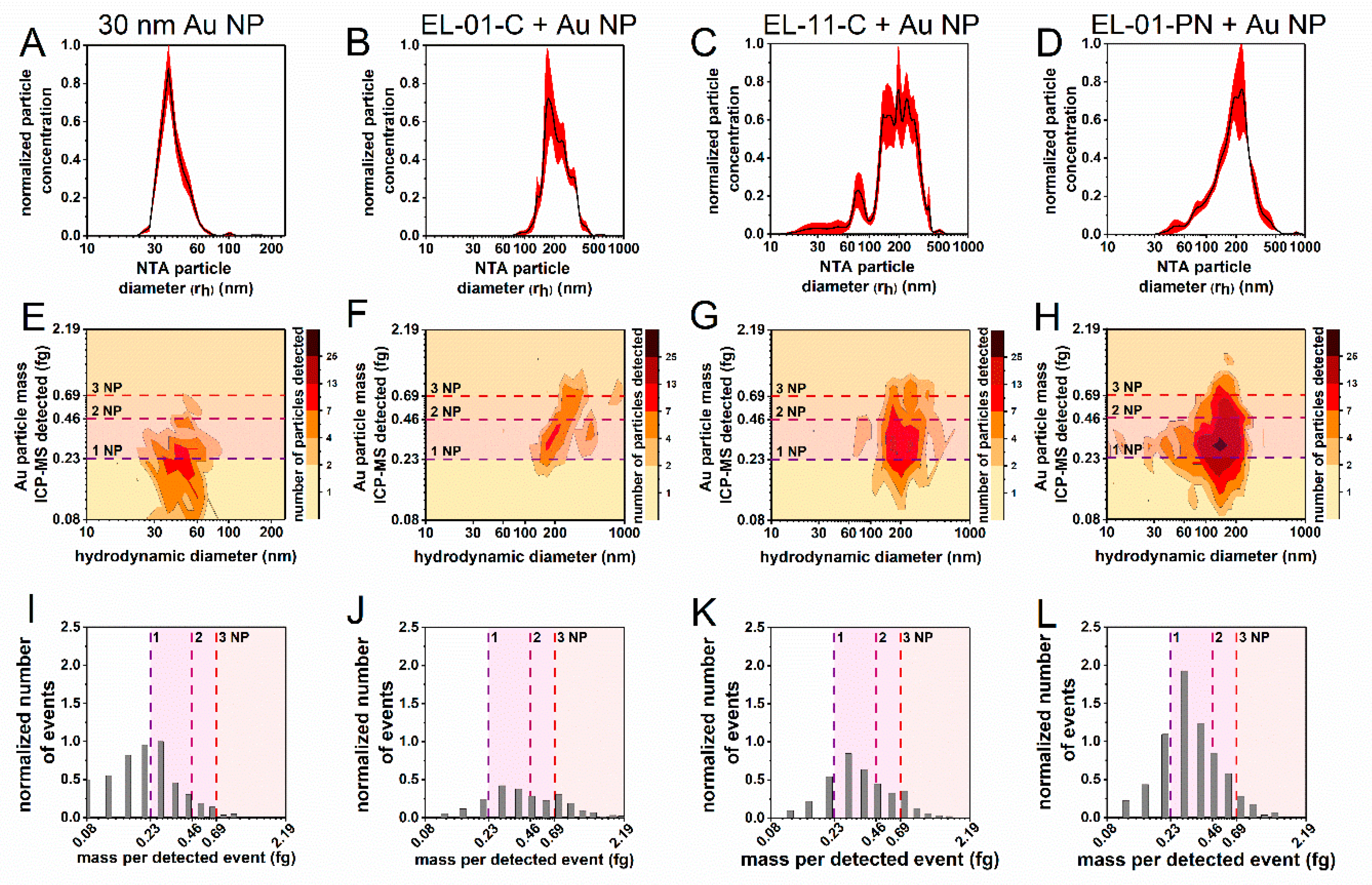
3.4.2. Cross Validation of NP Size Determination
3.4.3. Separation Capabilities of HDC-spICP-MS
3.5. Proof-of-Concept Application—Au-NPs Embedded in Liposomes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katz, L.M.; Dewan, K.; Bronaugh, R.L. Nanotechnology in cosmetics. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 85, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, M.E.; Kuiken, T.; Vejerano, E.P.; McGinnis, S.P.; Hochella, M.F.; Rejeski, D.; Hull, M.S. Nanotechnology in the real world: Redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory. Beilstein J. Nanotech. 2015, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tolaymat, T.; El Badawy, A.; Sequeira, R.; Genaidy, A. An integrated science-based methodology to assess potential risks and implications of engineered nanomaterials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakal, C.; Tsytsikova, L.; Carlander, D.; Duncan, T.V. Measurement Methods for the Oral Uptake of Engineered Nanomaterials from Human Dietary Sources: Summary and Outlook. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food 2014, 13, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramenko, N.B.; Demidova, T.B.; Abkhalimov, E.V.; Ershov, B.G.; Krysanov, E.Y.; Kustov, L.M. Ecotoxicity of different-shaped silver nanoparticles: Case of zebrafish embryos. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 347, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, B.; Owen, T.P.; Kuempel, E.D.; Jarabek, A.M. Dosimetry of inhaled elongate mineral particles in the respiratory tract: The impact of shape factor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 361, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Meyer, T.; Sieg, H.; Kastner, C.; Reichardt, P.; Tentschert, J.; Jungnickel, H.; Estrela-Lopis, I.; Burel, A.; Chevance, S.; et al. Characterization of aluminum, aluminum oxide and titanium dioxide nanomaterials using a combination of methods for particle surface and size analysis. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14377–14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.Y.; Jiao, R.Y.; Xu, H.; An, G.Y.; Wang, D.S. The influence of particle size and concentration combined with pH on coagulation mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci.-China 2019, 82, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, L.; Iglesias, M.; Margui, E.; Hidalgo, M.; Verdaguer, D.; Llorens, L.; Kodre, A.; Kavcic, A.; Vogel-Mikus, K. Uptake, translocation and ligand of silver in Lactuca sativa exposed to silver nanoparticles of different size, coatings and concentration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 384, 121201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.W.; Ng, D.Q.; Lin, Y.P.; Chen, P.J. Dissolved Organic Matter or Salts Change the Bioavailability Processes and Toxicity of the Nanoscale Tetravalent Lead Corrosion Product PbO2 to Medaka Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11292–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyre-Fonseca, V.; Medina-Reyes, E.I.; Tellez-Medina, D.I.; Paniagua-Contreras, G.L.; Monroy-Perez, E.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; Flores-Flores, J.O.; Lopez-Villegas, E.O.; Gutierrez-Lopez, G.F.; et al. Influence of shape and dispersion media of titanium dioxide nanostructures on microvessel network and ossification. Colloid Surf. B 2018, 162, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, I.; Shannahan, J.H.; Raghavendra, A.J.; Alsaleh, N.B.; Podila, R.; Brown, J.M. Biocorona formation contributes to silver nanoparticle induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, R.; Gradzielski, M. Experimental Aspects of Colloidal Interactions in Mixed Systems of Liposome and Inorganic Nanoparticle and Their Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11610–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcantara, K.P.; Zulfakar, M.H.; Castillo, A.L. Development, characterization and pharmacokinetics of mupirocin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for intravascular administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 571, 118705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakowski, S.; Jiang, K.; Prakash, G.; Kastrup, C. Delivery of mRNA to platelets using lipid nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Li, X.S.; Liang, F.; Yang, Y.W. Design of Multifunctional Fluorescent Hybrid Materials Based on SiO2 Materials and Core-Shell Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanoparticles for Metal Ion Sensing. Small 2019, 15, e1904569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caster, J.M.; Yu, S.K.; Patel, A.N.; Newman, N.J.; Lee, Z.J.; Warner, S.B.; Wagner, K.T.; Roche, K.C.; Tian, X.; Min, Y.; et al. Effect of particle size on the biodistribution, toxicity, and efficacy of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles in chemoradiotherapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Ran, F.; Cui, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.F.; Gao, Y.K.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.L. A comparison between sphere and rod nanoparticles regarding their in vivo biological behavior and pharmacokinetics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.C.; Kriegel, F.L.; Rosenkranz, D.; Dreiack, N.; Tentschert, J.; Jungnickel, H.; Jalili, P.; Fessard, V.; Laux, P.; Luch, A. Aluminum and aluminum oxide nanomaterials uptake after oral exposure—A comparative study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contado, C. Nanomaterials in consumer products: A challenging analytical problem. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano, M.L.; Zougagh, M.; Valcarcel, M.; Rios, A. Analytical Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: Where we are and where we are heading. Talanta 2018, 177, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, H.; Saunders, F.L.; Solc, J. Hydrodynamic Chromatography—New Approach to Particle-Size Analysis. Adv. Colloid Interfac 1976, 6, 237–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striegel, A.M.; Brewer, A.K. Hydrodynamic Chromatography. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiede, K.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Wang, X.M.; Gore, D.; Tiede, D.; Baxter, M.; David, H.; Tear, S.P.; Lewis, J. Application of hydrodynamic chromatography-ICP-MS to investigate the fate of silver nanoparticles in activated sludge. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, K.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Tiede, D.; Tear, S.P.; David, H.; Lewis, J. A robust size-characterisation methodology for studying nanoparticle behaviour in ‘real’ environmental samples, using hydrodynamic chromatography coupled to ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2009, 24, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.P.; Bruton, T.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Halden, R.U.; Westerhoff, P.; Ranville, J.F. Analysis of gold nanoparticle mixtures: A comparison of hydrodynamic chromatography (HDC) and asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) coupled to ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergantis, S.A.; Jones-Lepp, T.L.; Heithmar, E.M. Hydrodynamic Chromatography Online with Single Particle-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry for Ultratrace Detection of Metal-Containing Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6454–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Barber, A.; Bednar, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Silver nanoparticle characterization using single particle ICP-MS (SP-ICP-MS) and asymmetrical flow field flow fractionation ICP-MS (AF4-ICP-MS). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.Y.; Wold, S. Gold colloid analysis by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in a single particle mode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 555, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, D.; Kriegel, F.L.; Mavrakis, E.; Pergantis, S.A.; Reichardt, P.; Tentschert, J.; Jakubowski, N.; Laux, P.; Panne, U.; Luch, A. Improved validation for single particle ICP-MS analysis using a pneumatic nebulizer/microdroplet generator sample introduction system for multi-mode nanoparticle determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1099, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TS 19590:2017 Nanotechnologies—Size Distribution and Concentration of Inorganic Nanoparticles in Aqueous Media via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- DIN CEN ISO/TS 19590:2019-11 Nanotechnologien—Größenverteilung und Konzentration anorganischer Nanopartikel in wässrigen Medien durch Massenspektrometrie an Einzelpartikeln mit induktiv gekoppeltem Plasma (ISO/TS 19590:2017); German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- Lee, S.; Bi, X.Y.; Reed, R.B.; Ranville, J.F.; Herckes, P.; Westerhoff, P. Nanoparticle Size Detection Limits by Single Particle ICP-MS for 40 Elements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10291–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babick, F.; Mielke, J.; Wohlleben, W.; Weigel, S.; Hodoroaba, V.D. How reliably can a material be classified as a nanomaterial? Available particle-sizing techniques at work. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helsper, J.P.F.G.; Peters, R.J.B.; Brouwer, L.; Weigel, S. Characterisation and quantification of liposome-type nanoparticles in a beverage matrix using hydrodynamic chromatography and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.; Kim, Y.-T.; Kang, A.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, K.; Yun, W.S.; Kim, Y.H. Lipid Reconstitution-Enabled Formation of Gold Nanoparticle Clusters for Mimetic Cellular Membrane. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ionic Measurements | spICP-MS | HDC-spICP-MS |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (cps (ng mL−1)−1) | 3879.44 | 5675.94 |
| R2 | 0.99996 | 0.99587 (0.00050) |
| LOD (ng mL−1) | 0.028 (0.001) | 0.021 (0.001) |
| LOD (nm) | 12.7 (0.1) | 10.3 (0.2) |
| Particulate Parameters | spICP-MS | HDC-spICP-MS |
|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | 56.8 (1.5) | 55.2 (1.1) |
| Number of particles detected (×10³ mL−1) | 26.7 (2.3) | 26.5 (2.2) |
| Transport efficiency (%) of counting method | 2.54 (0.19) | 6.86 (0.56) |
| Recovery (%) | 100 (± 9) | 100 (± 8) |
| TEM † | spICP-MS | DLS | HDC | ηHDC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18.7 | 22.6 (0.8) | 31.2 (0.5) | 34.4 (5.7) | 1.12 (0.34) |
| 27.6 | 31.6 (1.1) | 43.0 (0.5) | 39.3 (2.3) | 0.61 (0.18) |
| 56 | 58.2 (1.0) | 76.3 (1.1) | 73.9 (19.1) | 0.50 (0.30) |
| 81.2 | 83.4 (8.1) | 96 (0.8) | 103.6 (24.7) | 0.45 (0.27) |
| 100.3 | 104.5(14.0) | 115.9 (0.7) | 119.5 (12.2) | 0.42 (0.17) |
| Separated Size (nm) | Peak Resolution (Number Distribution) | Background (Number of NP) | Background Corrected Peak Resolution (Number Distribution) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30/60 | 2.12 | 1.5 | 3.14 |
| 60/80 | 1.82 | 2.4 | 1.49 |
| 60/100 | 1.86 | 3.3 | 5.16 |
| 30/60/100 | 1.86/1.54 | 1.5 | 3.06/2.05 |
| 30/60/80/100 | 18.51/0.36/0.38 | 11.5 | 5.3/2.22/4.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hachenberger, Y.U.; Rosenkranz, D.; Kriegel, F.L.; Krause, B.; Matschaß, R.; Reichardt, P.; Tentschert, J.; Laux, P.; Jakubowski, N.; Panne, U.; et al. Tackling Complex Analytical Tasks: An ISO/TS-Based Validation Approach for Hydrodynamic Chromatography Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Materials 2020, 13, 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061447
Hachenberger YU, Rosenkranz D, Kriegel FL, Krause B, Matschaß R, Reichardt P, Tentschert J, Laux P, Jakubowski N, Panne U, et al. Tackling Complex Analytical Tasks: An ISO/TS-Based Validation Approach for Hydrodynamic Chromatography Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Materials. 2020; 13(6):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061447
Chicago/Turabian StyleHachenberger, Yves U., Daniel Rosenkranz, Fabian L. Kriegel, Benjamin Krause, René Matschaß, Philipp Reichardt, Jutta Tentschert, Peter Laux, Norbert Jakubowski, Ulrich Panne, and et al. 2020. "Tackling Complex Analytical Tasks: An ISO/TS-Based Validation Approach for Hydrodynamic Chromatography Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry" Materials 13, no. 6: 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061447
APA StyleHachenberger, Y. U., Rosenkranz, D., Kriegel, F. L., Krause, B., Matschaß, R., Reichardt, P., Tentschert, J., Laux, P., Jakubowski, N., Panne, U., & Luch, A. (2020). Tackling Complex Analytical Tasks: An ISO/TS-Based Validation Approach for Hydrodynamic Chromatography Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Materials, 13(6), 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061447