Temperature-Sensing Inks Using Electrohydrodynamic Inkjet Printing Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Temperature-Sensing Ink Preparation and Measurement
2.1. Ink Preparation
2.2. Arrangement of Particles in the Ink
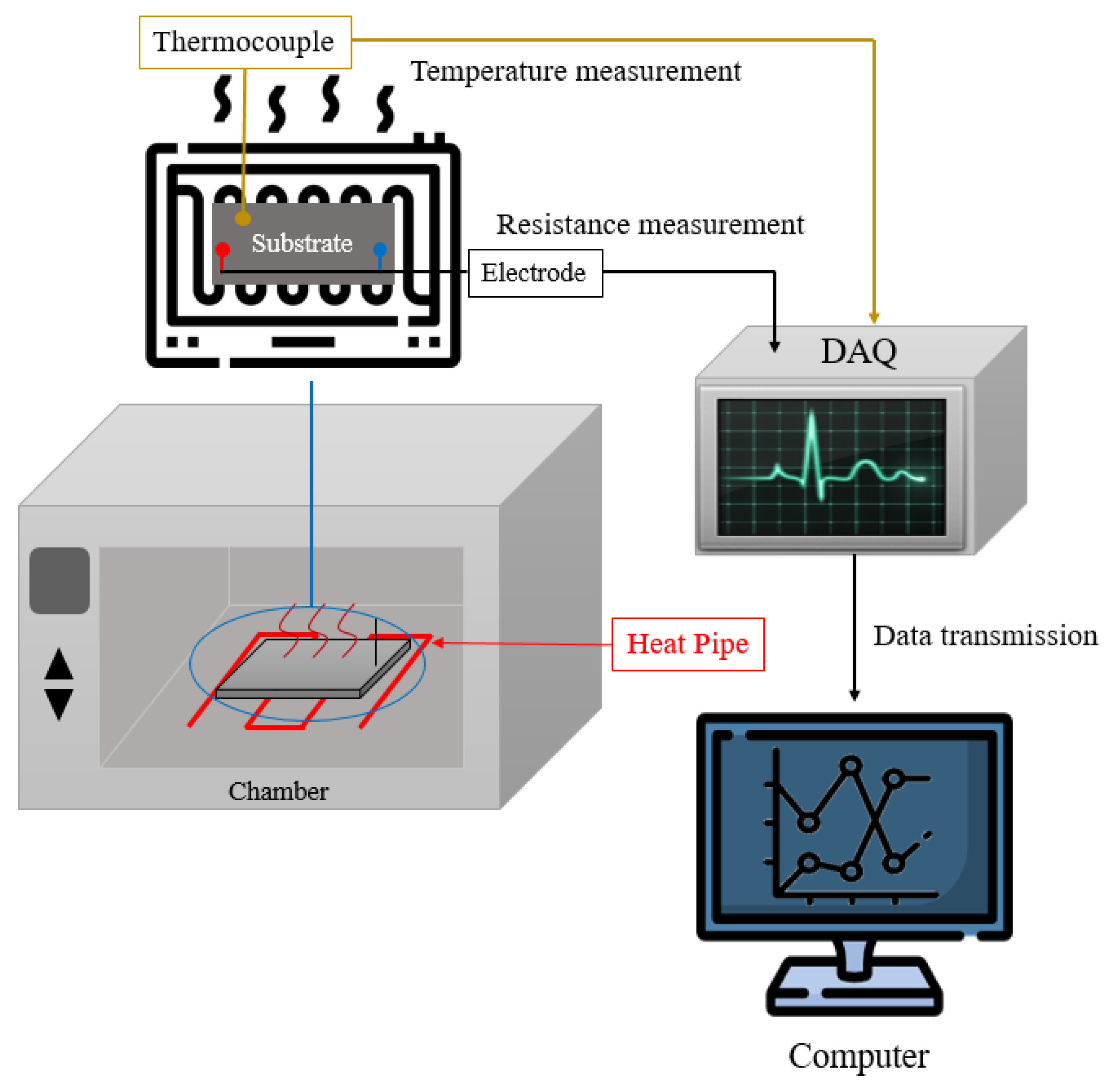
2.3. Experimental Details
2.4. Ink Measurements
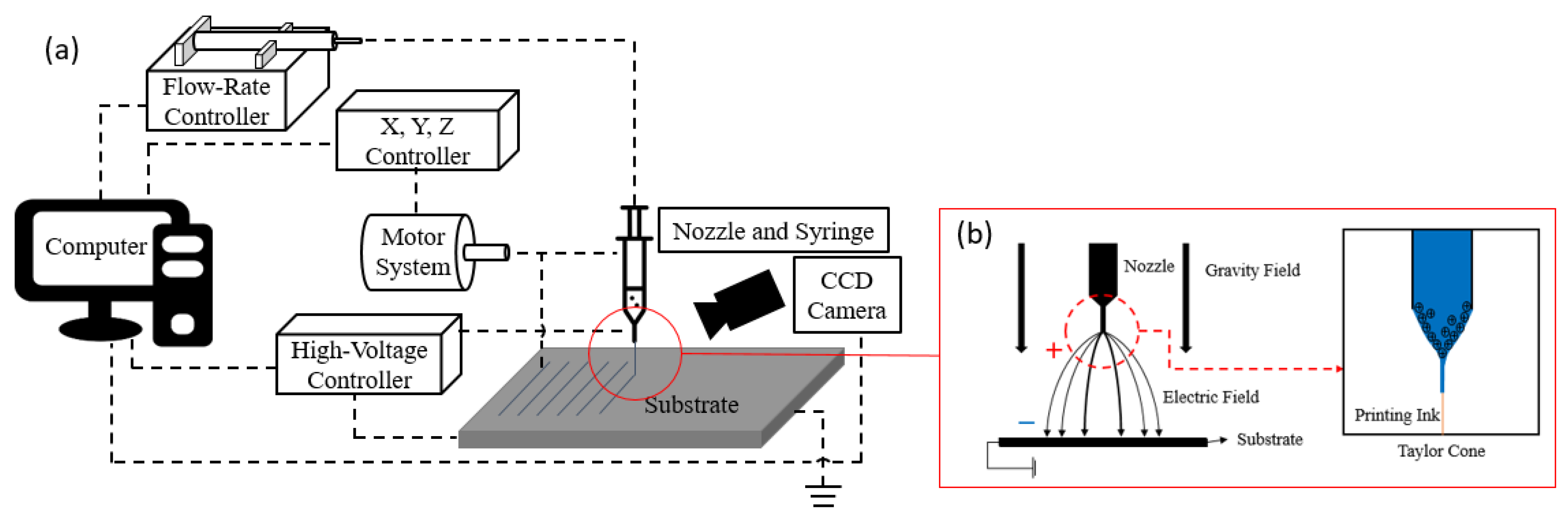
3. EHD Inkjet Printing
3.1. Printing Details
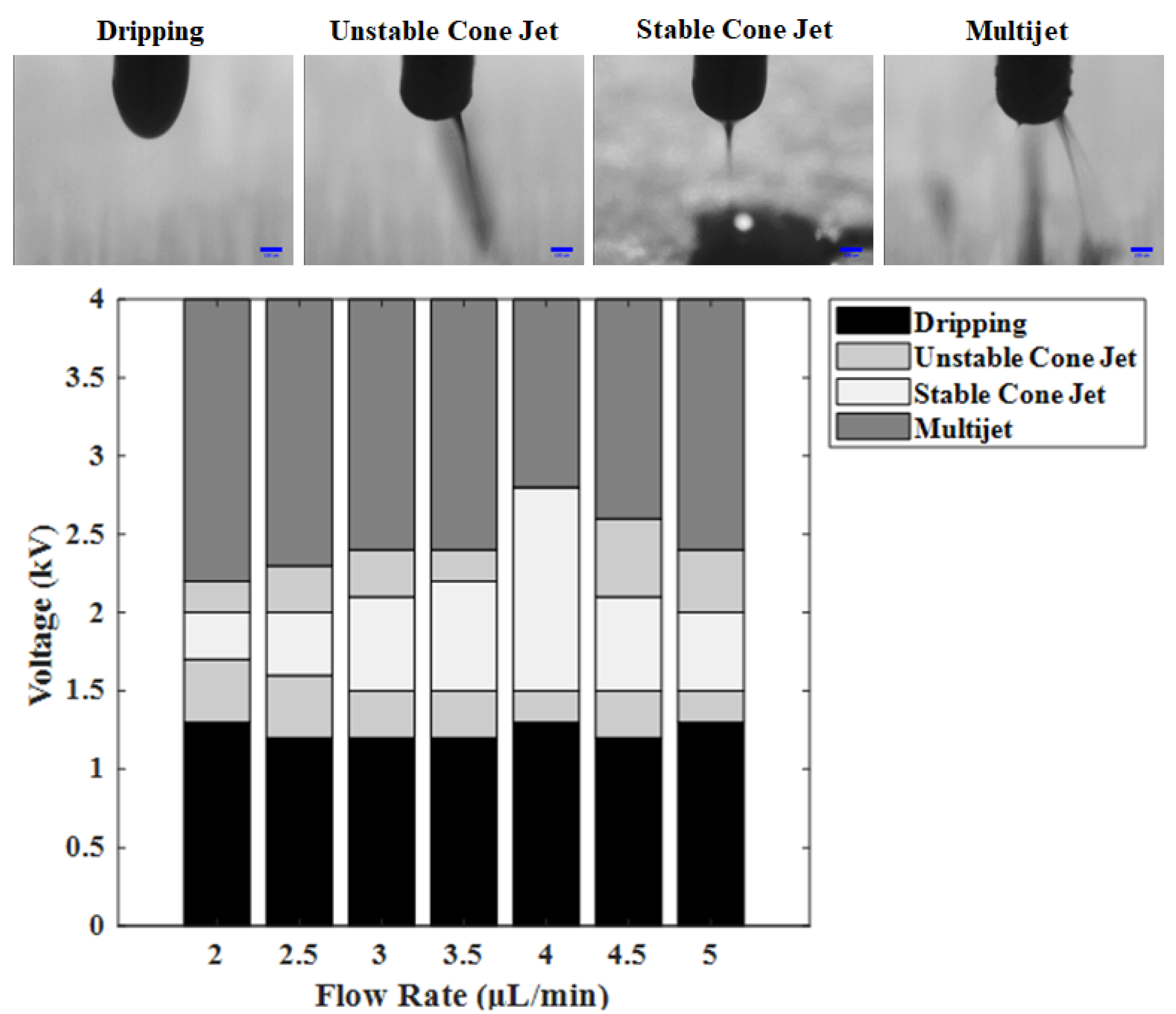
3.2. Printability Confirmation
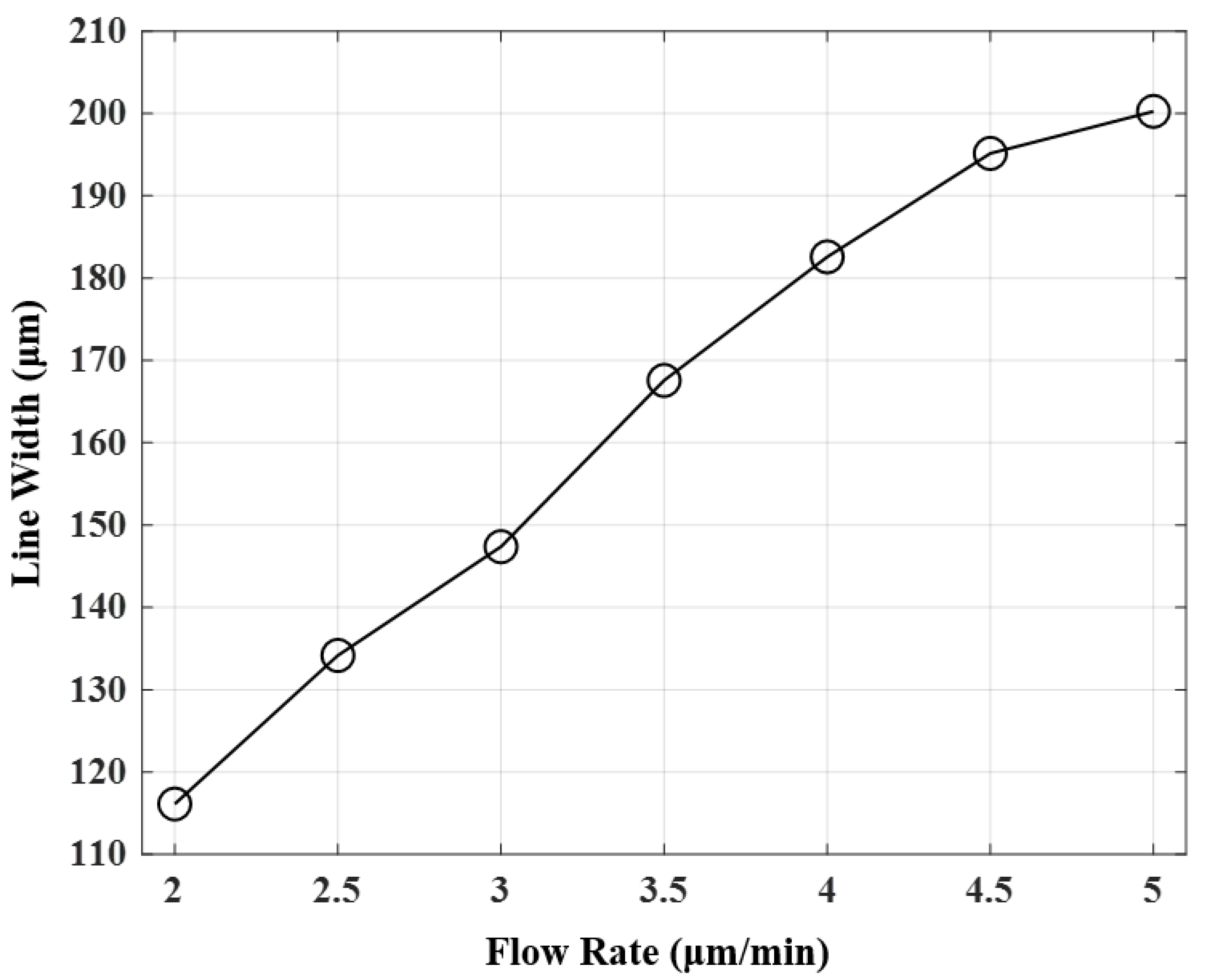
3.3. Printing Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albaik, I.; Al-Dadah, R.; Mahmoud, S.; Solmaz, I. Non-equilibrium numerical modelling of finned tube heat exchanger for adsorption desalination cooling system using segregated solution approach. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 183, 116171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Gan, Z.; Luo, X. Structural optimization of a microjet based cooling system for high power LEDs. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2008, 47, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Usui, T.; Benedict, M.; Hirose, S.; Lee, J.; Schwartz, D. A high-performance solid-state electrocaloric cooling system. Science 2020, 370, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadipour, A.; Zargarabadi, M.R.; Rashidi, S. An efficient pulsed- spray water cooling system for photovoltaic panels: Experimental study and cost analysis. Renew. Energ. 2021, 164, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, C. Surface pattern over a thick silica film to realize passive radiative cooling. Materials 2021, 14, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Hong, J.; Nam, S.Y.; Choi, H.H.; Li, X.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, S.H. Overview of recent progress in electrohydrodynamic jet printing in practical printed electronics: Focus on the variety of printable materials for each component. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 5593–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Printing Conductive Nanomaterials for Flexible and Stretchable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Processes, and Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Huang, Y.A.; Duan, Y.; Zhage, H. Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Writing for Flexible Electronic Manufacturing; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Marbou, K.; Gil, W.; Ghaferi, A.A.; Saadat, I.; Alhammadi, K.; Khair, A.M.; Younesm, H. Assessing the stability of inkjet-printed carbon nanotube for brine sensing applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 7644–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Leeghim, H.; Lee, C.Y. Micropatterning of Metal-Grid Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) Sensor for Crack Detection Using Electrohydrodynamic Printing System. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 4385–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J.L.; Yin, Z.F.; Li, L. Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) Nozzle Structure and Fabrication Optimization for Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) Nozzle Manufacture. Lasers Eng. 2021, 48, 317–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, E.; Yang, X.; Yin, Z.; Hu, W.; Li, L.; Zou, H. Fabrication of Poly(methyl methacrylate) Nozzles for Electrohydrodynamic Printing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 3249–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.U.; Hardy, M.; Kang, S.J.; Barton, K.; Adair, K.; Mukhopadhyay, D.K.; Lee, C.Y.; Strano, M.S.; Alleyne, A.G.; Georgiadis, J.G.; et al. High-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Al-Milaji, K.N.; Zhao, H.; Chen, D.R. Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) jet printing with a circulating dual-channel nozzle. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 035013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Kang, N.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; James, S.C.; Yoon, S.S. A study of ejection modes for pulsed-DC electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing. J. Aerosol Sci. 2012, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Nguyen, X.H.; Ko, H.S. Study on droplet formation with surface tension for electrohydrodynamic inkjet nozzle. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, J.; Byun, D. Invisible metal-grid transparent electrode prepared by electrohydrodynamic (EHD) jet printing. J. Phys. D 2013, 46, 155103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanov, N.S.; Rabadanov, K.S.; Suleymanov, S.I.; Amirow, A.M.; Isaev, A.B.; Sobola, D.S.; Murliev, E.K.; Ascarova, G.A. Water-soluble copper ink for the inkjet fabrication of flexible electronic components. Materials 2021, 14, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, C.Y. Electrical evaluations of anisotropic conductive film manufactured by electrohydrodynamic ink jet printing technology. Org. Electron. 2020, 78, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jung, E.M.; Kim, K.S.; Oh, J.H.; An, T.K.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, S.H. Printed Water-Based ITO Nanoparticle via Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) Jet Printing and Its Application of ZnO Transistors. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2019, 15, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.M.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, S.H. Printed ion-gel transistor using electrohydrodynamic (EHD) jet printing process. Org. Electron. 2018, 52, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloma, M.; Glod, M.A.; Walpuski, B. Printed flexible thermoelectric nanocomposites based on carbon nanotubes and polyaniline. Materials 2021, 14, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.T.; Huang, K.Y.; Lin, D.T.W.; Liao, W.C.; Lin, H.W.; Hu, Y.C. A flexible proximity sensor fully fabricated by inkjet printing. Sensors 2010, 10, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankoco, M.D.; Tesfay, G.Y.; Benevent, E.; Bendahan, M. Temperature sensor realized by inkjet printing process on flexible substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 205, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Henzeh, L.; Lee, C.Y. Resistance Characteristics and Particle Arrangement of Smart Paint for Surface Temperature Sensor. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 4263–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloupeau, M.; Prunet-Foch, B. Electrohydrodynamic spraying functioning modes: A critical review. J. Aerosol Sci. 1994, 25, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
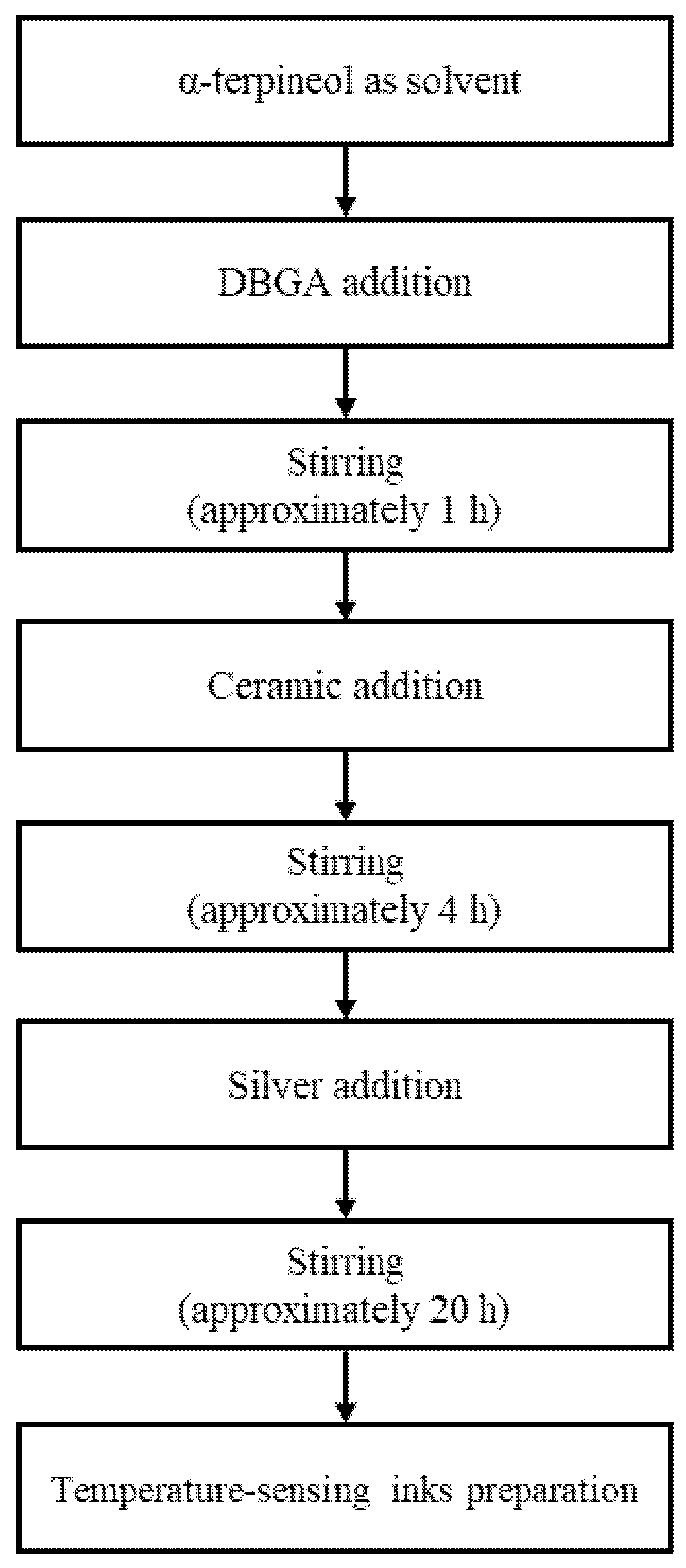
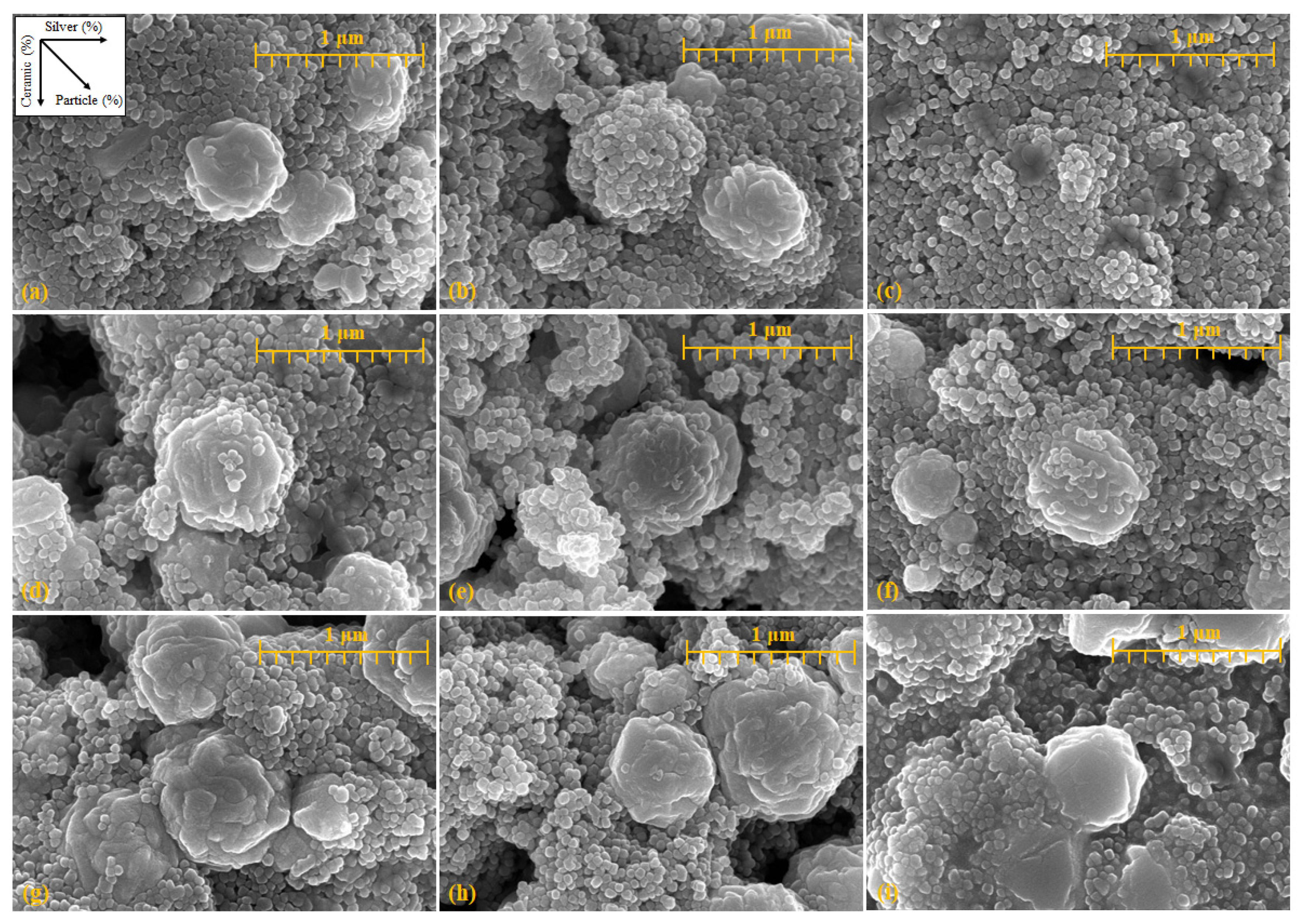
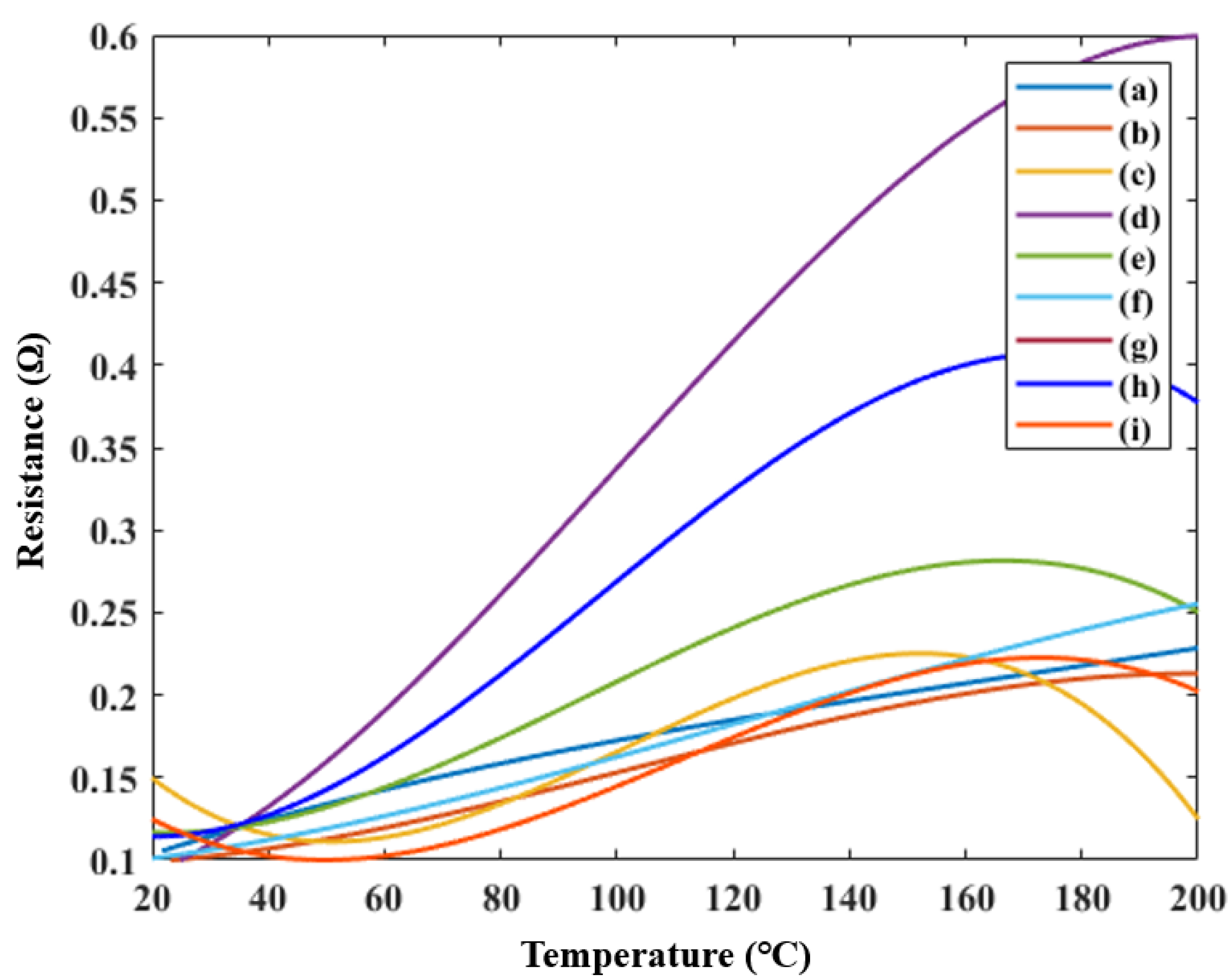
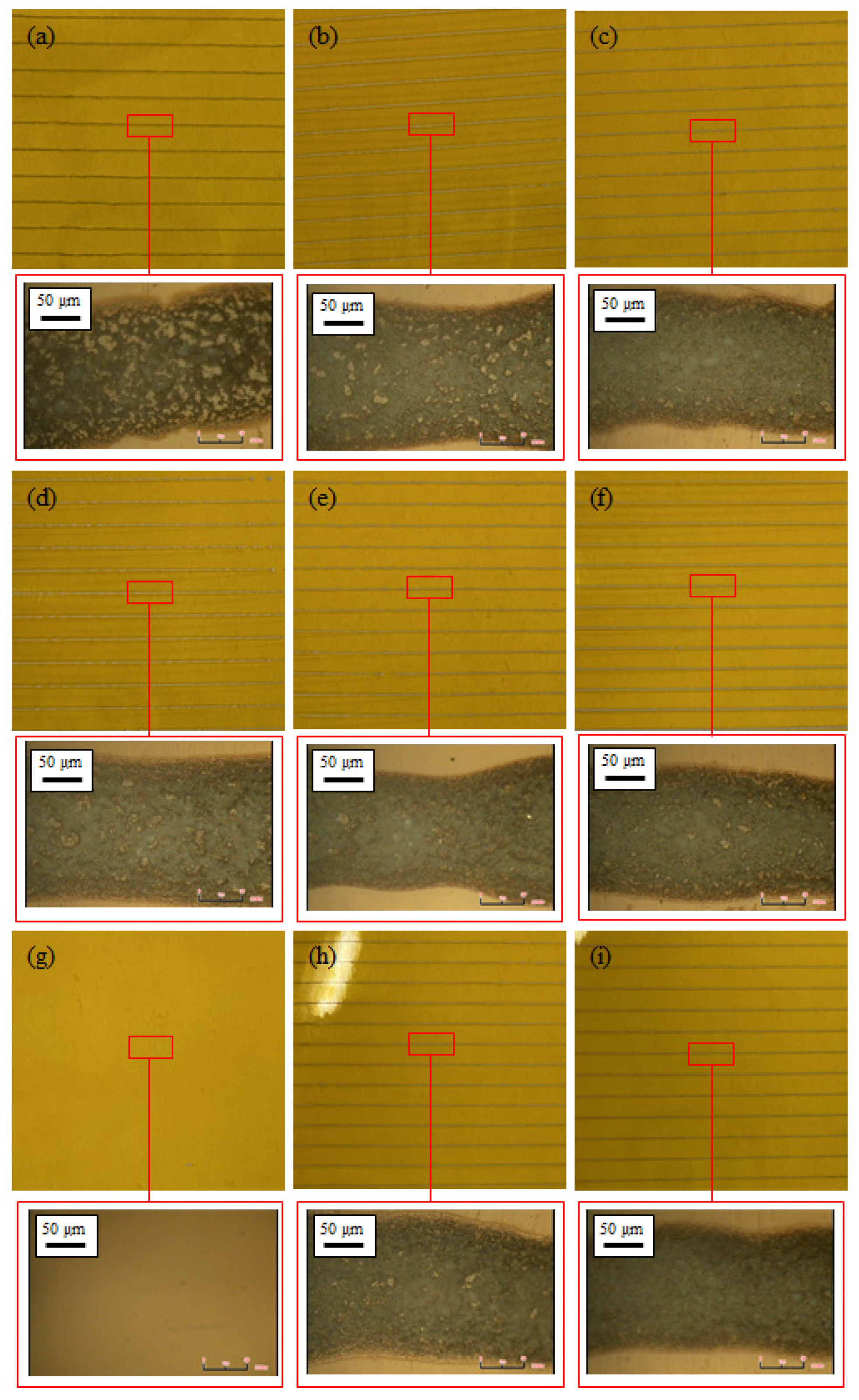
| Tag | α-terpineol + DBGA (%) | Ceramic (%) | Silver (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| (b) | 100 | 100 | 150 |
| (c) | 100 | 100 | 200 |
| (d) | 100 | 150 | 100 |
| (e) | 100 | 150 | 150 |
| (f) | 100 | 150 | 200 |
| (g) | 100 | 200 | 100 |
| (h) | 100 | 200 | 150 |
| (i) | 100 | 200 | 200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.-H.; Hong, H.-J.; Lee, C.-Y. Temperature-Sensing Inks Using Electrohydrodynamic Inkjet Printing Technology. Materials 2021, 14, 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195623
Ahn J-H, Hong H-J, Lee C-Y. Temperature-Sensing Inks Using Electrohydrodynamic Inkjet Printing Technology. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195623
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Ju-Hun, Hee-Ju Hong, and Chang-Yull Lee. 2021. "Temperature-Sensing Inks Using Electrohydrodynamic Inkjet Printing Technology" Materials 14, no. 19: 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195623
APA StyleAhn, J.-H., Hong, H.-J., & Lee, C.-Y. (2021). Temperature-Sensing Inks Using Electrohydrodynamic Inkjet Printing Technology. Materials, 14(19), 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195623






