Electrospun Nanofibers and Electrochemical Techniques for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electrospinning Design
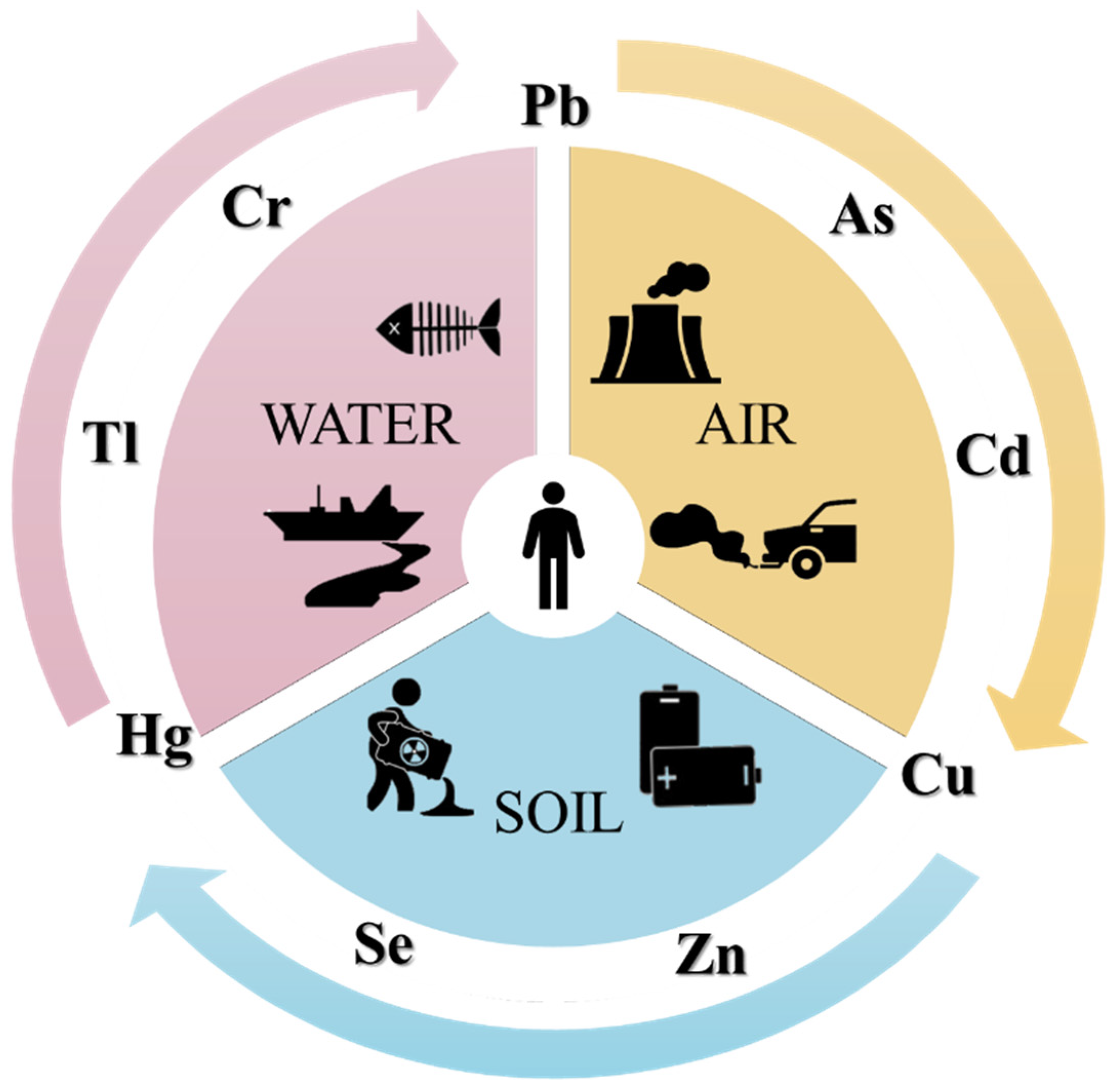
3. Contamination and Toxicity of Heavy Metals
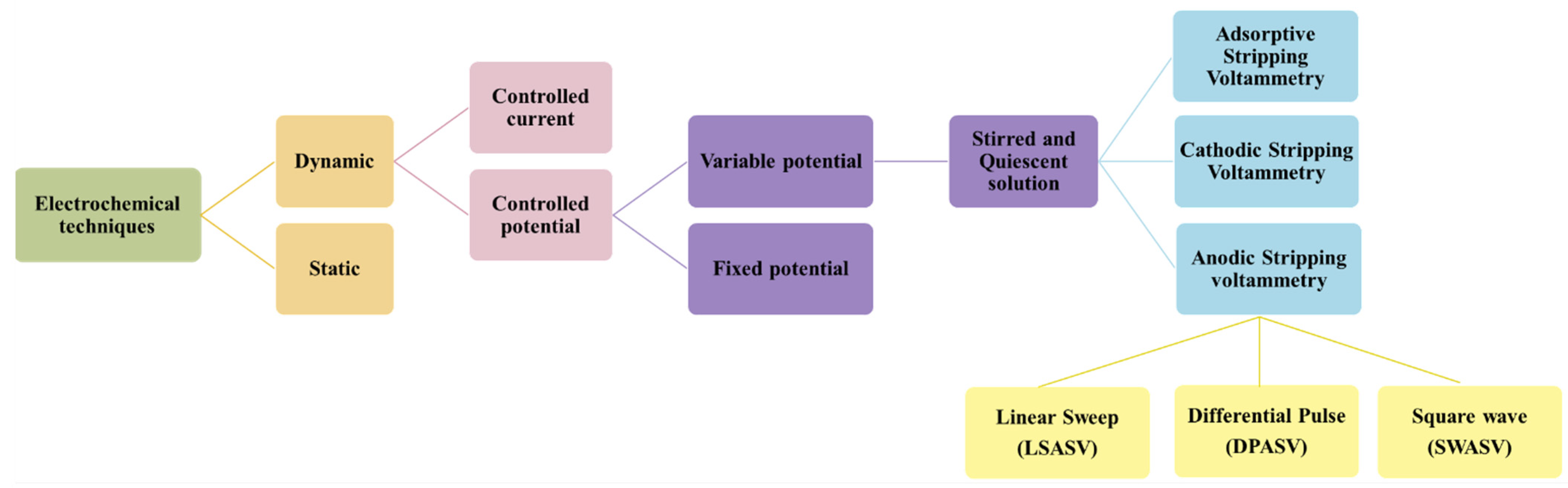
4. Electrochemical Techniques for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions
4.1. Linear Sweep Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
4.2. Differential Pulse Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
4.3. Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
5. Recent Nanofibers for HMIs Sensors
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toriello, M.; Afsari, M.; Shon, H.K.; Tijing, L.D. Progress on the Fabrication and Application of Electrospun Nanofiber Composites. Membranes 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yan, W.; Cao, H.; Song, Q.; Ding, H.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Material flow analysis on critical raw materials of lithium-ion batteries in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Sweetser, D. Recycled PET Nanofibers for Water Filtration Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malara, A.; Paone, E.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Mauriello, F.; Macario, A.; Frontera, P. Pd/Fe3O4 Nanofibers for the Catalytic Conversion of Lignin-Derived Benzyl Phenyl Ether under Transfer Hydrogenolysis Conditions. Catalysts 2019, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrández-Rives, M.; Beltrán-Osuna, Á.A.; Gómez-Tejedor, J.A.; Ribelles, J.L.G. Electrospun PVA/Bentonite Nanocomposites Mats for Drug Delivery. Materials 2017, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, R.; He, H.; Ma, J.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y. Electrospinning of Ultrafine Conducting Polymer Composite Nanofibers with Diameter Less than 70 nm as High Sensitive Gas Sensor. Materials 2018, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, P.; Trocino, S.; Donato, A.; Antonucci, P.L.; Faro, M.L.; Squadrito, G.; Neri, G. Oxygen-sensing properties of electrospun CNTs/PVAc/TiO2 composites. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2014, 10, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Frontera, P.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Antonucci, P.L. Hybrid Zeolite SAPO-34 Fibres Made by Electrospinning. Materials 2018, 11, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, P.; Kumita, M.; Malara, A.; Nishizawa, J.; Bonaccorsi, L. Manufacturing and Assessment of Electrospun PVP/TEOS Microfibres for Adsorptive Heat Transformers. Coatings 2019, 9, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freni, A.; Calabrese, L.; Malara, A.; Frontera, P.; Bonaccorsi, L. Silica gel microfibres by electrospinning for adsorption chillers. Energy 2019, 187, 115971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, L.; Fotia, A.; Malara, A.; Frontera, P. Advanced Adsorbent Materials for Waste Energy Recovery. Energies 2020, 13, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Covarrubias, J.G.; Soto-Muñoz, L.; Iglesias, A.L.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J. Electrospun Nanofibers Applied to Dye Solar Sensitive Cells: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruna, S.; Balaji, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Prakash, B.S. Electrospinning in solid oxide fuel cells—A review. Renew Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Pantò, F.; Santangelo, S.; Antonucci, P.L.; Fiore, M.; Longoni, G.; Ruffo, R.; Frontera, P. Comparative life cycle assessment of Fe2O3-based fibers as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 6786–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Roy, I.; Tice, A.; Chapman, C.; Udangawa, R.N.; Chakrapani, V.; Plawsky, J.L.; Linhardt, R.J. High-Conductivity and High-Capacitance Electrospun Fibers for Supercapacitor Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19369–19376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzio, A.; Canesi, E.V.; Bertarelli, C.; Caironi, M. Electrospun Polymer Fibers for Electronic Applications. Materials 2014, 7, 906–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qiao, R.; Su, J.; Yan, J.; Xie, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Recent Advances of Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes in the Development of Chemosensors for Heavy Metal Detection. Small 2017, 13, 1604293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balusamy, B.; Senthamizhan, A.; Uyar, T. Functionalized Electrospun Nanofibers as a Versatile Platform for Colorimetric Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Water: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musameh, M.M.; Klink, D.; Choi, J.; Truong, Y.B.; Kyratzis, I.L. Electrochemical Detection of Metals Using Thick Nanofibrous Nafion Web Modified Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, K.B.; Migliorini, F.L.; Facure, M.H.; Correa, D.S. Conductive electrospun nanofibers containing cellulose nanowhiskers and reduced graphene oxide for the electrochemical detection of mercury(II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, L.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, B.; Ni, S.; Zhang, L. Aminated electrospun nanofiber membrane as permeable reactive barrier material for effective in-situ Cr(VI) contaminated soil remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkra, R.; Kumar, P.; Bansod, B.K.S.; Bagchi, S.; Sharma, P.; Krishna, C.R. Classification of heavy metal ions present in multi-frequency multi-electrode potable water data using evolutionary algorithm. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3679–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Davide, F.; D’Amico, A.; Legin, A.; Vlasov, Y.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Selezenev, B. Multicomponent analysis on polluted waters by means of an electronic tongue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Paone, E.; Frontera, P.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Panzera, G.; Mauriello, F. Sustainable Exploitation of Coffee Silverskin in Water Remediation. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotia, A.; Malara, A.; Paone, E.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Frontera, P.; Serrano, G.; Caneschi, A. Self Standing Mats of Blended Polyaniline Produced by Electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipeaiyeda, A.R.; Ayoade, A.R. Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of heavy metals in aqueous solution and surface water preceded by co-precipitation procedure with copper(II) 8-hydroxyquinoline. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4449–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, A.A. Speciation of heavy metals in environmental water by ion chromatography coupled to ICP–MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2001, 372, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComb, J.Q.; Rogers, C.; Han, F.X.; Tchounwou, P.B. Rapid Screening of Heavy Metals and Trace Elements in Environmental Samples Using Portable X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer, A Comparative Study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, P.; Malara, A.; Stelitano, S.; Leonardi, S.G.; Bonavita, A.; Fazio, E.; Antonucci, P.; Neri, G.; Neri, F.; Santangelo, S. Characterisation and H2O2 sensing properties of TiO2 -CNTs/Pt electro-catalysts. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 170, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Leonardi, S.; Bonavita, A.; Fazio, E.; Stelitano, S.; Neri, G.; Neri, F.; Santangelo, S. Origin of the different behavior of some platinum decorated nanocarbons towards the electrochemical oxidation of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 184, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Tian, L.; Wang, Z. Portable and smart devices for monitoring heavy metal ions integrated with nanomaterials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buledi, J.A.; Amin, S.; Haider, S.I.; Bhanger, M.I.; Solangi, A.R. A review on detection of heavy metals from aqueous media using nanomaterial-based sensors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Yuan, H.; Liu, B.; Peng, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, D.-Z. Review of the distribution and detection methods of heavy metals in the environment. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5747–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gou, H.; Al-Ogaidi, I.; Wu, N. Nanostructured Sensors for Detection of Heavy Metals: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C. Effects of Working Parameters on Electrospinning BT—One-Dimensional nanostructures: Electrospinning Technique and Unique Nanofibers; Li, Z., Wang, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 15–28. ISBN 978-3-642-36427-3. [Google Scholar]
- Frontera, P.; Busacca, C.; Trocino, S.; Antonucci, P.; Faro, M.L.; Falletta, E.; Della Pina, C.; Rossi, M. Electrospinning of polyaniline: Effect of different raw sources. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 4744–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, P.; Malara, A.; Stelitano, S.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Scarpino, L.; Antonucci, P.L.; Santangelo, S. A new approach to the synthesis of titania nano-powders enriched with very high contents of carbon nanotubes by electro-spinning. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 153, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, J.E. The Heavy Elements: Chemistry, Environmental Impact and Health Effects; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; ISBN1 0080402755. ISBN2 9780080402758. ISBN3 0080348602. ISBN4 9780080348605. [Google Scholar]
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy metals” a meaningless term? (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradl, H. Chapter 1 Sources and origins of heavy metals. In Heavy Metals in the Environment: Origin, Interaction and Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, R. NW Lepp (Ed.): Effect of heavy metal pollution on plants. Vol. 1: Effects of trace metals on plant function. 352 S. Vol. 2: Metals in the environment. 257 S. Applied Science Publishers, London and New Jersey, 1981. £ 26.00 (Vol. 1) und £ 21.00 (Vol. 2). J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 1982, 145, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Gerson, B.; Subramaniam, S. The Role of Copper, Molybdenum, Selenium, and Zinc in Nutrition and Health. Clin. Lab. Med. 1998, 18, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandmann, O.; Weiss, K.H.; Kaler, S.G. Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystupa, A.; Błażewicz, A.; Kiciński, P.; Sak, J.J.; Niedziałek, J.; Załuska, W. Serum Concentrations of Selected Heavy Metals in Patients with Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis from the Lublin Region in Eastern Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Ravn-Haren, G. Acute human toxicity and mortality after selenium ingestion: A review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 58, 126435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, Y.R. An Overview of Carcinogenic Heavy Metal: Molecular Toxicity Mechanism and Prevention. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 20, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilova, J.; Arvay, J.; Vollmannova, A.; Toth, T.; Tomas, J. Environmental Contamination by Heavy Metals in Region with Previous Mining Activity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. Galanin 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edition, F. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO Chron. 2011, 38, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Tiemann, M. Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA): A Summary of the Act and Its Major Requirements; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tappero, J.W.; Cassell, C.H.; Bunnell, R.E.; Angulo, F.J.; Craig, A.; Pesik, N.; Dahl, B.A.; Ijaz, K.; Jafari, H.; Martin, R. US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Its Partners’ Contributions to Global Health Security. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, S5–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrill, A.J.; Reily, N.E.; Macpherson, J. V Addressing the practicalities of anodic stripping voltammetry for heavy metal detection: A tutorial review. Analyst 2019, 144, 6834–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazerie, I.; Geneste, F. Coupling of Anodic Stripping Voltammetry with Sampled-Current Voltammetry on an Electrode Array: Application to Lead Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouhamed, N.; Cheikhou, K.; Elhadji, G.; Bagha, D.M.; Guèye, M.-D.C.; Tzedakis, T. Determination of Lead in Water by Linear Sweep Anodic Stripping Voltammetry (LSASV) at Unmodified Carbon Paste Electrode: Optimization of Operating Parameters. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 9, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khun, N.; Liu, E. Linear sweep anodic stripping voltammetry of heavy metals from nitrogen doped tetrahedral amorphous carbon thin films. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukur, S.A.; Yusof, N.A.; Hajian, R. Linear sweep anodic stripping voltammetry: Determination of Chromium (VI) using synthesized gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrode. J. Chem. Sci. 2015, 127, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.M.; Van Hop, N.; Luyen, N.D.; Phong, N.H.; Thanh, T.; Toan, T. Simultaneous Determination of Zn (II), Cd (II), Pb (II), and Cu (II) Using Differential Pulse Anodic Stripping Voltammetry at a Bismuth Film-Modified Electrode. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisankar, P.; Vedhi, C.; Selvanathan, G.; Arumugam, P. Differential pulse stripping voltammetric determination of heavy metals simultaneously using new polymer modified glassy carbon electrodes. Microchim. Acta 2008, 163, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, T.; Araújo, D.; Marchini, L.; Moreti, A.; Olinda, R. Detection of metals by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) in pollen collected from a fragment of the atlantic forest in Piracicaba/SP. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2013, 8, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Su, Z.; Qin, C.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Yao, S.; Deng, L.; Xie, Q.; et al. Square wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead(II) using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a lead ionophore and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim. Acta 2011, 176, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, O.A.; Ghandour, M. Square-wave stripping voltammetry for direct determination of eight heavy metals in soil and indoor-airborne particulate matter. Environ. Res. 2005, 97, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, B.; Jiménez, F.N.; Giraldo, L.R. Potentiostat prototype with applications in electrochemical processes. Entre Cienc. Ing. 2016, 10, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Miao, Y.-E.; Liu, T. Electrospun fibrous membranes for efficient heavy metal removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, K.; He, N. Progress on sensors based on nanomaterials for rapid detection of heavy metal ions. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2017, 60, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanarat, P.; Rangkupan, R.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. An electrochemical sensor based on graphene/polyaniline/polystyrene nanoporous fibers modified electrode for simultaneous determination of lead and cadmium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhu, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Ma, H. Synthesis of a novel electrode material containing phytic acid-polyaniline nanofibers for simultaneous determination of cadmium and lead ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 947, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, J.; Peng, B.; Xie, X.; Lai, C.; Long, B.; Zhu, J. Determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ Based on Mesoporous Carbon Nitride/Self-Doped Polyaniline Nanofibers and Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Ge, Y.; Dai, Y.; Shang, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, J. Size-tunable polyaniline nanotube-modified electrode for simultaneous determination of Pb(II) and Cd(II). Electrochim. Acta 2018, 268, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Rodthongkum, N.; Cate, D.M.; Volckens, J.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Sensitive electrochemical sensor using a graphene–polyaniline nanocomposite for simultaneous detection of Zn(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II). Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 874, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narouei, F.H.; Livernois, L.; Andreescu, D.; Andreescu, S. Highly sensitive mercury detection using electroactive gold-decorated polymer nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jia, J.; Wang, J. Simultaneous determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry based on graphite nanofibers–Nafion composite modified bismuth film electrode. Talanta 2010, 83, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, T.; Han, D.; Rusinek, C.; Steckl, A.J.; Heineman, W.R. Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Modified Electrodes for Stripping Voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9315–9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, N.; Shao, S. Development of a new electrochemical sensor for determination of Hg(II) based on Bis(indolyl)methane/Mesoporous carbon nanofiber/Nafion/glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ràfols, C.P.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Ariño, C.; Esteban, M. Glutathione modified screen-printed carbon nanofiber electrode for the voltammetric determination of metal ions in natural samples. Talanta 2016, 155, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, T.; Zou, M.; Zhang, M.; Du, M. Facile and green fabrication of size-controlled AuNPs/CNFs hybrids for the highly sensitive simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 196, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.E.; Heineman, W.R.; Sagle, L.B.; Meyyappan, M.; Koehne, J.E. Carbon nanofiber electrode array for the detection of lead. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 73, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oularbi, L.; Turmine, M.; El Rhazi, M. Electrochemical determination of traces lead ions using a new nanocomposite of polypyrrole/carbon nanofibers. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 3289–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Ma, P.; Duan, F.; Dong, W.; Du, M. A self-supported electrochemical sensor for simultaneous sensitive detection of trace heavy metal ions based on PtAu alloy/carbon nanofibers. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6801–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Luo, J.; Mamat, X.; Sambasivam, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Wågberg, T.; Hu, G. Selective voltammetric determination of Cd(II) by using N,S-codoped porous carbon nanofibers. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oularbi, L.; Turmine, M.; Salih, F.E.; El Rhazi, M. Ionic liquid/carbon nanofibers/bismuth particles novel hybrid nanocomposite for voltammetric sensing of heavy metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhou, Z.; Qin, D.; Huang, W.; Feng, J.; Tang, T.; Hu, G.; Li, L. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Electrospun Three-Dimensional Carbon Nanofibers to Determine Trace Levels of Cu(II). Sci. Adv. Mater. 2020, 12, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Ge, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Liu, J. AuNPs-polyaniline nanosheet array on carbon nanofiber for the determination of As(III). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Luo, Z.; Ma, X.; Fan, X.; Xue, L.; Lin, X.; Chen, S. High Sensitive Sensor Fabricated by Reduced Graphene Oxide/Polyvinyl Butyral Nanofibers for Detecting Cu (II) in Water. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, G.; Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Yang, J. Fabrication of electrospun ZnO nanofiber-modified electrode for the determination of trace Cd(II). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 234, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.H.B.; Rechotnek, F.; da Silva, E.P.; de Sousa Marques, V.; Rubira, A.F.; Silva, R.; Lourenço, S.A.; Muniz, E.C. A sensitive electrochemical sensor for Pb2+ ions based on ZnO nanofibers functionalized by L-cysteine. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Su, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Electrospun amino-containing organosilica gel nanofibers for the ultrasensitive determination of Cu(II). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
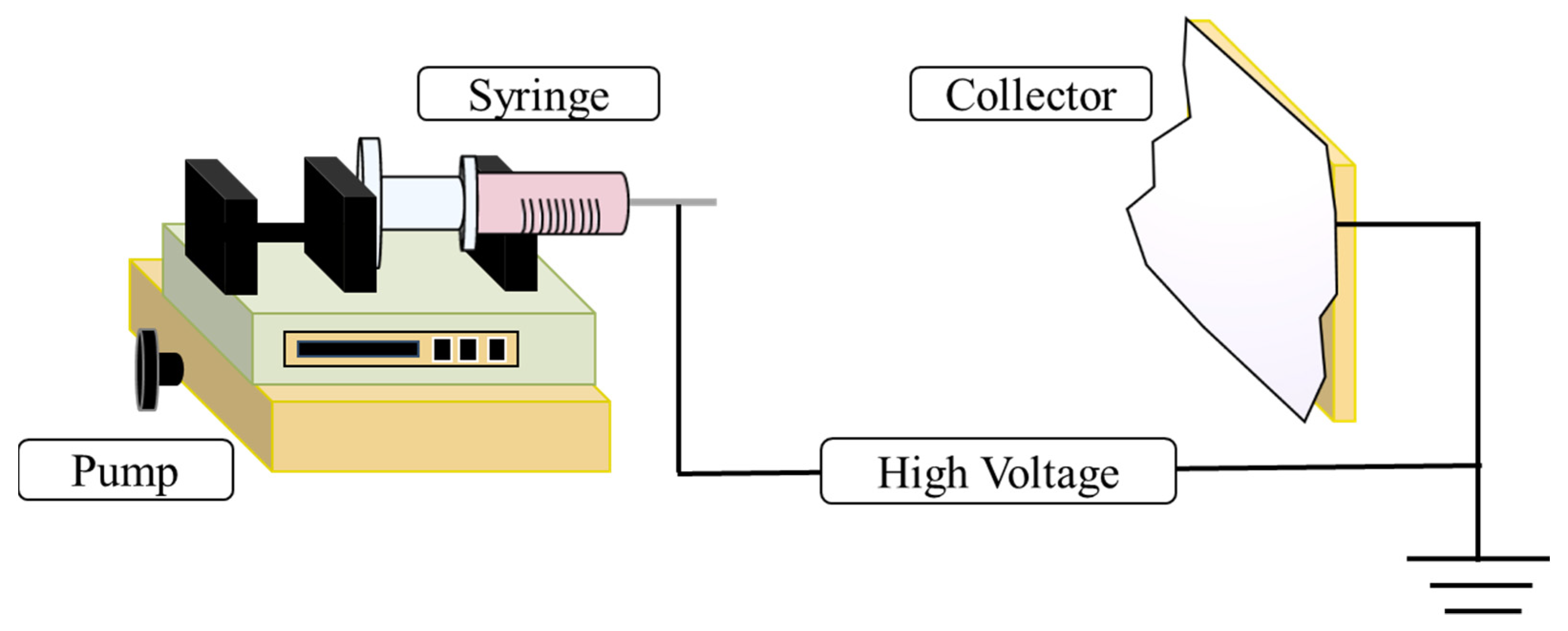



| Electrospinning Working Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solution | Process | Ambient |
| Molecular weight Concentration Viscosity Conductivity Surface tension | Applied voltage Flow rate Diameter of the needle Tip-collector distance | Temperature Humidity |
| Heavy Metals | Sources | Toxic Impact on Human Health | Permissible Limits [49,50] |
|---|---|---|---|
| As | drinking-water and food; industrial processes; tobacco | pigmentation changes, skin lesions, hyperkeratosis | 10 μg/L |
| Cd | corrosion of galvanized pipes, erosion of natural deposits, discharge from metal refineries, runoff from waste batteries and paints | renal tubular dysfunction, osteoporosis, acute pneumonitis, cancer | 3 μg/L |
| Cr | coal and oil combustion; electroplating; leather tanning; industrial processes, tobacco | contact dermatitis, hemolysis, renal diseases, allergic reaction, cancer | 50 μg/L |
| Pb | drinking-water and food; lead-containing pipes; children’s toys; cosmetics | microcytic anemia; nephropathy; immune system diseases; reproductive system diseases; developmental system disease | 10 μg/L |
| Hg | accidents, environmental pollution, dental care, preventive medical practices, industrial and agricultural operations, fish consumption | calcium homeostasis; neurological diseases, corrosive to skin, corrosive to eyes, cancer, corrosive to the gastrointestinal tract | 6 μg/L |
| Tl | drinking-water and food; air-borne contamination (fly ash) | gaseous emission of cement factories, coal-burning power plants, metal sewers | 0.5 µg/L |
| Se | natural deposits releases from copper smelting | endocrine function, hepatotoxicity, and gastrointestinal disturbances | 40 μg/L |
| Cu | industrial discharges, copper salts, plumbing material | brain and kidney damage, chronic anemia, stomach and intestine irritation | 2 mg/L |
| Zn | discharges of smelter slags and wastes, mine tailings, coal and bottom fly ash, fertilizers | dizziness, fatigue | 5 mg/L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malara, A.; Fotia, A.; Paone, E.; Serrano, G. Electrospun Nanofibers and Electrochemical Techniques for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Materials 2021, 14, 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113000
Malara A, Fotia A, Paone E, Serrano G. Electrospun Nanofibers and Electrochemical Techniques for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Materials. 2021; 14(11):3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113000
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalara, Angela, Antonio Fotia, Emilia Paone, and Giulia Serrano. 2021. "Electrospun Nanofibers and Electrochemical Techniques for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions" Materials 14, no. 11: 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113000
APA StyleMalara, A., Fotia, A., Paone, E., & Serrano, G. (2021). Electrospun Nanofibers and Electrochemical Techniques for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Materials, 14(11), 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113000









