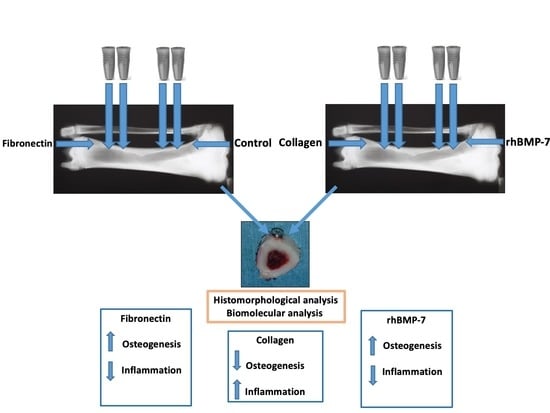
Role of rhBMP-7, Fibronectin, And Type I Collagen in Dental Implant Osseointegration Process: An Initial Pilot Study on Minipig Animals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Implant Insertion
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Biomolecular Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.6. Outcome Assessor
3. Results
3.1. Histological Analysis
3.2. Biomolecular Analysis
3.2.1. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
3.2.2. Cytokines
3.2.3. Osteocalcin
4. Discussion
4.1. rhBMP-7, Type 1 Collagen and Fibronectin Effects on Osteogenesis and Inflammation Process
4.1.1. rhBMP-7
4.1.2. Collagen
4.1.3. Fibronectin
4.2. Expression of BMP-4, BMP-7, TGF-β2, and Osteocalcin in Implant Sites Treated with rhBMP-7, Type 1 Collagen and Fibronectin
4.3. Histological Analysis
4.4. Limitations of the Study
- Since the report was a pilot study, for each experimental time, both histological and biomolecular analyses were carried out only in one site, generating a statistical problem.In fact, although it is possible to identify a trend, the sample number was reduced to apply a statistical model. Although each sample, for biomolecular analysis, was tested six time, for histological analysis, the inflammatory cells and osteoblasts were tested in 10 fields.
- It would have been good to investigate more anti-inflammatory proteins.
- If the study was to be redone, hetero-dimers would probably have to be used as they are less expensive. This could be the starting point for a future study. However, it must be kept in mind that hetero-dimers are the combination of more BMPs, reducing the possibility in distinguishing the effect of a single BMP type.
- Although the animal models are accepted as a standard in the study of dental implants, some obstacles can arise. The results obtained are not mathematically exportable to human beings. However, the experimentation of these proteins in vivo on humans, as regards to dental implants, is currently highly difficult in terms of authorization, at least in Italy.
4.5. Values of the Study
5. Conclusions
- Collectively, the reported results of this initial pilot study evidence, in a novelty way, that FN and rhBMP-7 addition during dental implant positioning in animals is able to early modulate the expression of cytokines belonging to the TGF-β superfamily (BMP-4, BMP-7, TGF-β2), suggesting that these signal transduction pathways are modulated by these proteins and contribute to improving the neo-osteogenesis and the osseointegration process of implants.
- Type 1 Collagen induces inflammatory infiltrate in the peri-implant tissues. It is not able to induce bone formation, although at 7 days, it increased the local expression of BMP-4 and TGF-β2.However, these results will need to be confirmed in future studies conducted on a larger sample to endorse the findings obtained.
Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schierano, G.; Canuto, R.A.; Navone, R.; Peirone, B.; Martinasso, G.; Pagano, M.; Maggiora, M.; Manzella, C.; Easton, M.; Davit, A.; et al. Biological Factors Involved in the Osseointegration of Oral Titanium Implants with Different Surfaces: A Pilot Study in Minipigs. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, G.; Martinasso, G.; Peirone, B.; Navone, R.; Manzella, C.; Muzio, G.; Russo, C.; Canuto, R.A.; Schierano, G. Cytokines and Growth Factors Involved in the Osseointegration of Oral Titanium Implants Positioned Using Piezoelectric Bone Surgery Versus a Drill Technique: A Pilot Study in Minipigs. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schierano, G.; Mussano, F.; Faga, M.G.; Menicucci, G.; Manzella, C.; Sabione, C.; Genova, T.; Von Degerfeld, M.M.; Peirone, B.; Cassenti, A.; et al. An Alumina Toughened Zirconia Composite for Dental Implant Application: In Vivo Animal Results. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 157360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schierano, G.; Vercellotti, T.; Modica, F.; Corrias, G.; Russo, C.; Cavagnetto, D.; Baldi, D.; Romano, F.; Carossa, S.; Carosa, S. A 4-Year Retrospective Radiographic Study of Marginal Bone Loss of 156 Titanium Implants Placed with Ultrasonic Site Preparation. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2019, 39, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacchi, C.; Bassi, F.; Troiano, G.; Rapani, A.; Lombardi, T.; Jokstad, A.; Sennerby, L.; Schierano, G. Piezoelectric bone surgery for implant site preparation compared with conventional drilling techniques: A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Int. J. Oral Implant. 2020, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, R.; Bruschi, G.B.; Capparé, P.; Gherlone, E. The Utility of the Electric Mallet. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, L.J. Immunohistochemical analysis of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) in osteosarcoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 1990, 19, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, T.; Nomura, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Hashimoto, J.; Hirota, S.; Kitamura, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Ono, K.; Takaoka, K. Transient and localized expression of bone morphogenetic protein 4 messenger RNA during fracture healing. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 9, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, T.; Ishidou, Y.; Nagamine, T.; Yone, K.; Imamura, T.; Kato, M.; Sampath, T.; Dijke, P.T.; Sakou, T. Distinct and Overlapping Patterns of Localization of Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) Family Members and a BMP Type II Receptor During Fracture Healing in Rats. Bone 1998, 22, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, Y.; Bessho, K.; Fujimura, K.; Iizuka, T.; Kusumoto, K.; Ogawa, Y. Expression of bone morphogenetic protein in the course of osteoinduction by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2002, 13, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, M.; Camilliere, J.J. In Vivo Stimulation of Bone Formation by Transforming Growth Factor-? Endocrinology 1989, 124, 2991–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, C.; Yates, A.J.; Mundy, G.R. In vivo effects of human recombinant transforming growth factor β on bone turnover in normal mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 5, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Nishimura, I. Different bone integration profiles of turned and acid-etched implants associated with modulated expression of extracellular matrix genes. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Derynck, R.; Akhurst, R.J. Differentiation plasticity regulated by TGF-β family proteins in development and disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morra, M.; Cassinelli, C.; Cascardo, G.; Fini, M.; Giavaresi, G.; Giardino, R. Covalently-linked hyaluronan promotes bone formation around Ti implants in a rabbit model. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Weng, W.; Li, Z.; Cheng, K.; Du, P.; Shen, G.; Han, G. Electrolytic deposition of octacalcium phosphate/collagen composite coating on titanium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X. Combination of scaffold and adenovirus vectors expressing bone morphogenetic protein-7 for alveolar bone regeneration at dental implant defects. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4635–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovarone, C.V.; Verne’, E.; Robiglio, L.; Appendino, P.; Bassi, F.; Martinasso, G.; Muzio, G.; Canuto, R. Development of glass–ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Characterisation, proliferation of human osteoblasts and nodule formation. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branemark, P.I.; Zarb, G.A.; Albrektsson, T. Procedure chirurgiche. In Osteointegrazione Tissutale. Osteointegrazione in Odontoiatria; Adell, R.U., Lekholm, U., Branemark, P.I., Eds.; Quintessenz Verlags-Gmbh, Special Edition for Nobelpharma: Berlin, Germany, 1987; pp. 211–232. ISBN 3-87652-539-X. [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-Step Method of RNA Isolation by Acid Guanidinium Thiocyanate–Phenol–Chloroform Extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, K.; Troulis, M.; Kaban, L.; Glowacki, J. IGF-I, TGF-β, and BMP-4 are expressed during distraction osteogenesis of the pig mandible. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 31, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; De Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du Sert, N.P.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bialy, I.; Jiskoot, W.; Nejadnik, M.R. Formulation, Delivery and Stability of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins for Effective Bone Regeneration. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1152–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urist, M.R. Bone: Formation by Autoinduction. Science 1965, 150, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargha, R.; Endemann, M.; Kratochwill, K.; Riesenhuber, A.; Wick, N.; Krachler, A.-M.; Malaga-Dieguez, L.; Aufricht, C. Ex vivo reversal of in vivo transdifferentiation in mesothelial cells grown from peritoneal dialysate effluents. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 2943–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mussano, F.; Ciccone, G.; Ceccarelli, M.; Baldi, I.; Bassi, F. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Bone Defects. Spine 2007, 32, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susin, C.; Qahash, M.; Polimeni, G.; Lu, P.H.; Prasad, H.S.; Rohrer, M.D.; Hall, J.; Wikesjö, U.M.E. Alveolar ridge augmentation using implants coated with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-7 (rhBMP-7/rhOP-1): Histological observations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Selph, S.; McDonagh, M.; Peterson, K.; Tiwari, A.; Chou, R.; Helfand, M. Effectiveness and Harms of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in Spine Fusion. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmonds, M.C.; Brown, J.V.; Heirs, M.K.; Higgins, J.P.; Mannion, R.J.; Rodgers, M.A.; Stewart, L.A. Safety and Effectiveness of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 for Spinal Fusion. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leknes, K.N.; Yang, J.; Qahash, M.; Polimeni, G.; Susin, C.; Wikesjö, U.M.E. Alveolar ridge augmentation using implants coated with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-7 (rhBMP-7/rhOP-1): Radiographic observations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlinger, B.; Pilling, E.; Huhle, M.; Mai, R.; Bierbaum, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Kuhlisch, E.; Loukota, R.; Eckelt, U. Evaluation of osseointegration of dental implants coated with collagen, chondroitin sulphate and BMP-4: An animal study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, T.K.; Reddi, A.H. Discovery of bone morphogenetic proteins—A historical perspective. Bone 2020, 140, 115548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.P.; Hammerle, C.H.F.; Bragger, U.; Lehmann, B.; Nyman, S.R. Guided tissue regeneration in jawbone defects prior to implant placement. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1994, 5, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, I.; Salt, S.; Heliotis, M. Successful long-term mandibular reconstruction and rehabilitation using non-vascularised autologous bone graft and recombinant human BMP-7 with subsequent endosseous implant in a patient with bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouly, I.; Pardiñas-López, S.; Ruff, R.R.; Strauss, F.-J. Efficacy of growth factors for the treatment of peri-implant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2141–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Della Bella, E.; Stoddart, M.J. Applications of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Dentistry: A Bibliometric Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, M.; Akamine, A. The Application of Tissue Engineering to Regeneration of Pulp and Dentin in Endodontics. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruber, R.; Kandler, B.; Fuerst, G.; Fischer, M.B.; Watzek, G. Porcine sinus mucosa holds cells that respond to bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-6 and BMP-7 with increased osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, A.; Pezzetti, F.; Brunelli, G.; Muzio, L.L.; Scarano, A.; Scapoli, L.; Martinelli, M.; Arlotti, M.; Guerzoni, L.; Rubini, C.; et al. Short-period Effects of Zirconia and Titanium on Osteoblast MicroRNAs. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2008, 10, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shen, J.; Zhang, P. Adenovirus encoding BMP-7 immobilized on titanium surface exhibits local delivery ability and regulates osteoblast differentiation in vitro. Arc. Oral. Biol. 2013, 58, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kämmerer, P.W.; Pabst, A.M.; Dau, M.; Staedt, H.; Al-Nawas, B.; Heller, M. Immobilization of BMP-2, BMP-7 and alendronic acid on titanium surfaces: Adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Jarsha, M.; Moulisova, V.; Leal-Egana, A.; Connell, A.; Naudi, K.B.; Ayoub, A.; Dalby, M.J.; Salmerón-Sánchez, M. Engineered coatings for titanium implants to present ultra-low doses of BMP-7. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.A.; Jin, Q.; Taba, M.; Franceschi, R.T.; Rutherford, R.B.; Giannobile, W.V. BMP gene delivery for alveolar bone engineering at dental implant defects. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Eap, S.; Schiavi, J.; Huck, O.; Jacomine, L.; Gauthier, C.; Sebastian, V.; Schwinté, P.; Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Fioretti, F. A living thick nanofibrous implant bifunctionalized with active growth factor and stem cells for bone regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimono, K.; Oshima, M.; Arakawa, H.; Kimura, A.; Nawachi, K.; Kuboki, T. The effect of growth factors for bone augmentation to enable dental implant placement: A systematic review. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2010, 46, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haimov, H.; Yosupov, N.; Pinchasov, G.; Juodzbalys, G. Bone Morphogenetic Protein Coating on Titanium Implant Surface: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2017, 8, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirano, F.R.; Togashi, A.Y.; Marques, M.M.; Pustiglioni, F.E.; Lima, L.A.P.A. Role of rhBMP-2 and rhBMP-7 in the Metabolism and Differentiation of Osteoblast-Like Cells Cultured on Chemically Modified Titanium Surfaces. J. Oral Implant. 2014, 40, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luginbuehl, V.; Meinel, L.; Merkle, H.P.; Gander, B. Localized delivery of growth factors for bone repair. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.J.; Liao, S.; Chan, C.K. Controlled release of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-7 in nanoscaffolds. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.W.-H.; Ulery, B.D.; Ashe, K.M.; Laurencin, C.T. Studies of bone morphogenetic protein-based surgical repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-David, D.; Srouji, S.; Shapira-Schweitzer, K.; Kossover, O.; Ivanir, E.; Kuhn, G.; Müller, R.; Seliktar, D.; Livne, E. Low dose BMP-2 treatment for bone repair using a PEGylated fibrinogen hydrogel matrix. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, J.; Keller, L.; Morand, D.-N.; De Isla, N.; Huck, O.; Lutz, J.C.; Mainard, D.; Schwinté, P.; Benkirane-Jessel, N. Active implant combining human stem cell microtissues and growth factors for bone-regenerative nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeherman, H.; Wozney, J.M. Delivery of bone morphogenetic proteins for orthopedic tissue regeneration. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, J.F.; Silva, G.A.; Azevedo, H.S.; Malafaya, P.B.; Sousa, R.A.; Silva, S.S.; Boesel, L.F.; Oliveira, J.M.; Santos, T.C.; Marques, A.P.; et al. Natural origin biodegradable systems in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Present status and some moving trends. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 999–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Q.M.; Takita, H.; Kohgo, T.; Atsumi, K.; Itoh, H.; Kuboki, Y. Effects of geometry of hydroxyapatite as a cell substratum in BMP-induced ectopic bone formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, P.C.; Casal, M.; Reis, R.L. Bone morphogenetic proteins in tissue engineering: The road from laboratory to clinic, part II (BMP delivery). J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2008, 2, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, B.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, T.; Cheng, X. The synergetic bone-forming effects of combinations of growth factors expressed by adenovirus vectors on chitosan/collagen scaffolds. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, M. Collagen sponges for bone regeneration with rhBMP-2. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Shin, H. Matrices and scaffolds for delivery of bioactive molecules in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 339–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, Z.S.; Hamdy, R.C.; Tabrizian, M. Delivery of recombinant bone morphogenetic proteins for bone regeneration and repair. Part B: Delivery systems for BMPs in orthopaedic and craniofacial tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, U.; Vukicevic, S. Bone morphogenetic protect. ins: From developmental biology to molecular therapeutics. South Afr. J. Sci 1995, 91, 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Blokhuis, T.J.; Patka, P.; Haarman, H.J.T.M.; Giltaij, L.R. Osteogenic Protein-1 (OP-1, BMP-7) for Stimulation of Healing of Closed Fractures: Evidence Based Medicine and Pre-Clinical Experience. In Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. From Laboratory to Clinical Practice; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 145–155. ISBN 978-3-0348-8121-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ripamonti, U.; Heliotis, M.; Ferretti, C. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and the Induction of Bone Formation: From Laboratory to Patients. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2007, 19, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautschi, O.P.; Frey, S.P.; Zellweger, R. BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTEINS IN CLINICAL APPLICATIONS. ANZ J. Surg. 2007, 77, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatakun, P.; Núñez-Toldrà, R.; López, E.J.D.; Gil-Recio, C.; Martínez-Sarrà, E.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Ferrés-Padró, E.; Giner-Tarrida, L.; Atari, M. The effect of five proteins on stem cells used for osteoblast differentiation and proliferation: A current review of the literature. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.J.; Reyes, C.D. Bio-adhesive Surfaces to Promote Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Hernández, V.; Cantini, M.; González-García, C.; Cheng, Z.A.; Yang, J.; Tsimbouri, P.M.; García, A.J.; Dalby, M.J.; Salmerón-Sánchez, M. Material-driven fibronectin assembly for high-efficiency presentation of growth factors. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, T. Biochemical surface modifications to titanium implants using the tresyl chlorideactivated method. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Lee, W.-F.; Feng, S.-W.; Huang, H.-M.; Lin, C.-T.; Teng, N.-C.; Chang, W.J. In Vitro Analysis of Fibronectin-Modified Titanium Surfaces. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Yang, P.; Guo, X.; Huang, N.; Shen, R. An in vitro evaluation of inflammation response of titanium functionalized with heparin/fibronectin complex. Cytokine 2011, 56, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, C.R.; Gaifem, J.; Oliveira, M.B.; Silvestre, R.; Mano, J.F. The influence of surface modified poly(l-lactic acid) films on the differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.K.; Kleinert, L.B.; Hagen, K.M.; Clapper, D.L. Covalent modification of porous implants using extracellular matrix proteins to accelerate neovascularization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 78, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, A.; Lojudice, F.; Halcsik, E.; Navarro, R.; Sogayar, M.; Granjeiro, J. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shi, P.; Tu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Fan, F.; Du, M. Bone morphogenetic proteins: Relationship between molecular structure and their osteogenic activity. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2014, 3, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houde, N.; Chamoux, E.; Bisson, M.; Roux, S. Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β1) Induces Human Osteoclast Apoptosis by Up-regulating Bim. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23397–23404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oursler, M.J. Osteoclast synthesis and secretion and activation of latent transforming growth factor β. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 9, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierano, G.; Pejrone, G.; Roana, J.; Scalas, D.; Allizond, V.; Martinasso, G.; Pagano, M.; Canuto, R.; Cuffini, A. A Split-Mouth Study on Microbiological Profile in Clinical Healthy Teeth and Implants Related to Key Inflammatory Mediators. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniatowski, Ł.; Wojdasiewicz, P.; Gasik, R.; Szukiewicz, D. Transforming Growth Factor Beta Family: Insight into the Role of Growth Factors in Regulation of Fracture Healing Biology and Potential Clinical Applications. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Gomi, K. Bone response of TGF-β2 immobilized titanium in a rat model. Dent. Mater. J. 2014, 33, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komori, T. What is the function of osteocalcin? J. Oral Biosci. 2020, 62, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, R.; Dolder, J.V.D.; Bierbaum, S.; Beutner, R.; Scharnweber, D.; Jansen, J.; Beckmann, F.; Worch, H. Osteoconductive modifications of Ti-implants in a goat defect model: Characterization of bone growth with SR μCT and histology. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3009–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Kirk, M.; Kahn, A.J. The role of type I collagen in the regulation of the osteoblast phenotype. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 11, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelt, S.; Schulze, E.; Bernhardt, R.; Hanisch, U.; Scharnweber, D.; Worch, H.; Zwipp, H.; Biewener, A. Coating of titanium implants with type-I collagen. J. Orthop. Res. 2004, 22, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliephake, H.; Aref, A.; Scharnweber, D.; Bierbaum, S.; Roessler, S.; Sewing, A. Effect of immobilized bone morphogenic protein 2 coating of titanium implants on peri-implant bone formation. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaoita, H.; Orimo, H.; Shirai, Y.; Shimada, T. Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins and rat distal-less homolog genes following rat femoral fracture. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2000, 18, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, N.; Cooper, G.; Marra, K. Chondrogenesis, bone morphogenetic protein-4 and mesenchymal stem cells. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkwood, K.; Rheude, B.; Kim, Y.J.; White, K.; Dee, K.C. In Vitro Mineralization Studies with Substrate-immobilized Bone Morphogenetic Protein Peptides. J. Oral Implant. 2003, 29, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, H.-D.; Kang, A.-R.; Kyung, H.-M.; Sung, J.-H.; Wozney, J.M.; Ryoo, H.-M. BMP-2-induced Runx2 Expression Is Mediated by Dlx5, and TGF-β1 Opposes the BMP-2-induced Osteoblast Differentiation by Suppression of Dlx5 Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34387–34394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wan, J.; Jiang, D.; Wu, X. BMP-7 counteracts TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. J. Nephrol. 2009, 22, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, G.; An, G.; Li, X.; Niu, P.; Chen, L.; Tian, L. BMP-7 attenuated silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of the balance between TGF-β/Smad and BMP-7/Smad signaling pathway. Chem. Interactions 2016, 243, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zai-Chun, X.; Wun-Lun, H.; Yun-Yun, Z. BMP-7 Attenuates TGF-β1-Induced Fibronectin Secretion and Apoptosis of NRK-52E Cells by the Suppression of miRNA-21. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2016, 23, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Gene | Accession Number | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| BMP-4 (SUS SCROFA) | [21] | FW 5′-CTCGCTCTATGTGGACTTC-3′ RV 5′-ATGGTTGGTTGAGTTGAGG-3′ |
| TGF-β2 (HOMO SAPIENS) | AY438979 | FW 5′-GAGACTTGATTGTCCTTCCTTC-3′ RV 5′-CTCCCCGAACCGTTGAGG-3′ |
| IL-1β (SUS SCROFA) | NM_001005149 | FW 5′-GGGGACTTGAAGAGAGAA-3′ RV 5′-CATCACACAAGACAGGTACAGA-3′ |
| OSTEOCALCIN (SUS SCROFA) | AY150038 | FW 5′-TATGGCATAGCCTAGACCTC-3′ RV 5′-GATGATGGGGACCTTACACTT-3′ |
| BMP-7 (HOMO SAPIENS) | NM_001719 | FW 5′-GTGGAACATGACAAGGAAT-3′ RV 5′-GAAAGATCAAACCGGAAC-3′ |
| GAPDH (HOMO SAPIENS) | NM_002046 | FW 5′-TGAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGT-3′ RV 5′-CATGTGGGCCATGAGGTCCACCAC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schierano, G.; Canuto, R.A.; Mauthe von Degerfeld, M.; Navone, R.; Peirone, B.; Preti, G.; Muzio, G. Role of rhBMP-7, Fibronectin, And Type I Collagen in Dental Implant Osseointegration Process: An Initial Pilot Study on Minipig Animals. Materials 2021, 14, 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092185
Schierano G, Canuto RA, Mauthe von Degerfeld M, Navone R, Peirone B, Preti G, Muzio G. Role of rhBMP-7, Fibronectin, And Type I Collagen in Dental Implant Osseointegration Process: An Initial Pilot Study on Minipig Animals. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092185
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchierano, Gianmario, Rosa Angela Canuto, Mitzy Mauthe von Degerfeld, Roberto Navone, Bruno Peirone, Giulio Preti, and Giuliana Muzio. 2021. "Role of rhBMP-7, Fibronectin, And Type I Collagen in Dental Implant Osseointegration Process: An Initial Pilot Study on Minipig Animals" Materials 14, no. 9: 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092185
APA StyleSchierano, G., Canuto, R. A., Mauthe von Degerfeld, M., Navone, R., Peirone, B., Preti, G., & Muzio, G. (2021). Role of rhBMP-7, Fibronectin, And Type I Collagen in Dental Implant Osseointegration Process: An Initial Pilot Study on Minipig Animals. Materials, 14(9), 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092185