Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
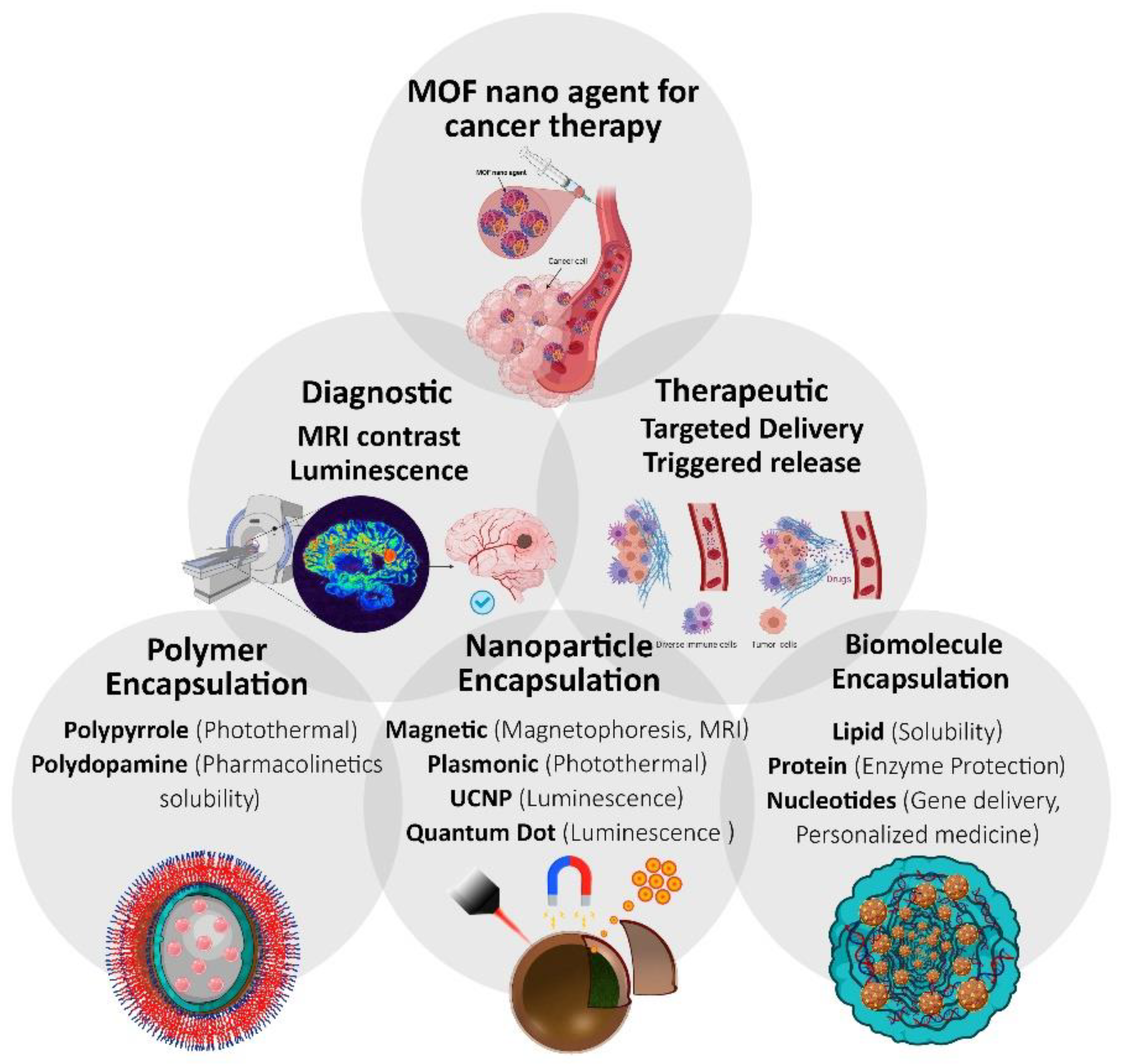
:1. MOFs for Cancer Therapy: So Far, So Close!
2. MOFs in Detecting Cancer Biomarkers
3. MOFs for Enhanced Cancer Therapy
4. Multifunctional MOFs for Cancer Theranostics
5. Conclusions, Challenging Features, and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hajebi, S.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Rabiee, M.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L.; Hamblin, M.R. Stimulus-responsive polymeric nanogels as smart drug delivery systems. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, N.; Ahmadi, S.; Afshari, R.; Khalaji, S.; Rabiee, M.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Nasal Drug Delivery to the Brain: Relevance to Alzheimer's Disease. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2000076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Ahmadvand, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Rabiee, M.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L.; Hamblin, M.R. Carbosilane dendrimers: Drug and gene delivery applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Yaraki, M.T.; Garakani, S.M.; Garakani, S.M.; Ahmadi, S.; Lajevardi, A.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Rabiee, M.; Tayebi, L.; Tahriri, M. Recent advances in porphyrin-based nanocomposites for effective targeted imaging and therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Heidarian Haris, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Matloubi Moghaddam, F.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R.; Jarahiyan, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Shokouhimehr, M. Polymer-Coated NH2-UiO-66 for the Codelivery of DOX/pCRISPR. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 10796–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Jouyandeh, M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Varma, R.S. Natural Polymers Decorated MOF-MXene Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin/pCRISPR. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5106–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Lollar, C.T.; Xiao, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.-C. Biomedical integration of metal–organic frameworks. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, M.R.; Rabiee, N.; Mozafari, M.; Mostafavi, E. Metal-organic frameworks-based nanomaterials for drug delivery. Materials 2021, 14, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Salehi, G.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R. ZnAl nano layered double hydroxides for dual functional CRISPR/Cas9 delivery and enhanced green fluorescence protein biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Fatahi, Y.; Baheiraei, N.; Safarkhani, M.; Aldhaher, A.; Dinarvand, R. Bio-multifunctional noncovalent porphyrin functionalized carbon-based nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiee, N.; Fatahi, Y.; Asadnia, M.; Daneshgar, H.; Kiani, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Atarod, M.; Mashhadzadeh, A.H.; Akhavan, O.; Bagherzadeh, M. Green porous benzamide-like nanomembranes for hazardous cations detection, separation, and concentration adjustment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, H.; Ahmadi, S.; Ghasemi, A.; Ghanbari, M.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Karimi, M.; Webster, T.J.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mostafavi, E. Carbon Nanotubes: Smart Drug/Gene Delivery Carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfarjam, N.; Ghomi, M.; Agarwal, T.; Hassanpour, M.; Sharifi, E.; Khorsandi, D.; Ali Khan, M.; Rossi, F.; Rossetti, A.; Nazarzadeh Zare, E. Antimicrobial ionic liquid-based materials for biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, M.; Rabiee, N.; Fatahi, Y.; Dinarvand, R. Zn-rich (GaN)1−x (ZnO)x: A biomedical friend? New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 4077–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B. Photofunctional MOF-based hybrid materials for the chemical sensing of biomarkers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8155–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, J.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Tang, Z. Core–Shell Upconversion Nanoparticle@ Metal–Organic Framework Nanoprobes for Luminescent/Magnetic Dual-Mode Targeted Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4075–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, Y.H.; Cai, S.J.; Yin, X.B.; He, X.W.; Zhang, Y.K. Fluorescent imaging-guided chemotherapy-and-photodynamic dual therapy with nanoscale porphyrin metal–organic framework. Small 2017, 13, 1603459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shang, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Sun, S.-K.; Yin, X.-B. Smart metal–organic framework-based nanoplatforms for imaging-guided precise chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 11, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z. Hypoxia-triggered nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for enhanced anticancer activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24638–24647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Lee, D.; Xie, J. Gd and Eu co-doped nanoscale metal–organic framework as a T1–T2 dual-modal contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Tomography 2016, 2, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhuri, A.R.; Bhattacharya, D.; Sahu, S.K. Magnetic nanoscale metal organic frameworks for potential targeted anticancer drug delivery, imaging and as an MRI contrast agent. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 2963–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Qiao, C.; Jia, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Highly Stable and Long-Circulating Metal-Organic Frameworks Nanoprobes for Sensitive Tumor Detection In Vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Xin, P.; An, L.; Xu, Y.; Tao, C.; Tian, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, B.; Yang, S. Fe3O4–ZIF-8 assemblies as pH and glutathione responsive T2 –T1 switching magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent for sensitive tumor imaging in vivo. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Gao, H.; Chu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Lin, G.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Engineering phototheranostic nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Zeng, C.; Du, Y.; Hui, H.; Liang, X.; Chi, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Tian, J. Core–shell gold Nanorod@ metal–organic framework nanoprobes for multimodality diagnosis of glioma. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, D.; Dougherty, C.A.; Lu, W.; Wu, H.; He, X.; Cai, T.; Van Dort, M.E.; Ross, B.D.; Hong, H. In vivo targeting and positron emission tomography imaging of tumor with intrinsically radioactive metal–organic frameworks nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4315–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabiee, N.; Khatami, M.; Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Fatahi, Y.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Diatoms with Invaluable Applications in Nanotechnology, Biotechnology, and Biomedicine: Recent Advances. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 3053–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Fatahi, Y.; Aldhaher, A.; Makvandi, P.; Dinarvand, R.; Jouyandeh, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Turning Toxic Nanomaterials into a Safe and Bioactive Nanocarrier for Co-Delivery of DOX/pCRISPR. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5336–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Kiani, M.; Fatahi, Y.; Tavakolizadeh, M.; Pourjavadi, A.; Jouyandeh, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Multifunctional 3D hierarchical bioactive green carbon-based nanocomposites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 8706–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, M.R.; Rabiee, N.; Seidi, F.; Far, B.F.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Lima, E.C.; Rabiee, M. Green CoNi2S4/Porphyrin Decorated Carbon-based Nanocomposites for Genetic Materials Detection. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghadiri, A.M.; Kiani, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Jajarmi, V.; Fatahi, Y.; Aldhaher, A.; Tahriri, M.; Webster, T.J. Calcium-based nanomaterials and their interrelation with chitosan: Optimization for pCRISPR delivery. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarghami Dehaghani, M.; Yousefi, F.; Sajadi, S.M.; Tajammal Munir, M.; Abida, O.; Habibzadeh, S.; Mashhadzadeh, A.H.; Rabiee, N.; Mostafavi, E.; Saeb, M.R. Theoretical Encapsulation of Fluorouracil 5-FU. Anti-Cancer Chemotherapy Drug into Carbon Nanotubes CNT. and Boron Nitride Nanotubes BNNT. Molecules 2021, 26, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyers, C. Targeted cancer therapy. Nature 2004, 432, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.W. Metal-organic framework-based cancer theranostic nanoplatforms. View 2020, 1, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, D.; Roy, S.; Sasmal, R.; Saha, N.D.; Viswanatha, R.; Agasti, S.S.; Maji, T.K. Solvent Adaptive Dynamic Metal-Organic Soft Hybrid for Imaging and Biological Delivery. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 5062–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Sung, S.Y.; Fadeev, M.; Cecconello, A.; Nechushtai, R.; Willner, I. Targeted VEGF-triggered release of an anti-cancer drug from aptamer-functionalized metal–organic framework nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4650–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhuri, A.R.; Laha, D.; Pal, S.; Karmakar, P.; Sahu, S.K. One-pot synthesis of folic acid encapsulated upconversion nanoscale metal organic frameworks for targeting, imaging and pH responsive drug release. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 18120–18132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippousi, M.; Turner, S.; Leus, K.; Siafaka, P.I.; Tseligka, E.D.; Vandichel, M.; Nanaki, S.G.; Vizirianakis, I.S.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Van Der Voort, P. Biocompatible Zr-based nanoscale MOFs coated with modified poly (ε-caprolactone) as anticancer drug carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhai, M.; Guan, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Damirin, A. Controllable synthesis of a smart multifunctional nanoscale metal–organic framework for magnetic resonance/optical imaging and targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-A.; Zhao, X.-D.; Yin, H.-P.; Chen, G.-J.; Yang, S.; Dong, Y.-B. A drug-loaded nanoscale metal–organic framework with a tumor targeting agent for highly effective hepatoma therapy. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 14113–14116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Huo, F.; Xu, H. Selenium-containing polymer@ metal-organic frameworks nanocomposites as an efficient multiresponsive drug delivery system. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chou, L.-Y.; Liu, D.-Y.; Weerapana, E.; Tsung, C.-K. Optimized metal–organic-framework nanospheres for drug delivery: Evaluation of small-molecule encapsulation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenot, C.C.; Robiette, R.L.; Collin, S. First evidence of the cysteine and glutathione conjugates of 3-sulfanylpentan-1-ol in hop Humulus lupulus L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4002–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun Kumar, S.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Bhunia, S.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Verma, K.; Khademhosseini, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Gaharwar, A.K. Two-dimensional metal organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.W. Metal–organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Small 2020, 16, 1906846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Ni, K.; Veroneau, S.S.; Luo, T.; You, E.; Lin, W. Nanoscale metal–organic framework hierarchically combines high-Z components for multifarious radio-enhancement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6859–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Lan, G.; Veroneau, S.S.; Duan, X.; Song, Y.; Lin, W. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for mitochondria-targeted radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Nanoscale polymer metal–organic framework hybrids for effective photothermal therapy of colon cancers. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, C.; Feng, L.; Fu, T.; Dong, Z.; Chao, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, M. Nanoscale metal–organic particles with rapid clearance for magnetic resonance imaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Ni, K.; Veroneau, S.S.; Feng, X.; Nash, G.T.; Luo, T.; Xu, Z.; Lin, W. Titanium-based nanoscale metal–organic framework for type I photodynamic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4204–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jiang, Q.; Feng, D.; Mao, L.; Zhou, H.-C. Size-controlled synthesis of porphyrinic metal–organic framework and functionalization for targeted photodynamic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3518–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; He, C.; Lin, W. A chlorin-based nanoscale metal–organic framework for photodynamic therapy of colon cancers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7600–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Shan, C.; Yan, H.; Wu, W.; Gao, X.; Cheng, B.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y. Functionalized Eu (III)-based nanoscale metal–organic framework to achieve near-IR-triggered and-targeted two-photon absorption photodynamic therapy. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lei, J.; Ma, F.; Ling, P.; Liu, J.; Ju, H. A porphyrin photosensitized metal–organic framework for cancer cell apoptosis and caspase responsive theranostics. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10831–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; He, C.; Lin, W. Nanoscale metal–organic framework for highly effective photodynamic therapy of resistant head and neck cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16712–16715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Kang, L.; Huang, Y.; Dong, K.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanozyme decorated metal–organic frameworks for enhanced photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C.; Tang, B. H2S-activable MOF nanoparticle photosensitizer for effective photodynamic therapy against cancer with controllable singlet-oxygen release. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13940–13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-L.; Guan, Q.; Li, Y.-A.; Zhou, Y.; Xin, Y.-B.; Dong, Y.-B. One-pot synthetic approach toward porphyrinatozinc and heavy-atom involved Zr-NMOF and its application in photodynamic therapy. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, J.-L.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, A.; Yu, Y.-H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Y.-B. Surface decorated porphyrinic nanoscale metal–organic framework for photodynamic therapy. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Chelora, J.; Xiong, Y.; Kershaw, S.V.; Li, K.F.; Lo, P.-K.; Cheah, K.W.; Rogach, A.L.; Zapien, J.A. Ruthenium (II) Complex Incorporated UiO-67 Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles for Enhanced Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5699–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, C.; Shi, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Q. In Situ One-Pot Synthesis of MOF–Polydopamine Hybrid Nanogels with Enhanced Photothermal Effect for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Sun, W.; Gao, H. Construction of an iridium (III)-complex-loaded MOF nanoplatform mediated with a dual-responsive polycationic polymer for photodynamic therapy and cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.; Garzón-Tovar, L.; Carné-Sánchez, A.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. Photothermal activation of metal–organic frameworks using a UV–vis light source. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9555–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolmark, N.; Wieand, H.S.; Hyams, D.M.; Colangelo, L.; Dimitrov, N.V.; Romond, E.H.; Wexler, M.; Prager, D.; Cruz, A.B., Jr.; Gordon, P.H. Randomized trial of postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy for carcinoma of the rectum: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol R-02. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yan, X.-P. Macrophage membrane coated persistent luminescence nanoparticle@ MOF-derived mesoporous carbon core–shell nanocomposites for autofluorescence-free imaging-guided chemotherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8071–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Long, X.-E.; Li, R.; Hu, C.-F.; Ge, X.-H. Adriamycin Loaded and Folic Acid Coated Zn-MOF for Tumor-Targeted Chemotherapy of Cervical Cancer. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2019, 9, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhou, M.; Jia, F.; Ruan, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Chai, Z. D-arginine-loaded metal-organic frameworks nanoparticles sensitize osteosarcoma to radiotherapy. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Lan, G.; Chan, C.; Duan, X.; Guo, N.; Veroneau, S.S.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Lin, W. Ultrathin metal-organic-layer mediated radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy. Matter 2019, 1, 1331–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Song, A.; Tian, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Luan, Y. Site-specific MOF-based immunotherapeutic nanoplatforms via synergistic tumor cells-targeted treatment and dendritic cells-targeted immunomodulation. Biomaterials 2020, 245, 119983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gong, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, S.; Miron, R.J.; Yuan, Q. Target Reprogramming Lysosomes of CD8+ T Cells by a Mineralized Metal–Organic Framework for Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.Y.; Zhang, M.K.; Peng, M.Y.; Gong, D.; Zhang, X.Z. Porphyrinic metal–organic frameworks coated gold nanorods as a versatile nanoplatform for combined photodynamic/photothermal/chemotherapy of tumor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; She, D.; Guo, H.; Sun, N.; Pang, Z.; Deng, C.; Yang, W. On-demand CO release for amplification of chemotherapy by MOF functionalized magnetic carbon nanoparticles with NIR irradiation. Biomaterials 2019, 195, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Liu, B.; Kuang, Y.; Gulzar, A.; He, F.; Gai, S.; Yang, P.; Lin, J. Recent advances in porphyrin-based MOFs for cancer therapy and diagnosis therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 439, 213945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, A.; Zeng, L. pH-Responsive metal–organic framework encapsulated gold nanoclusters with modulated release to enhance photodynamic therapy/chemotherapy in breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgan, R.S. The surface chemistry of metal–organic frameworks and their applications. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 9037–9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.P.; Mo, C.E.; Huang, Y.P.; Liu, Z.S. Preparation of liquid crystalline molecularly imprinted polymer coated metal organic framework for capecitabine delivery. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36, 1800355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xing, J.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, A.; Lu, G.; Wu, A. ZD2-Engineered Gold Nanostar@ Metal-Organic Framework Nanoprobes for T1-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Photothermal Therapy Specifically Toward Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1801144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, T.; Gorin, D.; Kotelevtsev, Y.; Mao, Z.; Tong, W. Construction and characterization of magnetic cascade metal-organic framework/enzyme hybrid nanoreactors with enhanced effect on killing cancer cells. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 601, 124990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadshafiee, V.; Naeimi, H.; Goliaei, B.; Bigdeli, B.; Sadighi, A.; Dehghani, S.; Lotfabadi, A.; Hosseini, M.; Nezamtaheri, M.S.; Amanlou, M. Magnetic bio-metal–organic framework nanocomposites decorated with folic acid conjugated chitosan as a promising biocompatible targeted theranostic system for cancer treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wu, Y.; Deng, C. Recognition of urinary N-linked glycopeptides in kidney cancer patients by hydrophilic carbohydrate functionalized magnetic metal organic framework combined with LC-MS/MS. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, S.M.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Abd-Elzaher, M.M.; Salem, S.R.; Moussa, H.A.; Mohamed, R.M.; Mkhalid, I.A. A novel biosensor for early diagnosis of liver cancer cases using smart nano-magnetic metal–organic framework. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehzari, H.; Amiri, M.; Safari, M. Enzyme-free sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for highly sensitive prostate specific antigen based on conjugation of quantum dots and antibody on surface of modified glassy carbon electrode with core–shell magnetic metal-organic frameworks. Talanta 2020, 210, 120641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimpour, A.; Alam, N.R.; Abdolmaleki, P.; Hajipour-Verdom, B.; Tirgar, F.; Ebrahimi, T.; Khoobi, M. Magnetic Metal–Organic Framework Based on Zinc and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid: MR Imaging and Brain Tumor Therapy. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of MOF | Imaging Method and Biomedical Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| UCNP@Fe-MIL-101-NH2 | Optical Imaging (OI)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging | [16] |
| DOX@NPMOFs | OI- Tumor imaging- Cancer diagnosis- Cancer therapy | [17] |
| DOX@Gd-MOFs-Glu | Computed tomography (CT)/MRI- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging- Targeted delivery of cancer drug | [18] |
| TPZ/Hf/TCPP/PEG | CT—Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging- Targeted delivery of cancer drug | [19] |
| Eu, Gd-NMOF@SiO2 | MRI- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging | [20] |
| Fe3O4@IFMOF-3/FA | MRI- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging | [21] |
| UiO-66@DOPA-LB | OI- Tumor imaging- Cancer diagnosis- Cancer therapy | [22] |
| Fe3O4-ZIF-8 | MRI- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging- Early detection of tumor sites | [23] |
| MOF@HA@ICG NPs | MRI- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging- Early detection of tumor sites | [24] |
| Au@MIL-88 (Fe) | CT/MRI- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging- Targeted delivery of cancer drug | [25] |
| 89Zr-UiO-66/Py-PGA-PEG-F3 | Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging- Cancer therapy- Tumor imaging- Targeted delivery of cancer drug | [26] |
| Method | NMOFs | In Vitro Cell Lines | In Vivo Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Cisplatin@NMOF-1/DOX@NMOF-1 | HeLa | - | [35] |
| DOX@NMOF-VEGF responsive | MDA-MB-231 | - | [36] | |
| ZIF-8/FA@UCNP | HeLa | - | [37] | |
| UiO-67/UiO-66 | U-87 MG/HSC-3 | - | [38] | |
| Fe-MIL-53-NH2-FA-5-FAM@5-FU | MGC-803 | - | [39] | |
| UiO-68-FA@DOX | HepG2 | Mice with HepG2 tumors | [40] | |
| Gd-MOF-Glu@DOX | HeLa | Mice with HeLa tumors | [18] | |
| IRMOF-3@Fe3O4/FA | Hea | - | [21] | |
| ZIF-8@P | MDA-MB-231 | - | [41] | |
| ZIF-8@Fe3O4 | MCF-7 | - | [42] | |
| 89Zr-UiO-66@Py-PGA-PEG@F3 | MDA-MB-231 | Mice with MDA-MB-231 tumors | [26] | |
| Fe3O4@IFMOF-3@OCMP@FA | HeLa | - | [43] | |
| DPB-UiO-based NMOFs | HeLa, MCF-7 and etc. | Mice with HeLa and MCF-7 tumors | [44,45] | |
| RT-RDT | W18@Hf12-DBB-Ir | MC38/CT26 | Mice with MC38/CT26 tumors | [46] |
| DBB-Ru-Hf | MC38/CT26 | Mice with MC38/CT26 tumors | [47] | |
| PTT | UiO-66@PAN | CT26/HCT116 | Mice with CT26 tumors | [48] |
| Mn-IR822@PEG-PDA | 4T1 | Mice with 4T1 tumors | [49] | |
| MOF@ICG@HA | MCF-7 | Mice with MCF-7 tumors | [24] | |
| PDT | Ti-TBP | CT26 | Mice with CT26 tumors | [50] |
| PCN-FA-224 | A549/HeLa | - | [51] | |
| UiO-DBC | HT29/CT26 | Mice with HT29/CT26 tumors | [52] | |
| MB@THA-MOF-76@cRGD | A549 | - | [53] | |
| MOF-FA@PS | HeLa | - | [54] | |
| UiO-DBP | SQ20B | Mice with SQ20B tumors | [55] | |
| PCN-224 (Pt) | 4T1/HeLa | Mice with H22 tumors | [56] | |
| NP-1 | HCT116/HepG2 | Mice with HCT116 tumors | [57] | |
| ZnDTPP-I2@UiO-66 | HepG2 | - | [58] | |
| TPP-SH@UiO-66 | HeLa | - | [59] | |
| Ru(bpy)32+@(UiO-67) | A549 | - | [60] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeb, M.R.; Rabiee, N.; Mozafari, M.; Verpoort, F.; Voskressensky, L.G.; Luque, R. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Cancer Therapy. Materials 2021, 14, 7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237277
Saeb MR, Rabiee N, Mozafari M, Verpoort F, Voskressensky LG, Luque R. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Cancer Therapy. Materials. 2021; 14(23):7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237277
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeb, Mohammad Reza, Navid Rabiee, Masoud Mozafari, Francis Verpoort, Leonid G. Voskressensky, and Rafael Luque. 2021. "Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Cancer Therapy" Materials 14, no. 23: 7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237277
APA StyleSaeb, M. R., Rabiee, N., Mozafari, M., Verpoort, F., Voskressensky, L. G., & Luque, R. (2021). Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Cancer Therapy. Materials, 14(23), 7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237277










