Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsions for Ophthalmic Applications: Role of Cationic Surfactants
Abstract
1. Introduction
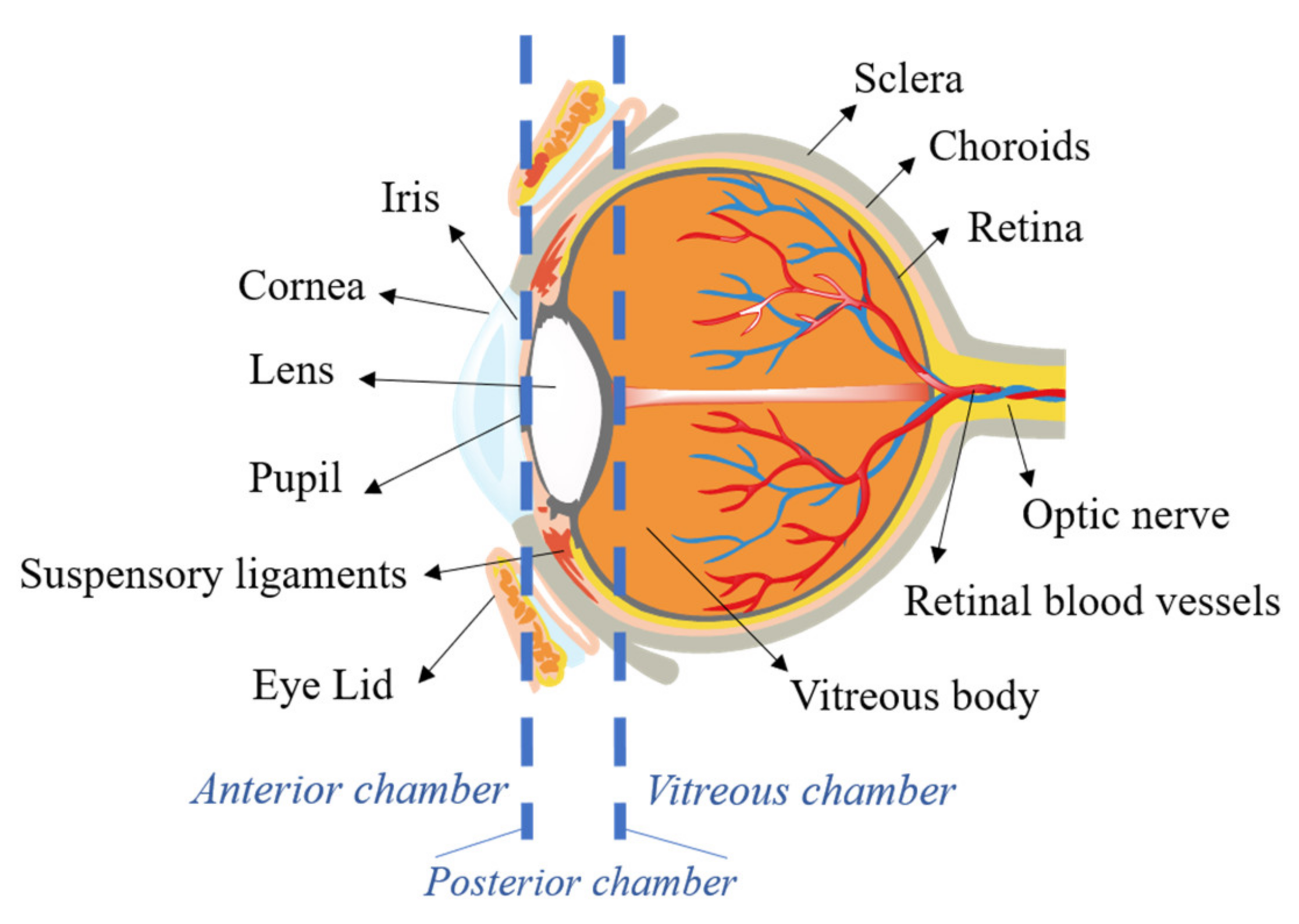
2. Ocular Barriers
3. Nanoemulsions for Ocular Delivery
3.1. Methods of Preparation of NEs
3.2. Characterization of NEs
4. Formulating Nanoemulsions for Ocular Delivery
4.1. Selection of Oil/Lipid
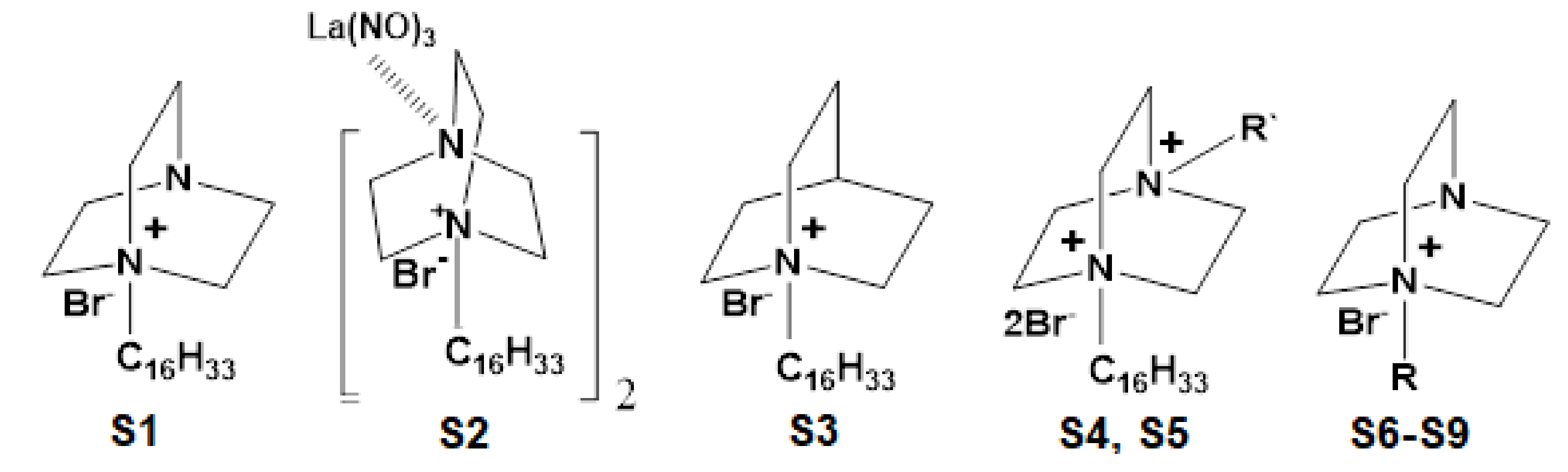
4.2. Selection of Surfactant and Cationic Agent
4.3. Selection of Co-Surfactant
4.4. Selection of Osmotic Agent
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajalakshmi, R.; Mahesh, K.; Kumar, C. A critical review on nanoemulsions. Int. J. Innov. Drug Discov. 2011, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: Terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Que, G. Influence of the HLB parameter of surfactants on the dispersion properties of brine in residue. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 320, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Gupta, A.; Myerson, A.S.; Trout, B.L.; Doyle, P.S. Low Energy Nanoemulsions as Templates for the Formulation of Hydrophobic Drugs. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1700020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Edible nanoemulsions: Fabrication, properties, and functional performance. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2297–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Eral, H.B.; Hatton, T.A.; Doyle, P.S. Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2826–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.S.; Weisspapir, M.R.; Friedman, D.I. Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Diazepam by Submicron Emulsion (SME) Creams. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgeson, M.; Moran, S.; An, H.Z.; Doyle, P.S. Mesoporous organohydrogels from thermogelling photocrosslinkable nanoemulsions. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallemand, F.; Daull, P.; Benita, S.; Buggage, R.; Garrigue, J.-S. Successfully Improving Ocular Drug Delivery Using the Cationic Nanoemulsion, Novasorb. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 604204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Misra, A.; Babbar, A.; Mishra, A.; Mishra, P.; Pathak, K. Intranasal nanoemulsion based brain targeting drug delivery system of risperidone. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 358, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Gorain, B.; Chatterjee, B.; Madheswaran, T.; Md, S.; Mak, K.K.; Tambuwala, M.; Chourasia, M.K.; Kesharwani, P. Chapter 9—Nanoemulsions as Effective Carriers for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. In Nanotechnology-Based Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Lung Cancer; Kesharwani, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 217–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseema, A.; Kovooru, L.; Behera, A.K.; Kumar, K.P.; Srivastava, P. A critical review of synthesis procedures, applications and future potential of nanoemulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 287, 102318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jin, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Nan, K.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, B. Recent Developments in Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems for Therapy of Both Anterior and Posterior Segment Diseases. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2018, 24, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.S.; Espina, M.; Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; García, M. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC): Overcoming the anatomical and physiological barriers of the eye—Part II—Ocular drug-loaded lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 110, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelMonte, D.W.; Kim, T. Anatomy and physiology of the cornea. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rózsa, A.J.; Beuerman, R.W. Density and organization of free nerve endings in the corneal epithelium of the rabbit. Pain 1982, 14, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, C.; Acosta, M.C.; Gallar, J. Neural basis of sensation in intact and injured corneas. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, B.; Bonanno, J.; Radke, C. Oxygen-deficient metabolism and corneal edema. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, L.P.; Werner, L.; Dighiero, P.; Legeais, J.-M.; Renard, G. Confocal microscopy in bowman and stromal corneal dystrophies. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, R.R. The normal surface of corneal epithelium: A scanning electron microscopic study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1973, 12, 654–668. [Google Scholar]
- Hazlett, L.; Wells, P.; Spann, B.; Berk, R. Epithelial Desquamation in the Adult-Mouse Cornea a Correlative TEM-SEM Study. Ophthalmic Res. 1980, 12, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybar, K. Wolff’s Anatomy of the Eye and Orbit. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1977, 61, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watsky, M.; Jablonski, M.M.; Edelhauser, H.F. Comparison of conjunctival and corneal surface areas in rabbit and human. Curr. Eye Res. 1988, 7, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosellini, A.; Papini, S.; Giannarini, C.; Nardi, M.; Revoltella, R.P. Human conjunctival epithelial precursor cells and their progeny in 3D organotypic culture. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; Mitra, A.K. Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Brandner, M.; Thaler-Saliba, S.; Plainer, S.; Vidic, B.; El-Shabrawi, Y.; Ardjomand, N. Retropupillary Fixation of Iris-Claw Intraocular Lens for Aphakic Eyes in Children. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Vroom, J.A.; Fishman, H.A.; Bent, S.F. Determination of human lens capsule permeability and its feasibility as a replacement for Bruch’s membrane. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asejczyk-Widlicka, M.; Pierscionek, B.K. The elasticity and rigidity of the outer coats of the eye. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, P.; Hao, J.; Li, S.K. Iontophoretic transport of charged macromolecules across human sclera. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.E. Chapter 11—Uvea. In Slatter’s Fundamentals of Veterinary Ophthalmology, 4ed.; Maggs, D.J., Miller, P.E., Ofri, R., Eds.; Saunders: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2008; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, M.; Dayhaw-Barker, P. The role of the retinal pigment epithelium: Topographical variation and ageing changes. Eye 2001, 15, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, O. The Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Visual Function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 845–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Barrios, A.; Álvarez, L.; García, M.; Artime, E.; Pereiro, R.; González-Iglesias, H. Antioxidant Defenses in the Human Eye: A Focus on Metallothioneins. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provis, J.M. Development of the Primate Retinal Vasculature. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmor, M.F. Mechanisms of retinal adhesion. Prog. Retin. Res. 1993, 12, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, D.T. Corneal angiogenic privilege: Angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in corneal avascularity, vasculogenesis, and wound healing (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis). Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2006, 104, 264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Le Bourlais, C.; Acar, L.; Zia, H.; Sado, P.A.; Needham, T.; Leverge, R. Ophthalmic drug delivery systems—Recent advances. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1998, 17, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Dilnawaz, F.; Krishnakumar, S. Nanotechnology in ocular drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukovski, B.J.; Juretić, M.; Bračko, D.; Randjelović, D.; Savic, S.; Crespo-Moral, M.; Diebold, Y.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Pepić, I.; Lovrić, J. Functional ibuprofen-loaded cationic nanoemulsion: Development and optimization for dry eye disease treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C.; Lin, X.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, L.; Chen, X.; Song, H. Cationic nanoemulsions with prolonged retention time as promising carriers for ophthalmic delivery of tacrolimus. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 144, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Nakrani, H.; Raval, M.; Sheth, N. Development of loteprednol etabonate-loaded cationic nanoemulsified in-situ ophthalmic gel for sustained delivery and enhanced ocular bioavailability. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henostroza, M.A.B.; Melo, K.J.C.; Yukuyama, M.N.; Löbenberg, R.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Cationic rifampicin nanoemulsion for the treatment of ocular tuberculosis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 597, 124755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Martens, M.; De Beer, J. Selecting optimal dosage volumes for eye irritation tests in the rabbit. J. Toxicol. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 1987, 6, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Bharadwaj, S.; Lee, K.E.; Kang, S.G. Therapeutic nanoemulsions in ophthalmic drug administration: Concept in formulations and characterization techniques for ocular drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 895–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freddo, T.F. Shifting the Paradigm of the Blood–Aqueous Barrier. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 73, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornof, M.; Toropainen, E.; Urtti, A. Cell culture models of the ocular barriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannermaa, E.; Vellonen, K.-S.; Ryhänen, T.; Kokkonen, K.; Ranta, V.-P.; Kaarniranta, K.; Urtti, A. Efflux Protein Expression in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Lines. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, E.S.; Geroski, D.H.; McCarey, B.E.; Edelhauser, H.F. Pharmacokinetics of Intraocular Drug Delivery of Oregon Green 488–Labeled Triamcinolone by Subtenon Injection Using Ocular Fluorophotometry in Rabbit Eyes. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4506–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.H.-L.; Robinson, J.R. Mechanistic and Quantitative Evaluation of Precorneal Pilocarpine Disposition in Albino Rabbits. J. Pharm. Sci. 1979, 68, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Chiang, B.; Wu, X.; Prausnitz, M.R. Ocular delivery of macromolecules. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenwald, R.D.; Huang, H.-S. Corneal Penetration Behavior of β-Blocking Agents I: Physicochemical Factors. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, M.F.; Bartels, S.P.; Freddo, T.F.; Kamm, R.D. The source of protein in the aqueous humor of the normal monkey eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 581–595. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenwald, R.D. Ocular Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. In Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 156–201. [Google Scholar]
- Duvvuri, S.; Majumdar, S.; Mitra, A.K. Drug delivery to the retina: Challenges and opportunities. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2003, 3, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, A.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Yin, T.; He, H.; Gou, J.; Kong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Penetratin-modified lutein nanoemulsion in-situ gel for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Yasueda, S.-I.; Isowaki, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kimura, M.; Inada, K.; Ohtori, A. Formulation of an ophthalmic lipid emulsion containing an anti-inflammatory steroidal drug, difluprednate. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 301, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Mizote, H.; Minamoto, A.; Suzuki, M.; Mishima, H.K.; Tanaka, H. Systemic FK506 improved tear secretion in dry eye associated with chronic graft versus host disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-Y.; Gao, Z.-G.; Park, J.-S.; Li, H.; Han, K. rhEGF/HP-β-CD complex in poloxamer gel for ophthalmic delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 233, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuangswasdi, A.; Charoensaeng, A.; Sabatini, D.A.; Scamehorn, J.F.; Acosta, E.J.; Osathaphan, K.; Khaodhiar, S. Mixtures of anionic and cationic surfactants with single and twin head groups: Adsorption and precipitation studies. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2006, 9, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.K.; Mishra, N.; Yadav, K.S.; Yadav, N.P. Nanoemulsion as pharmaceutical carrier for dermal and transdermal drug delivery: Formulation development, stability issues, basic considerations and applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cindio, B.; Grasso, G.; Cacace, D. Water-in-oil-in-water double emulsions for food applications: Yield analysis and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 1991, 4, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukovski, B.J.; Bračko, A.; Šare, M.; Pepić, I.; Lovrić, J. Evaluation of stearylamine cationic nanoemulsions for improved ocular drug delivery. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Jhang, J.-W.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wu, W.-C. Quercetin delivery to porcine cornea and sclera by solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100923–100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.K.; Fogler, H.S. Acoustic emulsification. Part 2. Breakup of the large primary oil droplets in a water medium. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 88, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; García-Celma, M.; Solans, Y. A Study of the Relation between Bicontinuous Microemulsions and Oil/Water Nano-emulsion Formation. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7196–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, S.; Tarabishi, H.; Leuenberger, H. Investigation of thermal phase inversion in emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 91, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Giri, T.K.; Tripathi, D.K.; Alexander, A. A Review on Novel Therapeutic Strategies for the Enhancement of Solubility for Hydrophobic Drugs through Lipid and Surfactant Based Self Micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery System: A Novel Approach. Am. J. Drug Discov. Dev. 2012, 2, 143–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, S.A.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Tadros, M.I.; Abd-Elsalam, W.H. Promising ion-sensitive in situ ocular nanoemulsion gels of terbinafine hydrochloride: Design, in vitro characterization and in vivo estimation of the ocular irritation and drug pharmacokinetics in the aqueous humor of rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Meena, M.; Prakash, T.; Rajeswari, T.; Goli, D.; Kumar, S. Reduction in drop size of ophthalmic topical drop preparations and the impact of treatment. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takegami, S.; Kitamura, K.; Kawada, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kitade, T.; Ishida, H.; Nagata, C. Preparation and Characterization of a New Lipid Nano-Emulsion Containing Two Cosurfactants, Sodium Palmitate for Droplet Size Reduction and Sucrose Palmitate for Stability Enhancement. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Kalyane, D.; Youngren-Ortiz, S.R.; Chougule, M.B.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 10—Importance of Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles in Pharmaceutical Product Development. In Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 369–400. [Google Scholar]
- Adkins, G.B.; Sun, E.; Coreas, R.; Zhong, W. Asymmetrical Flow Field Flow Fractionation Coupled to Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis for Rapid Online Characterization of Nanomaterials. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7071–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.D.; Shmytkova, E.A.; Khlebtsov, B. Multipolarization Dynamic Light Scattering of Nonspherical Nanoparticles in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 3070–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Guerrero, P.; Delgado, Á.V.; Donovan, K.J.; Scott, K.; Bellini, T.; Mantegazza, F.; Jiménez, M.L. Determination of the size distribution of non-spherical nanoparticles by electric birefringence-based methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biriukov, D.; Fibich, P.; Predota, M. Zeta Potential Determination from Molecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 3159–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Yokoi, N.; Nencheva, Y.; Peev, N.; Daull, P. Surface Chemistry Interactions of Cationorm with Films by Human Meibum and Tear Film Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgurević, M.H.; Juretić, M.; Hafner, A.; Lovrić, J.; Pepić, I. Tear fluid-eye drops compatibility assessment using surface tension. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 43, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobian, M.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Mansouri, Z. Development of thermosensitive in situ gel nanoemulsions for ocular delivery of acyclovir. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, U.; Xu, J. Effect of viscosity, surface tension and mucoadhesion on ocular residence time of lubricant eye drops. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4641. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H. Determination of entrapment efficiency and drug phase distribution of submicron emulsions loaded silybin. J. Microencapsul. 2008, 26, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benita, S.; Levy, M. Submicron Emulsions as Colloidal Drug Carriers for Intravenous Administration: Comprehensive Physicochemical Characterization. J. Pharm. Sci. 1993, 82, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.R.; dos Santos, T.; Granja, P.L.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Santini, A.; Garcia, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. DABCO-Customized Nanoemulsions: Characterization, Cell Viability and Genotoxicity in Retinal Pigmented Epithelium and Microglia Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watrobska-Swietlikowska, D.; Sznitowska, M. Partitioning of parabens between phases of submicron emulsions stabilized with egg lecithin. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 312, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Mohanty, B. Effect of formulation factors on in vitro transcorneal permeation of voriconazole from aqueous drops. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2013, 4, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, U.; Willcox, M.; Stapleton, F. Osmolality and tear film dynamics. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2012, 95, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, A.G. Top ten considerations in the development of parenteral emulsions. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1999, 2, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya, C.; Goud, K. Ion-activated in situ gelling ophthalmic delivery systems of azithromycin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 73, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, J.; Garcia, M.L.; Mallandrich, M.; Souto, E.B.; Calpena, A.C. Release profile and transscleral permeation of triamcinolone acetonide loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (TA-NLC): In vitro and ex vivo studies. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Nikolić, S.; Calpena, A.C.; Egea, M.A.; Souto, E.B.; García, M.L. Improved and Safe Transcorneal Delivery of Flurbiprofen by NLC and NLC-Based Hydrogels. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.; Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Egea, M.; Garcia, M.; Souto, E. Optimization and physicochemical characterization of a triamcinolone acetonide-loaded NLC for ocular antiangiogenic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 393, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draize, J.H. Methods for the study of irritation and toxicity of substances applied topically to the skin and mucous membranes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1944, 82, 377–390. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Esteruelas, G.; Ortiz, A.; Espina, M.; Prat, J.; Muñoz, M.; Cano, A.; Calpena, A.C.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Dexibuprofen Biodegradable Nanoparticles: One Step Closer towards a Better Ocular Interaction Study. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, R.V.; Morrison, P.W.J.; Steele, F.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Penetration Enhancers in Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.K.; Chhabra, G.; Pathak, K. Design and development of a novel pH triggered nanoemulsified in-situ ophthalmic gel of fluconazole: Ex-vivo transcorneal permeation, corneal toxicity and irritation testing. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobian, M.M.; Seyfoddin, A.; Aboofazeli, R.; Foroutan, S.M.; Rupenthal, I.D. Brinzolamide–loaded nanoemulsions: Ex vivo transcorneal permeation, cell viability and ocular irritation tests. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallarate, M.; Chirio, D.; Bussano, R.; Peira, E.; Battaglia, L.; Baratta, F.; Trotta, M. Development of O/W nanoemulsions for ophthalmic administration of timolol. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Carrasco, L.D.D.M. Cationic Antimicrobial Polymers and Their Assemblies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9906–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-Grade Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Fabrication, Properties, Performance, Biological Fate, and Potential Toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.M.; Assadpoor, E.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Re-coalescence of emulsion droplets during high-energy emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Maity, T.; Paliwal, A.; Wadhwa, S. Chapter 7—Technological Aspects of Nanoemulsions and Their Applications in the Food Sector. In Nanotechnology Applications in Food; Oprea, A.E., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagigit, T.; Abdulrazik, M.; Valamanesh, F.; Behar-Cohen, F.; Benita, S. Ocular antisense oligonucleotide delivery by cationic nanoemulsion for improved treatment of ocular neovascularization: An in-vivo study in rats and mice. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Santini, A.; dos Santos, T.; Garcia, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Mono- and Dicationic DABCO/Quinuclidine Composed Nanomaterials for the Loading of Steroidal Drug: 32 Factorial Design and Physicochemical Characterization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatluri, K.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Manna, M.S.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Saha, P. Separation of toxic heavy metals from its aqueous solution using environmentally benign vegetable oil as liquid membrane. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88331–88338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamante, L.M.; Lan, T. Absolute Viscosities of Vegetable Oils at Different Temperatures and Shear Rate Range of 64.5 to 4835 s−1. J. Food Process. 2014, 2014, 234583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddini, H.; Teoh, B.C.; Clements, L.D. Densities of vegetable oils and fatty acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, F.; Housaindokht, M.R.; Darroudi, M.; Bozorgmehr, M.R.; Sadeghi, A. Soybean oil-based nanoemulsion systems in absence and presence of curcumin: Molecular dynamics simulation approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, P.P.; Chaubal, M.V.; Shorr, R. Advances in lipid nanodispersions for parenteral drug delivery and targeting. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Partida, J.; Altamirano-Vallejo, J.C.; Franco, L.A.A.; Gonzalez-Cortes, J.; Mota, S.H.-D.; García-Aguirre, J.G.; Azuara-Galindo, C.D.; Castro-Castaneda, C.R.; Armendariz-Borunda, J.; Santos, A. Topical Triamcinolone Acetonide-Loaded Liposome Formulation Used as an Adjuvant to Intravitreal Ranibizumab Therapy for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahran, A.; Ismail, S.; Allam, A. Development of Triamcinolone Acetonide-Loaded Microemulsion as a Prospective Ophthalmic Delivery System for Treatment of Uveitis: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padula, C.; Telò, I.; Di Ianni, A.; Pescina, S.; Nicoli, S.; Santi, P. Microemulsion containing triamcinolone acetonide for buccal administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 115, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, N.; Mohamed, M.; Refai, H.; El Sorogy, H. Nanoemulsion as a novel ophthalmic delivery system for acetazolamide. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sc.i 2014, 6, 227–2366. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ahmad, F.; Iqbal, Z.; Khar, R.K.; Aqil, M.; Talegaonkar, S. Nanoemulsion Components Screening and Selection: A Technical Note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Vila-Jato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Comparative in vitro Evaluation of Several Colloidal Systems, Nanoparticles, Nanocapsules, and Nanoemulsions, as Ocular Drug Carriers. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, M.G.; Ahmed, A.-M.M.; Abdel-Rahman, H.H.; Moustafa, A.H. Use of Span 80 and Tween 80 for blending gasoline and alcohol in spark ignition engines. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, M.; Morrison, R.A.; Chong, S. Commonly used surfactant, Tween 80, improves absorption of P-glycoprotein substrate, digoxin, in rats. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2003, 26, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachane, P.; Jain, A.; Dhawan, V.; Joshi, G.; Date, A.; Mulherkar, R.; Nagarsenker, M. Cationic nanoemulsions as potential carriers for intracellular delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 23, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benita, S. Prevention of topical and ocular oxidative stress by positively charged submicron emulsion. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1999, 53, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Katoh-Kubo, K.; Tsuchido, T. Antibacterial activity of surfactants against Escherichia coli cells is influenced by carbon source and anaerobiosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashirova, T.; Sapunova, A.; Lukashenko, S.; Burilova, E.; Lubina, A.; Shaihutdinova, Z.; Gerasimova, T.; Kovalenko, V.; Voloshina, A.; Souto, E.; et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and biological evaluation of tetracationic gemini Dabco-surfactants for transdermal liposomal formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, L.Y.; Pashirova, T.N.; Doktorovova, S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, S.B. Cationic Surfactants: Self-Assembly, Structure-Activity Correlation and Their Biological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Anton, N.; Zuber, G.; Zhao, M.; Messaddeq, N.; Hallouard, F.; Fessi, H.; Vandamme, T.F. Iodinated α-tocopherol nano-emulsions as non-toxic contrast agents for preclinical X-ray imaging. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawin-Mikołajewicz, A.; Nartowski, K.P.; Dyba, A.J.; Gołkowska, A.M.; Malec, K.; Karolewicz, B. Ophthalmic Nanoemulsions: From Composition to Technological Processes and Quality Control. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3719–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Effect of process and formulation variables on the preparation of parenteral paclitaxel-loaded biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: A co-surfactant study. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.L.; Luo, A.Z.; Zhang, R.; Kozar, R.A.; Moore, F.A. Poloxamer 188 inhibition of ischemia/reperfusion injury: Evidence for a novel anti-adhesive mechanism. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2010, 40, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saberi, A.H.; Fang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Effect of glycerol on formation, stability, and properties of vitamin-E enriched nanoemulsions produced using spontaneous emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 411, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.F. The universality of low-energy nano-emulsification. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 377, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirhosseini, H.; Tan, C.P.; Taherian, A.R. Effect of glycerol and vegetable oil on physicochemical properties of Arabic gum-based beverage emulsion. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 228, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üstündağ Okur, N.; Çağlar, E.Ş.; Siafaka, P.I. Novel ocular drug delivery systems: An update on microemulsions. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 36, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, A.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Santos, T.d.; Garcia, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsions for Ophthalmic Applications: Role of Cationic Surfactants. Materials 2021, 14, 7541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247541
Fernandes AR, Sanchez-Lopez E, Santos Td, Garcia ML, Silva AM, Souto EB. Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsions for Ophthalmic Applications: Role of Cationic Surfactants. Materials. 2021; 14(24):7541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247541
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Ana R., Elena Sanchez-Lopez, Tiago dos Santos, Maria L. Garcia, Amelia M. Silva, and Eliana B. Souto. 2021. "Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsions for Ophthalmic Applications: Role of Cationic Surfactants" Materials 14, no. 24: 7541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247541
APA StyleFernandes, A. R., Sanchez-Lopez, E., Santos, T. d., Garcia, M. L., Silva, A. M., & Souto, E. B. (2021). Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsions for Ophthalmic Applications: Role of Cationic Surfactants. Materials, 14(24), 7541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247541







