Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Getter for Hydrogen Elimination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Methyl Vinyl Silicone Oil
2.3. Vinyl Content Quantification
2.4. Getter Preparation
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Absorption Test in Pure H2
2.7. Absorption Test in the Mixture Gas
2.8. Kinetic Study
3. Results and Discussion
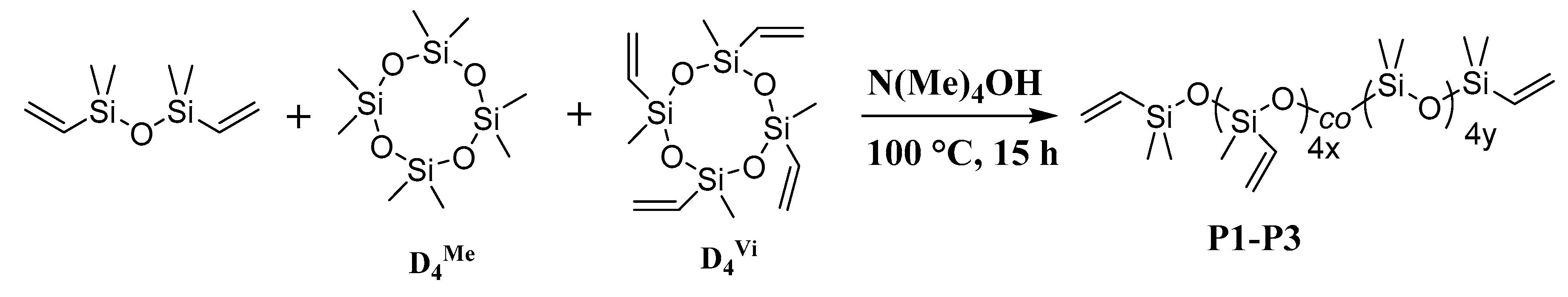
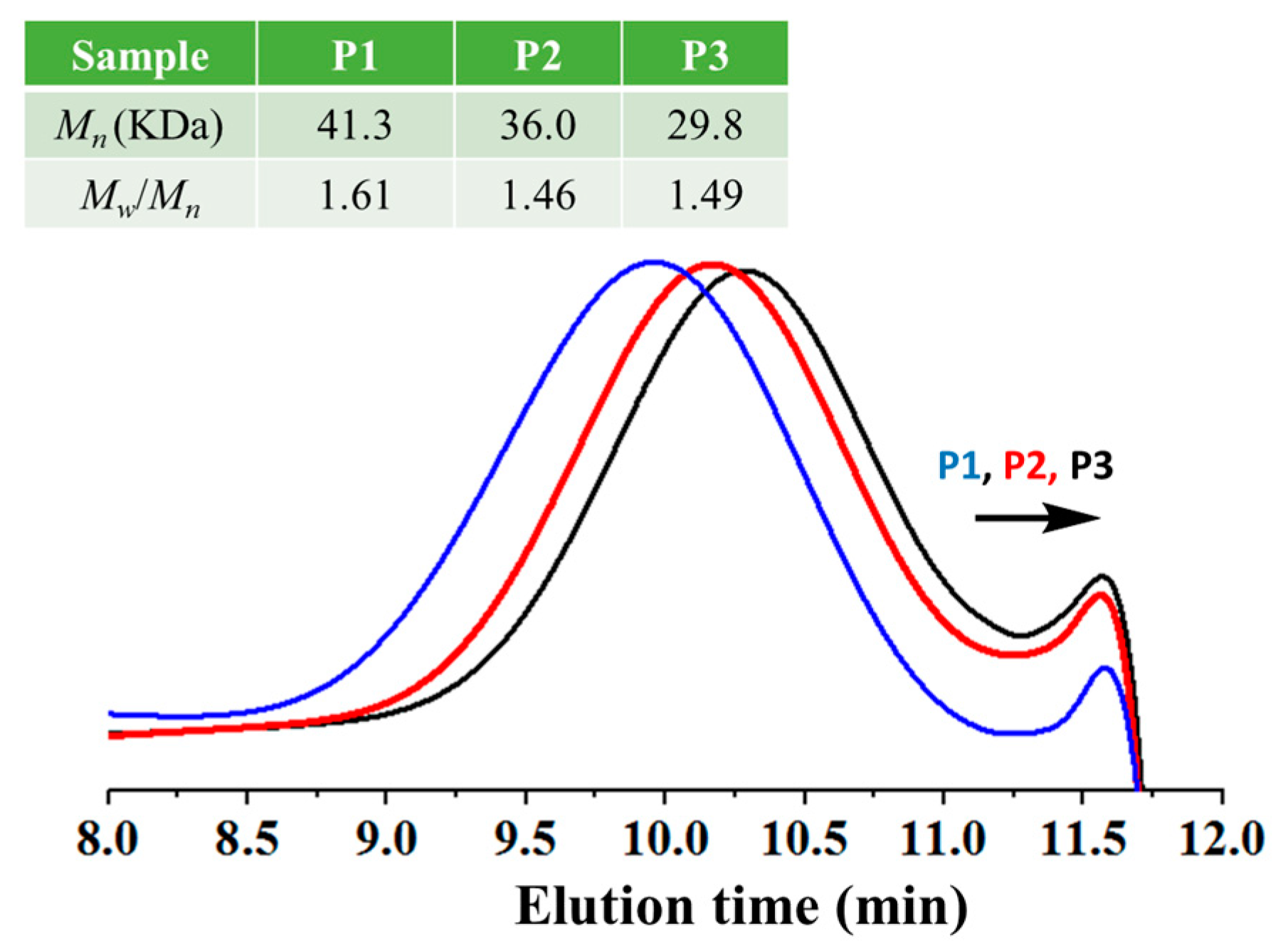
3.1. Polysiloxane Synthesis and Characterization
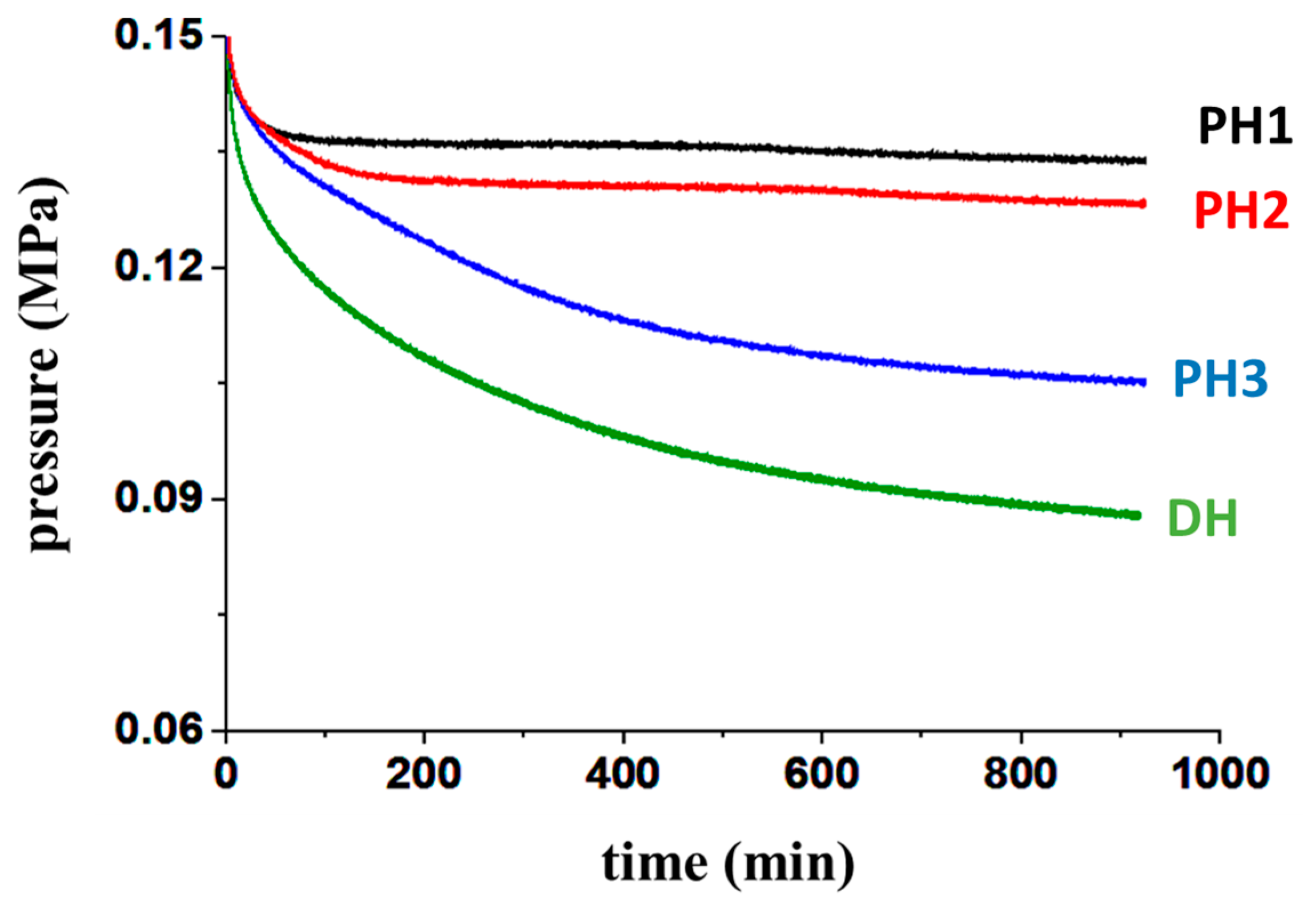
3.2. Uptake Performance in Pure H2 Atmosphere
3.3. Absorption under Low Hydrogen Partial Pressure
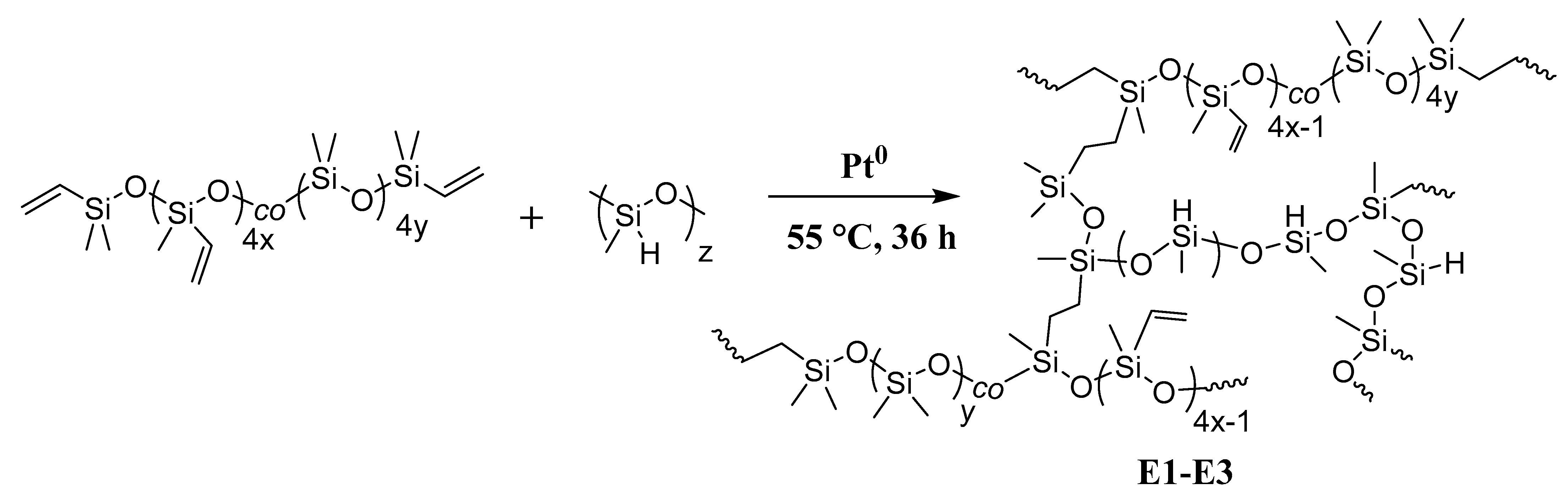
3.4. Synthesis and Characterization of Improved Getters
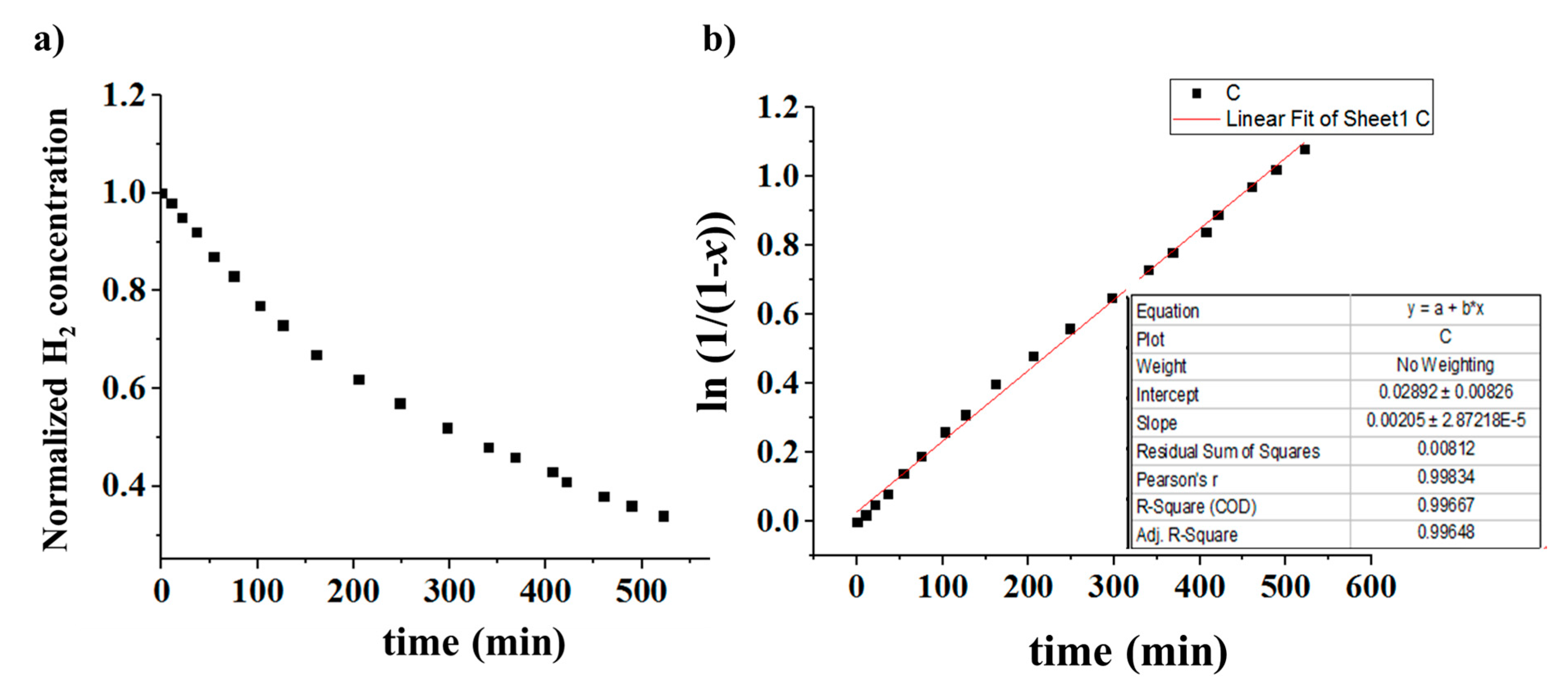
3.5. Kinetic Study
3.6. Compounded Getter Synthesis and Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortiz-Acosta, D.; Moore, T.; Safarik, D.J.; Hubbard, K.M.; Janicke, M. 3D-printed silicone materials with hydrogen getter capability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, R.L.; Harrah, L.A.; Schoenfelder, C.W.; West, L.A. Organic Hydrogen Getters. Part. I. Introductory Report; Sandia Labs.: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Fujimoto, M.S.; Canfield, N.L.; Elmore, M.R.; Varga, T.; Sevigny, G.J.; Senor, D.J. Probing the radial chemistry of getter components in light water reactors via controlled electrochemical dissolution. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13578–13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kautz, E.J.; Gwalani, B.; Lambeets, S.V.; Kovarik, L.; Schreiber, D.K.; Perea, D.E.; Senor, D.; Liu, Y.S.; Battu, A.K.; Tseng, K.P. Rapid assessment of structural and compositional changes during early stages of zirconium alloy oxidation. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2020, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigrey, P.J. An Issue Paper on the Use of Hydrogen Getters in Transportation Packaging; Sandia National Labs.: Livermore, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo, R.; Courtney, R. Organic hydrogen getters. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, G. Hydriding kinetics of an organic hydrogen getter-DPB. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, G. The hydriding kinetics of organic hydrogen getters. In Proceedings of the 2002 TMS Meet, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M.; Benson, M.; Orme, C.; Luther, T.; Peterson, E. Improved Hydrogen Gas. Getters for TRU Waste—Final Report; Idaho National Laboratory (INL): Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Livingston, R.; Duffey, J.; Shepodd, T.; McConnell, P. Enhanced Polymer Hydrogen Getters for Use in the Trupact-II; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shepodd, T.J.; Whinnery, L.L. Polymer Formulations for Gettering Hydrogen. U.S. Patent 5837158, 17 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Ye, M.; Tang, G.; Pan, J.; Xia, X. Polymer framework with continuous pores for hydrogen getters: Molding and a boost in getter rate. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3243–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balooch, M.; Wang, W.E.; Kirkpatrick, J. Hydrogen uptake mechanism of a silicone-rubber DEB getter mixture. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangalang, E.A.; Sharma, H.N.; Saw, C.K.; Gollott, R.; Matt, S.M.; Wilson, T.S.; McLean, W.; Maxwell, R.S.; Dinh, L.N. Hydrogen uptake kinetics of 1, 4-bis (phenylethynyl) benzene (DEB) rubberized coating on silicone foam substrate. Acs Appl. Mater. Interf. 2019, 12, 3993–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silicone, S.E. Characteristic Properties of Silicone Rubber Compounds. Silicone, Shin-Etsu. 2012. Available online: https://www.shinetsusilicone-global.com/catalog/pdf/rubber_e.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Ji, J.; Ge, X.; Pang, X.; Liu, R.; Wen, S.; Sun, J.; Liang, W.; Ge, J.; Chen, X. Synthesis and characterization of room temperature vulcanized silicone rubber using methoxyl-capped MQ silicone resin as self-reinforced cross-linker. Polymers 2019, 11, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepodd, T.J. Polymer Formulation for Removing Hydrogen and Liquid Water from an Enclosed Space. U.S. Patents 7001535, 21 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lueking, A.D.; Yang, R.T. Hydrogen spillover to enhance hydrogen storage—Study of the effect of carbon physicochemical properties. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 265, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parambhath, V.B.; Nagar, R.; Sethupathi, K.; Ramaprabhu, S. Investigation of spillover mechanism in palladium decorated hydrogen exfoliated functionalized graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15679–15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.D.; Kantor, S.W.; MacKnight, W.J. Thermally stable silphenylene vinyl siloxane elastomers and their blends. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvornic, P.R.; Perpall, H.J.; Uden, P.C.; Lenz, R.W. Exactly alternating silarylene–siloxane polymers. VII. Thermal stability and degradation behavior of p-silphenylene–siloxane polymers with methyl, vinyl, hydrido, and/or fluoroalkyl side groups. J. Polym. Part A Polym Chem. 1989, 27, 3503–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Capacity (mL/g) | Vinyl Content (mmol/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH1 | 52.6 a | 53.9 b | 2.7 ± 0.15 c | 0.3 ± 0.11 d |
| PH2 | 104.6 | 107.8 | 5.8 ± 0.25 | 1.0 ± 0.14 |
| PH3 | 202.5 | 211.2 | 10.8 + 0.32 | 1.4 ± 0.18 |
| DH | 237.2 | 247.1 | 11.5 ± 0.43 | 0.5 ± 0.12 |
| 1% H2 in N2 | 5% H2 in N2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 11 min | 40 min | 120 min | 240 min | 8 min | 25 min | 70 min | 120 min |
| PH1 | 85.8% | 58.7% | 12.2% | 0.8% | 74.7% | 29.8% | 6.3% | <10 ppm |
| PH2 | 64.2% | 40.8% | 3.1% | <10 ppm | 50.7% | 23.0% | 1.2% | <10 ppm |
| PH3 | 48.6% | 24.8% | 0.1% | <10 ppm | 18.6% | 7.8% | <10 ppm | <10 ppm |
| Sample | DH | PH2 | EH2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ea (KJ/mol) | 20.0 | 20.1 | 19.6 |
| Sample | CG1 | CG2 | CG3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total capacity (mL/g) a | 133 | 164 | 210 |
| Catalyst loading (wt %) b | 5.3 | 6.3 | 7.4 |
| Polymer contribution (mL) c | 25.0 | 34.4 | 58.8 |
| Vinyl conversion d | 19.2% | 32.6% | 75.4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, T.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Getter for Hydrogen Elimination. Materials 2021, 14, 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14081853
Xing T, Xu Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Yan L. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Getter for Hydrogen Elimination. Materials. 2021; 14(8):1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14081853
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Tao, Yong Xu, Juying Wu, Yu Wang, and Lifeng Yan. 2021. "Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Getter for Hydrogen Elimination" Materials 14, no. 8: 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14081853
APA StyleXing, T., Xu, Y., Wu, J., Wang, Y., & Yan, L. (2021). Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Vinyl Polysiloxane Getter for Hydrogen Elimination. Materials, 14(8), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14081853







