The Structure and Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
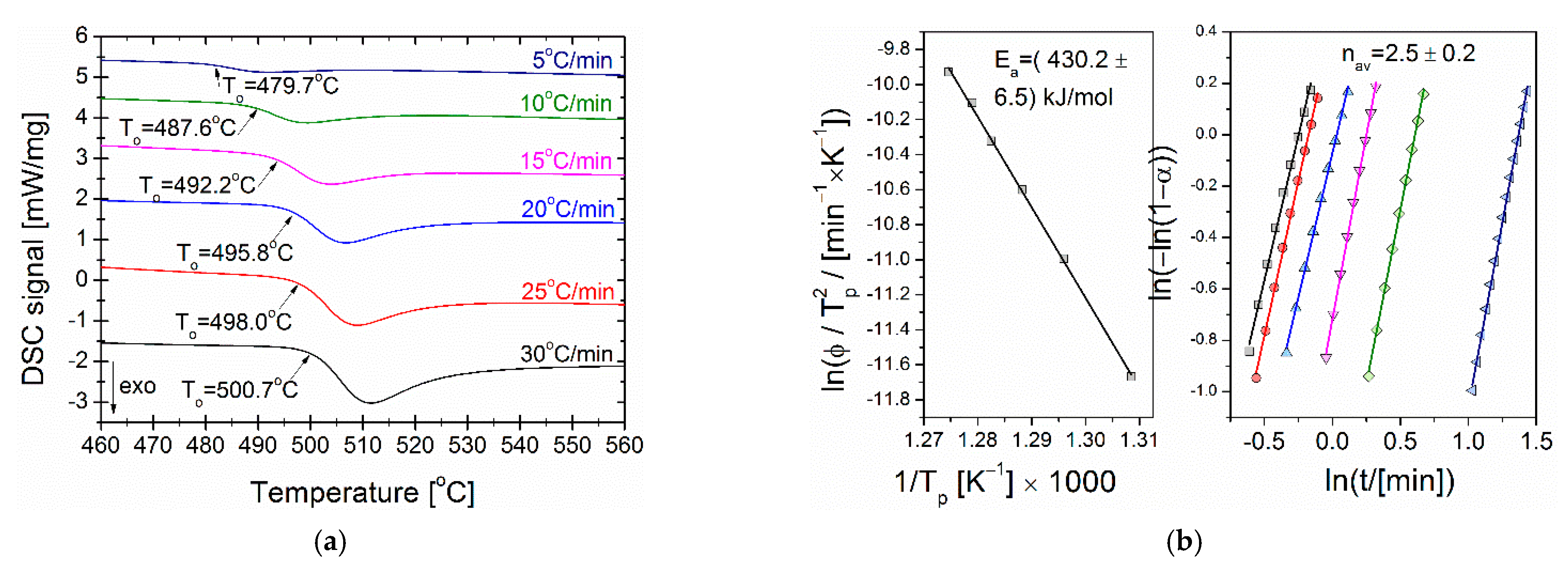
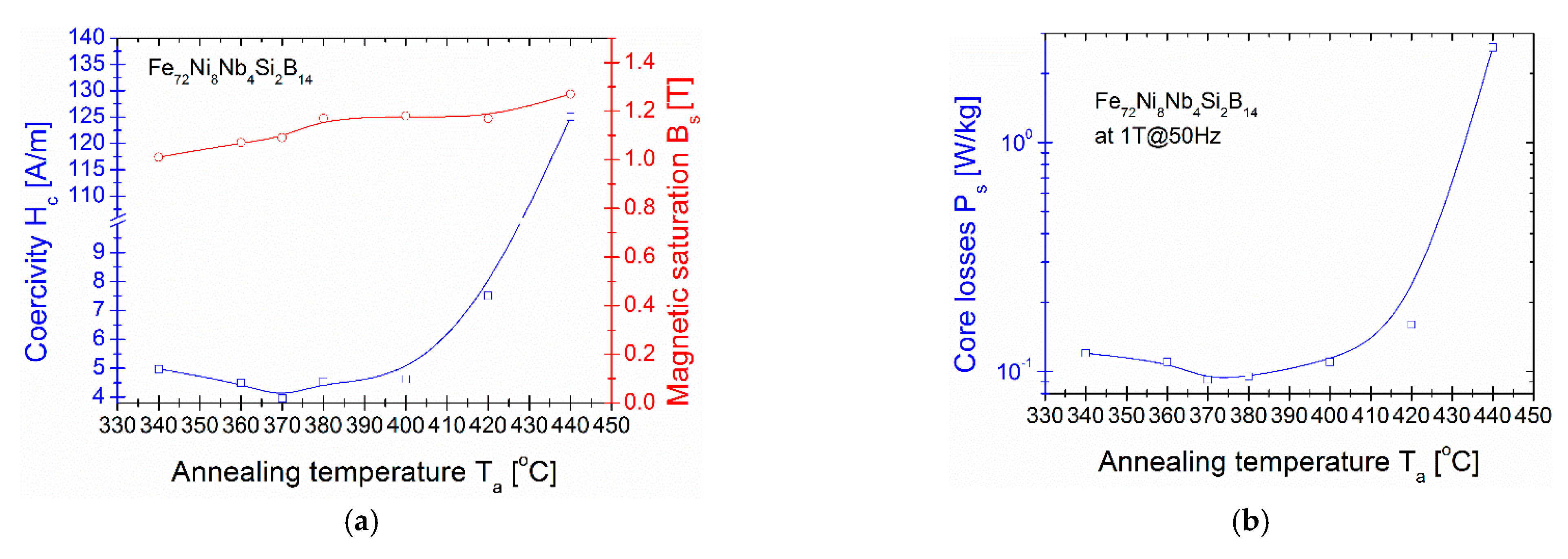
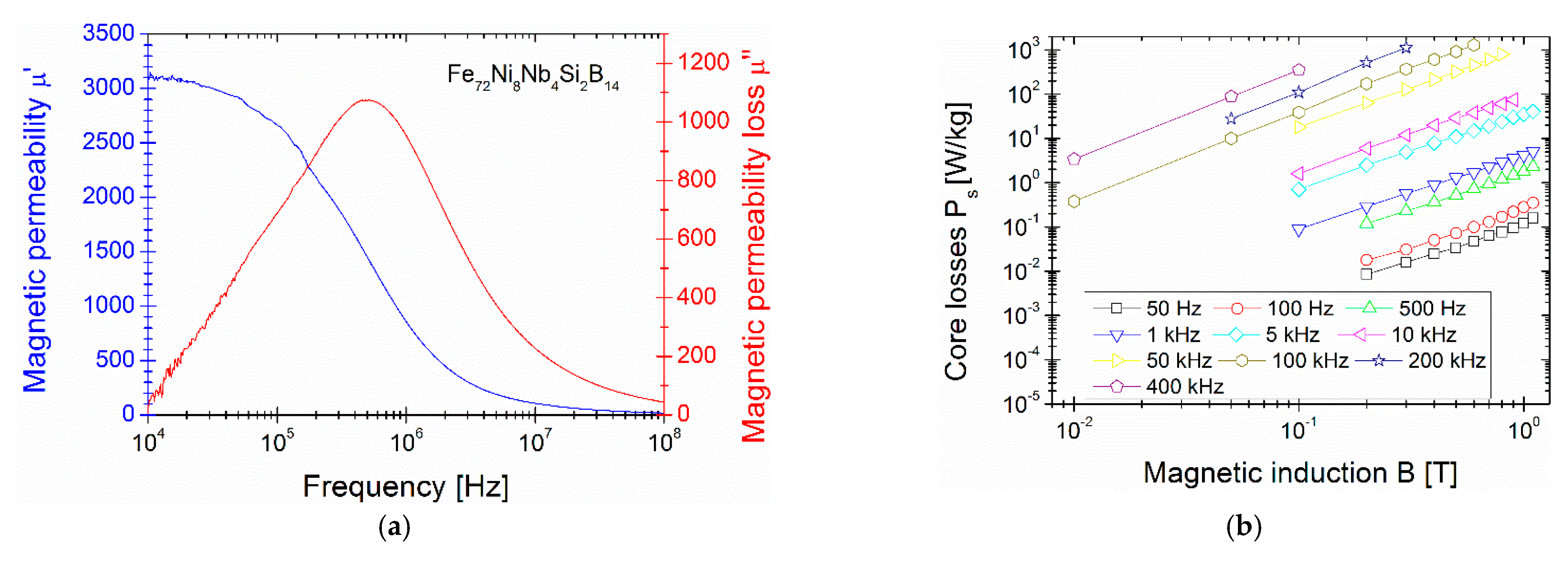
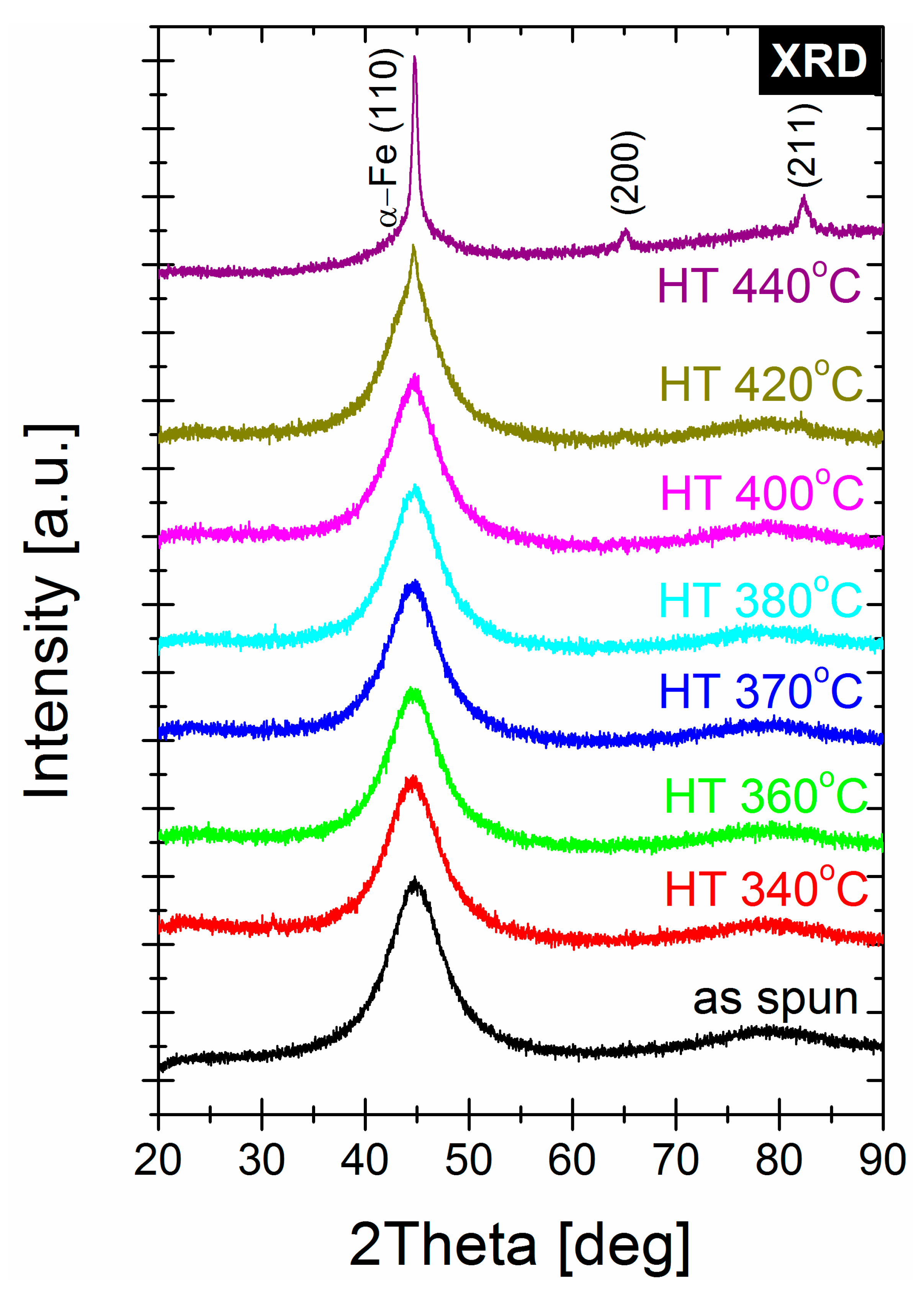
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simizu, S.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; McHenry, M.E. Metal amorphous nanocomposite soft magnetic material-enabled high power density, rare earth free rotational machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, A.M.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; McHenry, M.E. Soft magnetic materials in high-frequency, high-power conversion applications. JOM 2012, 64, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaleyrat, F.; Varga, L.K. Ferromagnetic nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 215, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, M.A. Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Alloys: Two Decades of Progress. Handb. Magn. Mater. 2013 21, 173–342.
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Shcherbinin, S.V.; Volchkov, S.O.; Bhagat, S.M.; Calle, E.; Pérez, R.; Vazquez, M. Soft magnetic materials for sensor applications in the high frequency range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W. Soft magnetic Co-based Co–Fe–B–Si–P bulk metallic glasses with high saturation magnetic flux density of over 1.2 T. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 843, 154862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warski, T.; Wlodarczyk, P.; Polak, M.; Zackiewicz, P.; Radon, A.; Wojcik, A.; Szlezynger, M.; Kolano-Burian, A.; Hawelek, L. Influence of Cu Content on Structure and Magnetic Properties in Fe86-xCuxB14 Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhukova, V.; Korchuganova, O.A.; Aleev, A.A.; Tcherdyntsev, V.V.; Churyukanova, M.; Medvedeva, E.V.; Seils, S.; Wagner, J.; Ipatov, M.; Blanco, J.M.; et al. Effect of annealing on magnetic properties and structure of Fe-Ni based magnetic microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 433, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagasti, A.; Palomares, V.; Porro, J.M.; Orue, I.; Sanchez-Ilarduya, M.B.; Lopes, A.C.; Gutierrez, J. Magnetic, Magnetoelastic and Corrosion Resistant Properties of (Fe–Ni)-Based Metallic Glasses for Structural Health Monitoring Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, J.; Guillaume, B. Review of critical material studies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Inoue, A.; Chang, C. Superhigh strength and good soft-magnetic properties of (Fe, Co)–B–Si–Nb bulk glassy alloys with high glass-forming ability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4911–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiya, K.; Urata, A.; Nishiyama, N.; Inoue, A. Thermal stability and magnetic properties of (Fe, Co)–Ga–(P, C, B, Si) bulk glassy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronhime, N.; Zoghlin, E.; Keylin, V.; Jin, X.; Ohodnicki, P.; McHenry, M.E. Magnetic properties and crystallization kinetics of (Fe100− xNix) 80Nb4Si2B14 metal amorphous nanocomposites. Scr. Mater. 2018, 142, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronhime, N.; DeGeorge, V.; Keylin, V.; Ohodnicki, P.; McHenry, M.E. The effects of strain-annealing on tuning permeability and lowering losses in Fe-Ni-based metal amorphous nanocomposites. JOM 2017, 69, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Cadogan, J.M.; Aoki, K.; Tsai, A.P.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Nanocrystallization and glass transition in Cu-Free Fe-Nb-B soft magnetic alloys. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, A.; Zhao, C.; Yue, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.T. Compositional design and crystallization mechanism of High Bs nanocrystalline alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 112, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Málek, J. The applicability of Johnson-Mehl-Avrami model in the thermal analysis of the crystallization kinetics of glasses. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 267, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, J.L. Gyromagnetic resonance in ferrites. Nature 1947, 160, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanov, K.N.; Koledintseva, M.Y. Application of generalized Snoek’s law over a finite frequency range: A case study. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 073901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Parsons, R.; Zang, B.; Kishimoto, H.; Shoji, T.; Kato, A.; Suzuki, K. Dramatic grain refinement and magnetic softening induced by Ni addition in FeB based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 181, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.A.; Oguma, S.; Yamauchi, K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6044–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Matusita, K.; Yokota, R. Volume changes during the structural relaxation and crystallization in FeNi based metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 1985, 69, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, N.; Wakeda, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Ogata, S. Prediction of pressure-promoted thermal rejuvenation in metallic glasses. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, C.; Rätzke, K.; Schmidtke, E.; Faupel, F.; Ulfert, W. Positron-annihilation studies of free-volume changes in the bulk metallic glass Zr65Al7.5Ni10Cu17.5 during structural relaxation and at the glass transition. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.M.; Bhandari, D.; Saxena, N.S. Enthalpy recovery during structural relaxation of Se96In4 chalcogenide glass. Phys B Condens. Matter 2001, 293, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipenyuk, A.; Eckert, J. Correlation between enthalpy change and free volume reduction during structural relaxation of Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseda, Y.; Masumoto, T. Structure of amorphous Fe80-P13-C7 alloy by X-ray diffraction. Z. Für. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1975, 22, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Hisatake, K.; Takahashi, M. Magnetic Relaxation in Amorphous (Fe1-xNix)77Si10B13 Alloys. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 22, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, M.A.; Yavari, A.R.; Barrue, R.; Perron, J.C. On the optimization of soft-magnetic properties of metallic glasses by dynamic current annealing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1992, 28, 1911–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ri, M.C.; Sohrabi, S.; Ding, D.W.; Dong, B.S.; Zhou, S.X.; Wang, W.H. Serrated magnetic properties in metallic glass by thermal cycle. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 066101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.E.; Laughlin, D.E. Physical Metallurgy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1881–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hono, K.; Ping, D.H.; Ohnuma, M.; Onodera, H. Cu clustering and Si partitioning in the early crystallization stage of an Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1 amorphous alloy. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, K.G.; Herzer, G.; Choi, P.; Raabe, D. Atom probe tomography study of ultrahigh nanocrystallization rates in FeSiNbBCu soft magnetic amorphous alloys on rapid annealing. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Satalkar, M.; Kane, S.N.; Ghodke, N.L.; Sinha, A.K.; Varga, L.K.; Araujo, J.P. Thermal treatment induced modification of structural, surface and bulk magnetic properties of Fe61. 5Co5Ni8Si13. 5B9Nb3 metallic glass. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1953, 120043. [Google Scholar]
- McCord, J. Progress in magnetic domain observation by advanced magneto-optical microscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 333001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
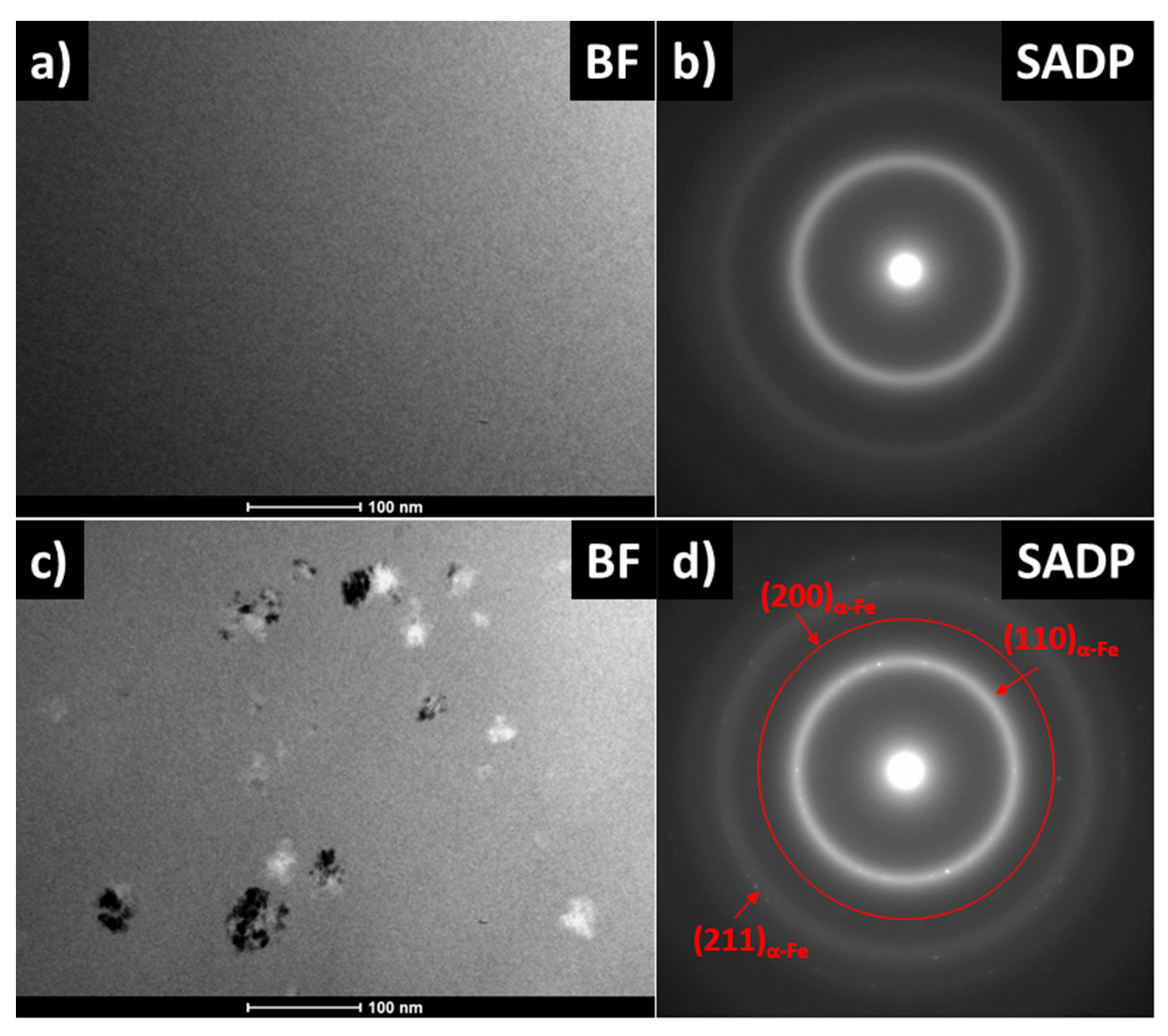

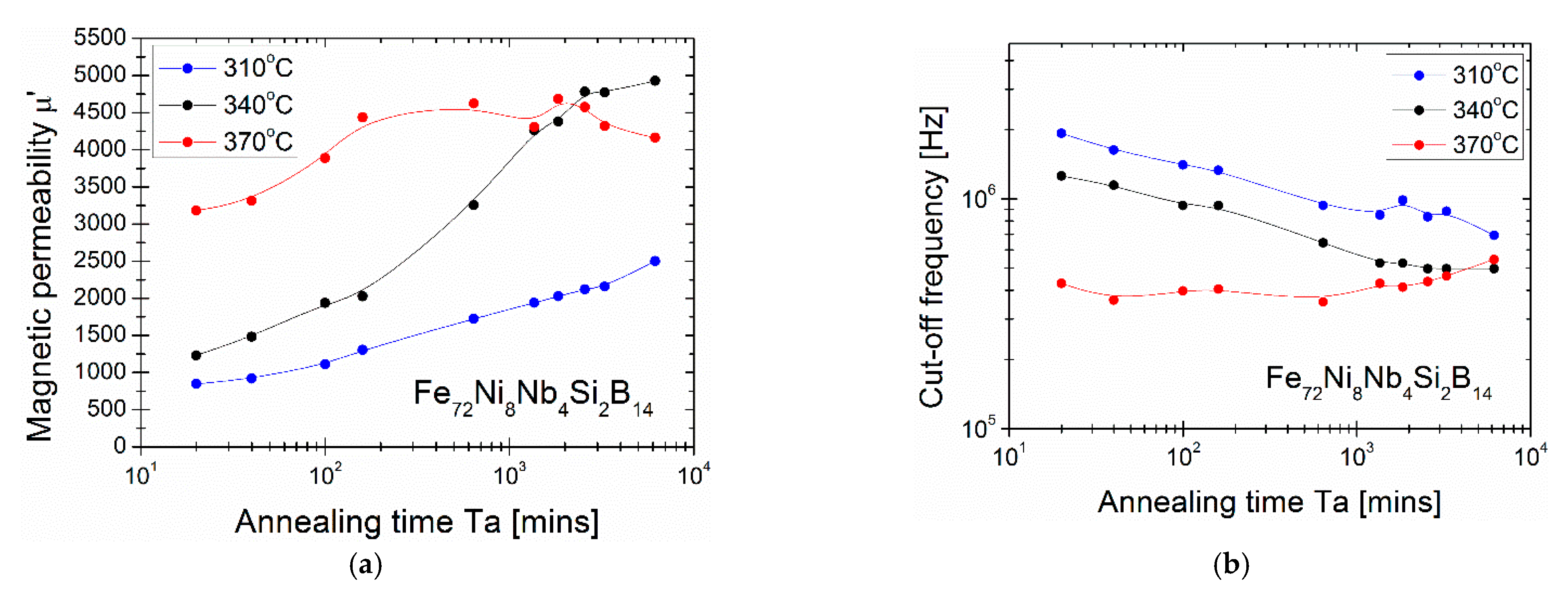
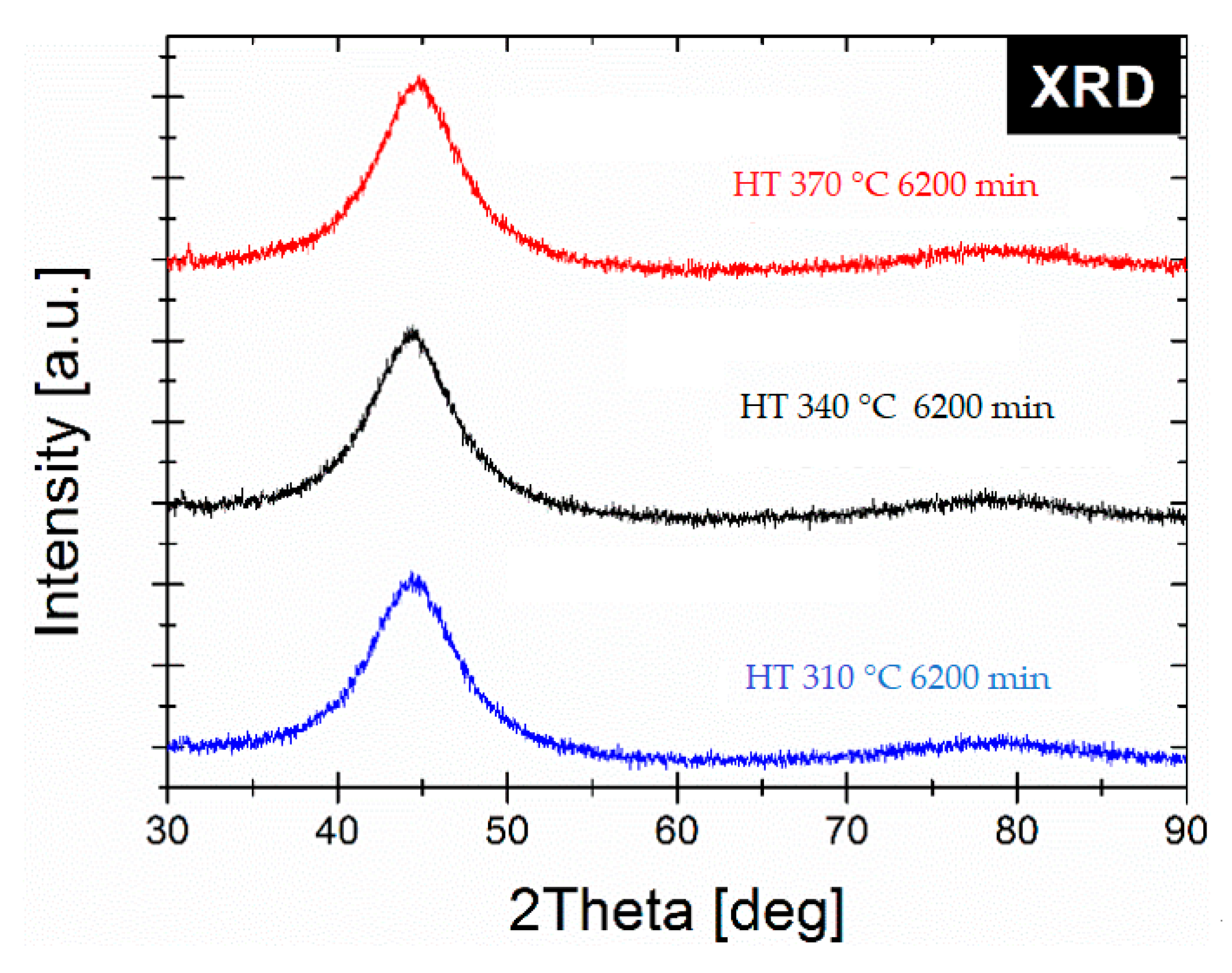
| Alloy | Ta [°C]/time | Ps [W/kg] | Bs [T] | Hc [A/m] | µ’ | fcut-off [kHz] | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 | 370/20 min | P10/50 = 0.092 | 1.09 | 3.95 | 3100 | 507 | This work |
| Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 | 440/20 min | P10/50 = 2.6 | 1.29 | 125 | - | - | This work |
| Fe70Ni10Nb4Si2B14 | as-cast | - | ~1.62 | - | - | - | [13] |
| Fe60Ni20Nb4Si2B14 | as-cast | - | ~1.44 | - | - | - | [13] |
| Fe56Ni24Nb4Si2B14 | 440/60 min | P1060 = 0.12 | ~1.1 | 7 | 4000 | - | [14] |
| Fe56Ni24Nb4Si2B14 | 440/60 min 200 MPa | - | 1.3 | - | 16,000 | - | [14] |
| Fe77.4Ni8.6B14 | RA* 490/0.5s | - | 1.7 | 2.6 | - | - | [21] |
| Fe68.8Ni17.2B14 | RA* 510/0.5s | - | 1.54 | 4.4 | - | - | [21] |
| Fe60.2Ni25.8B14 | RA* 510/0.5s | - | 1.37 | 3.2 | - | - | [21] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hawelek, L.; Warski, T.; Wlodarczyk, P.; Polak, M.; Zackiewicz, P.; Maziarz, W.; Wojcik, A.; Steczkowska-Kempka, M.; Kolano-Burian, A. The Structure and Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010005
Hawelek L, Warski T, Wlodarczyk P, Polak M, Zackiewicz P, Maziarz W, Wojcik A, Steczkowska-Kempka M, Kolano-Burian A. The Structure and Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 Alloy. Materials. 2021; 14(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleHawelek, Lukasz, Tymon Warski, Patryk Wlodarczyk, Marcin Polak, Przemyslaw Zackiewicz, Wojciech Maziarz, Anna Wojcik, Magdalena Steczkowska-Kempka, and Aleksandra Kolano-Burian. 2021. "The Structure and Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 Alloy" Materials 14, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010005
APA StyleHawelek, L., Warski, T., Wlodarczyk, P., Polak, M., Zackiewicz, P., Maziarz, W., Wojcik, A., Steczkowska-Kempka, M., & Kolano-Burian, A. (2021). The Structure and Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched Fe72Ni8Nb4Si2B14 Alloy. Materials, 14(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010005







