Study on Concrete Deterioration in Different NaCl-Na2SO4 Solutions and the Mechanism of Cl− Diffusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample and Solution Preparation
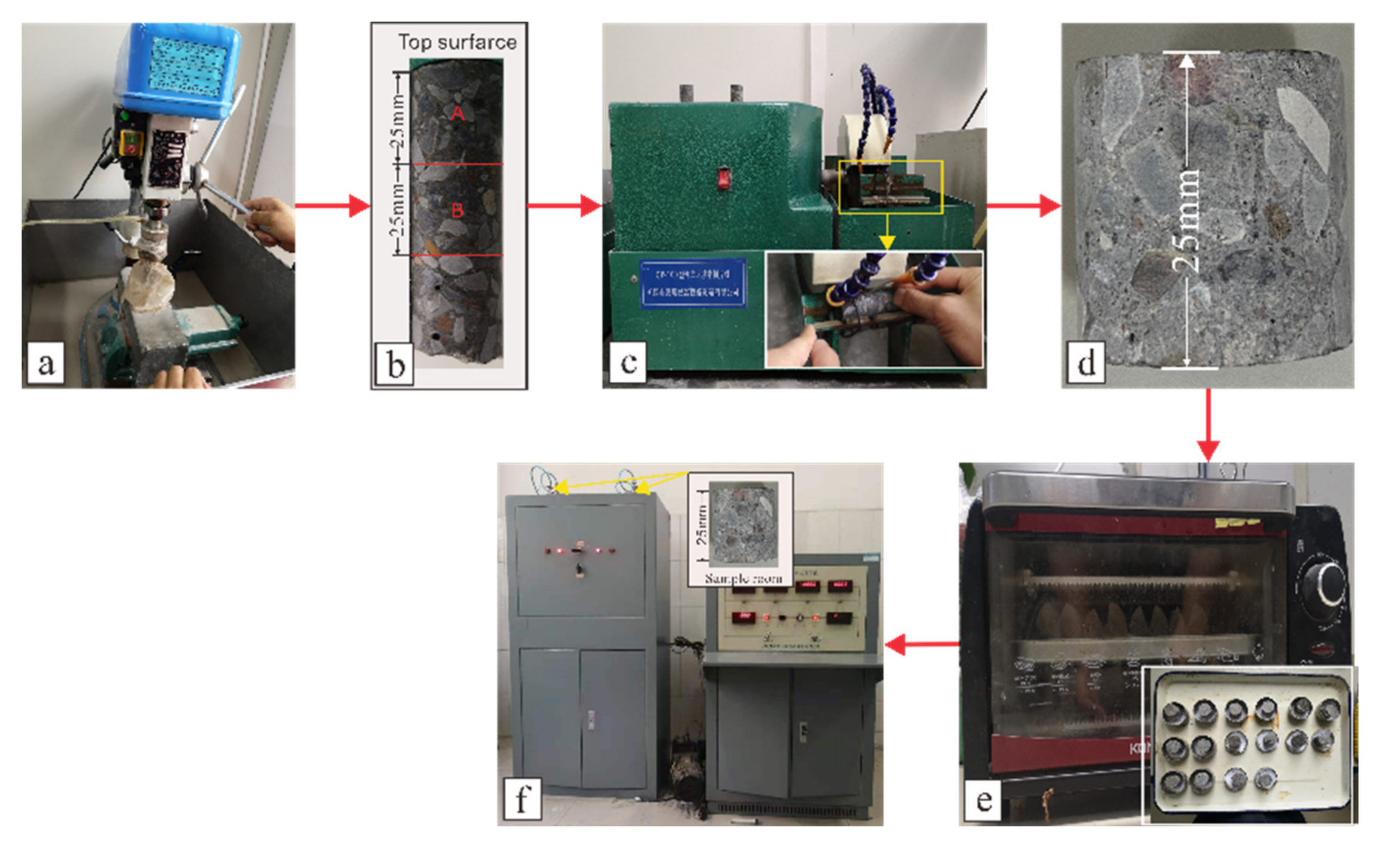
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.3.1. Weight Compressive Strength and RDEM
2.3.2. Cl− and SO42− Concentration
2.3.3. SEM, EDS, and XRD Analyses
2.3.4. Pore Analysis
3. Results
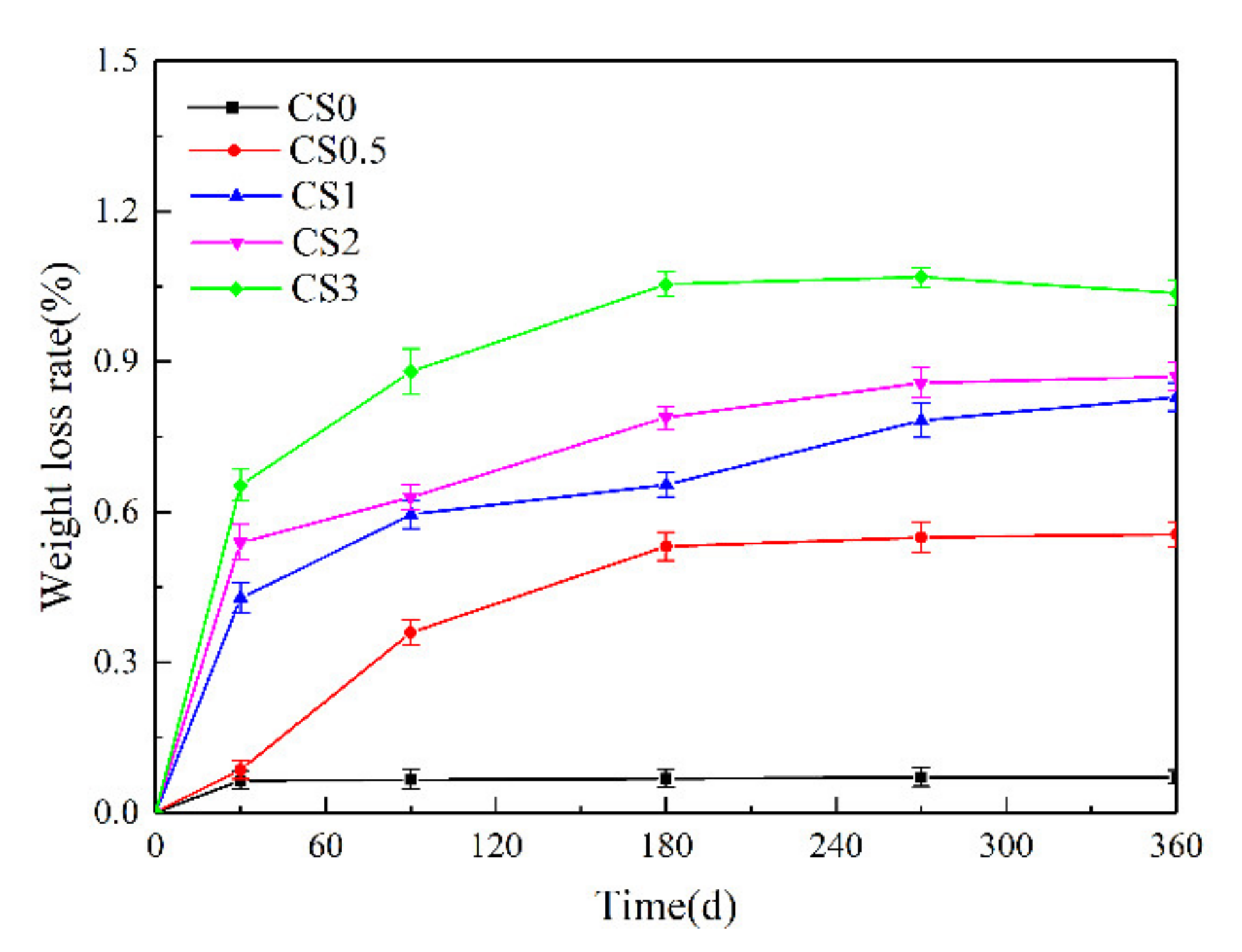
3.1. Weight Changes and Appearance of Performance
3.2. Compressive Strength and RDEM
3.2.1. Compressive Strength Changes and Failure Mode
3.2.2. Relative Dynamic Modulus of Elasticity
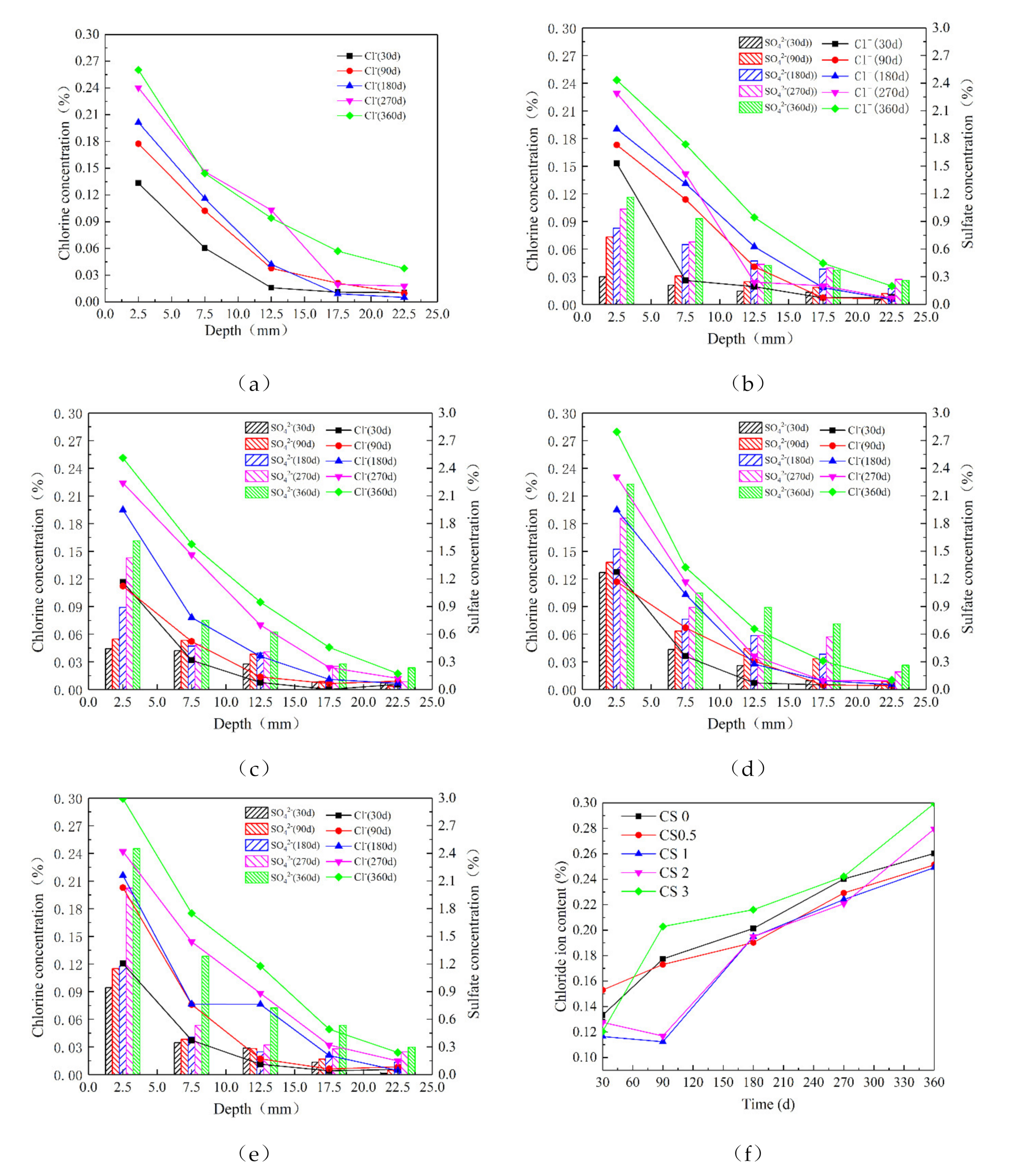
3.3. Chlorine Salt and Sulfate Concentration
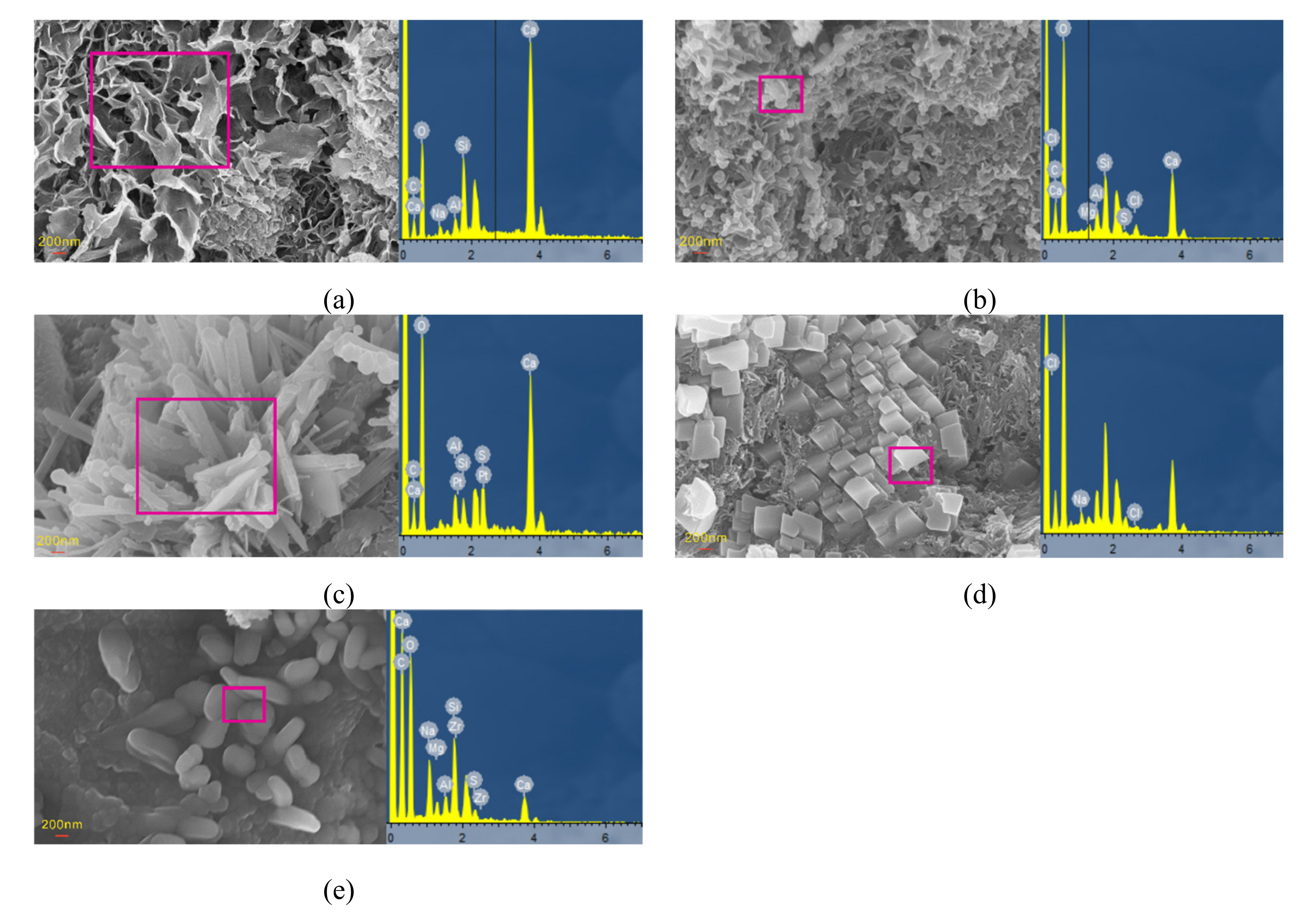
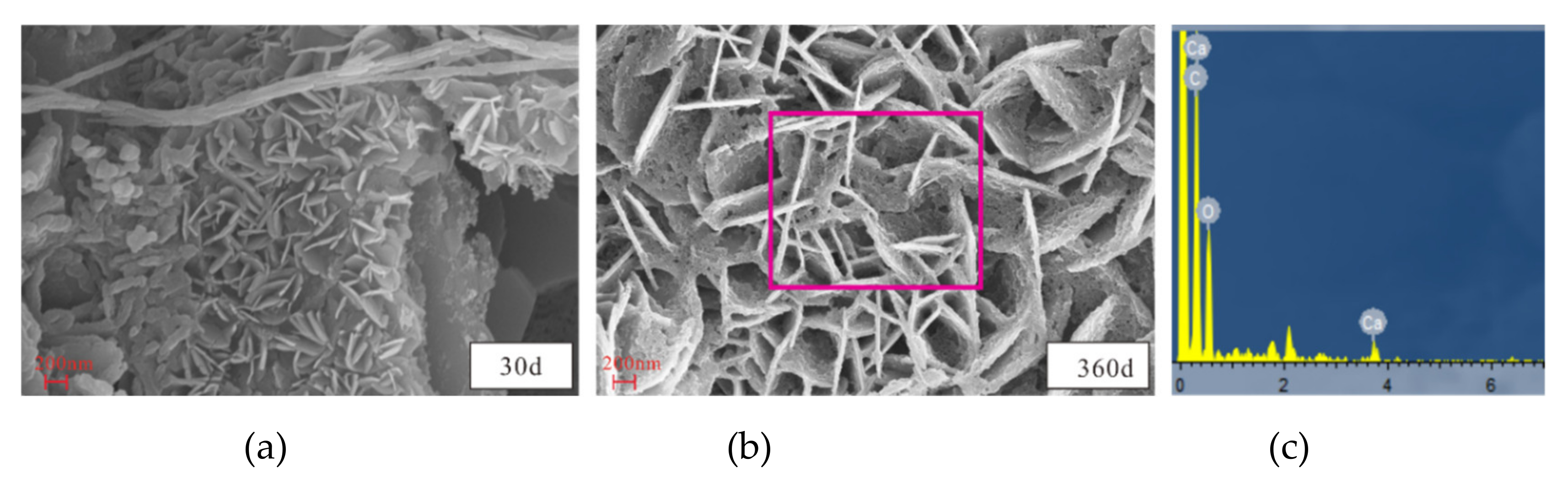
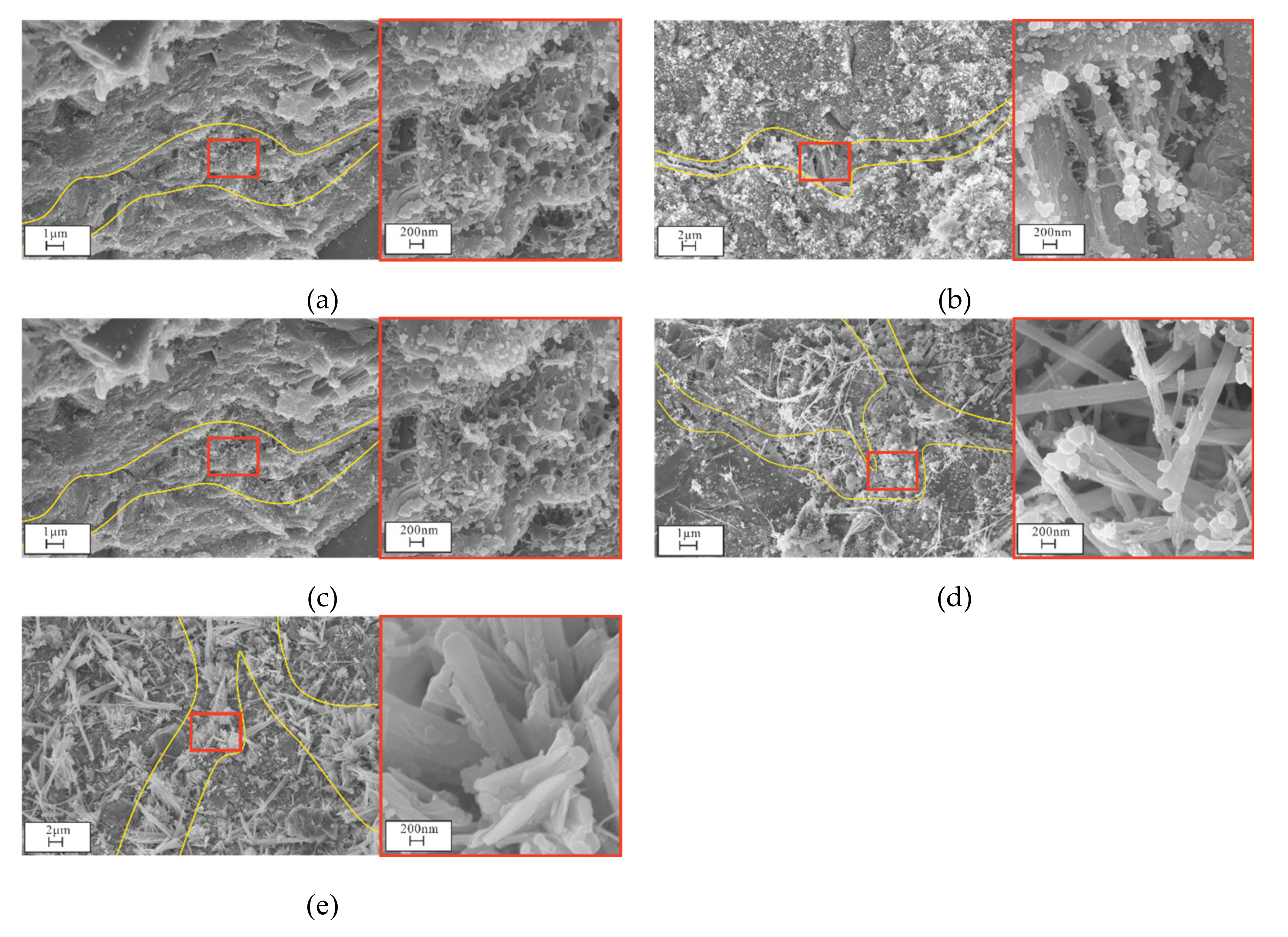
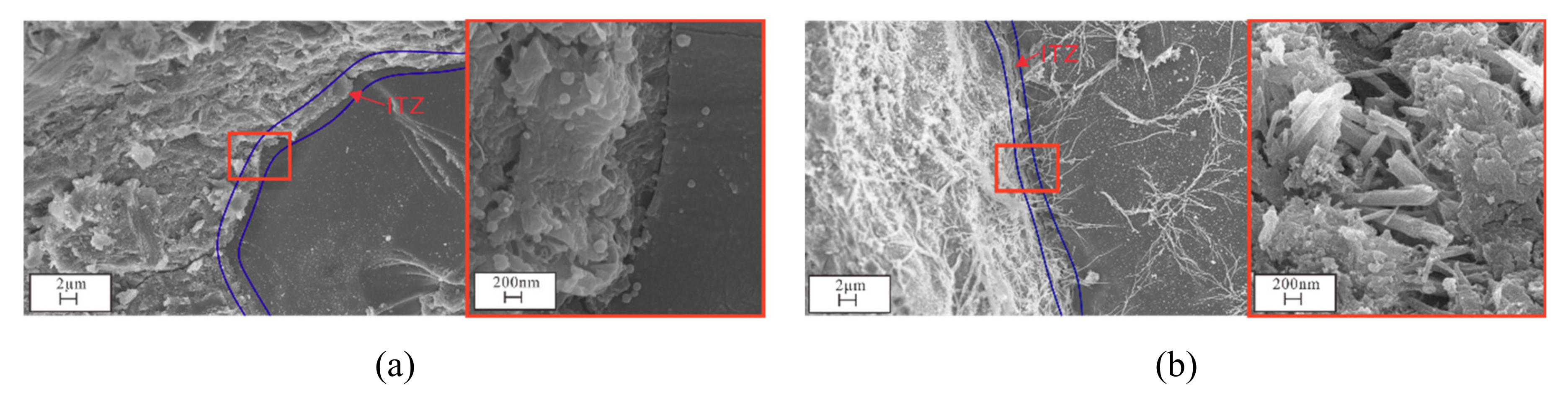
3.4. Microstructural and Mineral Analytical Results
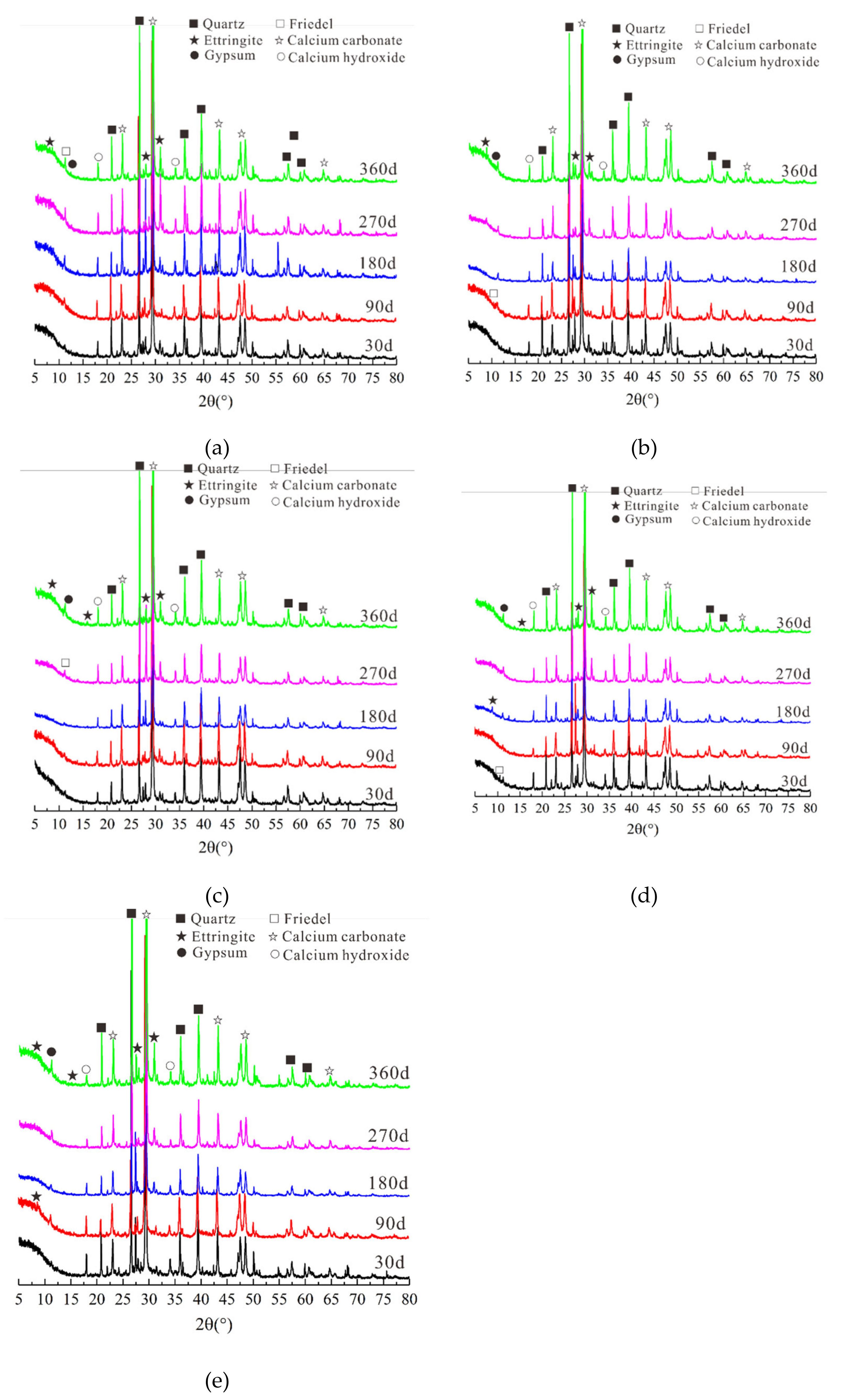
3.4.1. XRD Test
3.4.2. SEM and EDS Analyses
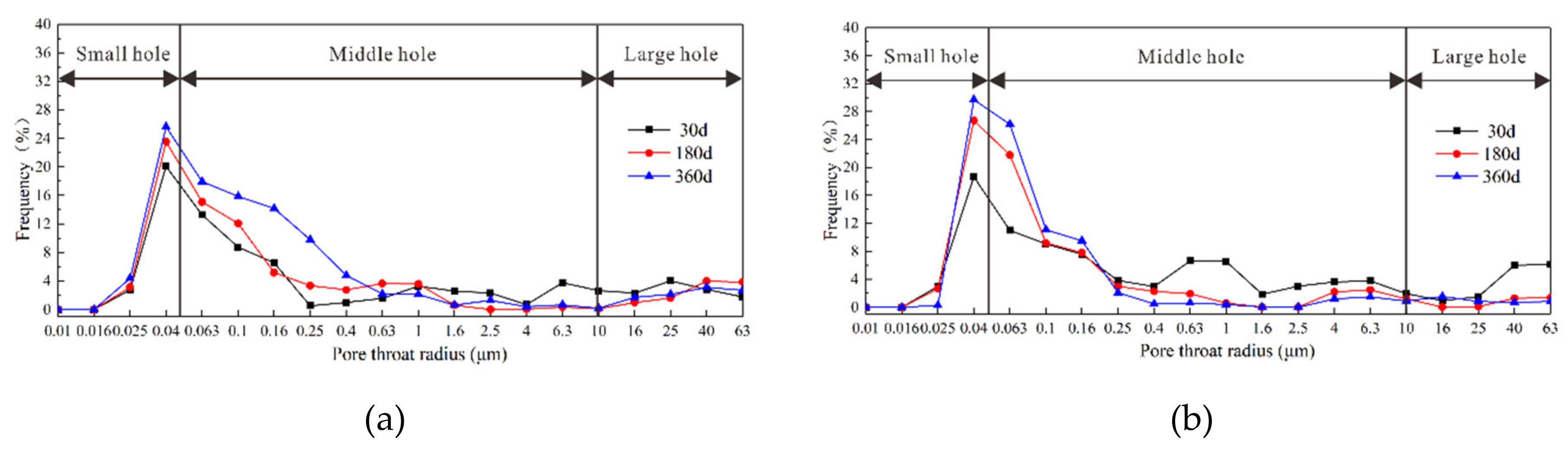
3.5. Pore Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanical Properties
4.2. Migration of Cl−
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.K.; Vennesland, Ø. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete — A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 1122–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, L.; Kropp, J.; Cleland, D.J. Assessment of the durability of concrete from its permeation properties: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2001, 15, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xie, N.; Fortune, K.; Gong, J. Durability of steel reinforced concrete in chloride environments: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Lewis, R. Carbonation of concrete and its prediction. Cem. Concr. Res. 1987, 17, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cheung, M.M. Non-uniform rust expansion for chloride-induced pitting corrosion in RC structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; D’Andrea, R.; Rebolledo, N. Chloride ion penetration in concrete: The reaction factor in the electrical resistivity model. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvar, A.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Rajaie, H. New method development for evaluation concrete chloride ion permeability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, F. Numerical analysis on efficiency of electrochemical chloride extraction of one side anode in concrete. Ocean Eng. 2019, 179, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazario, E.; Venegas, R.; Herrasti, P.; Alonso, M.; Recio, F.; Recio, J. Pitting corrosion and stress corrosion cracking study in high strength steels in alkaline media. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 20, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, O.S.B. Attack on plain and blended cements exposed to aggressive sulfate environments. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyuan, L.I.N.; Bo, Y.I.; Yunxiang, C.H.E.N. Research Development of the Corrosion of Reinforced Concrete in Saline Soil Environment. Materials Reports. 2014, 28, 137–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuquan, J.; Wei, S.; Yunsheng, Z.; Jinyang, J.; Jianzhong, L. Interaction between sulfate and chloride solution attack of concretes with and without fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. Evaluation of interaction effect of sulfate and chloride ions on reinforcements in simulated marine environment using electrochemical methods. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.; Goñi, S.; Allegro, V. Effect of temperature on the durability of class C fly ash belite cement in simulated radioactive liquid waste: Synergy of chloride and sulphate ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.-Q.; Shen, X.-H.; Hong, S.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Q.-F. Binding capacity and diffusivity of concrete subjected to freeze-thaw and chloride attack: A numerical study. Ocean Eng. 2019, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-H.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Hou, D.-S.; Hu, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.-F. Numerical study of carbonation and its effect on chloride binding in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Maslehuddin, M. The effect of chloride and sulfate ions on reinforcement corrosion. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; De Belie, N. Resistance of concrete and mortar against combined attack of chloride and sodium sulphate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, L.; Amleh, L.; Siad, H.; Lachemi, M. Effect of severe chloride environment on the flexural behaviour of hybrid concrete systems. Mag. Concr. Res. 2020, 72, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martın-Pérez, B.; Pantazopoulou, S.J.; Thomas, M.D.A. Numerical solution of mass transport equations in concrete structures. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luping, T.; Nilsson, L.-O. Chloride binding capacity and binding isotherms of OPC pastes and mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G.; Audenaert, K.; Deng, D. Chloride binding of cement-based materials subjected to external chloride environment – A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Jin, W.; Bai, Y. Effect of External Loads on Chloride Transport in Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, H.; Illston, J. The penetration of chlorides into hardened cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1984, 14, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, T.; Hamada, H. Relationship between free chloride and total chloride contents in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, L.-Y.; Wang, X. Chloride diffusion model for concrete in marine environment with considering binding effect. Mar. Struct. 2019, 66, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertolini, L.; Bolzoni, F.; Gastaldi, M.; Pastore, T.; Pedeferri, P.; Redaelli, E. Effects of cathodic prevention on the chloride threshold for steel corrosion in concrete. Electrochimica Acta 2008, 54, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peng, C.; Wan, L.; Wu, Q.; She, W. Effect of Crack Self-Healing on Concrete Diffusivity: Mesoscale Dynamics Simulation Study. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ma, R.; Li, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yan, Z. Effect of chloride attack on the bonded concrete system repaired by UHPC. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 272, 121971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Deng, D.; Xie, Y.; Long, G.; Tang, X. Physical sulfate attack on concrete lining–A field case analysis. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2017, 6, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J. Damage of concrete in sulfate and chloride solution. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 34, 630–635. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shannag, M.J.; Shaia, H.A. Sulfate resistance of high-perfor- mance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, M.; Nehdi, M.; Soliman, A.; Azabi, T. Damage mechanisms of two-stage concrete exposed to chemical and physical sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Mahadevan, S.; Meeussen, J.; van der Sloot, H.; Kosson, D. Numerical simulation of cementitious materials degradation under external sulfate attack. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basista, M.; Weglewski, W. Chemically Assisted Damage of Concrete: A Model of Expansion Under External Sulfate Attack. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2009, 18, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, E.; Marchand, J.; Snyder, K.; Beaudoin, J. Modeling ion and fluid transport in unsaturated cement systems in isothermal conditions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, R.; Dai, N.; Wang, Z. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Geopolymers Exposed to High Temperature: A Literature Review. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.H.; Zhao, S.B.; Yao, J.T. Thermal Analysis of Ettringite in Concrete Attacked by Sodium Sulfate in Dry-wet Cyclic Environment. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 950–958. [Google Scholar]
- Bassuoni, M.; Rahman, M. Response of concrete to accelerated physical salt attack exposure. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, L.; Xing, F. Evolution of the sulfate ion transport-deterioration process in concrete. Anti-Corrosion Methods Mater. 2016, 63, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Guo, M.; Cui, J.; Li, J.; Xu, L. Partially-exposed cast-in-situ concrete degradation induced by internal-external sulfate and magnesium multiple coupled attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Jiang, L.; Fei, Q. Deterioration mechanism of sulfate attack on concrete under freeze-thaw cycles. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2013, 28, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.W.; Li, J.P.; Han, F.; Shi, M.; Fan, H.H. Sulfate-induced degradation of cast-in-situ concrete influenced by magnesium. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 199, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Çopuroğlu, O.; Schlangen, E.; Han, N.X.; Xing, F. Expansion and degradation of cement paste in sodium sulfate solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, C. Cement hydration mechanism and research methods. Concrete 2011, 6, 76–82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Glasser, F.; Kindness, A.; Stronach, S. Stability and solubility relationships in AFm phases: Part I. Chloride, sulfate and hydroxide. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet, S.; Bussière, B.; Mbonimpa, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Aubertin, M. Reactivity and mineralogical evolution of an under-ground mine sulphidic cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; López, C.; Aguado, A. Diffusion–reaction model for the internal sulfate attack in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 102, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, J.; Easterbrook, D.; Li, L.-Y.; Mo, L.-W. The stability of bound chlorides in cement paste with sulfate attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 68, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, G.H.; Bryant, M. ‘‘Sulfate attack,” or is it ? Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 789–791. [Google Scholar]
- Glasser F, P.; Marchand, J.; Samson, E. Durability of concrete-degradation phenomena involving detrimental chemical reactions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, Z.; Dai, L.; Wen, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, D.; Song, X. Study on Corrosion Mechanism of Different Concentrations of Na2SO4 Solution on Early-Age Cast-In-Situ Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, N.; Flatt, R.J.; Scherer, G. Crystallization damage by sodium sulfate. J. Cult. Heritage 2003, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, F.; Möser, B.; Stark, J. Influence of sulfate solution concentration on the formation of gypsum in sulfate resistance test specimen. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrah, N.R.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Maslehuddin, M.; Ashiru, O.A.; Al-Mana, A.I. Electrochemical behaviour of steel in plain and blended cement concretes in sulphate and/or chloride environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 1995, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. The influence of sulphates on chloride binding and pore solution chemistry. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, L.; Tang, L.; Gao, G.; Xu, Y. Releases of bound chlorides from chloride-admixed plain and blended cement pastes subjected to sulfate attacks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 45, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, K.; Hong, B.; Yang, R.; Xu, W.; Tian, Q.; Liu, J. Experimental and numerical analysis on coupled hy-gro-thermo-chemo-mechanical effect in early-age concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 32, 817–826. [Google Scholar]








| Chemical Composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | Cl | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | MgO | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 5.08 | 20.1 | 2.02 | 0.028 | 0.341 | 2.94 | 0.700 | 0.350 | 1.50 | 60.7 |
| Concrete Grade | w/c | Cement (kg/m3) | Sand (kg/m3) | Gravel (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C35 | 0.4848 | 402.16 | 631 | 1199 | 195 |
| Specimen | Corrosive Environment | Specimen | Corrosive Environment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl (wt%) | Na2SO4 (wt%) | NaCl (wt%) | Na2SO4 (wt%) | ||
| CS0 | 5% | 0 | CS2 | 5% | 10% |
| CS0.5 | 5% | 2.5% | CS3 | 5% | 15% |
| CS1 | 5% | 5% | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Hu, Z.; Wei, F.; Wen, X.; Li, X.; Dai, L.; Liu, L. Study on Concrete Deterioration in Different NaCl-Na2SO4 Solutions and the Mechanism of Cl− Diffusion. Materials 2021, 14, 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14175054
Zhang F, Hu Z, Wei F, Wen X, Li X, Dai L, Liu L. Study on Concrete Deterioration in Different NaCl-Na2SO4 Solutions and the Mechanism of Cl− Diffusion. Materials. 2021; 14(17):5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14175054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fei, Zhiping Hu, Feng Wei, Xin Wen, Xiaoguang Li, Li Dai, and Long Liu. 2021. "Study on Concrete Deterioration in Different NaCl-Na2SO4 Solutions and the Mechanism of Cl− Diffusion" Materials 14, no. 17: 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14175054
APA StyleZhang, F., Hu, Z., Wei, F., Wen, X., Li, X., Dai, L., & Liu, L. (2021). Study on Concrete Deterioration in Different NaCl-Na2SO4 Solutions and the Mechanism of Cl− Diffusion. Materials, 14(17), 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14175054






