Micro-Structure Changes Caused by Thermal Evolution in Chalcogenide GexAsySe1−x−y Thin Films by In Situ Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source Material
2.2. Thermal Evaporation
2.3. In Situ Measurements
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
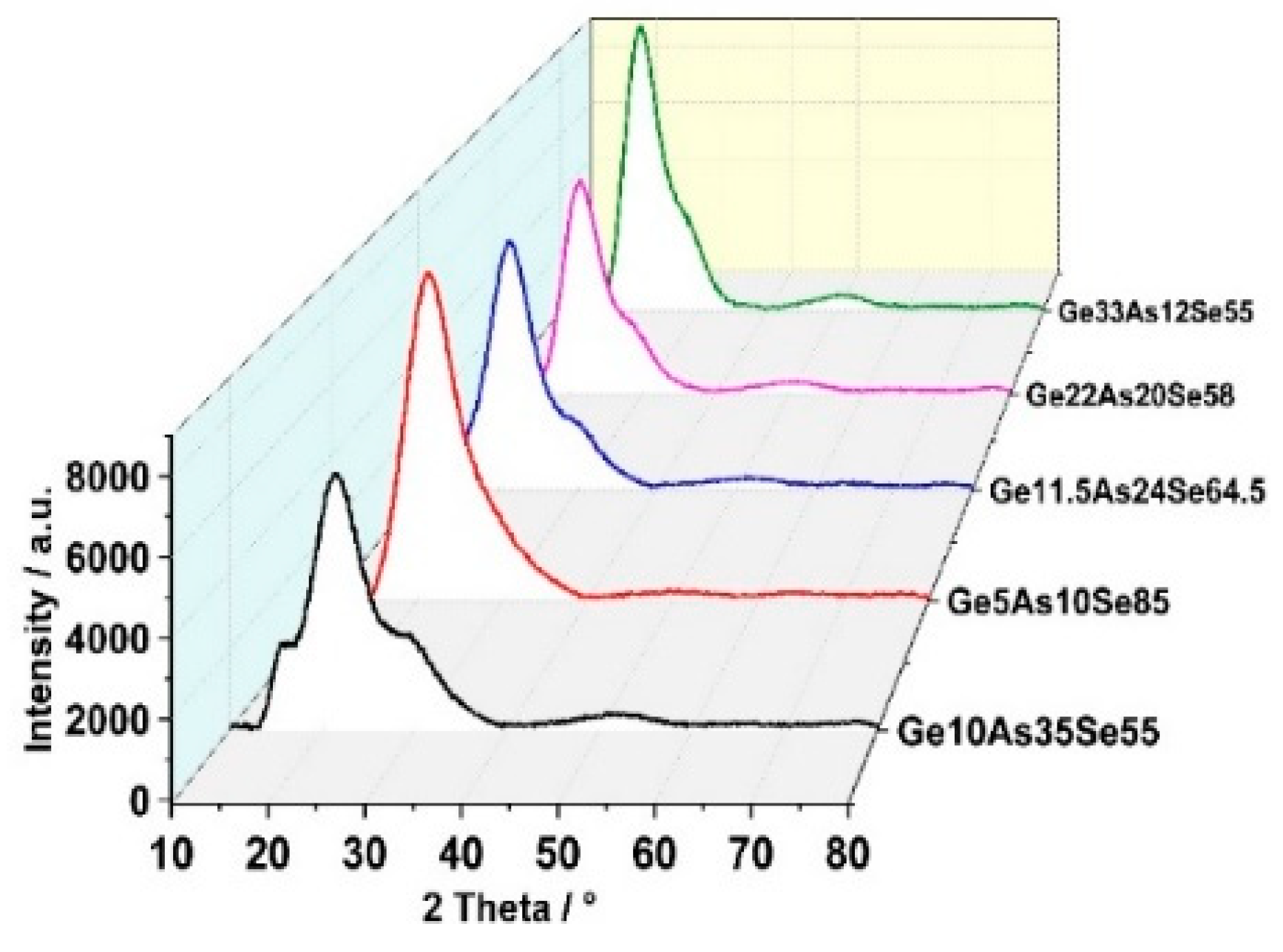
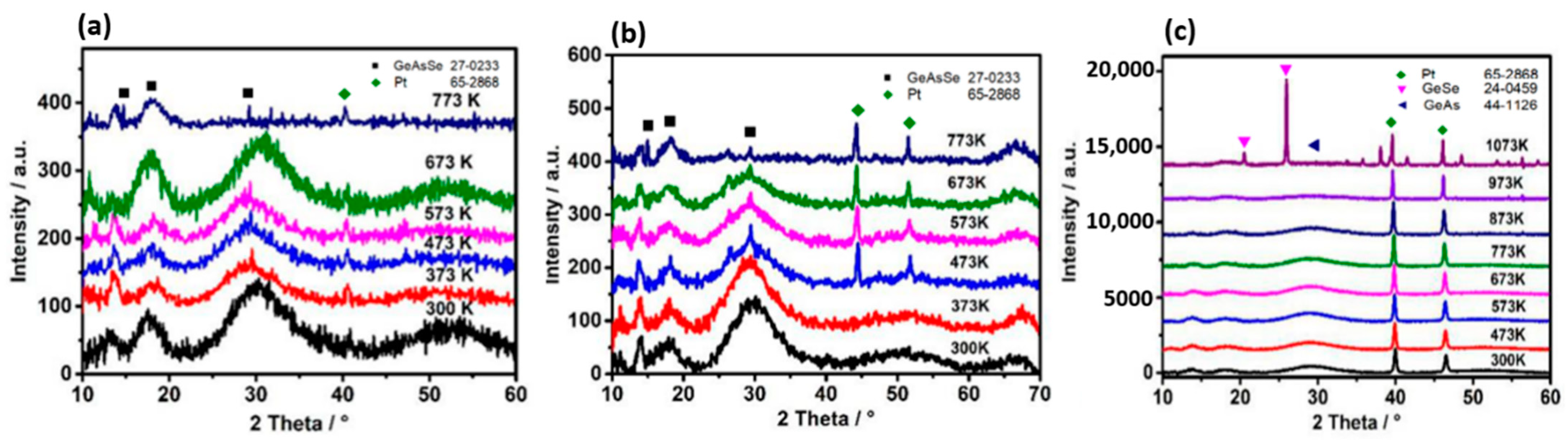
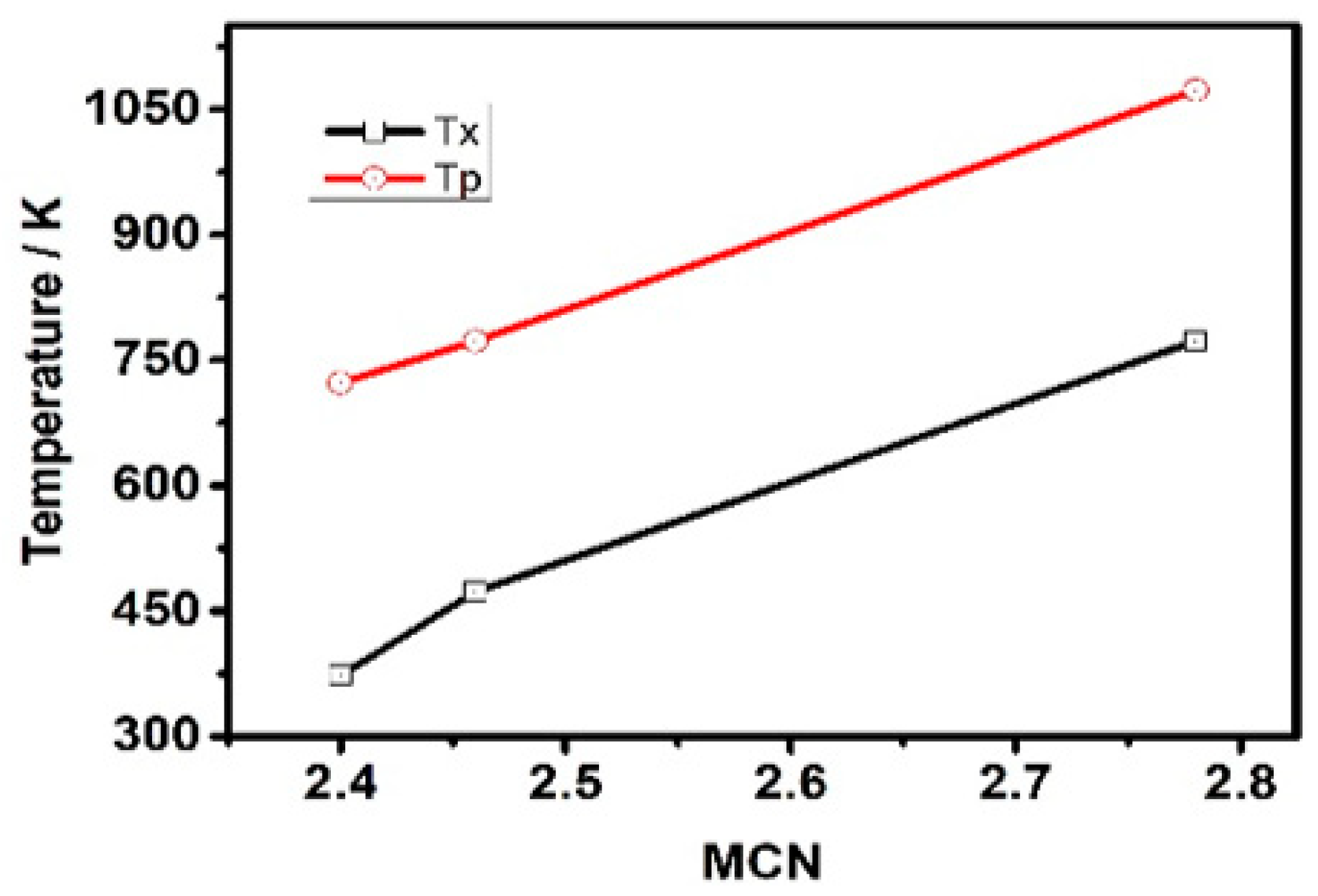
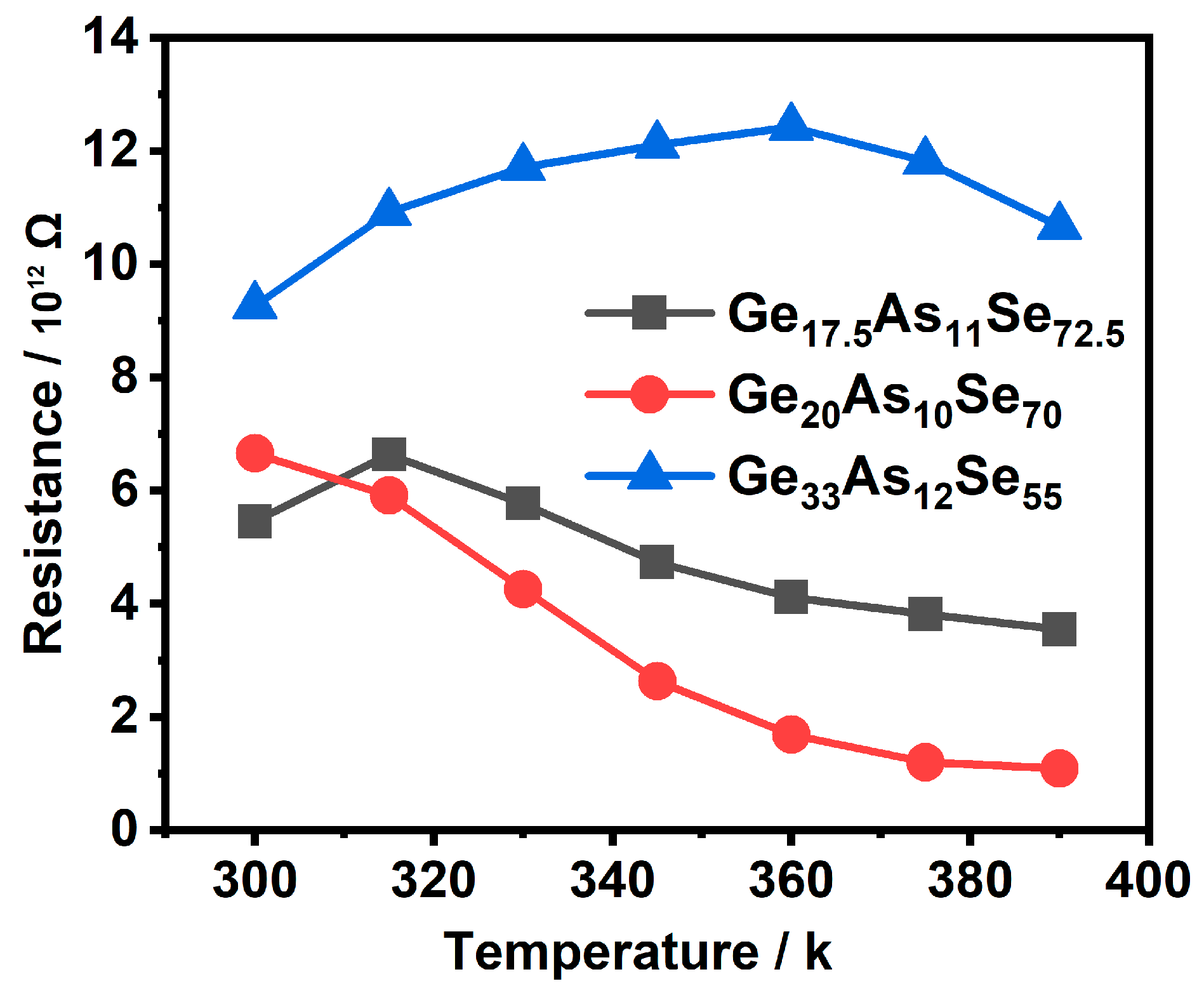
3.1. Structural Properties
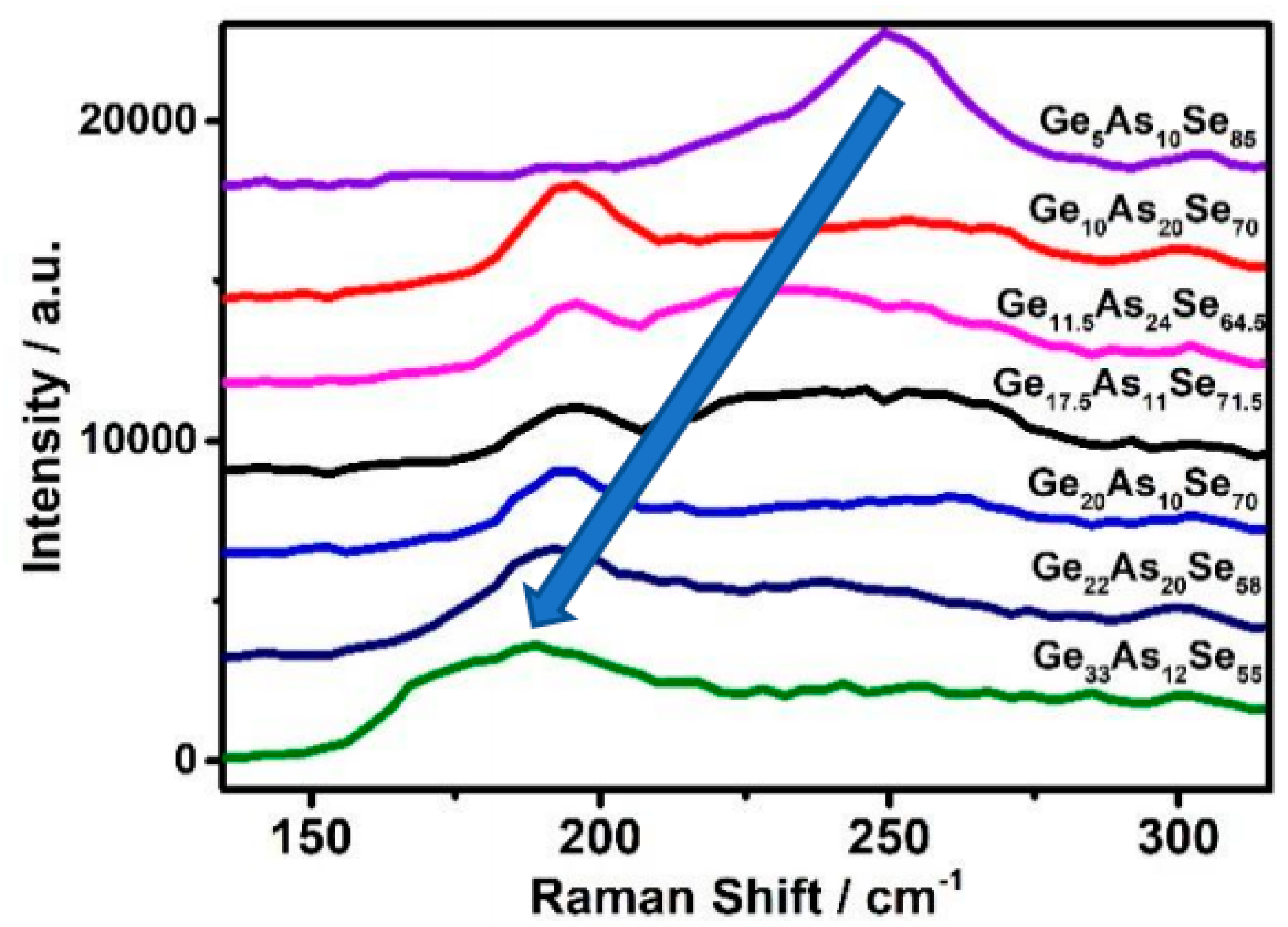
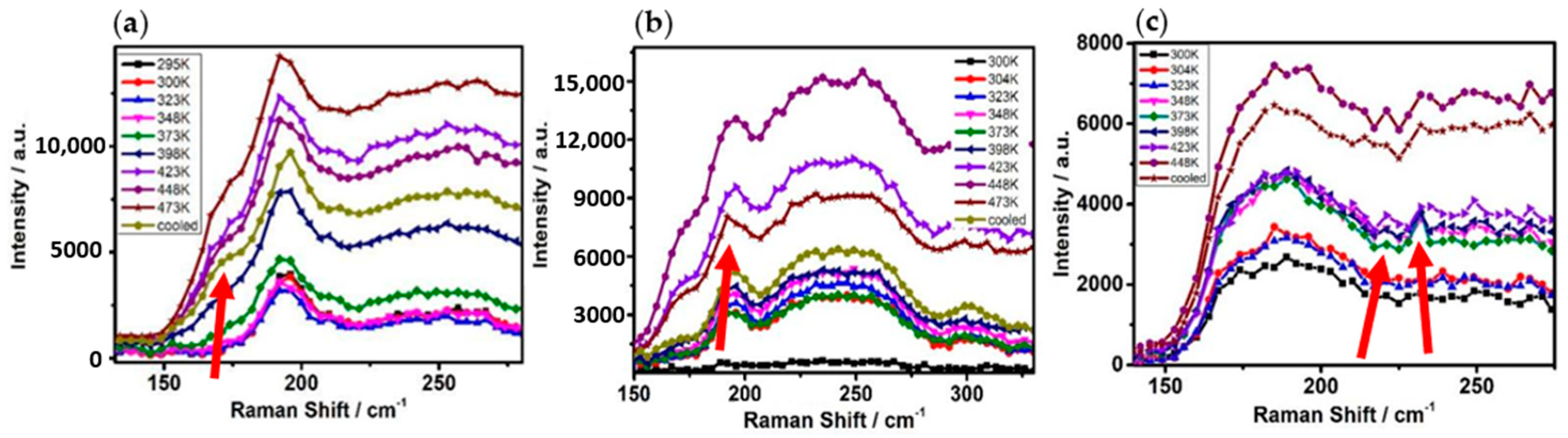
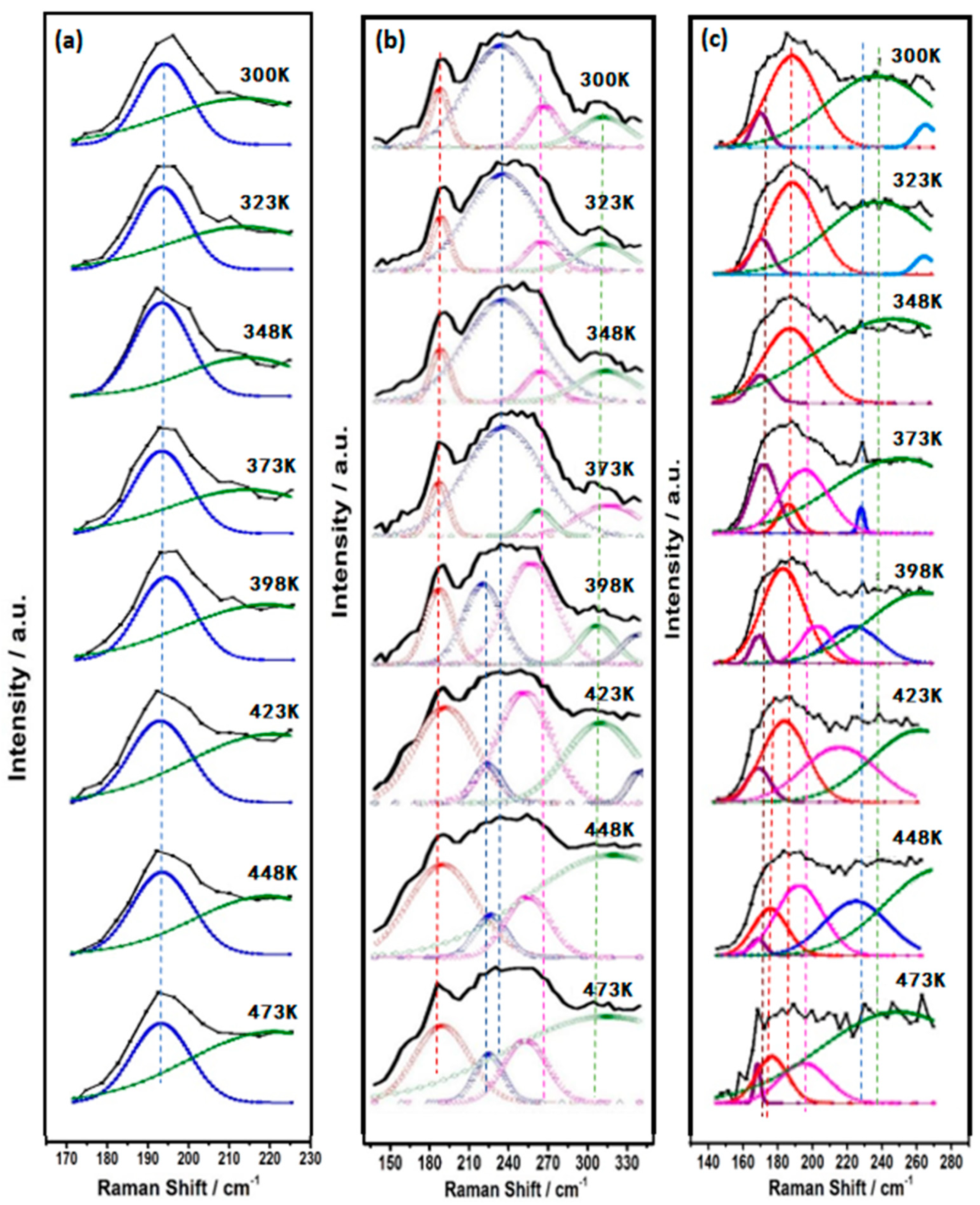
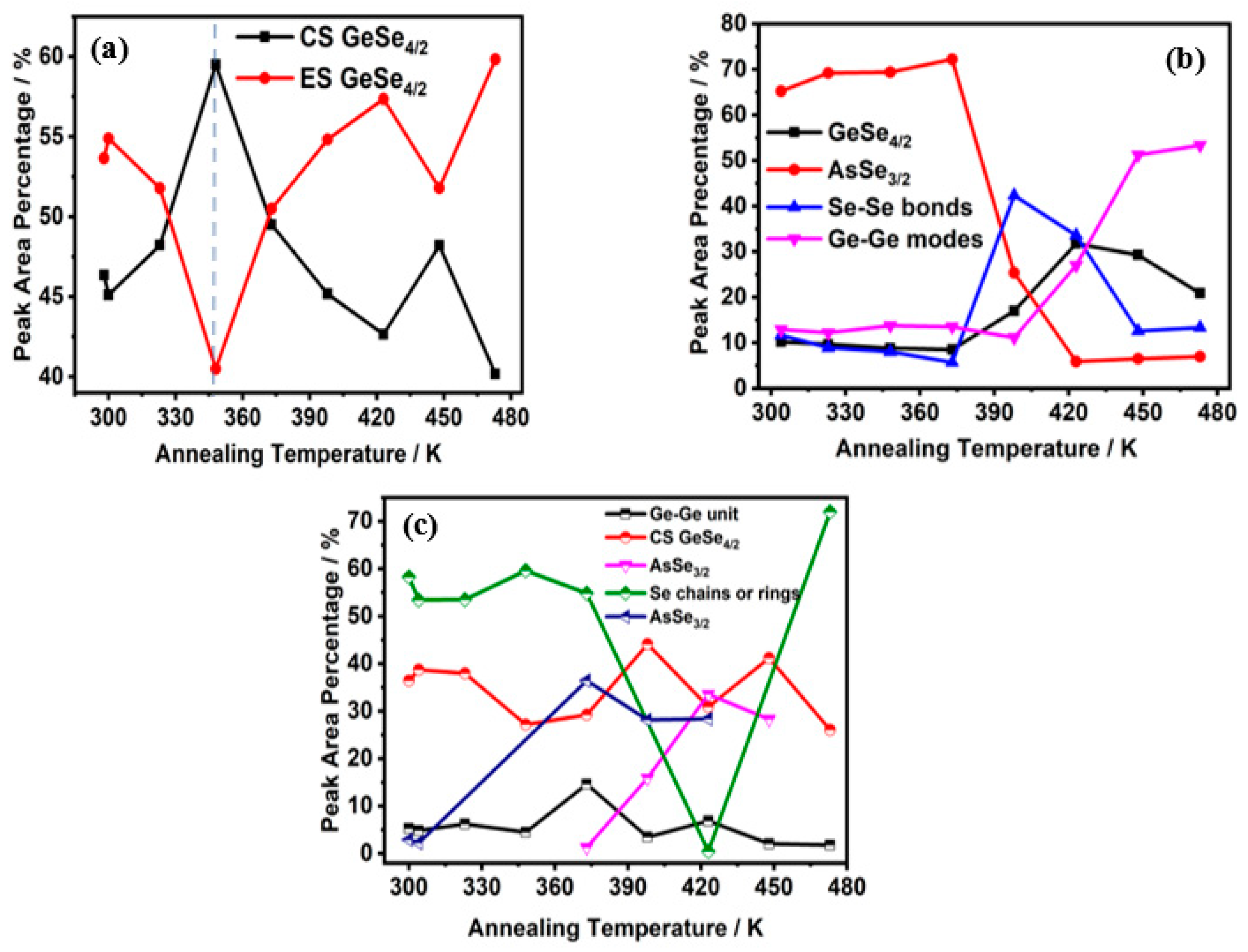
3.2. In Situ Raman
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, P.; Sarangan, A.M.; Agha, I. A review of germanium-antimony-telluride phase change materials for non-volatile memories and optical modulators. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P. Amorphous Chalcogenides: Advances and Applications; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Shimakawa, K. Amorphous Chalcogenide Semiconductors and Related Materials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boschker, J.E.; Wang, R.; Calarco, R. GeTe: A simple compound blessed with a plethora of properties. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 5324–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, R.A.; Mott, N.F. States in the Gap in Glassy Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1975, 35, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F. In Electrons in Glass. Science 1978, 201, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovshinsky, S.R. Localized States in the Gap of Amorphous Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1976, 36, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovshinsky, S.R. Reversible Electrical Switching Phenomena in Disordered Structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1968, 21, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D.; Henisch, H.K.; Mott, S.N. The mechanism of threshold switching in amorphous alloys. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1978, 50, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D.; Shur, M.S.; Silver, M.; Ovshinsky, S.R. Threshold switching in chalcogenide-glass thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 51, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, D. Current-driven switching of a small-polaron semiconductor to a meta-stable conductor. Phys. Status Solidi C 2008, 5, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, D.; Seager, C.H.; Quinn, R.K. Small-Polaron Hopping Motion in Some Chalcogenide Glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1972, 28, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, C.H.; Emin, D.; Quinn, R.K. Electrical Transport and Structural Properties of Bulk As-Te-I, As-Te-Ge, and As-Te Chalcogenide Glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 8, 4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, D. The sign of the Hall effect in hopping conduction. Philos. Mag. 1977, 35, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D.; Zhang, Y. Evidence for trap-limited transport in the subthreshold conduction regime of chalcogenide glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 192102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D.; Zhang, Y. Analytical model for subthreshold conduction and threshold switching in chalcogenide-based memory devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 054517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Energy losses in hopping conduction at high electric fields. J. Phys. C 1971, 4, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K.; Loh, C.K. Poole-Frenkel conduction in high alternating electric fields. J. Phys. C 1971, 4, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K.; Hill, R.M. Electrical Conduction in Non-Metallic Amorphous Films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1969, 6, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yina, J.; Zhang, P. Two-dimensional GeAsSe with high and unidirectional conductivity. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, R.P. Photo-induced effects in Ge-As-Se films in various states. Appl. Phys. Express 2020, 10, 385115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Pan, Y.; Gao, D.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, R.; Wang, L. The transport mechanisms at localized states of thin films of GexAsySe1−x−y chalcogenide glasses under off-equilibrium conditions. Thin Solid Film. 2020, 709, 138044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P.; Smith, A.; Luther-Davies, B.; Kokkonen, H.; Jackson, I. Observation of two elastic thresholds in GexAsySe1−x−y glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 056109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronc, P.; Bensoussan, M.; Brenac, A.; Sebenne, C. Optical-Absorption Edge and Raman Scattering in Gex Se1−x Glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 8, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Boolchand, P. Universal structural phase-transition in network glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.W.; Wang, R.P.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Luther-Davies, B. Evidence of homopolar bonds in chemically stoichiometric Gex-AsySe1−x−y glasses. Appl. Phys. Express 2015, 8, 015504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, N.; Shirafuji, J.; Inuishi, Y. Studies on vibrational properties of Ge-Se glasses. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1977, 42, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Briley, A.; Grossman, S.; Porezag, D.V.; Pederson, M.R. Raman-active modes of a-GeSe2 and a-GeS2: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, R14985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Bureau, B.; Rouxel, T.; Gueguen, Y.; Gulbiten, O.; Roiland, C.; Soignard, E.; Yarger, J.L.; Troles, J.; Sangleboeuf, J.C.; et al. Correlation between structure and physical properties of chalcogenide glasses in the AsxSe1−x system. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 195206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Seal, S.; Rivero, C.; Lopez, C.; Richardson, K.; Pope, A.; Schulte, A.; Myneni, S.; Jain, H.; Antoine, K.; et al. Role of S/Se Ratio in Chemical Bonding of As–S–Se Glasses Investigated by Raman, X-Ray Photoelectron, and Extended X-Ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectroscopies. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 053503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohoutek, T.; Wagner, T. Spin-coated As33S67−xSex thin films: The effect of annealing on structure and optical properties. NonCryst. Solids 2006, 352, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.Y.; Gulbiten, O. Mechanism of photostructural changes in mixed-chalcogen As-S-Se glasses investigated by Raman spectroscopy. Phys. D 2011, 44, 045404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bues, W.; Somer, M. Vibrational-spectra of the cage compounds P4S3, P4Se3, As4S3 and As4Se3. Naturforsch 1980, 35, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulla, D.A.P.; Wang, R.P. On the properties and stability of thermally evaporated Ge-As-Se thin films. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 96, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Q.; Wang, R.P. The dependence of photosensitivity on composition for thin films of GexAsySe1−x−y chalcogenide glasses. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, L. Nanolasers incorporating CoxGa0.6−xZnSe0.4 nanoparticle arrays with wavelength tunability at room temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 6795–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, X.; Pan, Y.; Gao, D.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, L. Micro-Structure Changes Caused by Thermal Evolution in Chalcogenide GexAsySe1−x−y Thin Films by In Situ Measurements. Materials 2021, 14, 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102572
Su X, Pan Y, Gao D, Li S, Wang J, Wang R, Wang L. Micro-Structure Changes Caused by Thermal Evolution in Chalcogenide GexAsySe1−x−y Thin Films by In Situ Measurements. Materials. 2021; 14(10):2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xueqiong, Yong Pan, Dongwen Gao, Shufeng Li, Jin Wang, Rongping Wang, and Li Wang. 2021. "Micro-Structure Changes Caused by Thermal Evolution in Chalcogenide GexAsySe1−x−y Thin Films by In Situ Measurements" Materials 14, no. 10: 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102572
APA StyleSu, X., Pan, Y., Gao, D., Li, S., Wang, J., Wang, R., & Wang, L. (2021). Micro-Structure Changes Caused by Thermal Evolution in Chalcogenide GexAsySe1−x−y Thin Films by In Situ Measurements. Materials, 14(10), 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102572






