Effect of the Particle Size and Matrix Strength on Strengthening and Damage Process of the Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
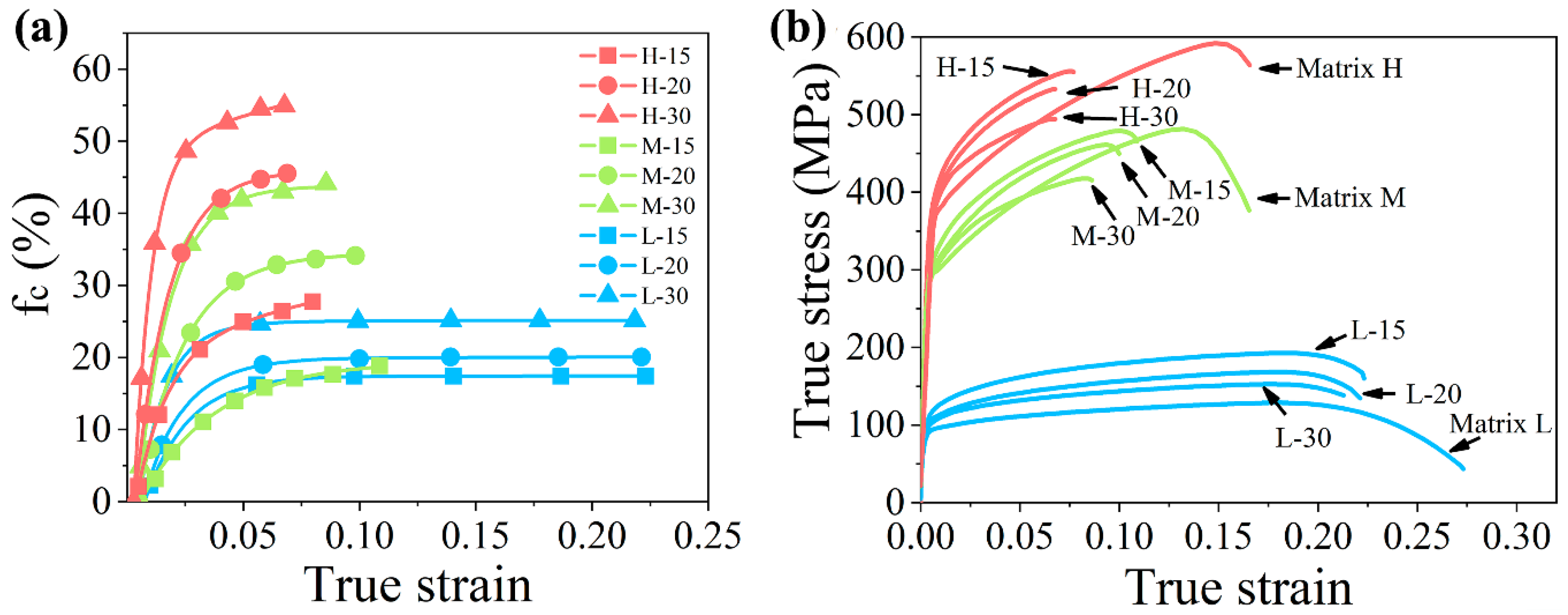
3.1. Mechanical Property
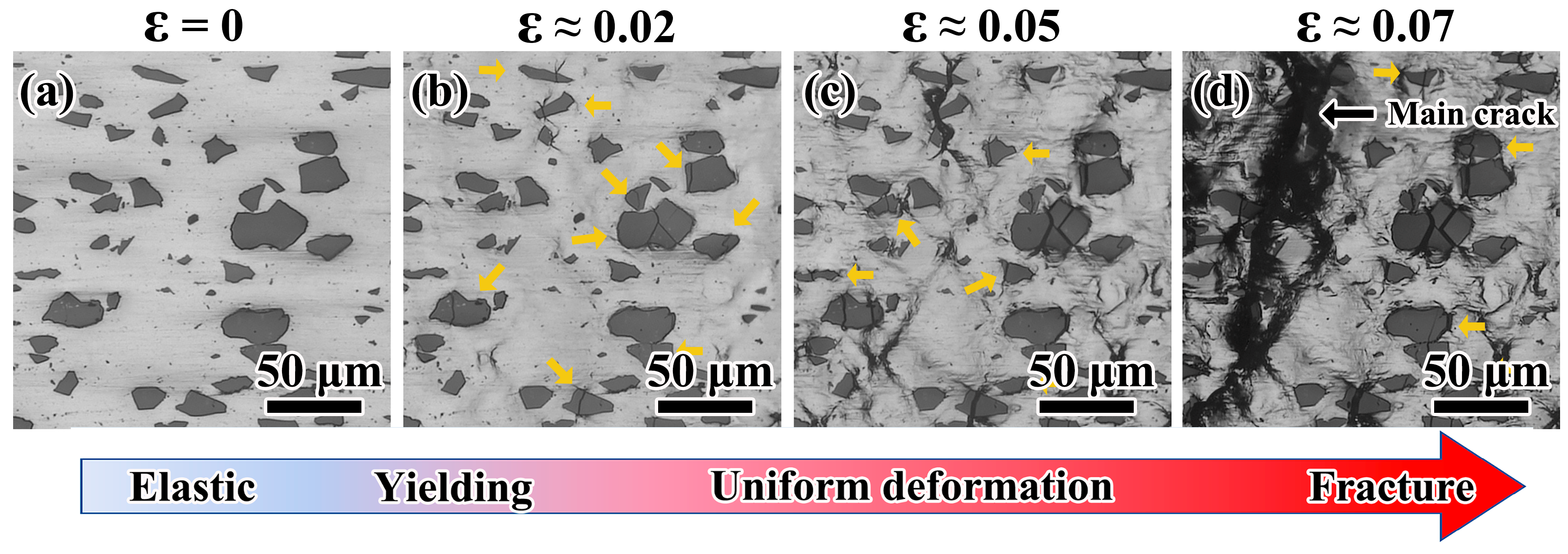
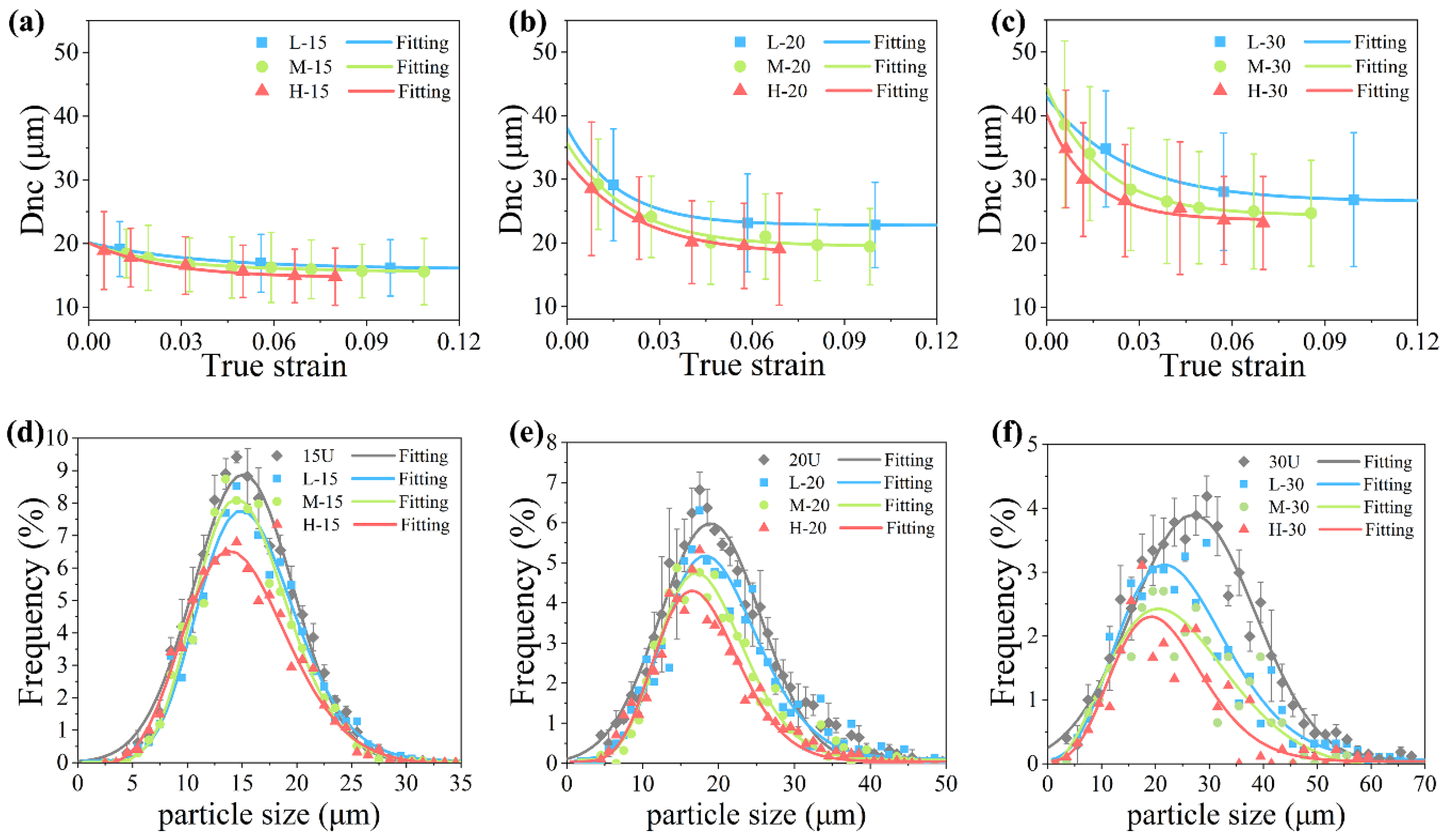
3.2. Particle Cracking
3.3. Crack Propagation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The larger size particles tend to crack earlier during deformation of the composite. Use of the particle with small average size and narrow size range can decrease the particle-induced damage and obtain a good strengthening effect on the composites.
- (2)
- Matrix strength also influences the particle cracking. With improper match of the high-strength matrix to the particle, large amount of particle cracking will occur. Too much particle-induced damage will reduce the strengthening effect of the particle and change the role of the particle from strengthening to even weakening.
- (3)
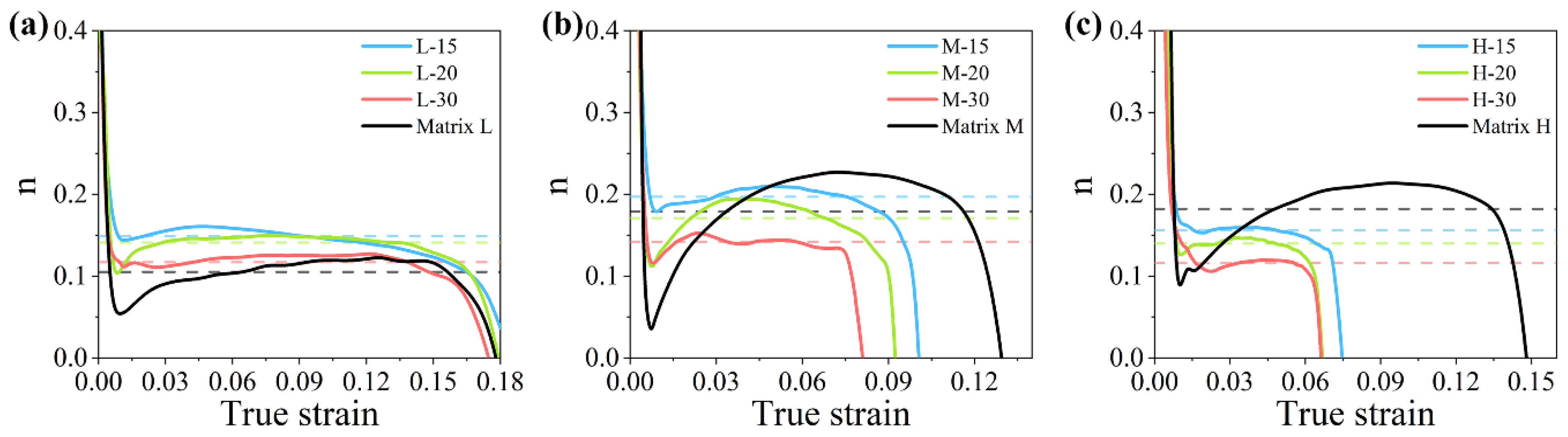
- The effective match range of the particle and the matrix is determined as the relation of the normalized strain hardening exponent n with the matrix strength and the particle size. The combination of the particle and the matrix should have an N value over 1 to obtain an effective strengthening. For the particles and the matrices used in this article, the largest particle sizes to obtain effective strengthening for matrix L, M, and H are 37 μm, 18 μm and 9 μm, respectively. The highest matrix strengths for particle size of 15, 20, and 30 μm to have an effective strengthening are 455 MPa, 399 MPa, and 259 MPa, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Metal matrix composite: A methodological review. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 6, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, T.; Soutis, C. Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.; Abu Qudeiri, J.; Abdudeen, A.; Ahammed, T.; Ziout, A. A Review on AA 6061 Metal Matrix Composites Produced by Stir Casting. Materials 2021, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, S.P. Metal-matrix composites for space applications. JOM 2001, 53, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Ezatpour, H.; Parizi, M.T. Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 aluminum alloy/Al2O3 composites fabricated by stir and compo-casting processes. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.; Hansen, N.F.; Godfrey, A.; Wu, G.; Liu, Q. High strength Al–Al2O3p composites: Optimization of extrusion parameters. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3810–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, A.E.; Corthay, S.; Firestein, K.L.; Kvashnin, D.G.; Kovalskii, A.M.; Matveev, A.T.; Sorokin, P.B.; Golberg, D.V.; Shtansky, D.V. Al-based composites reinforced with AlB2, AlN and BN phases: Experimental and theoretical studies. Mater. Des. 2018, 141, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, K.L.; Steinman, A.E.; Golovin, I.S.; Cifre, J.; Obraztsova, E.A.; Matveev, A.T.; Kovalskii, A.M.; Lebedev, O.I.; Shtansky, D.V.; Golberg, D. Fabrication, characterization, and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered Al–BN nanoparticle composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toptan, F.; Kilicarslan, A.; Karaaslan, A.; Cigdem, M.; Kerti, I. Processing and microstructural characterisation of AA 1070 and AA 6063 matrix B4Cp reinforced composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, S87–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasimman, D.; Sivasankaran, S.; Sivaprasad, K.; Narayanasamy, R.; Kambali, R. An investigation of the synthesis, consolidation and mechanical behaviour of Al 6061 nanocomposites reinforced by TiC via mechanical alloying. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wu, J. Mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Al/SiC composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 678, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.S.; Patel, D.A.D. Studies on Properties of Composite Material (Al-Sic MMC) for Valve Development of Light Vehicle Petrol Engine–A Technical Research. Global Research and Development. J. Eng. 2017, 2, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Song, M.; Wang, Z.; He, Y. Effect of Particle Size on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of SiC-Reinforced Pure Aluminum Composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tokaji, K. Effects of particle size on fatigue crack initiation and small crack growth in SiC particulate-reinforced aluminium alloy composites. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipenyuk, A.; Kuprin, V.; Milman, Y.; Goncharuk, V.; Eckert, J. Properties of P/M processed particle reinforced metal matrix composites specified by reinforcement concentration and matrix-to-reinforcement particle size ratio. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, G.; Bruno, G.; Wanner, A. Load transfer in short fibre reinforced metal matrix composites. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5389–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, R.; Shi, N. Dislocation generation due to differences between the coefficients of thermal expansion. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1986, 81, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, C.M.; Sinclair, I.; Foster, K.; Gregson, P.J. Workhardening effects in SiC particle reinforced aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1998, 14, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.; Humphreys, F. Strengthening mechanisms in particulate metal matrix composites. Scr. Met. et Mater. 1991, 25, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaati, R.; Amirkhanlou, S.; Toroghinejad, M.R.; Niroumand, B. Effect of particle size on microstructure and mechanical properties of composites produced by ARB process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, O.; Fathy, A. Effect of SiC particle size on the physical and mechanical properties of extruded Al matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.G.; Shi, N.; Gray, G.T.; Roberts, J.A. Reinforcement shape effects on the fracture behavior and ductility of particulate-reinforced 6061-Al matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1996, 27, 3739–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Flom, Z.; Amell, A.; Chawla, N.; Xiao, X.; De Carlo, F. Damage evolution in SiC particle reinforced Al alloy matrix composites by X-ray synchrotron tomography. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6194–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffière, J.Y.; Maire, E.; Cloetens, P.; Lormand, G.; Fougères, R. Characterization of internal damage in a MMCp using X-ray synchrotron phase contrast microtomography. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.M.; Lewandowski, J.J. Effects of heat treatment and reinforcement size on reinforcement fracture during tension testing of a SiCp discontinuously reinforced aluminum alloy. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Janowski, G.M.; Patterson, B.R. SiC particle cracking in powder metallurgy processed aluminum matrix composite materials. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ramesh, K.T. Influence of particle volume fraction, shape, and aspect ratio on the behavior of particle-reinforced metal–matrix composites at high rates of strain. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 5633–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazen, A.A.; Emara, M.M. Effect of Particle Cracking on the Strength and Ductility of Al-SiCp Powder Metallurgy Metal Matrix Composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2004, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Withers, P. Weibull modelling of particle cracking in metal matrix composites. Acta Met. et Mater. 1995, 43, 3685–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.-W.; Clarke, D. The influence of particle size and particle fracture on the elastic/plastic deformation of metal matrix composites. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 3801–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollomon, J.H. Tensile deformation. Trans. Metall. AIME 1945, 162, 268–290. [Google Scholar]




| Strengthening Effects on | Damage Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods in | Yield Strength | Ultimate Strength | Elongation | |
| Existing research | T (20–22), IS (28), N (30) | T (20,28), IS (28), N (27) | T (22), IS (28) | ST (23,24), IS (25,26), N (29) |
| This article | T, IS | T, IS | T, IS | IS |
| Matrix | Chemical Compositions (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Mg | Al | |
| L | – | – | 100 |
| M | 2.6 | 1.0 | Bal |
| H | 4.2 | 1.6 | Bal |
| Materials | L | L-15 | L-20 | L-30 | M | M-15 | M-20 | M-30 | H | H-15 | H-20 | H-30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n values | 0.105 | 0.149 | 0.141 | 0.117 | 0.179 | 0.197 | 0.171 | 0.142 | 0.182 | 0.156 | 0.140 | 0.116 |
| Materials | L-15 | L-20 | L-30 | M-15 | M-20 | M-30 | H-15 | H-20 | H-30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized n | 1.419 | 1.343 | 1.114 | 1.101 | 0.948 | 0.782 | 0.857 | 0.769 | 0.637 |
| a | b | c | d | e | f | R-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.94 | −3.29 × 10−2 | −5.11 × 10−4 | 2.23 × 10−4 | −1.64 × 10−6 | 1.17 × 10−5 | 0.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Nie, J.; Yang, Z.; Kang, Y. Effect of the Particle Size and Matrix Strength on Strengthening and Damage Process of the Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030675
Yang Z, Fan J, Liu Y, Nie J, Yang Z, Kang Y. Effect of the Particle Size and Matrix Strength on Strengthening and Damage Process of the Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(3):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030675
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhiyu, Jianzhong Fan, Yanqiang Liu, Junhui Nie, Ziyue Yang, and Yonglin Kang. 2021. "Effect of the Particle Size and Matrix Strength on Strengthening and Damage Process of the Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites" Materials 14, no. 3: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030675
APA StyleYang, Z., Fan, J., Liu, Y., Nie, J., Yang, Z., & Kang, Y. (2021). Effect of the Particle Size and Matrix Strength on Strengthening and Damage Process of the Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites. Materials, 14(3), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14030675






