Microscopic Characterization of Bioactivate Implant Surfaces: Increasing Wettability Using Salts and Dry Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- ABT: titanium grade 5 alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) surface obtained from a sandblasting process for the creation of macropores (20–40 microns) and double thermal etching for the creation of micropores (1–5 microns) (Alpha-Bio Tec Ltd.).
- (2)
- Nano: surface obtained by adding salts (potassium chloride and potassium phosphate) to the ABT surface through immersion in a saline solution and subsequently removed from the solution and dried in the air.
- (3)
- Nano H2O: a surface activated by the hydration of salts of Nano surface with distilled water.
2.1. Sample Size
2.2. Topographic Analysis
2.3. EDX
2.4. Contact Angle Characterization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
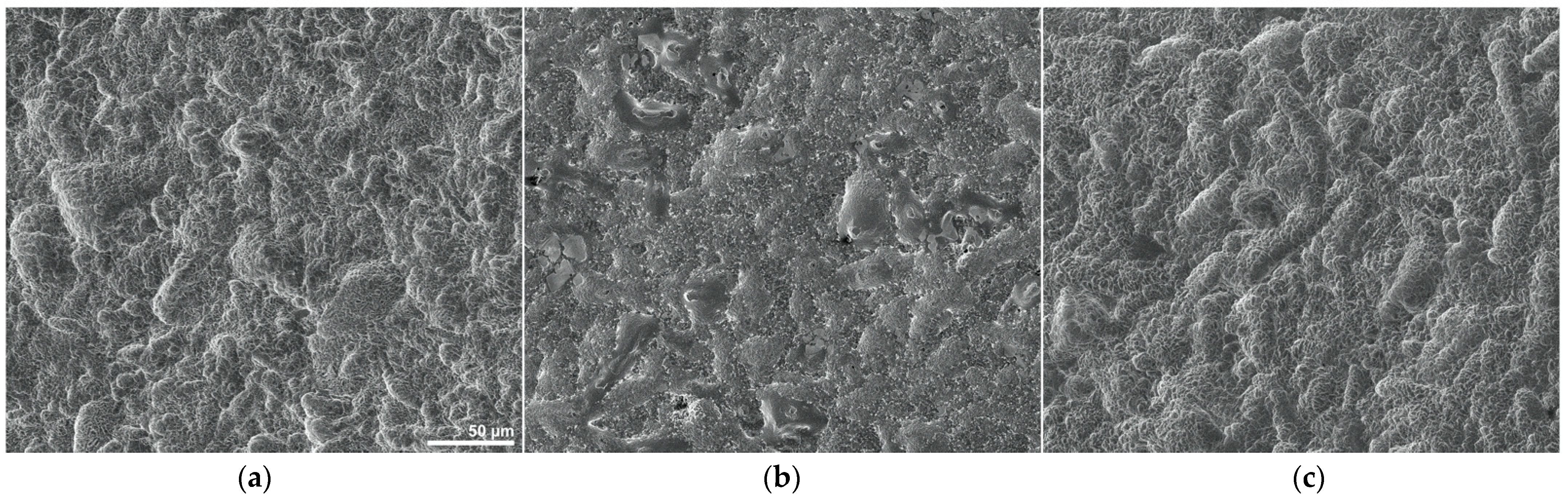
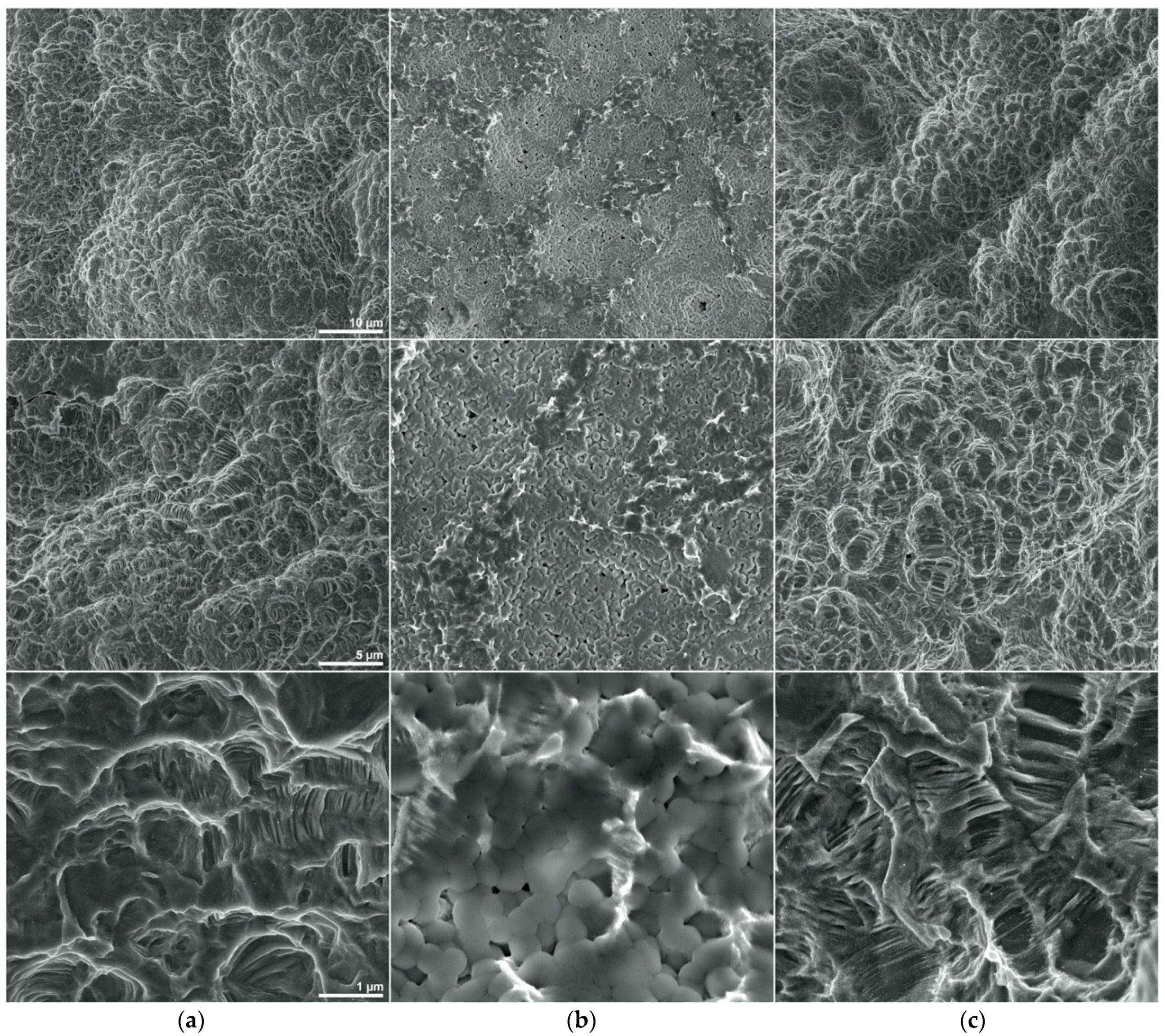
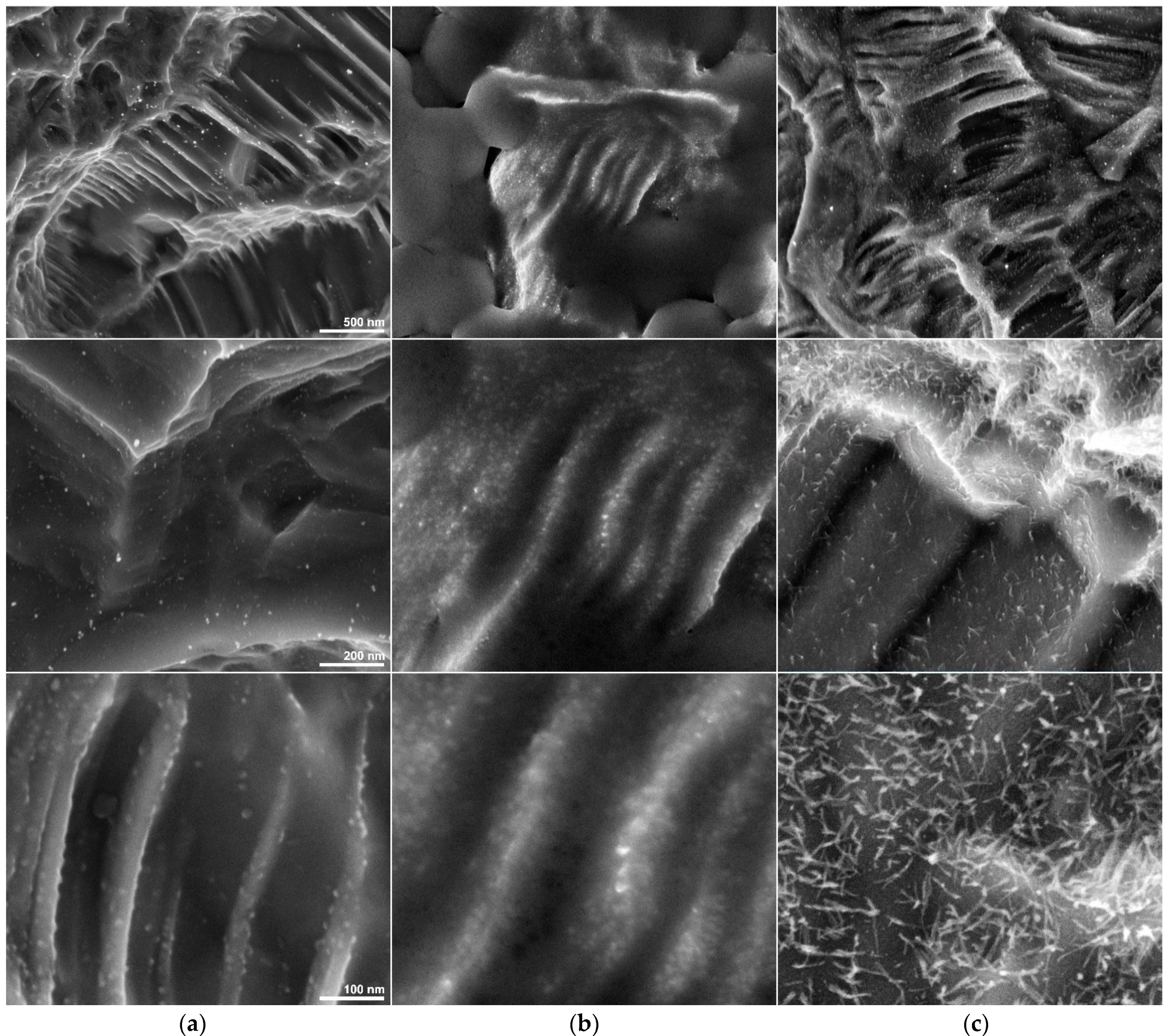
3.1. SEM Results
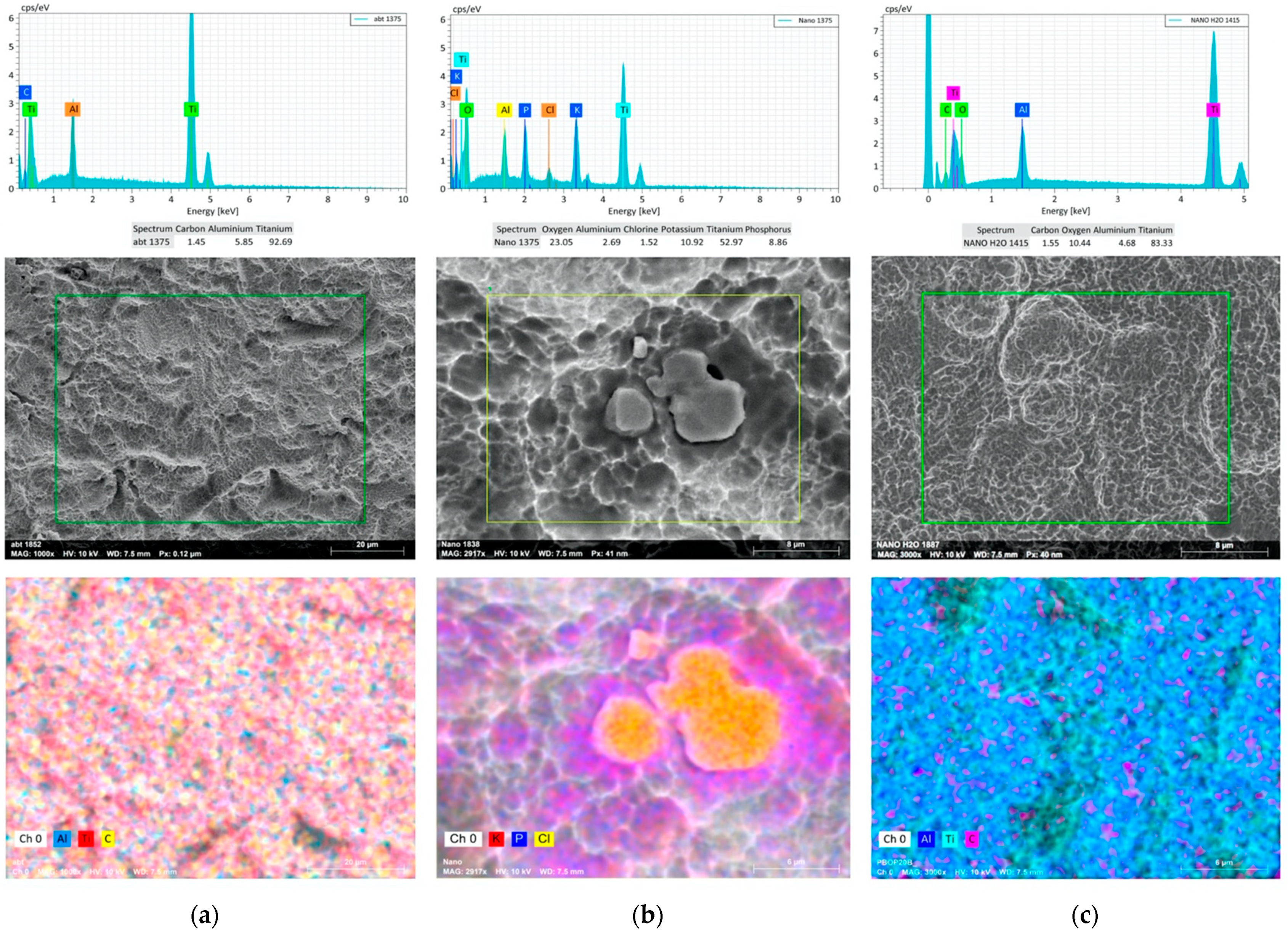
3.2. EDX Results
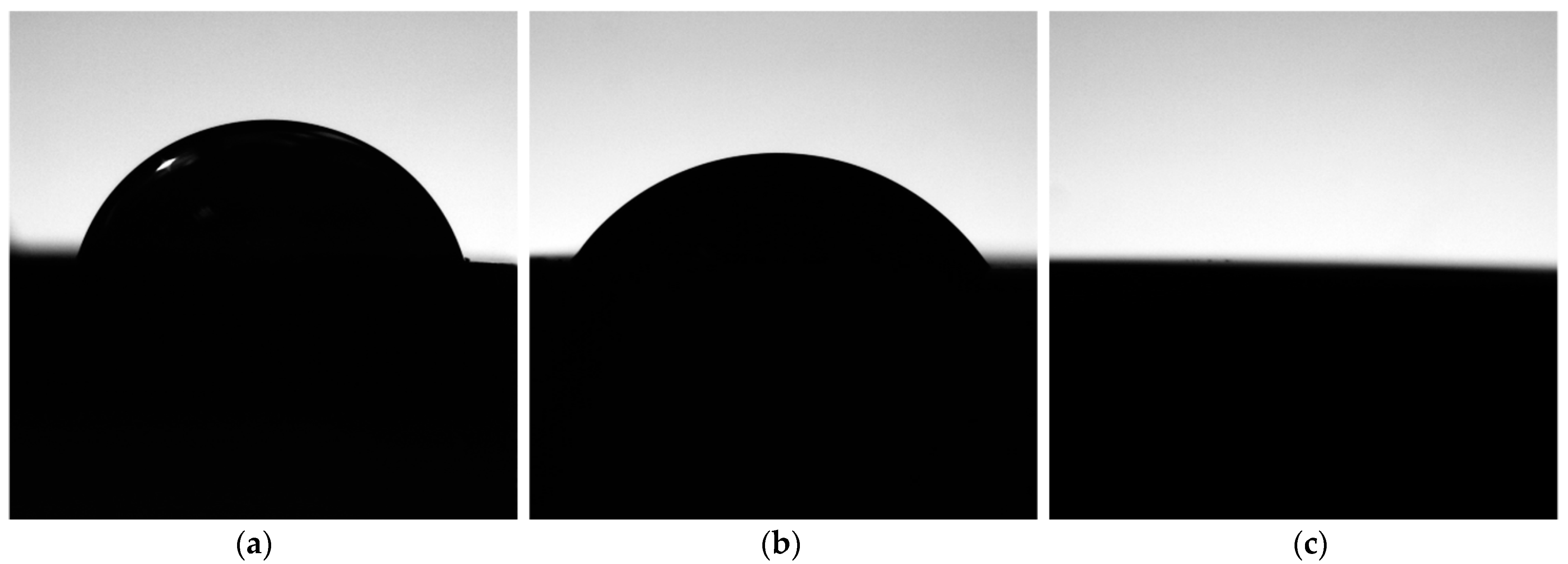
3.3. Contact Angle Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. The impact of oral implants—Past and future, 1966–2042. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 71, 327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1—Review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López-Valverde, N.; Flores-Fraile, J.; Ramírez, J.M.; De Sousa, B.M.; Herrero-Hernández, S.; López-Valverde, A. Bioactive Surfaces vs. Conventional Surfaces in Titanium Dental Implants: A Comparative Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, D.L. A Comparison of Endosseous Dental Implant Surfaces. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 1523–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.S.; Han, J.S.; Yang, J.H. Biomechanical and histomorphometric study of dental implants with different surface characteristics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H.; Aref, A.; Scharnweber, D.; Rösler, S.; Sewing, A. Effect of modifcations of dual acid-etched implant surfaces on periimplant bone formation. Part II: Calcium phosphate coatings. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, Y.T.; Johansson, C.B.; Jeong, Y.; Röser, K.; Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Oxidized implants and their influence on the bone response. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiropaidis, A.V.; Qahash, M.; Lim, W.H.; Shanaman, R.H.; Rohrer, M.D.; Wikesjö, U.M.; Hall, J. Bone-implant contact at calcium phosphate-coated and porous titanium oxide (TiUniteTM)-modified oral implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalabi, M.M.; Gortemaker, A.; Van’t Hof, M.A.; Jensen, J.A.; Creugers, N.H. Implant surface roughness and bone healing: A systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nawas, B.; Groetz, K.A.; Goetz, H.; Duschner, H.; Wagner, W. Comparative histomorphometry and resonance frequency anal-ysis of implants with moderately rough surfaces in a loaded animal model. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff, C.; Widmark, G.; Johansson, C.; Wennerberg, A. Histologic evaluation of bone response to oxidized and turned titanium micro-implants in human jawbone. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Shibli, J.A.; Grassi, S.; de Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M.; Iezzi, G.; Piatelli, A. Human peri-implant bone response to turned and oxidized titanium implants inserted and retrieved after 2 months. Implant. Dent. 2007, 16, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, N.; Xu, W.; Myers, D.; Shukla, R.; Tang, H.; Qian, M. The effect of ordered and partially ordered surface topography on bone cell responses: A review. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 6, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A. On Surface Roughness and Implant Incorporation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Goteborg, Göteborg, Sweden, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Schwartz, Z.; Wieland, M.; Rupp, F.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Cochran, D.L.; Boyan, B.D. High surface energy enhances cell response to titanium substrate microstructure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 74, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Jimbo, R.; Stübinger, S.; Obrecht, M.; Dard, M.; Berner, S. Nanostructures and hydrophilicity influence osseointegration—A biomechanical study in the rabbit tibia. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, K.; Miura, T.; Kou, I.; Muramatsu, T.; Furusawa, M.; Yoshinari, M. Influence of various superhydrophilic treatments of titanium on the initial attachment, proliferation, and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T. Ultraviolet Photofunctionalization of Titanium Implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, e95–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, C.; Nygren, H.; Ohlson, K. Implantation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic titanium discs in rat tibia: Cellular reactions on the surfaces during the first 3 weeks in bone. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4759–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.P.; Salvi, G.E.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Ivanovski, S.; Donos, N.; Bosshardt, D.D. Early osseointegration to hydrophilic and hydrophobic implant surfaces in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Mandracci, P.; Mussano, F.; Abundo, R.; Fiorellini, J. Morphometric Changes Induced by Cold Argon Plasma Treatment on Osteoblasts Grown on Different Dental Implant Surfaces. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Cassinelli, C.; Götz, W.; Tarnow, D. Plasma of Argon Accelerates Murine Fibroblast Adhesion in Early Stages of Titanium Disk Colonization. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.-S.L. Modifications of Dental Implant Surfaces at the Micro- and Nano-Level for Enhanced Osseointegration. Materials 2019, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Ogawa, T. The Biological Aging of Titanium Implants. Implant. Dent. 2012, 21, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential Causes of Titanium Particle and Ion Release in Implant Dentistry: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hori, N.; Att, W.; Ueno, T.; Sato, N.; Yamada, M.; Saruwatari, L.; Suzuki, T.; Ogawa, T. Age-dependent Degradation of the Protein Adsorption Capacity of Titanium. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Olshanska, N.; De Wild, M.; Wieland, M.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 76, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennissen, H. Stabilizing ultra-hydrophilic surfaces by an exsiccation layer of salts and implications of the Hofmeistereffect. Mater. Werkst. 2010, 41, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüers, S.; Laub, M.; Jennissen, H.P. Protecting ultra- and hyperhydrophilic implant surfaces in dry state from loss of wettability. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Micarelli, C.; Lembo-Fazio, L.; Iannello, G.; Clementini, M. Microscopical and microbiologic characterization of customized titanium abutments after different cleaning procedures. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 25, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Suggested guidelines for the topographic evaluation of implant surfaces. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 331–344. [Google Scholar]
- Sawase, T.; Wennerberg, A.; Hallgren, C.; Albrektsson, T.; Baba, K. Chemical and topographical surface analysis of five different implant abutments. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duske, K.; Koban, I.; Kindel, E.; Schroeder, K.; Nebe, B.; Holtfreter, B.; Jablonowski, L.; Weltmann, K.D.; Kocher, T. Atmospheric plasma enhances wettability and cell spreading on dental implant metals. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced Bone Apposition to a Chemically Modified SLA Titanium Surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Sager, M.; Ferrari, D.; Herten, M.; Wieland, M.; Becker, J. Bone regeneration in dehiscence-type defects at non-submerged and submerged chemically modified (slactive) and conventional sla titanium implants: An immuno-histochemical study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Wieland, M.; Schwartz, Z.; Zhao, G.; Rupp, F.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Schedle, A.; Broggini, N.; Bornstein, M.M.; Buser, D.; et al. Potential of chemically modified hydrophilic surface characteristics to support tissue integration of titanium dental implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 88, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metavarayuth, K.; Sitasuwan, P.; Zhao, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q. Influence of Surface Topographical Cues on the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, M.J.; Gadegaard, N.; Tare, R.; Andar, A.; Riehle, M.O.; Herzyk, P.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Oreffo, R.O.C. The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bauer, S.; von der Mark, K.; Schmuki, P. Nanosize and Vitality: TiO2 Nanotube Diameter Directs Cell Fate. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Shang, Y.; Sui, L. State of Osseointegrated Titanium Implant Surfaces in Topographical Aspect. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 8016–8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinelis, S.; Silikas, N.; Thomas, A.; Syres, K.; Eliades, G. Surface characterization of SLActive dental implants. Eur. J. Esthet. Dent. 2012, 7, 72–92. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, M.J.P.; Richards, R.G.; Dalby, M.J. Nanotopographical modification: A regulator of cellular function through focal adhesions. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morton, D.; Bornstein, M.M.; Wittneben, J.-G.; Martin, W.C.; Ruskin, J.D.; Hart, C.N.; Buser, D. Early Loading after 21 Days of Healing of Nonsubmerged Titanium Implants with a Chemically Modified Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Surface: Two-Year Results of a Prospective Two-Center Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2010, 12, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Galli, S.; Albrektsson, T. Current knowledge about the hydrophilic and nanostructured SLActive surface. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2011, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Qahtani, M.S.; Wu, Y.; Spintzyk, S.; Krieg, P.; Killinger, A.; Schweizer, E.; Stephan, I.; Scheideler, L.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Rupp, F. UV-A and UV-C light induced hydrophilization of dental implants. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, e157–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugulu, S.; Löwe, K.; Scharnweber, D.; Schlottig, F. Preparation of superhydrophilic microrough titanium implant surfaces by alkali treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2751–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Tallarico, M.; Botticelli, D.; Alccayhuaman, K.A.A.; Martins Neto, E.C.; Xavier, S.P. Hard and soft tissue changes around implants activated using plasma of argon: A histomorphometric study in dog. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Pesce, P.; Nakajima, Y.; Yonezawa, D.; Mussano, F. Surface bio-functionalization using plasma of argon could alter microbiological and topographic surface analysis of dental implants? Ann. Anat. 2020, 230, 151489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Genova, T.; Tallarico, M.; Gautier, G.; Mussano, F.; Botticelli, D. Plasma of Argon Affects the Earliest Biological Response of Different Implant Surfaces. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupbach, P.; Glauser, R.; Bauer, S. Al2O3 Particles on Titanium Dental Implant Systems following Sandblasting and Acid-Etching Process. Int. J. Biomater. 2019, 2019, 6318429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gianfreda, F.; Antonacci, D.; Raffone, C.; Muzzi, M.; Pistilli, V.; Bollero, P. Microscopic Characterization of Bioactivate Implant Surfaces: Increasing Wettability Using Salts and Dry Technology. Materials 2021, 14, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102608
Gianfreda F, Antonacci D, Raffone C, Muzzi M, Pistilli V, Bollero P. Microscopic Characterization of Bioactivate Implant Surfaces: Increasing Wettability Using Salts and Dry Technology. Materials. 2021; 14(10):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102608
Chicago/Turabian StyleGianfreda, Francesco, Donato Antonacci, Carlo Raffone, Maurizio Muzzi, Valeria Pistilli, and Patrizio Bollero. 2021. "Microscopic Characterization of Bioactivate Implant Surfaces: Increasing Wettability Using Salts and Dry Technology" Materials 14, no. 10: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102608
APA StyleGianfreda, F., Antonacci, D., Raffone, C., Muzzi, M., Pistilli, V., & Bollero, P. (2021). Microscopic Characterization of Bioactivate Implant Surfaces: Increasing Wettability Using Salts and Dry Technology. Materials, 14(10), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102608







