A Review of Friction Performance of Lubricants with Nano Additives
Abstract
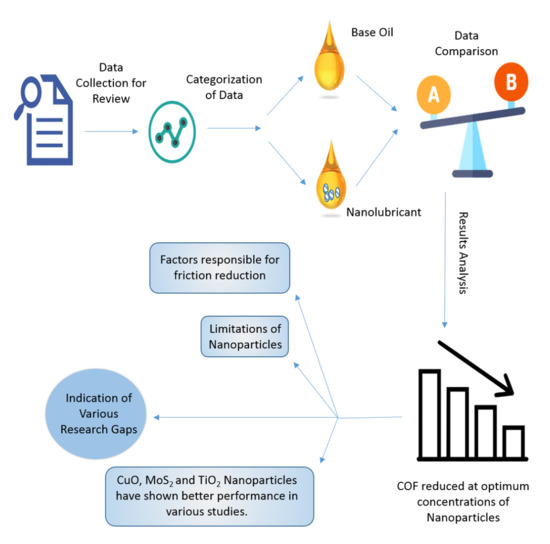
:1. Introduction
2. Lubrication Mechanisms of Nanoparticles
3. Nanoparticles in Synthetic Lubricants
3.1. TiO2 Nanoparticles
3.2. Graphene (Gr) Nanoparticles
3.3. Copper (Cu) Nanoparticles
3.4. Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles
3.5. Hexa-Boron Nitride (h-BN) Nanoparticles
3.6. Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) Nanoparticles
3.7. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
3.8. Copper Oxide (CuO) Nanoparticles
3.9. Alumina (Al2O3) Nanoparticles
3.10. Silica (SiO2) Nanoparticles
3.11. Tungsten Disulfide (WS2) Nanoparticles
4. Nanoparticles in Biolubricants
4.1. Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles
4.2. Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles
4.3. Hexa-Boron Nitride (h-BN) Nanoparticles
4.4. Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) Nanoparticles
4.5. Copper Oxide (CuO) Nanoparticles
4.6. Alumina (Al2O3) Nanoparticles
4.7. Silica (SiO2) Nanoparticles
5. Limitations of Nanolubricants
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.K.A.; Fuming, P.; Younus, H.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Essa, F.; Elagouz, A.; Xianjun, H. Fuel economy in gasoline engines using Al2O3/TiO2 nanomaterials as nanolubricant additives. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-Y.; Yang, S.; Chang, D. Oil Price Uncertainty, Transport Fuel Demand and Public Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uflyand, I.E.; Zhinzhilo, V.A.; Burlakova, V.E. Metal-containing nanomaterials as lubricant additives: State-of-the-art and future development. Friction 2019, 7, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Gulzar, M.; Elsheikh, A. Novel approach of the graphene nanolubricant for energy saving via anti-friction/wear in automobile engines. Tribol. Int. 2018, 124, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashvir Singh, D.V.; Kumar, N.; Rastogi, P.M.; Sharma, A.; Singla, A. Experimental evaluation on the tribological properties of cassia tora oil by addition of copper nanoparticles. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2019, 13, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumik, S.; Maggirwar, R.; Datta, S.; Pathak, S. Analyses of anti-wear and extreme pressure properties of castor oil with zinc oxide nano friction modifiers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H. Improving the tribological behavior of internal combustion engines via the addition of nano-particles to engine oils. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2015, 4, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoo, M.S.; Wani, M.F. Tribological properties of h-BN nanoparticles as lubricant additive on cylinder liner and piston ring. Lubr. Sci. 2017, 29, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jiang, B.; He, J.; Xia, X.; Pan, F. Lubrication performance of MoS2 and SiO2 nanoparticles as lubricant addi-tives in magnesium alloy-steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallasamy, P.; Saravanakumar, N.; Rajaram, G.; Kumar, R.R. Experimental study on the tribological properties of CuO-based biodegradable nanolubricants for machine tool slideways. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghani, W.; Ab Karim, M.S.; Bagheri, S.; Amran, N.A.M.; Gulzar, M. Enhancing the Tribological Behavior of Lubricating Oil by Adding TiO2, Graphene, and TiO2/Graphene Nanoparticles. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 62, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Gu, L.; Song, B.; Wang, L. Investigation of the tribological behavior of graphene oxide nanoplates as lubricant additives for ceramic/steel contact. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Tiwari, A.; Mandal, A.; Pramanik, V. Alokesh Influence of graphene and multi-walled carbon nanotube additives on tribological behaviour of lubricants. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Wu, Y.-P.; Li, Z.-Y.; Cai, Z.-B. Tribological properties of WS2/graphene nanocomposites as lubricating oil additives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14060–14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; He, A.; Yun, J.-H.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiao, S.; Huang, H. Synergistic tribological performance of a water based lubricant using graphene oxide and alumina hybrid nanoparticles as additives. Tribol. Int. 2019, 135, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, N.; Sivasankaran, S.; Prabu, G.; Yang, C.-H.; Alaboodi, A.S. Enhancing the tribological properties of nodular cast iron using multi wall carbonnano-tubes (MWCNTs) as lubricant additives. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.Y.; Wang, S.R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Yan, X.Y. The Influence of Nanocomposite Carbon additive on Tribological Be-havior of Cylinder Liner/Piston Ring. In International Conference on Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering; IOP Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.I.H.C.; Abdollah, M.F.B.; Amiruddin, H.; Tamaldin, N.; Nuri, N.R.M. The potential of hBN nano-particles as friction modifier and antiwear additive in engine oil. Mech. Ind. 2016, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Singh, R.C.; Chaudhary, R. Experimental Investigation of Influence of SiO2 Nanoparticles on the Tribo-logical and Rheological properties of SAE 40 Lubricating Oil. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 9, 4307–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, A.; Harsha, A. Tribological studies on chemically modified rapeseed oil with CuO and CeO2 nanoparticles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2016, 230, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, A.; Nabhan, A. Effects of TiO2 and SiO2 Nano Additive to Engine Lubricant Oils on Tribological Properties at Different Temperatures. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Aerospace, Mechanical, Automotive and Materials Engineering, Rome, Italy, 30–31 October 2018; Volume 20, pp. 2463–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Norazmira, A.; Devarajan, R.; Kadirgama, K.; Mahendran, S.; Najafi, G.; Sidik, N.A.C. An experimental study on charac-terization and properties of nanolubricant containing Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 130, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Namer, N.; Nama, S.; Mezher, M.T. The influence of nano particles additive on tribological properties of aa2024-t4 coated with tin or sin thin films. J. Mech. Eng. Res. Dev. 2019, 42, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Geng, J.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Hu, X. Lubricating mechanism of Fe3O4@MoS2 core-shell nano-composites as oil additives for steel/steel contact. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, M.; Velkavrh, I.; Vižintin, J. The Stribeck curve and lubrication design for non-fully wetted surfaces. Wear 2009, 267, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Elagouz, A.; Essa, F.; Xianjun, H. Mini review on the significance nano-lubricants in boundary lubrication regime. Int. J. Biosen. Bioelectron. 2017, 2, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Elagouz, A.; Essa, F.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Minimizing of the boundary friction coeffi-cient in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yao, W.; Ye, X.; Cao, L.; Shen, G.; Yue, Q. Tribological performance and action mechanism of certain S, N heterocyclic compounds as potential lubricating oil additives. Wear 1997, 210, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenne, L.R.N.F.R. Fullerene-like WS2 Nanoparticles: Superior Lubricants for Harsh Conditions. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 651–655. [Google Scholar]
- Binu, K.; Shenoy, B.; Rao, D.; Pai, R. A Variable Viscosity Approach for the Evaluation of Load Carrying Capacity of Oil Lubricated Journal Bearing with TiO2 Nanoparticles as Lubricant Additives. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Chauhan, P.; Mamatha, T. A review on tribological performance of lubricants with nanoparticles additives. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 25, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Simionesie, D.; Schaschke, C. Graphite and Hybrid Nanomaterials as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2014, 2, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Afzal, A.; Ramis, M. Investigation of physicochemical and tribological properties of TiO2 nano-lubricant oil of different concentrations. Tribol. Finn. J. Tribol. 2017, 35, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.A.; Varman, M.; Zulkifli, N.; Mufti, R.; Zahid, R.; Yunus, R. Dispersion stability and tribological characteristics of TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite-enriched biobased lubricant. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Mai, L.; Qingping, C.; Turkson, R.F.; Bicheng, C. Improving the tribological characteristics of piston ring assembly in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Tri-Bology Int. 2016, 103, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, R.; Fazlali, A.; Mohammadi, A.H. Effects of TiO2 nanoparticles and oleic acid surfactant on the rheological behavior of engine lubricant oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena Laad, V.K.S.J. Titanium Oxide nanoparticles as an additive in Engine Oil. J. King Saud Univ. 2018, 30, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zin, V.; Agresti, F.; Barison, S.; Colla, L.; Fabrizio, M. Influence of Cu, TiO2 Nanoparticles and Carbon Nano-Horns on Tribological Properties of Engine Oil. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3590–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elagouz, A.; Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Techniques used to improve the tribological performance of the piston ring-cylinder liner contact. In Paper Presented at the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G.; Shit, S.; Hirani, H.; Kuila, T.; Murmu, N. Tribological behavior of dodecylamine functionalized graphene nanosheets dispersed engine oil nanolubricants. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río, J.M.L.; Guimarey, M.J.; Comuñas, M.J.; López, E.R.; Amigo, A.; Fernandez, J. Thermophysical and tribological properties of dispersions based on graphene and a trimethylolpropane trioleate oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, S.; Sriram, G.; Arumugam, S. Tribological Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing under the Influence of Synthetic and Biolubricants. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Interactions of Cu nanoparticles with conventional lubricant additives on tribological performance and some physicochemical properties of an ester base oil. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Tobón, A.E.; Chaparro, W.A.; Misnaza-Rodríguez, Y.G. Evaluation of the lubricating power of chemical modified Sesame oil additivated with Cu and Al2O3 nanoparticles. DYNA 2018, 85, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S. Study on the tribological behaviors of copper nanoparticles in three kinds of commercially available lubricants. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2018, 70, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, C.; Hwang, Y.; Park, M.; Lee, J.; Choi, C.; Jung, M. Tribological behavior of copper nanoparticles as additives in oil. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, e124–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijerina, J.T.; Castillo, F.; Leal, J.; Parás, L.P.; Cortés, D.M.; Cruz, C.; García, G.G.; García, P. Nanoparticles of Zn and ZnO as extreme pressure (EP) additives for lubricants. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2018, 16, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elagouz, A.; Ali, M.K.A.; Xianjun, H.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Hassan, M.A. Frictional performance evaluation of sliding surfaces lubricated by zinc-oxide nano-additives. Surf. Eng. 2020, 36, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Farooq, W.; Khan, M.; Akhtar, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Ahmad, N.; Irfan, M. Effect of ZnO nanoparticles coat-ing layers on top of ZnO Nanowires for morphological, optical, and photovoltaic properties of dye-sensitized solar cells. Micromachines 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bondarev, A.; Kovalskii, A.; Firestein, K.; Loginov, P.; Sidorenko, D.; Shvindina, N.; Sukhorukova, I.; Shtansky, D. Hollow spherical and nanosheet-base BN nanoparticles as perspective additives to oil lubricants: Correlation between large-scale friction behavior and in situ TEM compression testing. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 6801–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak Davisa, A.F.S.; Bharat, B.; Panigrahib, S.S. Effect of Cr2AlC nanolamella addition on tribological properties of 5W-30 Engine Oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, A.; Anand, A. Tribological investigation of diamond nanoparticles for steel/steel contacts in boundary lubrica-tion regime. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kananathan, J.; Samykano, M.; Sudhakar, K.; Subramaniam, S.R.; Selavamani, S.K.; Kumar, N.M.; Keng, N.W.; Kadirgama, K.; Hamzah, W.A.W.; Harun, W.S.W. Nanofluid as coolant for grinding process: An overview. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 342, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Johnson, B.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Dong, G. Investigation on the lubrication advantages of MoS2 nanosheets compared with ZDDP using block-on-ring tests. Wear 2018, 394–395, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, P.; Kumar, A.; Thakre, G.D.; Jain, A.K. Investigation of tribo-performance and rheological behavior of lubricants: Influence of MoS2 nano-particles. Adv. Mater. Proc. 2018, 3, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raina, A.; Anand, A. Effect of nanodiamond on friction and wear behavior of metal dichalcogenides in synthetic oil. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, V.; Thakur, R.; Jain, A. Antiwear, antifriction, and extreme pressure properties of motor bike engine oil dis-persed with molybdenum disulfide nanoparticles. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najan, A.; Navthar, R.; Gitay, M. Experimental Investigation of tribological properties using nanoparticles as modifiers in lubricating oil. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Lu, X.; Cotter, J.; Eadie, D.; Wong, P.; Mitchell, K. Surface and friction characterization of MoS2 and WS2 third body thin films under simulated wheel/rail rolling–sliding contact. Wear 2008, 264, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Byon, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanoflowers and Nanosheets: Nanotribology. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajendhran, N.; Palanisamy, S.; Periyasamy, P.; Venkatachalam, R. Enhancing of the tribological characteristics of the lubricant oils using Ni-promoted MoS2 nanosheets as nano-additives. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, V.; Rao, C.K.R.; Rao, N.M. Lubricating and physico-chemical properties of CI- 4 plus engine oil dispersed with surface modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 12, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Su, F.; Chen, Y. Effective lubricant of Nano-Ag/MWCNTs nanocomposites produced by supercritical CO2 synthesis. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Su, F.; Chen, Y. Nickel/Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Synthesized in Supercritical Fluid as Efficient Lubricant Additive for Mineral Oil. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyavhare, K.; Aswath, P.B. Tribological Properties of Novel Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Phosphorus Containing Ionic Liquid Hybrids in Grease. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.A.S.; Hussein, H.A.; Namer, N.S. Influence of Adding CuO and MoS2 Nano-particles to Castor Oil and Mould-ing Oil on Tribological Properties. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Asnida, M.; Hisham, S.; Norazmira, A.; abdul kadir, A.; Noor, M.M.; Kadirgama, K.; Devarajan, R.; Najafi, G.; Tarlochan, F. Copper (II) oxide nanoparticles as additve in engine oil to increase thedurability of piston-liner contact. Fuel 2018, 212, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallusamy, S.; Logeshwaran, J. Experimental analysis on nanolubricants used in multi cylinder petrol engine with copper oxide as nanoparticle. Rasayan J. Chem. 2017, 10, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Xie, G.; Luo, J. Mechanical properties of nanoparticles: Basics and applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ettefaghi, E.-O.-L.; Ahmadi, H.; Rashidi, A.; Nouralishahi, A.; Mohtasebi, S.S. Preparation and thermal properties of oil-based nanofluid from multi-walled carbon nanotubes and engine oil as nano-lubricant. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 46, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotia, A.K.; Haldar, R.; Deval, A.; Ghosh, P.; Kumar, S. Characterization of Al2O3-SAE 15W40 engine oil nanolubricant and performance evaluation in 4- stroke diesel engine. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A. Improving the Performance of Automotive Engines and Tribological Behavior of the Piston Ring Assembly Using Nanomaterials as Smart Nano-Lubricant Additives. J. Mech. Eng. Res. Dev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakre, A.A.; Shinde, A.; Mundhe, G. Improvement in boundary lubrication characteristics of SAE20W40 oil using alu-minum oxide nanoparticles. J. Tribol. 2016, 138, 34501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Lin, B.; Sui, T.; Wang, A.; Yan, S.; Yang, Q. The excellent anti-wear and friction reduction properties of silica nanoparticles as ceramic water lubrication additives. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 14901–14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hu, N.; Zhou, G.; Wu, J. Tribological properties of lubricating oil with micro/nano-scale WS2 particles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2018, 13, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratoi, M.; Niste, V.B.; Zekonyte, J. WS2 nanoparticles—Potential replacement for ZDDP and friction modifier additives. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 21238–21245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, C.-H.; Tang, S.W.; Mohd, N.K.; Lim, W.H.; Yeong, S.K.; Idris, Z. Tribological behavior of biolubricant base stocks and additives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, G.C.; Cazamir, D.; Dima, D.; Georgescu, C.; Deleanu, L. Influence of TiO2 as nano additive in rapeseed oil. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; Volume 444, p. 22011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.Y.; Dwivedi, S.; Mishra, V. Influence of sliding speed on the tribological characteristics of pongamia oil with TiO2 nanoparticles. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kachoei, M.; Eskandarinejad, F.; Divband, B.; Khatamian, M. The effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles deposition for friction reduction on orthodontic wires. Dent. Res. J. 2013, 10, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y. Friction and wear mechanisms of castor oil with addition of hexagonal boron nitride nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2018, 124, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, C.P.; Rajendrakumar, P.K.; Thottackkad, M.V. Evaluation of the tribological and thermo-physical properties of coconut oil added with MoS2 nanoparticles at elevated temperatures. Wear 2015, 330–331, 288–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, M.; Kogovšek, J.; Remskar, M. Mechanisms and improvements in the friction and wear behavior using MoS2 nanotubes as potential oil additives. Wear 2012, 280–281, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomala, A.; Vengudusamy, B.; Ripoll, M.R.; Suarez, A.N.; Remškar, M.; Rosentsveig, R. Interaction between se-lected MoS2 nanoparticles and ZDDP tribofilms. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 59, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M.; Varman, M.; Zulkifli, N. Antiwear Behavior of CuO Nanoparticles as Additive in Bio-Based Lubricant. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 748, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.; Varman, M.; Kalam, A.; Mufti, R.; Zulkifli, N.; Yunus, R.; Zahid, R. Improving the AW/EP ability of chemically modified palm oil by adding CuO and MoS2 nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2015, 88, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, V.; Ortega, J.A. Evaluating the Rheological and Tribological Behaviors of Coconut Oil Modified with Nanoparticles as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2019, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillay, D.S.; Sidik, N.A.C. Tribological properties of biodegradable nano-lubricant. Adv. Res. Fluid. Mech. Sci. 2017, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lahouij, I.; Dassenoy, F.; de Knoop, L.; Martin, J.-M.; Vacher, B. In situ TEM observation of the behavior of an individual fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticle in a dynamic contact. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Jackson, R.L.; Khodadadi, J.M. Experimental analysis of stable CuO nanoparticle enhanced lubricants. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2015, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Sharma, A.; Singh, N.; Singla, A. Effect of alumina nanoparticles as additive on the friction and wear behavior of polanga-based lubricant. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- McElwain, S.E.; Blanchet, T.A.; Schadler, L.S.; Sawyer, W.G. Effect of Particle Size on the Wear Resistance of Alumina-Filled PTFE Micro- and Nanocomposites. Tribol. Trans. 2008, 51, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, T.D.-F.; González, A.F.; Del Reguero, Á.; Matos, M.; Díaz-García, M.E.; Badía-Laíño, R. Engineered silica nanoparticles as additives in lubricant oils. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y. Preparation and tribological properties of novel boehmite/graphene oxide nano-hybrid. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 6178–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Peng, W.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Effects of Size and Aggregation/Agglomeration of Nanoparticles on the Interfacial/Interphase Properties and Tensile Strength of Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xia, W.; Cheng, X.; He, A.; Yun, J.H.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Jiao, S.; Huang, L.; et al. A study of the tribological behaviour of TiO2 nano-additive water-based lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zare, Y. Study of nanoparticles aggregation/agglomeration in polymer particulate nanocomposites by mechanical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 84, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Renner, P.; Liang, H. Dispersion of Nanoparticles in Lubricating Oil: A Critical Review. Lubricants 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kałużny, J.; Kulczycki, A.; Dzięgielewski, W.; Piasecki, A.; Gapiński, B.; Mendak, M.; Kempa, K. The Indirect Tribo-logical Role of Carbon Nanotubes Stimulating Zinc Dithiophosphate Anti-Wear Film Formation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waqas, M.; Zahid, R.; Bhutta, M.U.; Khan, Z.A.; Saeed, A. A Review of Friction Performance of Lubricants with Nano Additives. Materials 2021, 14, 6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216310
Waqas M, Zahid R, Bhutta MU, Khan ZA, Saeed A. A Review of Friction Performance of Lubricants with Nano Additives. Materials. 2021; 14(21):6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216310
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaqas, Muhammad, Rehan Zahid, Muhammad Usman Bhutta, Zulfiqar Ahmad Khan, and Adil Saeed. 2021. "A Review of Friction Performance of Lubricants with Nano Additives" Materials 14, no. 21: 6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216310
APA StyleWaqas, M., Zahid, R., Bhutta, M. U., Khan, Z. A., & Saeed, A. (2021). A Review of Friction Performance of Lubricants with Nano Additives. Materials, 14(21), 6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216310