Dissimilar Laser Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Abrasion-Resistant Steel: Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties Enhanced by Post-Weld Heat Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
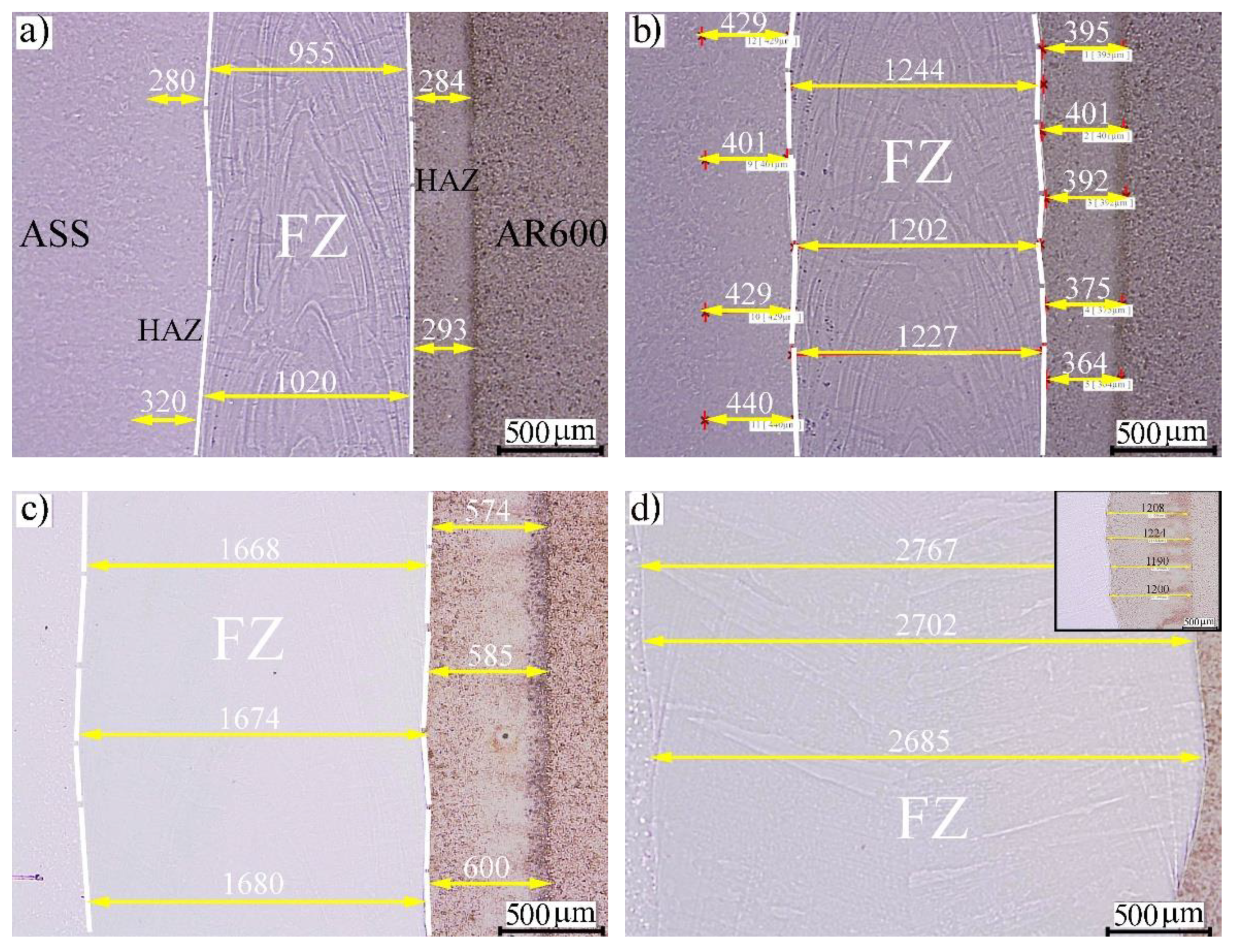
3.1. Weld Morphology of Laser-Welded Butt Joints with Different Energy Inputs
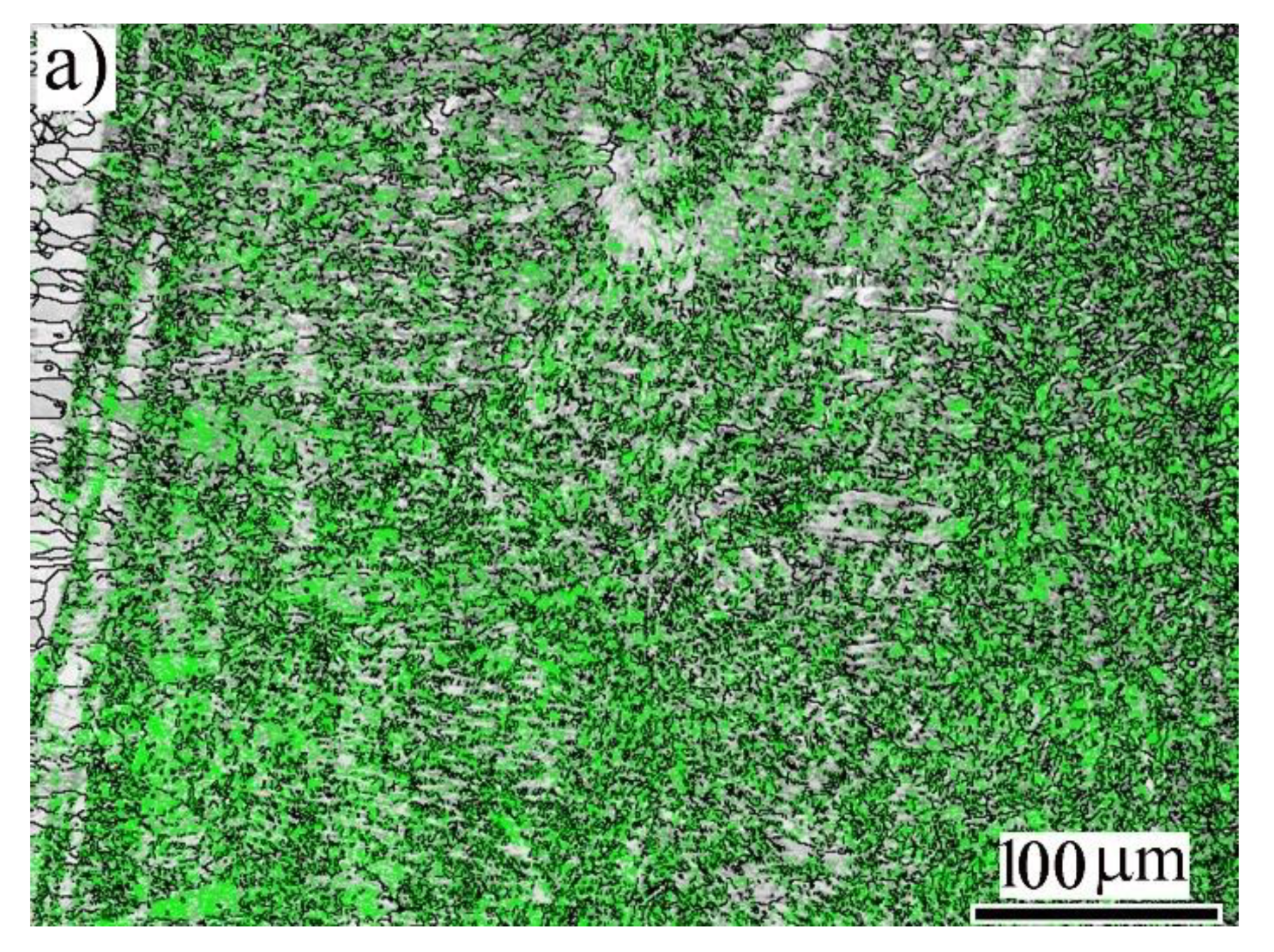
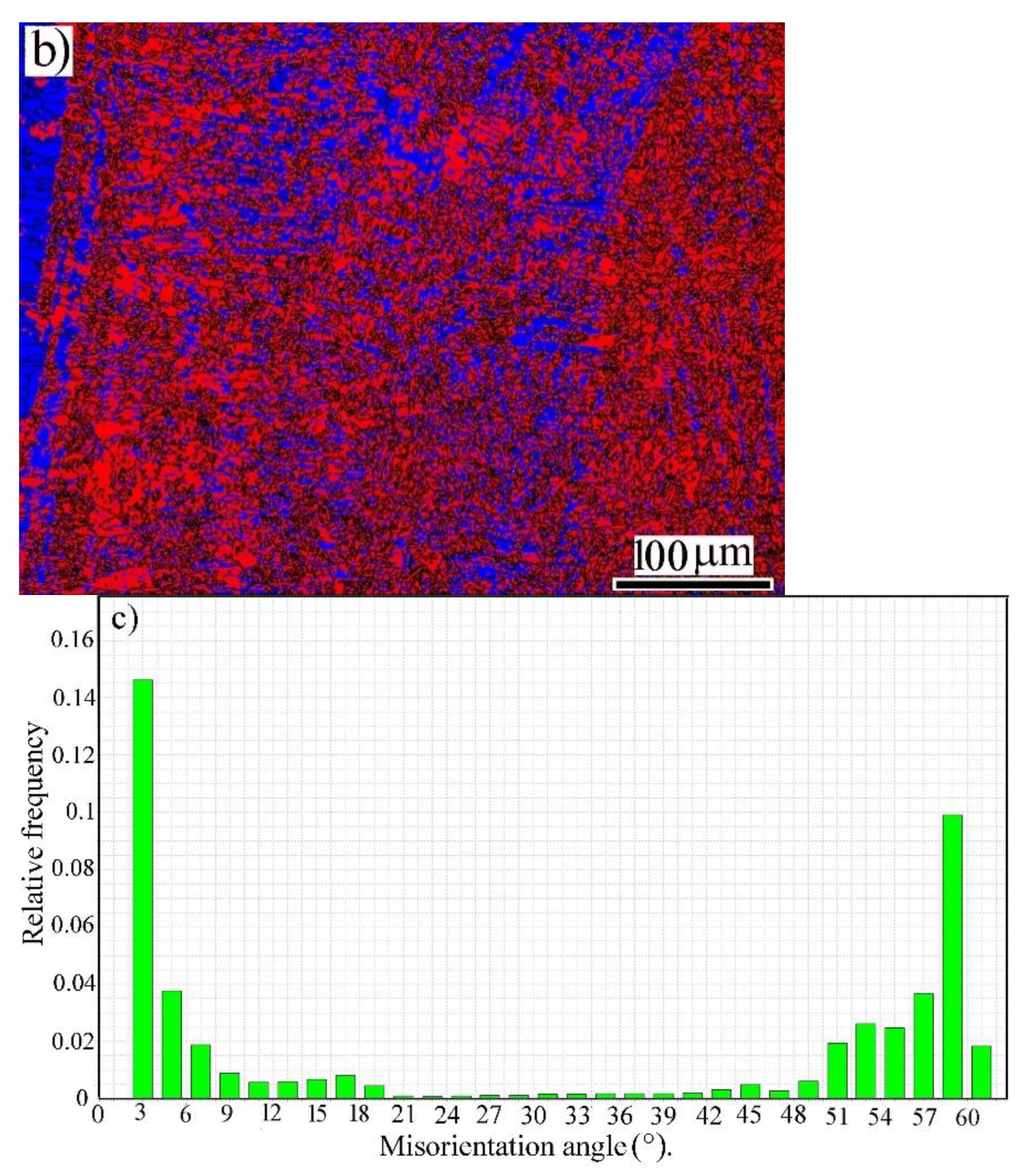
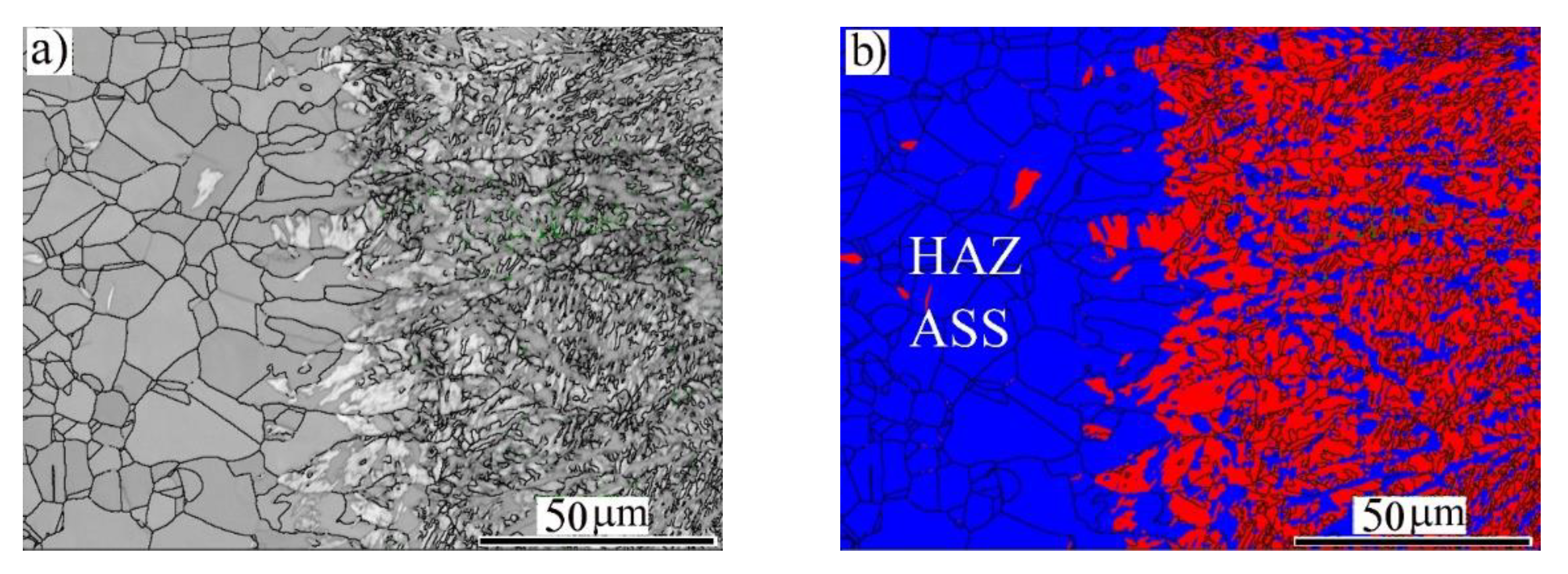
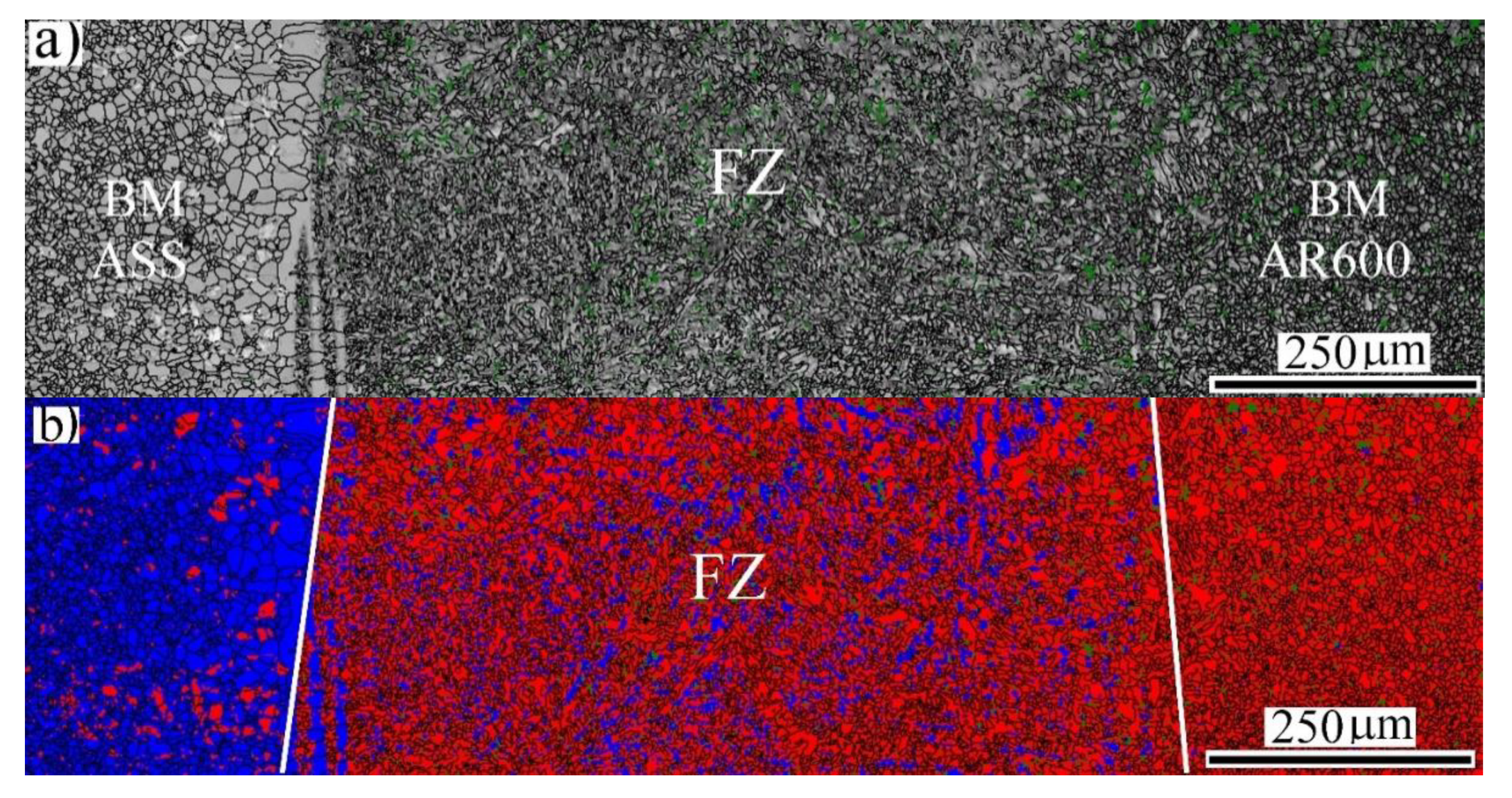
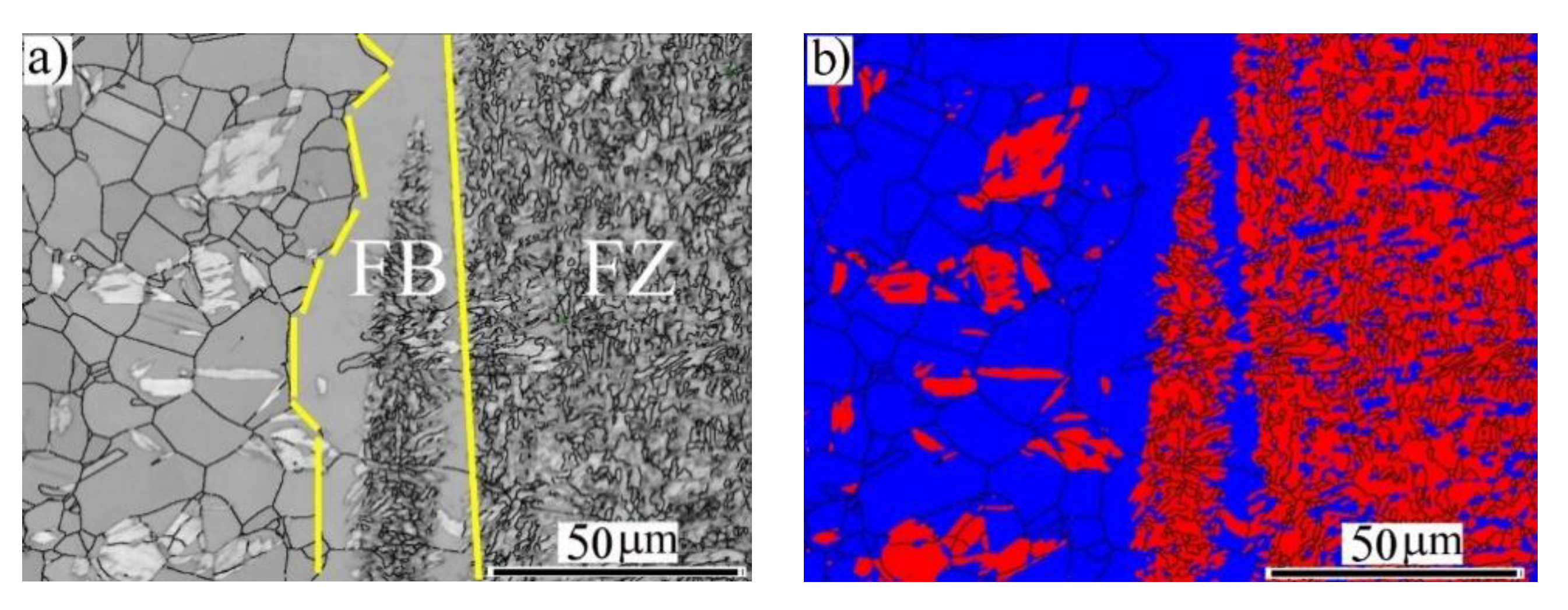
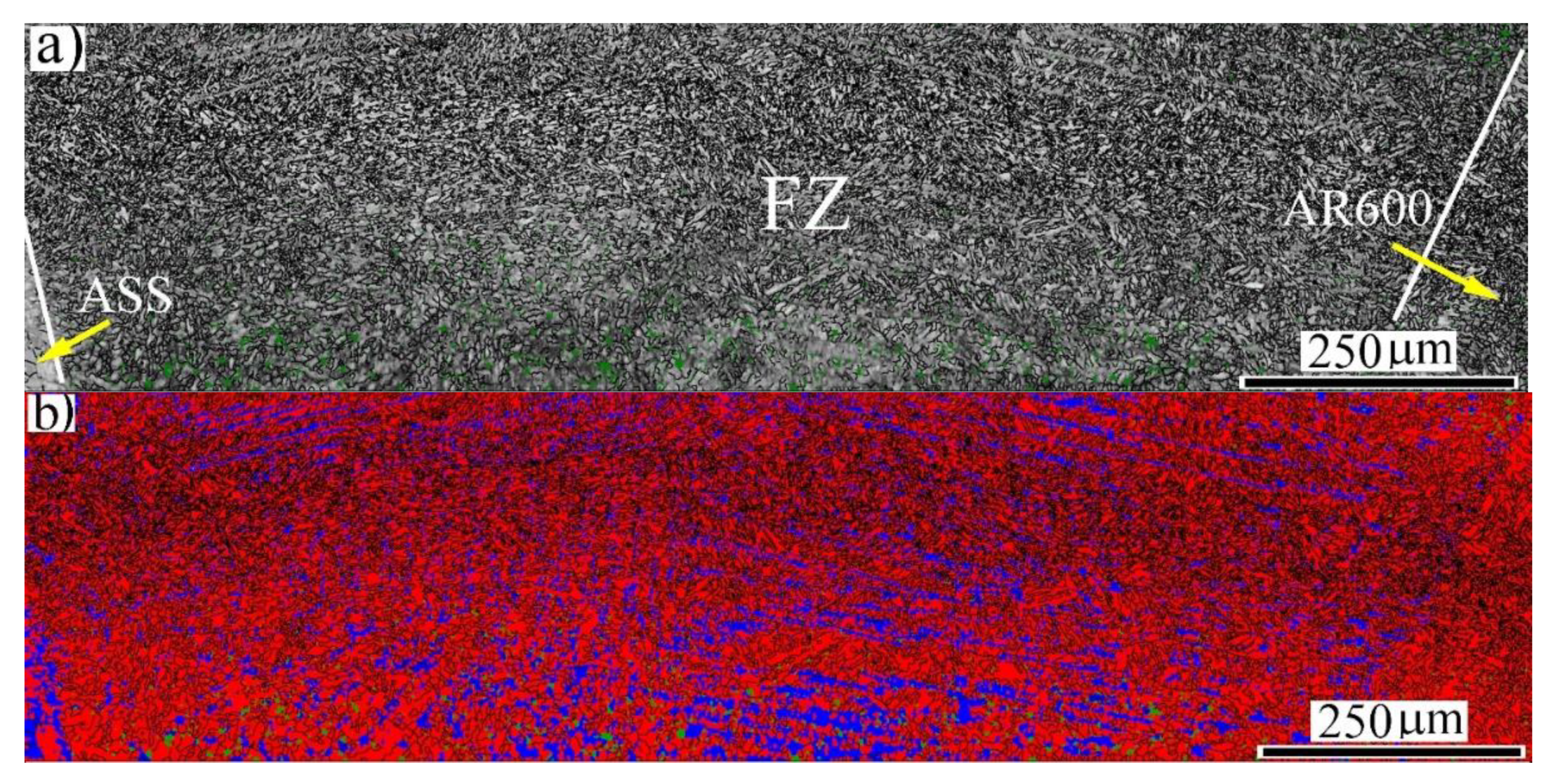
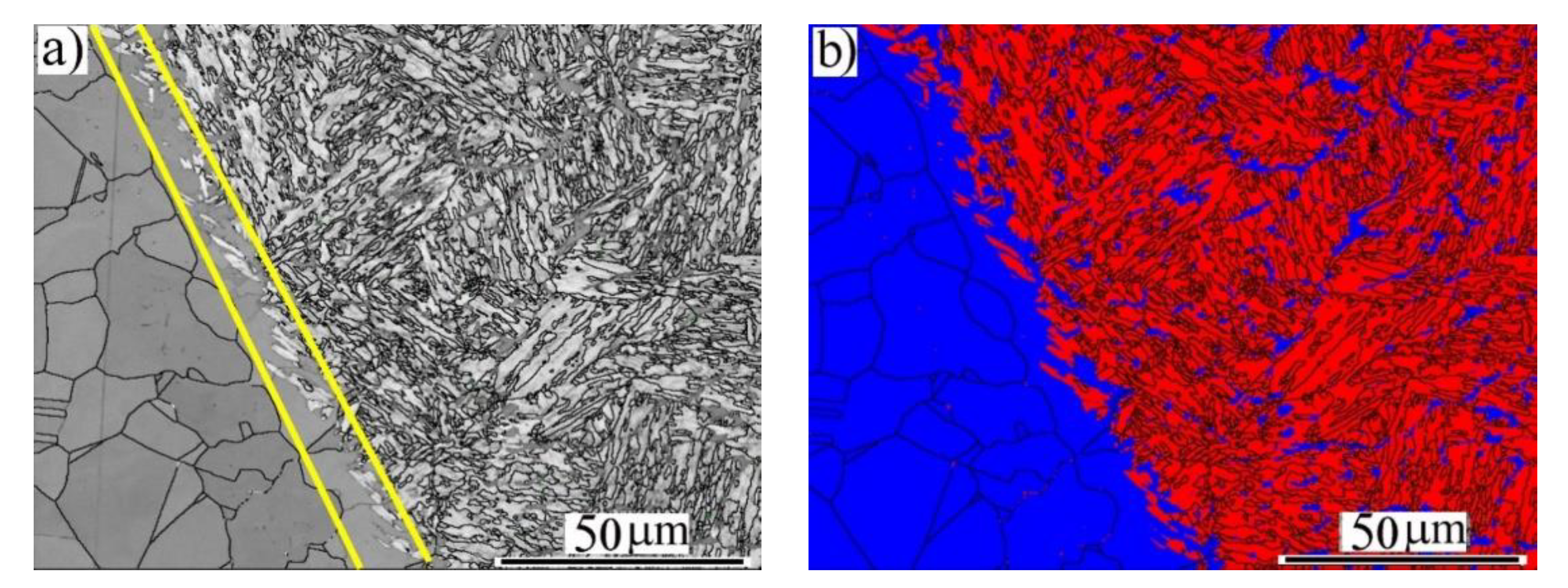
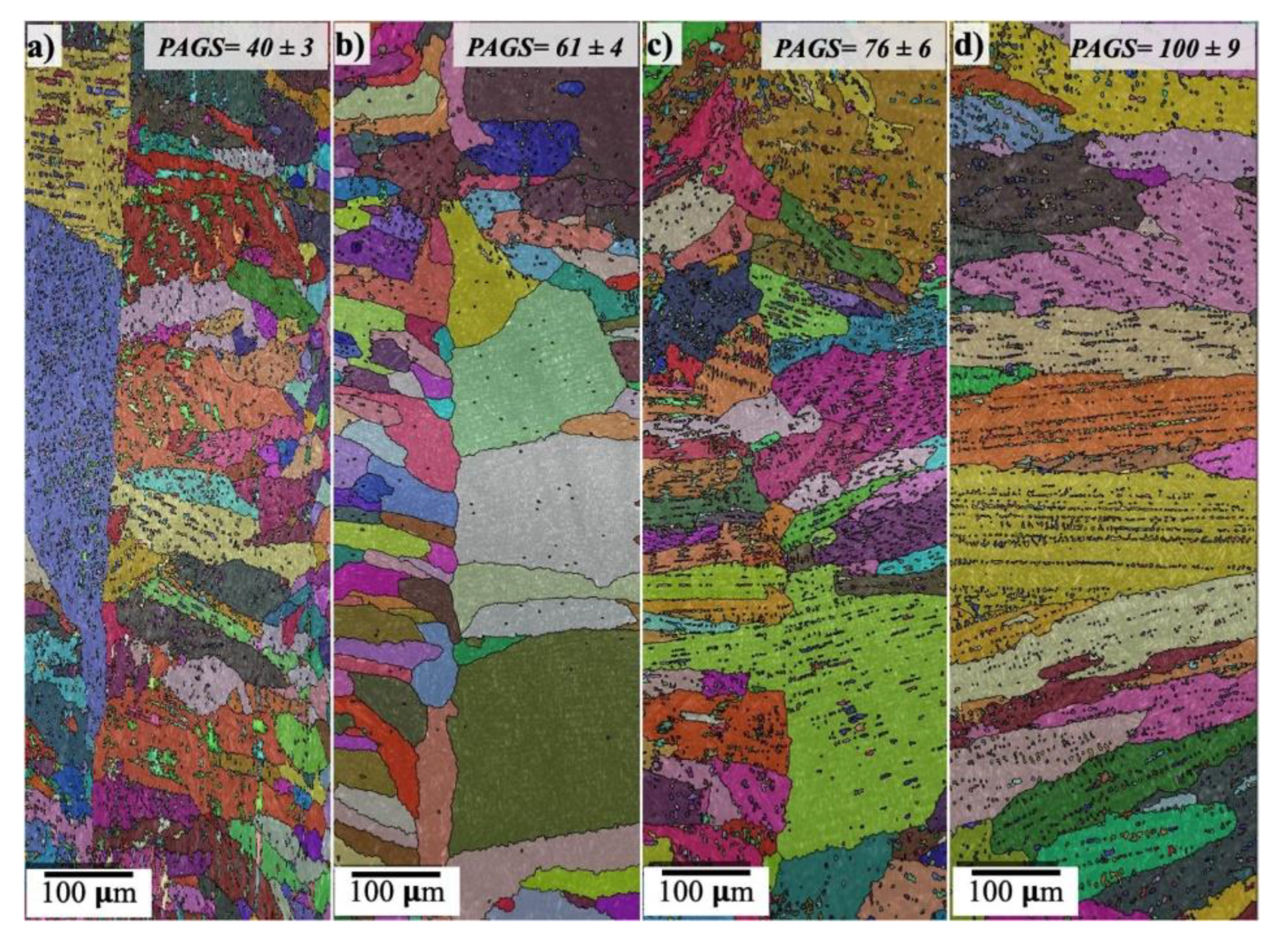
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
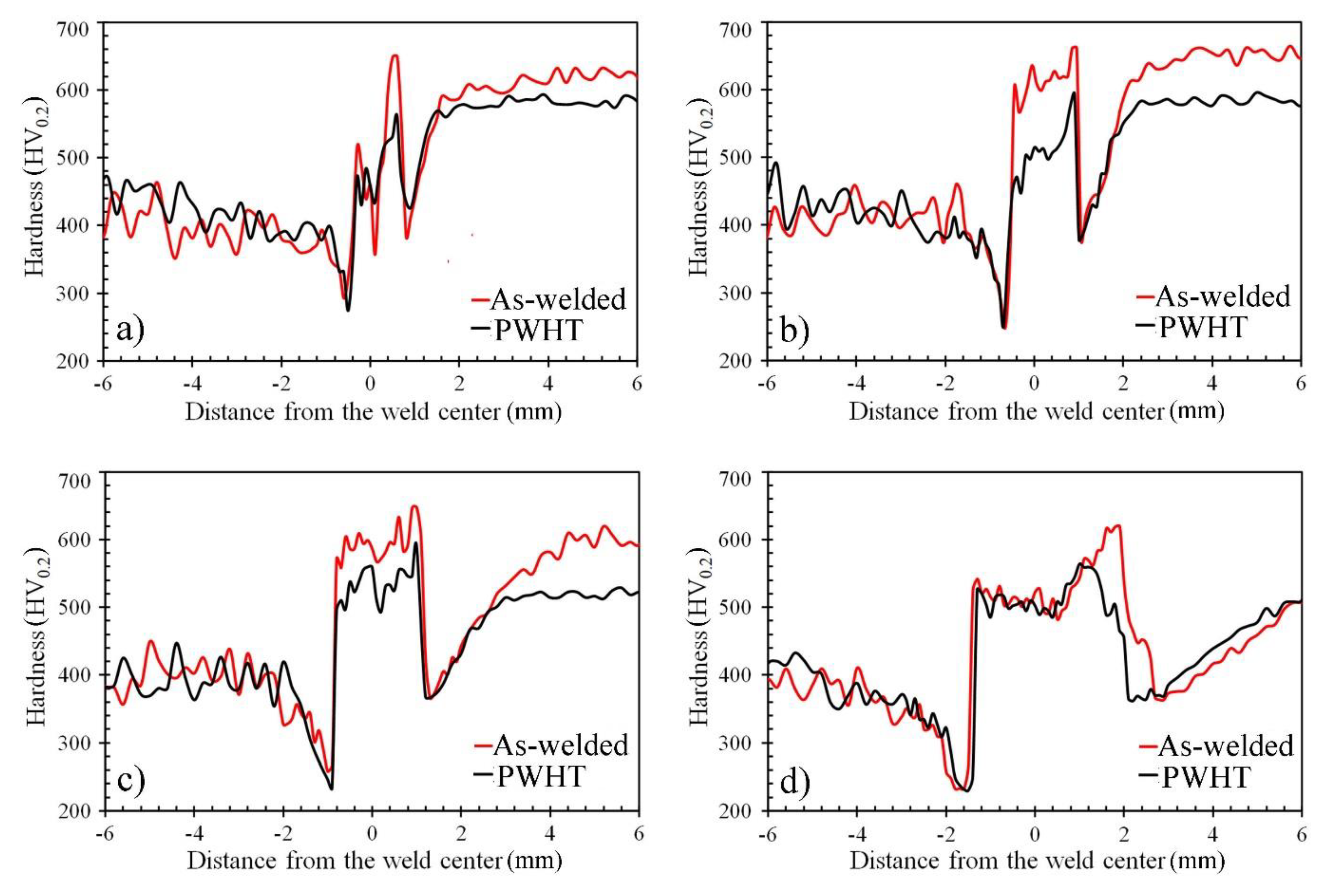
3.3. Hardness
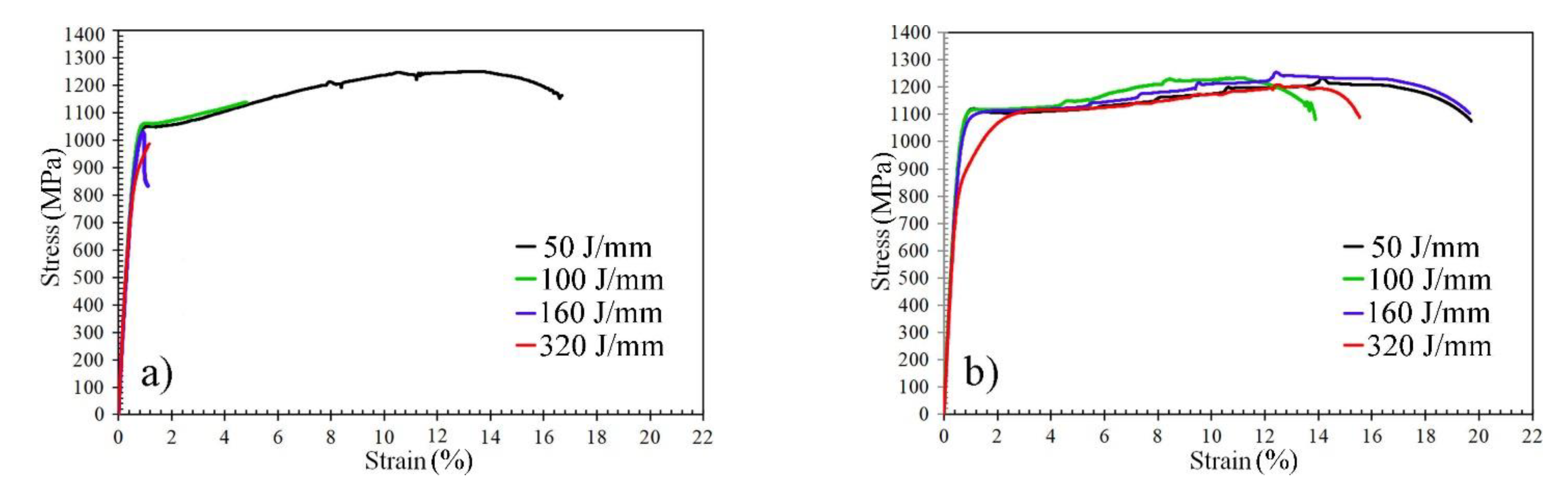
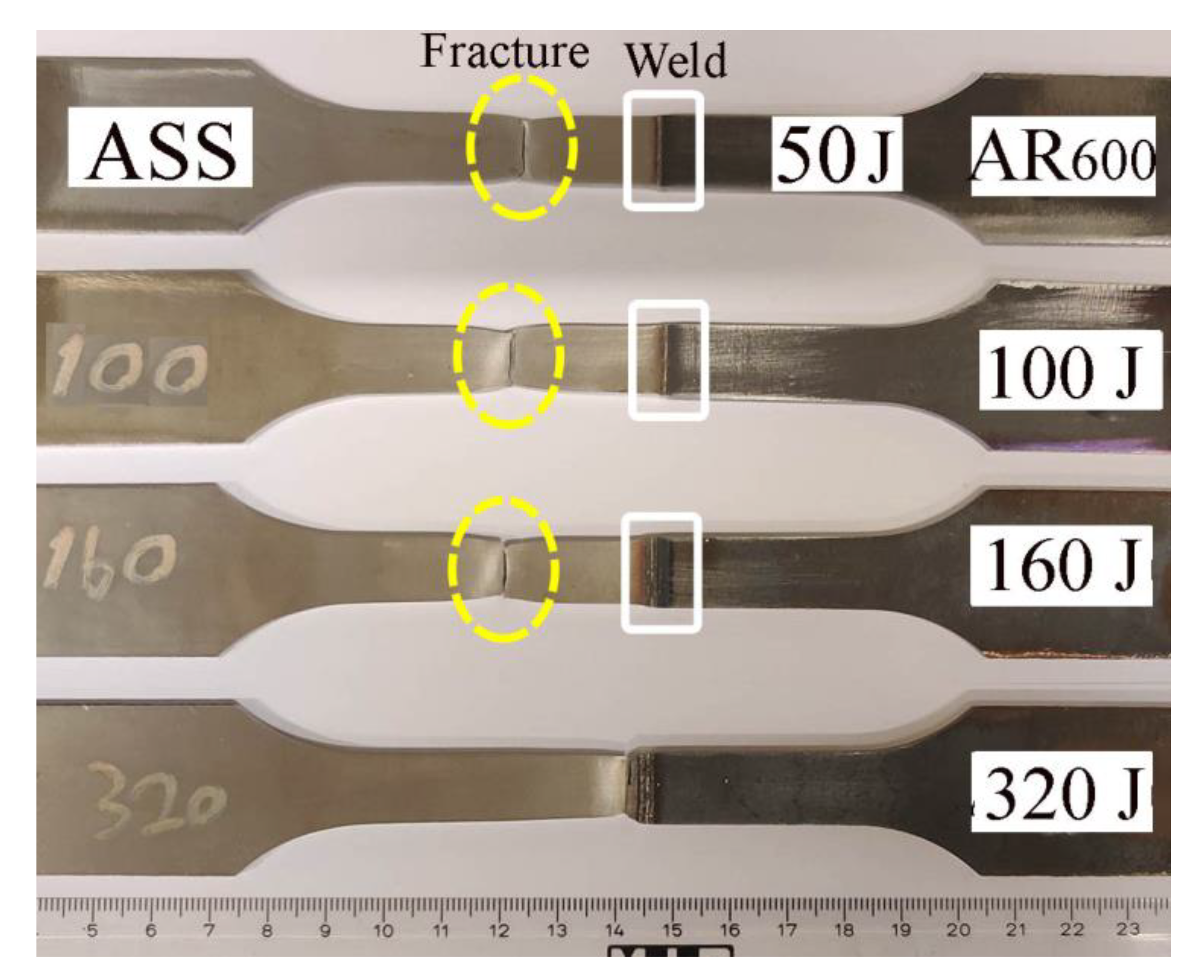
3.4. Tensile Strength
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, G.; Deng, M.; Zheng, G.; Li, Q. Design for cost performance of crashworthy structures made of high strength steel. Thin. Wall. Struct. 2019, 138, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kananen, M.; Mäntyjärvi, K.; Keskitalo, M.; Hietala, M.; Järvenpää, A.; Holappa, K.; Saine, K.; Teiskonen, J. Laser welded corrugated steel panels in industrial applications. Phys. Procedia 2015, 78, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghaee, A.M.; Ghoreishi, M.; Malekshahi, B.Z. Prediction of weld geometry, temperature contour and strain distribution in disk laser welding of dissimilar joining between copper & 304 stainless steel. Optik 2020, 219, 165288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, S.; Liao, H.; Wang, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of CLF-1/316 L steel dissimilar joints welded with fiber laser welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 54, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, K.; Keltamäki, K.; Kuokkala, V.T. High-stress abrasion of wear resistant steels in the cutting edges of loader buckets. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietala, M.; Ali, M.; Khosravifard, A.; Keskitalo, M.; Järvenpää, A.; Hamada, A. Optimization of the tensile-shear strength of laser-welded lap joints of ultra-high strength abrasion resistance steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, G.; Yeni, Ç.; Erim, S.; Ventzke, V.; Koçak, M. Investigation into properties of laser welded similar and dissimilar steel joints. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1998, 3, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkamany, M.J.; Sabbaghzadeh, J.; Hamedi, M.J. Effect of laser welding mode on the microstructure and mechanical performance of dissimilar laser spot welds between low carbon and austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duley, W.W. Laser Welding, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rogalski, G.; Świerczyńska, A.; Landowski, M.; Fydrych, D. Mechanical and Microstructural Characterization of TIG Welded Dissimilar Joints between 304L Austenitic Stainless Steel and Incoloy 800HT Nickel Alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pańcikiewicz, K.; Świerczyńska, A.; Hućko, P.; Tumidajewicz, M. Laser Dissimilar Welding of AISI 430F and AISI 304 Stainless Steels. Materials 2020, 13, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landowski, M.; Świerczyńska, A.; Rogalski, G.; Fydrych, D. Autogenous Fiber Laser Welding of 316L Austenitic and 2304 Lean Duplex Stainless Steels. Materials 2020, 13, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, M.P.; Kannan, G.R. Optimization of laser welding process parameters in dissimilar joint of stainless steel AISI316/AISI1018 low carbon steel to attain the maximum level of mechanical properties through PWHT. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 112, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, H.; Oi, K.; Yasuda, K. Effect of chemical composition on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser weld metal of high-tensile-strength steel. Weld. World 2015, 59, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, S.; Senthil Kumar, S.; Venugopal, N.; Upadhyaya, M.; Manjunath, T.C.; Chelladurai, S.J.S.; Padmanaban, G. Effect of laser power on microstructure and tensile properties of pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam welded AISI 301 austenitic stainless steel joints. Mater. Today: Proc. 2021, 37, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawa, E.M.; Olabi, A.G. Optimization of tensile strength of ferritic/austenitic laser-welded components. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2008, 46, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossini, M.; Russo Spena, P.; Cortese, L.; Matteis, P.; Firrao, D. Investigation on dissimilar laser welding of advanced high strength steel sheets for the automotive industry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 628, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Honeycombe, S.R. The Tempering of Martensite. In Steels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G. Tempering of Martensite in Carbon Steels. In Phase Transform Steels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 126–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Nyyssonen, T.; Grande, B.; Porter, D. Computational design of a novel medium-carbon, low-alloy steel microalloyed with niobium. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 2978–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyyssonen, T.; Isakov, M.; Peura, P.; Kuokkala, V.T. Iterative determination of the orientation relationship between austenite and martensite from a large amount of grain pair misorientations. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2016, 47, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nie, P.; Qu, Z.; Ojo, O.A.; Xia, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. Influence of heat input on the changes in the microstructure and fracture behavior of laser welded 800MPa grade high-strength low-alloy steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 50, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morito, S.; Yoshida, H.; Maki, T.; Huang, X. Effect of block size on the strength of lath martensite in low carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoko, W.; Pahlevani, F.; Hossain, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Stress-induced phase transformation and its correlation with corrosion properties of dual-phase high carbon steel. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, D.; Sun, S. Influence of martensitic transformation on welding residual stress in plates and pipes. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2017, 22, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalcska, A.; De Baets, P.; Ben Hamouda, H.; Theuwissen, K.; Sukumaran, J. Tribological investigation of abrasion resistant steels with martensitic and retained austenitic microstructure in single- and multi–asperity contact. Wear 2021, 482–483, 203980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weman, K. Welding Processes Handbook, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nekouie Esfahani, M.N.; Coupland, J.; Marimuthu, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a laser welded low carbon–stainless steel joint. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2014, 214, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Di, H.S. Microstructure and fracture behavior of laser welded joints of DP steels with different heat inputs. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 699, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, L.; Peng, P.; Jia, Q.; Wan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, W. Microstructural evolution and deformation behavior of fiber laser welded QP980 steel joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 717, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietala, M.; Hamada, A.; Keskitalo, M.; Jaskari, M.; Kumpula, J.; Järvenpää, A. Microstructural evolution and tensile strength of laser-welded butt joints of ultra-high strength steels: Low and high alloy steels. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 883, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Steel Code | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASS | 0.106 | 0.85 | 1.21 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 16.76 | 6.51 | 0.32 | 0.060 | 0.340 |
| AR600 | 0.326 | 0.31 | 0.49 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.81 | 2.01 | 0.48 | 0.003 | 0.014 |
| Steel Code | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | HV0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASS | 914 ± 19 | 1307 ± 17 | 21.5 ± 0.7 | 416 ± 14 |
| AR600 | 1774 ± 24 | 2164 ± 14 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 646 ± 9 |
| Laser Power (kW) | Welding Speed (m/min) | Energy Input (J/mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4.80 | 50 |
| 4 | 2.40 | 100 |
| 4 | 1.50 | 160 |
| 4 | 0.75 | 320 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hietala, M.; Jaskari, M.; Ali, M.; Järvenpää, A.; Hamada, A. Dissimilar Laser Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Abrasion-Resistant Steel: Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties Enhanced by Post-Weld Heat Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 5580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195580
Hietala M, Jaskari M, Ali M, Järvenpää A, Hamada A. Dissimilar Laser Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Abrasion-Resistant Steel: Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties Enhanced by Post-Weld Heat Treatment. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195580
Chicago/Turabian StyleHietala, Mikko, Matias Jaskari, Mohammed Ali, Antti Järvenpää, and Atef Hamada. 2021. "Dissimilar Laser Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Abrasion-Resistant Steel: Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties Enhanced by Post-Weld Heat Treatment" Materials 14, no. 19: 5580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195580
APA StyleHietala, M., Jaskari, M., Ali, M., Järvenpää, A., & Hamada, A. (2021). Dissimilar Laser Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Abrasion-Resistant Steel: Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties Enhanced by Post-Weld Heat Treatment. Materials, 14(19), 5580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195580







