Toward Eliminating Discontinuous Yielding Behavior of the EA4T Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cottrell, A.H.; Bilby, B.A. Dislocation theory of yielding and strain aging of iron. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1949, 62, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, A.H. Dislocations and Plastic Flow in Crystals, 1st ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Bilby, B.A. On the interactions of dislocations and solute atoms. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1950, 63, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Matsunaga, K.; Tochigi, E.; Shibata, N.; Ikuhara, Y.; Lagerlöf, K.P.D. Another origin of yield drop behavior in sapphire deformed via basal slip: Recombination of climb-dissociated partial dislocations. Scr. Mater. 2017, 138, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, R.; Tian, Y.; Mao, W.; Shibata, A.; Tsuji, N. Mechanism of huge Lüders-type deformation in ultrafine grained austenitic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2019, 159, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Wang, L.; Huang, M.X. Kinematic and thermal characteristics of Lüders and Portevin-Le Châtelier bands in a medium Mn transformation-induced plasticity steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.S.; Du, L.X.; Hu, J.; Misra, R.D.K. Microstructural evolution and recrystallization behavior of cold rolled austenitic stainless steel with dual phase microstructure during isothermal annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 709, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Dong, H.; Huang, M. Effect of intercritical annealing on the Lüders strains of medium Mn transformation-induced plasticity steels. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadoddin, E.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Daneshi, G.H. Correlation between Luder strain and retained austenite in TRIP-assisted cold rolled steel sheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tomota, Y.; Ohmura, T.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Tanaka, M. Continuous and discontinuous yielding behaviors in ferrite-cementite steels. Acta Mater. 2020, 196, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kang, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, S.J. Effect of austenitization of cold-rolled 10 wt. % Mn steel on microstructure and discontinuous yielding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 774, 138930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.C.; Yin, F.X.; Hanamura, T.; Nagai, K.; Atrens, A. Relationship between yield strength and grain size for a bimodal structural ultrafine-grained ferrite/cementite steel. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Gao, S.; Zhao, L.J.; Lu, S.; Pippan, R.; Zhang, Z.F.; Tsuji, N. Remarkable transitions of yield behavior and Lüders deformation in pure Cu by changing grain sizes. Scr. Mater. 2018, 142, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, N.; Tomota, Y.; Nagai, K.; Fukaura, K. A simple relationship between Lüders elongation and work-hardening rate at lower yield stress. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Shan, A. Lüders-like deformation induced by delta-ferrite-assisted martensitic transformation in a dual-phase high-manganese steel. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Lu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y. Transformation kinetics of retained austenite in the tensile Lüders strain range in medium Mn steel. Scr. Mater. 2019, 169, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Goodall, A.; Strangwood, M.; Davis, C. Characterisation of precipitation and carbide coarsening in low carbon low alloy Q&T steels during the early stages of tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 738, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janovec, J.; Svoboda, M.; Výrostková, A.; Kroupa, A. Time–temperature–precipitation diagrams of carbide evolution in low alloy steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 402, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalekian, M.; Radis, R.; Militzer, M.; Moreau, A.; Poole, W.J. In situ measurement and modeling of austenite grain growth in a Ti/Nb microalloyed steel. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, Y.; Zargaran, A.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, N.J. Effect of annealing conditions on the microstructure and tensile properties of 0.5 V containing Fe-16Mn-0.8C-0.5Si steel. Scr. Mater. 2019, 172, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natori, M.; Futamura, Y.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S. Difference in recrystallization behavior between lath martensite and deformed ferrite in ultralow carbon steel. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wu, S.C.; Wang, X.S. Fatigue evaluation for high-speed railway axles with surface scratch. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fintová, S.; Pokorný, P.; Fajkoš, R.; Hutař, P. EA4T railway axle steel fatigue behavior under very high-frequency fatigue loading. Eng. Failure Anal. 2020, 115, 104668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Liang, Y.L.; Wu, S.B.; Liang, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of tempering process on microstructure and properties of EA4T axle steel. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2012, 33, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heat Treatment Society of China Society of Mechanical Engineering. Heat Treatment Manual—Process Basis, 4th ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 42–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Björklund, S.; Donaghey, L.F.; Hillert, M. The effect of alloying elements on the rate of Ostwald ripening of cementite in steel. Acta Metall. 1972, 20, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellare, A.; Dadyburjor, D.B. Effect of the size dependence of particle diffusion and surface tension on the sintering of supported metal catalysts. AIChE J. 1987, 33, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.C.; Hanamura, T.; Hai, Q.; Nagai, K.; Ke, Y. Grain growth and Hall–Petch relation in dual-sized ferrite/cementite steel with nano-sized cementite particles in a heterogeneous and dense distribution. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, I.M.; Slyozov, V.V.J. The kinetics of precipitation from supersaturated solid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1961, 19, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardell, A.J. The effect of volume fraction on particle coarsening: Theoretical considerations. Acta Metall. 1972, 20, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Lu, Z.P.; Nieh, T.G. Thermal stability and coarsening of coherent particles in a precipitation-hardened (NiCoFeCr)94Ti2Al4 high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 147, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardell, A.J. Quantitative predictions of the trans-interface diffusion-controlled theory of particle coarsening. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 4325–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Lee, C.; Uhm, S.; Lee, J. Coarsening kinetics of TiN particle in a low alloyed steel in weld HAZ: Considering critical particle size. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Thornton, K.; Nie, Q.; Voorhees, P.W.; Lowengrub, J.S. Two- and three-dimensional equilibrium morphology of a misfitting particle and the Gibbs–Thomson effect. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5829–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibeyki, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Najafi, M. Fine-grained dual phase steel via intercritical annealing of cold-rolled martensite. Vacuum 2018, 155, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balliger, N.K.; Gladman, T. Work hardening of dual-phase steels. Met. Sci. J. 1981, 15, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hansen, N.; Tsuji, N. Hardening by annealing and softening by deformation in nanostructured metals. Science 2006, 312, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estrin, Y.; Vinogradov, A. Extreme grain refinement by severe plastic deformation: A wealth of challenging science. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 782–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Kao, P.W.; Chang, C.P. Transition of tensile deformation behaviors in ultrafine-grained aluminum. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4019–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.F. Lüders front propagation in low carbon steels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1962, 10, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Jeong, H.T. Pronounced yield drop phenomenon at high temperatures in Al-Mg alloys with high contents of Mg (5–13 wt. %). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenreich, H.; Hirth, J.P. Mechanism for dislocation density reduction in GaAs crystals by indium addition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1985, 46, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


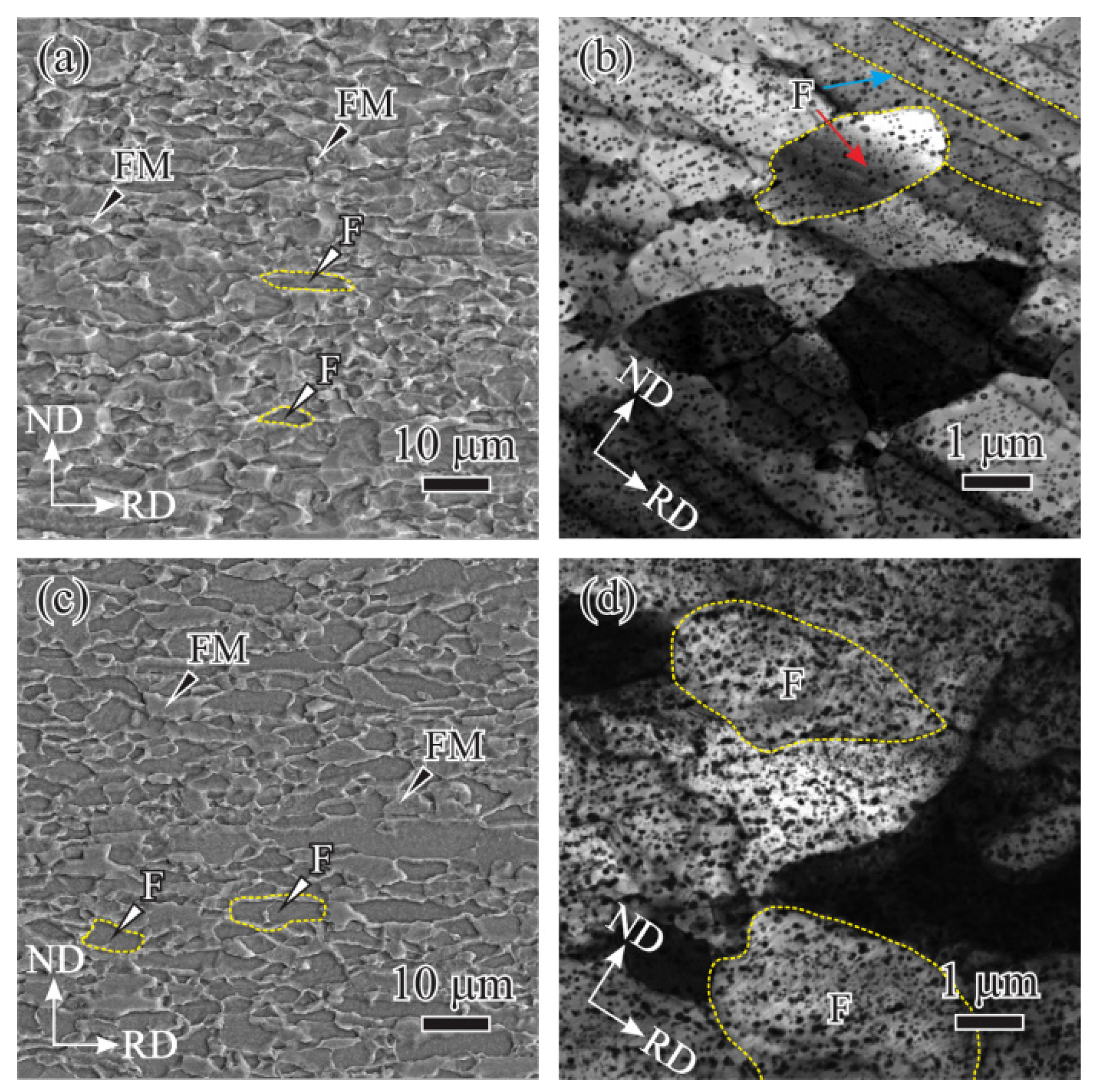

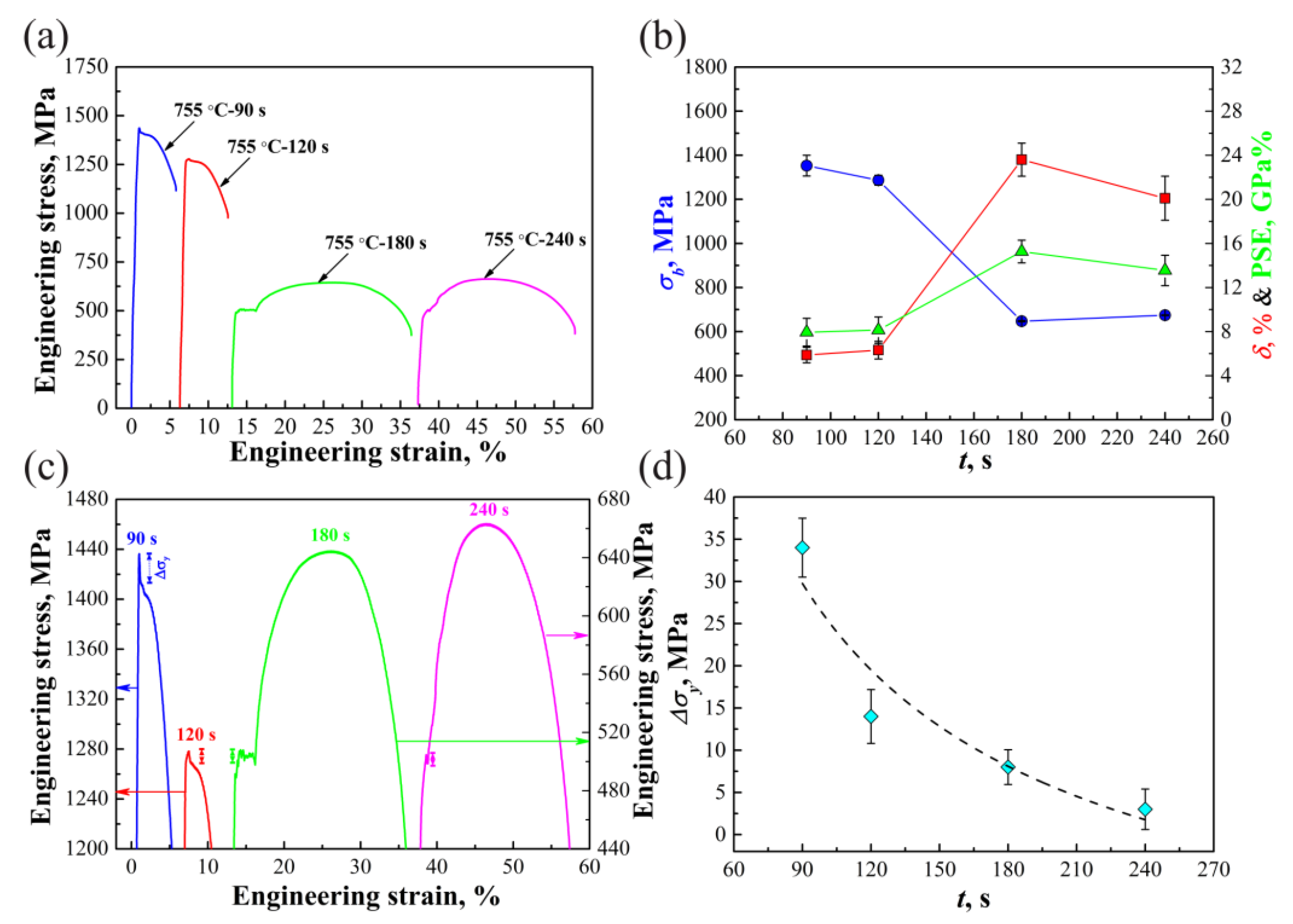
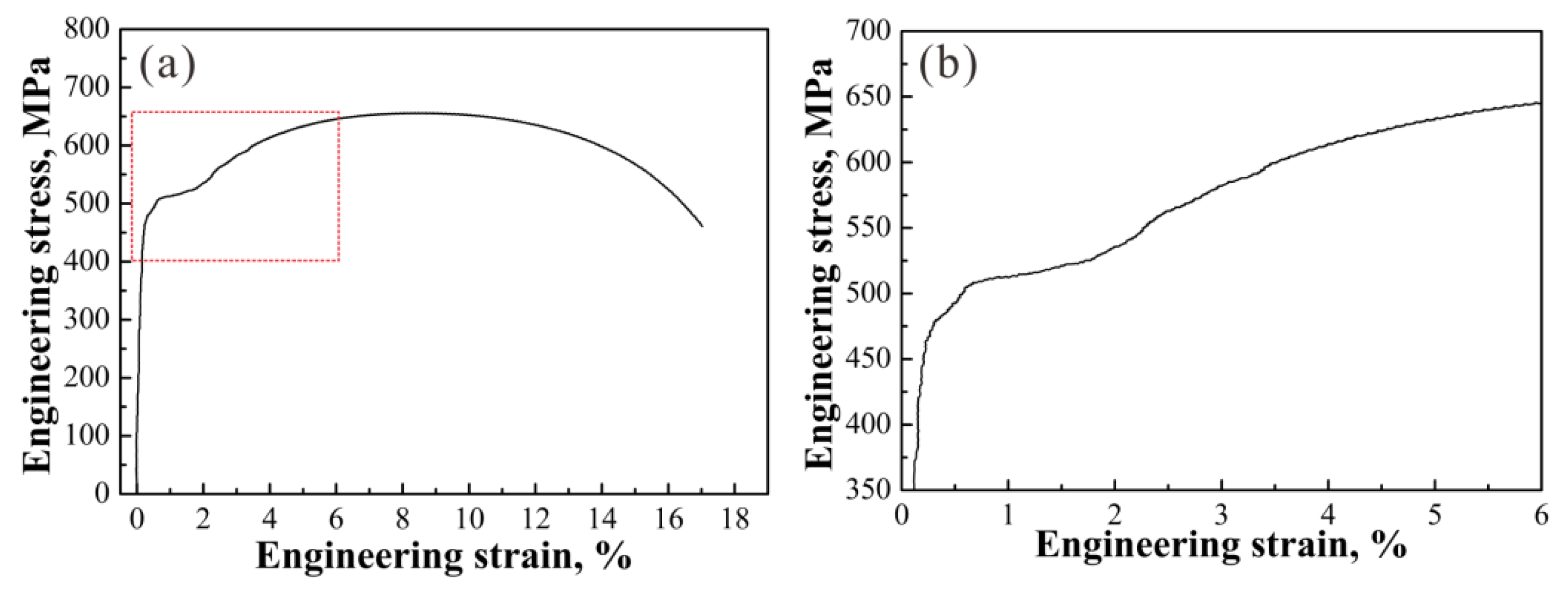
| C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Cu | Mo | Ni | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.74 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 1.17 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.032 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-Z.; Du, Q.; Zhang, G.-P.; Zhang, B. Toward Eliminating Discontinuous Yielding Behavior of the EA4T Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206121
Chen J-Z, Du Q, Zhang G-P, Zhang B. Toward Eliminating Discontinuous Yielding Behavior of the EA4T Steel. Materials. 2021; 14(20):6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206121
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jian-Zhi, Qin Du, Guang-Ping Zhang, and Bin Zhang. 2021. "Toward Eliminating Discontinuous Yielding Behavior of the EA4T Steel" Materials 14, no. 20: 6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206121
APA StyleChen, J.-Z., Du, Q., Zhang, G.-P., & Zhang, B. (2021). Toward Eliminating Discontinuous Yielding Behavior of the EA4T Steel. Materials, 14(20), 6121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14206121








