On the Features of Composite Coating, Based on Nickel Alloy and Aluminum–Iron Bronze, Processed by Direct Metal Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laser Machine Used
2.2. Materials
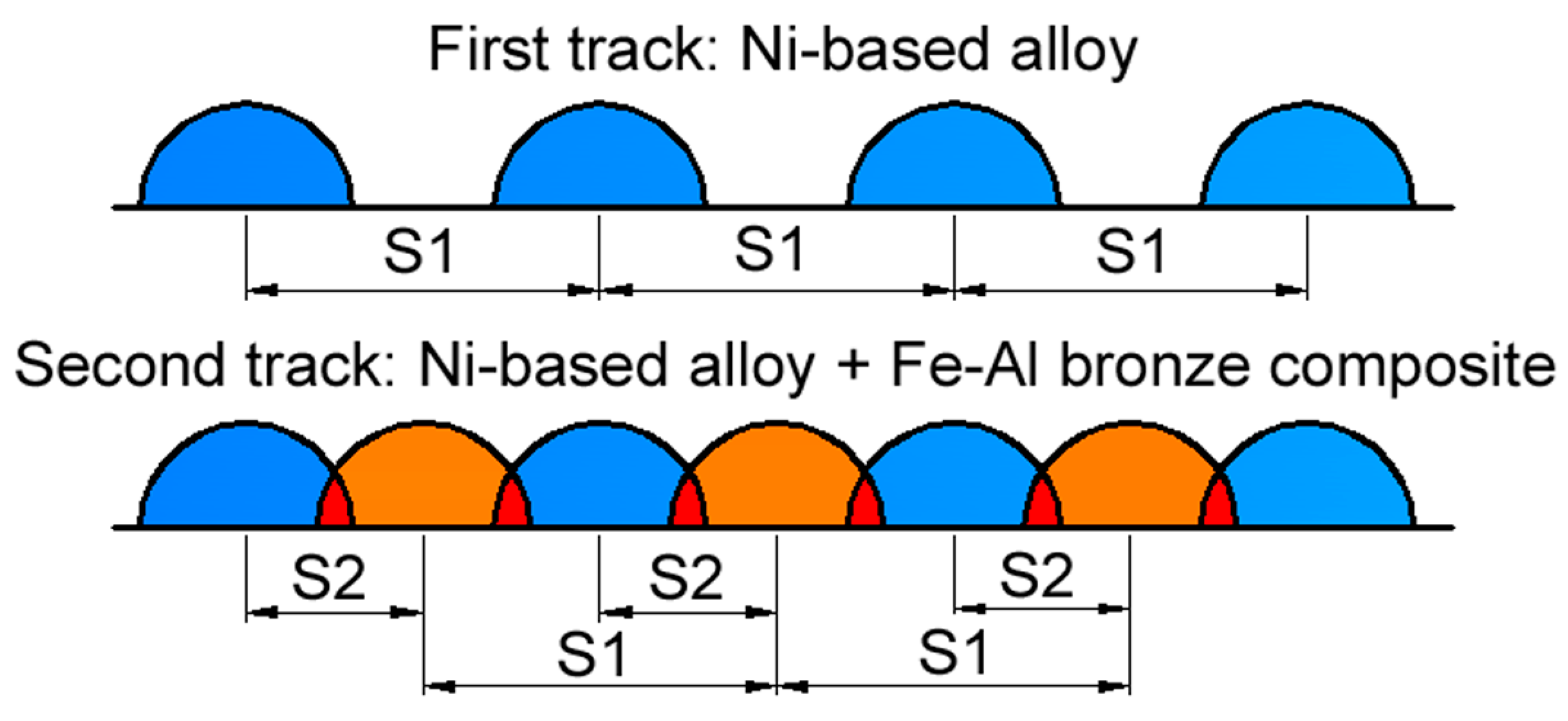
2.3. Preparation of Samples
2.4. Measuring Equipment
3. Results and Discussion
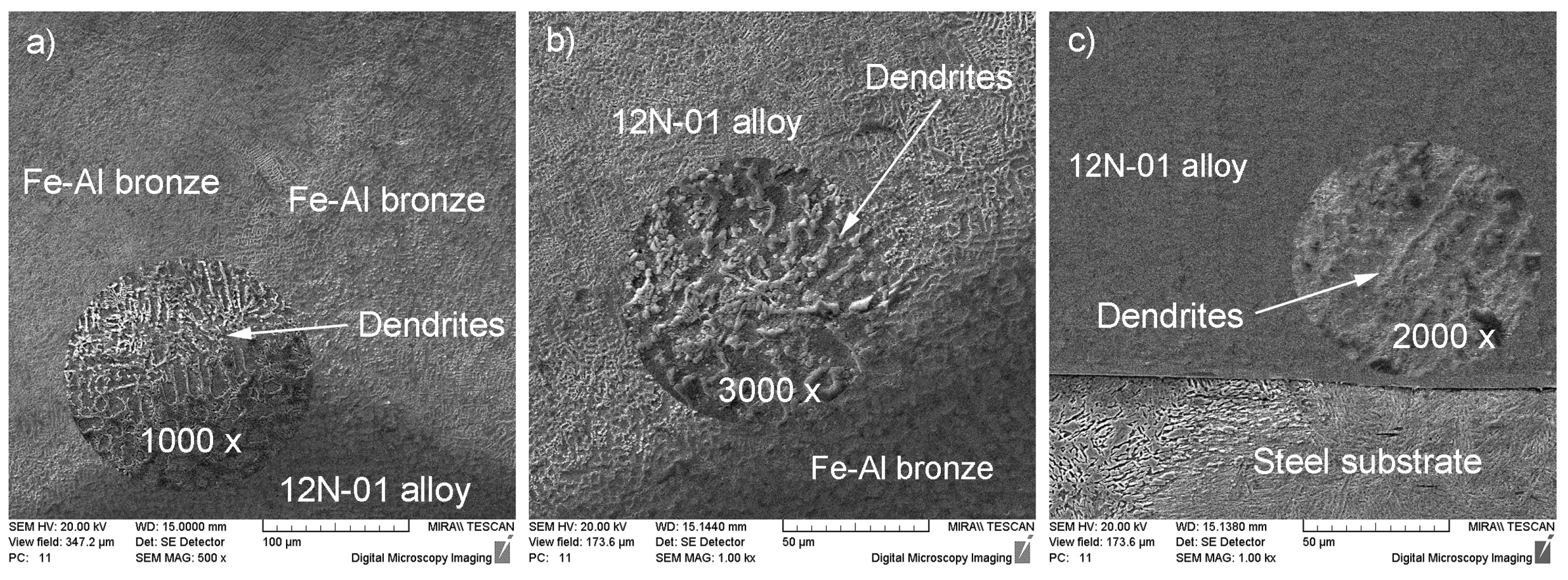
3.1. The Microstructure of Composite Coating
- Area I—the central transition zone between the Ni alloy track and the two bronze tracks;
- Area II—transition zone between the bronze and Ni alloy tracks; and
- Area III—transition zone between the Ni alloy track and the substrate.
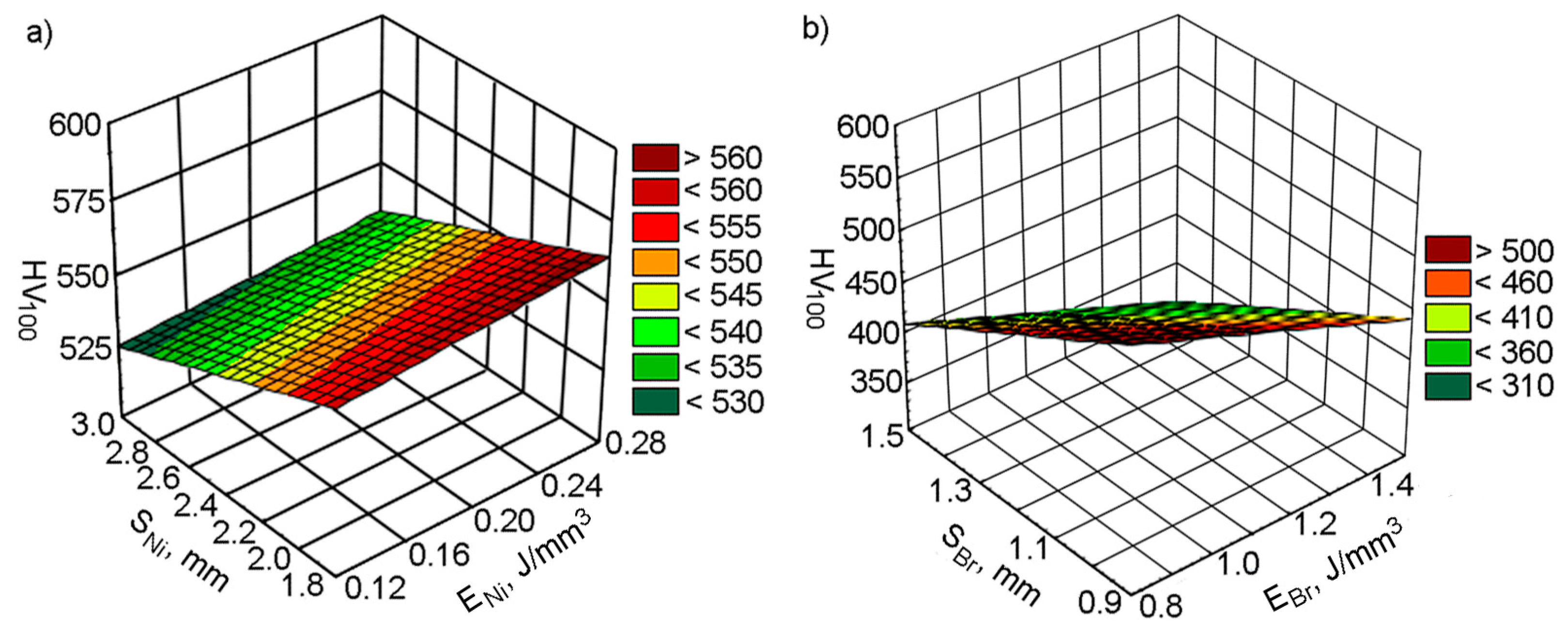
3.2. The Effect of Direct Metal Deposition (DMD) Parameters on the Micro-Hardness of the Composite Coating
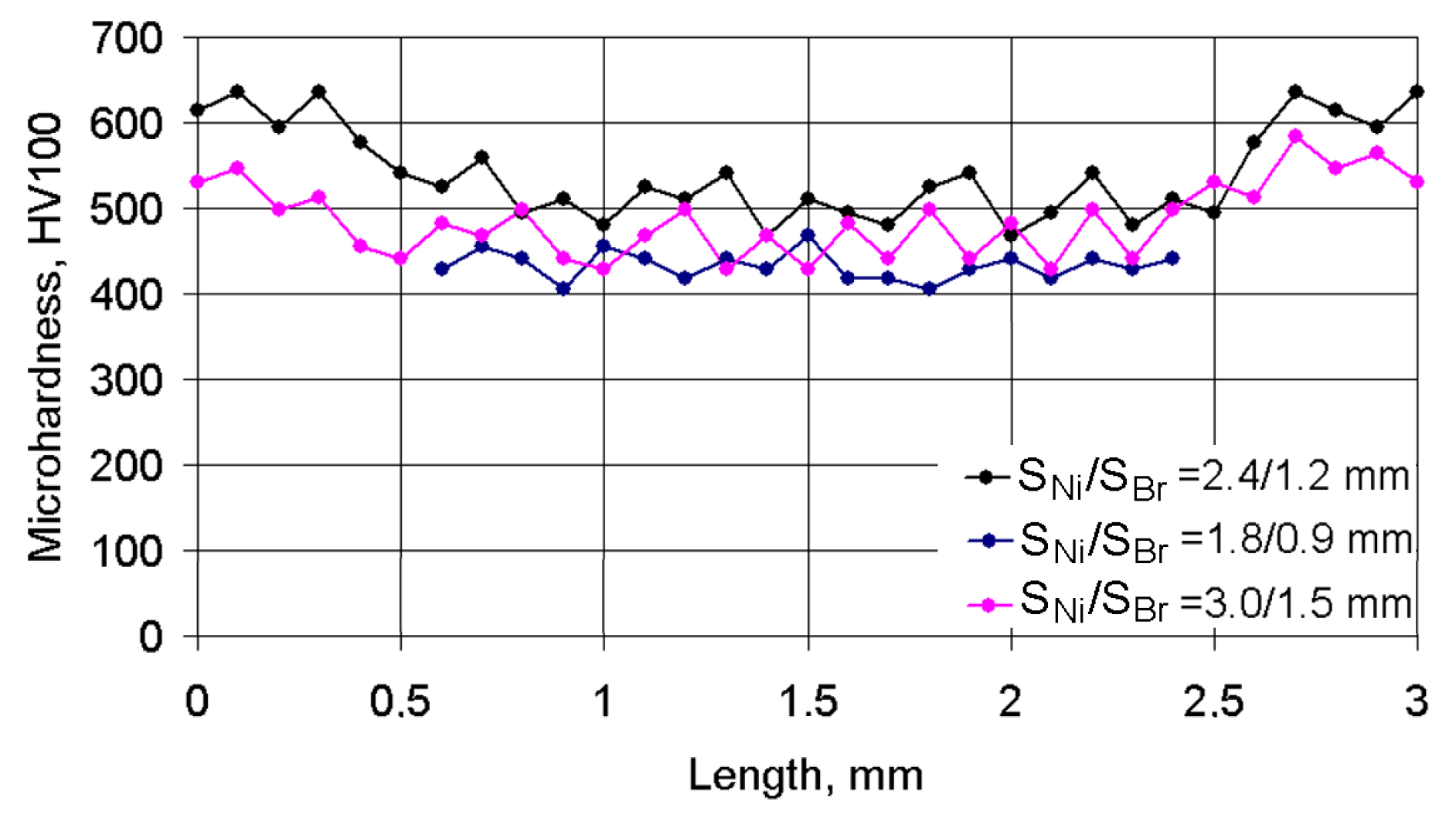
3.3. The Microhardness Characteristics of the Coating Layer
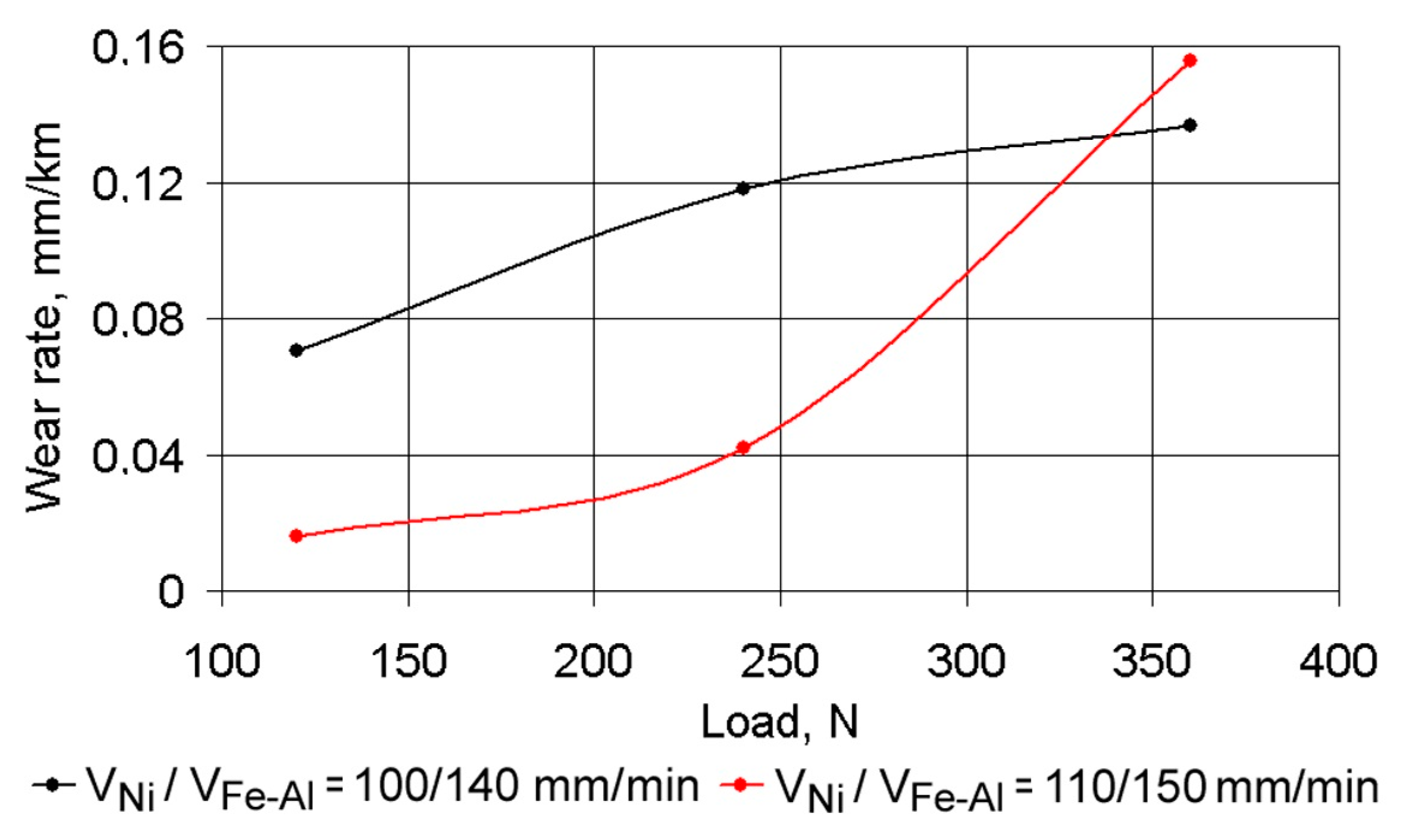
3.4. Tribological Behavior
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- The microstructure of the composite layer, deposited on the steel substrate, was very uniform. In particular, the bronze track, deposited between the tracks of Ni alloy, had a dendritic structure, which suggests a high level of crystallization. The Ni based alloy was characterized by its globular structure with the eutectic ingredient of the Ni alloy. When the depositing speed of the nickel based alloy increased, the thickness of the transition zone reduced and the dendrites passed to the quasi-eutectic state.
- Microhardness increased significantly at the interface between the substrate and the metals deposited. The transition zone extended into the substrate body and its thickness did not exceed 0.3 mm. At a distance of 0.1 mm from the substrate, the microhardness of the nickel alloy track nearly became constant throughout the whole coating thickness and was, on average, HV100 = 550. In the case of the bronze track, microhardness at the interface was close in value to the Ni alloy microhardness, but already at a distance of 0.3 mm from the interface, microhardness decreased to HV100 = 450 and remained at this level throughout the whole coating thickness.
- The microhardness of the coating layer depends on the depositing parameters. Increasing the cladding speed of Ni alloy reduced the microhardness, regardless of the cladding pitch. The microhardness of bronze in the composite coating did not depend on the cladding speed. The greatest microhardness, at all cladding speeds, was observed at the S1/S2 = 2.4/1.2 mm pitches. The changes indicated are due to changes in the volume of the molten pond and the hardening rate of the composite layer.
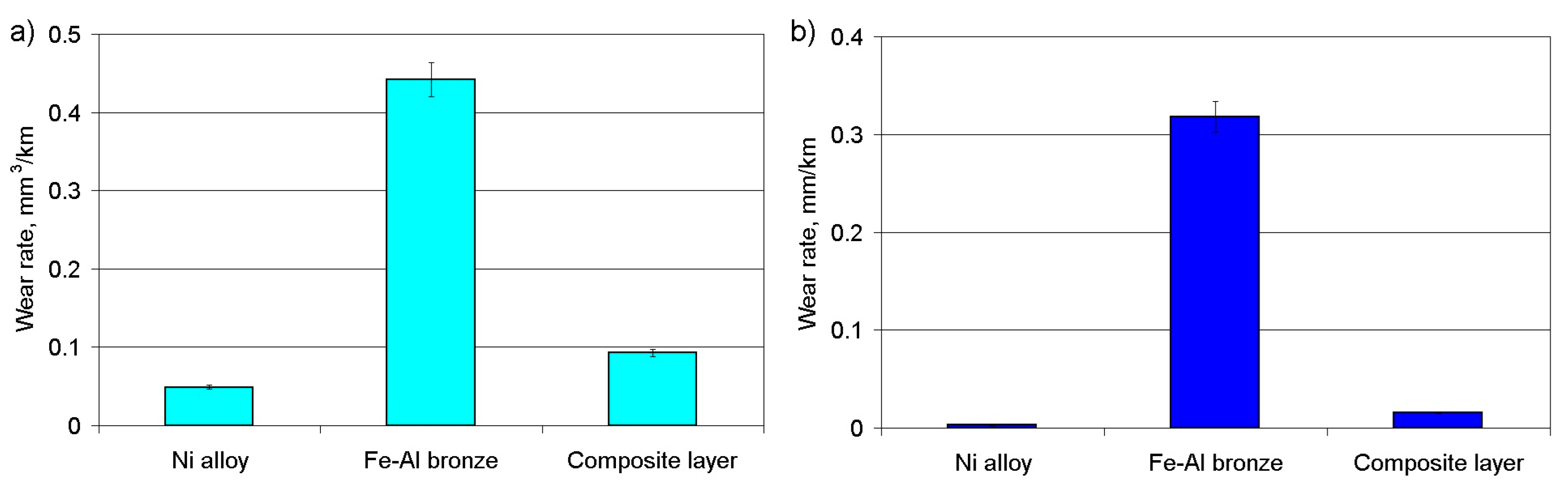
- During the running-in time of the coating layer under dry friction conditions, the CoF was less than 0.20 while in periods of stable wear, the CoF constantly increased to a level of 0.4–0.45, after which a period of accelerated wear was observed. There was an inversely proportional dependence between the values of the CoF and the wear rate under dry friction conditions. Under boundary friction conditions, where loading was increased by 120 to 240 N, the wear rate increased 2.2-fold, irrespective of the depositing conditions. At higher loads, the adhesion of coating material on the grain boundaries decreased and was destroyed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.; Chang, Y. Characteristics of laser aided direct metal/material deposition process for tool steel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Cheikh, H.; Courant, B.; Branchu, S.; Huang, X.; Hascoët, J.-Y.; Guillén, R. Direct Laser Fabrication process with coaxial powder projection of 316L steel. Geometrical characteristics and microstructure characterization of wall structures. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zeng, X. Control of shape and performance for direct laser fabrication of precision large-scale metal parts with 316L Stainless Steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 45, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, M.; Peyre, P.; Gorny, C.; Carin, M.; Morville, S.; Le Masson, P.; Carron, D.; Fabbro, R. Influence of various process conditions on surface finishes induced by the direct metal deposition laser technique on a Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Rombouts, M.; Maes, G. Cracking behavior and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel parts produced by laser metal deposition. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Whittaker, M.; Buckingham, R.; Johnston, R.; Bache, M.; Clark, D. Microstructural characterisation of a nickel alloy processed via blown powder direct laser deposition (DLD). Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F. Laser-aided Directed Metal Deposition of Ni-based superalloy powder. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 103, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govekar, E.; Jeromen, A.; Kuznetsov, A.; Kotar, M.; Kondo, M. Annular laser beam based direct metal deposition. Procedia CIRP 2018, 74, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Kovacevic, R. An investigation on mechanical and microstructural properties of 316LSi parts fabricated by a robotized laser/wire direct metal deposition system. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 23, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, M.; Wang, J. Optimization of Process Parameters, Microstructure, and Properties of Laser Cladding Fe-Based Alloy on 42CrMo Steel Roller. Materials 2018, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucato, F.; Aversa, A.; Doglione, R.; Biamino, S.; Valente, A.; Lombardi, M. Influence of Process Parameters and Deposition Strategy on Laser Metal Deposition of 316L Powder. Metals 2019, 9, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, J.C.; Schoenung, J.M.; Lavernia, E.J. Modelling particle impact on the melt pool and wettability effects in laser directed energy deposition additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 761, 138052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froend, M.; Ventzke, V.; Dorn, F.; Kashaev, N.; Klusemann, B.; Enz, J. Microstructure by design: An approach of grain refinement and isotropy improvement in multi-layer wire-based laser metal deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dong, S.; Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, D.; Lv, Y.; He, P.; Xu, B.; Han, H. The effect of different scanning strategies on microstructural evolution to 24CrNiMo alloy steel during direct laser deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 771, 138557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W. Effect of solution temperature on static recrystallization and ductility of Inconel 625 superalloy fabricated by directed energy deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kies, F.; Wilms, M.B.; Pirch, N.; Pradeep, K.G.; Schleifenbaum, J.H.; Haase, C. Defect formation and prevention in directed energy deposition of high-manganese steels and the effect on mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and fatigue behavior of a laser additive manufactured 12CrNi2 low alloy steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Inhomogeneous microstructure and its evolution of laser melting deposited 24CrNiMo steel: From single-track to bulk sample. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Xu, J.; Lu, H.; Yu, C. Effect of laser remelting processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel during laser direct metal deposition. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 284, 116738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankouhi, B.; Bertsch, K.; de Bellefon, G.M.; Thevamaran, M.; Thoma, D.; Suresh, K. Experimental validation and microstructure characterization of topology optimized, additively manufactured SS316L components. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 776, 139050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, A.; Piscopo, G.; Lai, M.; Salmi, A.; Biamino, S. An investigation on the effect of deposition pattern on the microstructure, mechanical properties and residual stress of 316L produced by Directed Energy Deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 780, 139179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendagaliyev, R.; Zadykyan, G.; Davletshin, A.; Mukashev, T.; Rashkovets, M. Direct laser deposition of cold-resistant steels for Arctic shelf development. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, D.; Liu, G.; Pu, Z.; Chang, B.; Ju, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high chromium nickel-based superalloy fabricated by laser metal deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 780, 139185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, S.; Van De Vorst, L.; Zalesak, J.; Todt, J.; Keckes, J.; Maier-Kiener, V.; Sartory, B.; Schell, N.; Hooijmans, J.; Saurwalt, J. Inconel-steel multilayers by liquid dispersed metal powder bed fusion: Microstructure, residual stress and property gradients. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Jiang, J. Control and prediction of forming quality in curved surface multi-track laser cladding with curve paths. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 3669–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.J.; Son, J.Y.; Baek, G.Y.; Shim, D.S. Excess deposition for suppressing interfacial defects induced on parts repaired using direct energy deposition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 106, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Chatterjee, D.; Samanta, S.K.; Nandi, T.; Lohar, A.K. A bottom-up approach to experimentally investigate the deposition of austenitic stainless steel in laser direct metal deposition system. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Qin, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Z. Analysis and design of coaxial nozzle with rectangular outlet for high power diode laser in laser metal deposition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 4789–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patalas-Maliszewska, J.; Feldshtein, E.; Devojno, O.; Śliwa, M.; Kardapolava, M.; Lutsko, N. Single Tracks as a Key Factor in Additive Manufacturing Technology—Analysis of Research Trends and Metal Deposition Behavior. Materials 2020, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, N.E.; O’Connor, R.; Brabazon, D. X-ray Tomography, AFM and Nanoindentation Measurements for Recyclability Analysis of 316L Powders in 3D Printing Process. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 47, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devojno, O.; Feldshtein, E.; Kardapolava, M.; Lutsko, N. On the formation features, microstructure and microhardness of single laser tracks formed by laser cladding of a NiCrBSi self-fluxing alloy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 106, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devojno, O.; Feldshtein, E.; Kardapolava, M.; Lutsko, N. On the formation features, structure, microhardness and tribological behavior of single tracks and coating layers formed by laser cladding of Al-Fe powder bronze. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Legesse, F.; Negi, S.; Karunakaran, K.P.; Bag, S. Hybrid layered manufacturing of a bimetallic injection mold of P20 tool steel and mild steel with conformal cooling channels. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Xu, G.; You, J. Eliminating the crack of laser 3D printed functionally graded material from TA15 to Inconel718 by base preheating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, K.; Babu, V.S.; Davidson, M. Interfacial microstructure and properties of Al-Cu functionally graded materials fabricated by powder metallurgy method. Mater. Today Proc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Xiaohui, Y.; Zhang, W.; Junfei, F.; Lijie, G.; Qunshuang, M.; Bing, C. Additive manufacturing of a functionally graded material from Inconel625 to Ti6Al4V by laser synchronous preheating. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 275, 116368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Tsutsumi, S.; Feng, J.; Ma, N. Impacts of laser cladding residual stress and material properties of functionally graded layers on titanium alloy sheet. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 12N-01 Alloy Composition, % | Fe–Al Bronze Composition, % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | B | Si | Cr | Fe | Ni | Al | Fe | Cu |
| 0.3–0.6 | 1.7–2.5 | 1.2–3.2 | 8–14 | 1.2–1.3 | The rest | 8.5–10.5 | 4 | The rest |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feldshtein, E.E.; Devojno, O.; Kardapolava, M.; Lutsko, N.; Patalas-Maliszewska, J. On the Features of Composite Coating, Based on Nickel Alloy and Aluminum–Iron Bronze, Processed by Direct Metal Deposition. Materials 2021, 14, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040957
Feldshtein EE, Devojno O, Kardapolava M, Lutsko N, Patalas-Maliszewska J. On the Features of Composite Coating, Based on Nickel Alloy and Aluminum–Iron Bronze, Processed by Direct Metal Deposition. Materials. 2021; 14(4):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040957
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeldshtein, Eugene E., Oleg Devojno, Marharyta Kardapolava, Nikolaj Lutsko, and Justyna Patalas-Maliszewska. 2021. "On the Features of Composite Coating, Based on Nickel Alloy and Aluminum–Iron Bronze, Processed by Direct Metal Deposition" Materials 14, no. 4: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040957
APA StyleFeldshtein, E. E., Devojno, O., Kardapolava, M., Lutsko, N., & Patalas-Maliszewska, J. (2021). On the Features of Composite Coating, Based on Nickel Alloy and Aluminum–Iron Bronze, Processed by Direct Metal Deposition. Materials, 14(4), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040957








