Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Modulus and Fatigue Life of Bituminous Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Binder
2.1.2. Aggregate
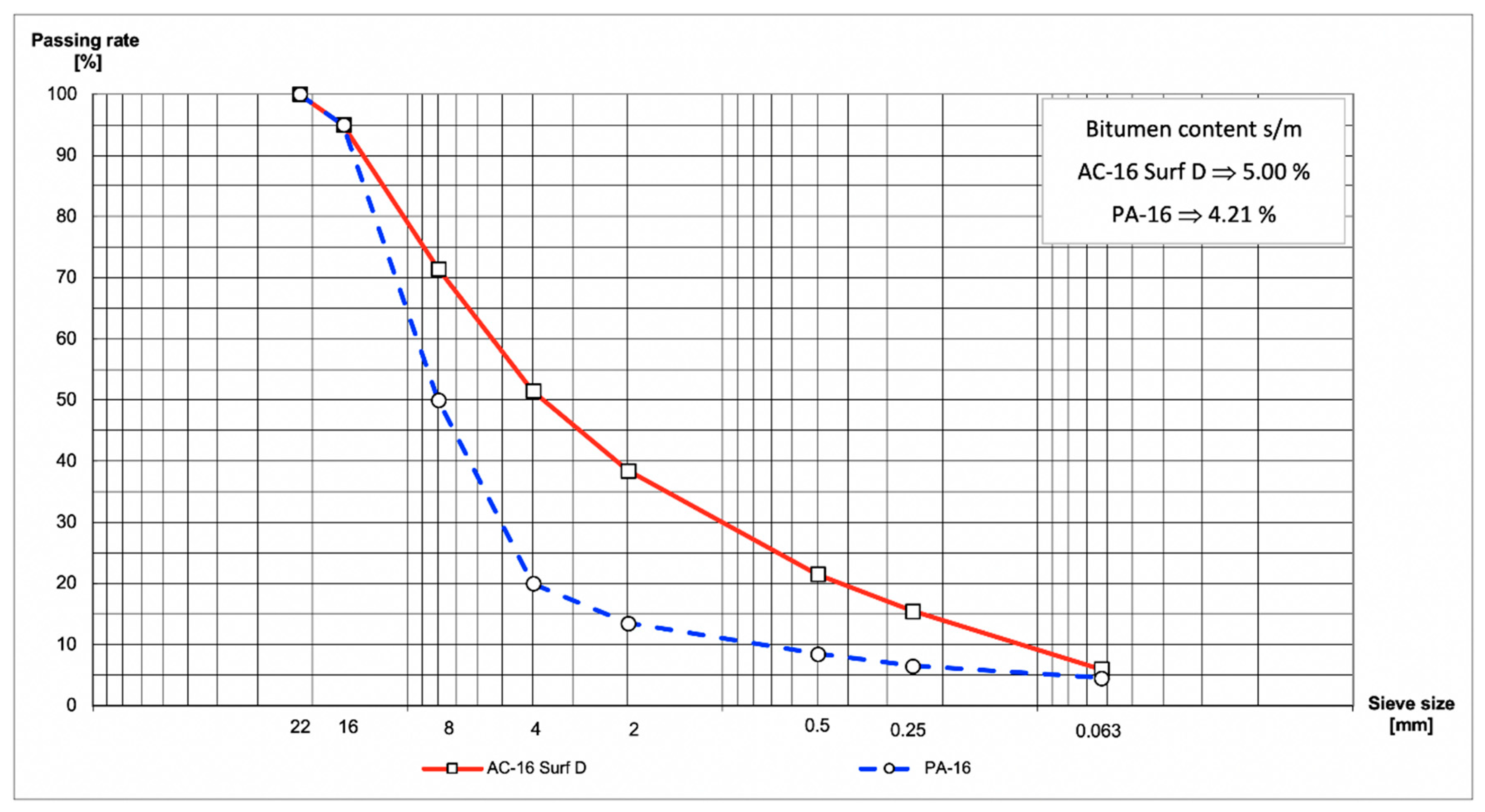
2.1.3. Bituminous Mixture
- Asphalt concrete:
- Density: 2.45–2.51 g/cm3.
- Air void content: 6.0–8.4%.
- Porous asphalt:
- Density: 2.17–2.22 g/cm3.
- Air void content: 16.7–19.8%.
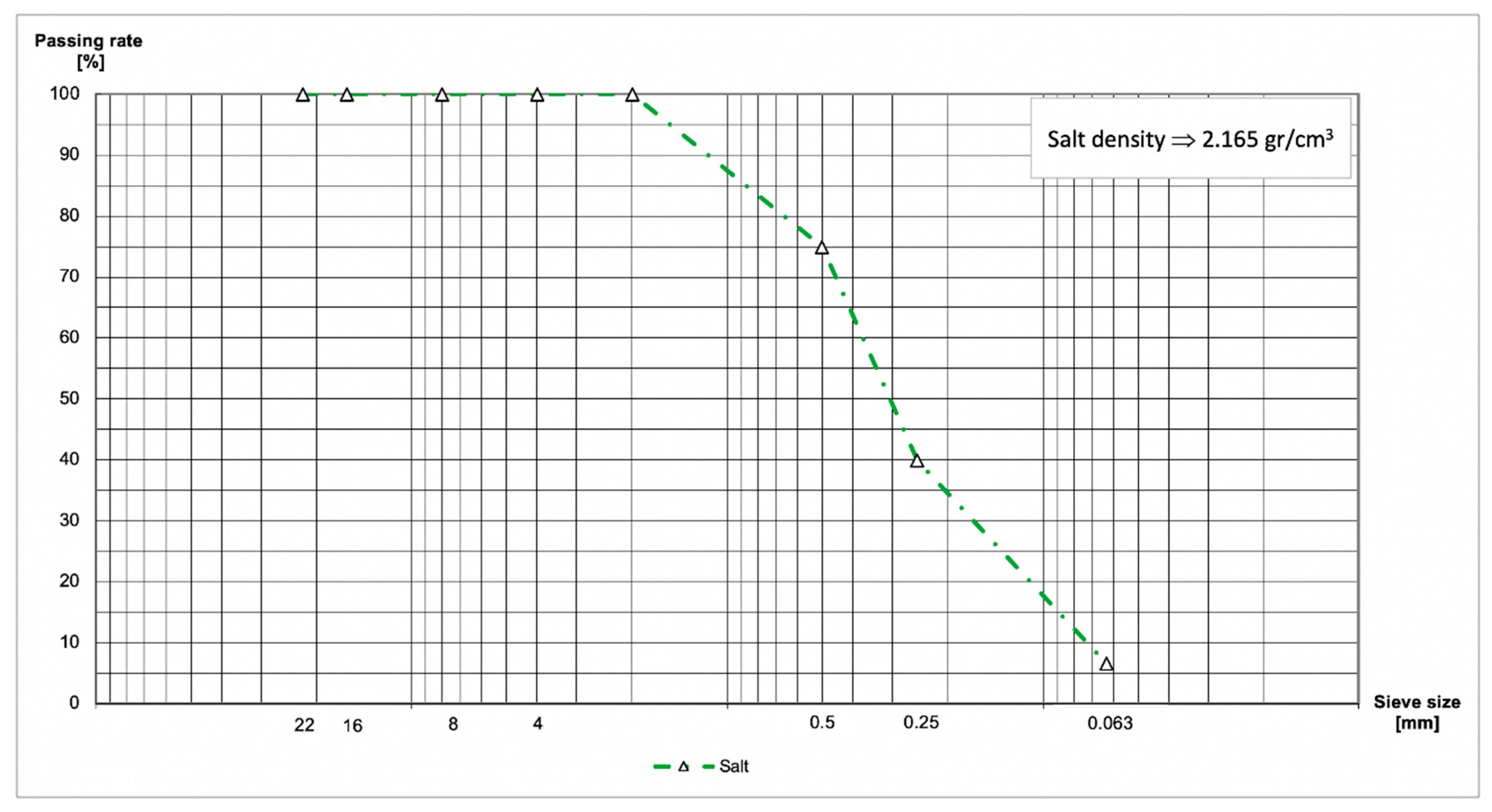
2.1.4. NaCl and Seawater
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Bituminous Mixture Immersed in Salt Water
- Series B1, 3.5% (seawater).
- Series B2, 5.0% amount of salt by weight of distilled water.
- Series B3, 10.0% amount of salt by weight of distilled water.
2.2.2. NaCl Introduced as Aggregate into the Bituminous Mixture
- Series C1, 5%.
- Series C2, 10%.
2.2.3. Bituminous Mixture Manufactured with an Aggregate Previously Saturated in Salt Water
- Series D1, 2.0%,
- Series D2, 3.5%.
2.3. Tests
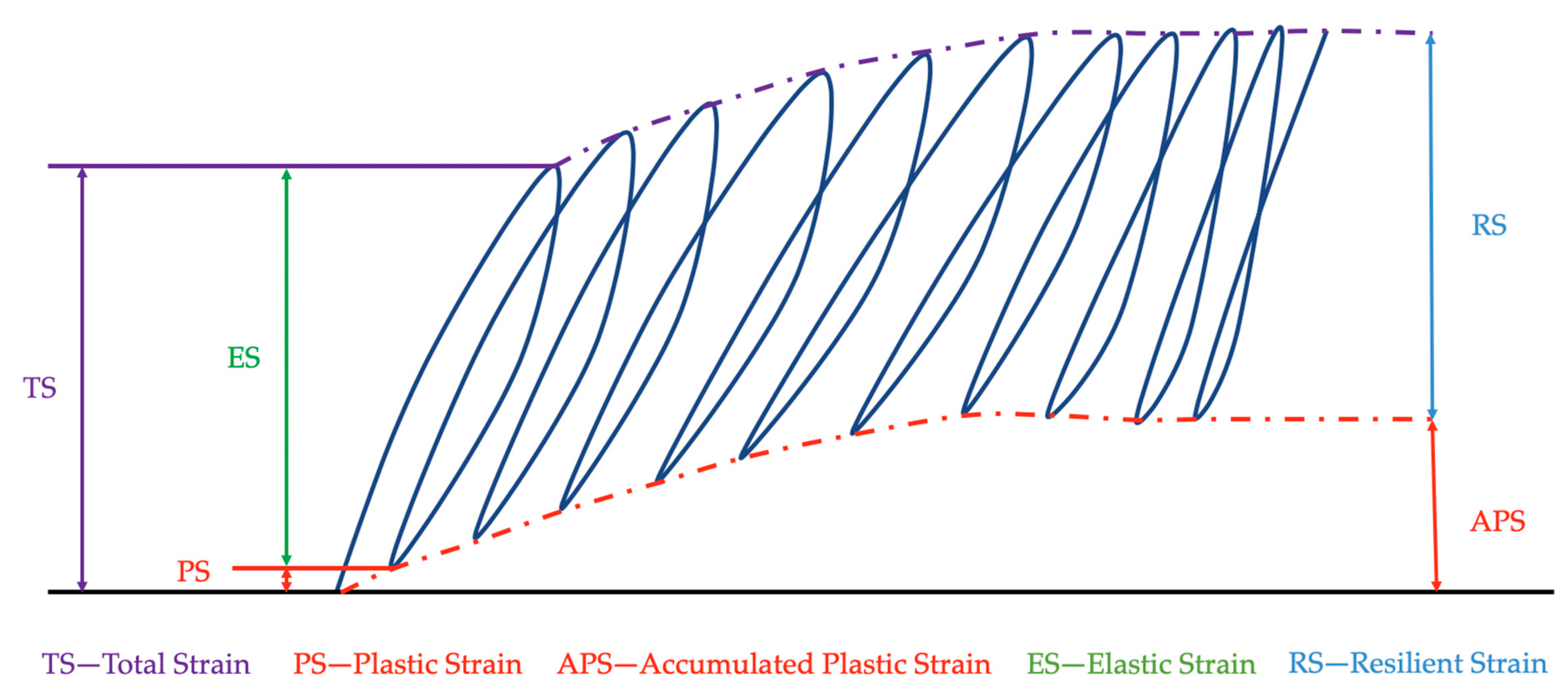
2.3.1. Resilient Modulus Test
2.3.2. Dynamic Modulus Test
2.3.3. Fatigue Test
3. Results
3.1. Resilient Modulus Test
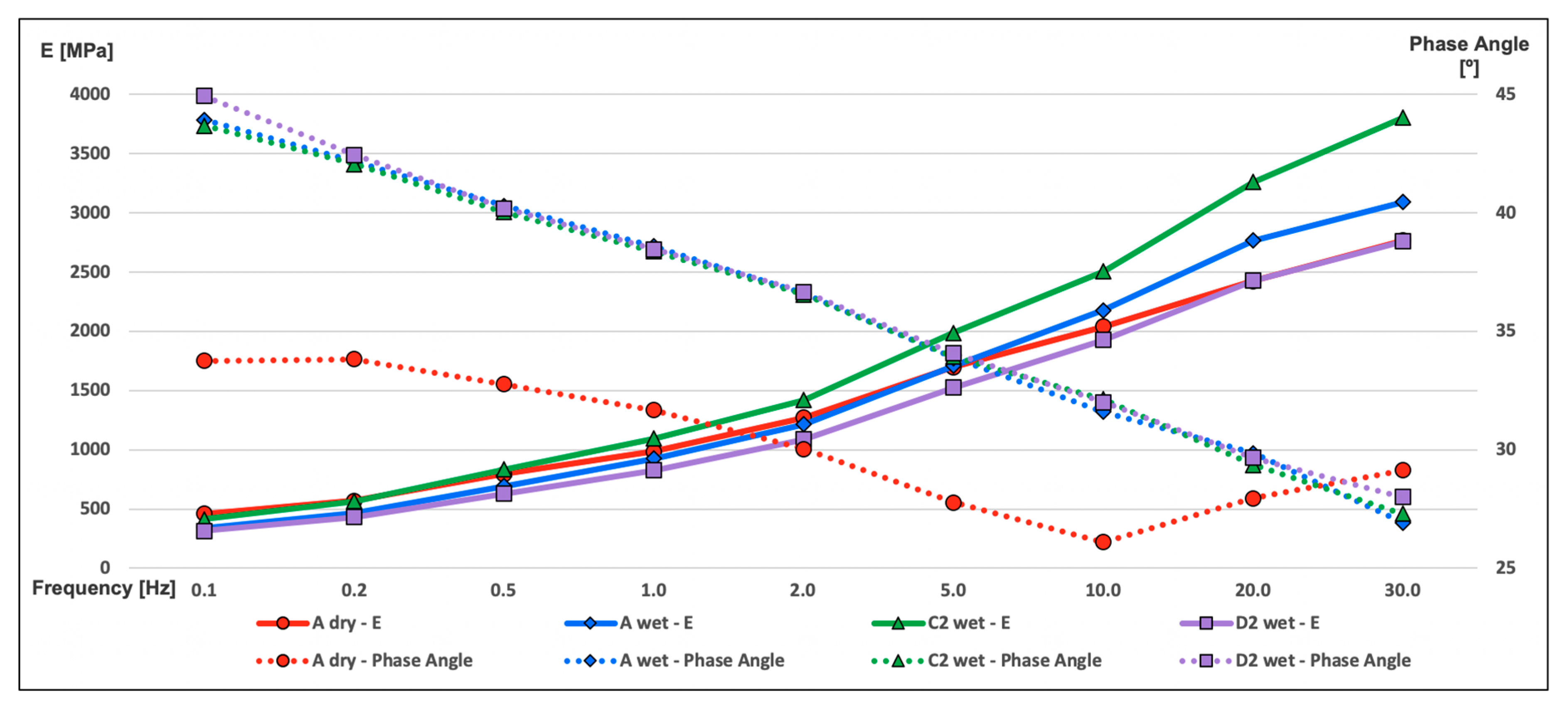
3.2. Dynamic Modulus Test
3.3. Fatigue Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthumani, A.; Fay, L.; Akin, M.; Wang, S.; Gong, J.; Shi, X. Correlating lab and field tests for evaluation of deicing and anti-icing chemicals: A review of potential approaches. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 97, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L. Eficiencia en Vialidad Invernal. Materiales Empleados en los Trabajos para el Mantenimiento de la Vialidad Invernal. In Proceedings of the XII Jornadas de Conservación de Carreteras, Madrid, Spain, 10–11 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Norrström, A.C. Metal mobility by de-icing salt from an infiltration trench for highway runoff. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1907–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, M.; Karlsson, S.; Bäckman, L.; Folkeson, L.; Lind, B. Mobilisation of heavy metals by deicing salts in a roadside environment. Water Res. 2003, 38, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrström, A.C.; Jacks, G. Concentration and fractionation of heavy metals in roadside soils receiving de-icing salts. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 218, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsen, C.J.; Wibetoe, G.; van der Sloot, H.A.; Lund, W.; Petkovic, G. Field site leaching from recycled concrete aggregates applied as sub-base material in road construction. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, J.W.; Moore, J.; Lev, S.M.; Casey, R.E.; Ownby, D.R.; Flora, R.F.; Izzo, G. Influence of Modern Stormwater Management Practices on Transport of Road Salt to Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4165–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Cuthbert, M.O.; Gamble, R.; Connon, L.E.; Pearson, A.; Shepley, M.G.; Davis, J. Highway deicing salt dynamic runoff to surface water and subsequent infiltration to groundwater during severe UK winters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikiz, N.; Galip, E. Computerized decision tree for anti-icing/pretreatment applications as a result of laboratory and field testings. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 126, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenouth, W.R.; Gharabaghi, B.; Perera, N. Road salt application planning tool for winter de-icing operations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Paste, A.; Wåhlin, J. Wet pavement anti-icing—A physical mechanism. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xie, X.; Oeser, M.; Steinauer, B. Influence of the gritting material applied during the winter services on the asphalt surface performance. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2015, 112, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Y.; el Halim, A.O.A.; Razaqpur, A.G.; Bekheet, W.; Farha, M.H. Effects of Runway Deicers on Pavement Materials and Mixes: Comparison with Road Salt. J. Transp. Eng. 2012, 128, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Yuan, H.; Meng, J. Evaluation of long-term performance of anti-icing asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 84, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, F.; Merusi, F.; Polacco, G.; Filippi, S.; Paci, M. Effectiveness of sodium chloride-based anti-icing filler in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xing, M.; Chen, S.; He, R.; Cong, P. Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 51, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Yi, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, L. Impact of salt and freeze–thaw cycles on performance of asphalt mixtures in coastal frozen region of China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obika, B.; Freer-Hewish, R.J.; Fookes, G.P. Soluble salt damage to thin bituminous road and runway surfaces. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1989, 22, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juli-Gándara, L.; Vega-Zamanillo, Á.; Calzada-Pérez, M.Á. Sodium chloride effect in the mechanical properties of the bituminous mixtures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 164, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, F.; Mikolaj, J.; Zatkalikova, V.; Sramek, J.; Durekova, D.; Remek, L. Deformation Properties and Fatigue of Bituminous Mixtures. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 701764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, S.; Saravanan, U.; Krishnan, J.M. On measurement of dynamic modulus for bituminous mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 20, 1073–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tino Ramos, R. Influencia de los Agentes Externos Sobre el Comportamiento Viscoelasticoplástico de las Mezclas Bituminosas para Firmes de Carreteras. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Zamanillo, Á.; Juli-Gándara, L.; Calzada-Pérez, M.Á.; Teijón-López-Zuazo, E. Impact of Temperature Changes and Freeze-Thaw Cycles on the Behaviour of Asphalt Concrete Submerged in Water with Sodium Chloride. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE-EN 12593:2015. Bitumen and Bituminous Binders. Determination of the Fraass Breaking Point; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 1427:2015. Bitumen and Bituminous Binders. Determination of the Softening Point. Ring and Ball Method; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 1426:2015. Bitumen and Bituminous Binders. Determination of Needle Penetration; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 1097-6:2014. Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 6: Determination of Particle Density and Water Absorption; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 1097-2:2010. Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 2: Methods for the Determination of Resistance to Fragmentation; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 933-3:2012. Tests for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates—Part 3: Determination of Particle Shape—Flakiness Index; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pliego de Prescripciones Técnicas Generales para Obras de Carreteras y Puentes (PG-3); 2017. Available online: http://www.carreteros.org/normativa/pg3/pg3.htm (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- UNE-EN 12697-34:2013. Bituminous Mixtures—Test Methods for Hot Asphalt—Part 34: Marshall Test; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 12697-26:2012. Bituminous Mixtures—Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt—Part 26: Stiffness; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN 12697-24:2013. Bituminous Mixtures—Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt—Part 24: Resistance to Fatigue; UNE: Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]

| Series | Resilient Modulus (MPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC-16 Surf D | PA-16 | ||||
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | ||
| Reference | A | 5146 | 4710 | 1875 | 1864 |
| Specimens immersed in salt water | B1 | 5146 | 4583 | 1875 | 1670 |
| B2 | 5146 | 4544 | 1875 | 1479 | |
| B3 | 5146 | 4603 | 1875 | 2246 | |
| NaCl introduced as aggregate | C1 | 5215 | 4927 | 1936 | 1670 |
| C2 | 5470 | 5936 | 2289 | 1470 | |
| Aggregate previously saturated in salt water | D1 | 3873 | 4378 | 1813 | 1712 |
| D2 | 3258 | 3649 | 1774 | 569 | |
| Series | Standard Deviation (MPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC-16 Surf D | PA-16 | ||||
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | ||
| Reference | A | 378 | 320 | 208 | 168 |
| Specimens immersed in salt water | B1 | 378 | 312 | 208 | 203 |
| B2 | 378 | 342 | 208 | 184 | |
| B3 | 378 | 350 | 208 | 192 | |
| NaCl introduced as aggregate | C1 | 278 | 301 | 236 | 211 |
| C2 | 399 | 410 | 315 | 268 | |
| Aggregate previously saturated in salt water | D1 | 287 | 354 | 305 | 242 |
| D2 | 354 | 298 | 289 | 290 | |
| R² | 0.971 |
| Adjusted R² | 0.967 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 5 | 31,629,381.51 | 6,325,876.30 | 203.63 | <0.0001 |
| Error | 30 | 931,953.49 | 31,065.12 | - | - |
| Corrected Total | 35 | 32,561,335.00 | - | - | - |
| R² | 0.972 |
| Adjusted R² | 0.967 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Squares | F | Pr > f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 4 | 11.29 | 2.82 | 222.16 | < 0.0001 |
| Error | 27 | 0.33 | 0.01 | - | - |
| Corrected Total | 31 | 11.62 | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juli-Gándara, L.; Vega-Zamanillo, Á.; Calzada-Pérez, M.Á.; Teijón-López-Zuazo, E. Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Modulus and Fatigue Life of Bituminous Mixtures. Materials 2020, 13, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13092126
Juli-Gándara L, Vega-Zamanillo Á, Calzada-Pérez MÁ, Teijón-López-Zuazo E. Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Modulus and Fatigue Life of Bituminous Mixtures. Materials. 2020; 13(9):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13092126
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuli-Gándara, Luis, Ángel Vega-Zamanillo, Miguel Ángel Calzada-Pérez, and Evelio Teijón-López-Zuazo. 2020. "Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Modulus and Fatigue Life of Bituminous Mixtures" Materials 13, no. 9: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13092126
APA StyleJuli-Gándara, L., Vega-Zamanillo, Á., Calzada-Pérez, M. Á., & Teijón-López-Zuazo, E. (2020). Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Modulus and Fatigue Life of Bituminous Mixtures. Materials, 13(9), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13092126






