Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia over Cerium-Modified Copper Aluminium Zinc Mixed Oxides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalysts Preparation
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Studies
3. Results
3.1. Mixed Metal Oxides Characterisation
3.1.1. Chemical Composition
3.1.2. Phase Composition and Morphology of Mixed Metal Oxides
3.1.3. Reducibility and Oxidation State of Cu- and Ce-Containing Oxides
3.2. Catalytic Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dammers, E.; McLinden, C.A.; Griffin, D.; Shephard, M.W.; Van Der Graaf, S.; Lutsch, E.; Schaap, M.; Gainairu-Matz, Y.; Fioletov, V.; Van Damme, M.; et al. NH3 emmisions from large point sources from CrIS and IASI satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 12261–12293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-García, M.A.; Pitchon, V.; Kiennemann, A. Pollution by nitrogen oxides: An approach to NOx abatement by using sorbing catalytic materials. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wu, H.; Yang, L. Study on the ammonia emission characteristics in an ammonia-based WFGD system. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insausti, M.; Timmis, R.; Kinnersley, R.; Rufino, M.C. Advances in sensing ammonia from agricultural sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Palkovits, R. Copper based catalysts for the selective ammonia oxidation into nitrogen and water vapour-Recent trends and open challenges. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basąg, S.; Piwowarska, Z.; Kowalczyk, A.; Węgrzyn, A.; Baran, R.; Gil, B.; Michalik, M.; Chmielarz, L. Cu-Mg-Al hydrotalcite-like materials as precursors of effective catalysts for selective oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen—The influence of Mg/Al ratio and calcination temperature. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 129, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Sani, Z.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Zhao, S.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y. Advances in selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia (NH3-SCO) to dinitrogen in excess oxygen: A review on typical catalysts, catalytic performances and reaction mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecka, S.; Pacultová, K.; Górecki, K.; Smýkalová, A.; Pamin, K.; Obalová, L. Cu-Mg-Fe-O-(Ce) complex oxides as catalysts of selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen (NH3-SCO). Catalysts 2020, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chmielarz, L.; Jabłońska, M. Advances in selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43408–43431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia into nitrogen and water vapour over transition metals modified Al2O3, TiO2 and ZrO2. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Nocuń, M.; Gołąbek, K.; Palkovits, R. Effect of preparation procedures on catalytic activity and selectivity of copper-based mixed oxides in selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia into nitrogen and water vapour. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Wei, G.; Liu, M.; Ning, P. Structural tuning and NH3-SCO performance optimization of CuO-Fe2O3 catalysts by impact of thermal treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qu, Z.; Sun, H. Rational design of spinel CoMn2O4 with Co-enriched surface as high-activity catalysts for NH3-SCO reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Kondratenko, E.V. Mechanism of ammonia oxidation over oxides studied by temporal analysis of products. J. Catal. 2007, 250, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M. TPR study and catalytic performance of noble metals modified Al2O3, TiO2 and ZrO2 for low-temperature NH3-SCO. Catal. Commun. 2015, 70, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shan, Y.; Shan, W.; Shi, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, K.; Ning, P.; et al. Promoting effect of acid sites on NH3-SCO activity with water vapor participation for Pt-Fe/ZSM-5 catalyst. Catal. Today 2020, 376, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; An, B.; Takei, T.; Shishido, T.; Ishida, T.; Haruta, M.; Murayama, T. Features of Nb2O5 as a metal oxide support of Pt and Pd catalysts for selective catalytic oxidation of NH3 with high N2 selectivity. J. Catal. 2020, 389, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Kim, G.J.; Hong, S.C. Reaction properties of ruthenium over Ru/TiO2 for selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Li, X.; Qu, Z.; Tade, M.; Liu, S. The role of copper species on Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for NH3-SCO reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3738–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Harle, G.; Ma, J.; Yi, J. The effect of textural properties of CeO2-SiO2 mixed oxides on NH3-SCO activity of Pt/CeO2-SiO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 604, 117775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.H.; Hong, S.C. Influence of calcination temperature on Ce/TiO2 catalysis of selective catalytic oxidation of NH3 to N2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 470, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, L.; Fan, C.; Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. A multiple-active-site Cu/SSZ-13 for NH3-SCO: Influence of Si/Al ratio on the catalytic performance. Catal. Commun. 2020, 135, 105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Pacia, I.; Basąg, S.; Kowalczyk, A.; Piwowarska, Z.; Duda, M.; Tarach, K.A.; Góra-Marek, K.; Michalik, M.; Díaz, U.; et al. Catalytic performance of commercial Cu-ZSM-5 zeolite modified by desilication in NH3-SCR and NH3-SCO processes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 246, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Gan, L.; Li, K.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Comparison of NH3-SCO performance over CuOx/H-SSZ-13 and CuOx/H-SAPO-34 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 585, 117119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Święs, A.; Gil, B.; Rutkowska, M.; Piwowarska, Z.; Borcuch, A.; Michalik, M.; Chmielarz, L. Effective catalysts for the low-temperature NH3-SCR process based on MCM-41 modified with copper by template ion-exchange (TIE) method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Jia, W. The catalytic properties of Cu modified attapulgite in NH3–SCO and NH3–SCR reactions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 480, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, T.; Lenihan, S. Copper exchanged beta zeolites for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Chem. Commun. 2003, 3, 1280–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, T.; O’Regan, F.; Deconinck, C.; Knüttle, N.; Hodnett, B.K. The catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Influence of water and sulfur on selectivity to nitrogen over promoted copper oxide/alumina catalysts. Catal. Today 2000, 55, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecka, S.; Pacultová, K.; Smýkalová, A.; Fridrichová, D.; Górecki, K.; Rokicińska, A.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Žebrák, R.; Obalová, L. Role of the Cu content and Ce activating effect on catalytic performance of Cu-Mg-Al and Ce/Cu-Mg-Al oxides in ammonia selective catalytic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 573, 151540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, L.; Anderson, B.G.; Van Grondelle, J.; Van Santen, R.A. NH3 oxidation to nitrogen and water at low temperatures using supported transition metal catalysts. Catal. Today 2000, 61, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, L.; Van Grondelle, J.; Anderson, B.G.; Van Santen, R.A. Selective low temperature NH3 oxidation to N2 on copper-based catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 186, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippits, M.J.; Gluhoi, A.C.; Nieuwenhuys, B.E. A comparative study of the selective oxidation of NH3 to N2 over gold, silver and copper catalysts and the effect of addition of Li2O and CeOx. Catal. Today 2008, 137, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Cao, N.; He, H. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia from MAP decomposition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 58, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.W.; Hävecker, M.; Knop-Gericke, A.; Schlügl, R. Investigation of ammonia oxidation over copper with in situ NEXAFS in the soft X-ray range: Influence of pressure on the catalyst performance. Catal. Lett. 2001, 74, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielarz, L.; Jabłońska, M.; Strumiński, A.; Piwowarska, Z.; Wegrzyn, A.; Witkowski, S.; Michalik, M. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over Mg-Al, Cu-Mg-Al and Fe-Mg-Al mixed metal oxides doped with noble metals. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 130–131, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, M.; Ramis, G.; Busca, G.; Montanari, B.; Vaccari, A. Ammonia adsorption and oxidation on Cu/Mg/Al mixed oxide catalysts prepared via hydrotalcite-type precursors. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4628–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Palomares, A.E.; Chmielarz, L. NOx storage/reduction catalysts based on Mg/Zn/Al/Fe hydrotalcite-like materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Tran, T.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, G. Synthesis, characterization and activity evaluation of Cu-based catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides (LDHs) for DeNOx reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Chang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Structural effects of iron spinel oxides doped with Mn, Co, Ni and Zn on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 376, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, A.J.; Di Cosimo, J.I.; Apesteguia, C.R. Influence of the chemical composition on the preparation of Cu-Co-Zn-Al mixed oxide catalysts with high metal dispersion. New Front. Catal. 1993, 75, 1771–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Obalová, L.; Karásková, K.; Wach, A.; Kustrowski, P.; Mamulová-Kutláková, K.; Michalik, S.; Jirátová, K. Alkali metals as promoters in Co-Mn-Al mixed oxide for N2O decomposition. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 462–463, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basąg, S.; Kovanda, F.; Piwowarska, Z.; Kowalczyk, A.; Pamin, K.; Chmielarz, L. Hydrotalcite-derived Co-containing mixed metal oxide catalysts for methanol incineration: Role of cobalt content, Mg/Al ratio and calcination temperature. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic Radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. 1976, A32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.J.; Da Silva, M.R.; Takashima, K. Preparation and characterization of Zno/CuO semiconductor and photocatalytic activity on the decolorization of direct red 80 azodye. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2015, 60, 2749–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Liang, X. Model construction of micro-pores in shale: A case study of Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale in Dianqianbei area, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basąg, S.; Kocoł, K.; Piwowarska, Z.; Rutkowska, M.; Baran, R.; Chmielarz, L. Activating effect of cerium in hydrotalcite derived Cu–Mg–Al catalysts for selective ammonia oxidation and the selective reduction of NO with ammonia. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2017, 121, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabłońska, M.; Chmielarz, L.; Węgrzyn, A.; Guzik, K.; Piwowarska, Z.; Witkowski, S.; Walton, R.I.; Dunne, P.W.; Kovanda, F. Thermal transformations of Cu-Mg (Zn)-Al(Fe) hydrotalcite-like materials into metal oxide systems and their catalytic activity in selective oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.M.; Hong, S.C. Promotional effect of vanadium on the selective catalytic oxidation of NH3 to N2 over Ce/V/TiO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 163, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qu, Z.; Quan, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Fan, R. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over CuO-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by surfactant-templated method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 134–135, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.C.; Hung, C.M.; Yang, S.F. Selective Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia over Copper-Cerium Composite Catalyst. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Qu, Z. Adsorption and surface reaction pathway of NH3 selective catalytic oxidation over different Cu-Ce-Zr catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, H. Mechanism of selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over Ag/Al2O3. J. Catal. 2009, 268, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigdollers, A.R.; Schlexer, P.; Tosoni, S.; Pacchioni, G. Increasing oxide reducibility: The role of metal/oxide interfaces in the formation of oxygen vacancies. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6493–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
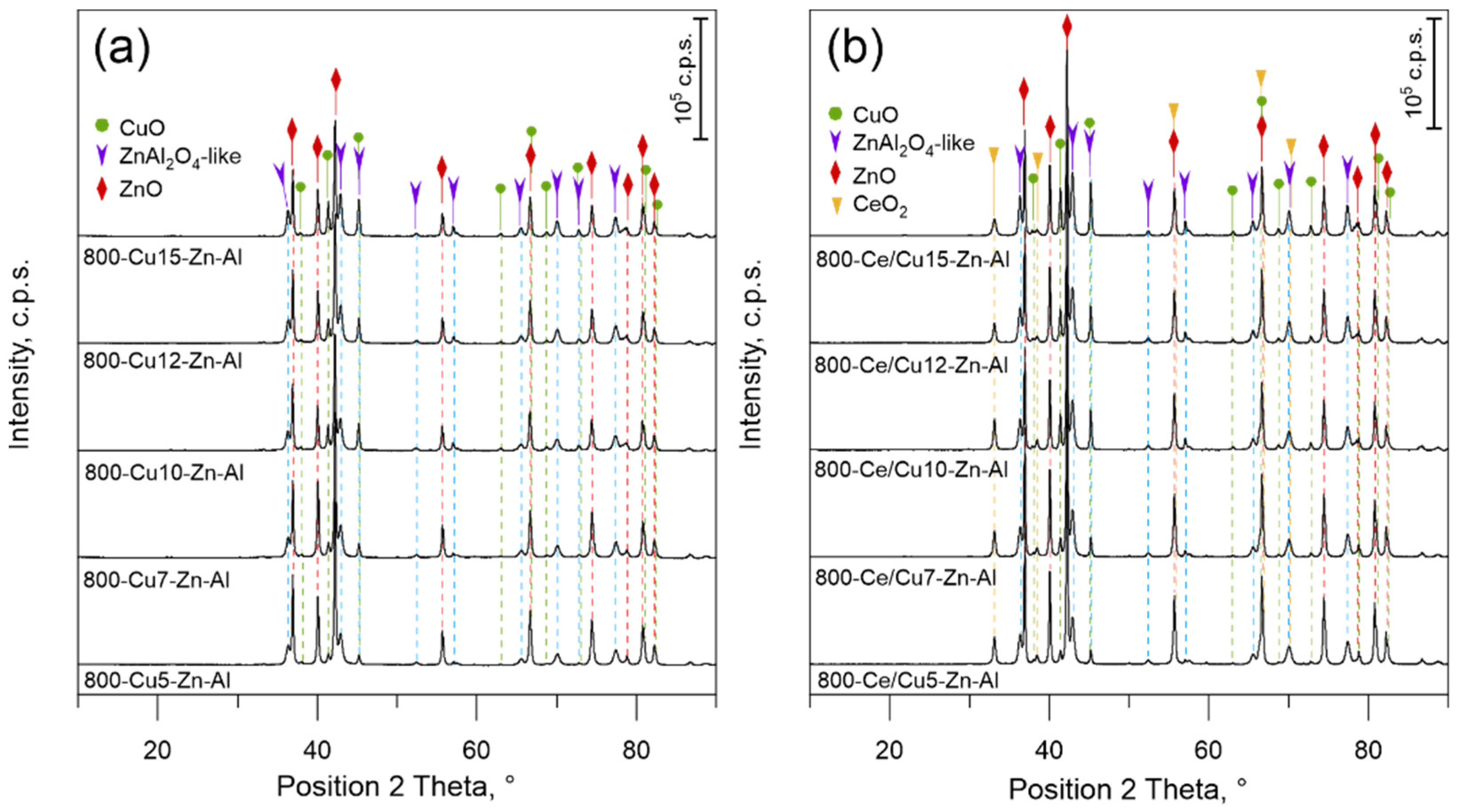
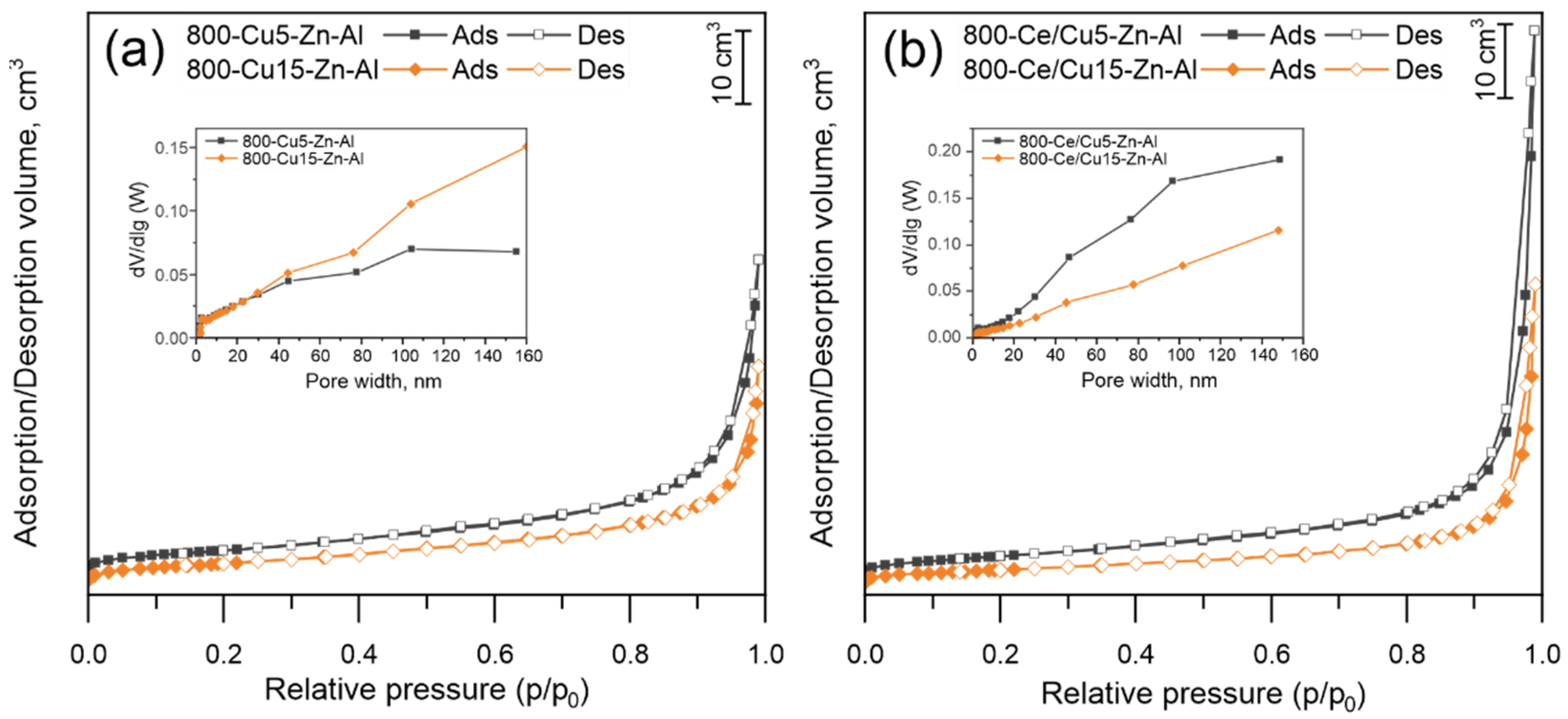
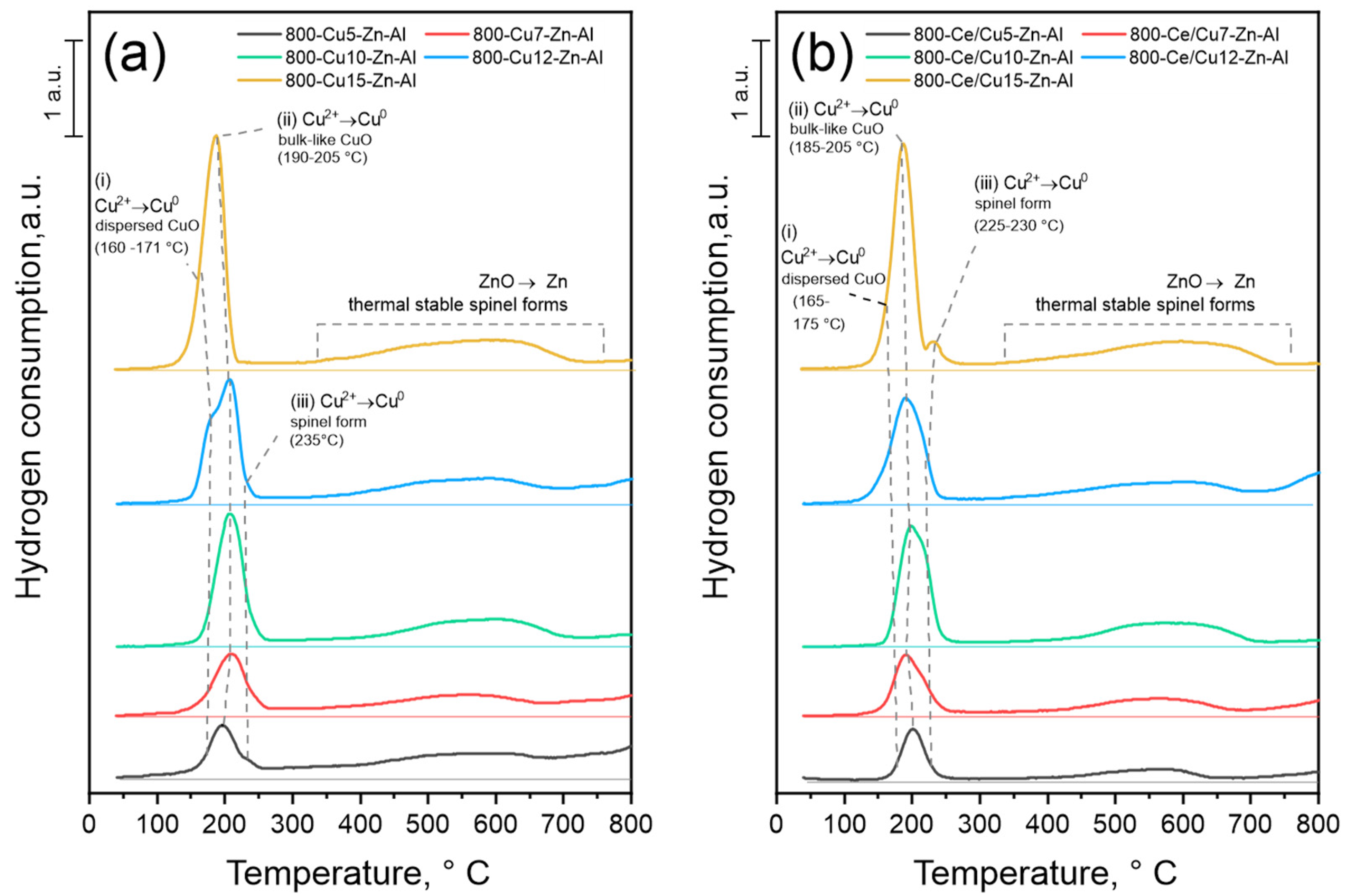
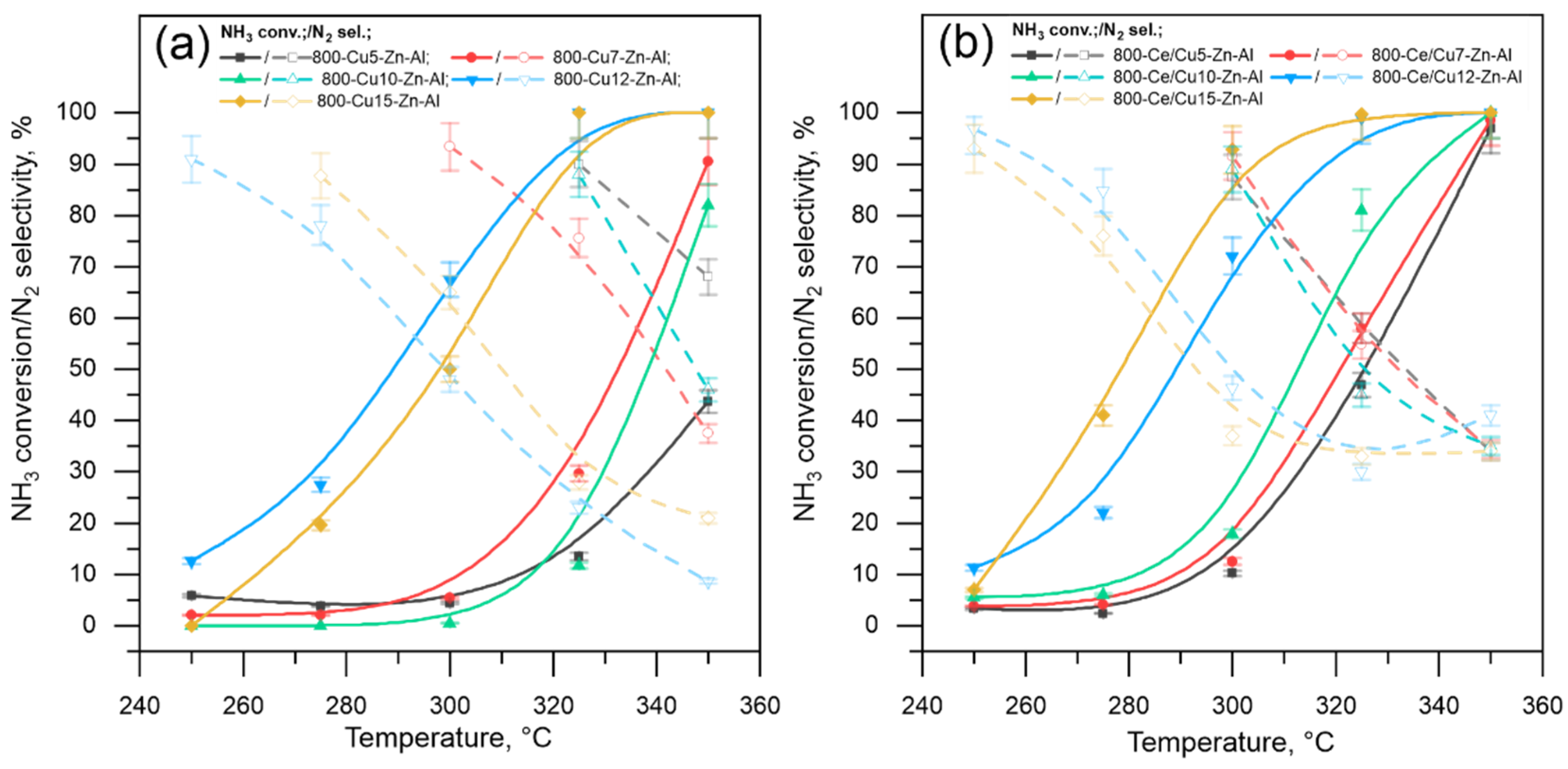

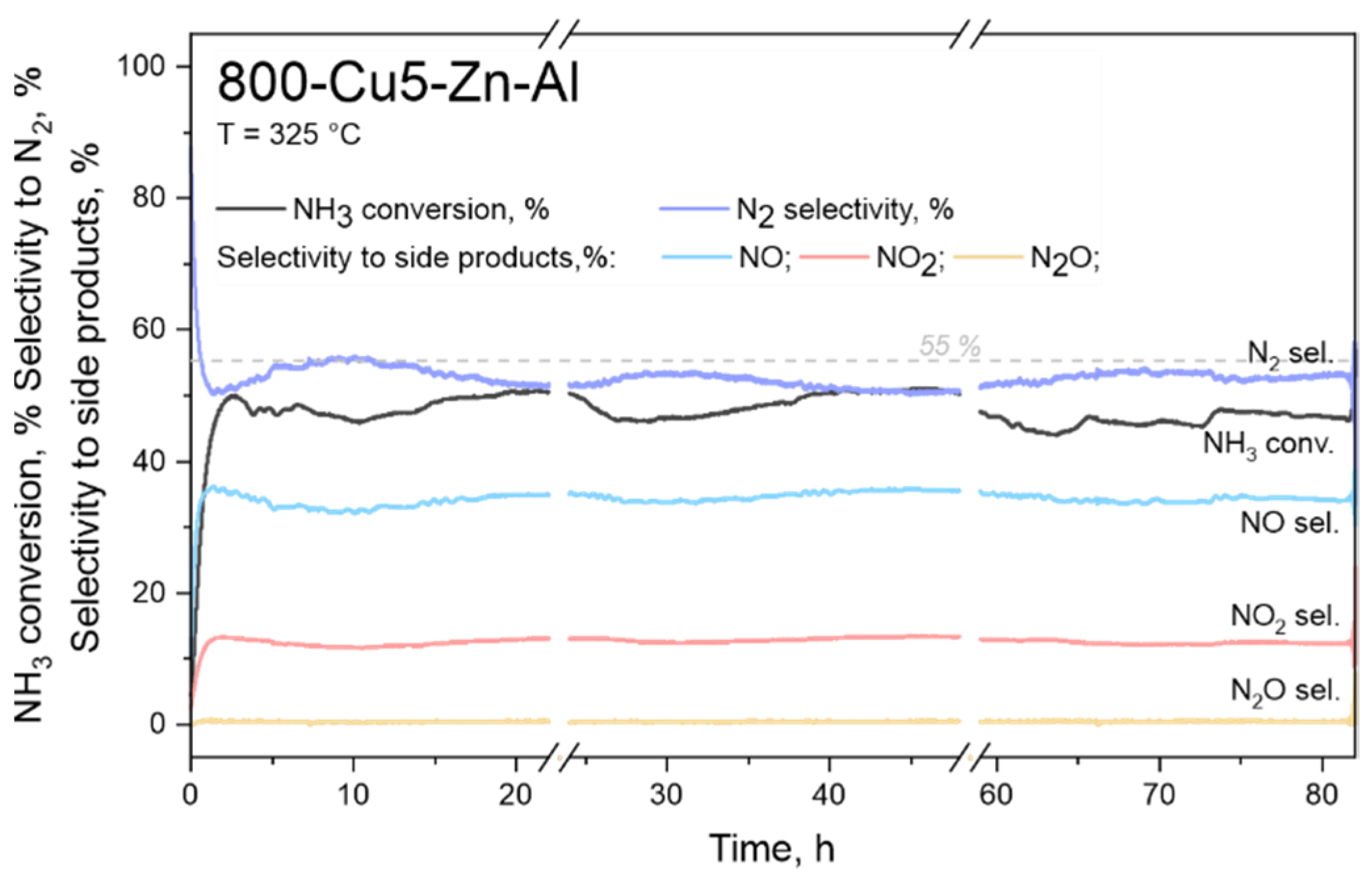

| Series 800-Cux-Zn-Al ‘Un-Modified’ | Series 800-Ce/Cux-Zn-Al ‘Modified by Ce’ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Code | Intended Chemical Composition, mol.% | Sample Code | Intended Chemical Composition, mol.% | |||||
| Cu | Zn | Al | Cu | Zn | Al | Ce | ||
| 800-Cu5-Zn-Al | 5 | 62 | 33 | 800-Ce/Cu5-Zn-Al | 4.8 | 59.2 | 31 | 5 |
| 800-Cu7-Zn-Al | 7 | 60 | 33 | 800-Ce/Cu7-Zn-Al | 6.8 | 57.2 | 31 | 5 |
| 800-Cu10-Zn-Al | 10 | 57 | 33 | 800-Ce/Cu10-Zn-Al | 9.6 | 54.4 | 31 | 5 |
| 800-Cu12-Zn-Al | 12 | 55 | 33 | 800-Ce/Cu12-Zn-Al | 11.5 | 52.5 | 31 | 5 |
| 800-Cu15-Zn-Al | 15 | 52 | 33 | 800-Ce/Cu15-Zn-Al | 14.4 | 49.6 | 31 | 5 |
| Sample | Molar Ratio Int. | EDS Chem. Com., wt. % 1 | Molar Ratio Cal. 2 | Ce wt. % 1 (EDS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu/Zn | Cu/Al | Cu | Zn | Al | Cu/Zn | Cu/Al | ||
| 800-Cu5-Zn-Al | 0.08 | 0.15 | 5.5 | 68.9 | 25.6 | 0.08 | 0.09 | - |
| 800-Cu7-Zn-Al | 0.12 | 0.21 | 7.9 | 69.7 | 22.3 | 0.12 | 0.15 | - |
| 800-Cu10-Zn-Al | 0.17 | 0.30 | 13.7 | 62.5 | 23.8 | 0.22 | 0.24 | - |
| 800-Cu12-Zn-Al | 0.22 | 0.36 | 13.0 | 65.1 | 21.9 | 0.20 | 0.25 | - |
| 800-Cu15-Zn-Al | 0.29 | 0.45 | 17.1 | 62.4 | 20.4 | 0.28 | 0.36 | - |
| 800-Ce/Cu5-Zn-Al | 0.08 | 0.15 | 5.4 | 64.1 | 22.1 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 8.43 |
| 800-Ce/Cu7-Zn-Al | 0.12 | 0.21 | 7.1 | 60.5 | 24.9 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 7.61 |
| 800-Ce/Cu10-Zn-Al | 0.17 | 0.31 | 12.3 | 55.2 | 23.1 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 9.39 |
| 800-Ce/Cu12-Zn-Al | 0.22 | 0.37 | 12.2 | 62.4 | 18.0 | 0.20 | 0.29 | 7.41 |
| 800-Ce/Cu15-Zn-Al | 0.29 | 0.46 | 18.0 | 58.7 | 15.2 | 0.31 | 0.50 | 8.14 |
| Sample | XRD Intensity Ratio 1 | Crystallite Size, nm 2 | Egd 3, eV | Text. Prop., m2 g−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT/IZ | IG/IZ | IC/IZ | CuO | ZnAl2O4 | ZnO | CeO2 | BET | t-Plot | ||
| 800-Cu5-Zn-Al | 0.07 | 0.19 | - | 26 | 19 | 44 | - | 3.24 | 21 | 6 |
| 800-Cu7-Zn-Al | 0.11 | 0.22 | - | 38 | 15 | 32 | - | 3.23 | 21 | 6 |
| 800-Cu10-Zn-Al | 0.22 | 0.27 | - | 41 | 20 | 42 | - | 3.20 | 16 | 2 |
| 800-Cu12-Zn-Al | 0.19 | 0.29 | - | 31 | 23 | 35 | - | 3.21 | 20 | 5 |
| 800-Cu15-Zn-Al | 0.29 | 0.36 | - | 38 | 18 | 40 | - | 3.21 | 15 | 2 |
| 800-Ce/Cu5-Zn-Al | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 30 | 22 | 38 | 23 | 3.21 | 18 | 4 |
| 800-Ce/Cu7-Zn-Al | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 31 | 22 | 49 | 28 | 3.17 | 17 | 5 |
| 800-Ce/Cu10-Zn-Al | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 38 | 23 | 49 | 29 | 3.21 | 19 | 3 |
| 800-Ce/Cu12-Zn-Al | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 41 | 23 | 48 | 26 | 3.23 | 15 | 4 |
| 800-Ce/Cu15-Zn-Al | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 36 | 27 | 49 | 19 | 3.17 | 12 | 3 |
| Sample | Theoretical H2 Consumption 1, mmol g−1 | Measured H2 Consumption (40–300 °C), mmol g−1 | % of Theoretical H2 Consumption 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 800-Cu5-Zn-Al | 0.864 | 0.402 | 47 |
| 800-Cu7-Zn-Al | 1.258 | 0.528 | 42 |
| 800-Cu10-Zn-Al | 2.161 | 0.888 | 41 |
| 800-Cu12-Zn-Al | 2.046 | 0.846 | 41 |
| 800-Cu15-Zn-Al | 2.703 | 1.269 | 47 |
| 800-Ce/Cu5-Zn-Al | 0.845 | 0.281 | 33 |
| 800-Ce/Cu7-Zn-Al | 1.114 | 0.442 | 40 |
| 800-Ce/Cu10-Zn-Al | 1.938 | 0.834 | 43 |
| 800-Ce/Cu12-Zn-Al | 1.928 | 0.832 | 43 |
| 800-Ce/Cu15-Zn-Al | 2.830 | 1.125 | 40 |
| Samples Set | Phase Composition | Reduction of Cu2+, °C | BET Surface Area m2 g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 800-Cux-Zn-Al | CuO, (Cu,Zn)Al2O4, ZnO | 160–170 (D) 190–205 (B) 235 (S) | 15–21 |
| 800-Ce/Cux-Zn-Al | CuO, (Cu,Zn)Al2O4, ZnO, CeO2 | 165–175 (D) 185–205 (B) 225–230 (S) | 12–18 |
| 800-Cux-Mg-Fe | CuO, (Cu,Mg)Fe2O4, MgO, CeO2 | 180 (D) 250 (B) 580 (S) | 6–18 |
| 800-Ce/Cux-Mg-Al | CuO, (Cu,Mg)Fe2O4, MgO, CeO2 | 195 (D) 260 (B) 580 (S) | 6–18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górecka, S.; Pacultová, K.; Fridrichová, D.; Górecki, K.; Bílková, T.; Žebrák, R.; Obalová, L. Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia over Cerium-Modified Copper Aluminium Zinc Mixed Oxides. Materials 2021, 14, 6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216581
Górecka S, Pacultová K, Fridrichová D, Górecki K, Bílková T, Žebrák R, Obalová L. Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia over Cerium-Modified Copper Aluminium Zinc Mixed Oxides. Materials. 2021; 14(21):6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216581
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórecka, Sylwia, Kateřina Pacultová, Dagmar Fridrichová, Kamil Górecki, Tereza Bílková, Radim Žebrák, and Lucie Obalová. 2021. "Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia over Cerium-Modified Copper Aluminium Zinc Mixed Oxides" Materials 14, no. 21: 6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216581
APA StyleGórecka, S., Pacultová, K., Fridrichová, D., Górecki, K., Bílková, T., Žebrák, R., & Obalová, L. (2021). Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia over Cerium-Modified Copper Aluminium Zinc Mixed Oxides. Materials, 14(21), 6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216581







