Preparation and Characterization of Narrow Size Distribution PMSQ Microspheres for High-Frequency Electronic Packaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
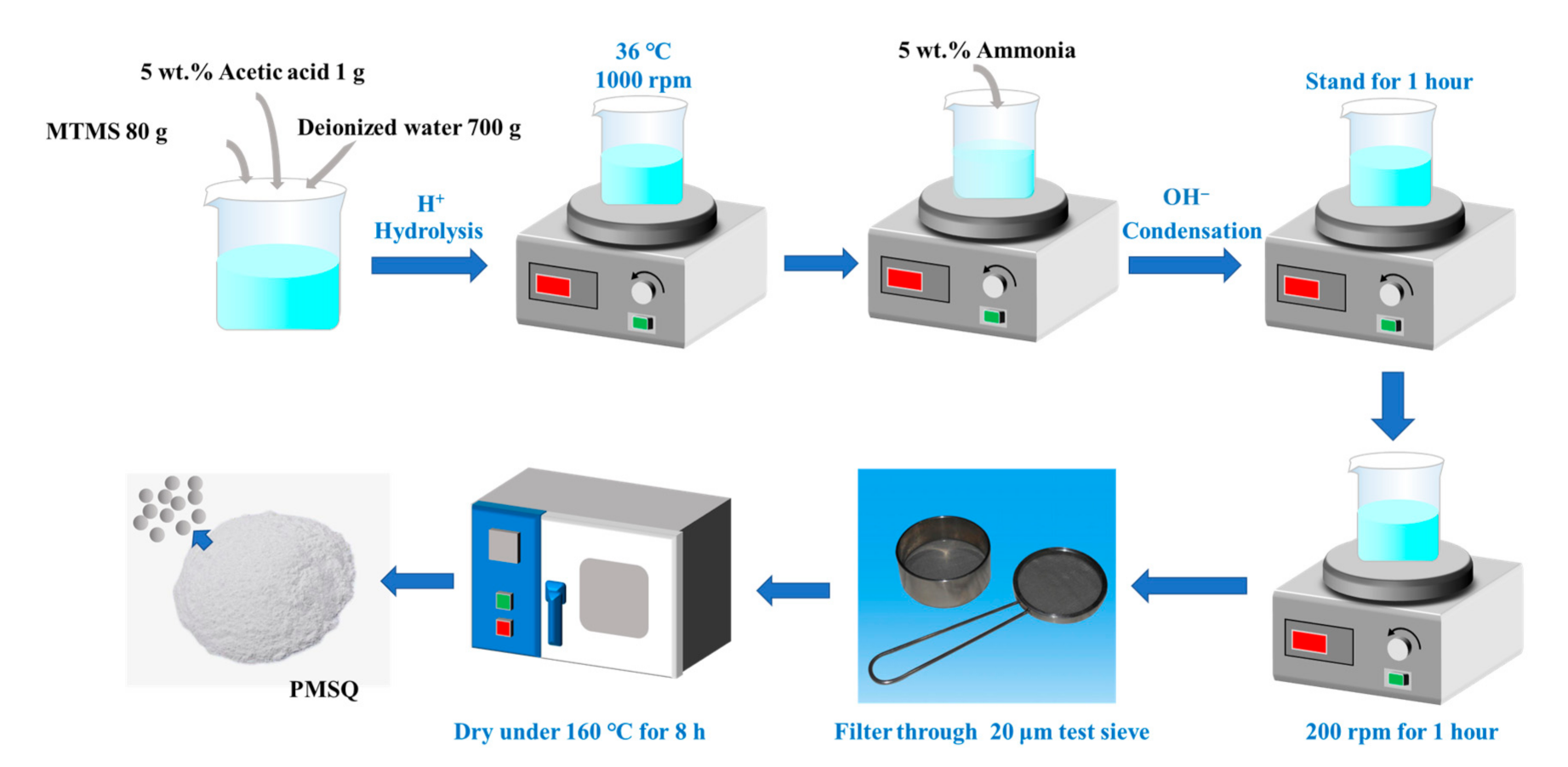
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology-Controlled Synthesis of PMSQ Microspheres
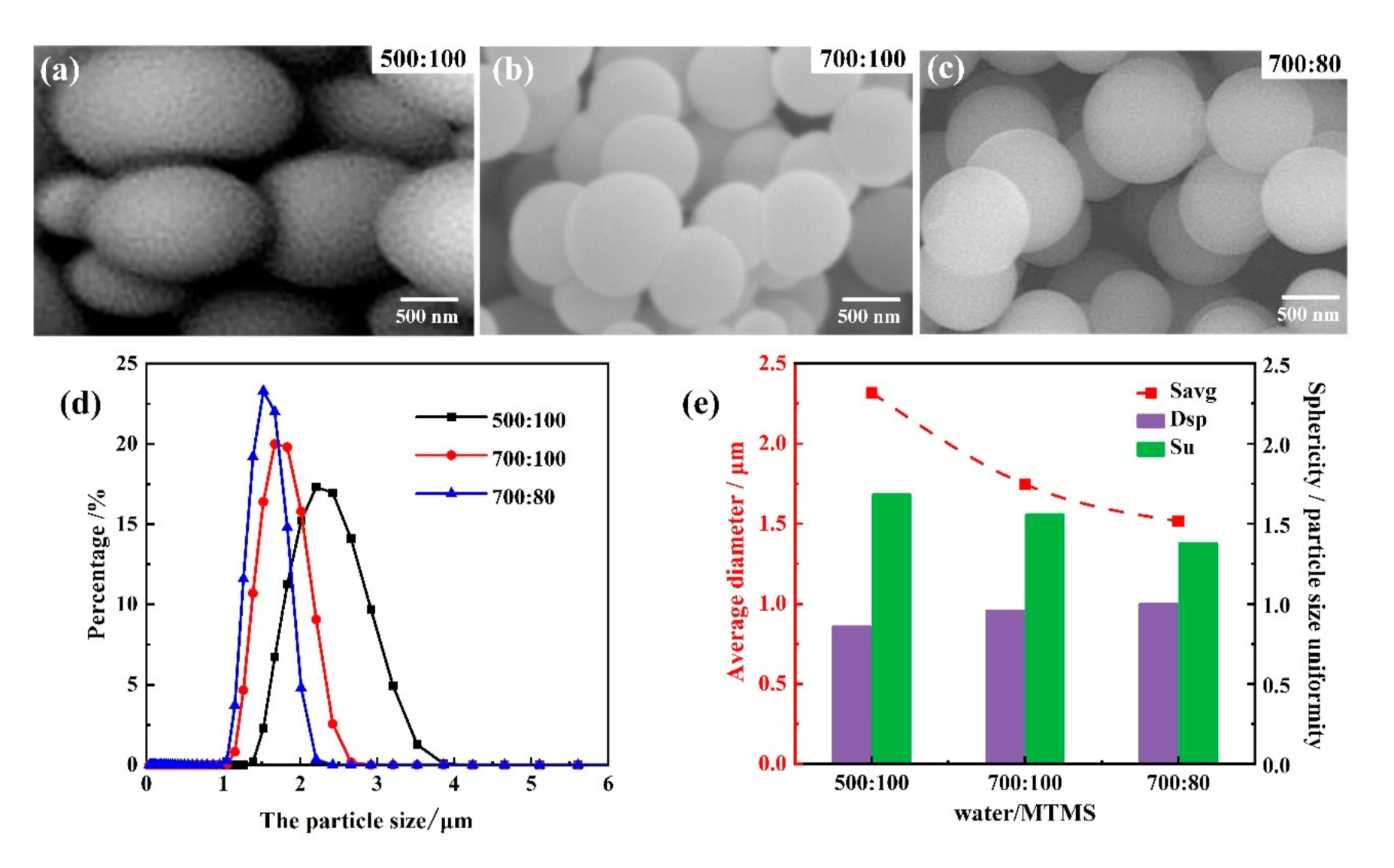
3.1.1. Influence of Water/MTMS Ratios
3.1.2. Influence of Reaction Temperatures
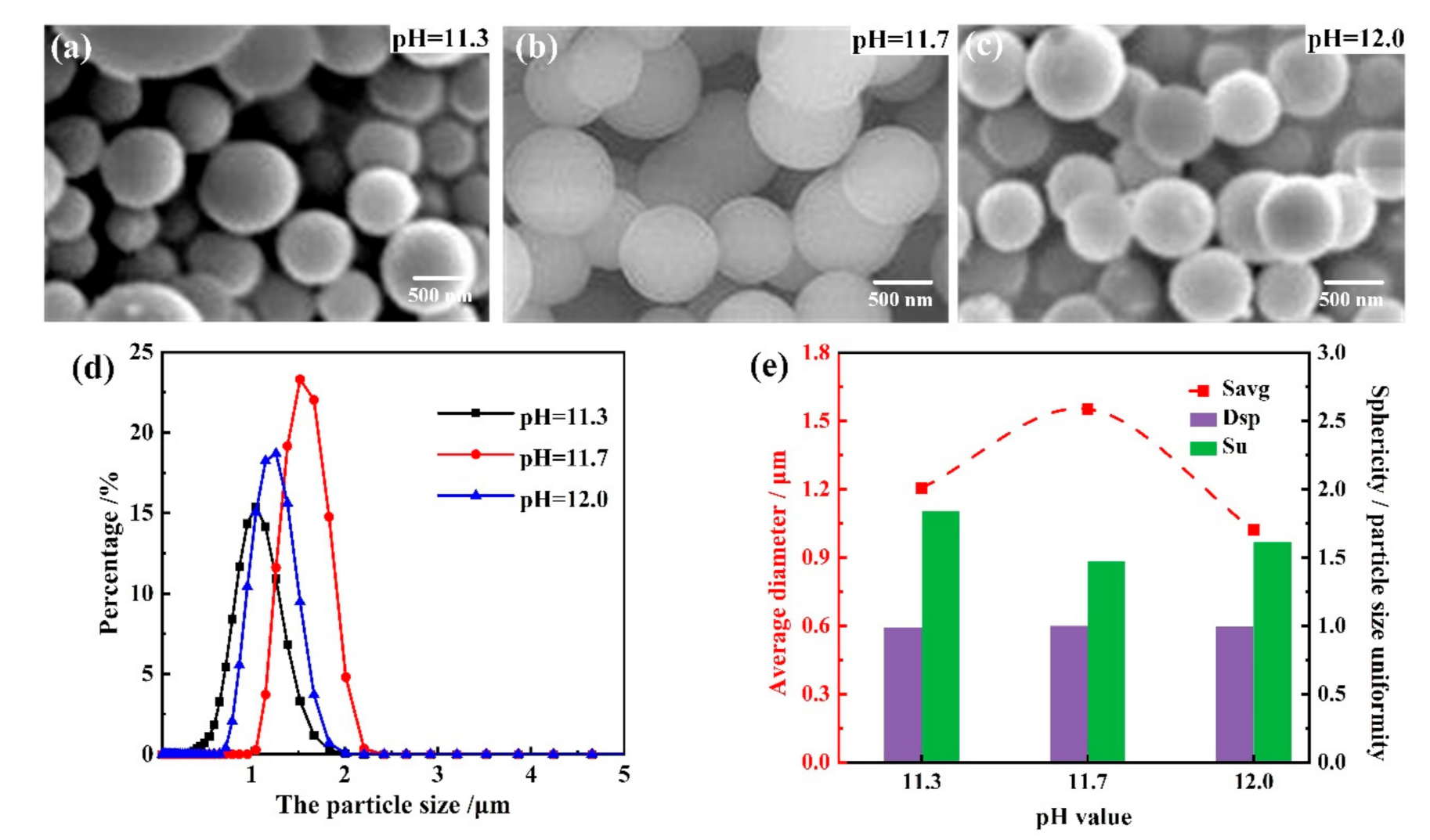
3.1.3. Influence of the Base Catalyst Concentrations
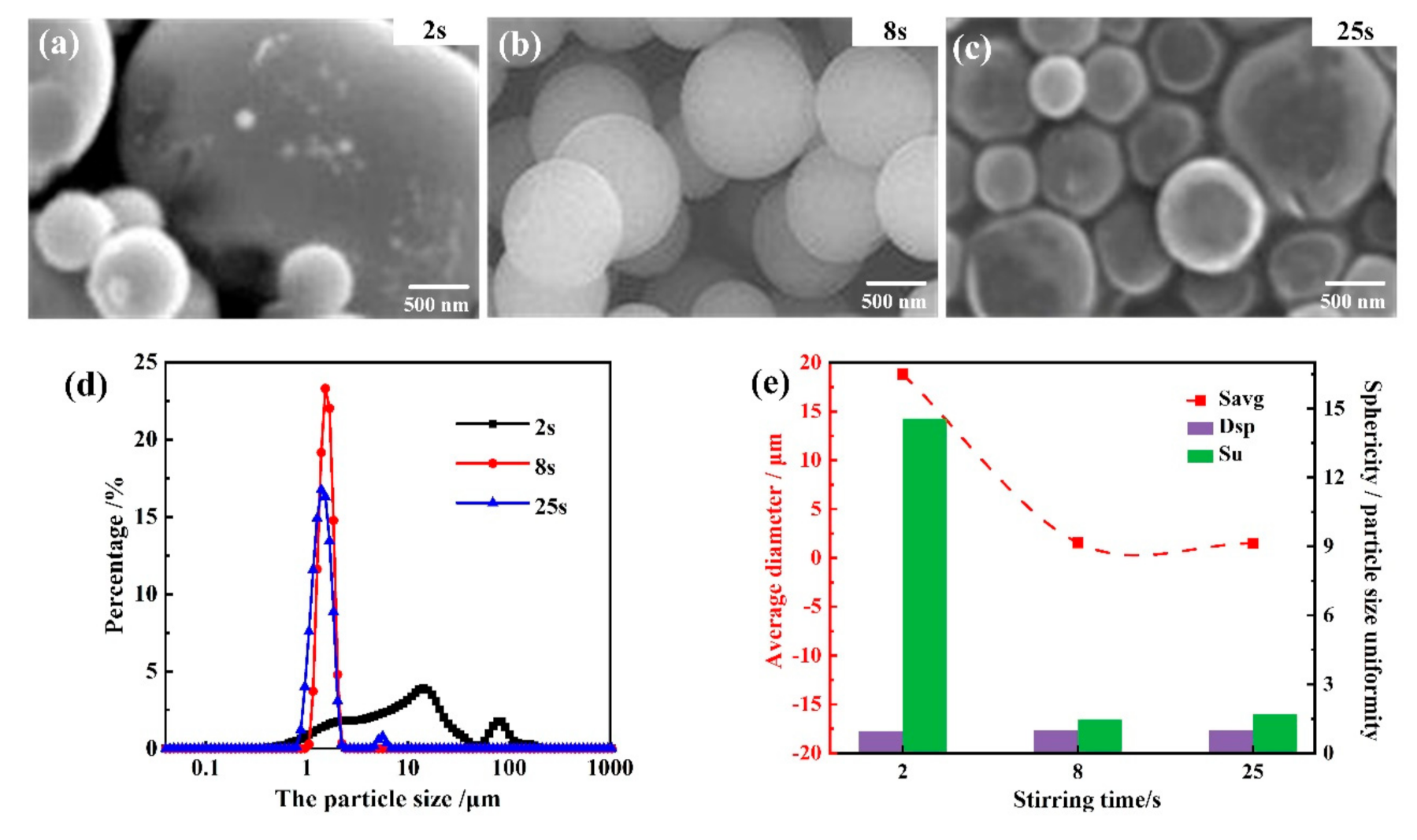
3.1.4. Influence of High-Speed Stirring Time
3.1.5. Summary of the Influence of Different Reaction Conditions on the PMSQ Microspheres
3.2. Structure of the PMSQ Microparticles
3.3. Thermal Stability of PMSQ Microspheres
3.4. Dielectric Properties of PMSQ Microspheres at High Frequency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Apeldorn, T.; Keilholz, C.; Wolff-Fabris, F.; Altstadt, V. Dielectric properties of highly filled thermoplastics for printed circuit boards. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 3758–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, K.P.; Rajesh, S.; Nijesh, K.J.; Ratheesh, R. Effect of Particle Size on the Microwave Dielectric Properties of Alumina-Filled PTFE Substrates. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2010, 7, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, B.; Sanapala, R.; Das, D.; Pecht, M.; Huang, C.Y.; Tsai, M.Y. Comparison of Printed Circuit Board Property Variations in Response to Simulated Lead-Free Soldering. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2010, 33, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenojar, J.; Tutor, J.; Ballesteros, Y.; del Real, J.C.; Martinez, M.A. Erosion-wear, mechanical and thermal properties of silica filled epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 120, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.; Yoon, H. Filler effect of low loss dielectricity in printed circuit board material. J. Electroceram. 2009, 23, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.L.; Peng, X. Space charge and dielectric behavior of epoxy composite with SiO2-Al2O3 nano-micro fillers at varied temperatures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Veena, M.G.; Renukappa, N.M.; Shivakumar, K.N.; Seetharamu, S. Dielectric properties of nanosilica filled epoxy nanocomposites. Sadhana Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 2016, 41, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yao, Y.M.; Zeng, X.L.; Guo, K.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.B. The effect of interfacial state on the thermal conductivity of functionalized Al2O3 filled glass fibers reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 69, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickelbick, G. Silsesquioxanes. In Functional Molecular Silicon Compounds I; Structure and Bonding; Scheschkewitz, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 155, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Devaraju, S.; Vengatesan, M.R.; Selvi, M.; Kumar, A.A.; Alagar, M. Synthesis and characterization of bisphenol-A ether diamine-based polyimide POSS nanocomposites for low K dielectric and flame-retardant applications. High Perform. Polym. 2012, 24, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Guan, D. Preparation and properties of epoxy resin/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane hybrid materials. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Jiang, L.; Loh, X.J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Li, Z. Biodegradable polyester unimolecular systems as emerging materials for therapeutic applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5488–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-G.; Park, J.-H.; Oh, C.; Oh, S.-G.; Kim, Y.C. Preparation of highly monodispersed hybrid silica spheres using a one-step sol-gel reaction in aqueous solution. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10875–10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaraiah, S.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.W. Preparation and characterization of surface-functionalized polysilsesquioxane hard spheres in aqueous medium. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6195–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.-S.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Shen, X.; Zhu, K.-T.; Wu, J.-L. One-step synthesis of highly monodisperse hybrid silica spheres in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hou, Y.; Zha, J.; Xin, Z. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Monodispersed Poly(3-mercaptopropylsilsesquioxane) Microspheres by a Two-Step Sol-Gel Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14659–14663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Shim, S.-B.; Lee, Y.-G.; Oh, S.-G. Effects of the concentrations of precursor and catalyst on the formation of monodisperse silica particles in sol-gel reaction. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2064–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Deng, T.; Zhang, G. Preparation and size control of highly monodisperse vinyl functionalized silica spheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xin, Z. Synthesis and characterization of polymethylsilsesqui oxane microspheres by the two-step sol-gel method. e-Polymers 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, F.; Ha, C.-S. Multifunctional materials based on polysilsesquioxanes. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Li, C.; Sun, G.; Zhang, G.; Mu, Z. Morphology-controlled synthesis of polymethylsilsesquioxane (PMSQ) microsphere and its applications in enhancing the thermal properties and flow improving ability of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Powder Technol. 2018, 329, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Hu, S. Tailoring structural and physical properties of polymethylsilsesquioxane aerogels by adjusting NH3·H2O concentration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 258, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, D.; Duan, Y.; Wang, H. Highly monodisperse polysilsesquioxane spheres: Synthesis and application in cotton fabrics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 392, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Char, K.; Rhee, H.W.; Ro, H.W.; Yoo, D.Y.; Yoon, D.Y. Synthetic control of molecular weight and microstructure of processible poly(methylsilsesquioxane)s for low-dielectric thin film applications. Polymer 2001, 42, 9085–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunji, T.; Tanikawa, S.; Arimitsu, K.; Abe, Y. Preparation of polymethylsilsesquioxanes by the base-catalyzed hydrolytic polycondensation of triisopropoxy(methyl)silane. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 3623–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, K.; He, H.; Xu, D.; Ge, R.; Meng, Z.; Jia, X.; Yu, X. Ultra low dielectric constant polysilsesquioxane films using T8(Me4NO)8 as porogen. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, 4768–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, W.-P.; Sheen, Y.-C.; Wei, S.-M.; Yen, M.-Y.; Ma, C.-C.M. Structural control of silane-grafted polymethylsilsesquioxane. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.J.; Kim, S.; Char, K. Preparation of nanoporous poly(methyl silsesquioxane) thin films derived from chemically linked carbon cages. Macromol. Res. 2005, 13, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Choi, S.S.; Baek, K.Y.; Lee, E.C.; Hong, S.M.; Lee, J.C.; Hwang, S.S. Structural analysis of high molecular weight PMSQs and their related properties for interlayer dielectric (ILD) application. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Ma, W. Silsesquioxane Oligomer as Replacement of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane and Its Homo-Blended Polysilsesquioxane Flexible Thin Film with Low Dielectric Constant. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2019, 61, 323–333. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa, M.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Simazoe, H. Silica Filler and Method for Its Production. U.S. Patent 5,883,746[P], 10 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Laidler, K.J. The development of the arrhenius equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1984, 61, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.J.; Searles, D.J.; Mittag, E. Fluctuation theorem for Hamiltonian systems: Le Chatelier’s principle. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 05110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.S.; Ro, H.W.; Nguyen, C.V.; Jaffe, R.L.; Yoon, D.Y. Infrared spectroscopy study of microstructures of poly(silsesquioxane)s. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.F.; Vogt, L.H.; Katchman, A.; Eustance, J.W.; Kiser, K.M. Double chain polymers of phenylsilsesquioxane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 6194–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Kajiwara, T.; Abe, Y.; Gunji, T. Synthesis and structure of ladder polymethylsilsesquioxanes from sila-functionalized cyclotetrasiloxanes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2010, 695, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, M.; Suto, A.; Matsumoto, T. Laddersiloxanes—Silsesquioxanes with defined ladder structure. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2013, 82, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, A.; Almangano, M.; Portugal, A.A.; Patricio, R.; Simoes, P.N. Methylsilsesquioxane-Based Aerogel Systems-Insights into the Role of the Formation of Molecular Clusters. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 4079–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baatti, A.; Erchiqui, F.; Bebin, P.; Godard, F.; Bussieres, D. A two-step Sol-Gel method to synthesize a ladder polymethylsilsesquioxane nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvola, A.H.; Alanen, E. Studies of Mixing Formulas in the Complex-Plane. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 1991, 29, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebara, H.; Inoue, T.; Hashimoto, O. Measurement method of complex permittivity and permeability for a powdered material using a waveguide in microwave band. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2006, 7, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample Serial No. | Reaction Condition | Morphology Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water/MTMS (g) | Temperatures (℃) | Acetic Acid/Ammonia (g) | Stirring Time (s) | Sphericity | Average Particle Size (µm) | Particle Size Uniformity | |
| 1 | 700:80 | 36 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.998 | 1.52 | 1.38 |
| 2 | 500:100 | 36 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.856 | 2.32 | 1.68 |
| 3 | 700:100 | 36 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.956 | 1.75 | 1.56 |
| 4 | 700:80 | 10 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.949 | 3.57 | 2.81 |
| 5 | 700:80 | 25 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.968 | 2.96 | 2.94 |
| 6 | 700:80 | 45 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.994 | 1.17 | 1.65 |
| 7 | 700:80 | 60 | 1:25 | 8 | 0.982 | 1.11 | 1.60 |
| 8 | 700:80 | 36 | 1:5 | 8 | 0.986 | 1.21 | 1.84 |
| 9 | 700:80 | 36 | 1:100 | 8 | 0.991 | 1.02 | 1.62 |
| 10 | 700:80 | 36 | 1:25 | 2 | 0.941 | 18.8 | 14.6 |
| 11 | 700:80 | 36 | 1:25 | 25 | 0.998 | 1.49 | 1.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, C.; Gao, W.; Cheng, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Narrow Size Distribution PMSQ Microspheres for High-Frequency Electronic Packaging. Materials 2021, 14, 4233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154233
Meng G, Li Y, Wang Z, Pan C, Gao W, Cheng Y. Preparation and Characterization of Narrow Size Distribution PMSQ Microspheres for High-Frequency Electronic Packaging. Materials. 2021; 14(15):4233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154233
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Guodong, Yimeng Li, Zhengdong Wang, Cheng Pan, Wenwu Gao, and Yonghong Cheng. 2021. "Preparation and Characterization of Narrow Size Distribution PMSQ Microspheres for High-Frequency Electronic Packaging" Materials 14, no. 15: 4233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154233
APA StyleMeng, G., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Pan, C., Gao, W., & Cheng, Y. (2021). Preparation and Characterization of Narrow Size Distribution PMSQ Microspheres for High-Frequency Electronic Packaging. Materials, 14(15), 4233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154233






