Impact of Ball Burnished Regular Reliefs on Fatigue Life of AISI 304 and 316L Austenitic Stainless Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
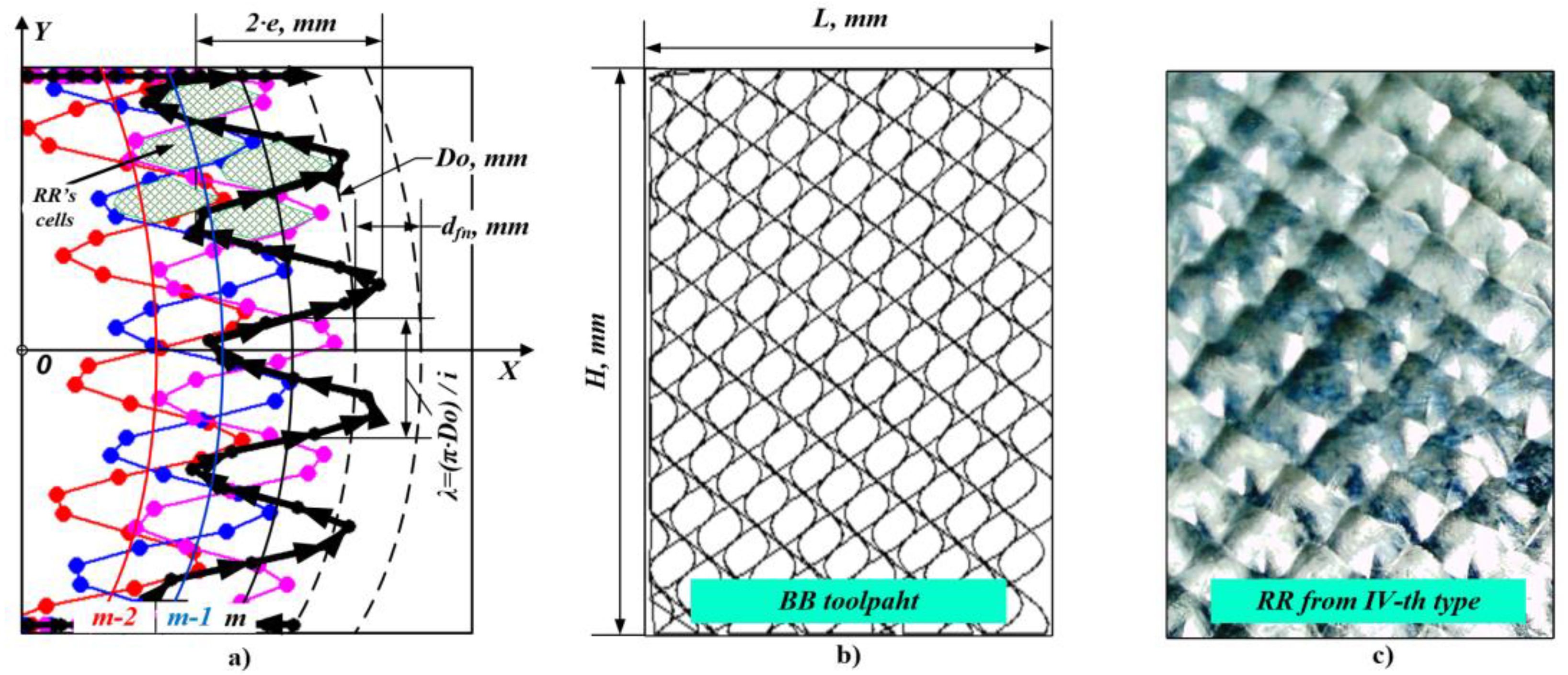
2.2. Obtaining RR of the IV-th Type by BB Process, Implemented on CNC Milling Machine
2.2.1. Calculating the Toolpath Trajectory of the Ball Tool
2.2.2. Preparing the NC Code for the BB Operation
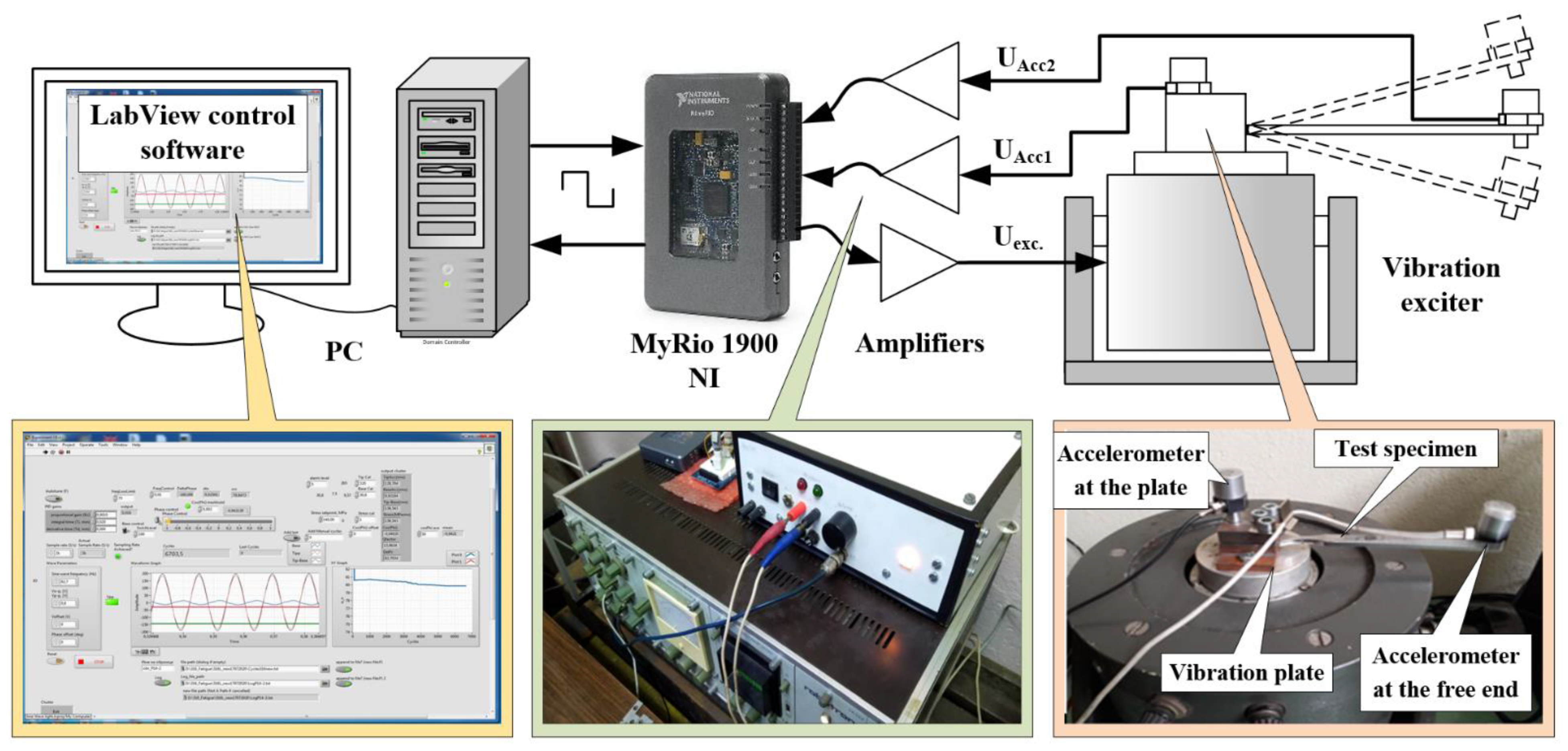
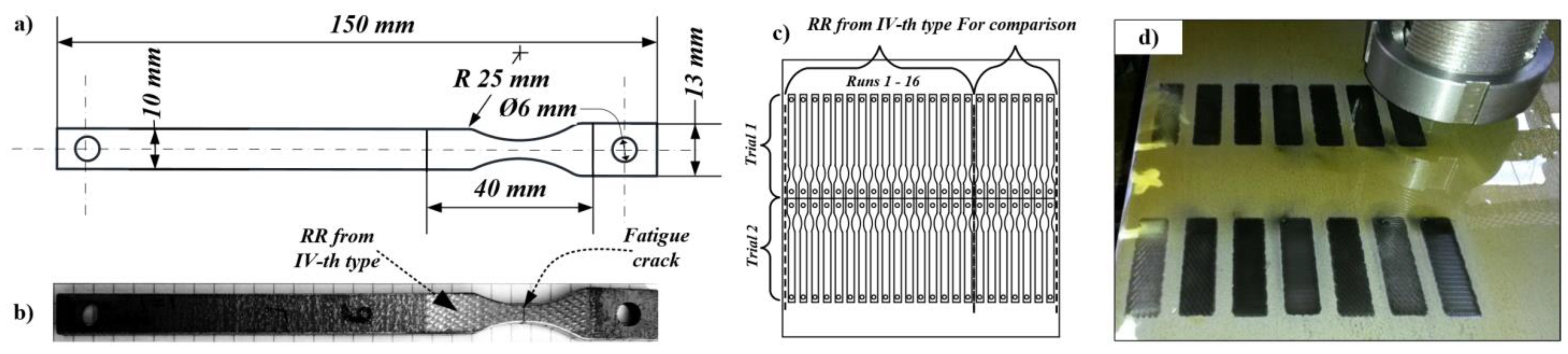
2.3. Fatigue Failure Test Setup
2.3.1. Description of the Experimental Method and Setup
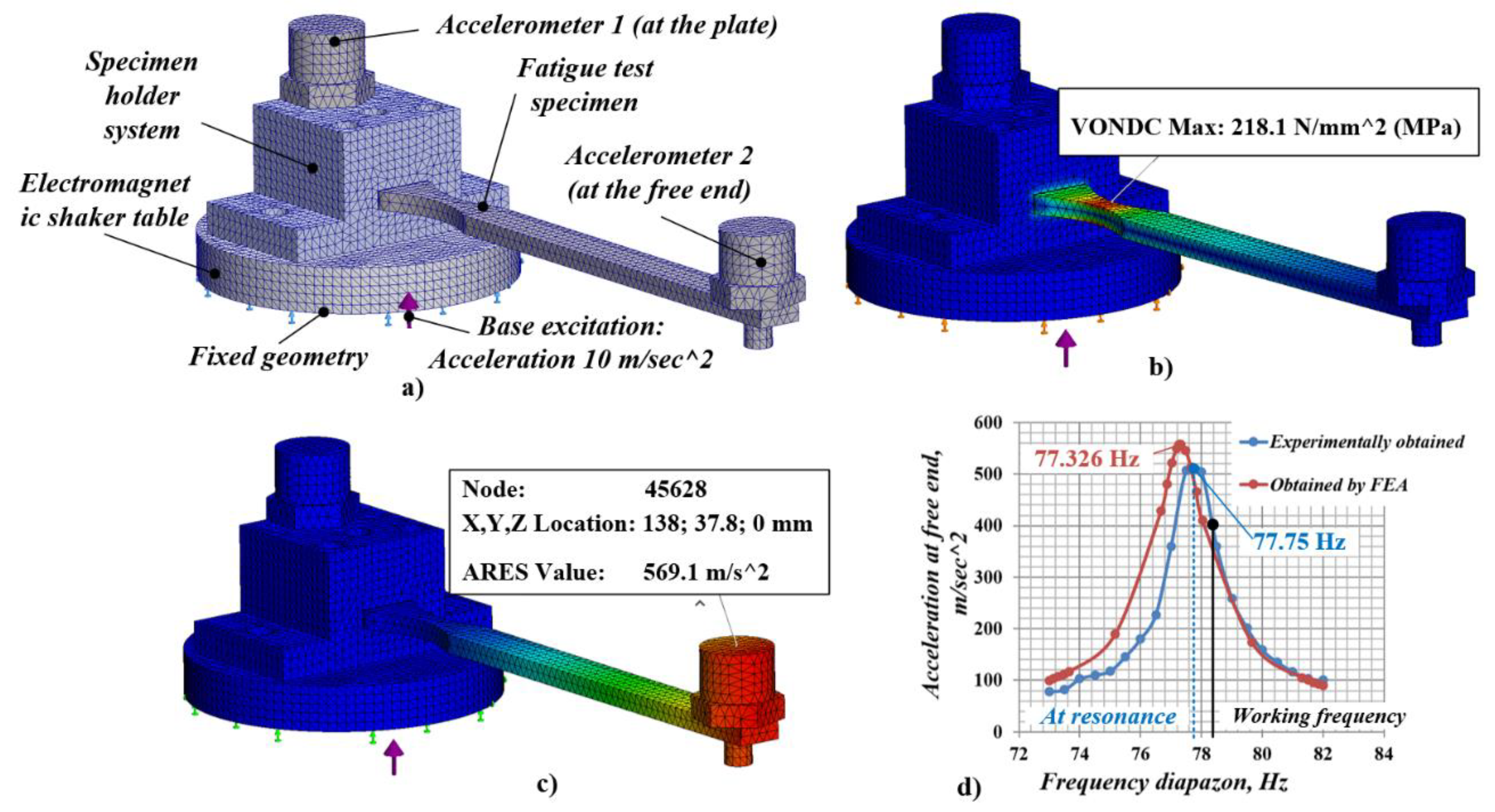
2.3.2. Determining Experimental Conditions of the Fatigue Failure Test Using FE Analysis
3. Experimental Research
4. Results
4.1. Preprocessing Data
4.2. Effects and T-Test
4.3. Regression Model
4.3.1. Ordinary Least Square Regression (OLS).
4.3.2. Robust Regression
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griza, S.; Kwietniewski, C.; Tarnowski, G.; Bertoni, F.; Reboh, Y.; Strohaecker, T.R.; Baumvol, I.J.R. Fatigue failure analysis of a specific total hip prosthesis stem design. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, E.; Ölander, A.; Oberg, M. Fatigue of gears in the finite life regime—Experiments and probabilistic modelling. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 62, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.T.; Surhone, M. (Eds.) Safe-Life Design; Betascript Publishing: Beau Bassin, Mauritius, 2010; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, R. Fatigue Design Criteria. Encycl. Mat.: Sci. Technol. 2001, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, T.V.; Byrne, J. Factors Affecting Fatigue Behaviour. In Fatigue as a Design Criterion; Palgrave: London, UK, 1977; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Swirad, S. The effect of burnishing parameters on steel fatigue strength, Nonconventional Technologies Review. Nonconv. Technol. Rev. 2007, 1, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, L.; Ludian, T.; Wollmann, M. Ball-Burnishing and Roller-Burnishing to Improve Fatigue Performance of Structural Alloys. In Proceedings of the Engineering against Fracture; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Prevéy, P.S.; Cammett, J.T. The influence of surface enhancement by low plasticity burnishing on the corrosion fatigue perfor-mance of AA7075-T6. Int. J. Fatigue 2004, 26, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintcov, L.G. Complex and combined approaches for strengthening work pieces as a way for development the ball burnishing methodologies. In Proceedings of the All Soviet Union Scientific and Technical Conference “New Technologies, Processes and Equipment for Ball Burnishing of the Materials”, Briansk, Russia, 21–23 October 1986. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Jerez-Mesa, R.; Fargas, G.; Roa, J.J.; Llumà, J.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A. Superficial Effects of Ball Burnishing on TRIP Steel AISI 301LN Sheets. Metals 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, T.J.; Sines, G.; Waisman, J.L. (Eds.) Metal Fatigue; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Nagîţ, G.; Slătineanu, L.; Dodun, O.; Rîpanu, M.I.; Mihalache, A.M. Surface layer microhardness and roughness after applying a vibroburnishing process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4333–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Q. The effect of burnishing parameters on burnishing force and surface microhardness. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 28, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Z.; Viharos, Z.J.; Kodácsy, J. The effects of machining strategies of magnetic assisted roller burnishing on the resulted surface structure. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 448, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terres, M.A.; Laalai, N.; Sidhom, H. Effect of nitriding and shot-peening on the fatigue behavior of 42CrMo4 steel: Experimental analysis and predictive approach. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadache, H.; Bourebia, M.; Taamallah, O.; Laouar, L. Surface hardening of 36 NiCrMo 6 steel by ball burnishing process. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, M. Modeling and experimental validation of the force–surface roughness relation for smoothing burnishing with a spherical tool. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiou, F.-J.; Huang, S.-J.; Shih, A.J.; Zhu, J.; Yoshino, M. Fine Surface Finish of a Hardened Stainless Steel Using a New Burnishing Tool. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Heine, B.; Engelberg, D.L. Performance Optimization of Cold Rolled Type 316L Stainless Steel by Sand Blasting and Surface Linishing Treatment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, D.; Tajane, R. A review on ball burnishing process. Int. J. Sci. and Res. Publ. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Oдинцов, Л. Упpочнeниe и Отдeлкa Дeтaлeй Повepxноcтным Плacтичecким Дeφоpмиpовaниeм. Cпpaвочник. 1987. Available online: https://bg1lib.org/book/2393123/26298c?regionChanged=&redirect=185274069 (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Dzierwa, A.; Markopoulos, A.P. Influence of Ball-Burnishing Process on Surface Topography Parameters and Tribological Properties of Hardened Steel. Machines 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, F.; Sghaier, S.; Al-Fadhalah, K.J.; Benameur, T. Effect of ball burnishing process on the surface quality and microstructure properties of aisi 1010 steel plates. J. Mat. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gras, G.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A.; A González-Rojas, H.; Nápoles-Alberro, A.; Carrillo, F.J.; Dessein, G. Study of a ball-burnishing vibration-assisted process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 229, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdouni, H.; Bouzaiene, H.; Montagne, A.; Van Gorp, A.; Coorevits, T.; Nasri, M.; Iost, A. Experimental study of a six new ball-burnishing strategies effects on the Al-alloy flat surfaces integrity enhancement. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, F.; Sghaier, S.; Hamdi, H.; Benameur, T. Ductility improvement of aluminum 1050A rolled sheet by a newly de-signed ball burnishing tool device. Int. J. of Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 60, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez-Mesa, R.; Plana-García, V.; Llumà, J.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A. Enhancing Surface Topology of Udimet®720 Superalloy through Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Ball Burnishing. Metals 2020, 10, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Шнeйдep, Ю.Г. Экcплyaтaционныe Cвойcтвa Дeтaлeй c Peгyляpным Микpоpeльeφом. 2001. Available online: https://books.ifmo.ru/file/pdf/147.pdf. (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Slavov, S.D.; Dimitrov, D.M. Modelling the dependence between regular reliefs ridges height and the ball burnishing regime’s parameters for 2024 aluminum alloy processed by using CNC-lathe machine. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1037, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, D.S.; Slavov, S.D. Methodology for determination of force of friction and coefficient of friction for the flat surfaces which have a regular distributed roughness obtained by using a flat vibratory burnishing. In Proceedings of the 1st International Congress MEET/MARIND, Varna, Bulgaria, 7 October 2002; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305754324 (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Iliev, I.V. Research on the influence of the five-axis ball-burnishing process regime parameters on the resulted cells properties from regularly shaped roughness. Annu. J. Tech. Univ. Varna 2019, 3, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, D.S.; Slavov, S.D. Research on tribological characteristics of the planar sliding pairs which have regular shaped roughness obtained by using vibratory ball burnishing process. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference Research and Development in Mechanical Industry, Herceg Novi, Serbia and Montenegro, 19–23 September 2003; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318563346 (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Slavov, S.D. A contemporary approach for obtaining regularly shaped roughness by ball-burnishing process carried out using CNC controlled milling machines. Fiabil. şi Durabilitate 2017, 1, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Slavov, S. An Algorithm for Generating Optimal Toolpaths for CNC Based Ball-Burnishing Process of Planar Surfaces. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyura, V.; Maruschak, P.; Kozbur, H.; Kryvyi, P.; Prentkovskis, O. Determining Optimal Parameters of Grooves of Partially Regular Microrelief Formed on End Faces of Rotary Bodies. Smart Sustain. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 5, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyan, D.S.; Diyan, M.D. Experimental research of the effect of the regular shaped roughness formatted by using new kinematical scheme for surface plastic deformation process on the number of cycles to fatigue failure of stainless steel 304L (CR18NI8). Eвpaзийcкий Cоюз Учeныx (ECУ) 2016, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Carlin, J.B.; Stern, H.S.; Dunson, D.B.; Vehtari, A.; Rubin, D.B. Bayesian Data Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Česnik, M.; Slavič, J.; Boltežar, M. Uninterrupted and accelerated vibrational fatigue testing with simultaneous monitoring of the natural frequency and damping. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 5370–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments. 2012. Available online: http://faculty.business.utsa.edu/manderso/STA4723/readings/Douglas-C.-Montgomery-Design-and-Analysis-of-Experiments-Wiley-2012.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Slavov, S.D.; Dimitrov, D.M. A study for determining the most significant parameters of the ball-burnishing process over some roughness parameters of planar surfaces carried out on CNC milling machine. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 178, 02005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Slavov, S.D.; Iliev, I.V. Design and FEM static analysis of an instrument for surface plastic deformation of non-planar functional surfaces of machine parts. Fiability Durab. 2016, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Haas Automation, Inc. USA, TM-1 Vertical Toolroom Mill Haas CNC Machine. Available online: https://www.haascnc.com/machines/vertical-mills/toolroom-mills/models/tm-1.html. (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Duchesnay, E. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, J. A systematic methodology for design of experiments. In Design of Experiments for Engineers and Scientists, 2nd ed.; Antony, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and statistical modeling with python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28–30 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kruschke, J.K. Bayesian Estimation Supersedes the t Test. PsycEXTRA Dataset 2012, 142, 573–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatier, J.; Wiecki, T.V.; Fonnesbeck, C. Probabilistic programming in Python using PyMC3. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2016, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Simpson, D.; Betancourt, M. The Prior Can Often Only Be Understood in the Context of the Likelihood. Entropy 2017, 19, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Jakulin, A.; Pittau, M.G.; Su, Y.-S. A weakly informative default prior distribution for logistic and other regression models. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2008, 2, 1360–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travieso-Rodríguez, J.A.; Jerez-Mesa, R.; Gómez-Gras, G.; Llumà-Fuentes, J.; Casadesús-Farràs, O.; Madueño-Guerrero, M. Hardening effect and fatigue behavior enhancement through ball burnishing on AISI 1038. J. Mat. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5639–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, J.T.; Anchev, A.P.; Dunchev, V.P.; Ganev, N.; Duncheva, G.V.; Selimov, K.F. Effect of slide burnishing basic parameters on fatigue performance of 2024-Т3 high-strength aluminium alloy. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2017, 40, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.M.; Slavov, S.D. Experimental research on the effect of the ball burnishing process, using new kinematical scheme on hardness and phase composition of surface layer of AISI 304L stainless steel. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 112, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Akita, M.; Uematsu, Y.; Tokaji, K. Effect of strain-induced martensitic transformation on fatigue behavior of type 304 stainless steel. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Bollenhagen, C.; Zimmermann, M.; Christ, H.-J. Very high cycle fatigue behaviour of austenitic stainless steel and the effect of strain-induced martensite. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Chemical Compositions % | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | C | Cr | Mn | Mo | N | Ni | P | S | Si | Co |
| AISI 304 | 0.021 | 18.20 | 1.550 | - | 0.059 | 8.100 | 0.031 | 0.001 | 0.380 | - |
| AISI 316L | 0.022 | 16.63 | 1.285 | 2.031 | 0.050 | 10.065 | 0.030 | 0.004 | 0.340 | 0.226 |
| Mechanical Properties | ||||||||||
| Material | Yield Strength, MPa | Tensile Strength, MPa | Elongation A5, % | HRB | ||||||
| AISI 304 | 324.00 | 626.00 | 55.00 | 188.0 | ||||||
| AISI 316L | 353.15 | 628.58 | 49.18 | 82.0 | ||||||
| Factor | Code | Low Level (−1) | High Level (+1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deforming force, F, N | A | 1060 | 1735 |
| Number of sinewave wavelengths, i | B | 600.15 | 1200.15 |
| Amplitude, e, mm | C | 1.0 | 2.5 |
| Feed rate, f, mm/min | D | 150 | 300 |
| Factor Level | Low Number: B = −1 | High Number: B = +1 |
|---|---|---|
| Low amplitude: C= −1 |  Toolpath length: 1011.75 mm | 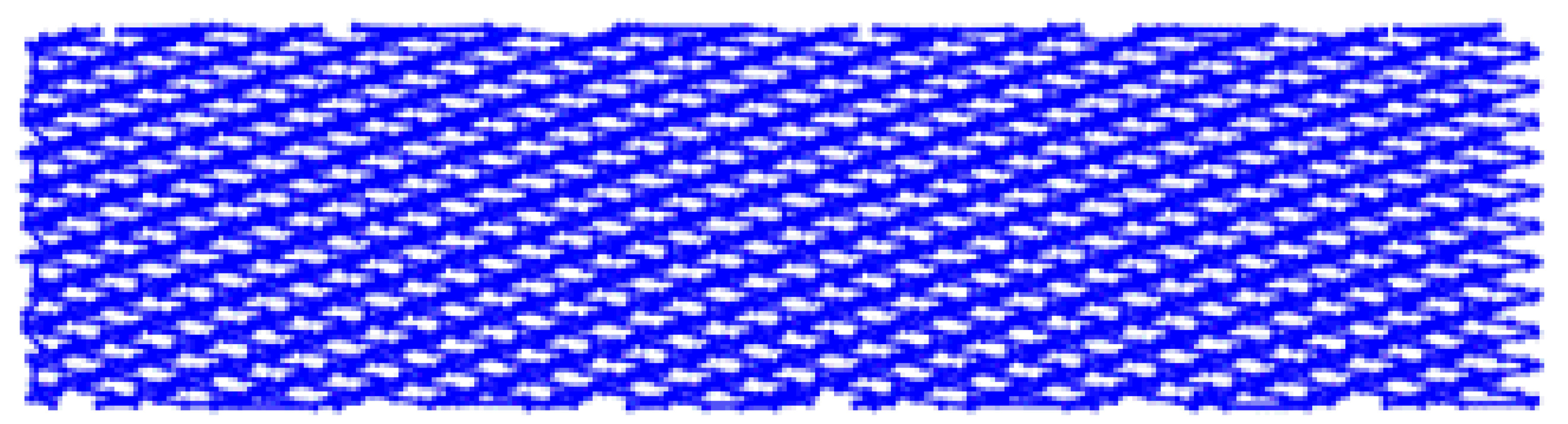 Toolpath length: 1783.25 mm |
| High amplitude: C= +1 | 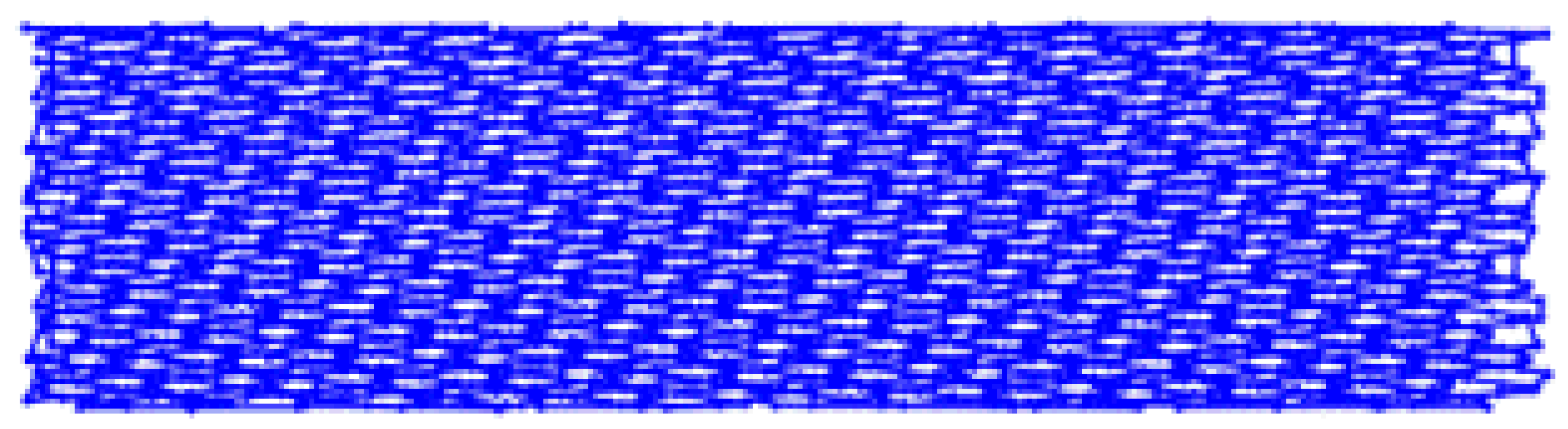 Toolpath length: 2231.34 mm | 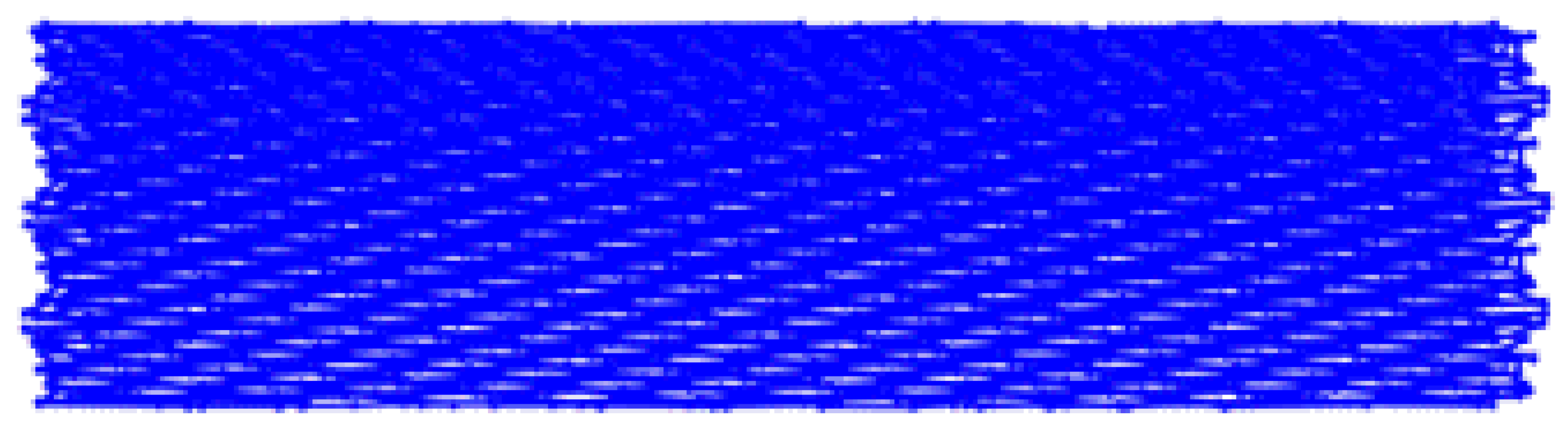 Toolpath length: 4164.44 mm |
| Steel | Cycles to Failure (Nf) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Mean | std | min | 25% | 50% | 75% | max | |
| 304 | 32 | 152,909 | 101,099 | 23,929 | 61,192 | 152,450 | 234,882 | 419,450 |
| 316L | 32 | 1,353,132 | 1,422,401 | 138,868 | 418,176 | 694,903 | 1,807,082 | 6,022,466 |
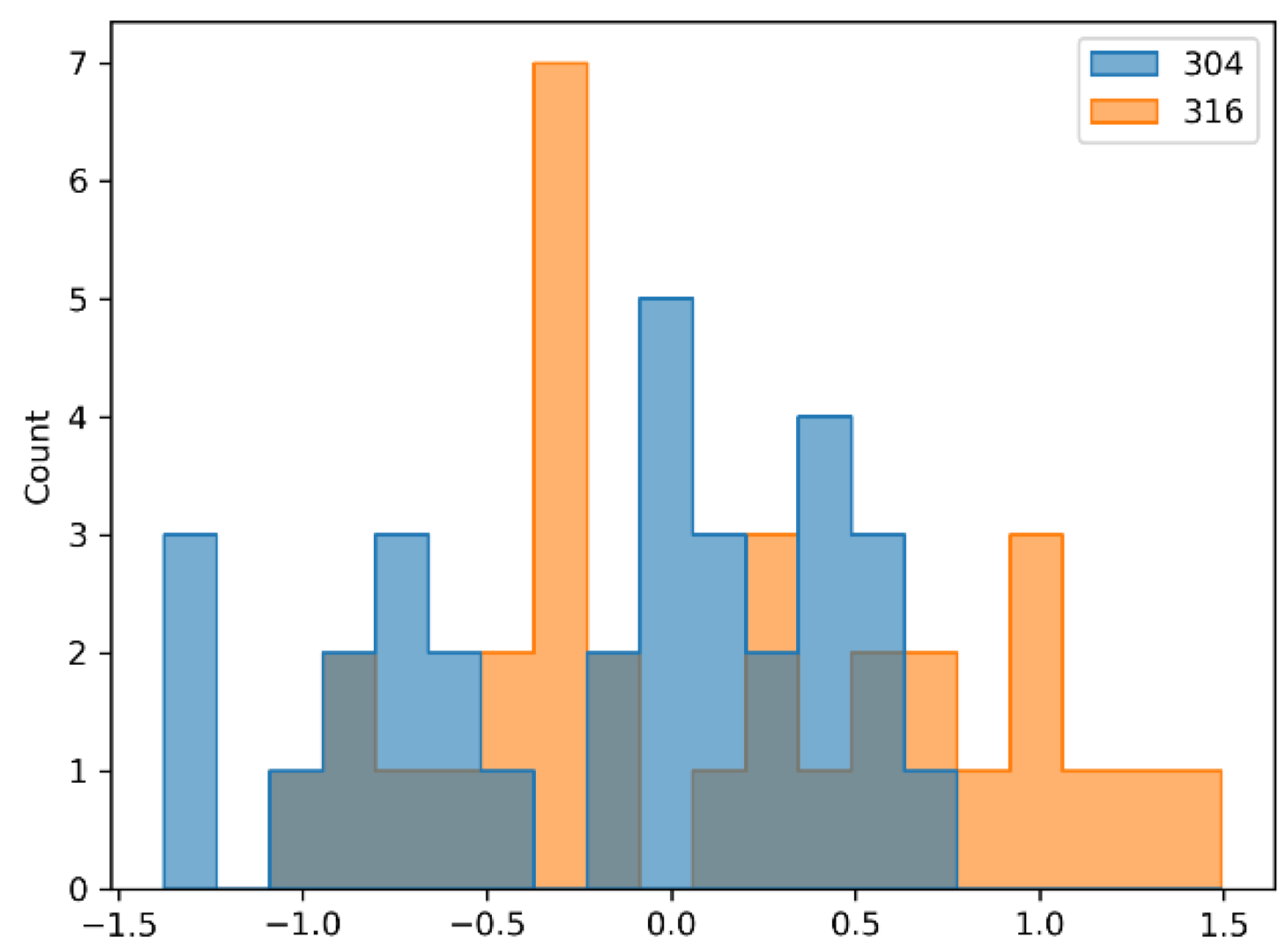
| Steel | logCycles (dB) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Mean | std | min | 25% | 50% | 75% | max | |
| 304 | 32.0 | 15.35 | 6.98 | 1.56 | 9.71 | 17.64 | 21.39 | 26.43 |
| 316 | 32.0 | 15.45 | 8.81 | −0.07 | 9.50 | 13.68 | 22.22 | 32.67 |
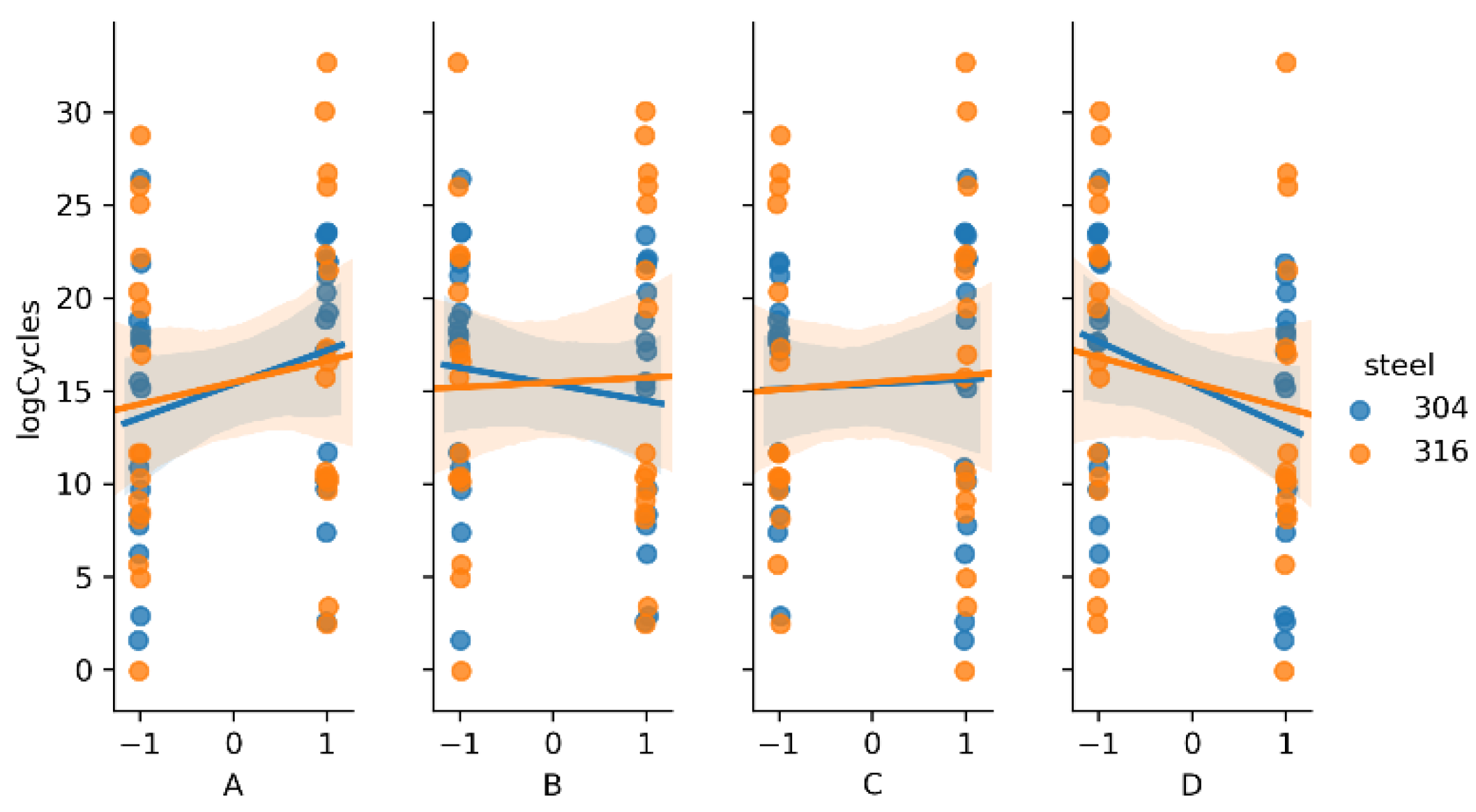
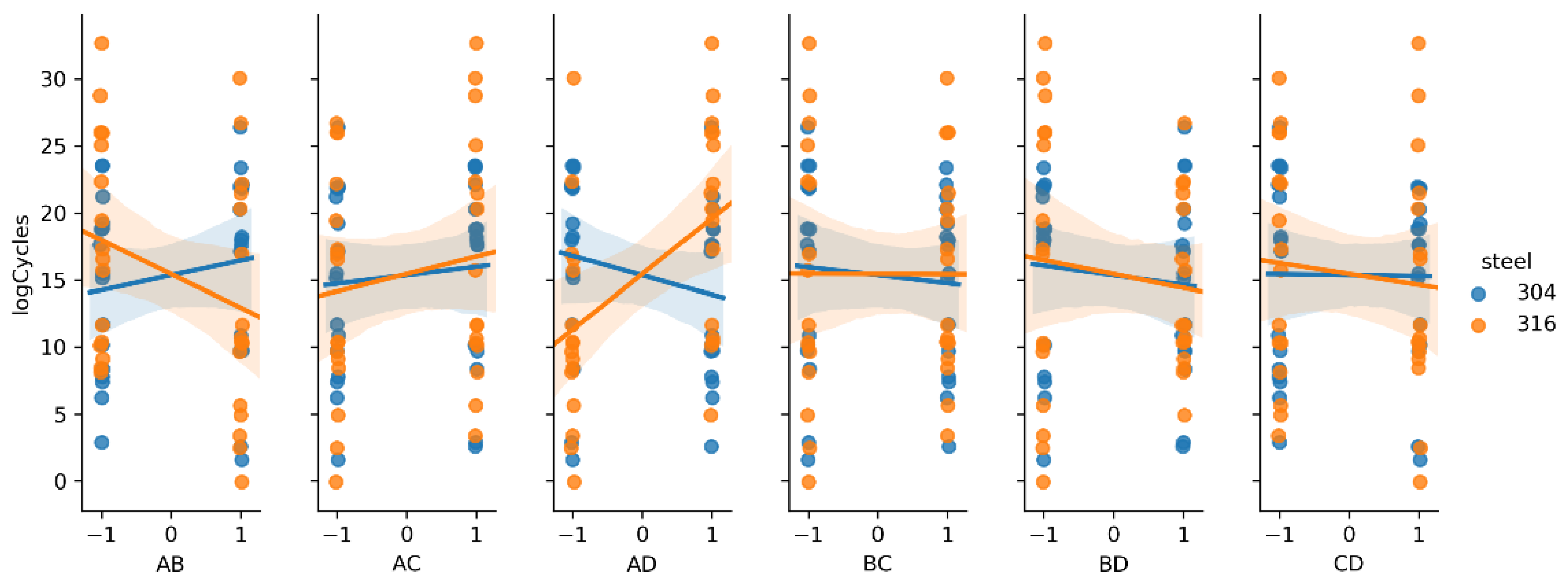
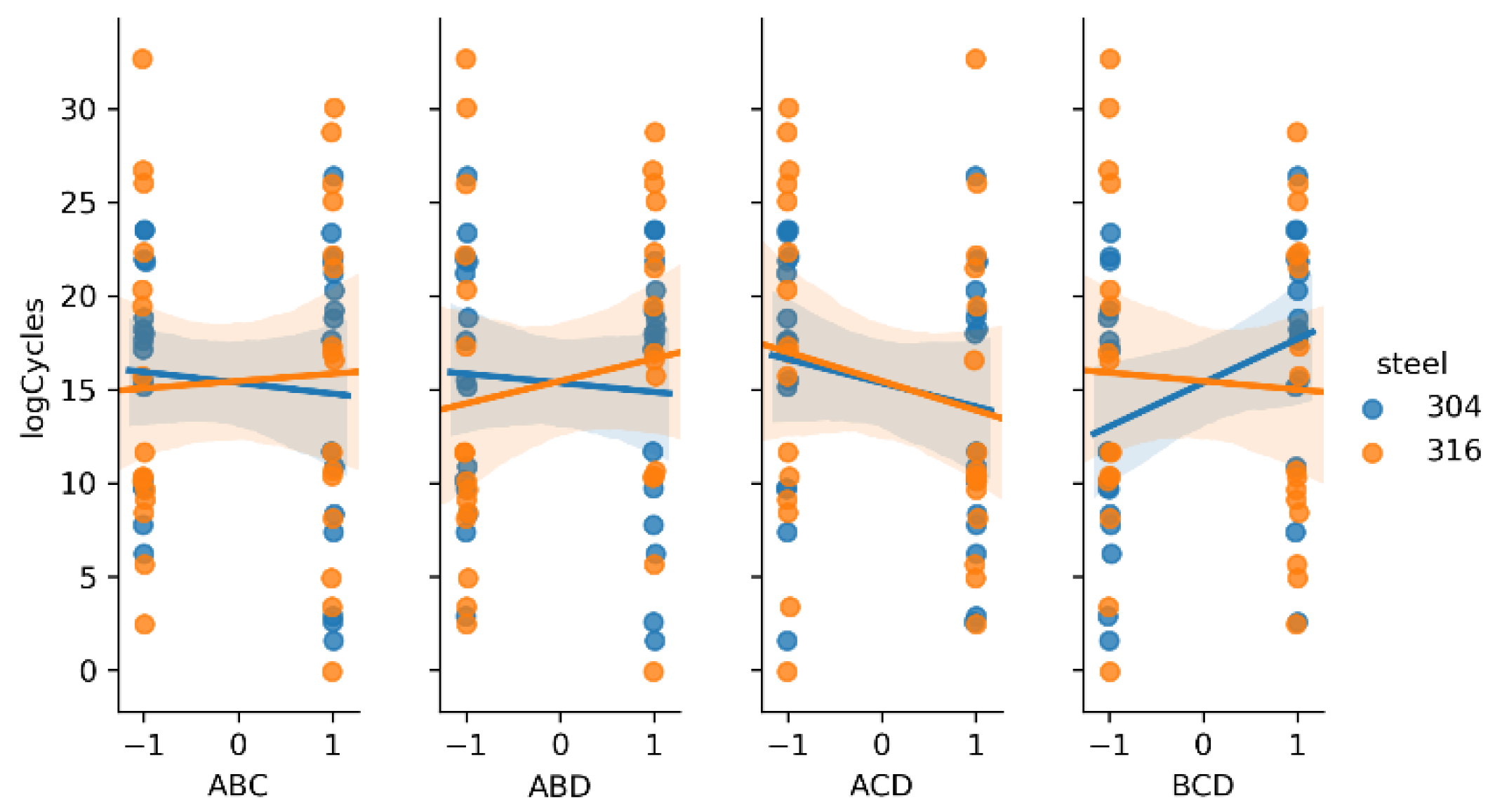
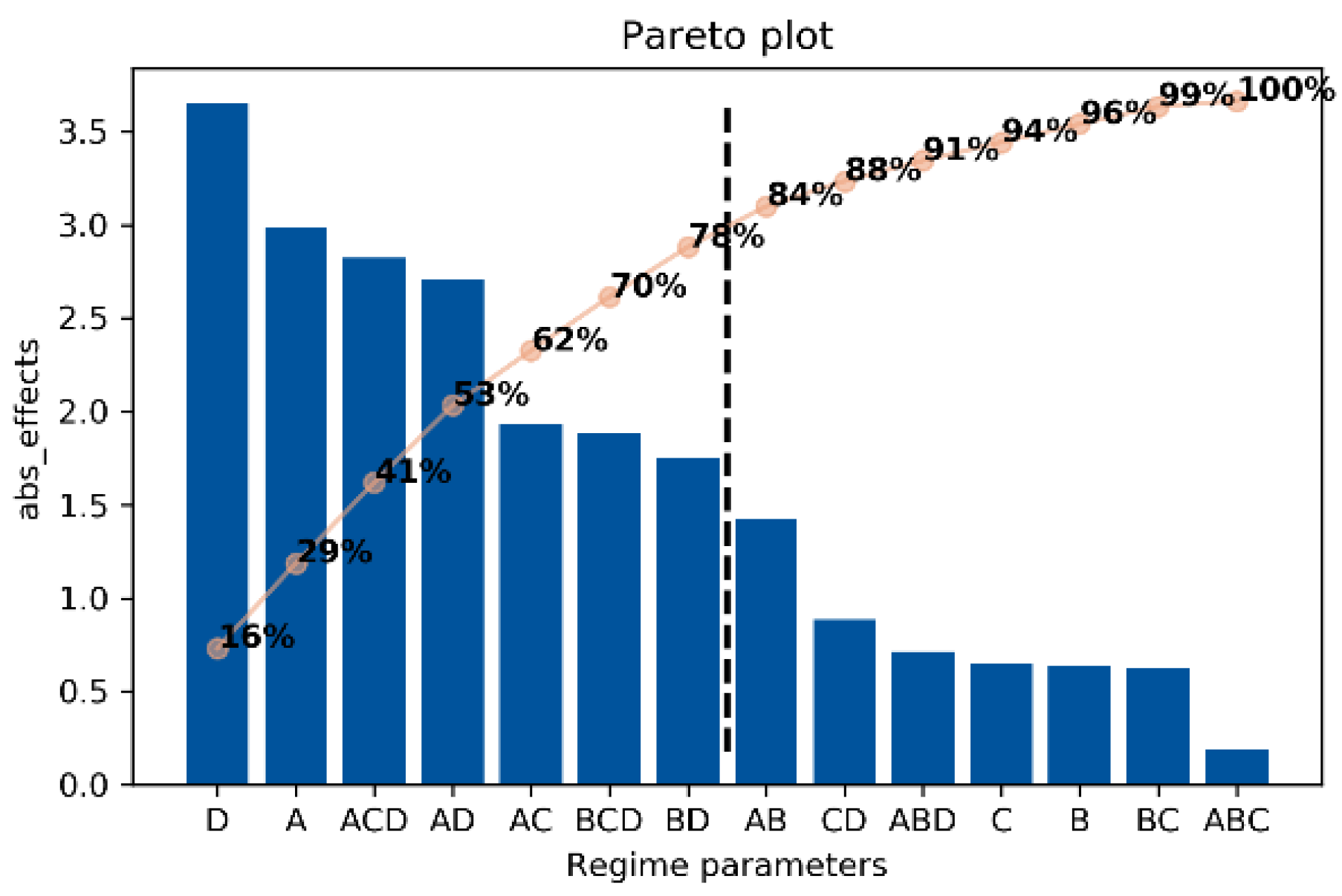
| Factors | Effect | abs(Effect) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| D | −3.654 | 3.654 | 0.084 |
| A | 2.984 | 2.984 | 0.108 |
| ACD | −2.824 | 2.824 | 0.222 |
| AD | 2.707 | 2.707 | 0.206 |
| AC | 1.927 | 1.927 | 0.371 |
| BCD | 1.885 | 1.885 | 0.316 |
| BD | −1.750 | 1.750 | 0.417 |
| AB | −1.426 | 1.426 | 0.541 |
| CD | −0.886 | 0.886 | 0.705 |
| ABD | 0.715 | 0.715 | 0.742 |
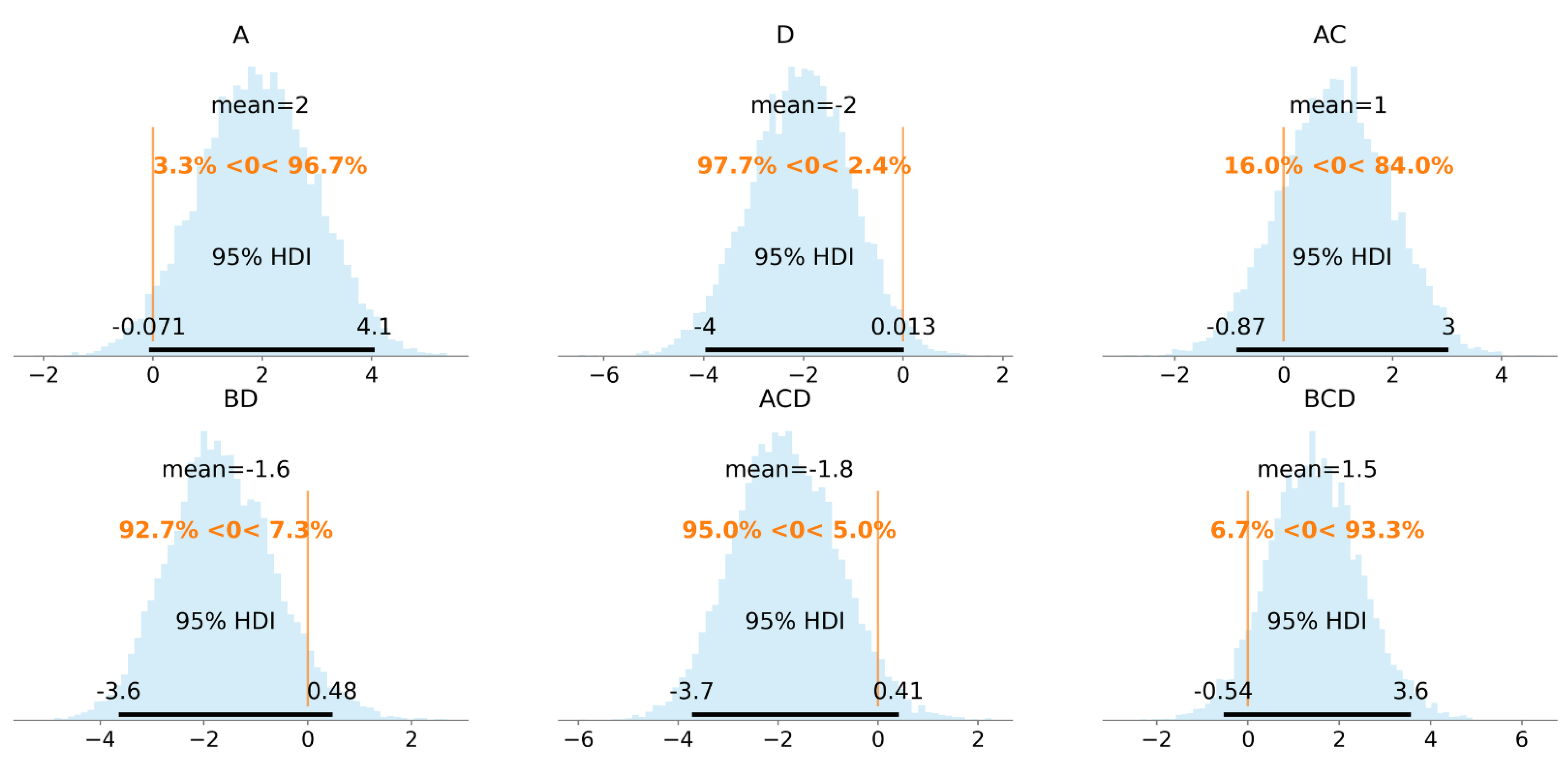
| βi Effect | βi Mean | βi std err | βi 95% HDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [0.025 | 0.975] | |||
| Intercept | 15.4010 | 0.937 | 13.524 | 17.278 |
| D | −1.8272 | 0.937 | −3.704 | 0.050 |
| A | 1.4918 | 0.937 | −0.385 | 3.369 |
| ACD | −1.4118 | 0.937 | −3.289 | 0.465 |
| AD | 1.3537 | 0.937 | −0.524 | 3.231 |
| AC | 0.9636 | 0.937 | −0.913 | 2.841 |
| BCD | 0.9427 | 0.937 | −0.934 | 2.820 |
| BD | −0.8748 | 0.937 | −2.752 | 1.002 |
| Predictors | Summary Statistics of Posterior | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | sd | hdi_2.5% | hdi_97.5% | mcse_mean | ess_mean | ess_sd | ess_tail | r_hat | |
| Intercept | 15.007 | 0.991 | 13.007 | 16.883 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 7124.0 | 7105.0 | 1.0 |
| A | 2.074 | 1.035 | −0.013 | 4.002 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 6936.0 | 6707.0 | 1.0 |
| D | −1.964 | 0.978 | −3.935 | −0.077 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 8201.0 | 7225.0 | 1.0 |
| AD | −0.251 | 1.117 | −2.454 | 1.914 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 5470.0 | 5470.0 | 1.0 |
| AC | 1.133 | 1.000 | −0.775 | 3.147 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 7253.0 | 6608.0 | 1.0 |
| BD | −1.403 | 1.104 | −3.508 | 0.844 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 6169.0 | 6169.0 | 1.0 |
| ACD | −1.873 | 1.084 | −3.873 | 0.352 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 6311.0 | 6311.0 | 1.0 |
| BCD | 1.545 | 1.045 | −0.461 | 3.669 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 7049.0 | 6335.0 | 1.0 |
| lam | 0.063 | 0.023 | 0.026 | 0.109 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 5794.0 | 4586.0 | 1.0 |
| Relief Parameters (B, C). | Regime Parameters Values: Force Federate (A, D) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1, 1) | (1, −1) | (−1, 1) | (−1, −1) | |
| (1, 1) | 0.21 | 0.97 | 0.29 | 0.62 |
| (−1, 1) | 0.50 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.30 |
| (1, −1) | 0.55 | 0.83 | 0.07 | 0.89 |
| (−1, −1) | 0.82 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slavov, S.; Dimitrov, D.; Konsulova-Bakalova, M.; Vasileva, D. Impact of Ball Burnished Regular Reliefs on Fatigue Life of AISI 304 and 316L Austenitic Stainless Steels. Materials 2021, 14, 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102529
Slavov S, Dimitrov D, Konsulova-Bakalova M, Vasileva D. Impact of Ball Burnished Regular Reliefs on Fatigue Life of AISI 304 and 316L Austenitic Stainless Steels. Materials. 2021; 14(10):2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102529
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlavov, Stoyan, Diyan Dimitrov, Mariya Konsulova-Bakalova, and Dimka Vasileva. 2021. "Impact of Ball Burnished Regular Reliefs on Fatigue Life of AISI 304 and 316L Austenitic Stainless Steels" Materials 14, no. 10: 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102529
APA StyleSlavov, S., Dimitrov, D., Konsulova-Bakalova, M., & Vasileva, D. (2021). Impact of Ball Burnished Regular Reliefs on Fatigue Life of AISI 304 and 316L Austenitic Stainless Steels. Materials, 14(10), 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102529






