Spicy Bitumen: Curcumin Effects on the Rheological and Adhesion Properties of Asphalt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
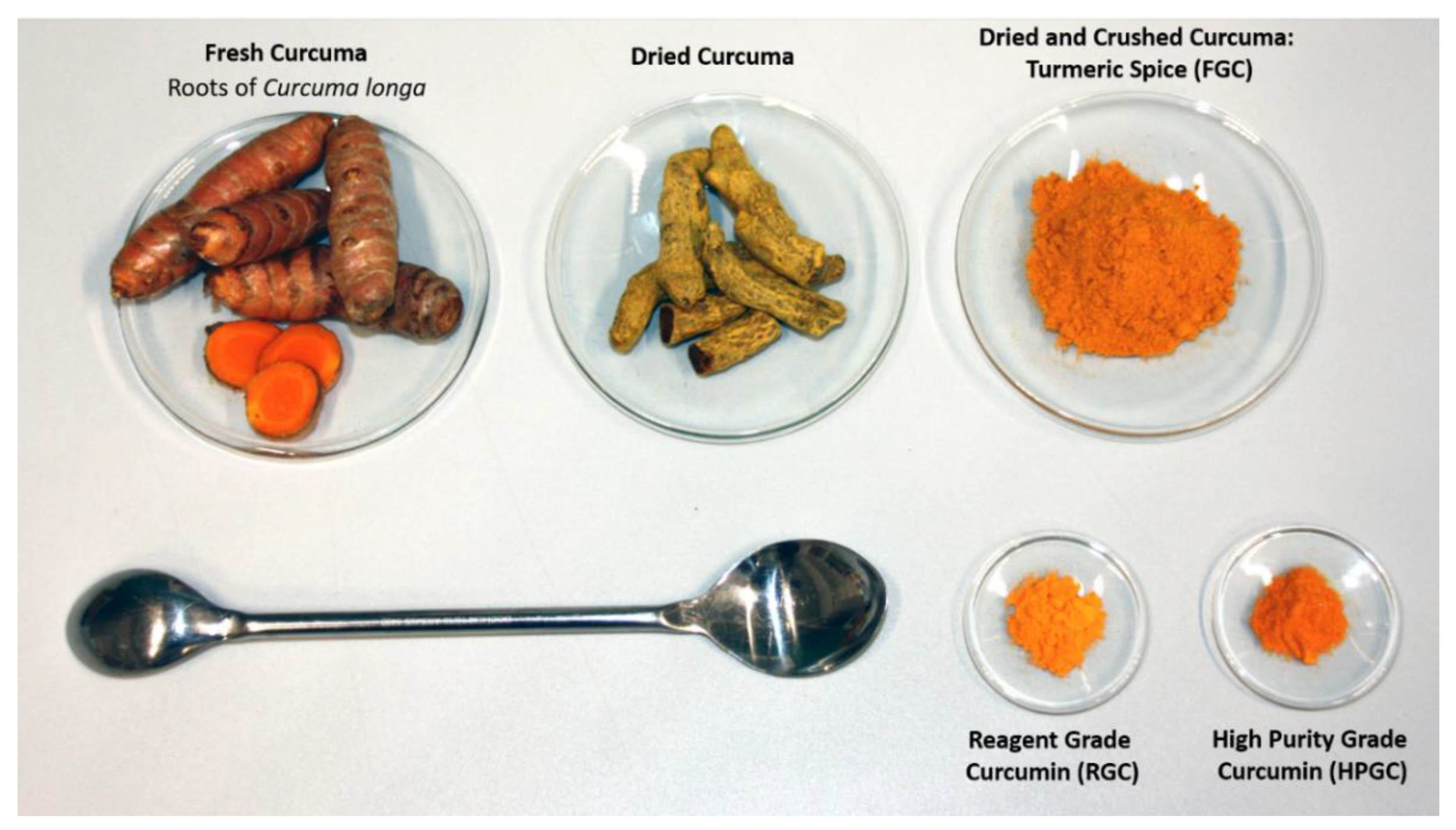
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Rheological Analysis
2.4. Boiling Test
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
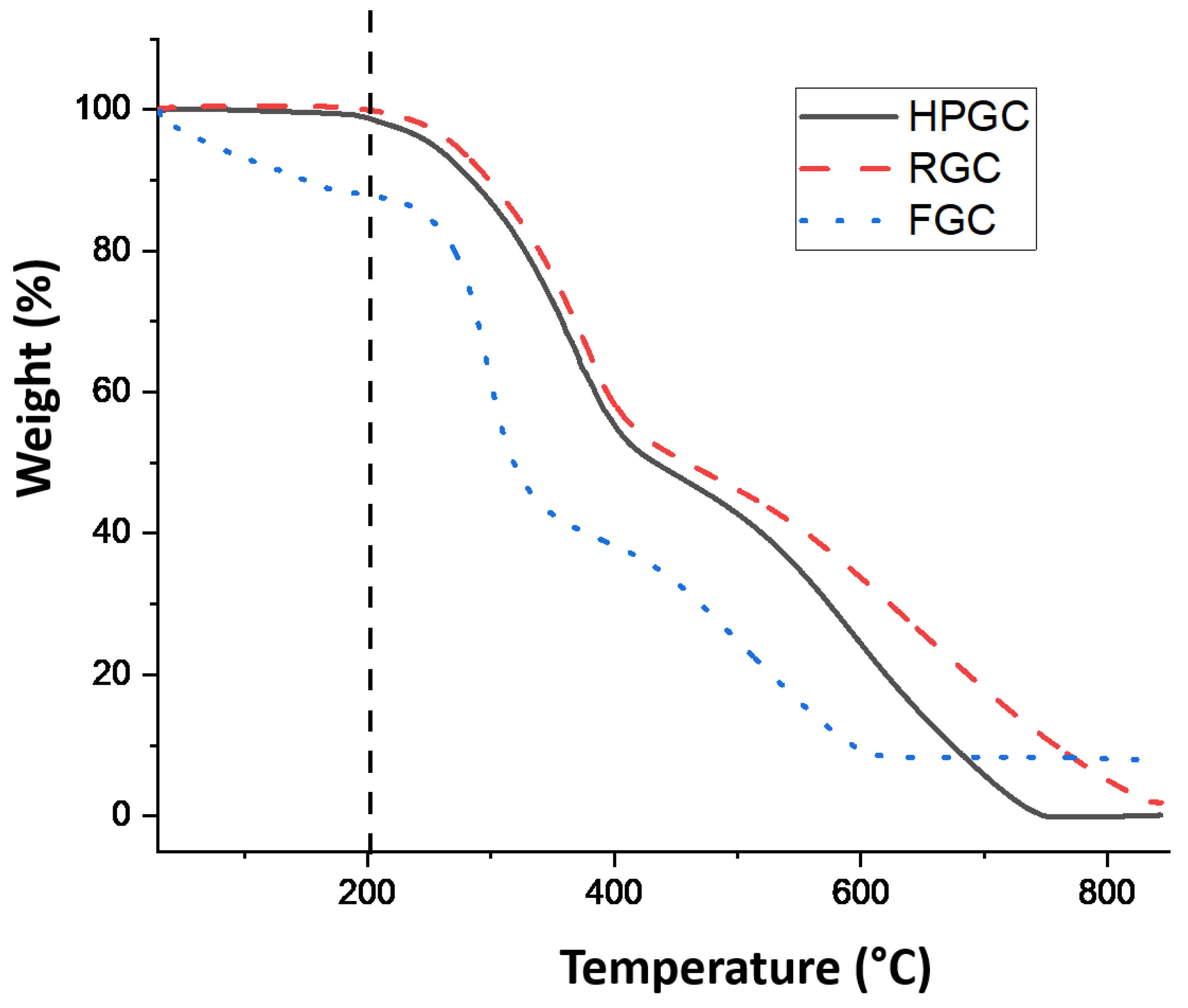
2.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
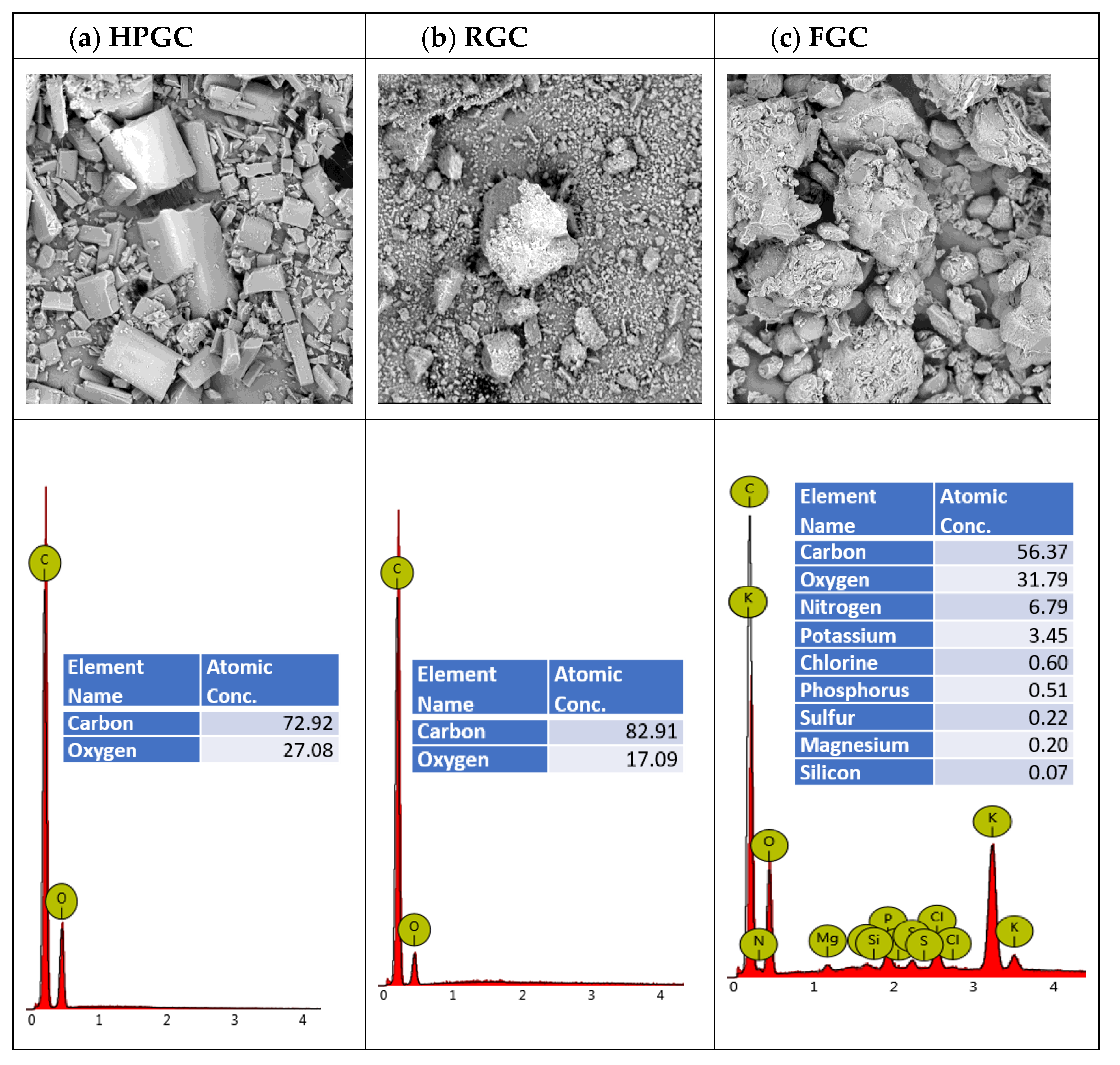
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
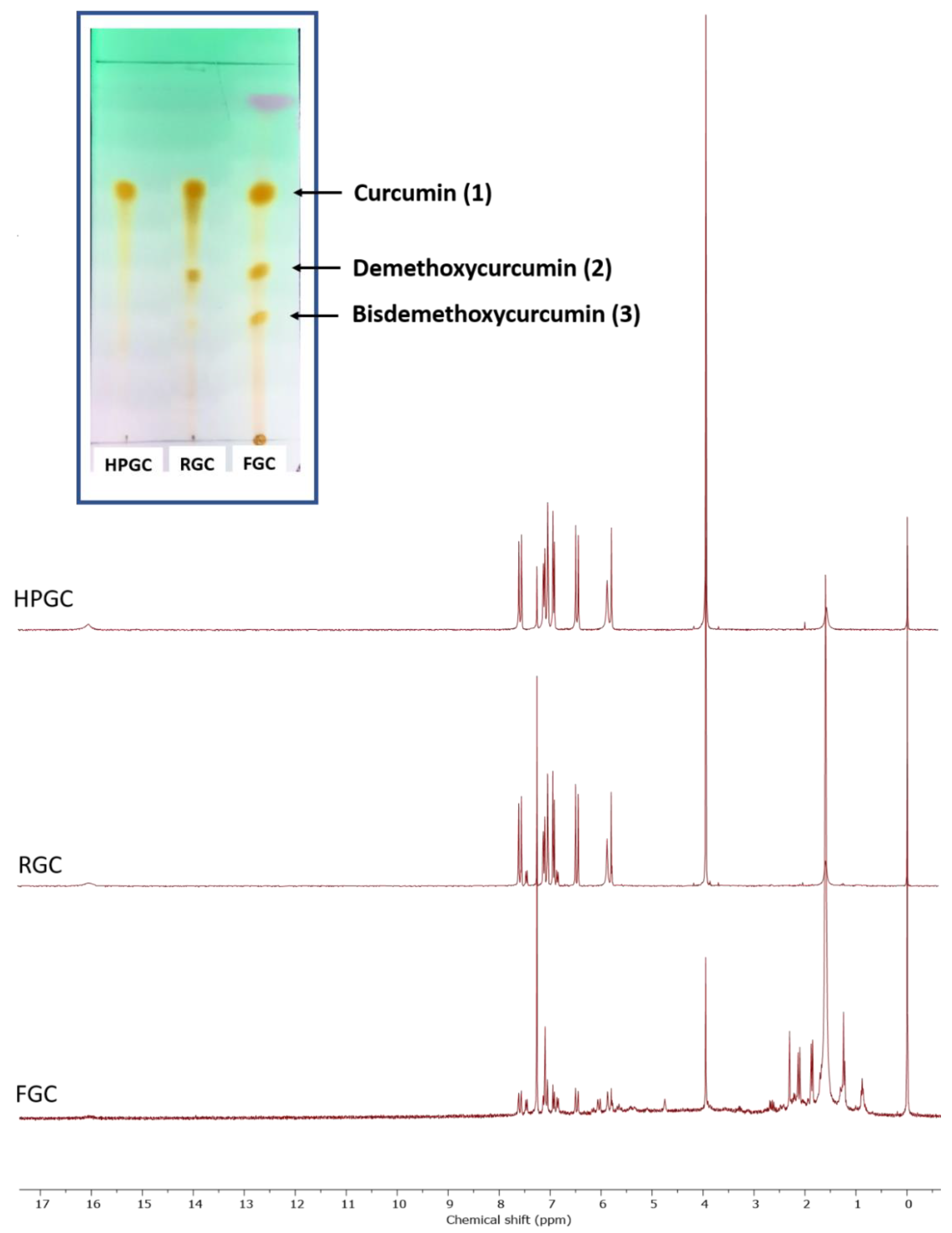
2.8. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
3. Results and Discussion
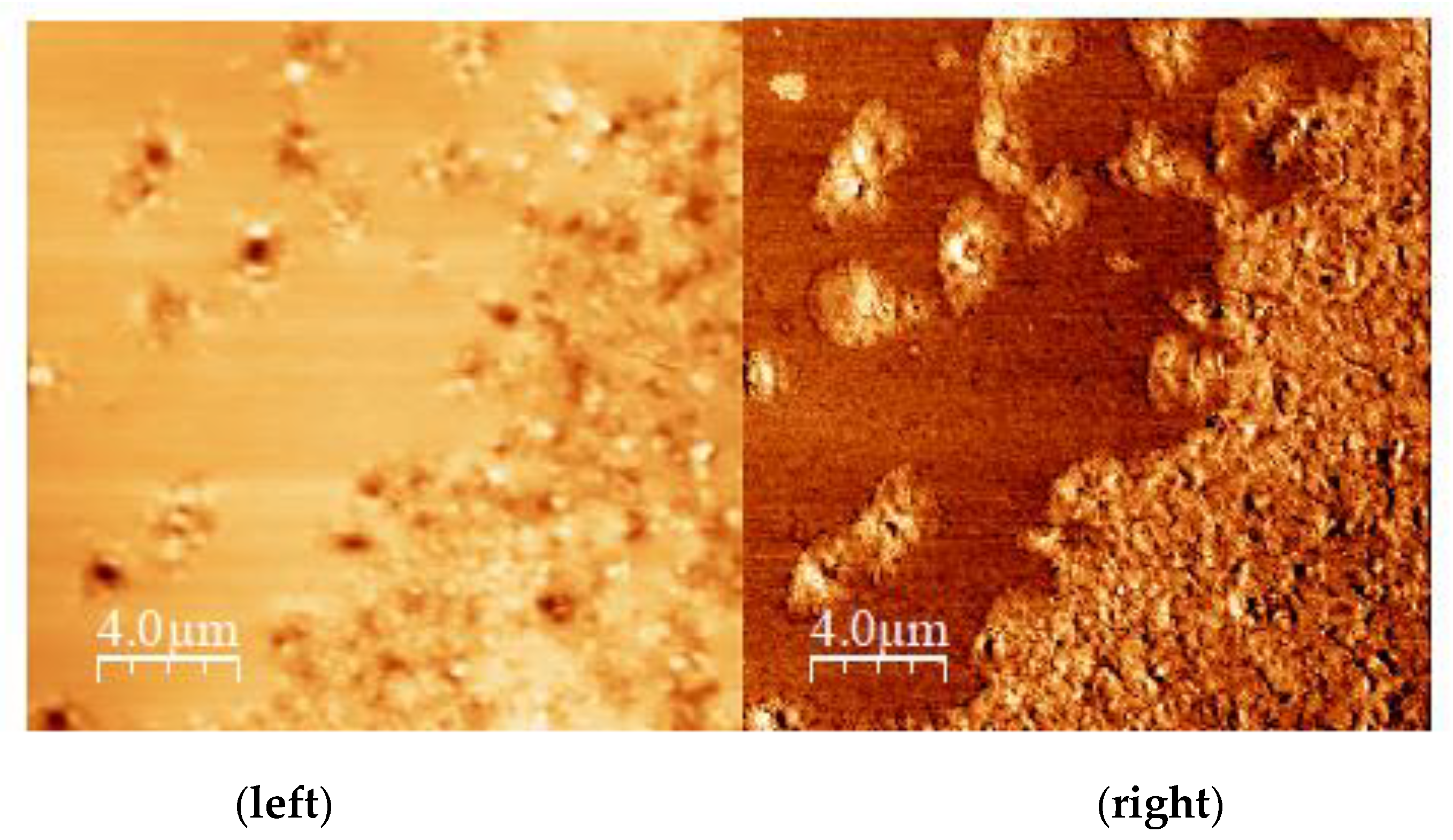
3.1. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Observation
3.2. Adhesion Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashimova, S.; Teltayev, B.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Caputo, P.; Eskandarsefat, S. Organic-based recycling agents for road paving applications in cold-climate regions. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montepara, A.; Giuliani, F. L’invecchiamento primario dei bitumi stradali: Analisi sperimentale sulle proporzioni e sull’evoluzione chimica dei gruppi costituenti. In Atti del Convegno Società Italiana Infrastrutture Viarie; Politecnico di Milano: Milano, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Ma, F.; Phospholipids, S.; Krezhova, D. (Eds.) Recent Trends for Enhancing the Diversity and Quality of Soybean Products; InTech: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-533-4. [Google Scholar]
- Galantini, L.; Pavel, N.V. Collective diffusion and self-diffusion coefficients comparison to separate interactions and micellar size effects on ionic micelle diffusivities: Cylindrical micelles of sodium taurodeoxycholate. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galantini, L.; di Gregorio, M.C.; Gubitosi, M.; Travaglini, L.; Tato, J.V.; Jover, A.; Meijide, F.; Soto Tellini, V.H.; Pavel, N.V. Bile salts and derivatives: Rigid unconventional amphiphiles as dispersants, carriers and superstructure building blocks. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 20, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Ambrosone, L.; Palazzo, G.; Mortensen, K.; Olsson, U. Ordering fluctuation in a shear-banding wormlike micellar system. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 8856–8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero Rossi, C.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Miriello, D.; Teltayev, B.; Angelico, R. Role of a food grade additive in the high temperature performance of modified bitumen. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 592, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldino, N.; Gabriele, D.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Seta, L.; Lupi, F.R.; Caputo, P.; Falvo, T. Rheological effects on bitumen of polyphosphoric acid (PPA) addition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, G.; Sabbagh Mollahosseini, H. Improving the performance of Crumb Rubber bitumen by means of Poly Phosphoric Acid (PPA) and Vestenamer additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3108–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, A.; Grünfelder, T.; Bates, F.S.; Macosko, C.W.; Stroup-Gardiner, M.; Newcomb, D.E. Asphalt modified by SBS triblock copolymer: Structures and properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, P.; Porto, M.; Loise, V.; Teltayev, B.; Oliviero Rossi, C. Analysis of mechanical performance of bitumen modified with waste plastic and rubber (SBR) additives by rheology and PGSE NMR experiments. Eurasian Chem. Technol. J. 2019, 21, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Sha, A.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, C. Improvement of asphalt-aggregate adhesion using plant ash byproduct. Materials 2019, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliviero Rossi, C.; Caputo, P.; Baldino, N.; Ildyko Szerb, E.; Teltayev, B. Quantitative evaluation of organosilane-based adhesion promoter effect on bitumen-aggregate bond by contact angle test. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 72, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, T.B.; Baaj, H. The use of rejuvenating agents in production of recycled hot mix asphalt: A systematic review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Ashimova, S.; Teltayev, B.; Vaiana, R.; Oliviero Rossi, C. Inverse Laplace Transform (ILT)NMR: A powerful tool to differentiate a real rejuvenator and a softener of aged bitumen. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 574, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Lee, S.-J. The effects of rejuvenating agents on recycled aged CRM binders. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2005, 6, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero Rossi, C.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Ashimova, S.; Teltayev, B.; Sangiorgi, C. A New Green Rejuvenator: Evaluation of Structural Changes of Aged and Recycled Bitumens by Means of Rheology and NMR. In RILEM 252-CMB-Symposium on Chemo Mechanical Characterization of Bituminous Materials; Poulikakos, L.D., Falchetto, A.C., Wistuba, M.P., Hofko, B., Porot, L., Di Benedetto, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 20, pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwański, M.; Mazurek, G. Hydrated lime as the anti-aging bitumen agent. Procedia Eng. 2013, 57, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, P.; Marí, A.; Pasandín, R.; Carvalho Pais, J.; Alves Pereira, P.A. Use of lignin biopolymer from industrial waste as bitumen extender for asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, M.; Zarei, A.; Zarei, M. The effect of lignin on mechanical and dynamical properties of asphalt mixtures SN. Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
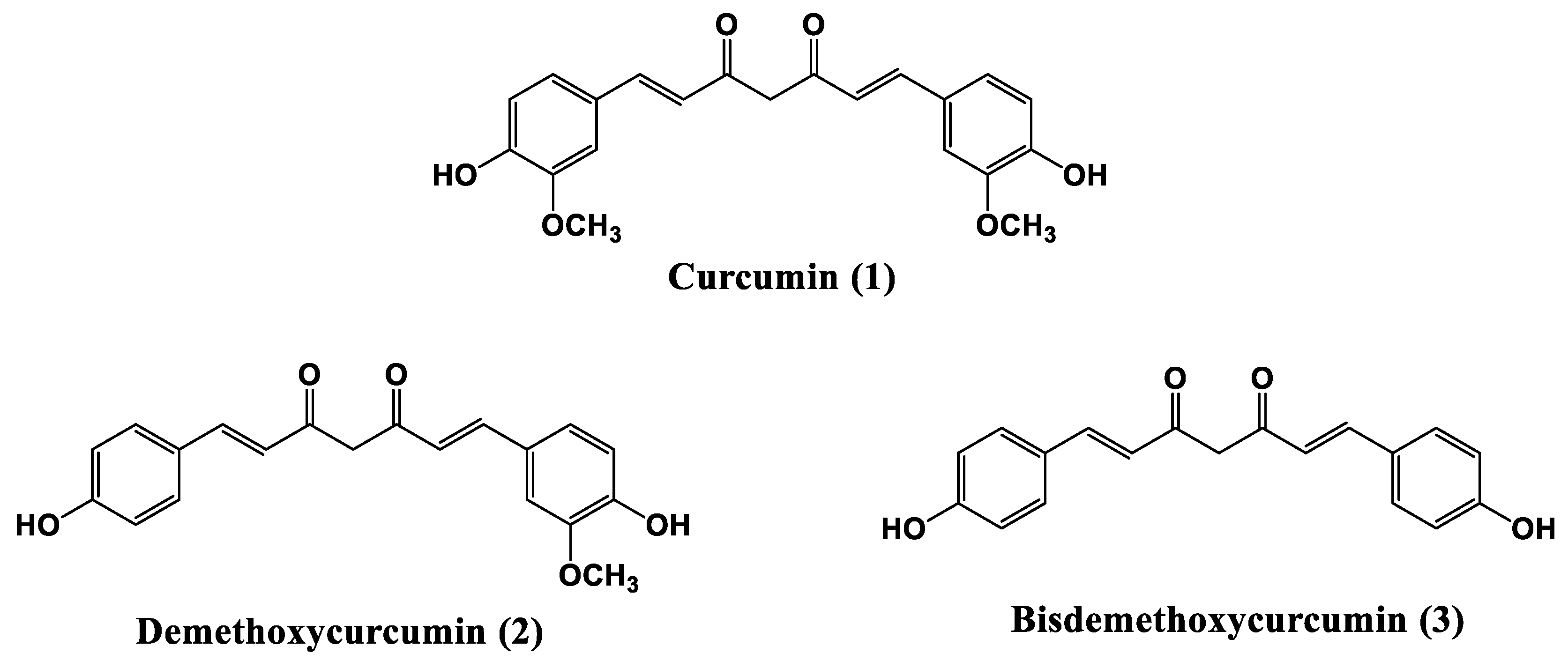
- Paramasivam, M.; Poi, R.; Banerjee, H.; Bandyopadhyay, A. High performance thin layer chromatographic method for quantitative determination of curcuminoids in Curcuma longa germplasm. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Malani, N.; Ichikawa, H. Curcumin: The Indian Solid Gold; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981-2002. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-C.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Ren, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Lin, L.-G.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.-W. Turmeric: A review of its chemical composition, quality control, bioactivity, and pharmaceutical application. In Natural and Artificial Flavoring Agents and Food Dyes, Handbook of Food Bioengineering; chapter 10; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ikpeama, A.; Onwuka, G.I.; Nwankwo, C. Nutritional Composition of Tumeric (Curcuma longa) and its antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, R.; Singh, A.; Gaddipati, J.; Srimal, R. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short review. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, K. The chemistry of curcumin: From extraction to therapeutic agent. Molecules 2014, 19, 20091–20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milobedzka, J.; von Kostanecki, S.; Lampe, V. Zur Kenntnis des Curcumins. [Information about curcumin]. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1910, 43, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pabon, H.J.J. A synthesis of curcumin and related compounds. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays B 1964, 83, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, R.R.; Luthria, D.L. Curcumin: Biological, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and analytical aspects. Molecules 2019, 24, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vellampatti, S.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Babu Mitta, S.; Lakshmanan, V.-K.; Ha Park, S. Metallo-Curcumin-conjugated DNA complexes induces preferential prostate cancer cells cytotoxicity and pause growth of bacterial cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanninger, S.; Lorenz, V.; Subhanb, A.; Edelmann, F.T. Metal complexes of curcumin—Synthetic strategies, structures and medicinal applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4986–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pröhl, M.; Schubert, U.S.; Weigand, W.; Gottschaldt, M. Metal complexes of curcumin and curcumin derivatives for molecular imaging and anticancer therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.P.; Sudheer, A.R. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 595, 105–125. [Google Scholar]
- Amalraj, A.; Pius, A.; Gopi, S. Biological activities of curcuminoids, other biomolecules from turmeric and their derivatives—A review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porto, M.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; De Filpo, G.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Calandra, P. Polysaccharides-reinforced bitumens: Specificities and universality of rheological behavior. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caputo, P.; Porto, M.; Calandra, P.; De Santo, M.P.; Oliviero Rossi, C. Effect of epoxidized soybean oil on mechanical properties of bitumen and aged bitumen. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 675, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stulirova, J.; Pospisil, K. Observation of bitumen microstructure changes using Scanning Electron Microscopy. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2008, 9, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Whiteoak, D. The Shell Bitumen Handbook, 5th ed.; Hunter, R.N., Ed.; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lesueur, D. The colloidal structure of bitumen: Consequences on the rheology and on the mechanisms of bitumen modification. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 42–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.G. The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Franck, A. Measuring structure of low viscosity fluids in oscillations using rheometers with and without a separate torque transducer. Ann. Trans. Nordic Rheol. Soc. 2003, 11, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zanzotto, L.; Stastna, J.; Vacin, O. Thermomechanical properties of several polymer modified asphalts. Appl. Rheol. 2000, 10, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Tan, X.; Shi, S.; Zhang, H. Influence of filler–bitumen ratio on performance of modified asphalt mortar by additive. J. Mod. Transp. 2013, 21, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson, J.-F.; Leblond, V.; Margeson, J. Bitumen morphologies by phase-detection atomic force microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 221, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Burnham, N.A.; Tao, M. Surface microstructure of bitumen characterized by atomic force microscopy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 218, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.K.; Kringos, N.; Wallqvist, V.; Birgisson, B. Micromechanical investigation of phase separation in bitumen by combining atomic force microscopy with differential scanning calorimetry results. Road Mater. Pavement Design. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, A.; Lackner, R.; Eisenmenger-Sittner, C.; Blab, R. Identification of four material phases in bitumen by atomic force microscopy. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2004, 5, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, M. A new preparation method and imaging parameters of asphalt binder samples for atomic force microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubev, Y.A.; Kovaleva, O.V.; Yushkin, N.P. Observations and morphological analysis of supermolecular structure of natural bitumens by atomic force microscopy. Fuel 2008, 87, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliukaitė, M.; Vorobjovas, V.; Bulevičius, M.; Andrejevas, V. Evaluation of different test methods for bitumen adhesion properties. Transp. Res. Proc. 2016, 14, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, C.; Hanz, A.; Bahia, H. Measuring moisture susceptibility of Cold Mix Asphalt with a modified boiling test based on digital imaging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Apeagyei, A.K.; Airey, V.; Grenfell, J.R.A. Influence of aggregate mineralogical composition on water resistance of aggregate–bitumen adhesion. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 62, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, F.; Xu, T.; Wang, H. Impact of minerals and water on bitumen-mineral adhesion and debonding behaviours using molecular dynamics simulations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Measured Properties | Standard | Unit | LC50 | C170 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50/70 | 170/210 | |||
| Penetration at 25 °C | EN 1426 | 0.1 mm | 68 ± 1 | 185 ± 1 |
| Softening point (R&B) | EN 1427 | °C | 48.8 ± 0.2 | 42.6 ± 0.2 |
| Flash point | EN 2592 | °C | ≥230 | ≥220 |
| Solubility | EN 12592 | % (m/m) | ≥99 | ≥99 |
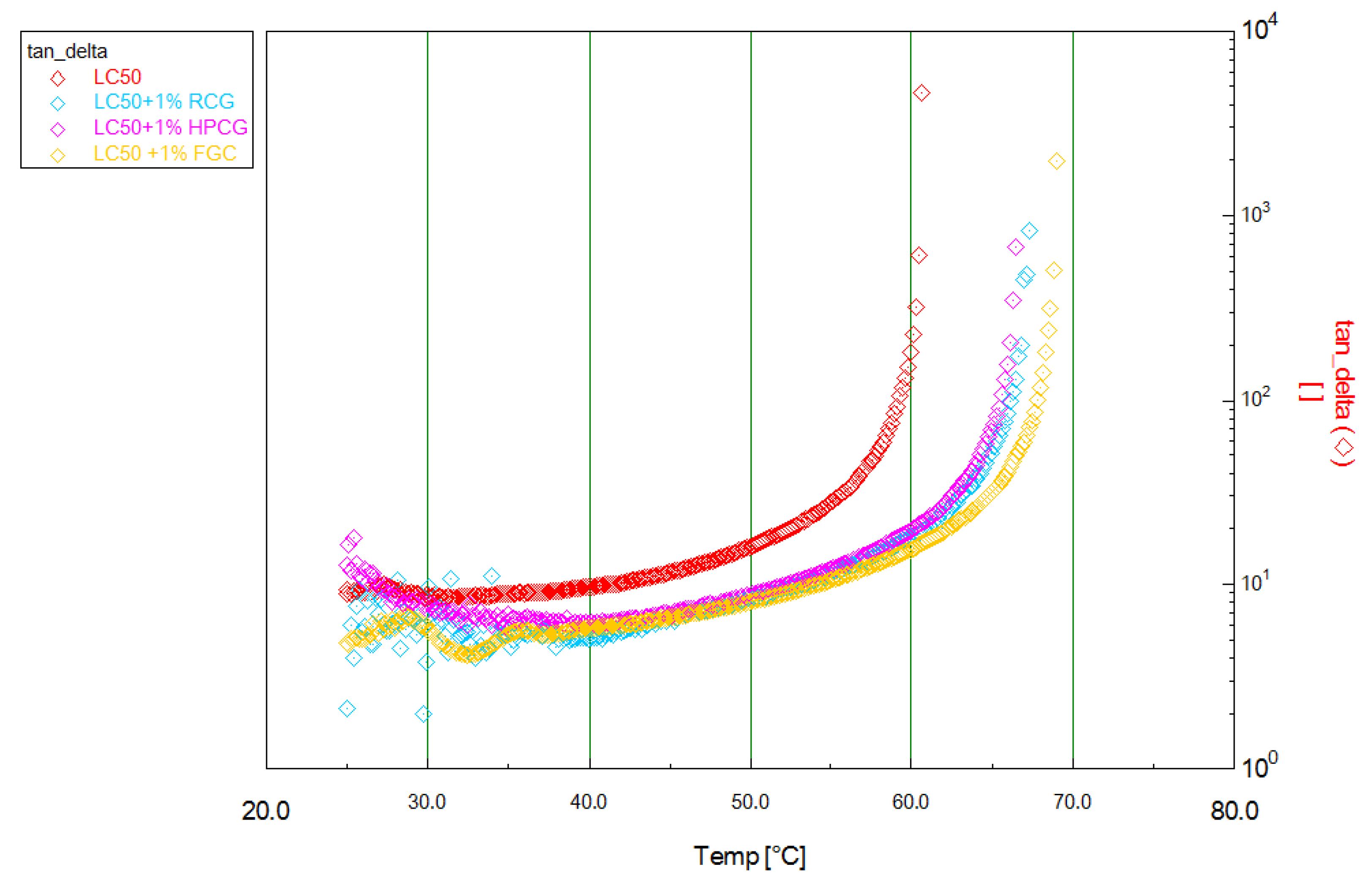
| Sample | Transition Temperature (°C) ±0.1 | ∆ (°C) ±0.2 | ∆ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 | 60.5 | - | - |
| LC50 + 1% CaCO3 | 65.0 | 4.5 | 7.4 |
| LC50 + 1% FGC | 66.6 | 6.1 | 10.1 |
| LC50 + 3% FGC | 66.5 | 6.0 | 9.9 |
| LC50 + 1% RGC | 67.5 | 7.0 | 11.6 |
| LC50 + 3% RGC | 70.1 | 9.6 | 15.9 |
| LC50 + 1% HPGC | 65.5 | 5.0 | 8.3 |
| LC50 + 3% HPGC | 67.5 | 7.0 | 11.6 |
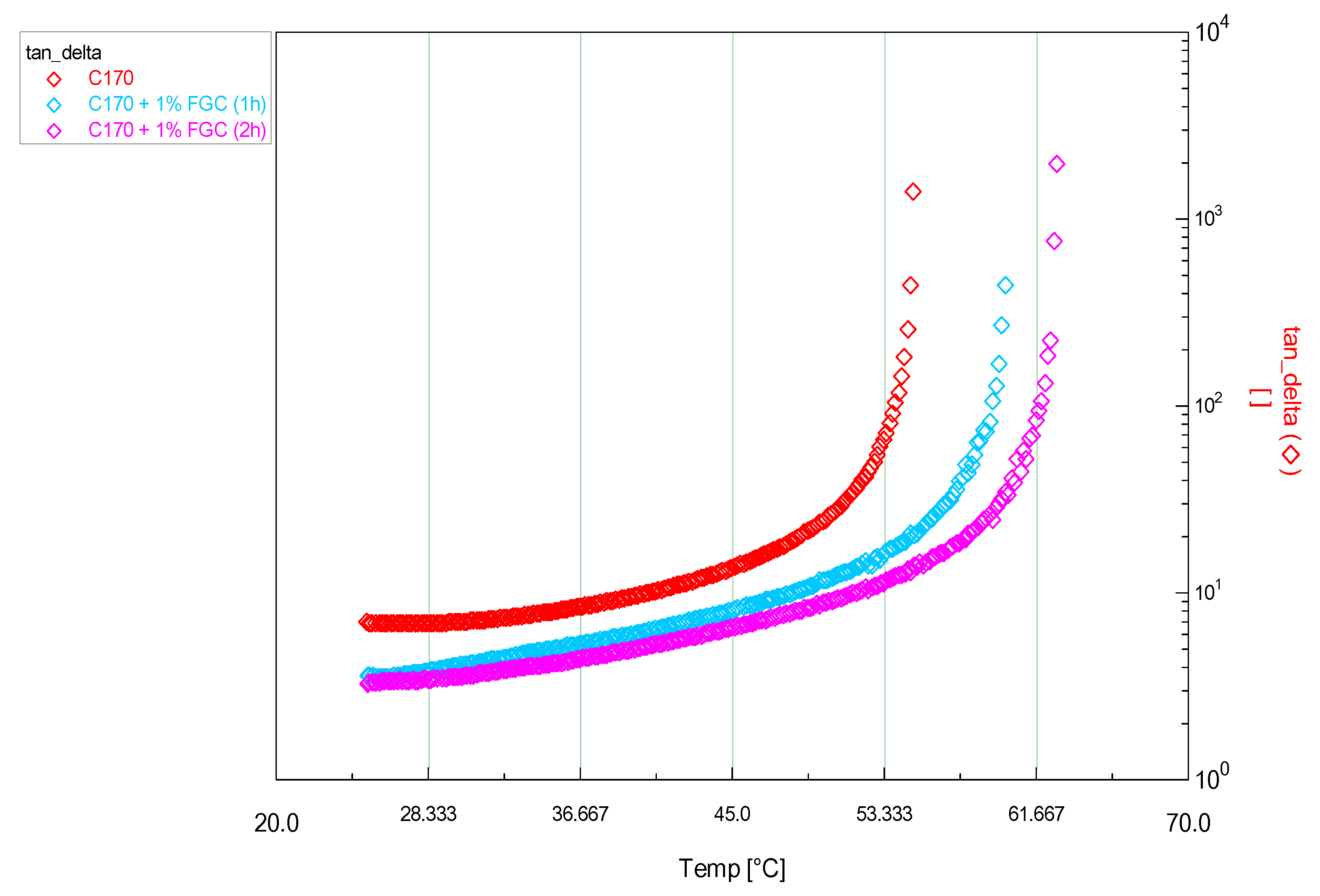
| Sample | Transition Temperature (°C) ±0.1 | Δ (°C) ±0.2 | Δ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C170 | 51.1 | - | - |
| 1% HPGC | 62.2 | 11.1 | 21.7 |
| 1% RGC | 60.9 | 9.8 | 19.2 |
| 1% FGC (1h) | 61.5 | 10.4 | 20.4 |
| 1% FGC (2h) | 62.3 | 11.2 | 21.9 |
| 1% CaCO3 | 55.0 | 3.9 | 7.6 |
| Sample | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|
| PURE LC50 | 15 |
| LC50 + 1% RGC | 80 |
| LC50 + 3% RGC | 80 |
| LC50 + 1% HPGC | 75 |
| LC50 + 3% HPGC | 75 |
| LC50 + 1% FGC | 35 |
| LC50 + 3% FGC | 40 |
| Sample | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|
| PURE C170 | 70 |
| C170 + 1% RGC | 75 |
| C170 + 1% HPGC | 90 |
| C170 + 1% FGC | 90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, A.A.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Caputo, P.; De Santo, M.P.; Godbert, N.; Aiello, I. Spicy Bitumen: Curcumin Effects on the Rheological and Adhesion Properties of Asphalt. Materials 2021, 14, 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071622
Abe AA, Oliviero Rossi C, Caputo P, De Santo MP, Godbert N, Aiello I. Spicy Bitumen: Curcumin Effects on the Rheological and Adhesion Properties of Asphalt. Materials. 2021; 14(7):1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071622
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Abraham A., Cesare Oliviero Rossi, Paolino Caputo, Maria Penelope De Santo, Nicolas Godbert, and Iolinda Aiello. 2021. "Spicy Bitumen: Curcumin Effects on the Rheological and Adhesion Properties of Asphalt" Materials 14, no. 7: 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071622
APA StyleAbe, A. A., Oliviero Rossi, C., Caputo, P., De Santo, M. P., Godbert, N., & Aiello, I. (2021). Spicy Bitumen: Curcumin Effects on the Rheological and Adhesion Properties of Asphalt. Materials, 14(7), 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071622











