Improvement of Drug Release and Compatibility between Hydrophilic Drugs and Hydrophobic Nanofibrous Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
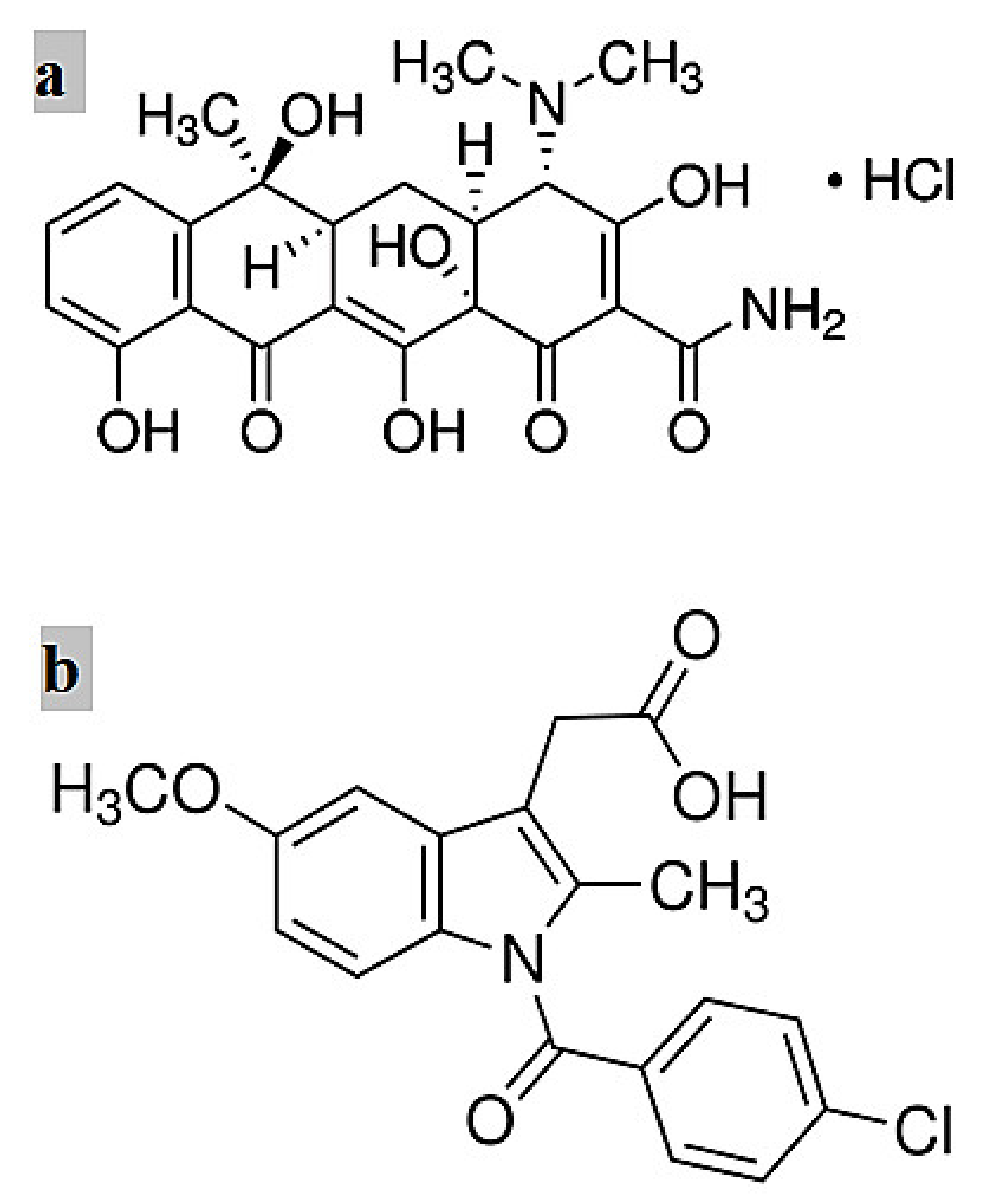
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. In Vitro Drug Release Study
2.4. Mathematical Models for Drug Release Kinetics
2.4.1. Zero-Order Model
2.4.2. First-Order Model
2.4.3. Higuchi Model
2.4.4. Ritger–Peppas Model
2.4.5. Zeng Model
2.5. In Vitro Biodegradation Study
3. Characterisation Techniques
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Drug Effect on Fiber Morphology
4.2. Crystallinity Level
4.3. Thermal Properties
4.4. TGA Analysis
4.5. FTIR Evaluation
4.6. In Vitro Drug Release
4.7. Release Kinetics
4.8. Mass Loss of Fibre Mats
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.-W.; Li, S.-S.; Hu, Z.-M.; Yu, J.-R.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J. Effects of three parameters on the diameter of electrospun poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Chen, T.; Branford-White, C.; Zhu, L. Electrospun shikonin-loaded PCL/PTMC composite fiber mats with potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroosh, H.J.; Dong, Y.; Lau, K.-T. Tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH)-loaded drug carrier based on PLA: PCL nanofibre mats: Experimental characterisation and release kinetics modelling. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 6270–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Feng, T.; Li, B.; Han, Y. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison Study of Electrospun PLA and PLA/PVA/SA Fiber Membranes for Wound Healing. Polymers 2020, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, M.; Jia, D. Carboxylated butadiene-styrene rubber/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites: Interfacial interaction and performance. Polymer 2008, 49, 4871–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroosh, H.J.; Dong, Y.; Ingram, G.D. Synthesis, Morphological Structures, and Material Characterization of Electrospun PLA: PCL/Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites for Drug Delivery. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroosh, H.J.; Dong, Y.; Chaudhary, D.S.; Ingram, G.D.; Yusa, S. Electrospun PLA: PCL composites embedded with unmodified and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (ASP) modified halloysite nanotubes (HNT). Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2013, 110, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenawy, E.; Abdel-Hay, F.; El-Newehy, M.; Wnek, G. Processing of polymer nanofibers through electrospinning as drug delivery systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, H.Y.; Yoo, M.K.; Park, I.K.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, J.S.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C.S. A novel degradable polycaprolactone networks for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Downes, S. Physicochemical characterisation of novel ultra-thin biodegradable scaffolds for peripheral nerve repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Sui, G.; Zhao, M.L.; Chen, G.Q.; Yang, X.P. Poly (L-lactic acid)/hydroxyapatite hybrid nanofibrous scaffolds prepared by electrospinning. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroosh, H.J.; Chaudhary, D.S.; Dong, Y. Electrospun PLA/PCL fibers with tubular nanoclay: Morphological and structural analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 3930–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonés, A.; Peponi, L.; Lieblich, M.; Benavente, R.; Fiori, S. In Vitro Degradation of Plasticized PLA Electrospun Fiber Mats: Morphological, Thermal and Crystalline Evolution. Polymers 2020, 12, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; He, F.; Wang, X.; Gao, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Wu, C.; Guo, D.; Li, X. Novel nanocomposite of nano Fe3O4 and polylactide nanofibers for application in drug uptake and induction of cell death of leukemia cancer cells. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Yoon, H.; Park, Y. Drug release from various thicknesses of layered mats consisting of electrospun polycaprolactone and polyethylene oxide micro/nanofibers. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2010, 100, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, A.I.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, C.S. Poly (ε-Caprolactone)/Poly (Glycerol Sebacate) Composite Nanofibers Incorporating Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and Simvastatin for Bone Tissue Regeneration and Drug Delivery Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupka, V.; Dvořáková, E.; Manakhov, A.; Michlíček, M.; Petruš, J.; Vojtová, L.; Zajíčková, L. Well-blended PCL/PEO electrospun nanofibers with functional properties enhanced by plasma processing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Buschle Diller, G. Electrospun poly (D, L lactide) fibers for drug delivery: The influence of cosolvent and the mechanism of drug release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; An, L.; Wu, X. Modeling Drug-Carrier Interaction in the Drug Release from Nanocarriers. J. Drug Deliv. 2011, 2011, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, H.; Khorashadizadeh, M.; Haseloer, A.; Klein, A. Characterization and release behavior of a thiosemicarbazone from electrospun polyvinyl alcohol core-shell nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, S.; Trajtman, A.; Alfa, M. Electrospun PEG–PLA nanofibrous membrane for sustained release of hydrophilic antibiotics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschle-Diller, G.; Cooper, J.; Xie, Z.; Wu, Y.; Waldrup, J.; Ren, X. Release of antibiotics from electrospun bicomponent fibers. Cellulose 2007, 14, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamaneni, S.; Zhong, B.; Lama, R.; Su, B. COX inhibitors Indomethacin and Sulindac derivatives as antiproliferative agents: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and mechanism investigation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 56, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Luan, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z. Sustained release of 5-fluorouracil by incorporation into sodium carboxymethylcellulose sub-micron fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 419, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Encapsulation of curcumin in alginate-chitosan-pluronic composite nanoparticles for delivery to cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittur, K.K. FTIR/ATR for protein adsorption to biomaterial surfaces. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Ghataura, A.; Takagi, H.; Haroosh, H.J.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Lau, K.-T. Polylactic acid (PLA) biocomposites reinforced with coir fibres: Evaluation of mechanical performance and multifunctional properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 63, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, J.; Pereira, C.G.; de Almeida Junior, J.C.; Viana, C.C.R.; de Oliveira Neves, L.N.; da Silva, P.H.F.; Bell, M.J.V.; dos Anjos, V.d.C. FTIR-ATR determination of protein content to evaluate whey protein concentrate adulteration. Lwt 2019, 99, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.; Bowlin, G.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.; Sanders, E.; Wnek, G. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly (ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly (lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L.; Sung, H.W.; Shyu, S.S. Release of indomethacin from a novel chitosan microsphere prepared by a naturally occurring crosslinker: Examination of crosslinking and polycation–anionic drug interaction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, M.; Murtomaa, M.; Salonen, J. Fabrication and characterization of drug particles produced by electrospraying into reduced pressure. J. Electrost. 2010, 68, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassman, S.A.; Lee, L.S. Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: Assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boultif, A.; Louer, D. Powder pattern indexing with the dichotomy method. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2004, 37, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Piras, A.; Detta, N.; Dinucci, D.; Chiellini, F. Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) electrospun fibrous meshes for the controlled release of retinoic acid. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kolb, V.M.; Jiang, W.-T.; Hong, H. Ftir and XRD INVestigations of tetracycline intercalation in smectites. Clays Clay Miner. 2010, 58, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanambe, L.; Vasudevan, S. Anionic clays containing anti-inflammatory drug molecules: Comparison of molecular dynamics simulation and measurements. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 15651–15658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Coaxial electrospun poly (l-lactic acid) ultrafine fibers for sustained drug delivery. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2006, 45, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natu, M.; de Sousa, H.; Gil, M. Effects of drug solubility, state and loading on controlled release in bicomponent electrospun fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vergaro, V.; Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y.M.; Zeitoun, A.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R.; Leporatti, S. Cytocompatibility and uptake of halloysite clay nanotubes. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Material Sample | Tg (°C) PCL | Tm (°C) PCL | TC (°C) PLA | Tm (°C) PLA | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA:PCL | −52.19 | 63.75 | 83.97 | 152.54 | 58.84 |
| PLA:PCL/IMC | −58.55 | 54.57 | 82.01 | 148.98 | 48.89 |
| PLA:PCL/TCH | −58.48 | 59.64 | 105.77 | 151.93 | 53.69 |
| PLA:PCL/HNT-ASP/TCH | −61.43 | 59.17 | 102.77 | 149.07 | 43.60 |
| Mathematical Model | Zero-Order | First-Order | Higuchi | Ritger–Peppas | Zeng |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | Mt/M∞= K0t | Mt/M∞ = 1 − e−K1t | Mt/M∞= KH t1/2 | Mt/M∞= KRtn | ** |
| PLA:PCL/IMC | K0 = 0.002 R2 = 0.564 | K1 = 0.436 R2 = 0.822 | KH = 0.037 R2 = 0.801 | KR = 1.618 n = 0.251 R2 = 0.938 | Kon = 0.0049 h−1 Koff = 0.0025 h−1 Ks = 1.006 h−1 * ΔG = -2.1 × 10−21J R2 = 0.945 |
| PLA:PCL/TCH | K0 = 0.002 R2 = 0.434 | K1 = 0.582 R2 = 0.839 | KH = 0.038 R2 = 0.691 | KR = 1.262 n = 0.204 R2 = 0.927 | Kon = 0.0034 h−1 Koff = 0.0033 h–1 Ks = 1.160 h−1 * ΔG = −2.0 × 10−22J R2 = 0.920 |
| PLA:PCL/ HNT-ASP / TCH | K0 = 0.0012 R2 = 0.314 | K1 = 0.857 R2 = 0.961 | KH = 0.024 R2 =0.534 | KR = 2.025 n = 0.323 R2 = 0.684 | Kon = 0.0012 h−1 Koff = 0.00068 h−1 Ks = 1.025 h−1 * ΔG = -2.2×10−21J R2 = 0.986 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haroosh, H.J.; Dong, Y.; Jasim, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Improvement of Drug Release and Compatibility between Hydrophilic Drugs and Hydrophobic Nanofibrous Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 5344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185344
Haroosh HJ, Dong Y, Jasim S, Ramakrishna S. Improvement of Drug Release and Compatibility between Hydrophilic Drugs and Hydrophobic Nanofibrous Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(18):5344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185344
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaroosh, Hazim J., Yu Dong, Shaimaa Jasim, and Seeram Ramakrishna. 2021. "Improvement of Drug Release and Compatibility between Hydrophilic Drugs and Hydrophobic Nanofibrous Composites" Materials 14, no. 18: 5344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185344
APA StyleHaroosh, H. J., Dong, Y., Jasim, S., & Ramakrishna, S. (2021). Improvement of Drug Release and Compatibility between Hydrophilic Drugs and Hydrophobic Nanofibrous Composites. Materials, 14(18), 5344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185344