Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Weathered Halloysite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Characterization of Weathered Halloysite
2.3. Chemical Analyses
2.4. Experimental Procedures
2.4.1. Batch Test
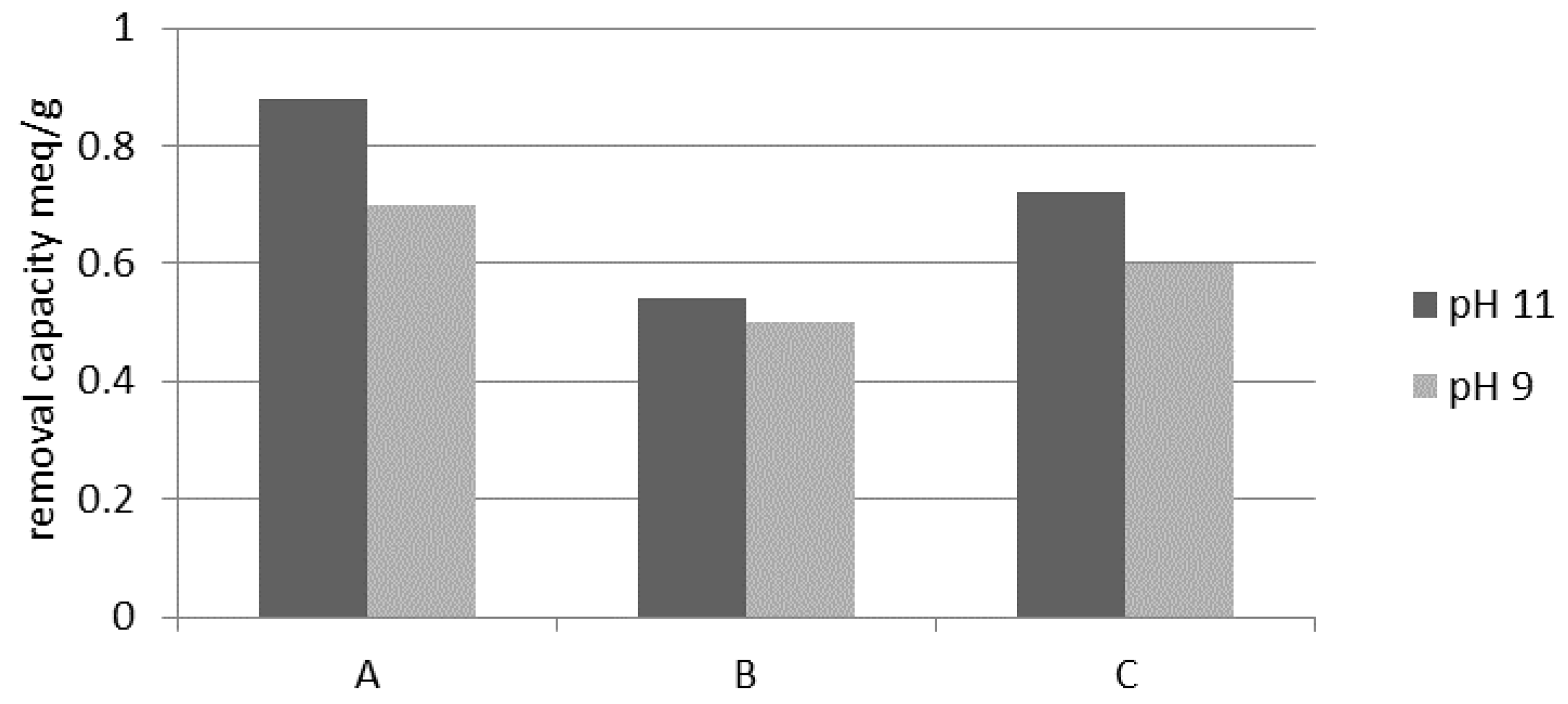
2.4.2. Regeneration
2.4.3. Column Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Batch Study
3.1.1. Influence of Contact Time and Initial NH4+ Concentration
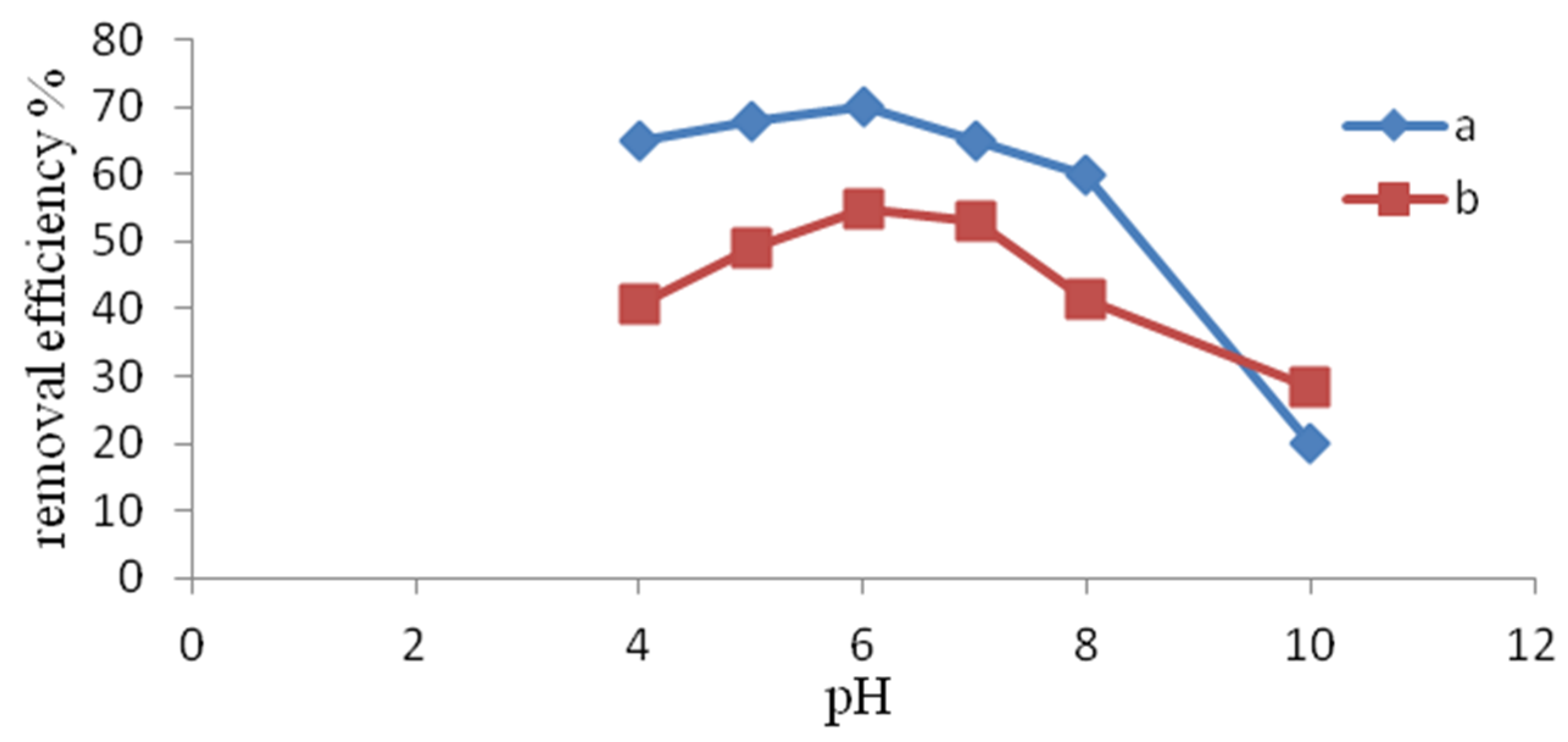
3.1.2. Influence of pH
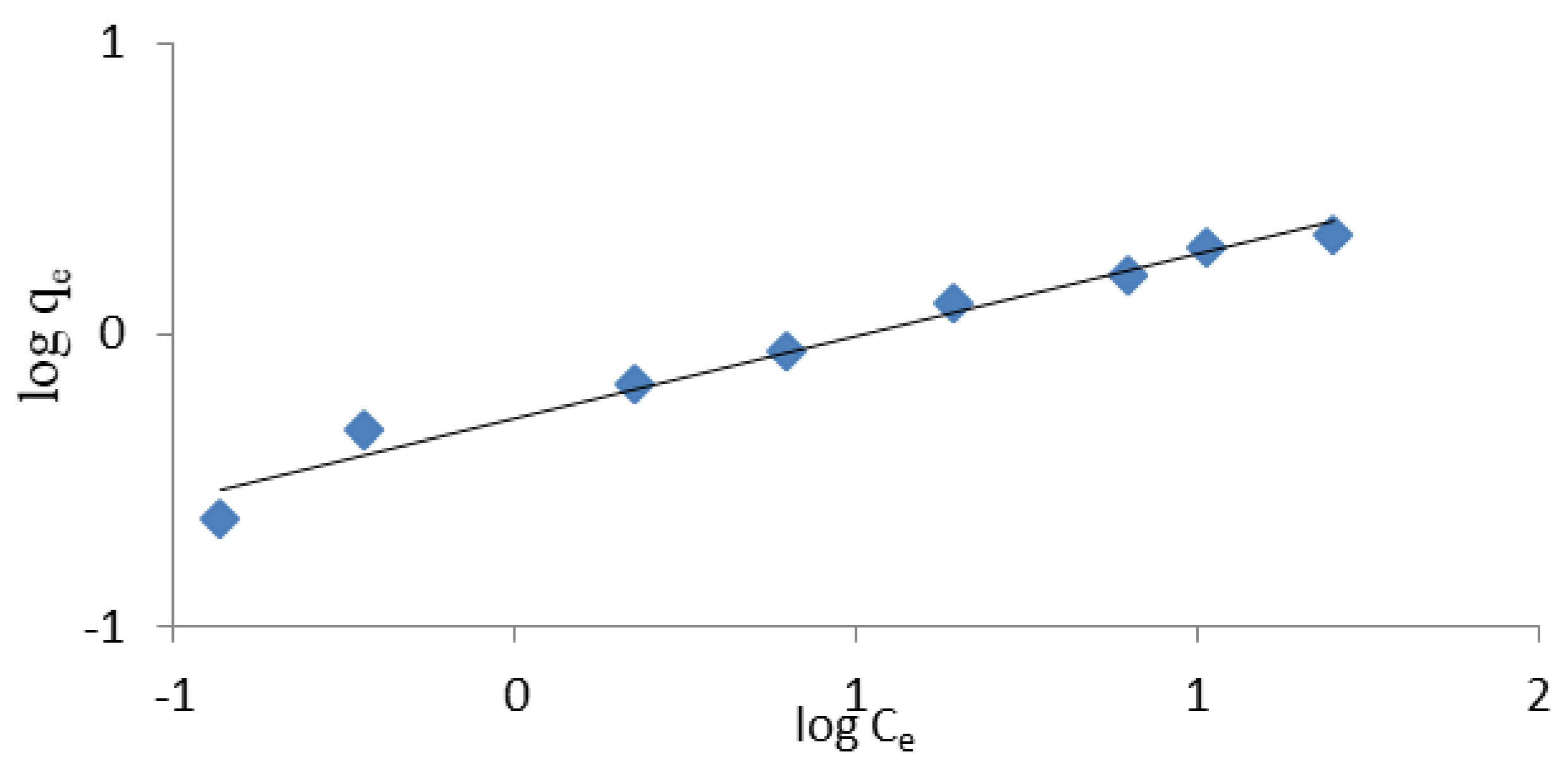
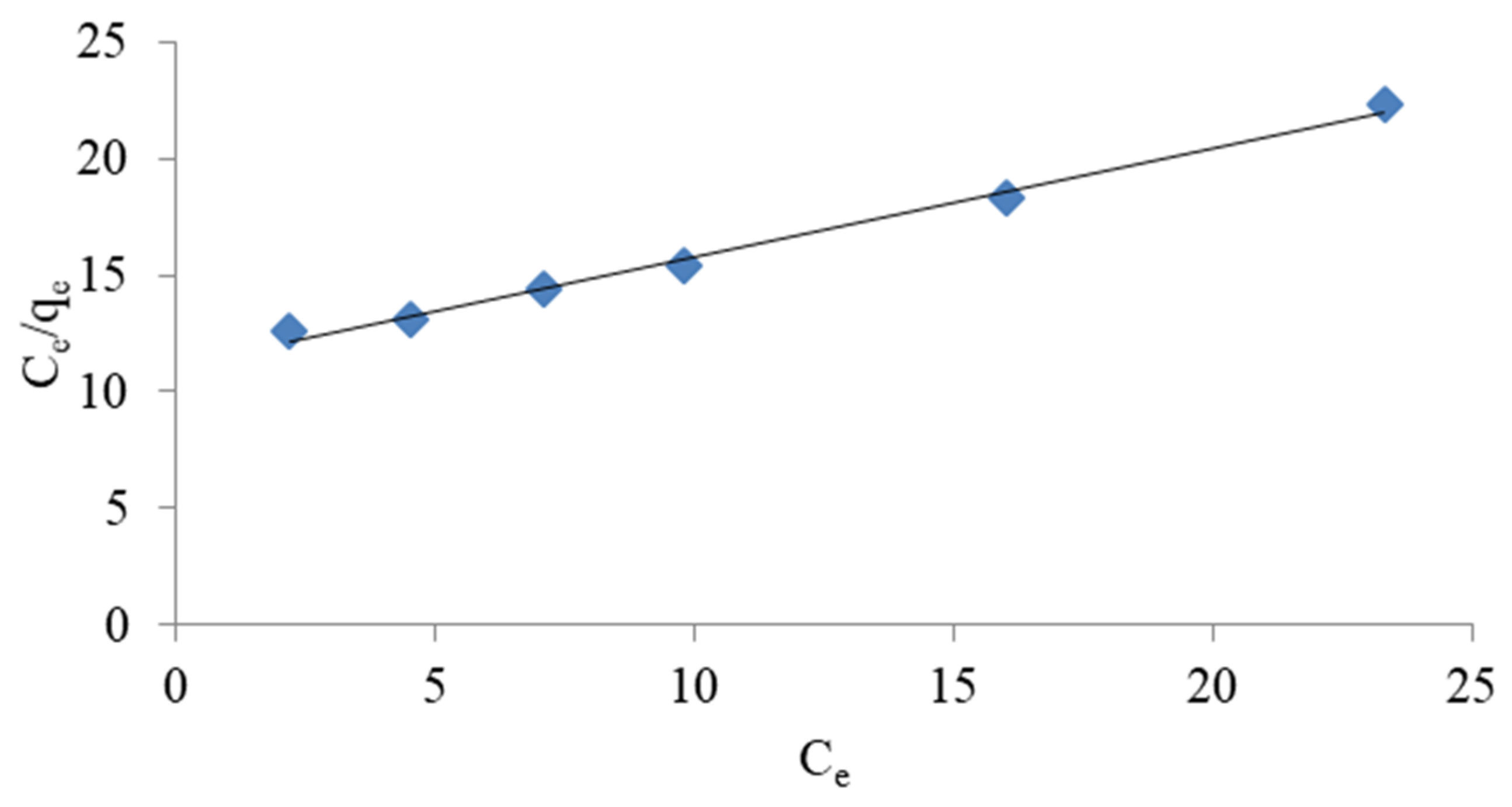
3.1.3. Ammonium Exchange Isotherm
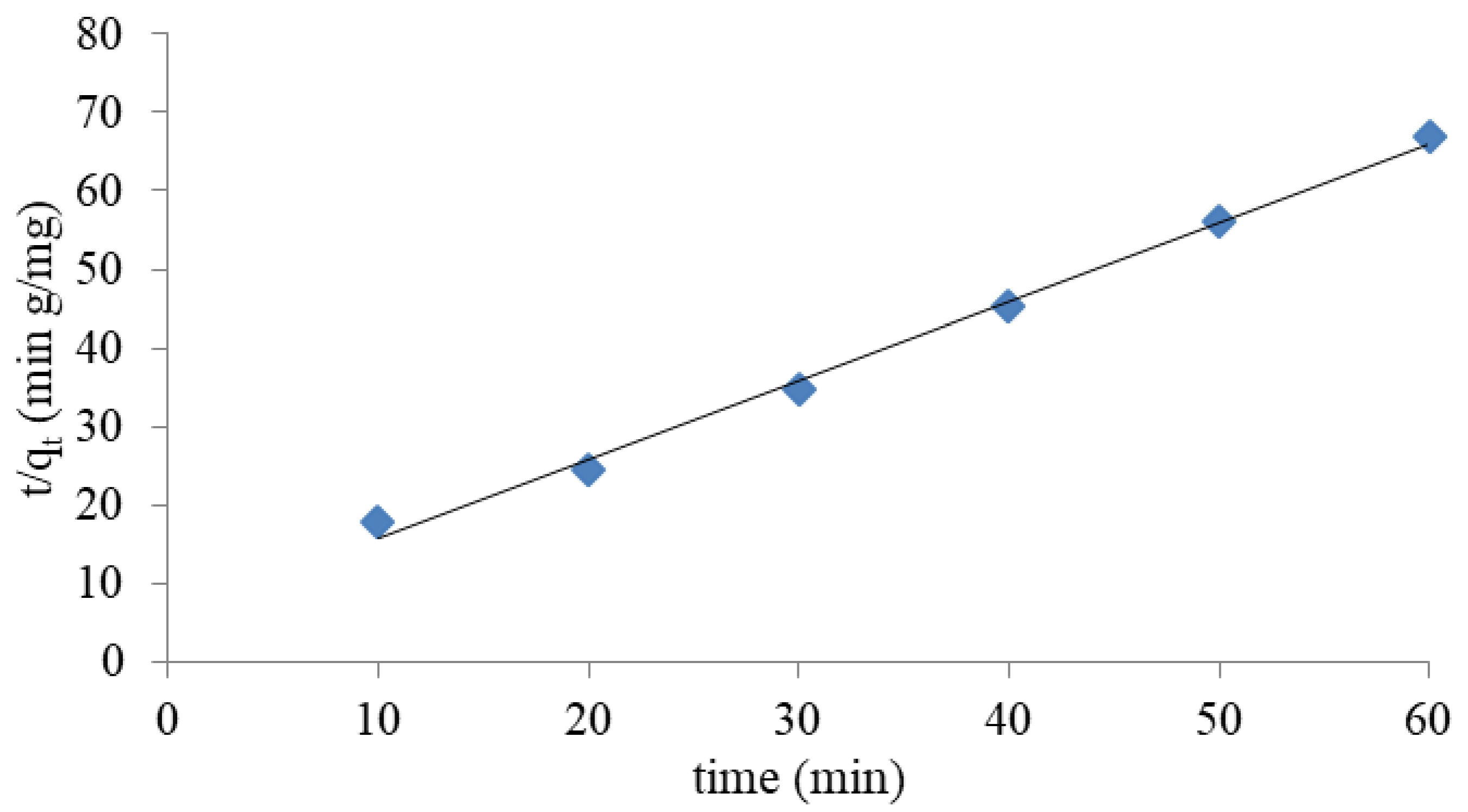
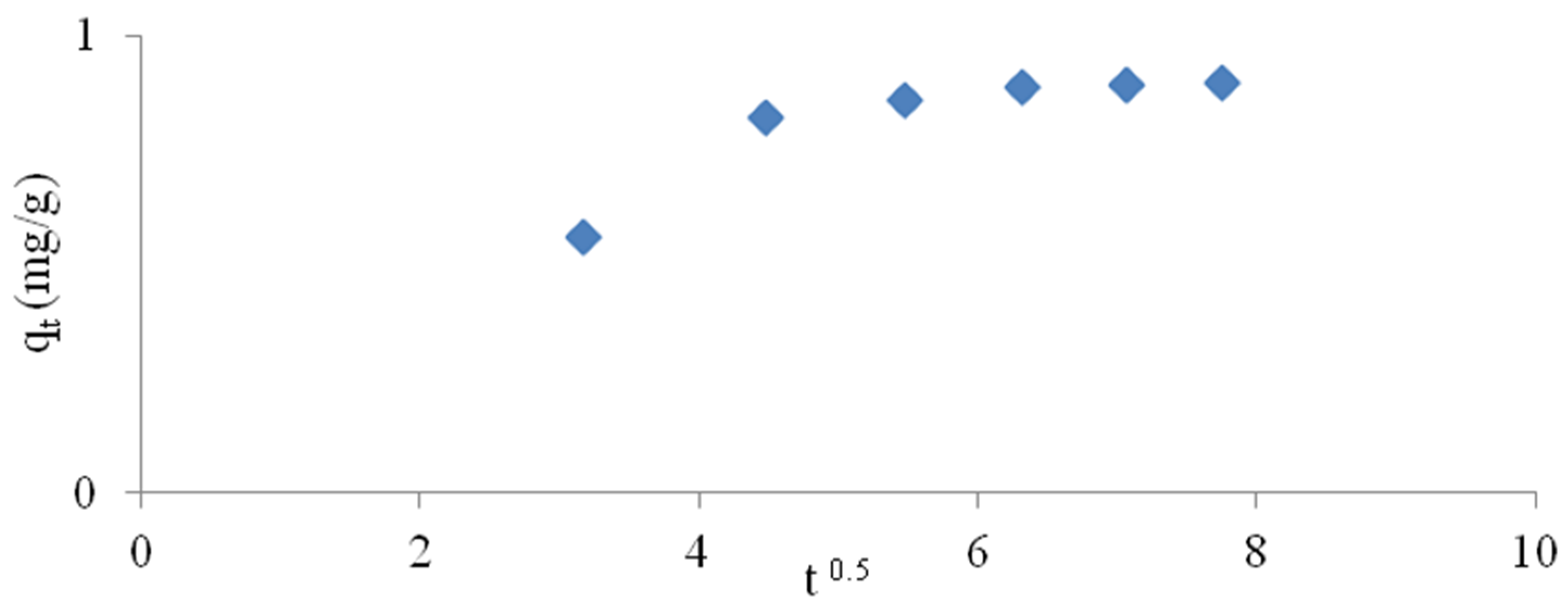
3.1.4. Kinetic Study
3.1.5. Regeneration
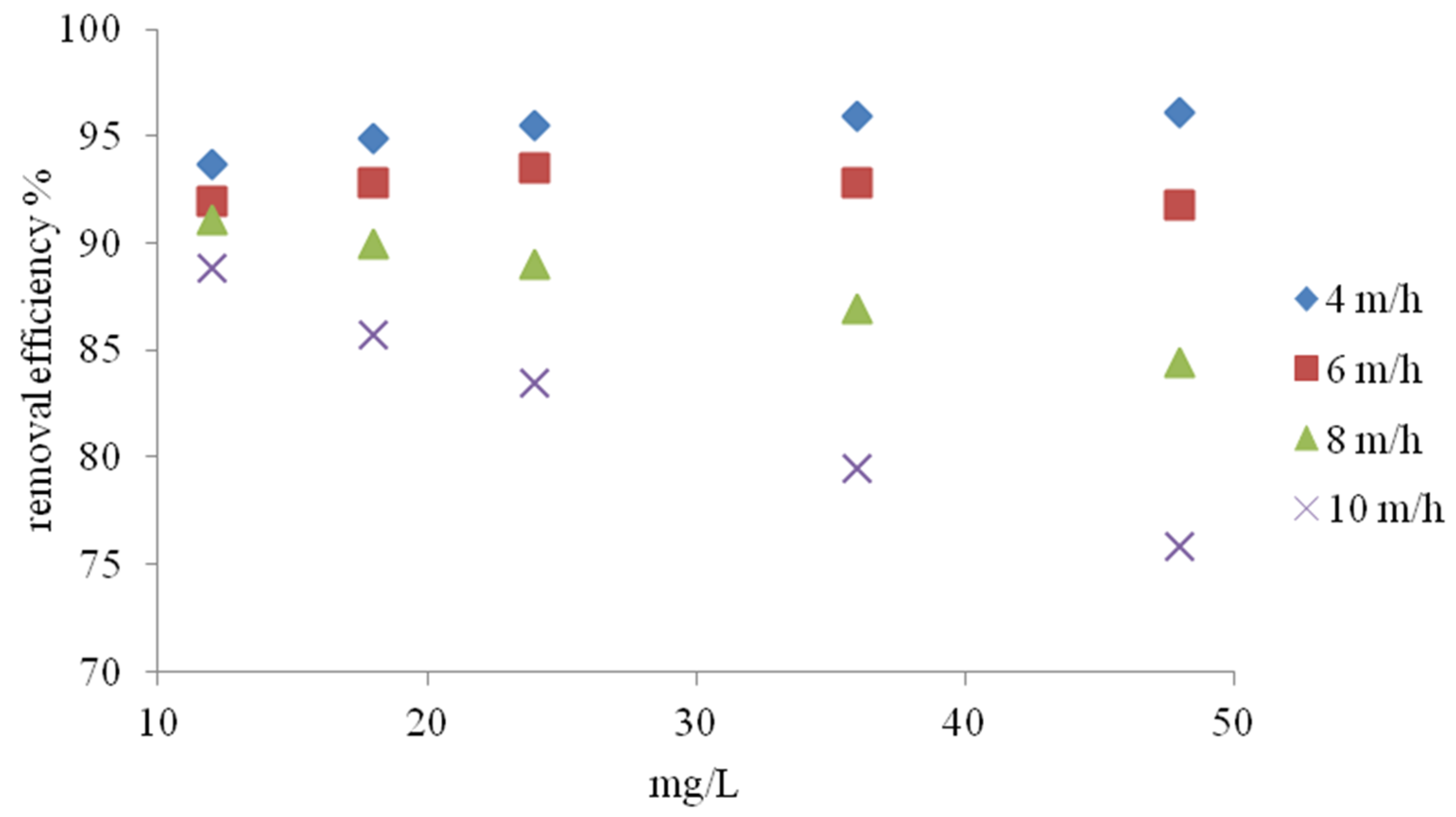
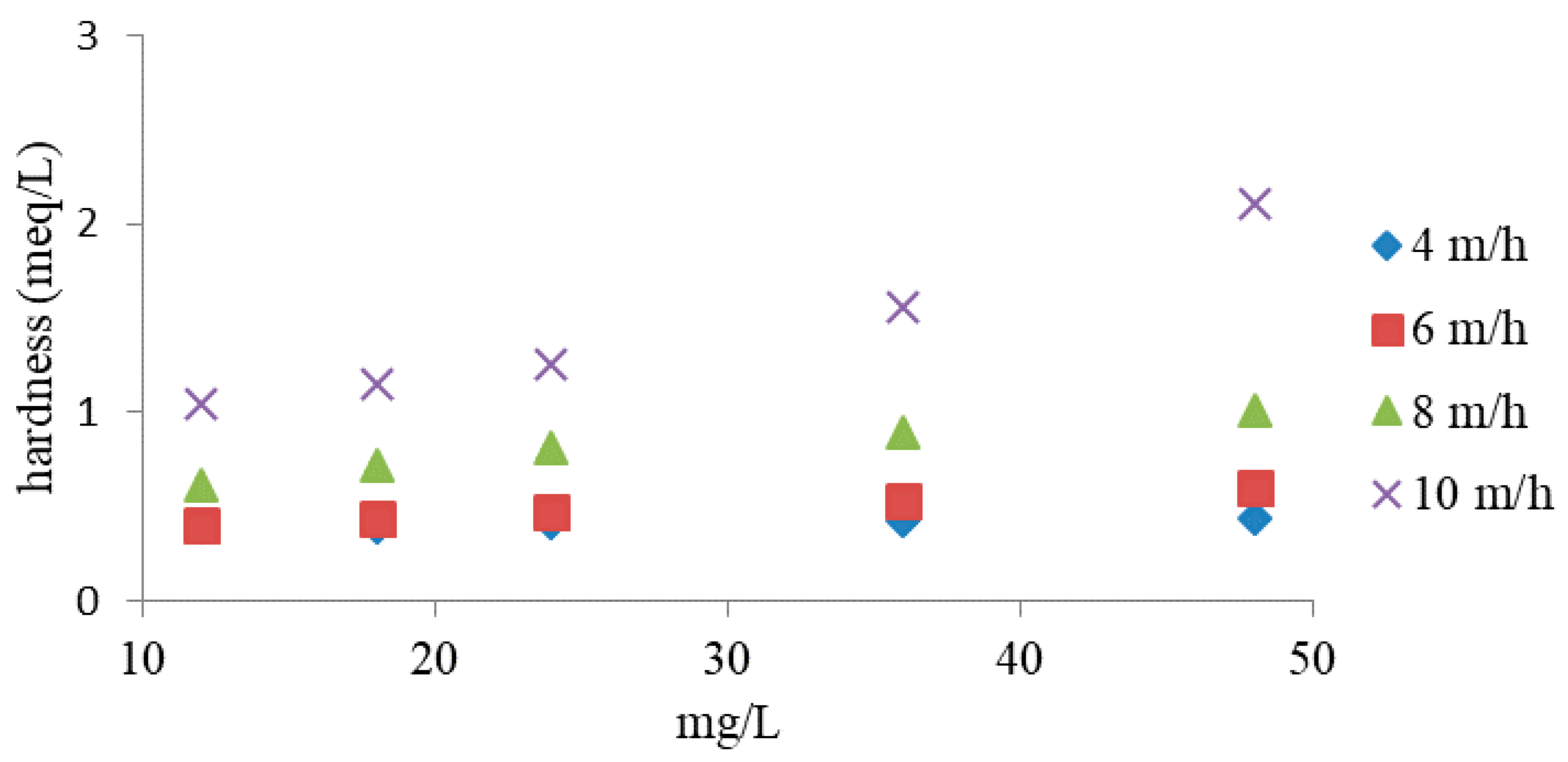
3.2. Column Study
4. Conclusions
- The studies showed the usefulness of weathered halloysite to remove ammonium nitrogen from aqueous solutions. In addition, the results obtained confirm that properly prepared halloysite has a high ammonia removal efficiency, comparable to other aluminosilicates.
- In a periodic study, the effectiveness of NH4+ removal increased with the initial concentration, while the presence of hardness causing ions (Ca2+, Mg2+) in tap water decreased the effectiveness of the process.
- The removal of NH4+ also depended on the pH of the aqueous solution NH4Cl. The best result was obtained at a pH of 6, although a similar process efficiency was also recorded at pH 7. In the studied range of pH 4, 5, as well as 8, 9, the efficiencies of ammonium ion removal significantly decreased.
- Under dynamic conditions, the removal of NH4+ ions was closely related to the flow velocity and initial NH4+ concentration. In the study, it was observed that at a higher filtration speed and higher initial NH4+ concentration, weathered halloysite exhibited higher NH4+ removal efficiency than the ions causing water hardness.
- The experimental data described by the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms provide the appropriate correlation coefficient value (R2 > 0.9). However, the Langmuir isotherm described the removal of ammonium ions by weathered halloysite slightly better.
- The pseudo second-order kinetic model provided the best correlation with experimental data for all systems tested.
- The weathered halloysite exchange capacity for NH4+ ions was evaluated as 0.99 meq/g at the initial NH4+ concentration of 500 mg/L. The highest capacity was obtained during weathered halloysite regeneration with a 5% NaCl solution using a five-fold excess. Apart from NaCl concentration, the excess of the regeneration solution was also an important parameter during the regeneration. Regeneration with a NaCl solution of pH 10.5 significantly increased the ion exchange capacity of the mineral, especially with a smaller excess of the regenerating agent.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, R.; Donovan, A.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Adams, C.; Yang, J.; Hua, B.; Inniss, E.; Eichholz, T.; Shi, H. Simultaneous removal of ammonia and N-nitrosamine precursors from high ammonia water by zeolite and powdered activated carbon. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 64, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, B.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ye, T.; Hu, C.; Lu, Y.; Cao, T.; Tang, Y.; Gao, N. A Mechanistic study on chlorine/nitrogen transformation and disinfection by-product generation in a UV-activated mixed chlorine/chloramines system. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, G.J.; Winnett, A.; Thompson, T.; Couperthwaite, S.J. Equilibrium studies of ammonium exchange with Australian natural zeolites. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 9, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malovanyy, A.; Sakalova, H.; Yatchyshyn, Y.; Plaza, E.; Malovanyy, M. Concentration of ammonium from municipal wastewater using ion exchange process. Desalination 2011, 329, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papciak, D.; Kaleta, J.; Puszkarewicz, A. Ammonium nitrogen removal from underground waters in the two-stage biofiltration process on the chalcedonite beds. Rocznik Ochrona Środowiska 2013, 15, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Lebedynets, M.; Terzyk, A.P.; Kowalczyk, P.; Namieśnik, J.; Buszewski, B. Ammonium sorption from aqueous solutions by the natural zeolite Transcarpathian clinoptilolite studied under dynamic conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabochnicka-Świątek, M.; Malińska, K. Removal of ammonia by clinoptilolite. Glob. Nest J. 2010, 12, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Reeve, P.J.; Fallowfield, H.J. Natural and surfactant modified zeolites: A review of their applications for water remediation with a focus on surfactantdesorption and toxicity towards microorganisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Kankanamge, N.R.; Chow, C.; Welsh, D.T.; Li, T.; Teasdale, P.R. Removing ammonium from water and wastewater using cost-effective adsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, A.H.; Rubio, J. Characterization and environmental application of a Chilean natural zeolite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 75, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaweda, A.; Saxenab, V.; Pandey, L.M. Engineered nanomaterials and their surface functionalization for the removal of heavy metals: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 33, 101009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkowski, A.; Franus, W.; Waniak-Nowicka, H.; Czímerová, A. Textural properties vs. CEC and EGME retention of Na–X zeolite prepared from fly ash et room temperature. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 82, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Stylianou, M.A.; Loizidou, M.; Zorpas, A.A. Experimental studies and modeling of clinoptilolite and vermiculite fixed beds for Mn2+, Zn2+, and Cr3+ removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11610–11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Zhu, Q.; Lee, S. Nitrification of low concentration ammonia nitrogen using zeolite biological aerated filter (ZBAF). Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wua, Y.; Changc, C.C.; Guanc, C.Y.; Changc, C.C.; Lia, J.W.; Changc, C.Y.; Yu, C.P. Enhanced removal of ammonium from the aqueous solution using a high gravity rotating packed bed loaded with clinoptilolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Yoon, T.I. The evaluation of enhanced nitrification by immobilized biofilm on a clinoptilolite carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherley, L.R.; Miladinovic, N.D. Comparison of the ion exchange uptake of ammonium ion onto New Zeland clinoptilolite and mordenite. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, S.; Dinçel, Y. Ammonium ion adsorption with sepiolite: Use of transient uptake method. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2002, 41, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, M. Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater using natural Turkish (Dogantepe) zeolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Lebedynets, M.; Zbytniewski, R.; Namieśnik, J.; Buszewski, B. Ammonium removal from aqueous solution by natural zeolite, Transcarpathian mordenite, kinetics, equilibrium and column tests. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 46, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozic, M.; Cerjan-Stefanovic, S.; Kurajica, S.; Vancina, V.; Hodzic, E. Ammonical nitrogen removal from water treatment with clays and zeolites. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Buszewski, B.; Terzyk, A.P.; Namiesnik, J. Study of the selec-tion mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Feng, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chi, R.; Hou, H. Adsorption and desorption performances of ammonium on the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 613, 126139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, S.M.; Williams, C.D. Pure zeolite LTJ synthesis from kaolinite under hydrothermal conditions and its ammonium removal efficiency. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 318, 111006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, B.K.; Chung, K.-L.; Chang, S.-M. Removal of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) by Cu-loaded amino-functionalized adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutynski, M.; Sakiewicz, P.; Lutynska, S. Characterization of diatomaceous earth and halloysite resources of Poland. Minerals 2019, 9, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłapyta, Z.; Żabiński, W. Mineral Sorbents of Poland; AGH Press: Cracow, Poland, 2008. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Tomiczek, B.; Pawlyta, M.; Król, M. Aluminium AlMg1SiCu matrix composite materials reinforced with halloysite particles. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nadziakiewicza, M.; Kehoe, S.; Micek, P. Physico-chemical properties of clay minerals and their use as a health promoting feed additive. Animals 2019, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiewicz, P.; Nowosielski, R.; Pilarczyk, W.; Gołombek, K.; Lutyński, M. Selected properties of the halloysite as a component of Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCL). J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2011, 48, 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Sakiewicz, P.; Lutynski, M.; Sołtys, J.; Pytlinski, A. Purification of halloysite by magnetic separation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2016, 52, 991–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Mrówka, M.; Szymiczek, M.; Machoczek, T.; Pawlyta, M. Influence of the Halloysite Nanotube(HNT) addition on selectedmechanical and biological properties of thermoplastic polyurethane. Materials 2021, 14, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, J.L. The Mineralogy, Geology and Occurrences of Halloysite; Apple Academic Press: Oakville, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Liu, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y. Ammonia removal from aqueous solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiastuti, N.; Wu, H.; Ang, H.M.; Zhang, D. Removal of ammonium from greywater using natural zeolite. Desalination 2011, 277, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dimova, G.; Mihailov, G.; Tzankov, T. Combined filter for ammonia removal—Part I: Minimal zeolite contact time and requirements for desorption. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, W.; Wdowin, M. Removal of ammonium ions by selected natural and synthetic zeolites. Miner. Resour. Manag. 2010, 26, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by natural Iranian zeolite in the presence of organic acids, cations and anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sartaj, M. Optimization of ammonia removal by ion-exchange resin using response surface methodology. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, N.P.; Pliankarom, S.; Hilal, N. An equilibrium ion-exchange study on the removal of NH4+ ion from aqueous effluent using clinoptilolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 3639–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, D.; Koc, Y.; Turan, M.; Armagan, B. Removal of ammonium ion from aqueous solution using natural Turkish clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.H.; Green, D. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook; McGraw-Hill, International Editions: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.H. Adsorption mechanisms of high-levels of ammonium onto natural and NaCl-modified zeolites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, S. Nature of ammonium ion adsorption by sepiolite: Analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherms. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kmiya, Y.; Okuhara, T. Removal of low-concentration ammonia in water by ion-exchange using Na-mordenite. Water Res. 2007, 41, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Aziz, H.A.; Foo, K.Y. Semi-aerobic stabilized landfill leachate treatment by ion exchange resin: Isotherm and kinetic study. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Tian, Y. Sorption characteristics and mechanisms of ammonium by coal by-products: Slag, honeycomb-cinder and coal gangue. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Constituent | Value-wt.% |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 35.74 |
| Al2O3 | 24.09 |
| Fe2O3 | 22.66 |
| TiO2 | 3.92 |
| CaO | 1.24 |
| MgO | 0.61 |
| Na2O | 0.10 |
| K2O | 0.05 |
| Loss of ignition (1000 °C) | 6.64 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.4 |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 450 |
| Alkalinity (mg CaCO3/L) | 185.2 |
| Total hardness (mg CaCO3/L) | 246.3 |
| KMnO4 (mg O2/L) | 2.3 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 76.5 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 13.2 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 9.6 |
| K+ (mg/L) | 1.3 |
| Type of Sample | Freundlich | Langmuir | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 1/n | R2 | qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | |
| distilled water | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.971 | 2.75 | 0.226 | 0.974 |
| tap water | 0.11 | 0.76 | 0.987 | 2.139 | 0.042 | 0.993 |
| Initial Concentration (mg NH4+/L) | Pseudo First-Order | Pseudo Second-Order | Diffusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (1/min) | R2 | k2 (g/mg min) | R2 | R2 | |
| 20 | 0.0599 | 0.91 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leszczyński, J. Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Weathered Halloysite. Materials 2021, 14, 4359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164359
Leszczyński J. Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Weathered Halloysite. Materials. 2021; 14(16):4359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164359
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeszczyński, Jacek. 2021. "Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Weathered Halloysite" Materials 14, no. 16: 4359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164359
APA StyleLeszczyński, J. (2021). Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Weathered Halloysite. Materials, 14(16), 4359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164359





