Re-Design of Machine Tool Joint Components Based on Polymer Fillings for High-Speed Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of the Measurement, Materials, and Re-Designed Components
- −
- An accelerometer PCB model 352A60, PCB Piezotronics, Depew, NY, USA, with a frequency range up to 65 kHz and a sensitivity of 10 mV/g; Dynamic Signal Acquisition device PXI-4462 PXI Sound and Vibration Module Meter, National Instruments Corporation, Austin, TX, USA, A/D converter resolution 24-bits, sample rates, samples-per-second 1 kS/s to 204.8 kS/s in 181.9 μS/s increments;
- −
- Acoustic emission sensor Vallen-VS45-H with the range of 20 kHz–400 kHz, Dynamic Signal Acquisition device NI-9223 module meter, signal level ±10 V, resolution 16 Bit, sample rates 1 MS/s/ch, National Instruments Corporation, Austin, TX, USA;
- −
- Software for advanced analysis of the dynamic signal base on LabView Sound and Vibration Toolkit software, National Instruments Corporation, Austin, TX, USA.
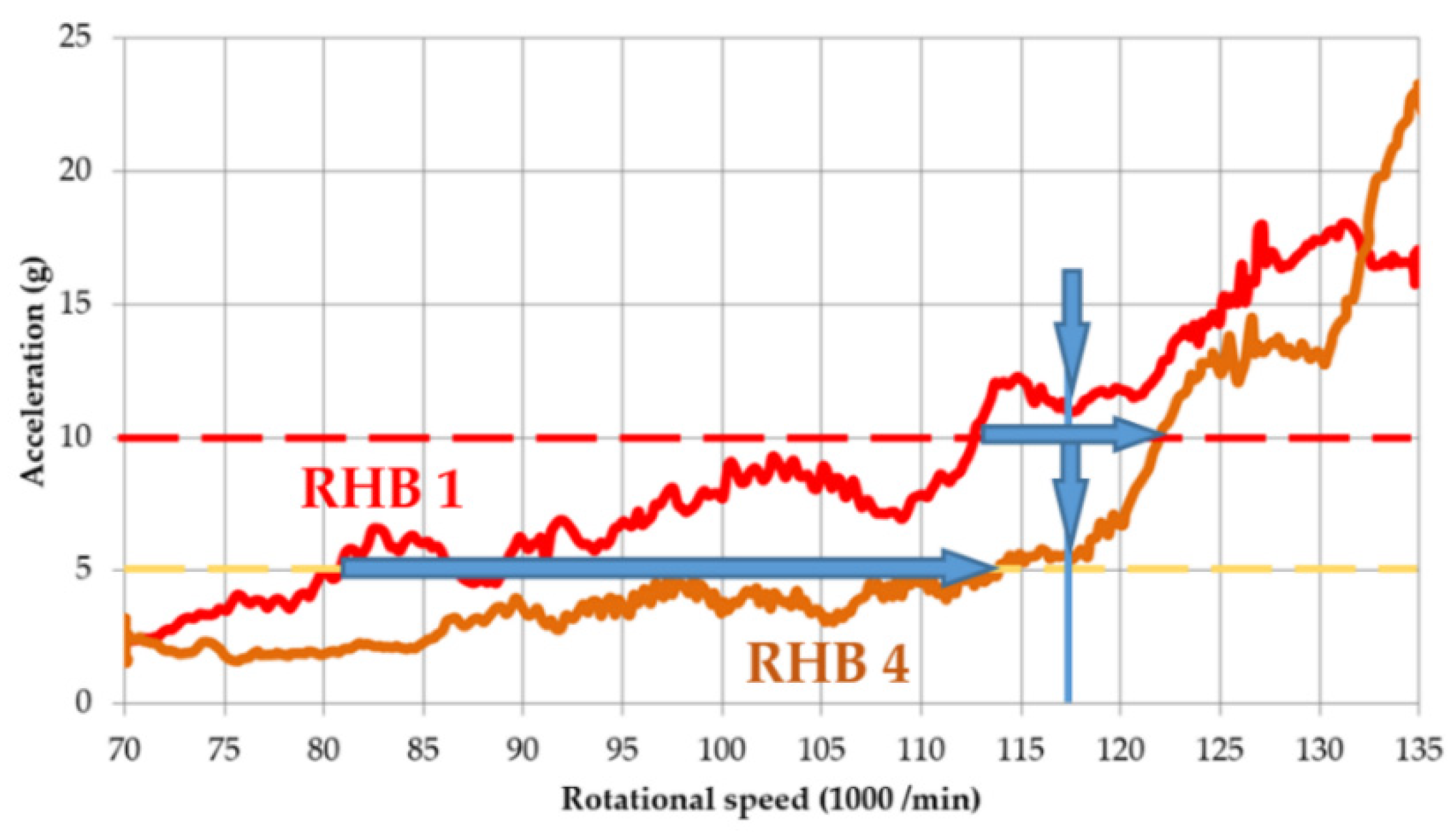
3. Re-Designed Rotor Housing Body and Results
3.1. Bump Test
3.2. The Response to High-Frequency Excitation
3.3. Wavelet Transform
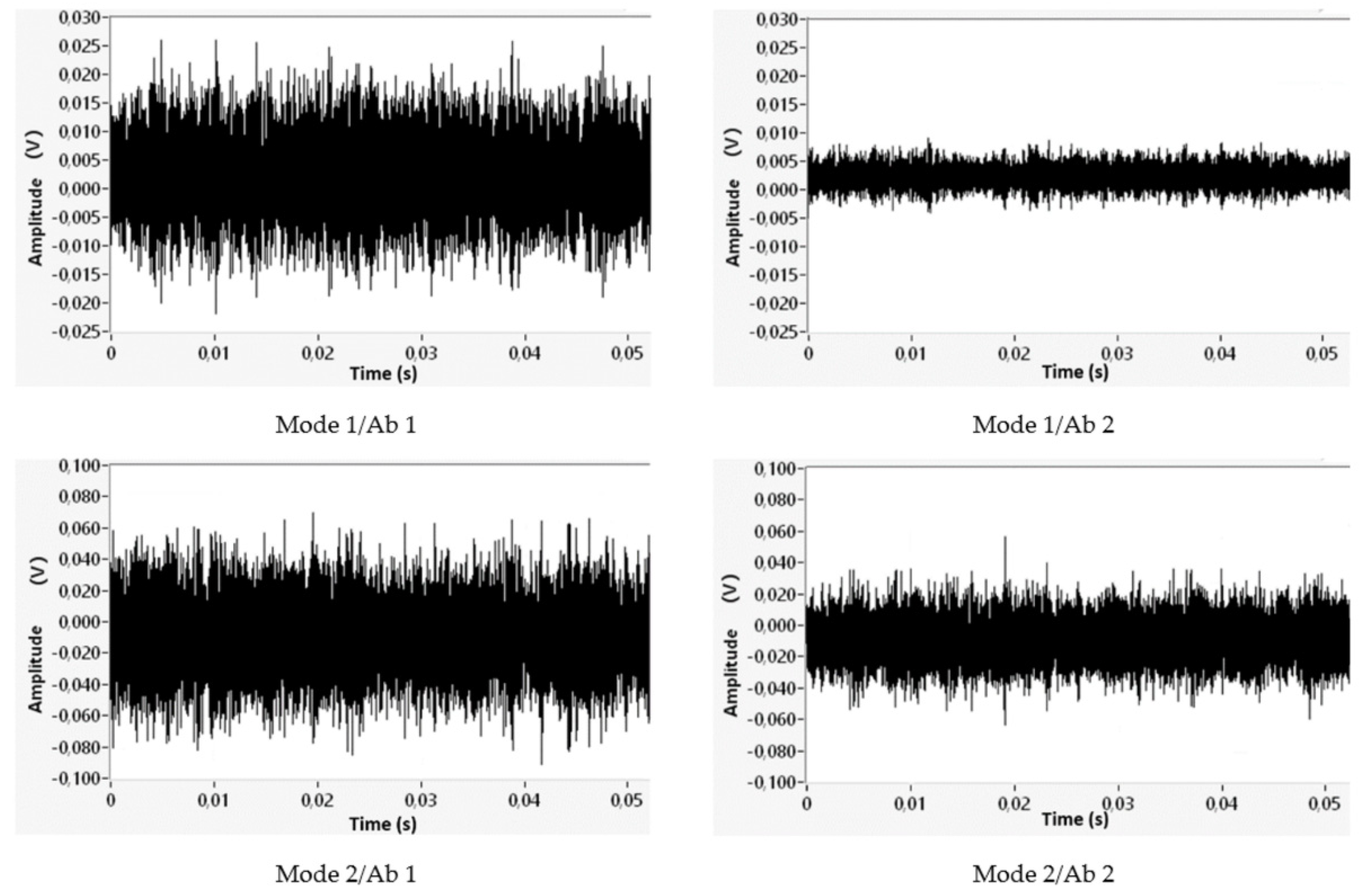
4. Re-Designed Absorber and Results
5. Summary and Conclusions
- A reduction in the dynamic response for the area of safe operation, i.e., a decrease in the amplitudes of vibration acceleration by approximately 50% when using damping material;
- Response stabilisation, i.e., reductions in the range of amplitude values for the whole range of tested excitation frequencies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Möhring, H.C.; Brecher, C.; Abele, E.; Fleischer, J.; Bleicher, F. Materials in machine tool structures. CIRP Ann. 2015, 64, 725–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, L.; Blau, P.; Wabner, M.; Frieß, U.; Eulitz, J.; Klärner, M. Lightweight components for energy-efficient machine tools. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulíšek, V.; Kolar, P.; Vrba, P.; Smolík, J.; Janota, M.; Růžička, M.; Machálka, M. On passive damping in machine tool hybrid structural parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 1925–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, J. Konstrukce CNC Obráběcích Strojů IV. 0; MM Publishing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vivek, A.; Holla, V.; Krupashankara, M.S.; Vignesh, A.; Kulkarni, P. Effect of improving damping ratio on surface finish by filling particulate reinforced polymer composites in machine tool structures. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 13664–13673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, L.H. Sound and Vibration Damping with Polymers: Basic Viscoelastic Definitions and Concepts; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/bk-1990-0424.ch001 (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Nabavi, S.F. Influence of polymers on concrete damping properties. In Advances in Control, Chemical Engineering, Civil Engineering and Mechanical Engineering, Puerto De La Cruz, Tenerife, 30 November–2 December 2010; Mladenov, V., Psarris, K., Mastorakis, N., Caballero, A., Vachtsevanos, G., Eds.; WSEAS Press: Athens, Greece, 2010; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Žmindák, M.; Pelagić, Z. Modeling of shock wave resistance in composite solids. Procedia Eng. 2014, 96, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halama, R.; Markopoulos, A.; Fojtík, F.; Fusek, M.; Poruba, Z.; Famfulík, J. Effect of stress amplitude on uniaxial ratcheting of aluminum alloy 2124-T851: Einfluss der Mittelspannung auf das Ratcheting-Verhalten der Aluminiumlegierung 2124-T851. Mater. Und Werkst. 2017, 48, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, H.; Al Kobaisi, M. Optimization of the polymer concrete used for manufacturing bases for precision tool machines. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, I.G. Research on the influence of the type of microfiller on the damping characteristics of polymer-concrete composites. Mach. Technol. Mater. 2014, 8, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Murčinková, Z.; Živčák, J.; Zajac, J. Experimental study of parameters influencing the damping of particulate, fibre-reinforced, hybrid, and sandwich composites. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 111, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, A.; Dounar, S. Dynamic Finite Element Analysis of Rotor-Shaft Fastening into a Heavy Precise Lathe. Scientific Journals of the Maritime University of Szczecin, 2021; p. 6. Available online: https://repository.am.szczecin.pl/handle/123456789/2668 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Heidarnezhad, F.; Jafari, K.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Effect of polymer content and temperature on mechanical properties of lightweight polymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, J.; Petruška, O.; Radchenko, S.; Dupláková, D.; Goldyniak, D. Hardness Testing of Polymer Concrete Castings by Schmidt Hammer. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Lokuge, W.; Aravinthan, T. Effect of fly ash on the behaviour of polymer concrete with different types of resin. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C.; Poon, C.S. A novel polymer concrete made with recycled glass aggregates, fly ash and metakaolin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, L.; Patel, V.K.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, A.; Winczek, J. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Natural Leaf Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Polyester Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanavel, V.; Raja, T.; Yadav, A.; Ravichandran, M.; Winczek, J. Evaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Jute and Ramie Reinforced Epoxy-based Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendrakumar, N.; Thyla, P.R.; Mohanram, P.V.; Sabareeswaran, A.; Manas, R.B.; Srivatsan, S. Mechanical and dynamic properties of nettle-polyester composite. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, P.; Li, Y. Multi-objective optimization design and performance analysis of machine tool worktable filled with BFPC. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, November 2018; Volume 439, p. 042005. [Google Scholar]
- Saribiyik, M.; Piskin, A.; Saribiyik, A. The effects of waste glass powder usage on polymer concrete properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, J.; Queiroz Barbosa, A.F.; Yezerska, O.; Lehmhus, D.; Baumeister, J. Mechanical Behavior of Particulate Aluminium-Epoxy Hybrid Foams Based on Cold-Setting Polymers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, L. Preparation and Damping Properties of Al2O3 Hollow Spheres/Epoxy Composites Encapsulating Q195 Steel Pipes. ES Mater. Manuf. 2020, 10, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Suh, J. Design and manufacture of hybrid polymer concrete bed for high-speed CNC milling machine. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2008, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, S.H. The application of polymer composites to the table-top machine tool components for higher stiffness and reduced weight. Comp. Struct. 2011, 93, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunaj, P.; Marchelek, K.; Berczyński, S.; Mizrak, B. Rigid Finite Element Method in Modeling Composite Steel-Polymer Concrete Machine Tool Frames. Materials 2020, 13, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Forcellese, A.; Gabrielli, F.; Simoncini, M. Effect of the lubrication-cooling technique, insert technology and machine bed material on the workpart surface finish and tool wear in finish turning of AISI 420B. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balalayeva, E.; Artiukh, V.; Kukhar, V.; Tuzenko, O.; Glazko, V.; Prysiazhnyi, A.; Kankhva, V. Researching of the stress-strain state of the open-type press frame using of elastic compensator of errors of “press-die” system. In Energy Management of Municipal Transportation Facilities and Transport; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, April 2017; pp. 220–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Vazquez, J.M.; Garitaonandia, I.; Fernandes, M.H.; Muñoa, J.; Lacalle, L.N.L.D. A consistent procedure using response surface methodology to identify stiffness properties of connections in machine tools. Materials 2018, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonkwic, P. Optimisation of the Lift Carrying Frame Construction by Using Finite Element Method. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2018, 12, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murčinková, Z. Composite Materials: Micro and Macro Behaviour, Numerical Simulation and Experiment, Applications in Mechanical Engineering; RAM-Verlag: Lüdenscheid, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Růžička, M.; Had, J.; Kulíšek, V.; Uher, O. Multiscale modeling of hybrid composite structures. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 471, pp. 916–921. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilevich, Y.V.; Dounar, S.S.; Karabaniuk, I.A. Finite element analysis of concrete filler influence on dynamic rigidity of heavy machine tool portal. Sci. Tech. 2016, 15, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cienciala, J.; Frydrýšek, K.; Podešva, J. Nonlinear vibration-stochastic approach. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference Engineering Mechanics, Svratka, Czech Republic, 15–18 May 2017; Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics of the Czech Academy of Sciences: Prague, Czech Republic, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, C.W. (Ed.) Vibration Damping, Control, and Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heil, C.; Walnut, D.F. Fundamental Papers in Wavelet Theory; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]

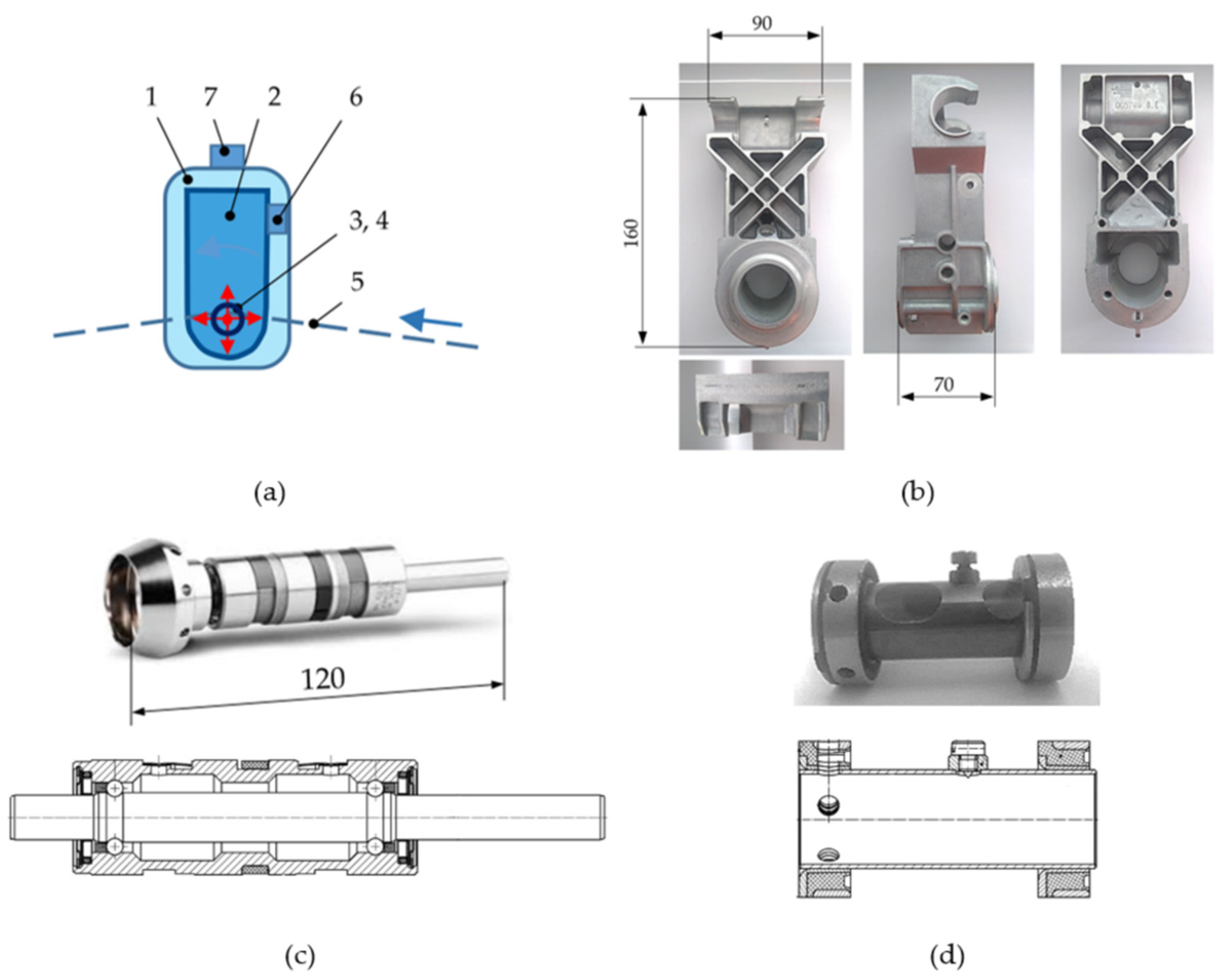
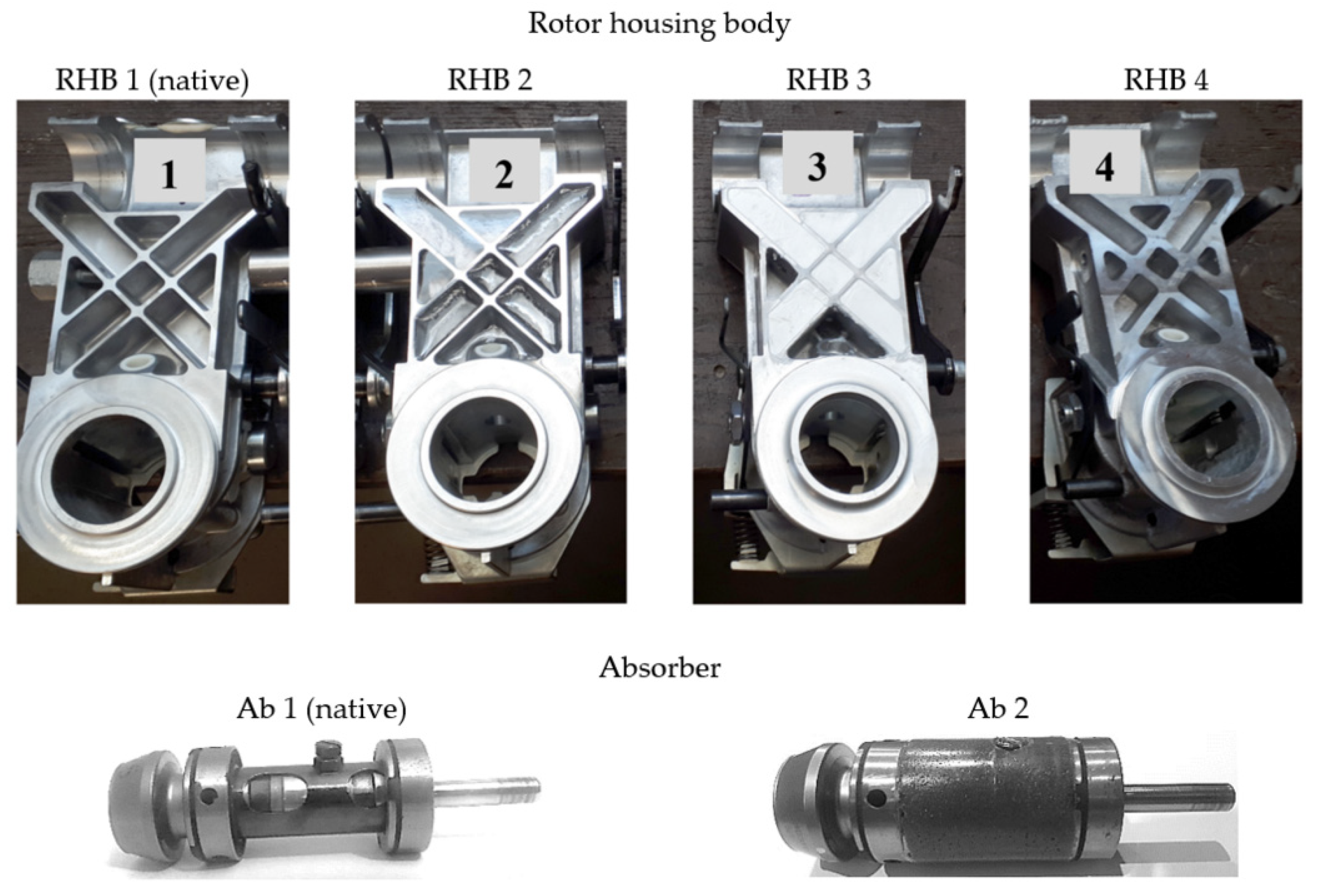
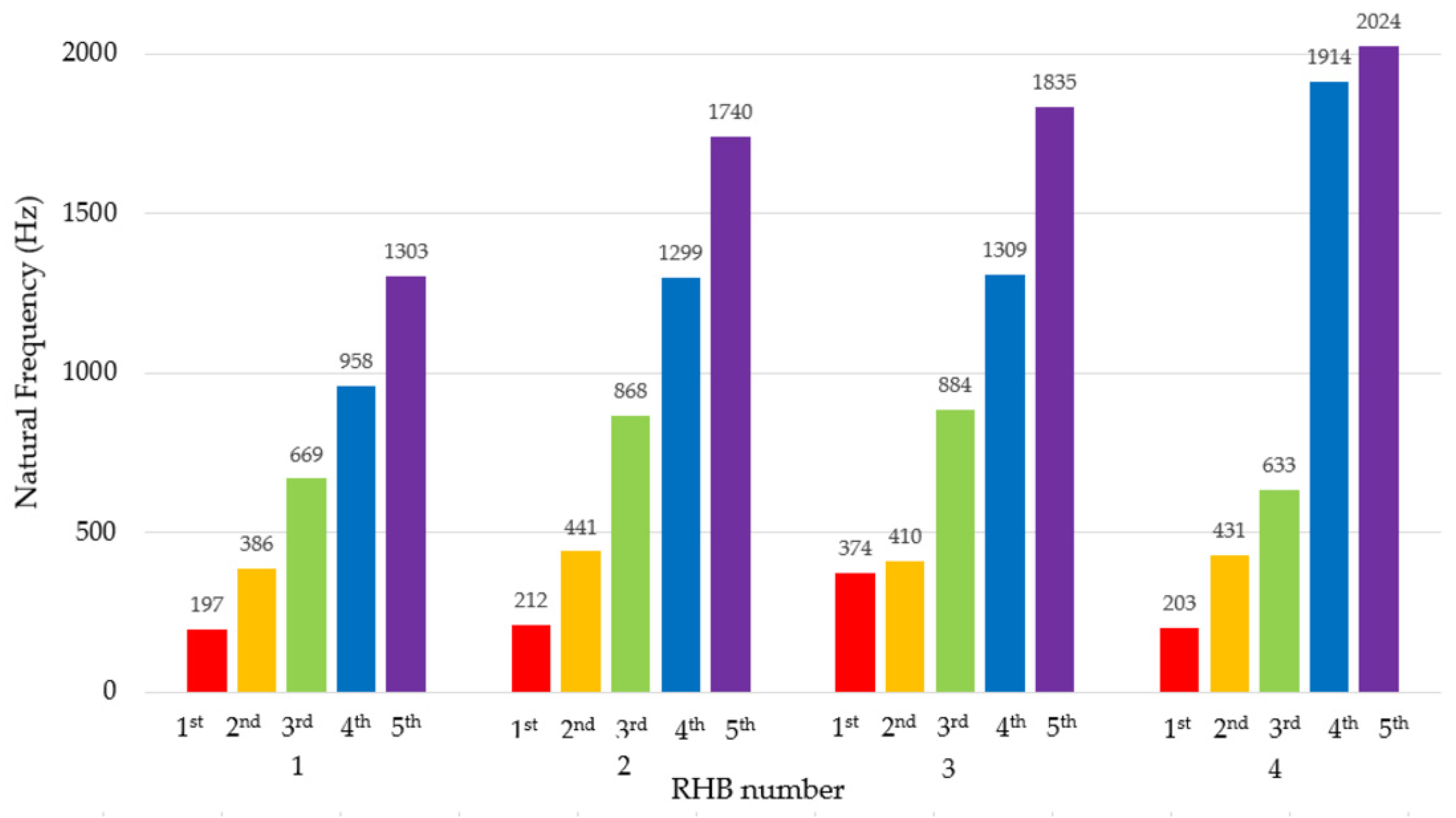

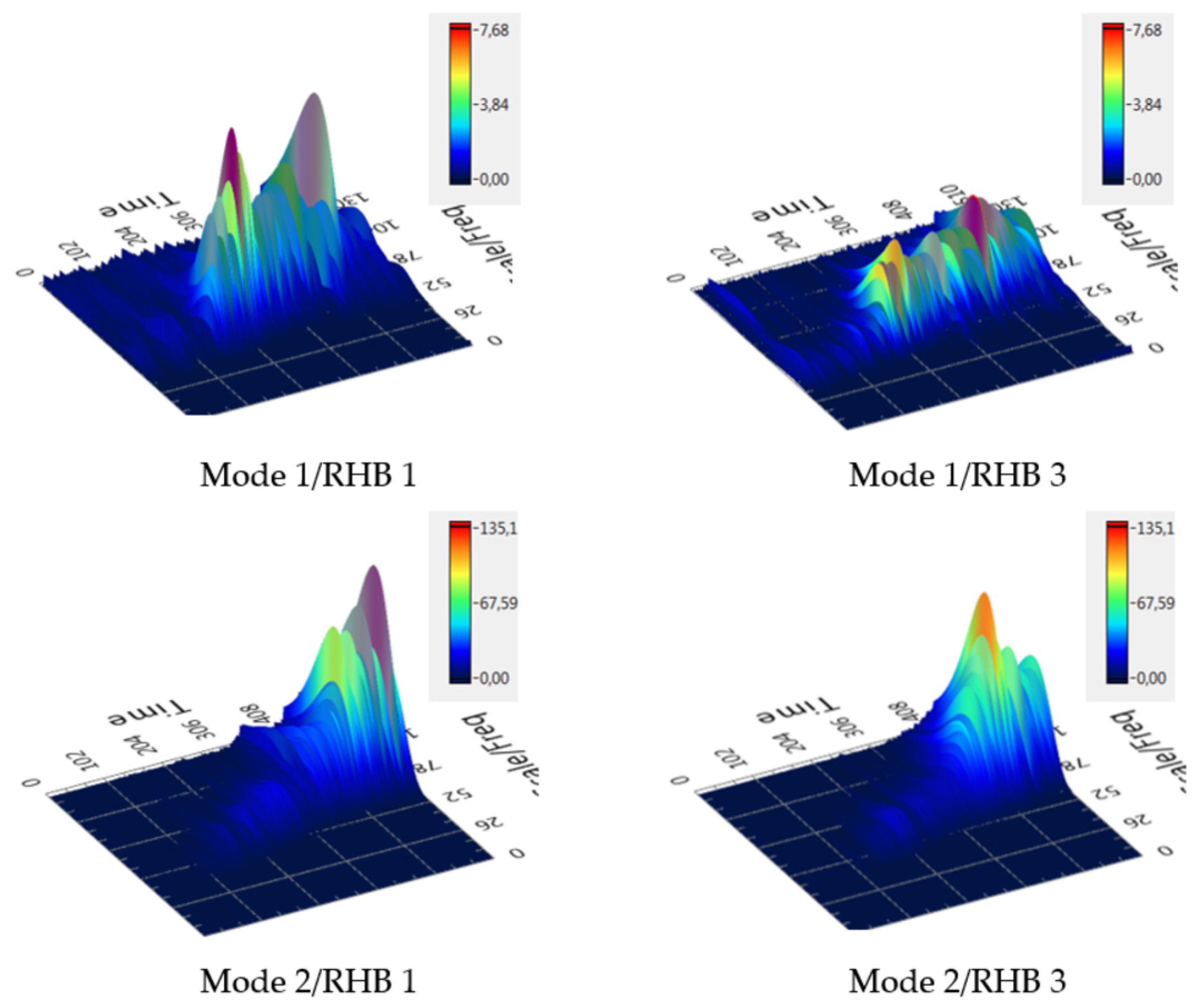

| Materials | Mass m (gm) | Thickness of Ribs (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separately | Together | |||
| RHB 1 | Aluminium alloy | 579 | 2 | |
| RHB 2 | Aluminium alloy | 579 69 | 648 | 2 |
| Damping material A: epoxy resin in front cavities | ||||
| RHB 3 | Aluminium alloy | 579 191 | 770 | 2 |
| Damping material B: silane resin in front and back cavities | ||||
| RHB 4 | Aluminium alloy | 770 | 4 | |
| Ab 1 | Steel | 87 | - | |
| Rubber: encased in bushing | ||||
| Ab 2 | Steel | 87 63 | 150 | - |
| Rubber: encased in bushing | ||||
| Damping material C: polymer concrete in volume between bushings | ||||
| RHB 1 | RHB 2 | RHB 3 | RHB 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logarithmic decrement | 0.081 | 0.093 | 0.131 | 0.083 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murčinková, Z.; Adamčík, P.; Živčák, J. Re-Design of Machine Tool Joint Components Based on Polymer Fillings for High-Speed Performance. Materials 2021, 14, 6913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226913
Murčinková Z, Adamčík P, Živčák J. Re-Design of Machine Tool Joint Components Based on Polymer Fillings for High-Speed Performance. Materials. 2021; 14(22):6913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226913
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurčinková, Zuzana, Pavel Adamčík, and Jozef Živčák. 2021. "Re-Design of Machine Tool Joint Components Based on Polymer Fillings for High-Speed Performance" Materials 14, no. 22: 6913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226913
APA StyleMurčinková, Z., Adamčík, P., & Živčák, J. (2021). Re-Design of Machine Tool Joint Components Based on Polymer Fillings for High-Speed Performance. Materials, 14(22), 6913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226913







