Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Hydroxyapatite Containing PEO Coating Produced on AZ31 Mg Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microstructural Characterization
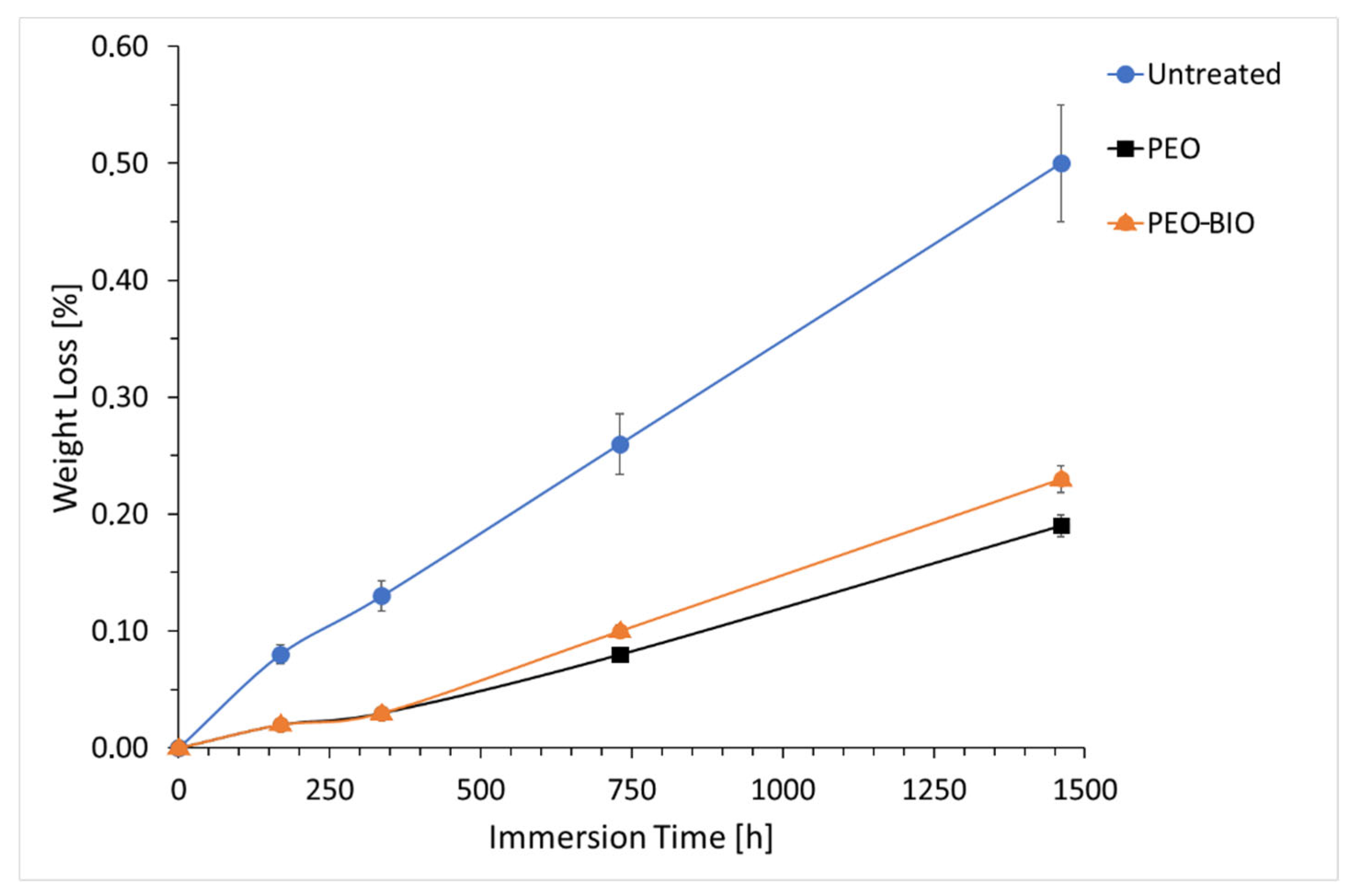
2.2. Corrosion Tests
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure and Composition
3.2. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Ren, Z.; Xu, Y.; Pang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y. Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys Developed as Bone Repair Materials: A Review. Scanning 2018, 2018, 9216314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Curtin, J.; Duffy, B.; Jaiswal, S. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopedic applications: A review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witte, F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, H.S.; Wong, J.; Manuel, M.V. Investigation of the mechanical and degradation properties of Mg-Sr and Mg-Zn-Sr alloys for use as potential biodegradable implant materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Shadanbaz, S.; Woodfield, T.B.; Staiger, M.P.; Dias, G.J. Magnesium biomaterials for orthopedic application: A review from a biological perspective. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1316–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sankar, J. Recent advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4561–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Gill, R.S.; Batra, U. Challenges and opportunities for biodegradable magnesium alloy implants. Mater. Technol. 2017, 33, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordike, L.; Ebert, T. Magnesium: Properties—Applications—Potential. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.K.; Ehrensberger, M.T. Bio-Corrosion of Magnesium Alloys for Orthopaedic Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Wen, C.; Hodgson, P.; Li, Y. Effect of alloying elements on the corrosion behavior and biocompatibility of biodegradable magnesium alloys: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 1912–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, M.; Skaret, P.C.; Fabrizi, A.; Varone, A.; Montanari, R.; Roven, H.J.; Ferro, P.; Berto, F.; Torgersen, J. The effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing on the stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of AZ31 alloy in simulated body fluid. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 106, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeneva, M.A.; Tyurin, A.I.; Mukhametkaliyev, T.M.; Pirozhkova, T.S.; Shuvarin, I.A.; Syrtanov, M.S.; Surmenev, R.A. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy via nanostructured hydroxyapatite thin films fabricated via radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 46, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimann, R.B. Magnesium alloys for biomedical application: Advanced corrosion control through surface coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Ghali, E.; Song, G. Anodizing treatments for magnesium alloys and their effect on corrosion resistance in various environments. Adv. Eng. Mat. 2006, 8, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Coelho, L.B.; Bertolini, R.; Settimi, A.G.; Brunelli, K.; Olivier, M.; Dabalà, M. Corrosion and mechanical properties of plasma electrolytic oxidation-coated AZ80 magnesium alloy. Mater. Corros. 2019, 70, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Cerchier, P.; Brunelli, K.; Bartolozzi, A.; Bertani, R.; Dabalà, M. Plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings with fungicidal properties. Surf. Eng. 2019, 35, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchier, P.; Pezzato, L.; Moschin, E.; Coelho, L.B.; Olivier, M.M.; Moro, I.; Magrini, M. Antifouling properties of different Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation coatings on 7075 aluminium alloy. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 33, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, T.W.; Troughton, S.C. A review of recent work on discharge characteristics during plasma electrolytic oxidation of various metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 127–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohedano, M.; Luthringer, B.J.C.; Mingo, B.; Feyerabend, F.; Arrabal, R.; Sanchez-Egido, P.J.; Blawert, C.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Matykina, E. Bioactive plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on Mg-Ca alloy to control degradation behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 315, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazzo, S.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; Campos, D.D.; Ogeda, T.L.; Ferreira, C.V.; Bertran, C.A. Hydroxyapatite surface solubility and effect on cell adhesion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2010, 78, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, J.A.; Clyne, T.W. Porosity in plasma electrolytic oxide coatings. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.J.; Markaki, A.E.; Collier, C.A.; Clyne, T.W. Cell adhesion to plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) titania coatings, assessed using a centrifuging technique. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matykina, E.; Garcia, I.; Arrabal, R.; Mohedano, M.; Mingo, B.; Sancho, J.; Merino, M.C.; Pardo, A. Role of PEO coatings in long-term biodegradation of a Mg alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darband, G.B.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Hamghalam, P.; Valizade, N. Plasma electrolytic oxidation of magnesium and its alloys: Mechanism, properties and applications. J. Magnes. Alloys 2017, 5, 74–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blawert, C.; Bala Srinivasian, P. Plasma electrolytic oxidation treatment of magnesium alloys. In Surface Engineering of Light Alloys; Dong, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2010; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, P.B.; Liang, J.; Blawert, C.; Störmer, M.; Dietzel, W. Characterization of calcium containing plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on AM50 magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4017–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohedano, M.; Guzman, R.; Arrabal, R.; Lacomba, J.L.L.; Matykina, E. Bioactive plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings—the role of the composition, microstructure, and electrochemical stability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Coquillat, A.; Tenorio, R.G.; Mohedano, M.; Martinez-Campos, E.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. Tailoring of antibacterial and osteogenic properties of Ti6Al4V by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 454, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, R.B.; Lehmann, H.D. Recent Research and Patents on Controlling Corrosion of Bioresorbable Mg Alloy Implants: Towards Next Generation Biomaterials. Recent Pat. Mater. Sci. 2017, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnedenkov, S.V.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Khrisanfova, O.A.; Legostaeva, E.V.; Zavidnaya, A.G.; Puz’, A.V.; Khlusov, I.A.; Opra, D.P. Functional coatings formed on the titanium and magnesium alloys as implant materials by plasma electrolytic oxidation technology: Fundamental principles and synthesis conditions. Corros. Rev. 2016, 34, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombik, E.; Bombik, A.; Rymuza, K. The influence of environmental pollution with fluorine compounds on the level of fluoride in soil, feed and eggs of laying hens in Central Pomerania, Poland. Env. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnedenkov, S.; Sinebryukhov, S.; Zavidnaya, A.; Egorkin, V.; Mashtalyar, D.; Sergienko, V.; Yerokhin, A.; Matthews, A. Composite hydroxyapatite-PTFE coatings on Mg–Mn–Ce alloy for resorbable implant applications via a plasma electrolytic oxidation-based route. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 3104–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarek, E.; Janusz, W.; Sternik, D. The influence of the hydroxyapatite synthesis method on the electrochemical, surface and adsorption properties of hydroxyapatite. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monetta, T.; Acquesta, A.; Carangelo, A.; Donato, N.; Bellucci, F. Durability of AZ31 magnesium biodegradable alloys polydopamine aided: Part 1. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2017, 5, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Babbolin, R.; Cerchier, P.; Marigo, M.; Dolcet, P.; Dabalà, M.; Brunelli, K. Sealing of PEO coated AZ91magnesium alloy using solutions containing neodymium. Corr. Sci. 2020, 173, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D.; Chastain, J. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscop; Perkin Elemer Corp: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database 20, Version 3.0; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, ML, USA, 2000.
- Bertolini, R.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A.; Pezzato, L.; Dabalà, M. The Effect of Cooling Strategies and Machining Feed Rate on the Corrosion Behavior and Wettability of AZ31 Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Procedia CIRP 2017, 65, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, D.; Lamaka, S.V.; Lu, X.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Selecting medium for corrosion testing of bioabsorbable magnesium and other metals–A critical review. Corros. Sci. 2020, 171, 108722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xia, L.; Li, W.; Han, J. Effect of Ca/P Ratio on Bioactivity of PEO Coatings. J. Adv. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdu, S.; Deniz, Ö.F.; Kutbay, I.; Usta, M. Characterization and formation of hydroxyapatite on Ti6Al4V coated by plasma electrolytic oxidation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 551, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Brunelli, K.; Babbolin, R.; Dolcet, P.; Dabalà, M. Sealing of PEO Coated AZ91 Magnesium Alloy Using La-Based Solutions. Int. J. Corros. 2017, 2017, 5305218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Coquillat, A.; Martínez-Campos, E.; Mohedano, M.; Martínez-Corriá, R.; Ramos, V.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of PEO-modified titanium for bone implant applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 347, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Rigon, M.; Martucci, A.; Brunelli, K.; Dabalà, M. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) as pre-treatment for sol-gel coating on aluminum and magnesium alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 366, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H. Updates on the research and development of absorbable metals for biomedical applications. Prog. Biomater. 2018, 7, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

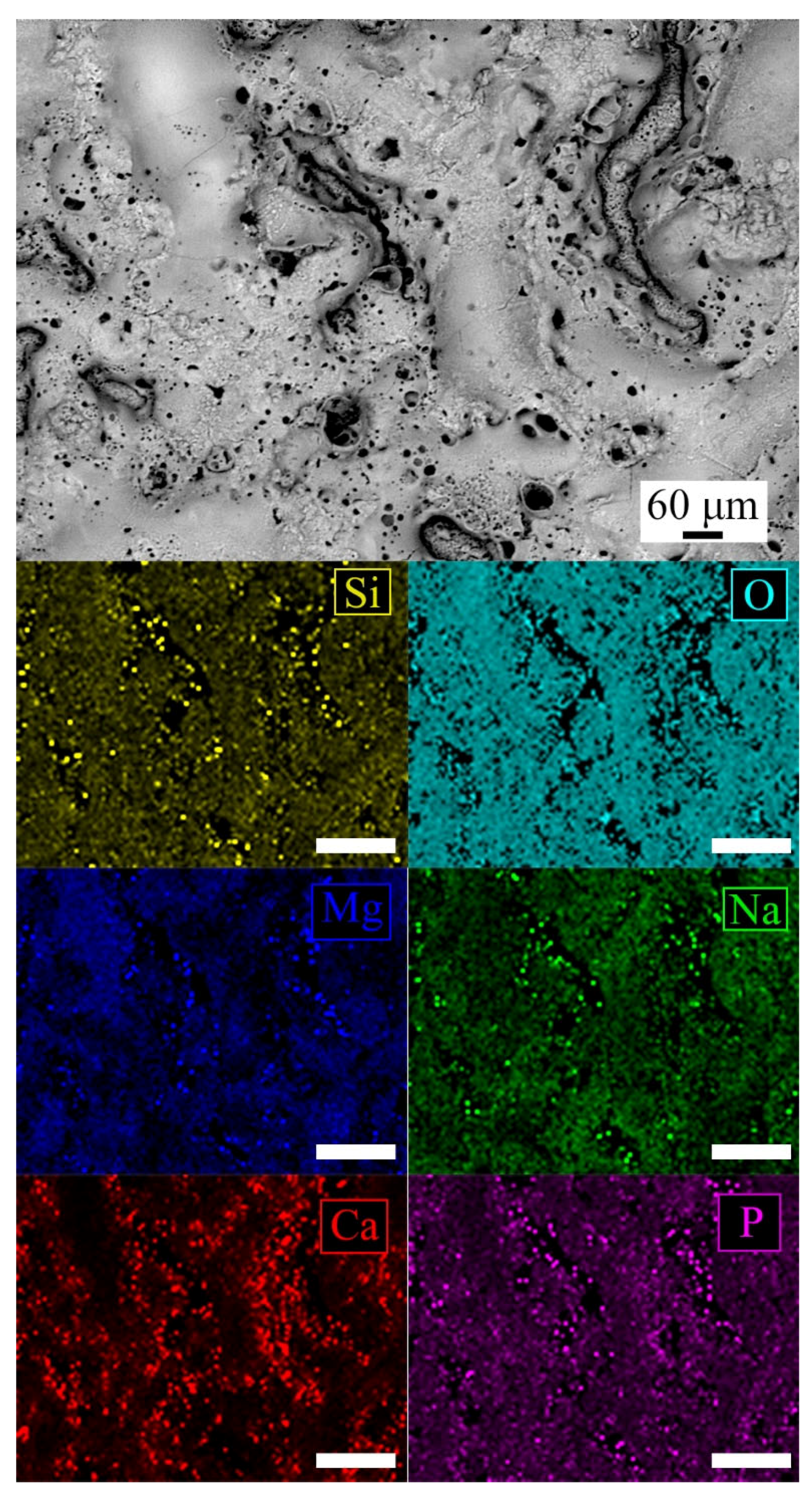
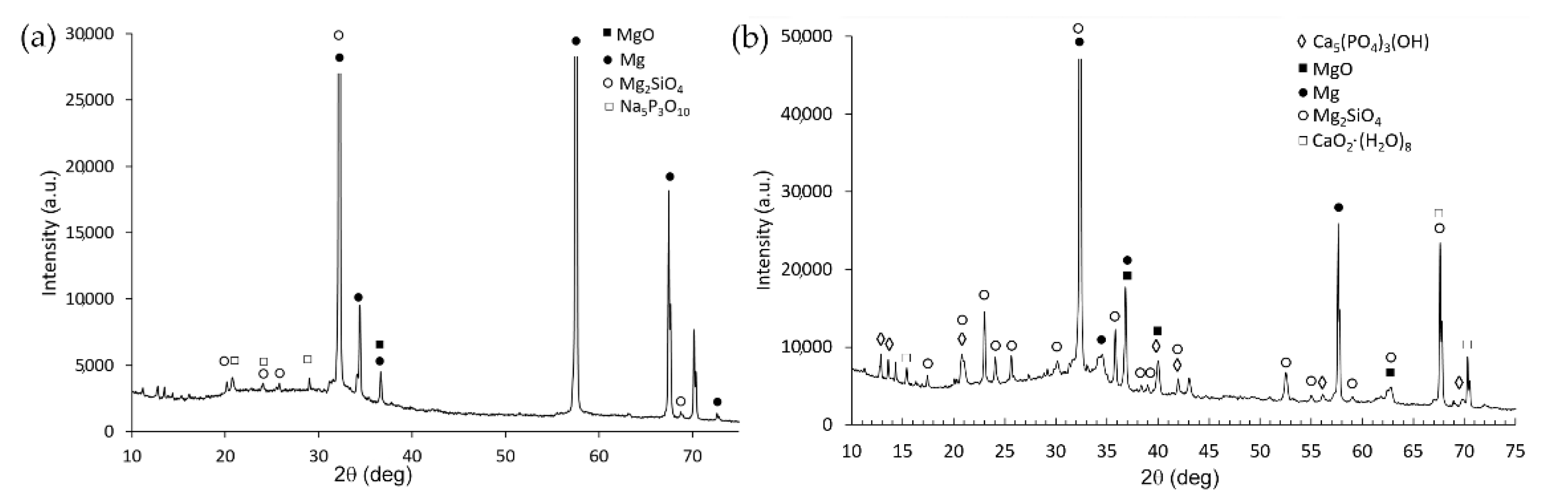
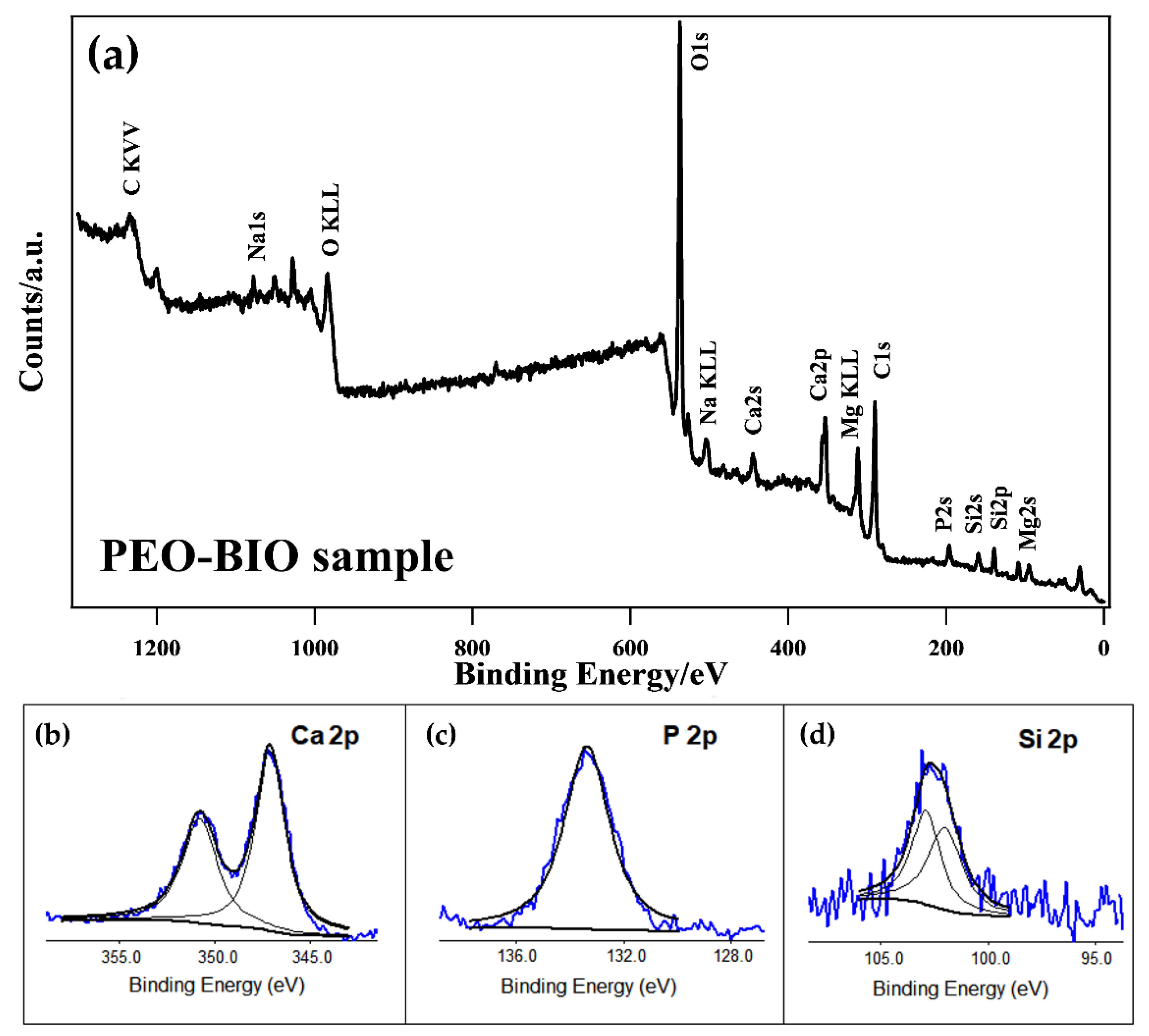
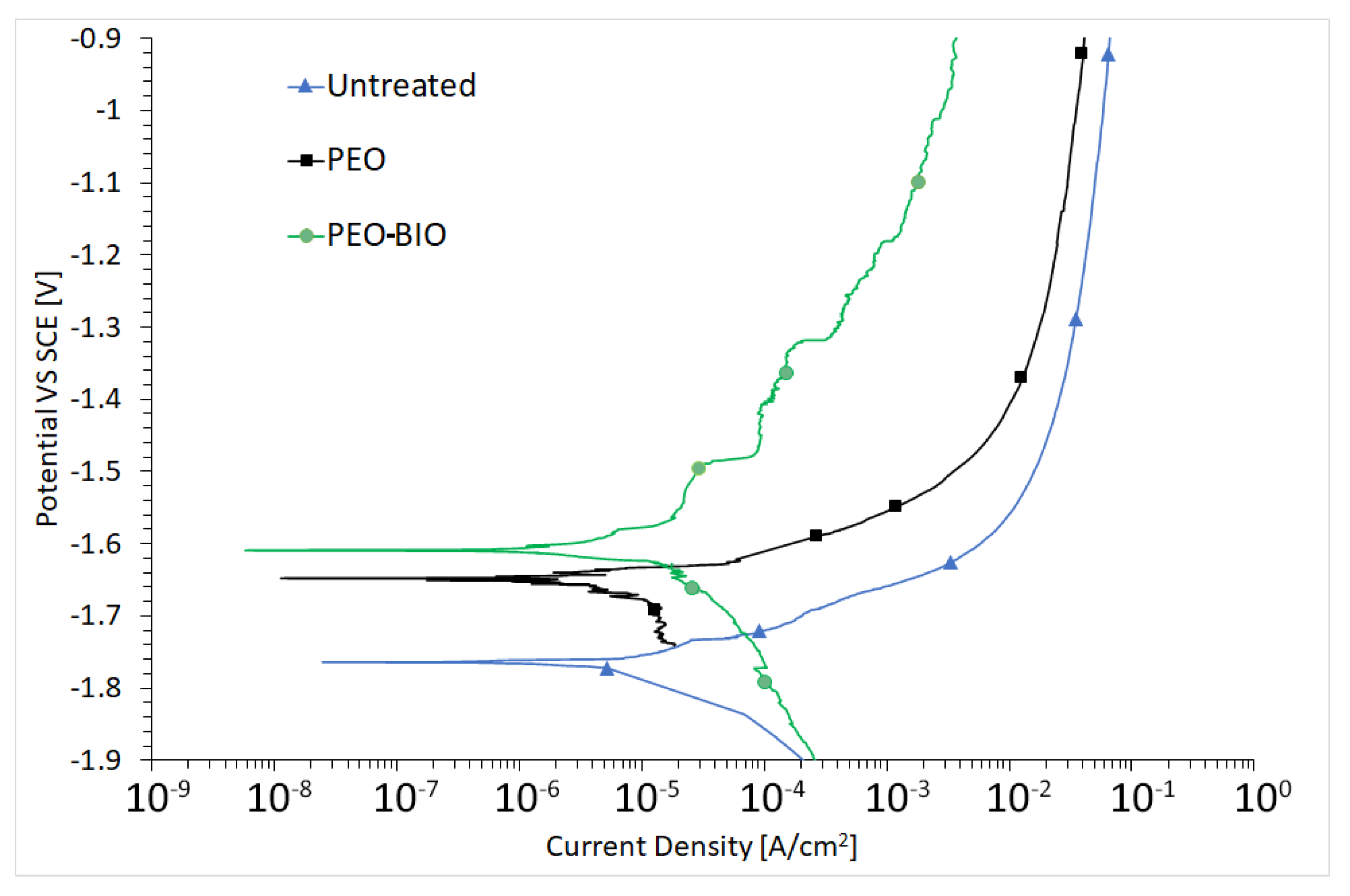
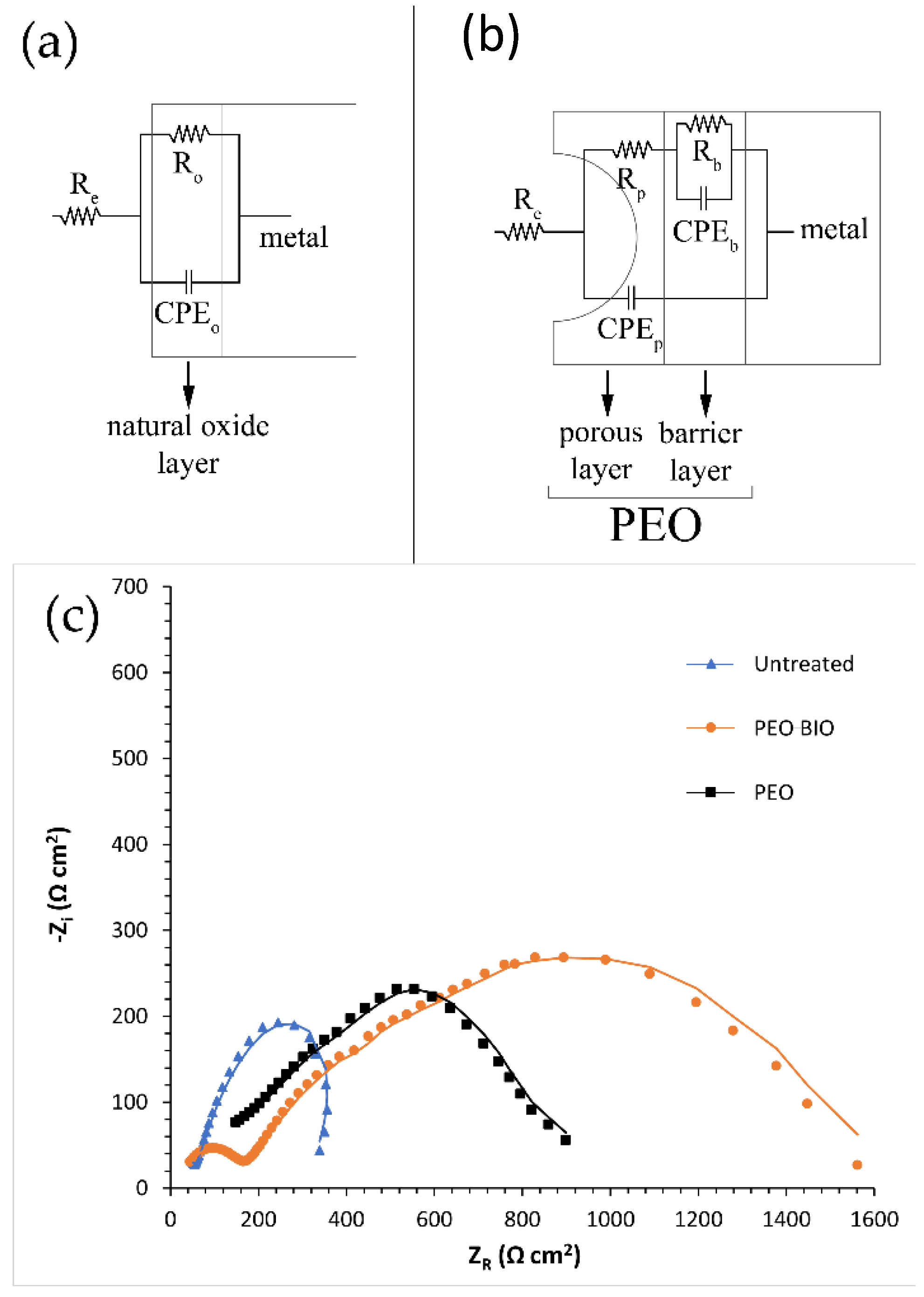
| Sample | Mg% | Al% | O% | Si% | Na% | P% | Ca% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO Surface | 19.7 | 1.0 | 40.2 | 16.3 | 18.9 | 3.9 | - |
| PEO Barrier Layer (1) | 48.9 | 1.3 | 34.1 | 8.7 | 4.4 | 2.6 | - |
| PEO Porous Layer (2) | 17.7 | 0.6 | 38.8 | 20.1 | 17.1 | 5.7 | - |
| PEO-BIO Surface (Extended analysis) | 17.9 | 0.8 | 41.4 | 9.4 | 8.1 | 11.9 | 10.5 |
| PEO-BIO Surface (1) | 32.4 | - | 50.7 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 6.3 | 2.9 |
| PEO-BIO Surface (2) | 10.7 | - | 48.9 | 8.5 | 7.7 | 12.5 | 10.8 |
| PEO-BIO Barrier Layer (3) | 50.0 | 2.0 | 34.7 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 4.7 | 1.7 |
| PEO-BIO Porous Layer/Rough Zone (2) | 24.8 | 1.1 | 31.4 | 14.0 | 2.0 | 13.7 | 13.0 |
| PEO-BIO Porous Layer/Smooth Zone (2) | 38.9 | 0.8 | 37.3 | 10.4 | 1.6 | 6.3 | 4.7 |
| Sample | C% | O% | Mg% | Ca% | Si% | P% | Na% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO-BIO | 36.9 | 42.9 | 6.3 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 0.9 |
| Sample | Re [Ω cm2] | Ro and Rb [Ω cm2] | Rp [Ω cm2] | Qo and Qb [F cm−2 Hz1−n] | no and nb | Qp [F cm−2 Hz1−n] | np | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 44 | 462 | - | 2.05 × 10−5 | 0.7 | - | - | 0.002 |
| PEO | 45 | 480 | 257 | 3.91 × 10−6 | 0.86 | 1.56 × 10−6 | 0.74 | 0.003 |
| PEO-BIO | 45 | 877 | 103 | 9.10 × 10−4 | 0.55 | 1.59 × 10−6 | 0.93 | 0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pezzato, L.; Brunelli, K.; Diodati, S.; Pigato, M.; Bonesso, M.; Dabalà, M. Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Hydroxyapatite Containing PEO Coating Produced on AZ31 Mg Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061531
Pezzato L, Brunelli K, Diodati S, Pigato M, Bonesso M, Dabalà M. Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Hydroxyapatite Containing PEO Coating Produced on AZ31 Mg Alloy. Materials. 2021; 14(6):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061531
Chicago/Turabian StylePezzato, Luca, Katya Brunelli, Stefano Diodati, Mirko Pigato, Massimiliano Bonesso, and Manuele Dabalà. 2021. "Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Hydroxyapatite Containing PEO Coating Produced on AZ31 Mg Alloy" Materials 14, no. 6: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061531
APA StylePezzato, L., Brunelli, K., Diodati, S., Pigato, M., Bonesso, M., & Dabalà, M. (2021). Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Hydroxyapatite Containing PEO Coating Produced on AZ31 Mg Alloy. Materials, 14(6), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061531









