The Influence of Hydroxyapatite and Alumina Particles on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Mg-Zn Hybrid Composites for Implants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
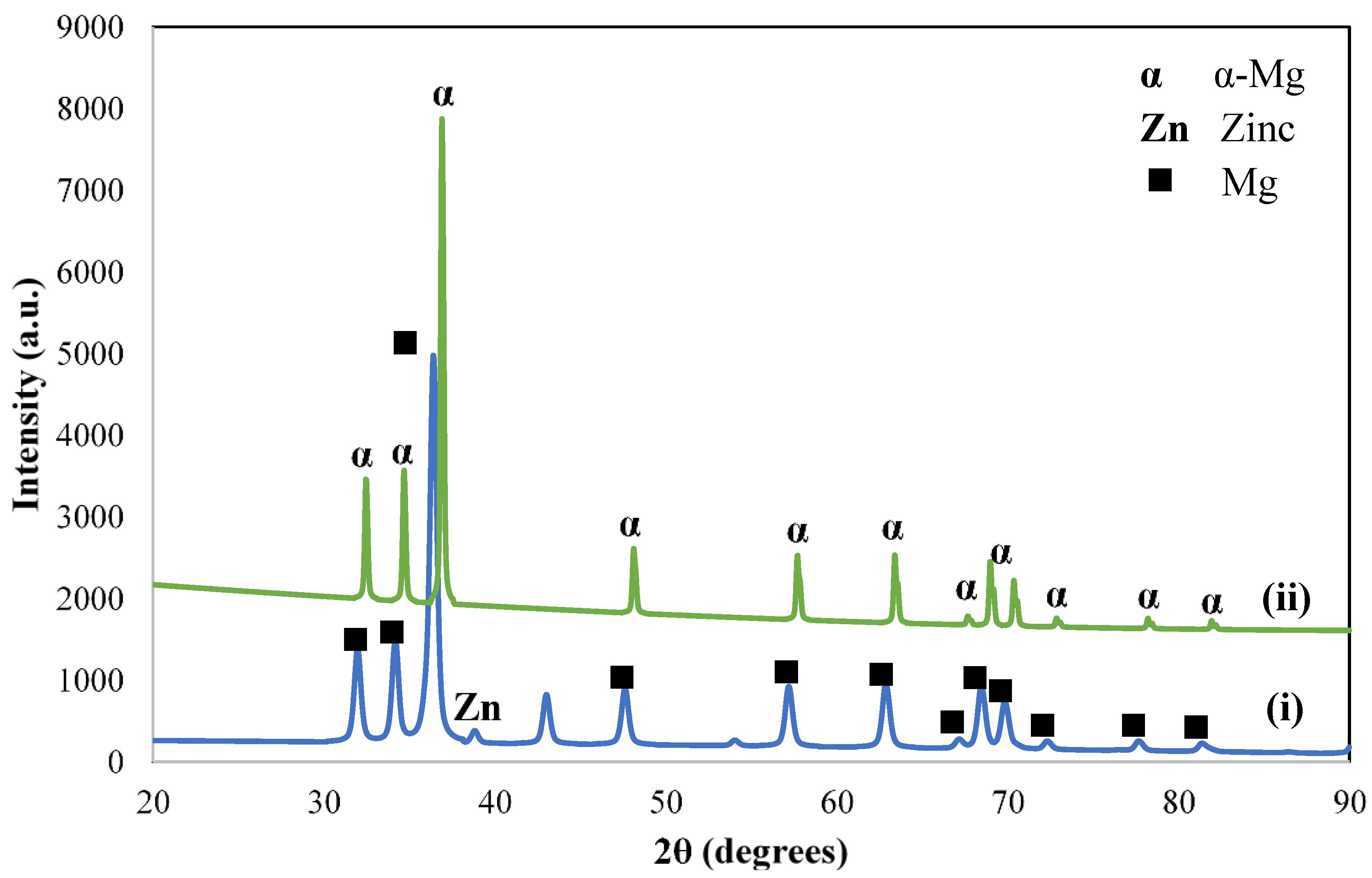
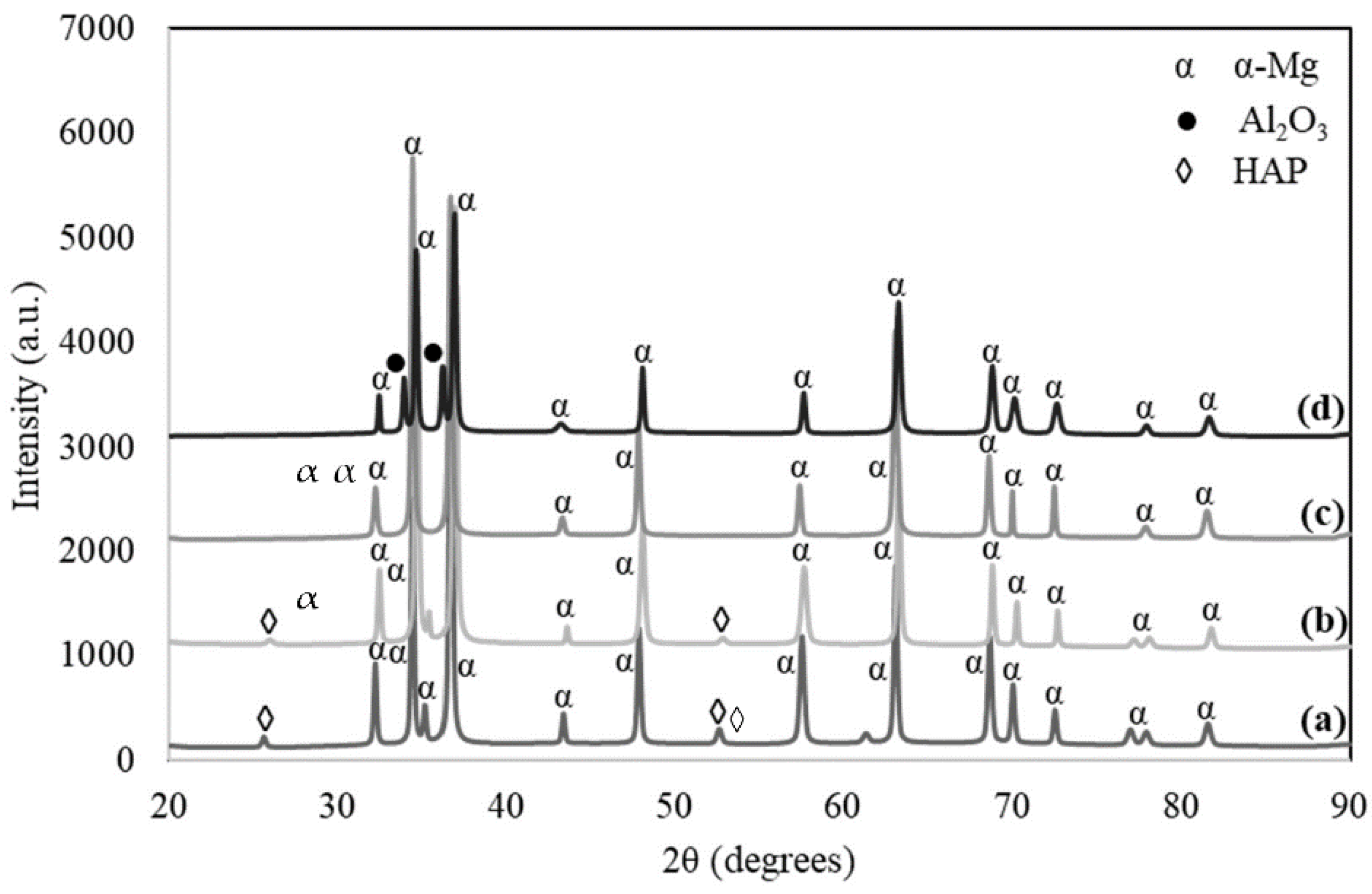
3.1. XRD Analysis
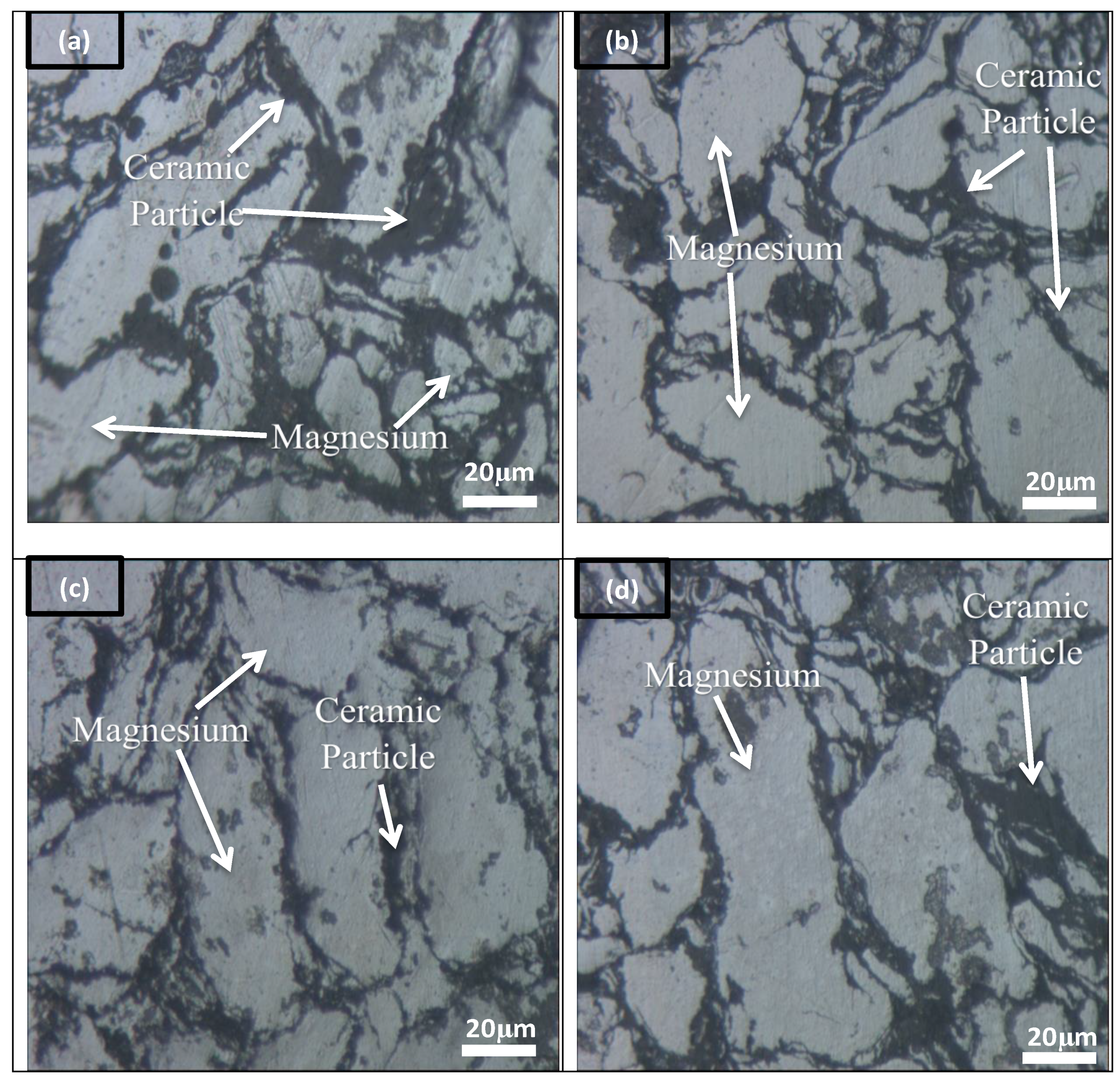
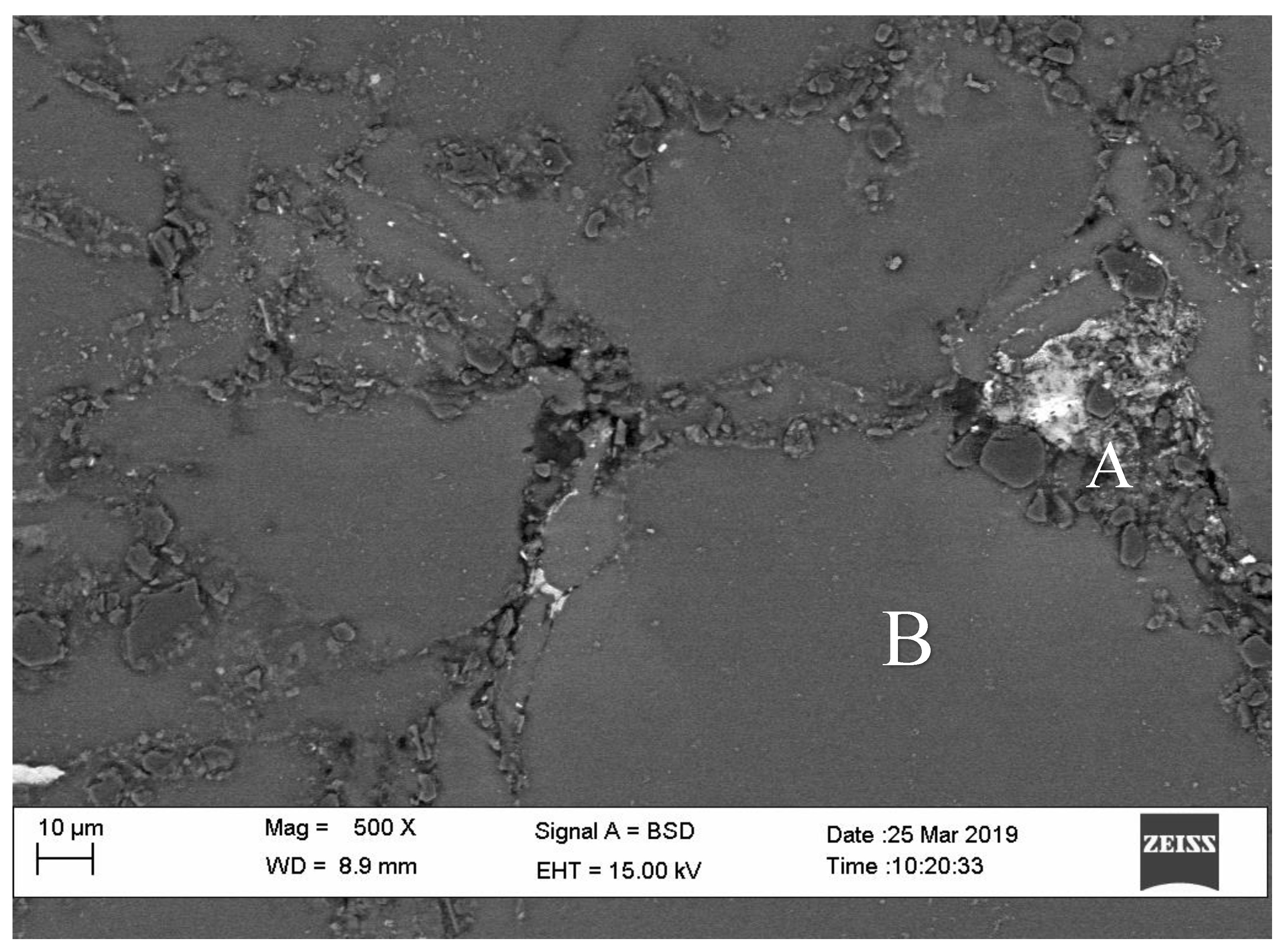
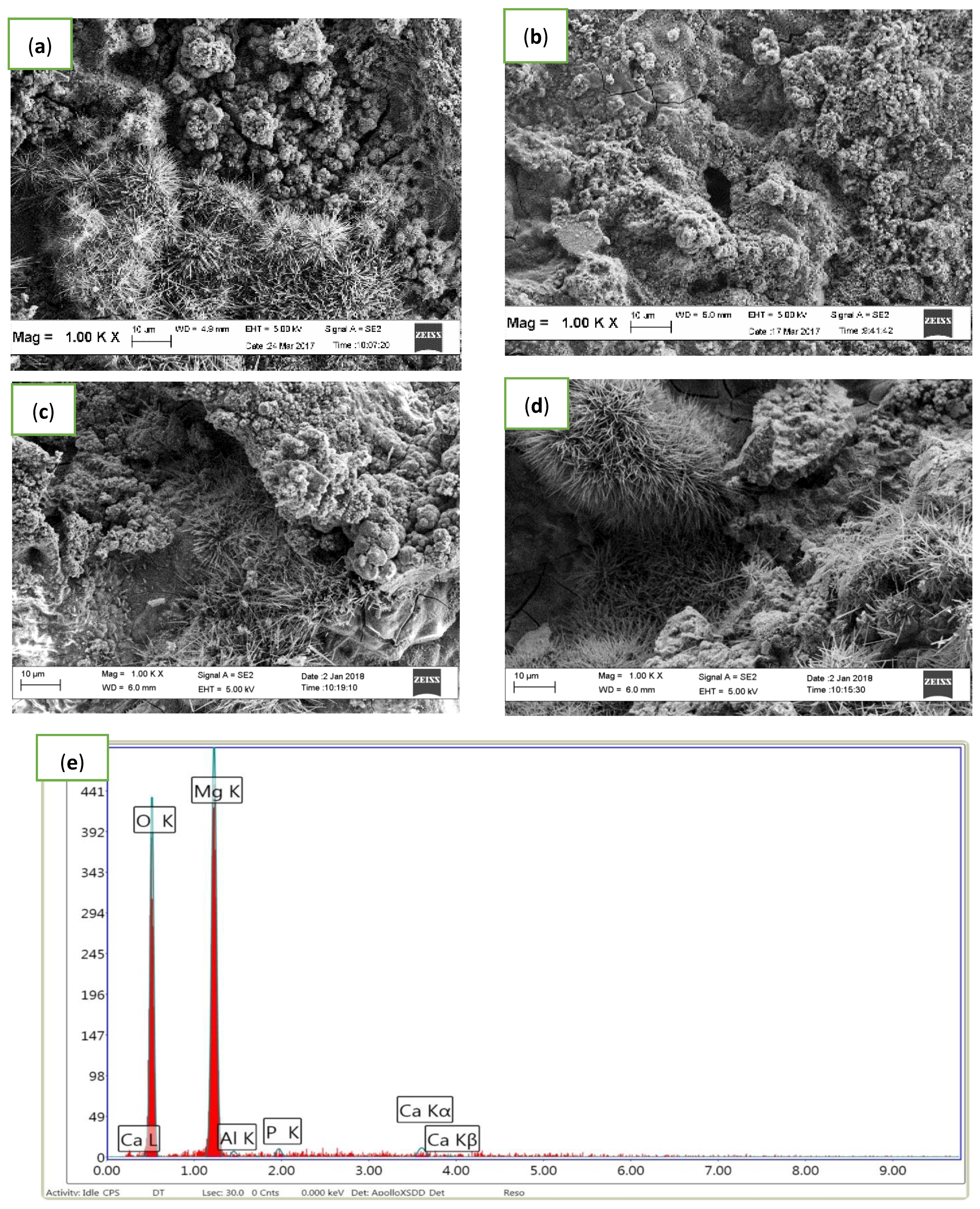
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
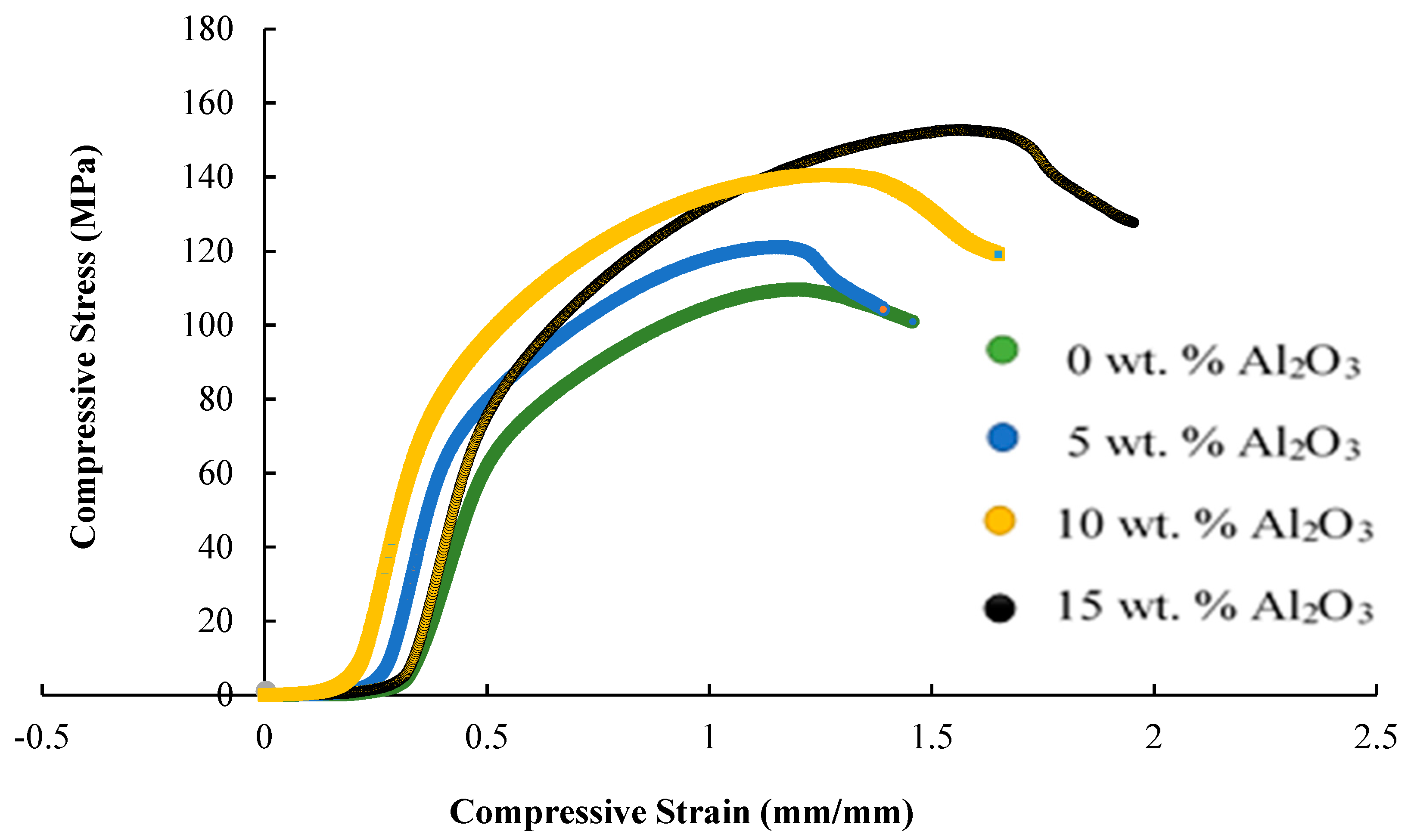
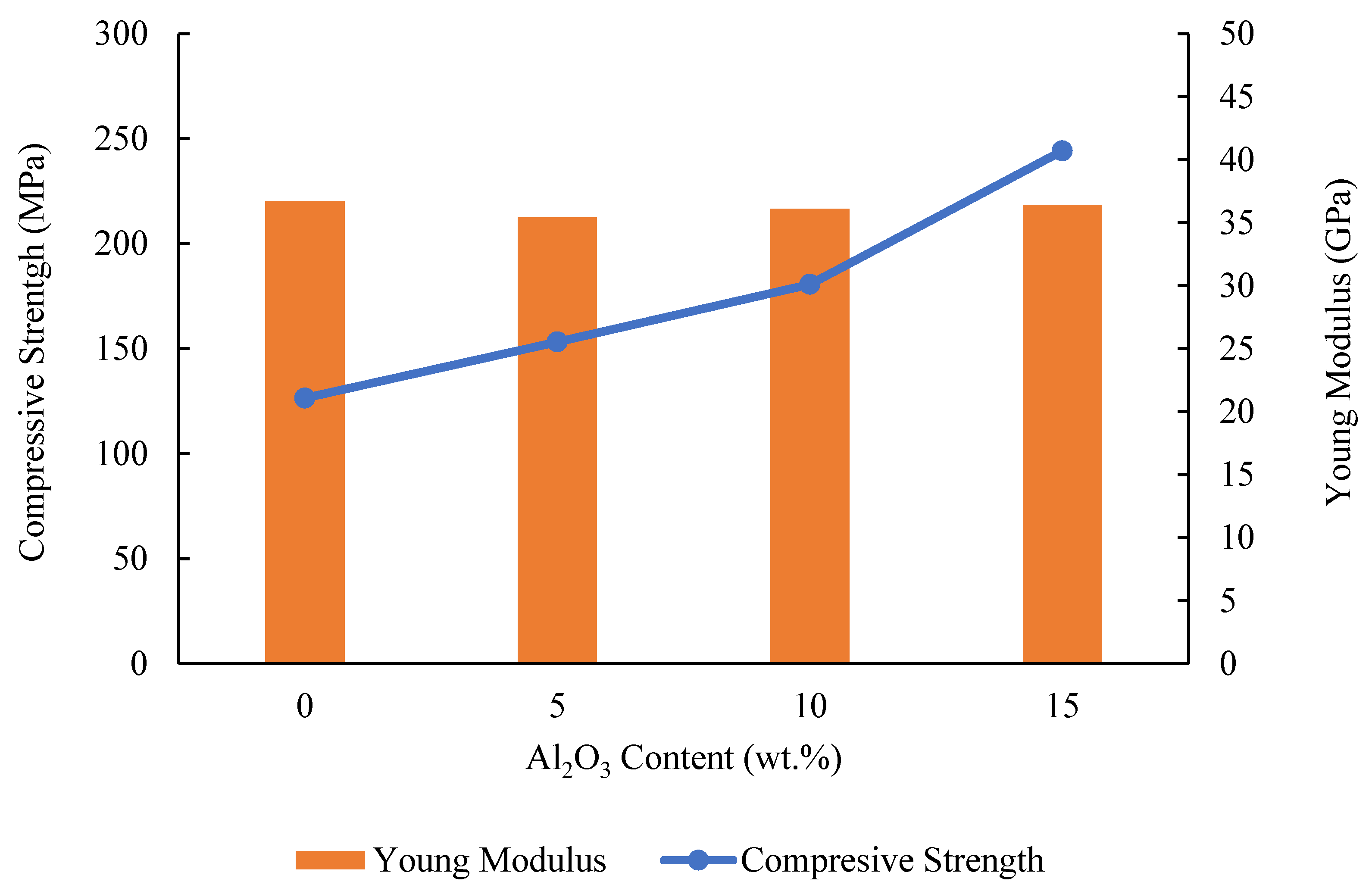
3.3. Mechanical Properties
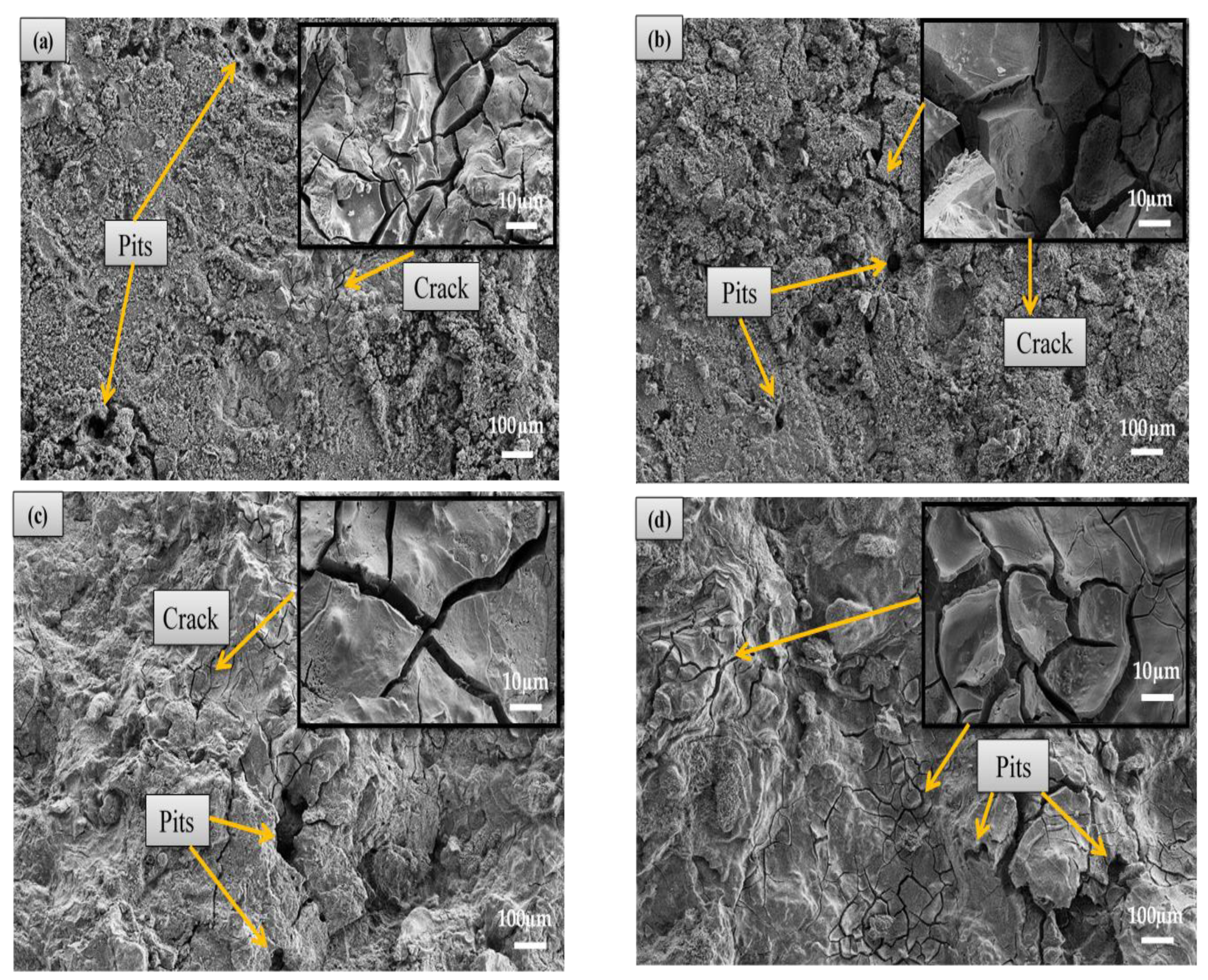
3.4. Corrosion Behaviour
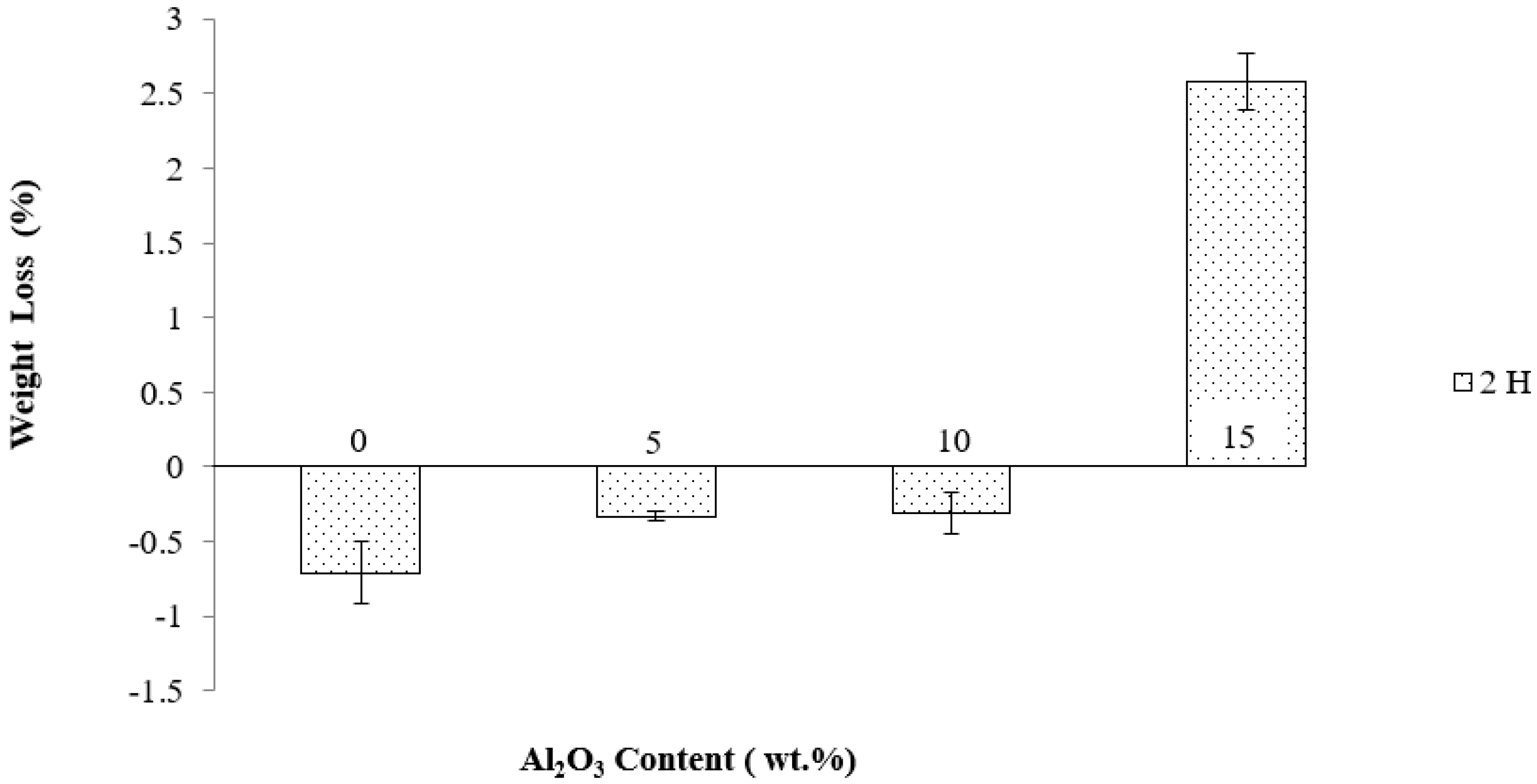
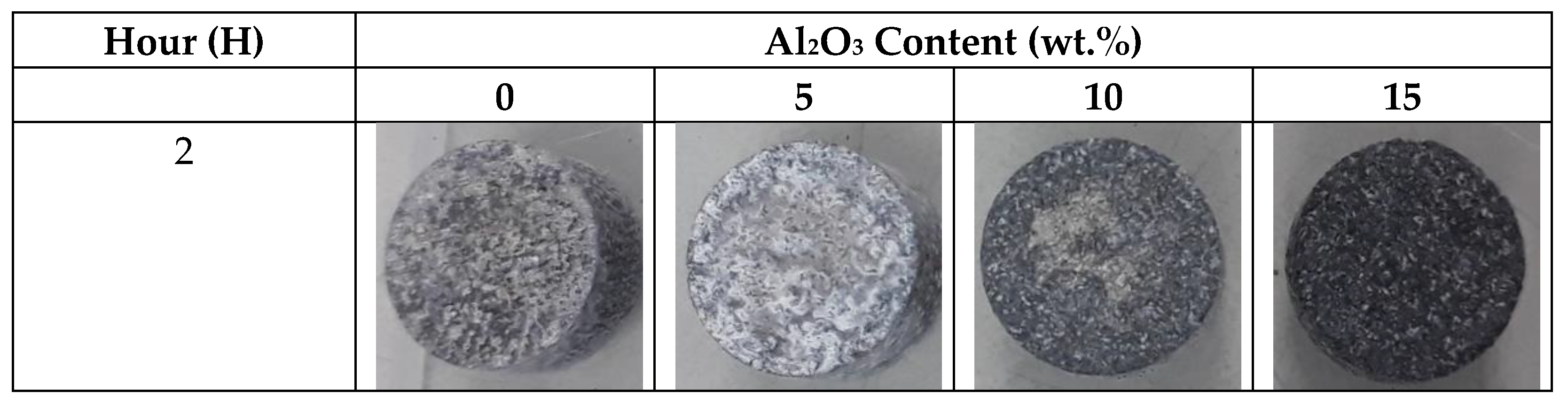
3.4.1. Immersion Test
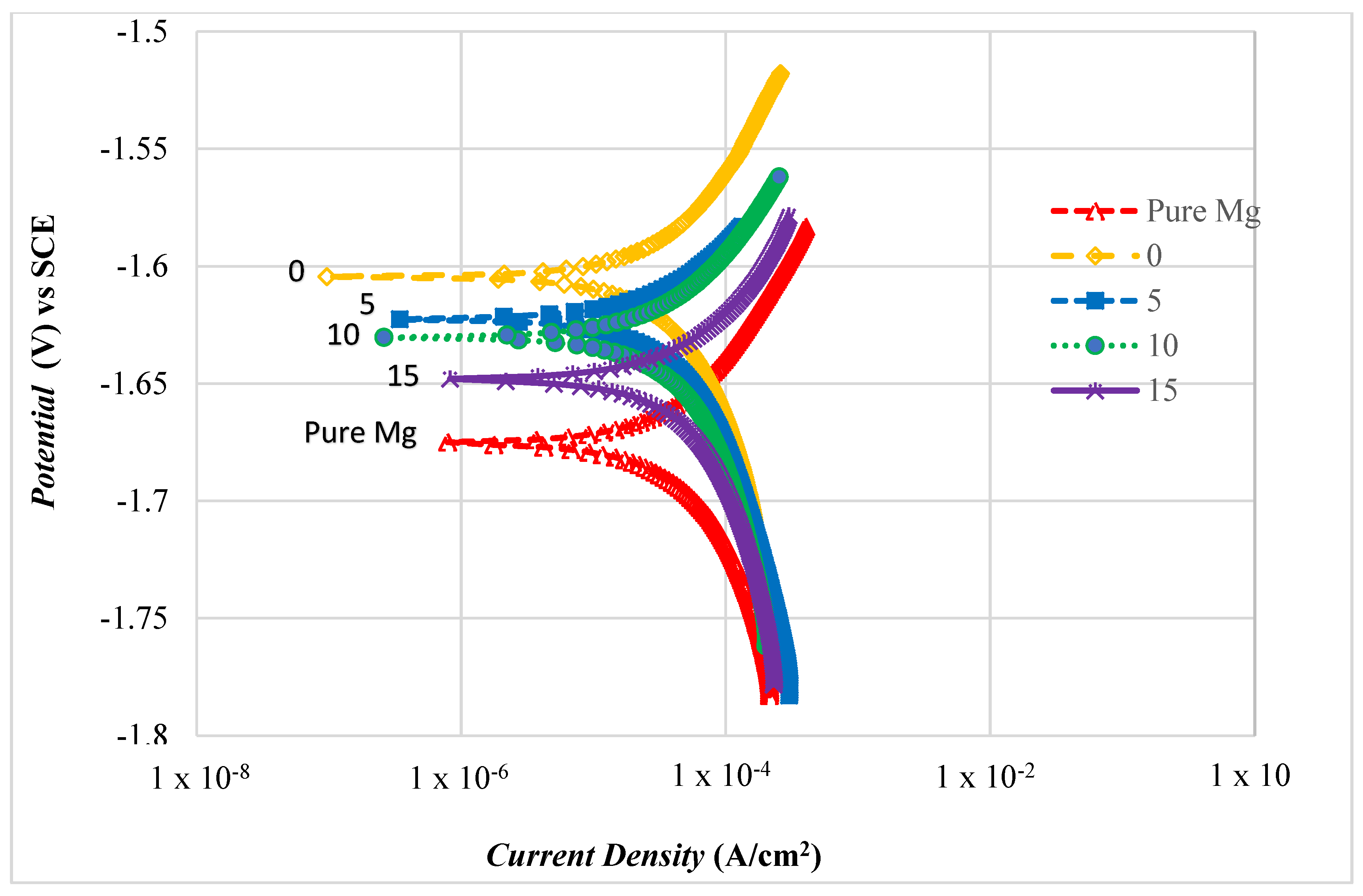
3.4.2. Polarization Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staiger, M.; Pietak, P.; Huadmai, A.M.; Dias, G. Magnesium and Its Alloys as Orthopedic Biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, F.; Hort, N.; Vogt, C.; Cohen, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Degradable Biomaterials Based on Magnesium Corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, N.; Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. Tribocorrosion Behaviors of a Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Ca Bulk Metallic Glass for Potential Biomedical Implant Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 745, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Applications of Magnesium and Its Alloys: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.X.; Li, J.A.; Zeng, R.C.; Guan, S.K. Advances in Coatings on Magnesium Alloys for Cardiovascular Stents—A Review. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4729–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herber, V.; Okutan, B.; Antonoglou, G.; Sommer, N.G.; Payer, M. Bioresorbable Magnesium-Based Alloys as Novel Biomaterials in Oral Bone Regeneration: General Review and Clinical Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhang, W.; Xin, W. Effects of Sr and Sn on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Mg-Zr-Ca Magnesium Alloy for BiomedicalApplications. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.Z.; Sarhan, A.A.D.; Yusuf, F.; Hamdi, M. Biomedical Materials and Techniques to Improve the Tribological, Mechanical and Biomedical Properties of Orthopedic Implants—A review article. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 636–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohri, M.; Miki, K.; Waite, D.E.; Nakajima, H.; Okabe, T. In Vitro Stability of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Ceramics. Biomaterials 1993, 14, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalajabadi, S.Z.; Abdul Kadir, M.R.; Izman, S.; Marvibaigi, M. The Effect of MgO on The Biodegradation, Physical Properties and Biocompatibility of a Mg/Ha/MgO Nanocomposite Manufactured by Powder Metallurgy Method. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 655, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Feyerabend, F.; Maier, P.; Fischer, J.; Störmer, M.; Blawert, C.; Hort, N. Biodegradable Magnesium-Hydroxyapatite Metal Matrix Composites. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, K.A. A New-Developed Nanostructured Mg/Hap Nanocomposite by High Frequency Induction Heat Sintering Process. Int. J. Electr. Sci. 2012, 7, 10698–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, L.L.; Zuhailawati, H.; Suhaina, I.; Dhindaw, B.K. Prediction of Compressive Strength of Biodegradable Mg-Zn/Ha Composite Via Response Surface Methodology and Its Biodegradation. Acta Metall. Sin. 2016, 29, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salleh, E.M.; Zuhailawati, H.; Mohd Noor, S.N.F.; Othman, N.K. In Vitro Biodegradation and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Alloy and Mg-Zn-Hydroxyapatite Composite Produced by Mechanical Alloying for Potential Application in Bone Repair. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 5888–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, H. Hard Tissue Replacement. Clin. Mater. 1987, 2, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzotti, G.; Munisso, M.C.; Porporati, A.A.; Lessnau, K. On the Role of Oxygen Vacancies and Lattice Strain in the Tetragonal to Monoclinic Transformation in Alumina/Zirconia Composites and Improved Environmental Stability. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6901–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, Y.T. Osseoinductive Magnesium-Titanate Implant and Method of Manufacturing the Same. U.S. Patent US 20060161263, 4 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, X.; Mao, L.; Niu, J.; Ding, W. Comparison of Biodegradable Behaviors of AZ31 and Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr Alloys in Hank’s Physiological Solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Tang, W.; Cai, S.H.; Feng, F.F.; Li, N.F. On the Corrosion Behaviour of Newly Developed Biodegradable Mg-Based Metal Matrix Composites Produced by in Situ Reaction. Corros. Sci. 2012, 54, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazirah, R.; Zuhailawati, H. The Effect of Alumina and Hydroxyapatite Content on Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Mg Hybrid Composite for Biodegradable Implants Materials. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 1082, p. 012078. [Google Scholar]
- Pinc, J.; Capek, J.; Kubasek, J.; Hybasek, V.; Vertat, P.; Sedlarova, I.; Vojtech, D. Characterization of a Zn- Ca5(PO4)3(OH) Composite with a High Content of the Hydroxyapatite Particles Prepared by the Spark Plasma Sintering Process. Metals 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, E.; Yin, D.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, K.; Datta, M.K.; Robson, J. Microstructure, Mechanical and Corrosion Properties and Biocompatibility of Mg-Zn-Mn Alloys for Biomedical Application. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 6, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Idris, M.H.; Abdul-Kadir, M.R.; Ourdjini, A.; Medraj, M.; Daroonparvar, M.; Hamzah, E. Mechanical and Bio-Corrosion Properties of Quaternary Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn Alloys Compared with Binary Mg-Ca Alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayun, B.; Afshar, A. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behavior and Cytotoxicity of Mg-Zn-Al-Ca Alloys as Biodegradable Materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 607, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasali, E.; Bordbar-Khiabani, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Mozafari, M.; Niazmand, M.; Kazemzadeh, H.; Ebadzadeh, T. Corrosion Behavior and In-Vitro Bioactivity of Porous Mg/Al2O3 and Mg/Si3N4 Metal Matrix Composites Fabricated Using Microwave Sintering Process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 225, 31–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, E. Biocorrosion Behavior of Magnesium Alloy in Different Simulated Fluids for Biomedical Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodzi, S.N.H.M.; Zuhailawati, H.; Dhindaw, B.K. Mechanical and Degradation Behaviour of Biodegradable Magnesium Zinc/Hydroxyapatite Composite with Different Powder Mixing Techniques. J. Magnes. Alloys 2019, 7, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F. Reprint of: The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomat. 2015, 23, S28–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.Y.; Chen, M.M.F.; Yang, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, D.B.; Khan, A.; Bian, Y. Biodegradable Magnesium-Hydroxyapatite Metal Matrix Composites. Biomaterials 2010, 28, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.N.; Nazirah, R.; Zuhailawati, H. Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of Mg-Zn/HAP/Al2O3 Hybrid Composite. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 1349, p. 012136. [Google Scholar]
- Waizy, H.; Seitz, J.M.; Reifenrath, J.; Weizbauer, A.; Bach, F.W.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Windhagen, H. Biodegradable Magnesium Implants for Orthopedic Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.N.; Zhou, W. Effect of Grain Size and Twins on Corrosion Behaviour of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Al2O3 Content (wt.%) | Average Grain Size (µm) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 180.03 |
| 5 | 178.68 |
| 10 | 218.48 |
| 15 | 368.40 |
| Al2O3 Content (wt.%) | Theoretical Density (g/cm3) (Calculated from ROM) | Sintered Density (g/cm3) | Relative Density (Sintered Density Divide Theoretical Density × 100) (%) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.947 | 1.846 | 94.81 | 5.19 |
| 5 | 1.959 | 1.875 | 95.71 | 4.29 |
| 10 | 1.971 | 1.899 | 96.35 | 3.65 |
| 15 | 1.984 | 1.947 | 98.14 | 1.86 |
| Al2O3 Content (wt.%) | Atomic Percentage (%) | Ratio Ca/P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | O | Ca | P | Al | ||
| 0 | 39.45 | 59.52 | 0.72 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 2.32 |
| 5 | 39.72 | 59.08 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.63 | 1.55 |
| 10 | 39.50 | 58.94 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.87 | 0.73 |
| 15 | 39.93 | 58.69 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.94 | 0.57 |
| Composition Al2O3 (wt.%) | Corrosion Potential Ecorr, vs SCE (V) | Corrosion Current Density (Icorr, A/cm2) × 10−6 | Corrosion Rate (mm/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Mg | −1.675 | 0.530 | 3.24 |
| 0 | −1.604 | 0.252 | 1.25 |
| 5 | −1.622 | 0.281 | 1.37 |
| 10 | −1.630 | 0.379 | 2.32 |
| 15 | −1.648 | 0.474 | 2.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazirah, R.; Zuhailawati, H.; Siti Nur Hazwani, M.R.; Abdullah, T.K.; Azzura, I.; Dhindaw, B.K. The Influence of Hydroxyapatite and Alumina Particles on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Mg-Zn Hybrid Composites for Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 6246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216246
Nazirah R, Zuhailawati H, Siti Nur Hazwani MR, Abdullah TK, Azzura I, Dhindaw BK. The Influence of Hydroxyapatite and Alumina Particles on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Mg-Zn Hybrid Composites for Implants. Materials. 2021; 14(21):6246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216246
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazirah, Rashid, Hussain Zuhailawati, Mohamad Rodzi Siti Nur Hazwani, Tuti Katrina Abdullah, Ismail Azzura, and Brij Kumar Dhindaw. 2021. "The Influence of Hydroxyapatite and Alumina Particles on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Mg-Zn Hybrid Composites for Implants" Materials 14, no. 21: 6246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216246
APA StyleNazirah, R., Zuhailawati, H., Siti Nur Hazwani, M. R., Abdullah, T. K., Azzura, I., & Dhindaw, B. K. (2021). The Influence of Hydroxyapatite and Alumina Particles on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Mg-Zn Hybrid Composites for Implants. Materials, 14(21), 6246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216246






