Ti-Ions and/or Particles in Saliva Potentially Aggravate Dental Implant Corrosion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Electrolyte Preparation
2.3. Electrochemical Tests
2.4. Surface Analysis
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
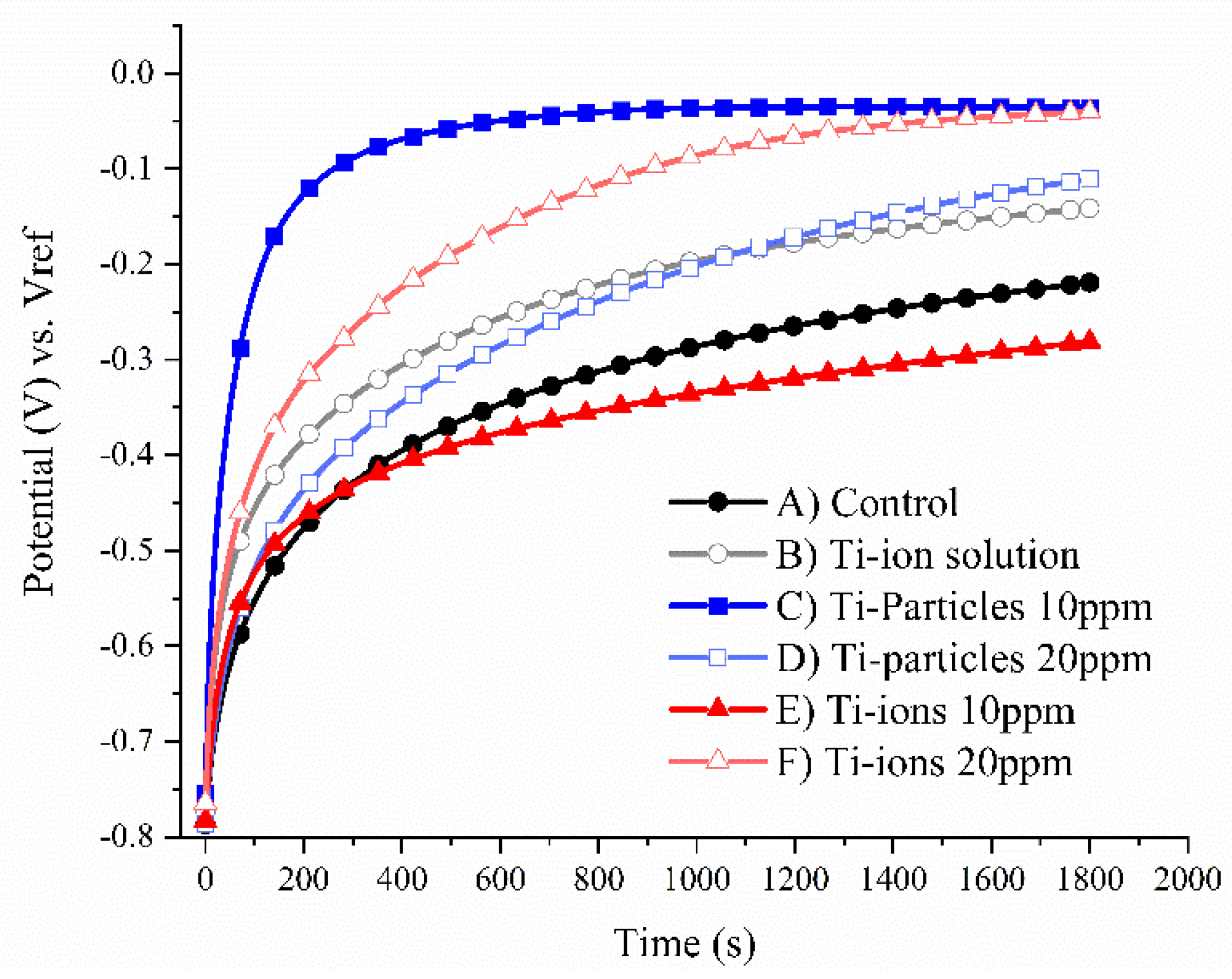
3.1. Open Circuit Potential (OCP)
3.2. Cyclic Polarization Curves
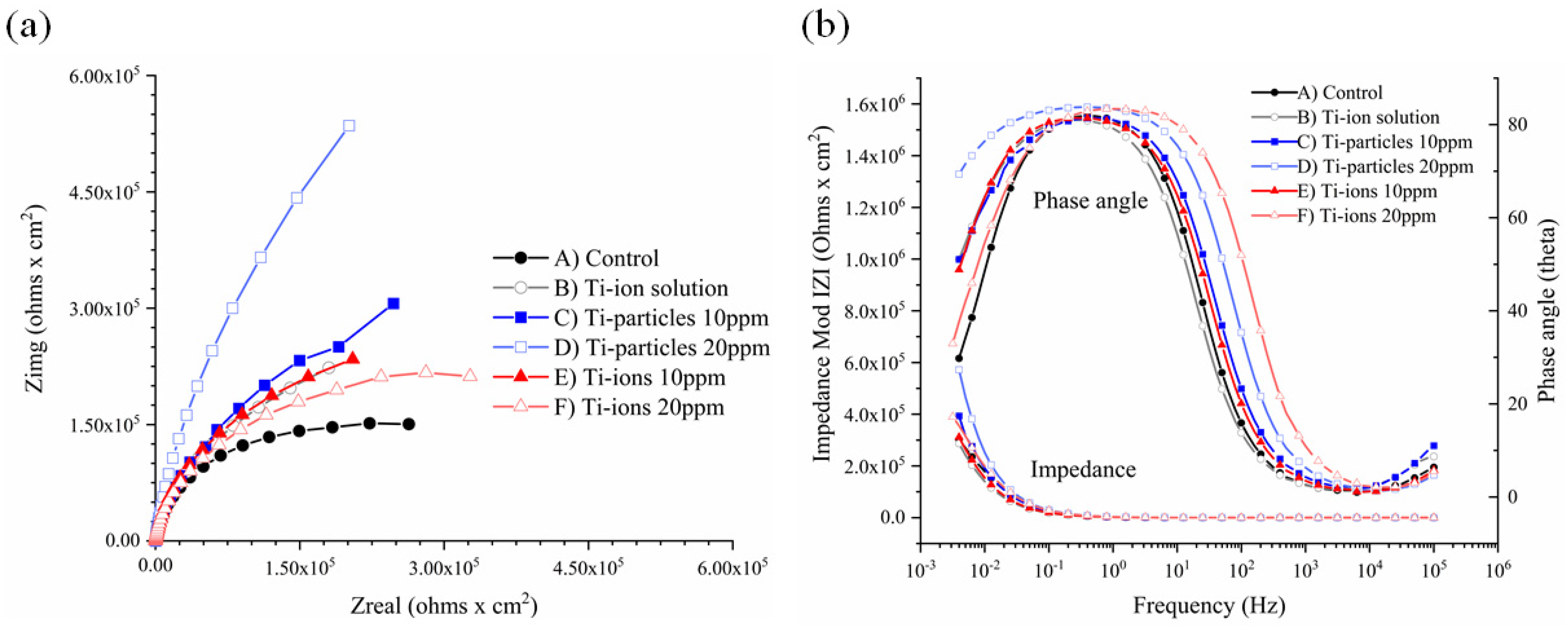
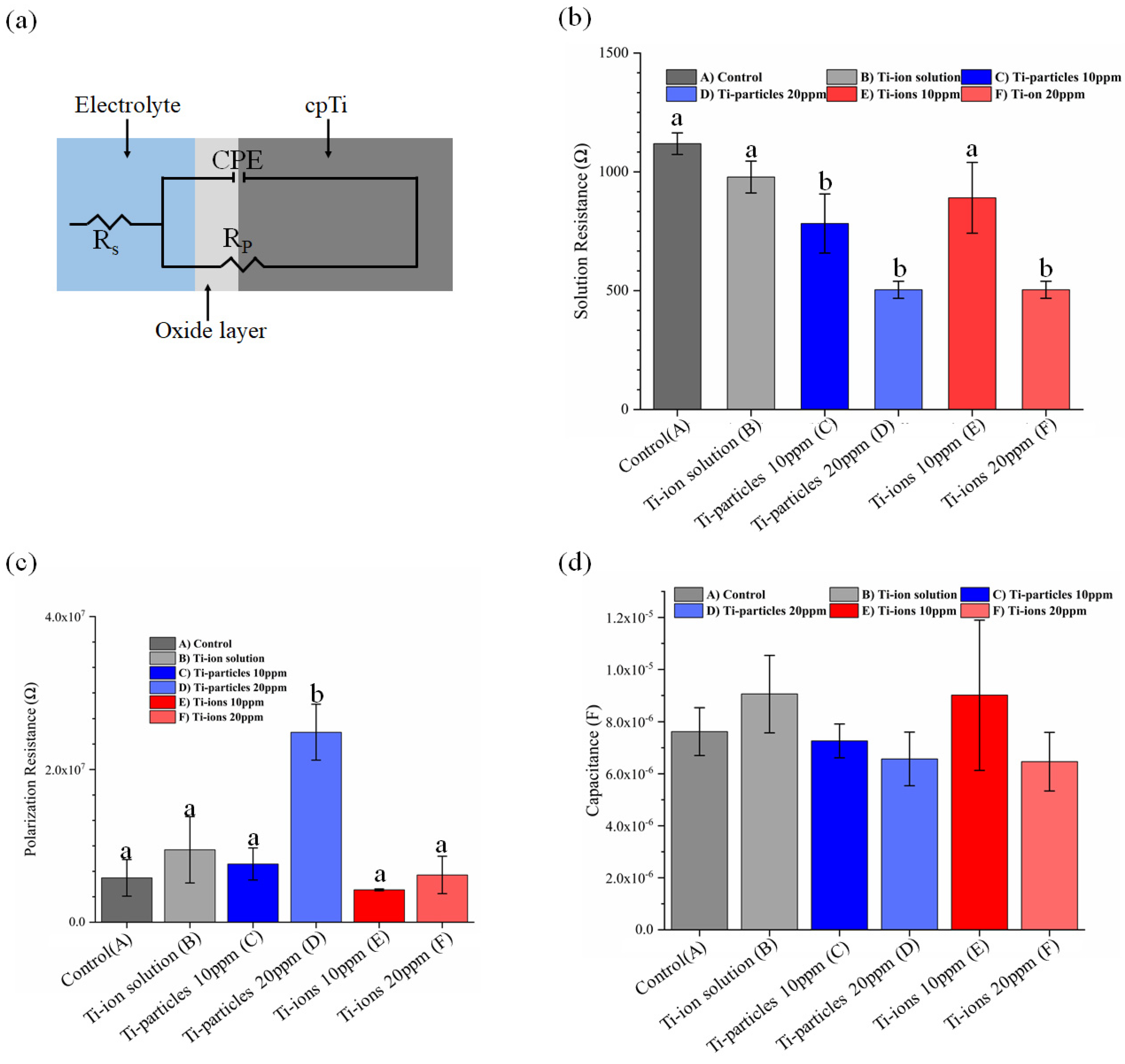
3.3. EIS Analysis
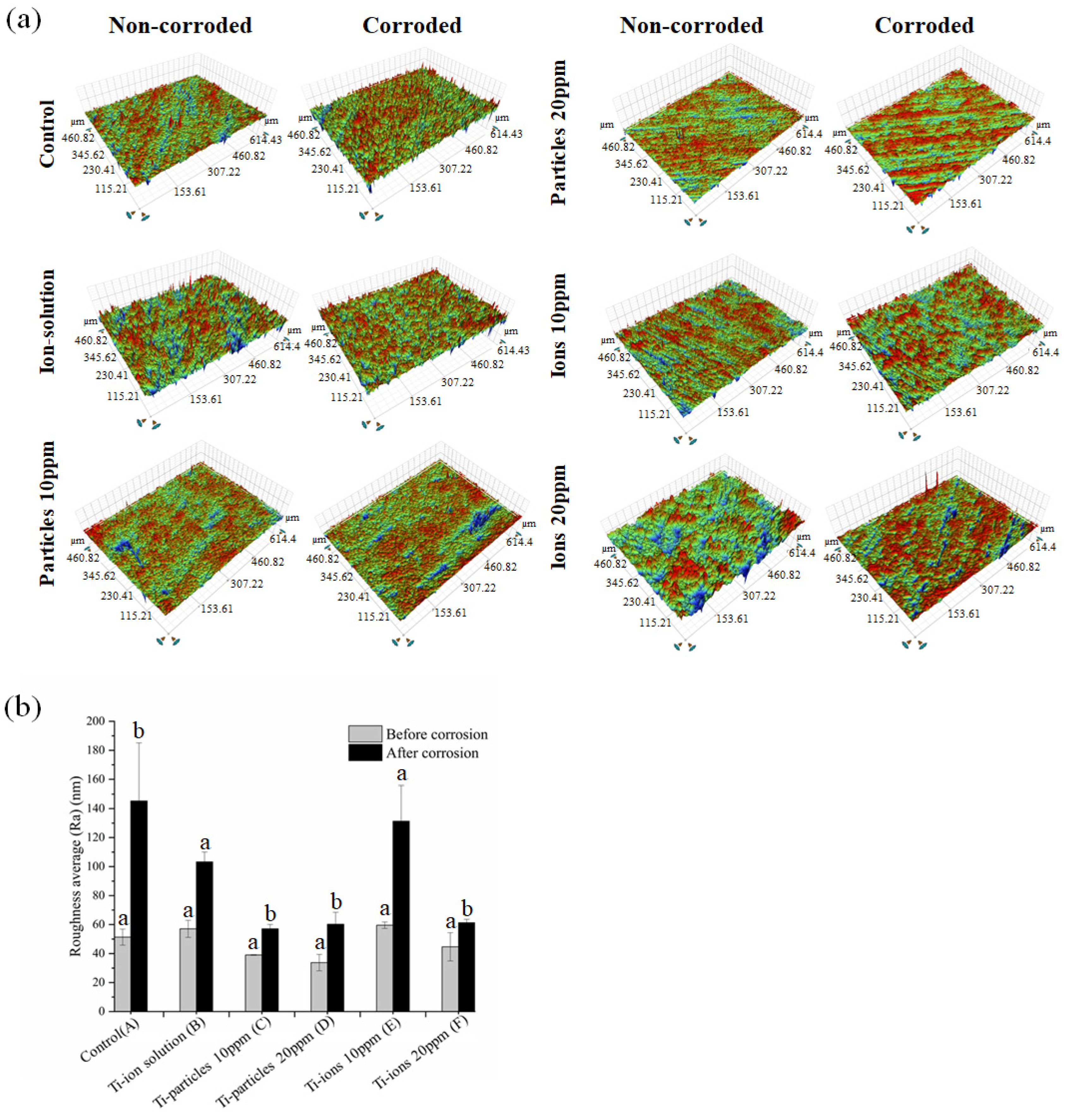
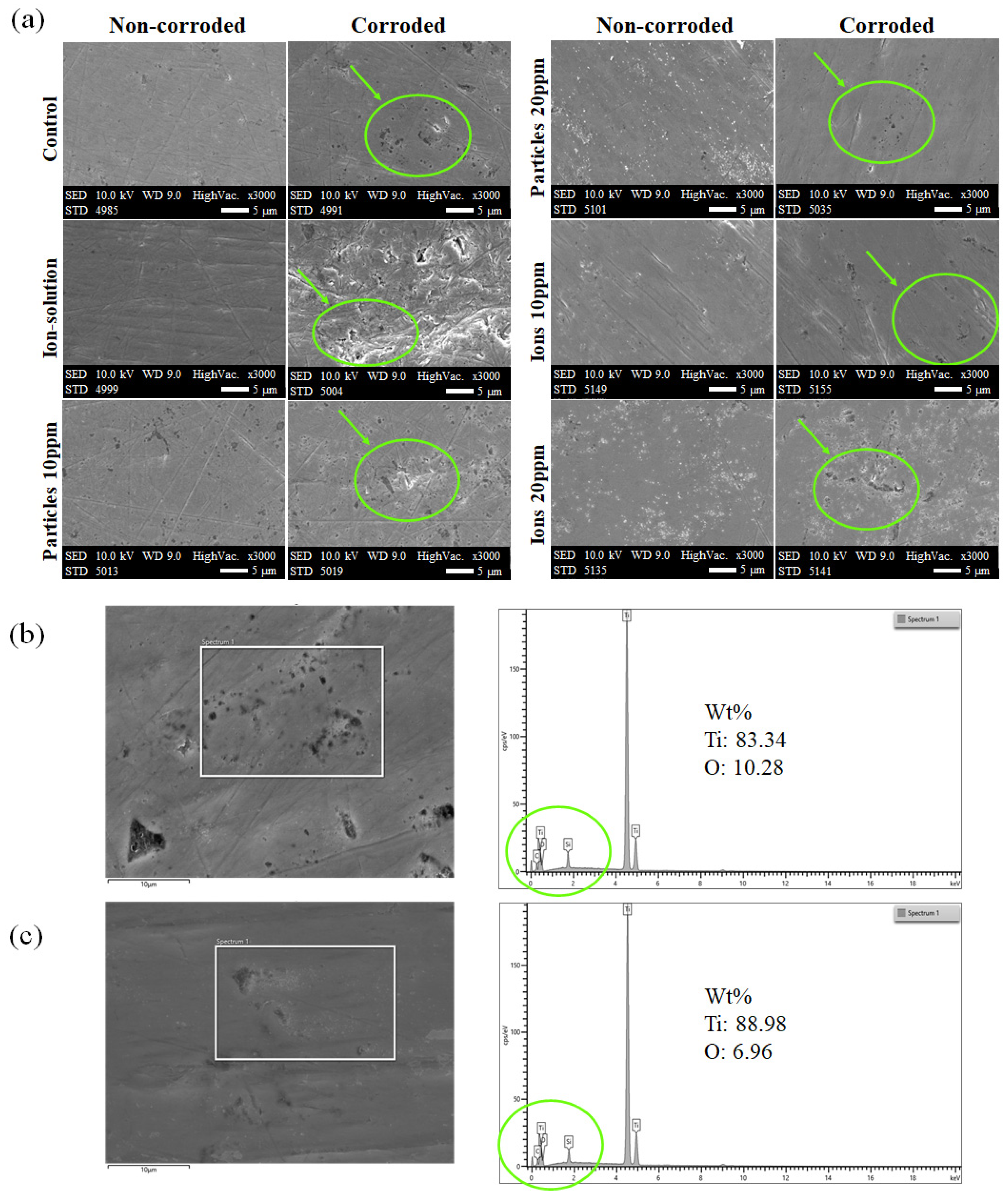
3.4. Surface Characterization
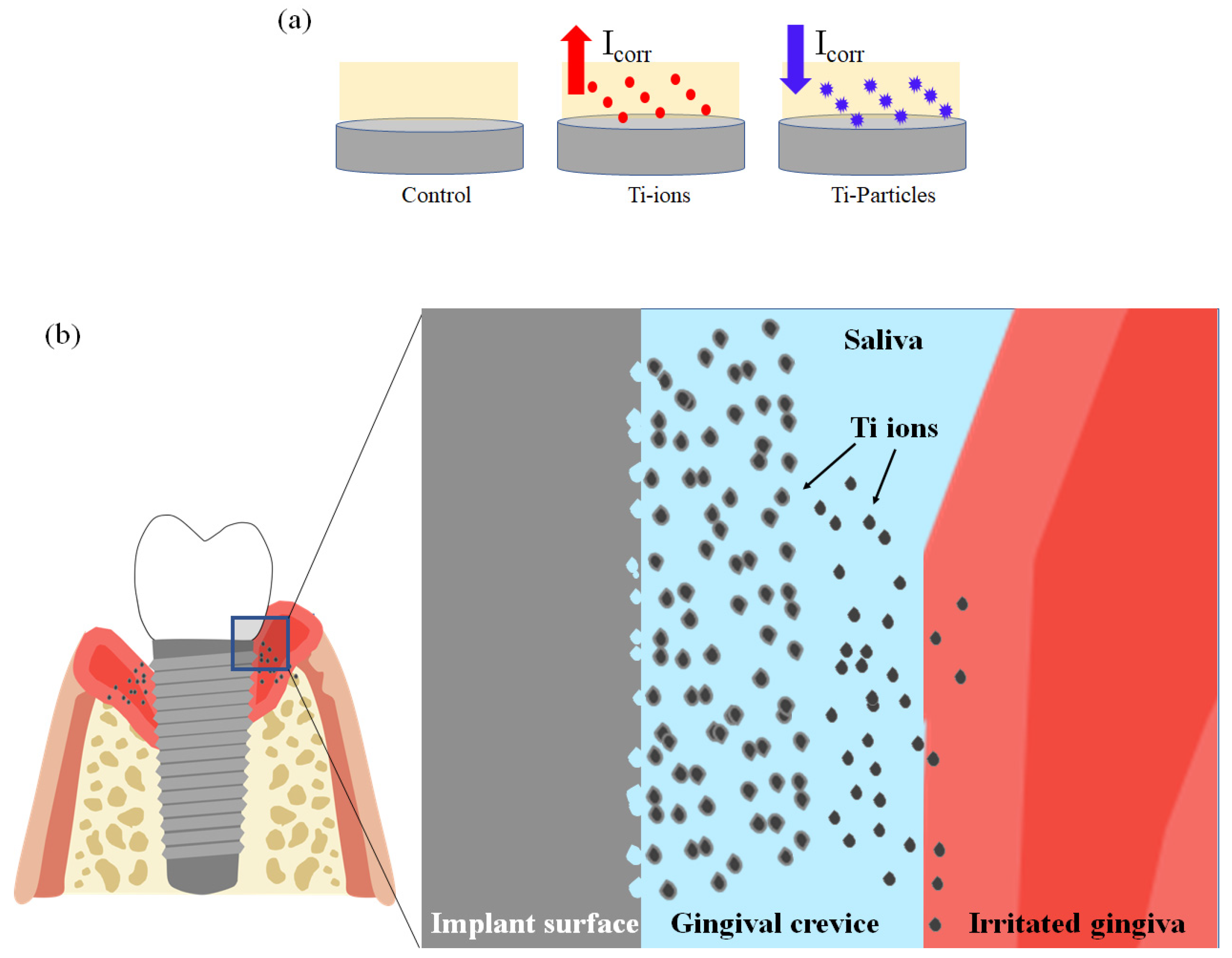
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elani, H.W.; Starr, J.R.; Da Silva, J.D.; Gallucci, G.O. Trends in Dental Implant Use in the U.S., 1999–2016, and Projections to 2026. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, D.G.; Nalli, G.; Verdú, S.; Paparella, M.L.; Cabrini, R.L. Exfoliative Cytology and Titanium Dental Implants: A Pilot Study. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prando, D.; Brenna, A.; Diamanti, M.V.; Beretta, S.; Bolzoni, F.; Ormellese, M.; Pedeferri, M. Corrosion of Titanium: Part 1: Aggressive Environments and Main Forms of Degradation. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2017, 15, e291–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senna, P.; Antoninha Del Bel Cury, A.; Kates, S.; Meirelles, L. Surface Damage on Dental Implants with Release of Loose Particles after Insertion into Bone. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mareci, D.; Chelariu, R.; Gordin, D.-M.; Ungureanu, G.; Gloriant, T. Comparative Corrosion Study of Ti-Ta Alloys for Dental Applications. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3625–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, C.L.; Alfaro, M.F.; Yuan, J.C.-C.; Barao, V.A.; Sukotjo, C.; Mathew, M.T. Wear and Corrosion Interactions at the Titanium/Zirconia Interface: Dental Implant Application. J. Prosthodont. Off. J. Am. Coll. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolopoulou, F. Saliva and Dental Implants. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.-L. Peri-Implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. 20), S246–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elemek, E.; Agrali, O.B.; Kuru, B.; Kuru, L. Peri-Implantitis and Severity Level. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soler, M.D.; Hsu, S.-M.; Fares, C.; Ren, F.; Jenkins, R.J.; Gonzaga, L.; Clark, A.E.; O’Neill, E.; Neal, D.; Esquivel-Upshaw, J.F. Titanium Corrosion in Peri-Implantitis. Materials 2020, 13, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukur, E.; Akman, Y.E.; Ozturkmen, Y.; Kucukdurmaz, F. Particle Disease: A Current Review of the Biological Mechanisms in Periprosthetic Osteolysis After Hip Arthroplasty. Open Orthop. J. 2016, 10, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fretwurst, T.; Nelson, K.; Tarnow, D.P.; Wang, H.-L.; Giannobile, W.V. Is Metal Particle Release Associated with Peri-Implant Bone Destruction? An Emerging Concept. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Langer, M.; Hagena, T.; Hartig, B.; Sader, R.; Becker, J. Cytotoxicity and Proinflammatory Effects of Titanium and Zirconia Particles. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrabeah, G.O.; Brett, P.; Knowles, J.C.; Petridis, H. The Effect of Metal Ions Released from Different Dental Implant-Abutment Couples on Osteoblast Function and Secretion of Bone Resorbing Mediators. J. Dent. 2017, 66, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.G.S.; Costa Oliveira, B.E.; Bertolini, M.; Lima, C.V.; Retamal-Valdes, B.; de Faveri, M.; Feres, M.; Barão, V.A.R. Titanium Particles and Ions Favor Dysbiosis in Oral Biofilms. J. Periodontal Res. 2020, 55, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pier-Francesco, A. Titanium Surface Modification and Its Effect on the Adherence of Porphyromonas Gingivalis: An in Vitro Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 16, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, S.; Haugland, H.K.; Lilleng, P.; Ellison, P.; Hallan, G.; Høl, P.J. Wear Particles and Ions from Cemented and Uncemented Titanium-Based Hip Prostheses—A Histological and Chemical Analysis of Retrieval Material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pioletti, D.P.; Takei, H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Wood, D.; Sung, K.L. The Cytotoxic Effect of Titanium Particles Phagocytosed by Osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, Y.; Makihira, S.; Nikawa, H.; Murata, H.; Hosokawa, R.; Hiyama, A.; Mimura, S. Impact of Titanium Ions on Osteoblast-, Osteoclast- and Gingival Epithelial-like Cells. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2010, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H. Effects of Fluoride Concentration and Elastic Tensile Strain on the Corrosion Resistance of Commercially Pure Titanium. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabilleau, G.; Bourdon, S.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Filmon, R.; Baslé, M.F.; Chappard, D. Influence of Fluoride, Hydrogen Peroxide and Lactic Acid on the Corrosion Resistance of Commercially Pure Titanium. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaroto, H.N.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Pereira, L.T.; de Almeida, A.B.; Nociti Junior, F.H.; Rangel, E.C.; Azevedo Neto, N.F.; da Silva, J.H.D.; Barão, V.A.R. Sputtered Crystalline TiO2 Film Drives Improved Surface Properties of Titanium-Based Biomedical Implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Shu, X.; Liu, E.; Han, Z. A Comparative Study of the Corrosion Performance of Titanium (Ti), Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) and Nitrogen-Doped Titanium Oxides (N–TiO2), as Coatings for Biomedical Applications. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 11844–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, C.; Costa, R.C.; Sukotjo, C.; Takoudis, C.G.; Mathew, M.T.; Barão, V.A.R. Progression of Bio-Tribocorrosion in Implant Dentistry. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Reichl, F.-X.; Wang, Y.; Michalke, B.; Milz, S.; Yang, Y.; Stolper, P.; Lindemaier, G.; Graw, M.; Hickel, R. Analysis of Titanium and Other Metals in Human Jawbones with Dental Implants–A Case Series Study. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.-M.; Qiu, J.; Tian, F.; Guo, X.-K.; Zhang, F.-Q.; Huang, Q.-F. Corrosion Behavior of Pure Titanium in the Presence of Actinomyces Naeslundii. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barão, V.A.R.; Mathew, M.T.; Assunção, W.G.; Yuan, J.C.-C.; Wimmer, M.A.; Sukotjo, C. Stability of Cp-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Dental Implants as a Function of Saliva PH—An Electrochemical Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barão, V.A.; Mathew, M.T.; Assunção, W.G.; Yuan, J.C.; Wimmer, M.A.; Sukotjo, C. The Role of Lipopolysaccharide on the Electrochemical Behavior of Titanium. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H.; Reiss, G.; Urban, R.; Neukam, F.W.; Guckel, S. Metal Release from Titanium Fixtures during Placement in the Mandible: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1993, 8, 502–511. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, D.C.; Valderrama, P.; Wilson, T.G.; Palmer, K.; Thomas, A.; Sridhar, S.; Adapalli, A.; Burbano, M.; Wadhwani, C. Titanium Corrosion Mechanisms in the Oral Environment: A Retrieval Study. Materials 2013, 6, 5258–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential Causes of Titanium Particle and Ion Release in Implant Dentistry: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martini, D.; Fini, M.; Franchi, M.; Pasquale, V.D.; Bacchelli, B.; Gamberini, M.; Tinti, A.; Taddei, P.; Giavaresi, G.; Ottani, V.; et al. Detachment of Titanium and Fluorohydroxyapatite Particles in Unloaded Endosseous Implants. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.D.; Wilson, M. The Effects of Surface Roughness and Type of Denture Acrylic on Biofilm Formation by Streptococcus Oralis in a Constant Depth Film Fermentor. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rokn, A.; Aslroosta, H.; Akbari, S.; Najafi, H.; Zayeri, F.; Hashemi, K. Prevalence of Peri-Implantitis in Patients Not Participating in Well-Designed Supportive Periodontal Treatments: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Covani, U.; Botticelli, D.; Serino, G.; Penarrocha, M. Clinical and Microbiological Findings in Patients with Peri-Implantitis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safioti, L.M.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Pozhitkov, A.E.; Chung, W.O.; Daubert, D.M. Increased Levels of Dissolved Titanium Are Associated with Peri-Implantitis—A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, Z.; Bridger, L.; Hussaini, H.M.; Rich, A.M.; Atieh, M.; Tawse-Smith, A. Titanium Particles: An Emerging Risk Factor for Peri-Implant Bone Loss. Saudi Dent. J. 2020, 32, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obando-Pereda, G.A.; Fischer, L.; Stach-Machado, D.R. Titanium and Zirconia Particle-Induced pro-Inflammatory Gene Expression in Cultured Macrophages and Osteolysis, Inflammatory Hyperalgesia and Edema in Vivo. Life Sci. 2014, 97, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Kelk, P.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Bylund, D.; Molin Thorén, M.; Johansson, A. Titanium Ions Form Particles That Activate and Execute Interleukin-1β Release from Lipopolysaccharide-Primed Macrophages. J. Periodontal Res. 2017, 52, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, J.L.; Sivan, S.; Liu, Y.; Kocagöz, S.B.; Arnholt, C.M.; Kurtz, S.M. Direct in Vivo Inflammatory Cell-Induced Corrosion of CoCrMo Alloy Orthopedic Implant Surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bijukumar, D.R.; Salunkhe, S.; Zheng, G.; Barba, M.; Hall, D.J.; Pourzal, R.; Mathew, M.T. Wear Particles Induce a New Macrophage Phenotype with the Potential to Accelerate Material Corrosion within Total Hip Replacement Interfaces. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

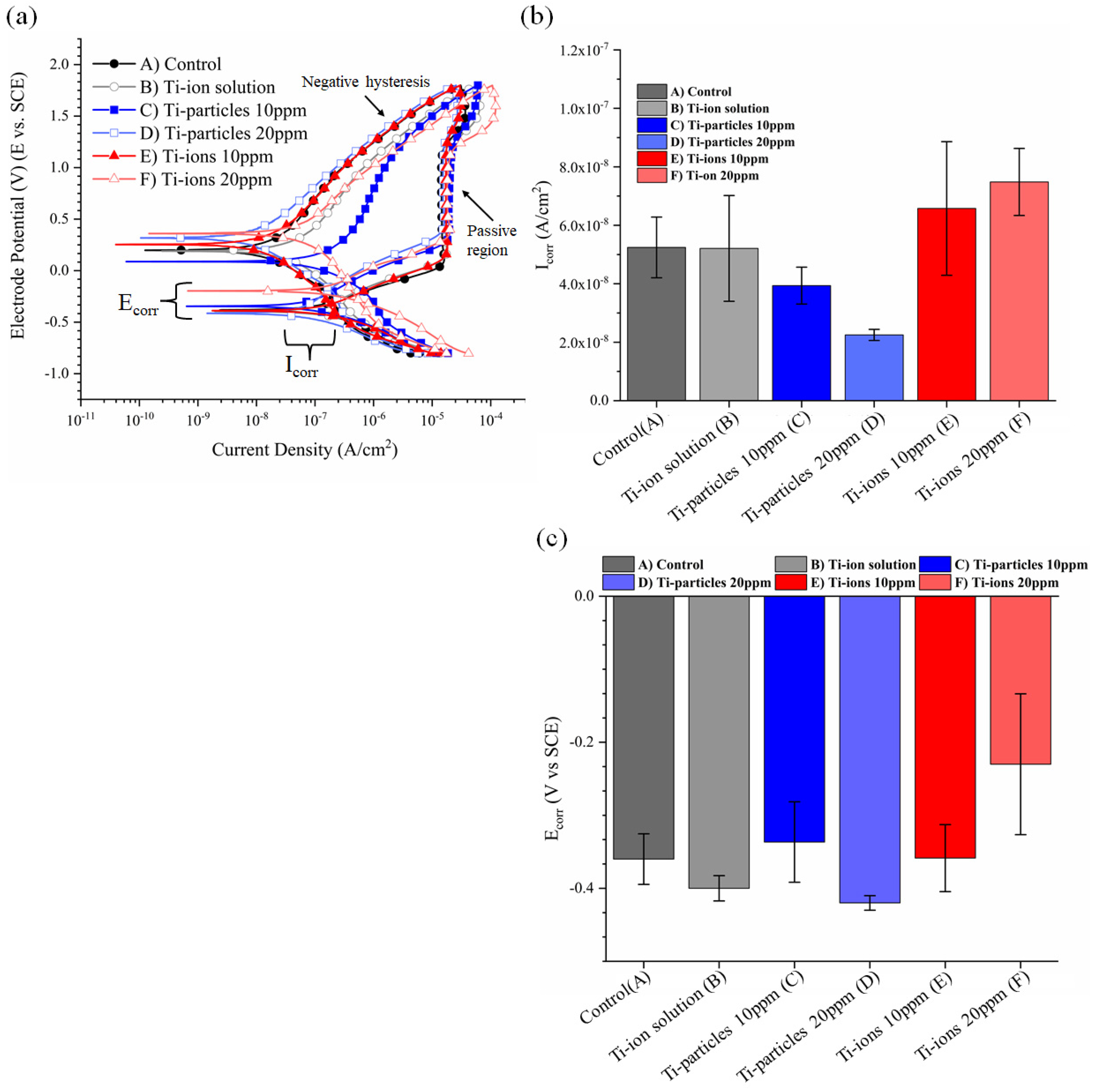
| Corrosion Parameter | Control | Ti-Ion Solution | Ti-Particles 10 ppm | Ti-Particles 20 ppm | Ti-Ions 10 ppm | Ti-Ions 20 ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Icorr | 5.24−8 (±1.04−8) | 5.21−8 (±1.80−8) | 3.94−8 (±6.29−9) | 2.25−8 (±1.90−9) | 6.58−8 (±2.28−8) | 7.48−8 (±1.15−8) |
| Ecorr | −0.36 (±0.03) | −0.40 (±0.02) | −0.34 (±0.05) | −0.42 (±0.01) | −0.36 (±0.04) | −0.23 (±0.10) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhamad, M.; Barão, V.A.R.; Sukotjo, C.; Cooper, L.F.; Mathew, M.T. Ti-Ions and/or Particles in Saliva Potentially Aggravate Dental Implant Corrosion. Materials 2021, 14, 5733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195733
Alhamad M, Barão VAR, Sukotjo C, Cooper LF, Mathew MT. Ti-Ions and/or Particles in Saliva Potentially Aggravate Dental Implant Corrosion. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195733
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhamad, Mostafa, Valentim A. R. Barão, Cortino Sukotjo, Lyndon F. Cooper, and Mathew T. Mathew. 2021. "Ti-Ions and/or Particles in Saliva Potentially Aggravate Dental Implant Corrosion" Materials 14, no. 19: 5733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195733
APA StyleAlhamad, M., Barão, V. A. R., Sukotjo, C., Cooper, L. F., & Mathew, M. T. (2021). Ti-Ions and/or Particles in Saliva Potentially Aggravate Dental Implant Corrosion. Materials, 14(19), 5733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195733







