Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Creep Property of Cast Fe-Ni-Based Alloys with High-Al Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
3.1. Phase Stability Calculation
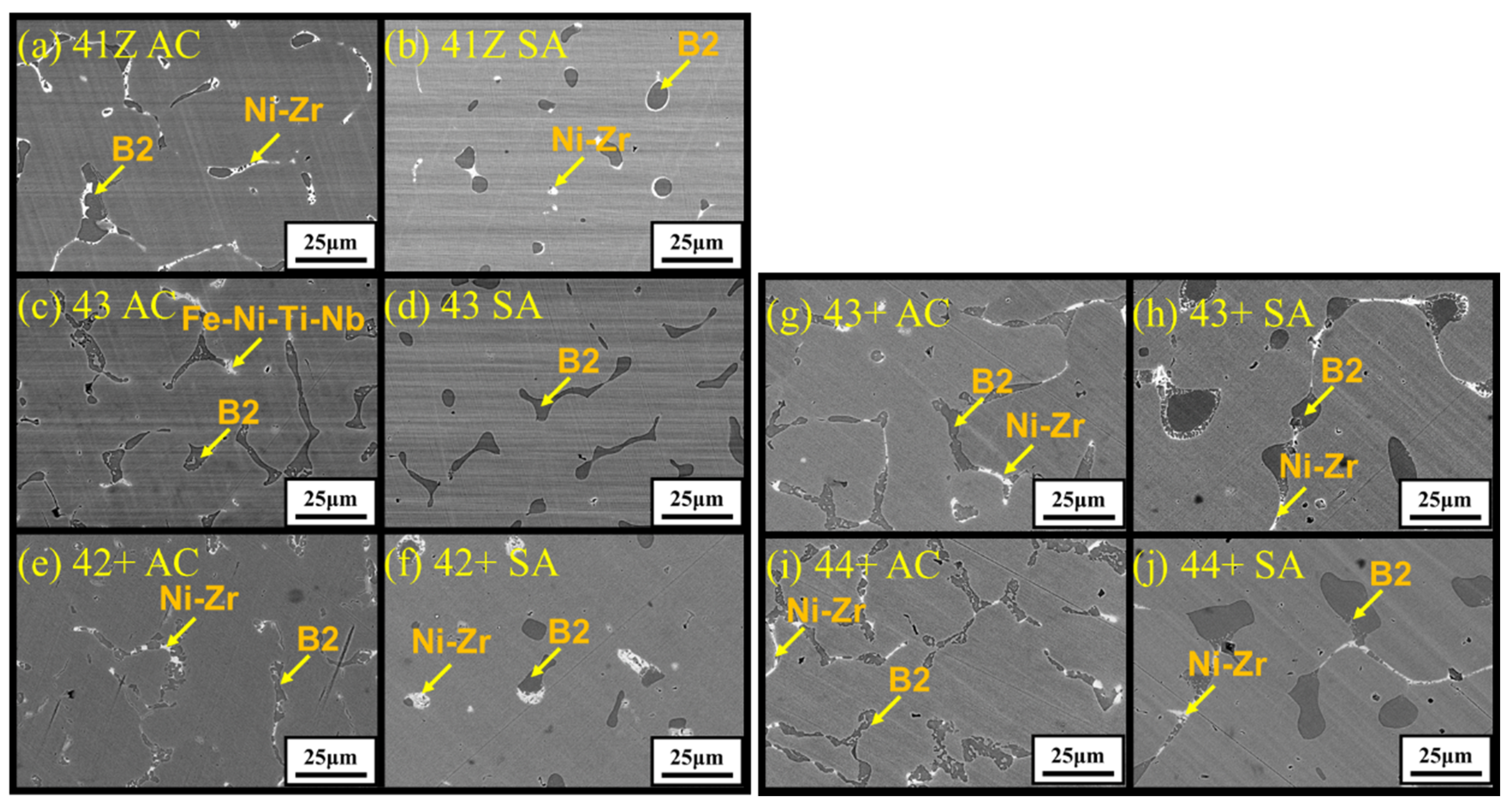
3.2. Microstructure of Cast Alloys
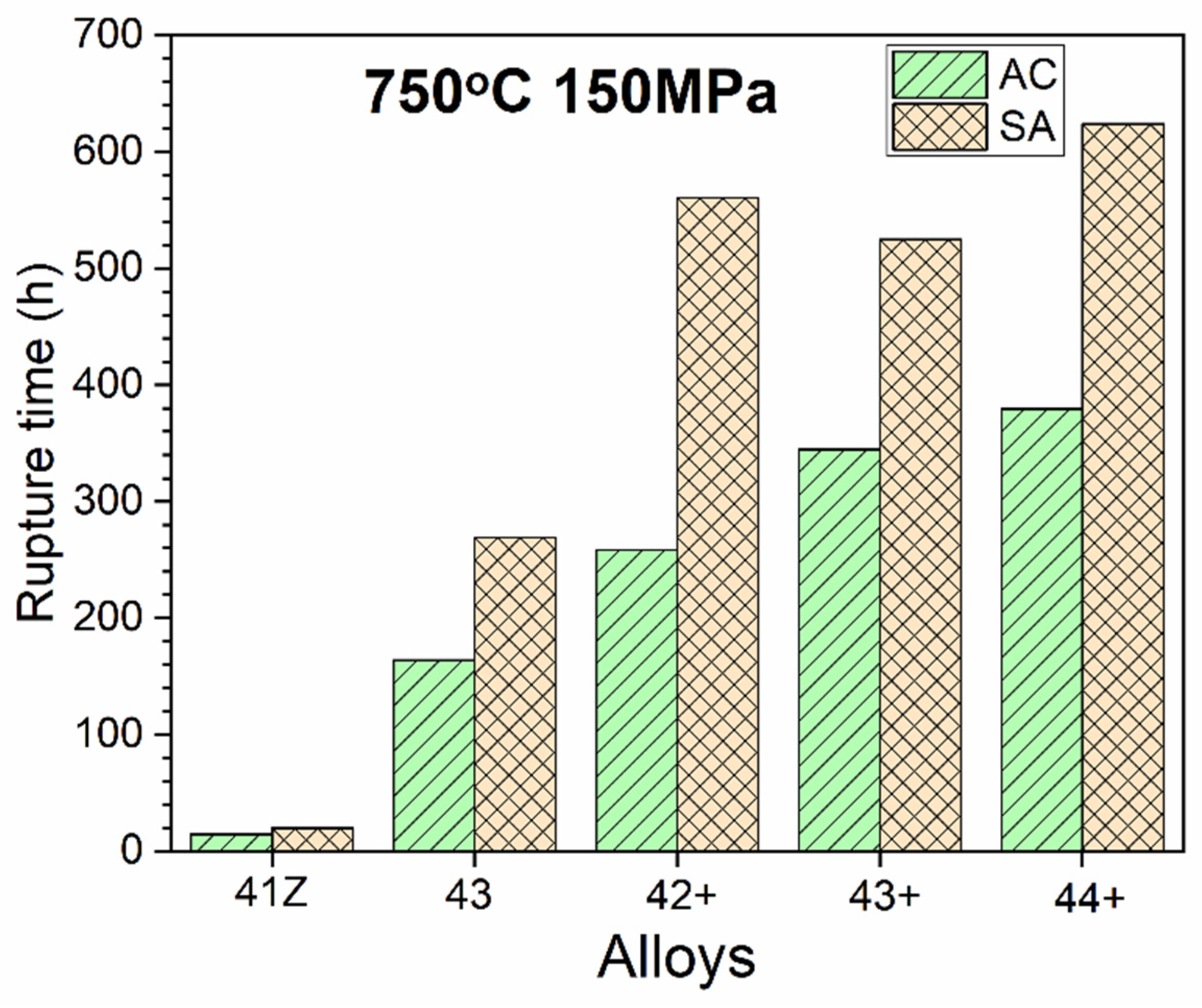
3.3. High-Temperature Mechanical Properties
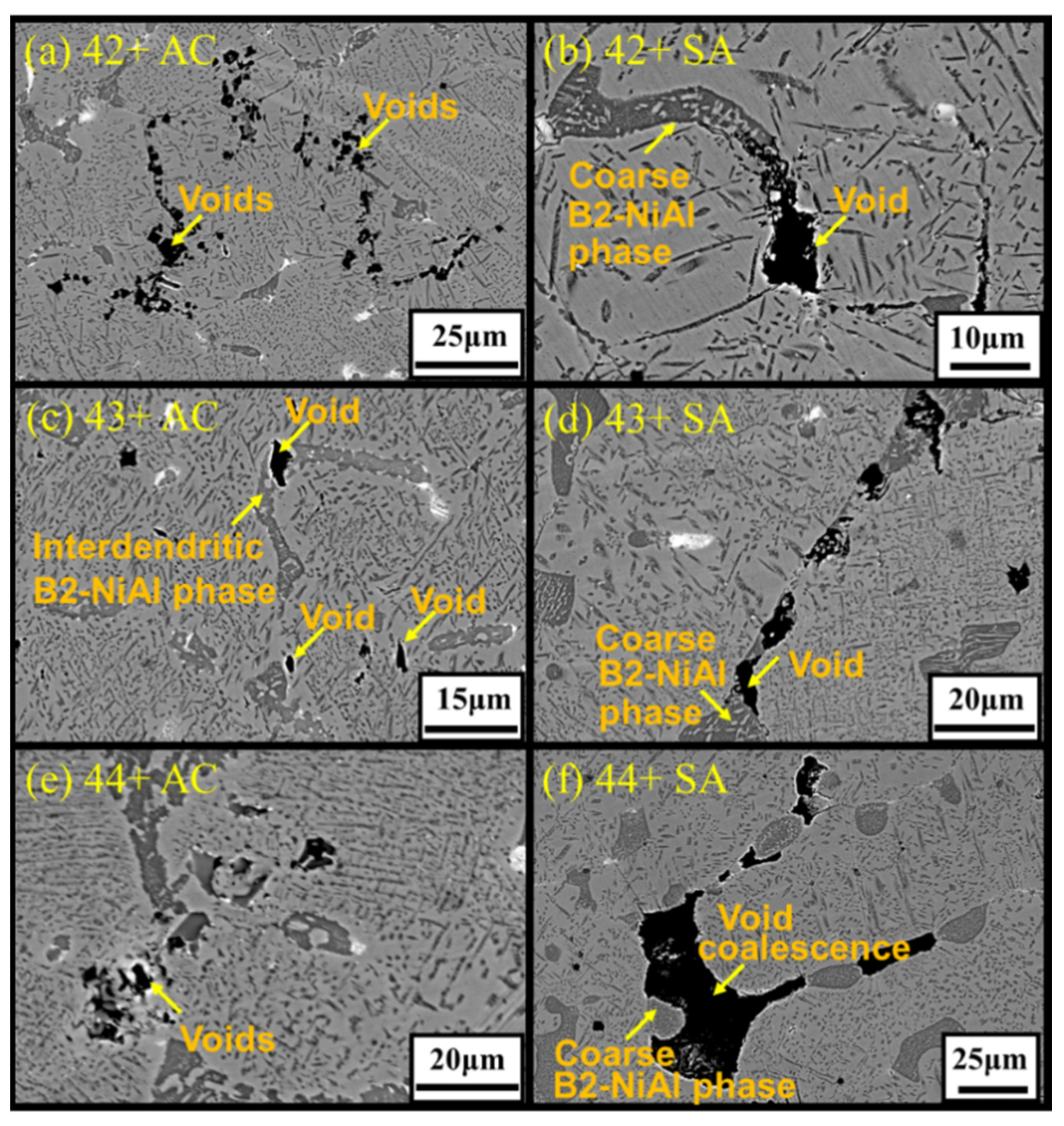
3.4. Microstructure of Crept Alloys
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
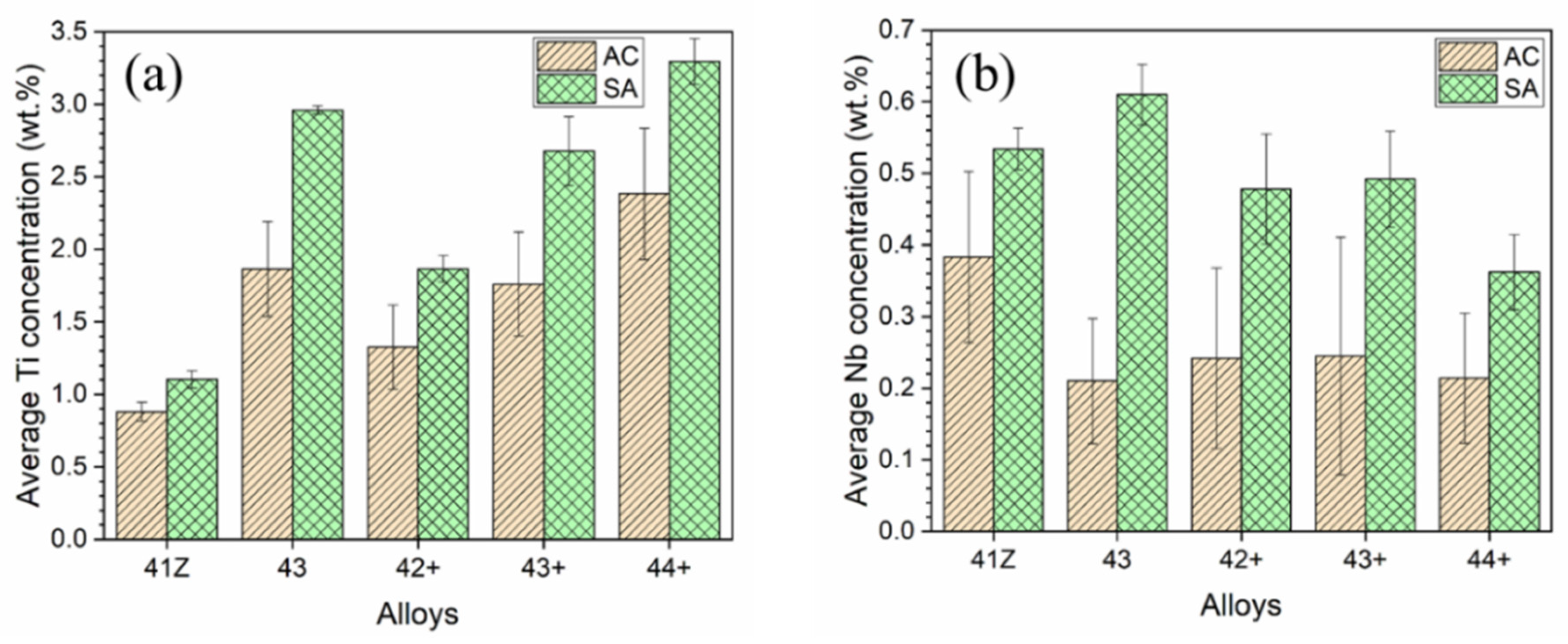
- The as-cast alloys showed dendritic microstructure with B2-NiAl and Ni-Zr rich interdendritic phases. Solution annealing at 1200 °C partially dissolved the interdendritic phases while some coarse B2-NiAl and Ni-Zr rich phases existing. The fraction and size of the coarse B2-NiAl phases after solution annealing increased with Ti content. Solution annealing also increased the Ti and Nb content in the austenite matrix.
- The 35Ni–(2~4)Ti alloys showed much increased creep rupture life compared to 30Ni–1Ti alloy, attributed to the increase in γ’-Ni3(Al,Ti) precipitates from higher Ni and Ti content. Among the 35Ni–(2~4)Ti alloys, increasing Ti content from 2 to 4 wt% gradually increased the creep rupture life in the as-cast condition.
- The model alloys consisted of nano-sized, spherical-shaped, and coherent γ’-Ni3(Al,Ti) precipitates that enhanced the creep rupture life. Extensive precipitation of needle-like B2-NiAl phases was observed but inadequate for improving the creep rupture life at 750 °C. Fine Laves phase and σ-phase were present adjacent to the needle-like B2-NiAl phases. The Laves phase was dispersed regularly in solution annealed condition while it was limitedly observed in the as-cast condition.
- Solution annealing improved the creep rupture life of the alloys compared to as-cast condition, attributed to the increased Ti and Nb content in austenite matrix. Nevertheless, no direct correlation between Ti content and creep rupture life could be obtained for 35Ni–(2~4)Ti alloys in the solution annealed condition. For high-Ti alloys, the increase in fraction and size of coarse B2-NiAl phases after solution annealing resulted in considerable increase of creep void formation and their coalescences during creep test, and the beneficial effect of higher Ti content was not fully achieved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Gianfrancesco, A. The fossil fuel power plants technology. In Materials for Ultra-Supercritical and Advanced Ultra-Supercritical Power Plants; Di Gianfrancesco, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Parma, E.J.; Wright, S.A.; Vernon, M.E.; Fleming, D.D.; Rochau, G.E.; Suo-Anttila, A.J.; Rashdan, A.A.; Tsvetkov, P.V. Supercritical CO2 Direct Cycle Gas Fast Reactor (SC-GFR) Concept; Sandia National Laboratory Report, SAND2011-2525; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.; Bae, S.J.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.K.; Baik, S.; Lee, J.I.; Cha, J.E. Review of supercritical CO2 power cycle technology and current status of research and development. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2015, 47, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holcomb, G.R. High Pressure Steam Oxidation of Alloys for Advanced Ultra-Supercritical Conditions. Oxid. Met. 2014, 82, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Anderson, M.; Taylor, D.; Allen, T.R. Corrosion of austenitic and ferritic-martensitic steels exposed to supercritical carbon dioxide. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, C. Corrosion and carburization behavior of chromia-forming heat resistant alloys in a high-temperature supercritical-carbon dioxide environment. Corros. Sci. 2015, 99, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Cha, J.H.; Jang, C. Corrosion and creep behavior of a Ni-base alloy in supercritical-carbon dioxide environment at 650 °C. Corros. Sci. 2020, 174, 108843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Brady, M.P.; Lu, Z.P.; Maziasz, P.J.; Liu, C.T.; Pint, B.A.; More, K.L.; Meyer, H.M.; Payzant, E.A. Creep-Resistant, Al2O3-Forming Austenitic Stainless Steels. Science 2007, 316, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Brady, M.P.; Santella, M.L.; Bei, H.; Maziasz, P.J.; Pint, B.A. Overview of Strategies for High-Temperature Creep and Oxidation Resistance of Alumina-Forming Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Lu, Z. Improvement of high-temperature oxidation resistance and strength in alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3285–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Muralidharan, G.; Brady, M.P. Development of L12-ordered Ni3(Al,Ti)-strengthened alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel alloys. Scripta Mater. 2013, 69, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M.P.; Magee, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Helmick, D.; Wang, L. Co-optimization of wrought alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel composition ranges for high-temperature creep and oxidation/corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 590, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, G.; Rayner, G.; Baker, I.; Munroe, P.R. Accelerated precipitation in the AFA stainless steel Fe–20Cr–30Ni–2Nb–5Al via cold working. Intermetallics 2014, 53, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Dong, X.; Sun, F.; Zhang, L. Formation of L12-ordered precipitation in an alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel via Cu addition and its contribution to creep/rupture resistance. Scripta Mater. 2015, 109, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.Q.; Zhao, W.X.; Mao, H.H.; Hu, Y.X.; Xu, X.Q.; Sun, X.Y.; Lu, Z.P. Precipitate characteristics and their effects on the high-temperature creep resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 622, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Kang, J.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, C. Improved creep strength of alumina-forming austenitic heat-resistant steels through W addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 696, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, B.B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G.Q.; Tang, R.; Zhang, R.Q.; Dong, C.; Liaw, P.K. Effects of Nb/Ti/V/Ta on phase precipitation and oxidation resistance at 1073 K in alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, I.; Afonina, N.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M. Preliminary creep testing of the alumina-forming austenitic stainless steel Fe-20Cr-30Ni-2Nb-5Al. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 718, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hao, A.; Qu, F.; Lin, X.; Li, H. The effect of isothermal aging on creep behavior of modified 2.5Al alumina-forming austenitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 797, 140219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.F.; Roman, P.; Leng, B.; Sridharan, K.; Anderson, M.; Allen, T.R. Corrosion behavior of an alumina forming austenitic steel exposed to supercritical carbon dioxide. Corros. Sci. 2014, 82, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M.P.; Yamamoto, Y.; Santella, M.L.; Pint, B.A. Effects of minor alloy additions and oxidation temperature on protective alumina scale formation in creep-resistant austenitic stainless steels. Scripta Mater. 2007, 57, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreen, S.; Davidson, J.M. The effects of B and Zr on the creep and fatigue crack growth behavior of a Ni-base superalloy. Metall. Trans. A 1983, 14, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, G.; Yamamoto, Y.; Brady, M.P.; Walker, L.R.; Meyer, H.M., III; Leonard, D.N. Development of cast alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels. JOM 2016, 68, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, F.; Shoji, T. Development of heat-resistant Fe-based alloys for A-USC steam boiler using ultra-high purity (UHP) technology. Corr. Sci. 2018, 144, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yang, Y.; Tan, L. Phase Stability in the Fe-Rich Fe-Cr-Ni-Zr Alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 5009–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jang, H.; Obulan Subramanian, G.; Kim, C.; Jang, C. Development of alumina-forming duplex stainless steels as accident-tolerant fuel cladding materials for light water reactors. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 507, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Alloys | Fe | Ni | Cr | Al | Ti | Nb | Si | Zr | C | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41Z | Bal. | 30 | 18 | 4.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.025 | - |
| 43 | Bal. | 35 | 18 | 4.5 | 3 | 1 | - | - | 0.025 | - |
| 42+ | Bal. | 35 | 16 | 4.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 0.015 |
| 43+ | Bal. | 35 | 16 | 4.5 | 3 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 0.015 |
| 44+ | Bal. | 35 | 16 | 4.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 0.015 |
| Alloy | Phase | Fe | Ni | Cr | Al | Ti | Nb | Si | Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43+ AC | B2-NiAl phase | 13.2 | 42.4 | 4.6 | 23.4 | 12.9 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 1.3 |
| Ni-Zr phase | 15.2 | 42.3 | 5.2 | 8.0 | 2.7 | 3.2 | 11.7 | 11.7 | |
| 43+ SA | B2-NiAl phase | 22.3 | 39.8 | 8.1 | 21.9 | 6.9 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| Ni-Zr phase | 18.5 | 49.5 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.0 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 11.3 |
| Alloy | 700 °C Tensile Test | 750 °C Tensile Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength, MPa | Tensile Strength, MPa | Elongation, % | Yield Strength, MPa | Tensile Strength, MPa | Elongation, % | |
| 41Z | 331.1 | 493.5 | 41.8 | 309.6 | 385.2 | 30.3 |
| 43 | 514.7 | 593.2 | 11.0 | 503.3 | 553.7 | 18.7 |
| 42+ | 509.9 | 614.7 | 33.1 | 479.1 | 511.8 | 42.1 |
| 43+ | 612.3 | 711.9 | 17.3 | 492.6 | 553.5 | 35.9 |
| 44+ | 665.6 | 737.4 | 17.3 | 521.7 | 551.9 | 43.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subramanian, G.O.; Jang, C.; Shin, J.H.; Jeong, C. Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Creep Property of Cast Fe-Ni-Based Alloys with High-Al Content. Materials 2021, 14, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010082
Subramanian GO, Jang C, Shin JH, Jeong C. Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Creep Property of Cast Fe-Ni-Based Alloys with High-Al Content. Materials. 2021; 14(1):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010082
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubramanian, Gokul Obulan, Changheui Jang, Ji Ho Shin, and Chaewon Jeong. 2021. "Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Creep Property of Cast Fe-Ni-Based Alloys with High-Al Content" Materials 14, no. 1: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010082
APA StyleSubramanian, G. O., Jang, C., Shin, J. H., & Jeong, C. (2021). Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Creep Property of Cast Fe-Ni-Based Alloys with High-Al Content. Materials, 14(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010082





