Ag–ZnO Nanocomposites Are Used for SERS Substrates and Promote the Coupling Reaction of PATP
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of Ag–ZnO Nanocomposite
3. Results and Discussion
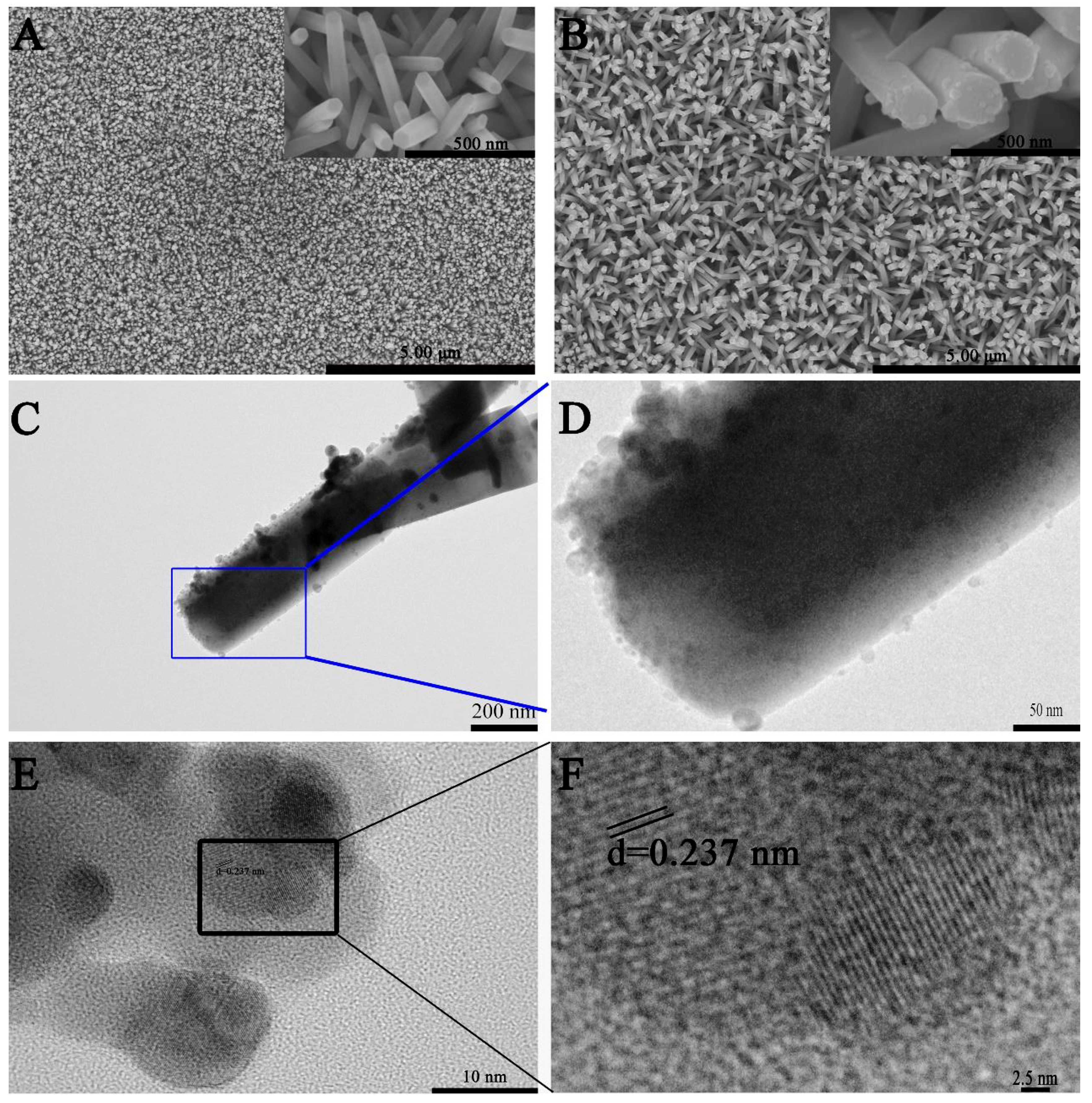
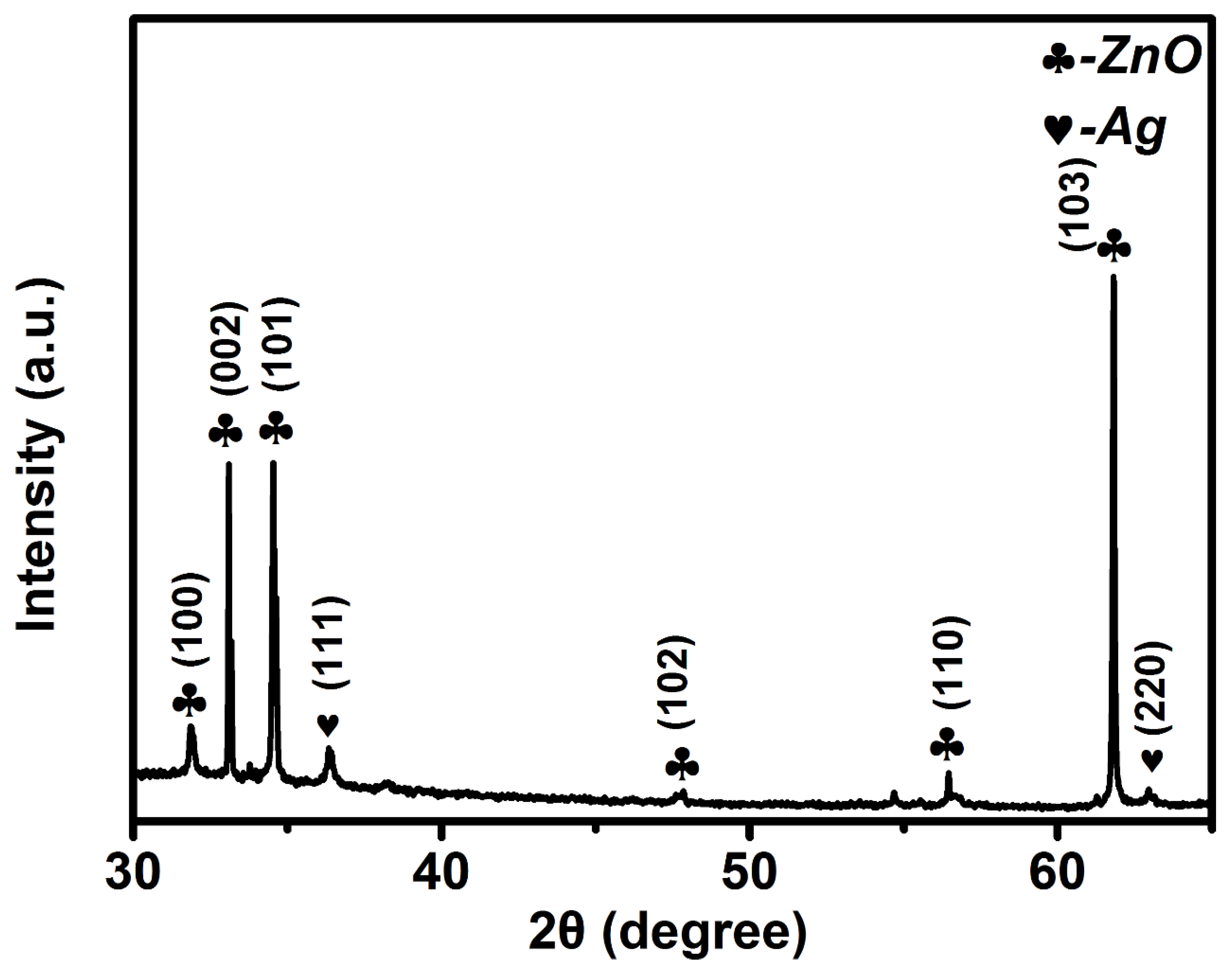
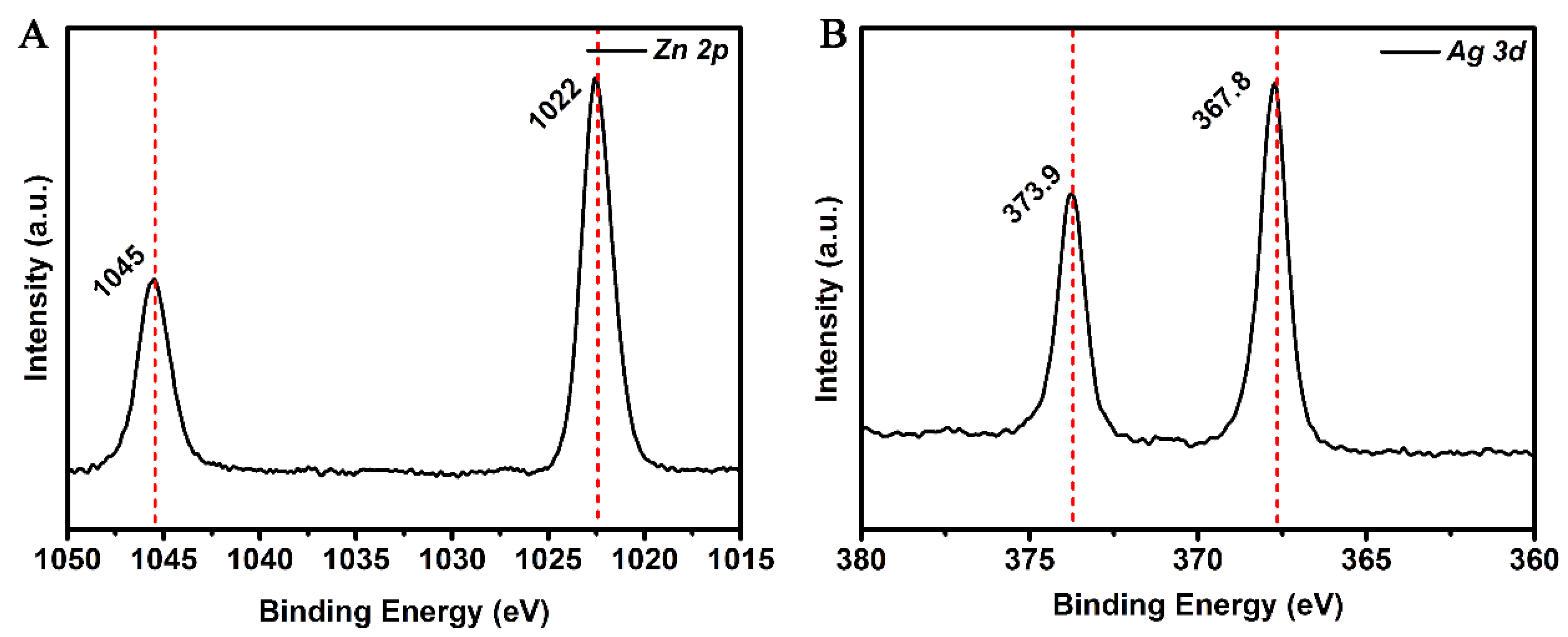
3.1. Characterization of Ag–ZnO Nanocomposite
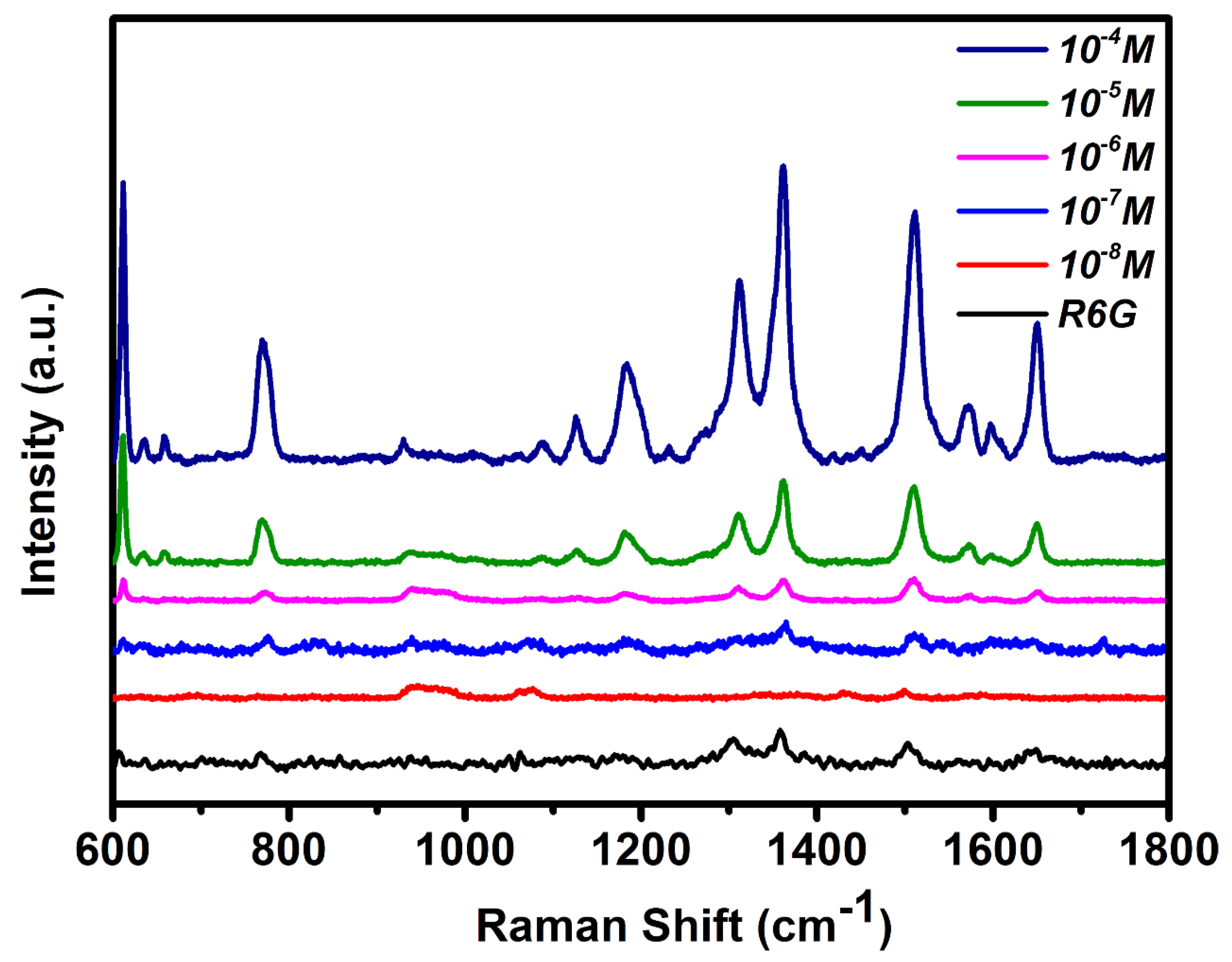
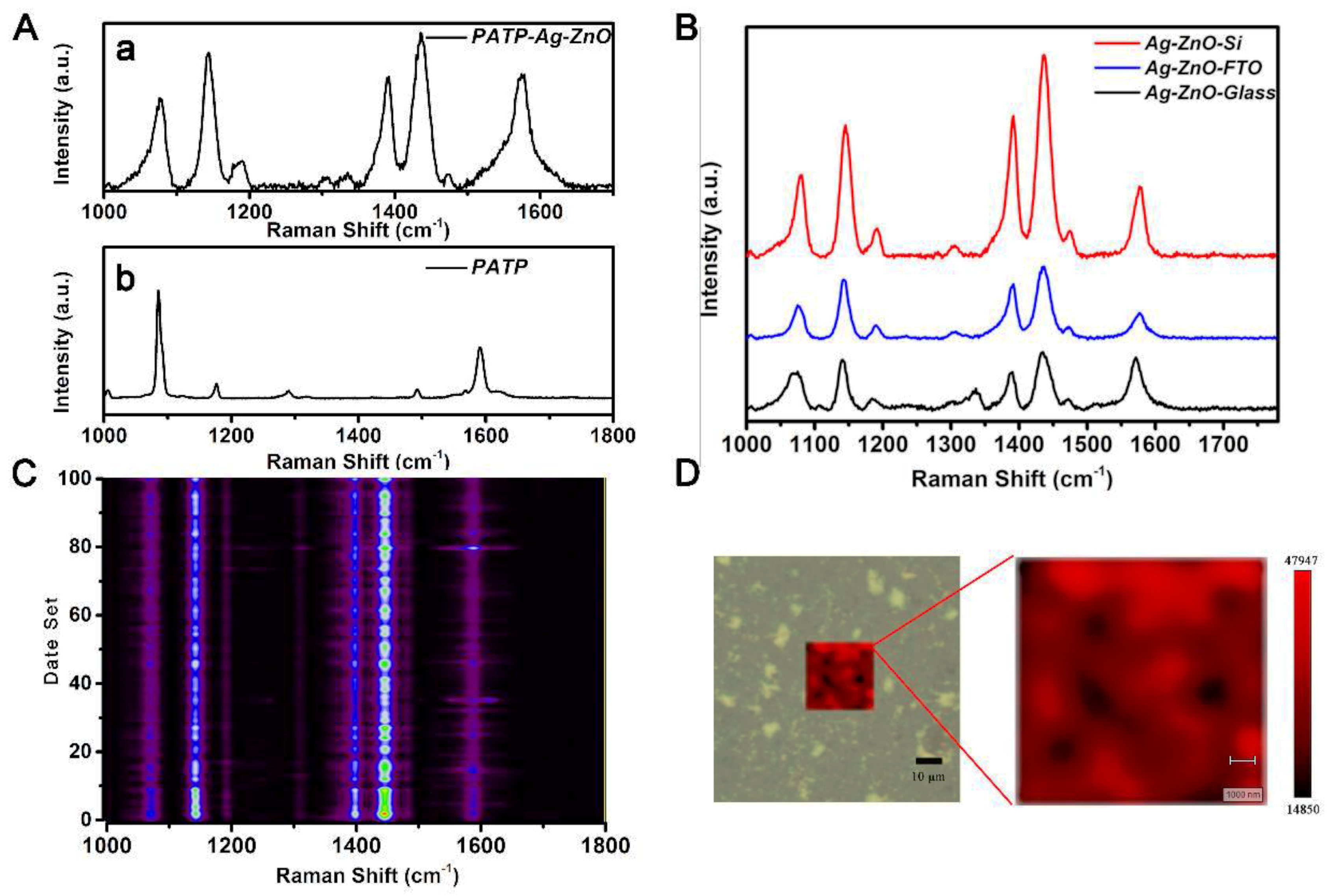
3.2. Ag–ZnO as the SERS Substrate
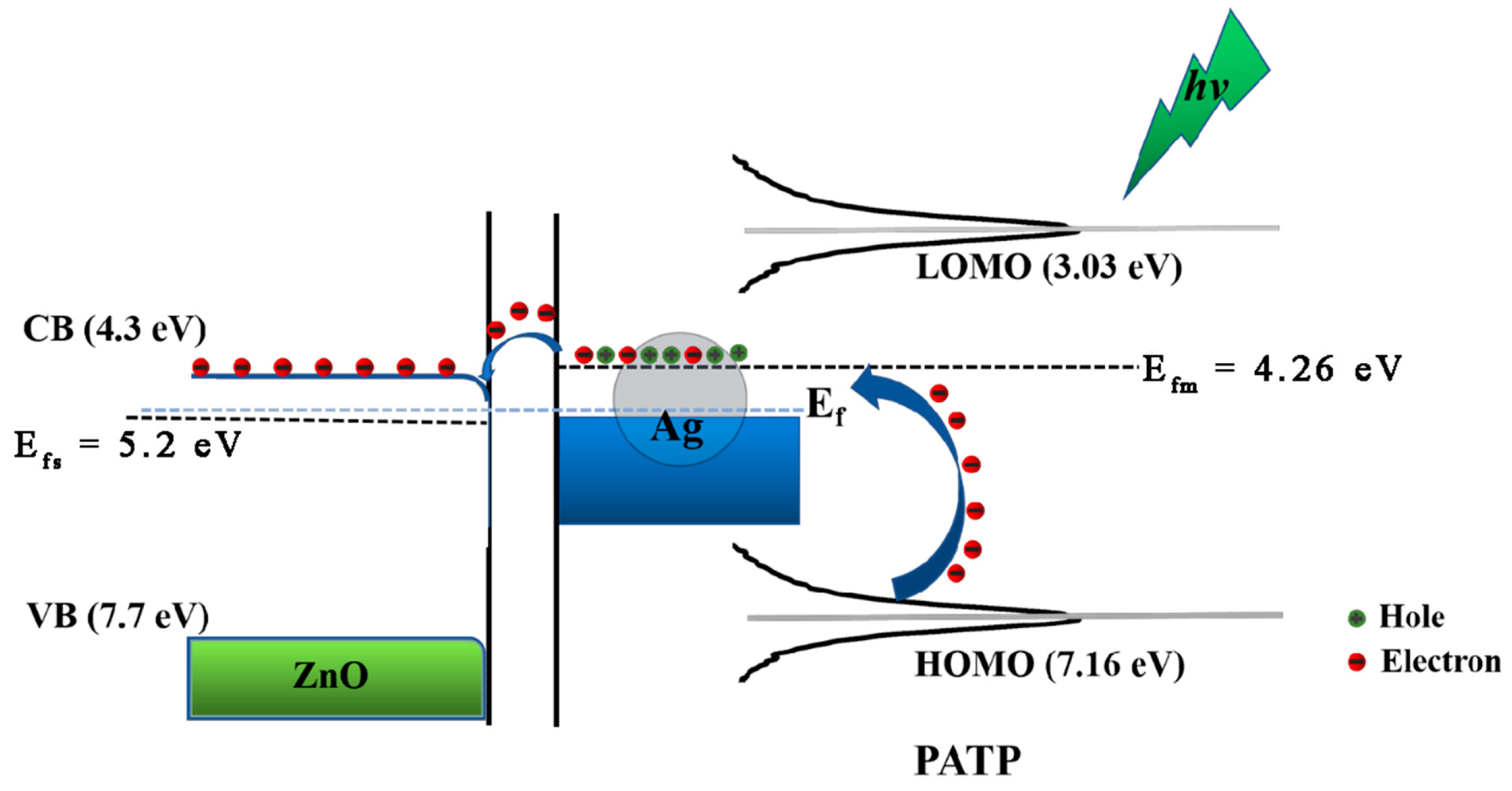
3.3. Coupling Reaction of PATP on Ag–ZnO Substrate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Creighton, J.A.; Blatchford, C.G.; Albrecht, M.G. Plasma resonance enhancement of Raman scattering by pyridine adsorbed on silver or gold sol particles of size comparable to the excitation wavelength. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. Mol. Chem. Phys. 1979, 75, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.Y.; Yi, J.; Li, J.F.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.Y.; Panneerselvam, R.; Tian, Z.Q. Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, J.; Aberasturi, D.J.D.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Present and Future of Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moskovits, M. Surface-enhanced spectroscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 783–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovits, M. Surface roughness and the enhanced intensity of Raman scattering by molecules adsorbed on metals. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 69, 4159–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, K.; Cialla, D.; Ackermann, K. SERS: A versatile tool in chemical and biochemical diagnostics. Anal. Bioanal. Chemi. 2007, 390, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, A.A.-P.; Luis, M.L.-M. SERS Detection of Small Inorganic Molecules and Ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 11214–11223. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Koo, K.M.; Trau, M.; Shen, A.G.; Hu, J.M. Watching SERS glow for multiplex biomolecular analysis in the clinic: A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman, S.L.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.I.; Dieringer, J.A.; Duyne, R.P.V. Creating, characterizing, and controlling chemistry with SERS hot spots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Q.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.Y. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: From Noble to Transition Metals and from Rough Surfaces to Ordered Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9463–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-M.; Cui, Y.; Xu, Y.-H.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.-Q. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Substrate-related issues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1729–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lombardi, J.R.; Birke, R.L. Time-dependent picture of the charge-transfer contributions to surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 175–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musumeci, A.; Gosztola, D.; Schiller, T.; Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Mujica, V.; Martin, D.; Rajh, T. SERS of Semiconducting Nanoparticles (TiO2 Hybrid Composites). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6040–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Z. Chemical contribution to surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 207401.1–207401.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Ai, K.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, X. Large-Area Silver-Coated Silicon Nanowire Arrays for Molecular Sensing Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yan, B.; She, M.W.; Li, X.; Hong, J.F. Fabrication and SERS Performance of Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Si/ZnO Nanotrees in Ordered Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1824–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.S.; Chen, K.Y.; Hong, S.J.; Chen, S.W.; Syu, W.S.; Kuo, C.W.; Syu, W.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Chiang, H.P.; Chattopadhyay, S. The preparation of silver nanoparticle decorated silica nanowires on fused quartz as reusable versatile nanostructured surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 025502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ruan, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Xu, W.; Zhao, B.; Lombardi, J.R. Direct observation of surface-enhanced Raman scattering inZnO nanocrystals. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 8, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Bing, Z.; Lombardi, J.R. ZnO nanoparticle size-dependent excitation of surface Raman signal from adsorbed molecules: Observation of a charge-transfer resonance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Ho, H.-C.; Shih, B.-W.; Tsai, F.-Y.; Hsueh, C.-H. High performance and reusable SERS substrates using Ag/ZnO heterostructure on periodic silicon nanotube substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Manohari, A.G.; Shi, Z. Template-free synthesis of porous ZnO/Ag microspheres as recyclable and ultra-sensitive SERS substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gu, L.; Xue, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X. Facile synthesis of highly uniformZnO multipods as the supports of Au and Ag nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 122, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yue, C.; Zang, Y.; Yin, J.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Kang, J. Multi-hot spot configuration on urchin-like Ag nanoparticle/ZnO hollow nanosphere arrays for highly sensitive SERS. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 15010–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Mao, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, C.; Cohick, Z.; Huang, P.-H.; Huang, T.J. In Situ Fabrication of 3D Ag@ZnO Nanostructures for Microfluidic Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Systems. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12175–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Z.; Li, Z. Silver Nanoparticles Coated Zinc Oxide Nanorods Array as Superhydrophobic Substrate for the Amplified SERS Effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9977–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zang, Y.; Yue, C.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Wu, Z. Ag nanoparticle/ZnO hollow nanosphere arrays: Large scale synthesis and surface plasmon resonance effect induced Raman scattering enhancement. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7902–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.E.; Law, M.; Tan, D.H.; Montano, M.; Goldberger, J.; Somorjai, G.; Yang, P. General route to vertical ZnO nanowire arrays using textured ZnO seeds. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.; Yang, B.; Wu, M.; Xu, J.; Fu, Z.; Guo, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, C. Synthesis of Ag/ZnO nanorods array with enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yu, X. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Zinc Oxide Hollow Spheres. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Na, G.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Gan, S. Facile synthesis of Ag/ZnO micro-flower and improved the ultraviolet and visible light photocatalytic activity. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Jia, H.; Xu, B. Synthesis of spherical Ag/ZnO heterostructural composites with excellent photocatalytic activity under visible light and UV irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.B.; Huang, Y.F.; Liu, X.M.; Jason, R.; Anema, R.B.; Tian, Z.Q. A DFT study on photoinduced surface catalytic coupling reactions on nanostructured silver: Selective formation of azobenzene derivatives from para-substituted nitrobenzene and aniline. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.D.; Xiao, X.H.; Xu, J.X.; Cai, G.X.; Ren, F.; Jiang, C.Z. Mechanism of the enhancement and quenching of ZnO photoluminescence by ZnO-Ag coupling. EuroPhys. Lett. Assoc. 2011, 93, 57009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PATP | DMAB | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Assignment | Measured Frequency (cm−1) | Assignment | Measured Frequency (cm−1) |
| N(CS) + N(CC) | 1087 | ν(CN) + δ(CH) | 1146 |
| Δ(CH) | 1179 | ν(NN) + ν(CC) + δ(CH) | 1390 |
| N(CC) + Δ(CH) | 1289 | ν(NN) + δ(CH) + ν(CC) | 1435 |
| N(CC) + Δ(CH) | 1493 | ||
| N(CC) + Δ(NH2) + Δ(CH) | 1592 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Gao, C.; Song, P.; Xia, L. Ag–ZnO Nanocomposites Are Used for SERS Substrates and Promote the Coupling Reaction of PATP. Materials 2021, 14, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040922
Ma L, Zhang Q, Li J, Lu X, Gao C, Song P, Xia L. Ag–ZnO Nanocomposites Are Used for SERS Substrates and Promote the Coupling Reaction of PATP. Materials. 2021; 14(4):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040922
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Liping, Qijia Zhang, Jia Li, Xuemei Lu, Ce Gao, Peng Song, and Lixin Xia. 2021. "Ag–ZnO Nanocomposites Are Used for SERS Substrates and Promote the Coupling Reaction of PATP" Materials 14, no. 4: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040922
APA StyleMa, L., Zhang, Q., Li, J., Lu, X., Gao, C., Song, P., & Xia, L. (2021). Ag–ZnO Nanocomposites Are Used for SERS Substrates and Promote the Coupling Reaction of PATP. Materials, 14(4), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040922






