Evolution of the Numerical Model Describing the Distribution of Non-Metallic Inclusions in the Tundish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Object of Research
2.2. Models Description Used in Current CFD Calculations
2.3. Numerical Modeling
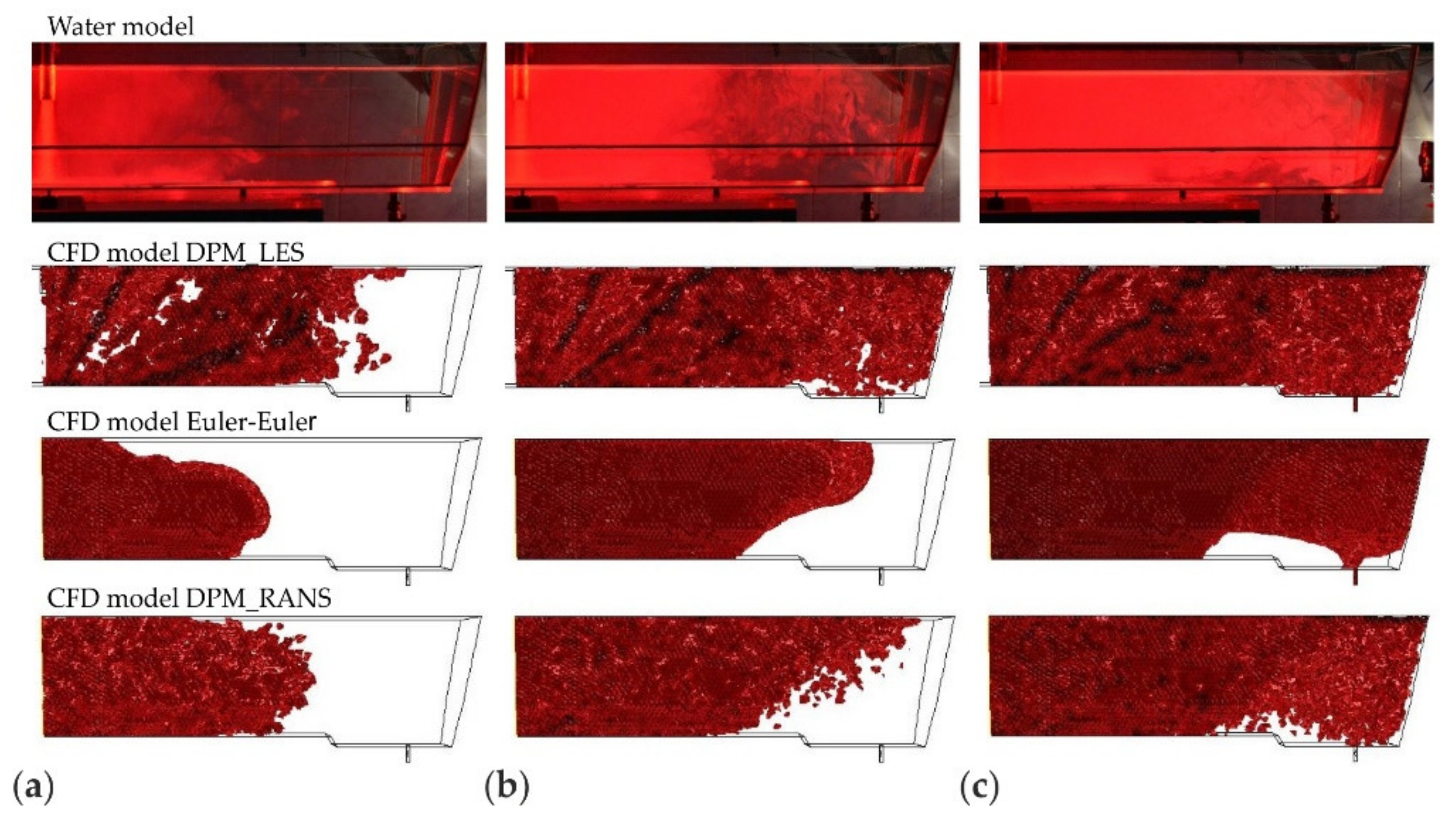
2.4. Physical Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
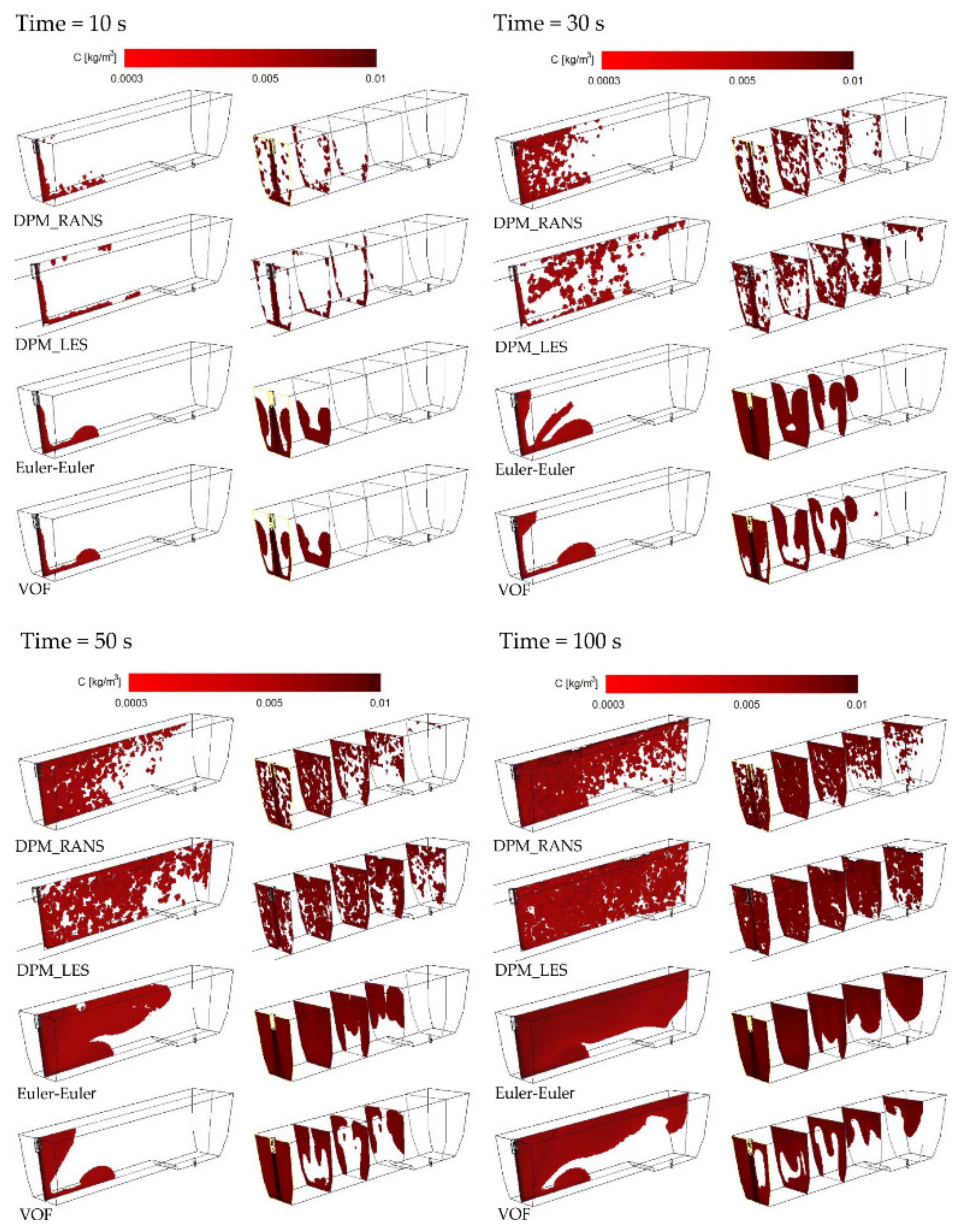
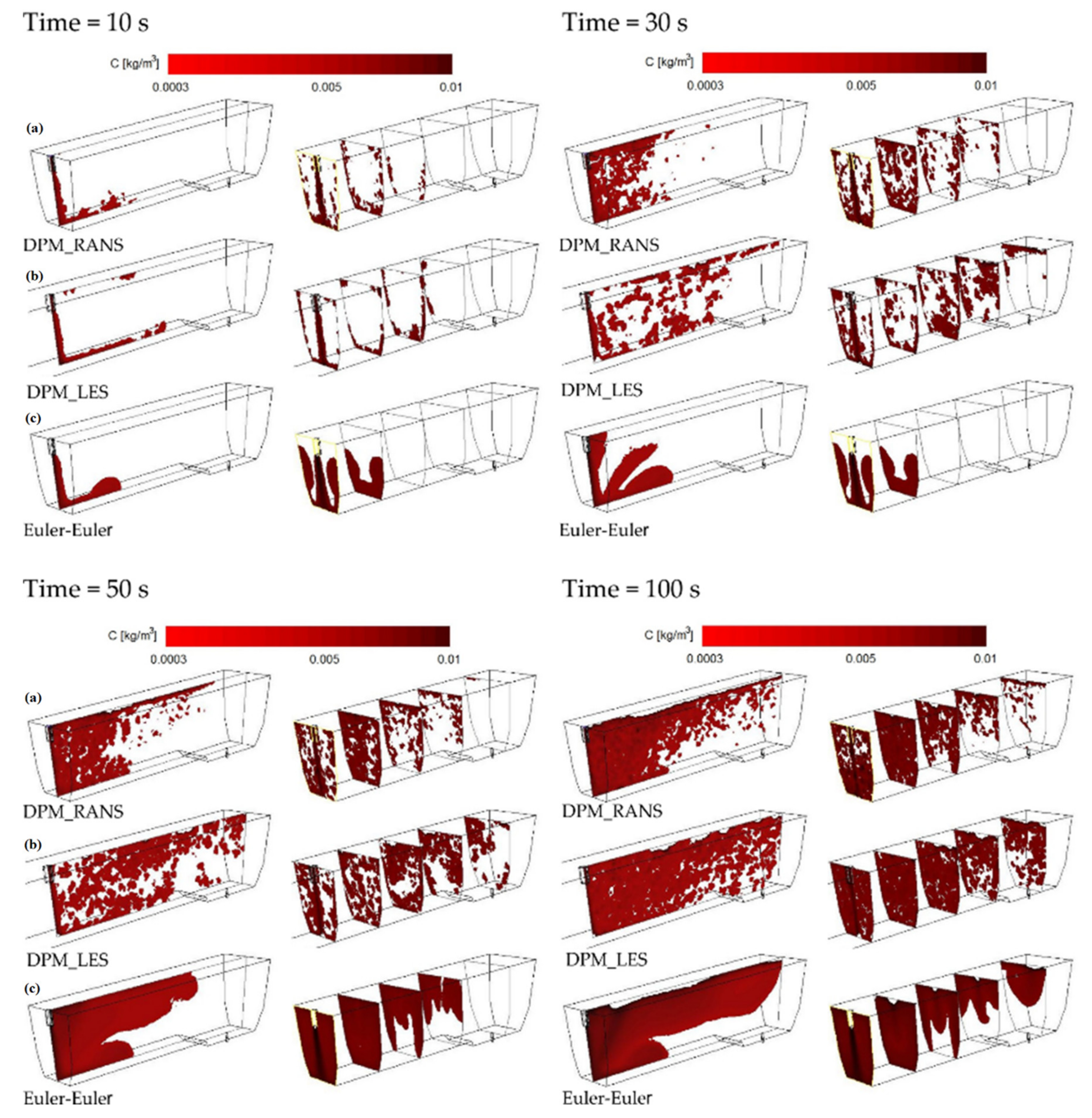
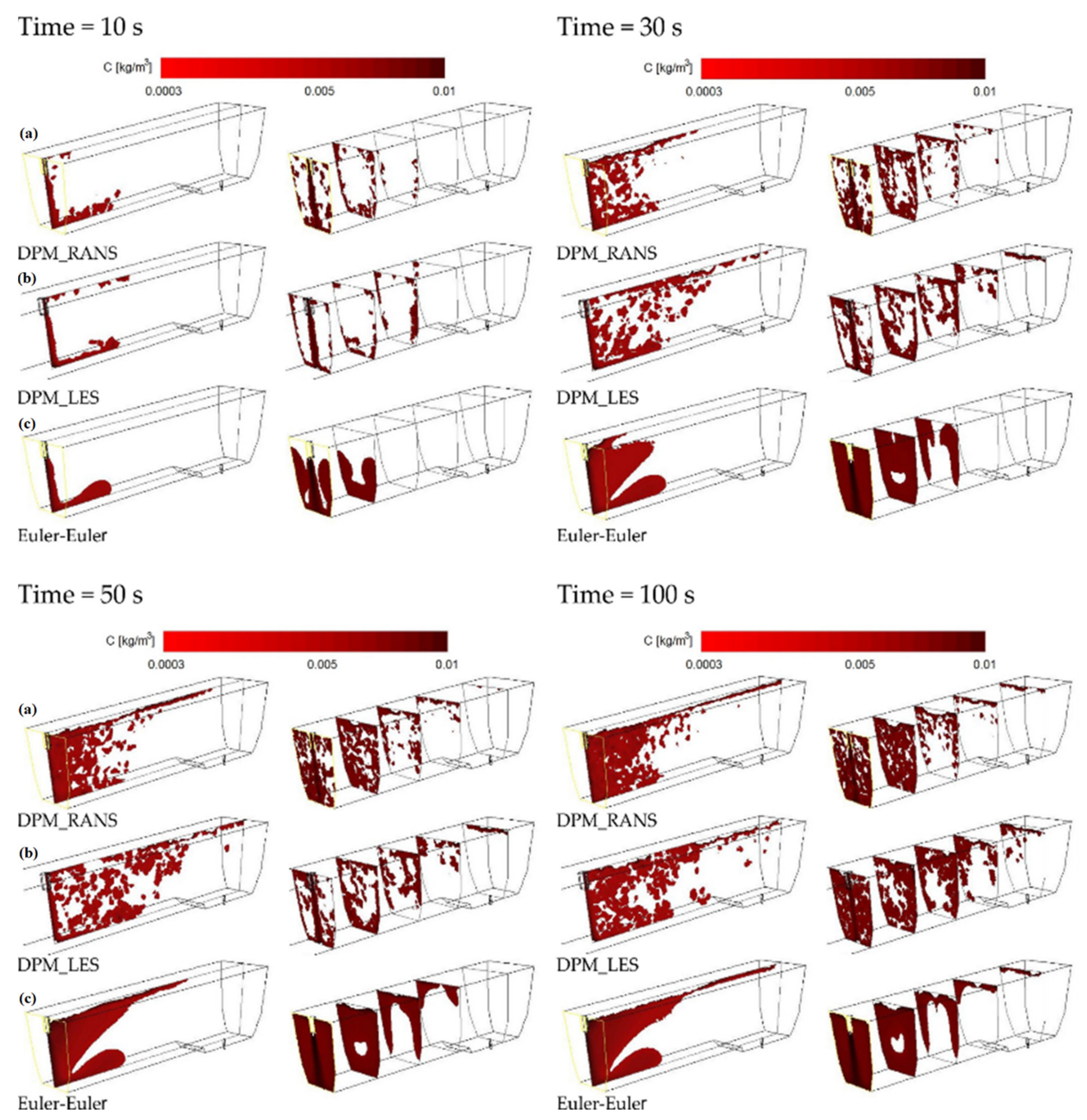
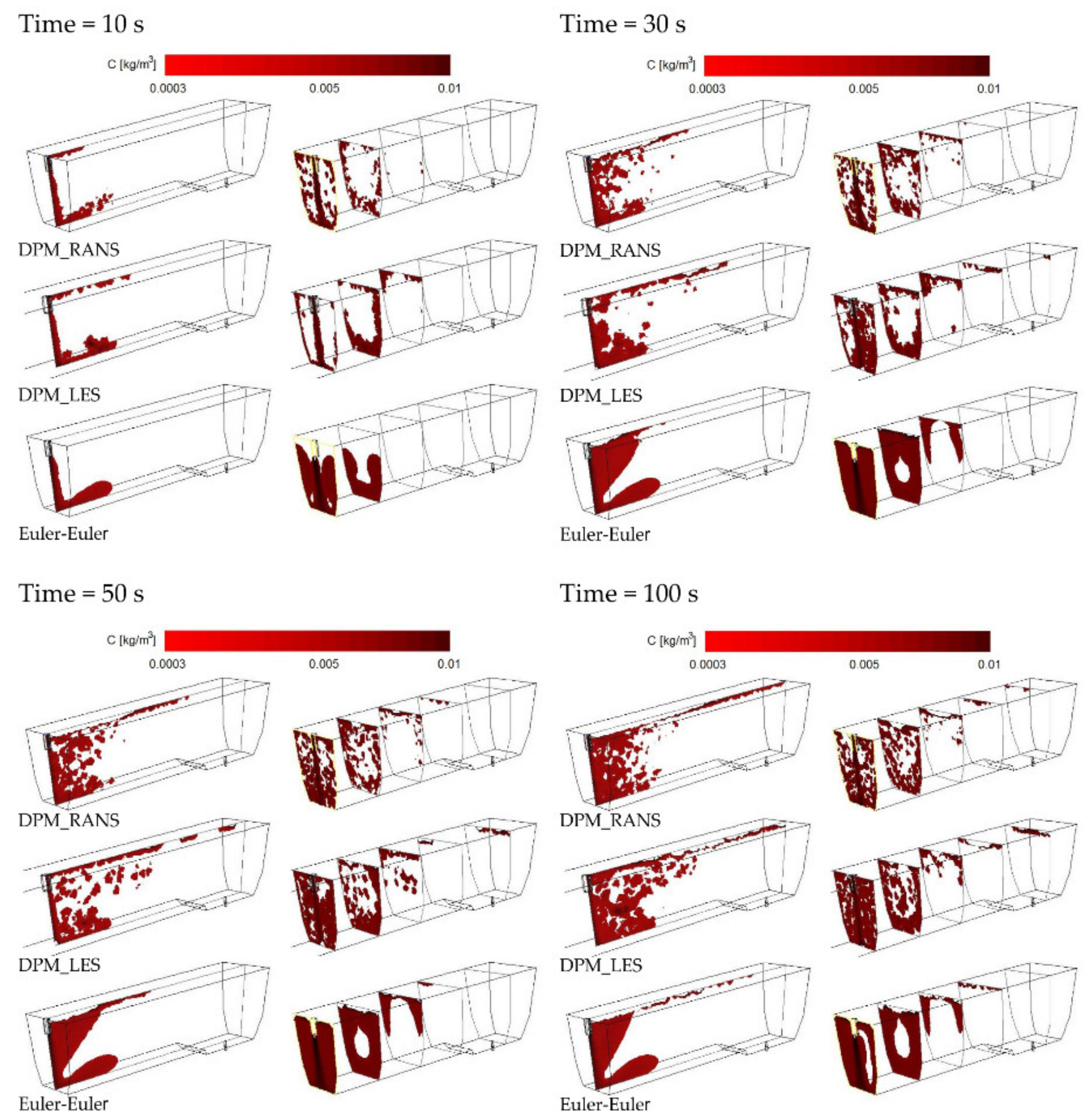
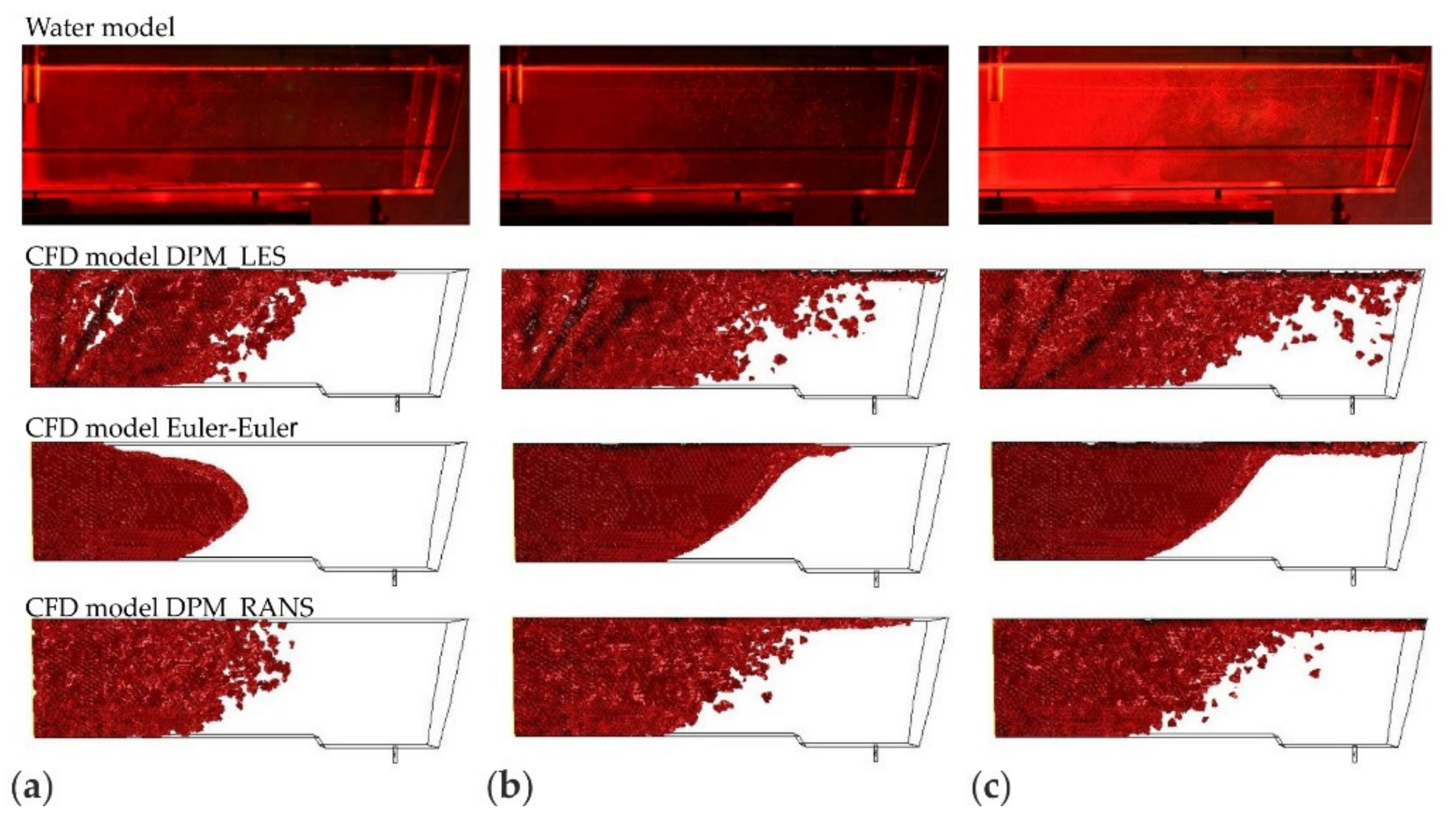
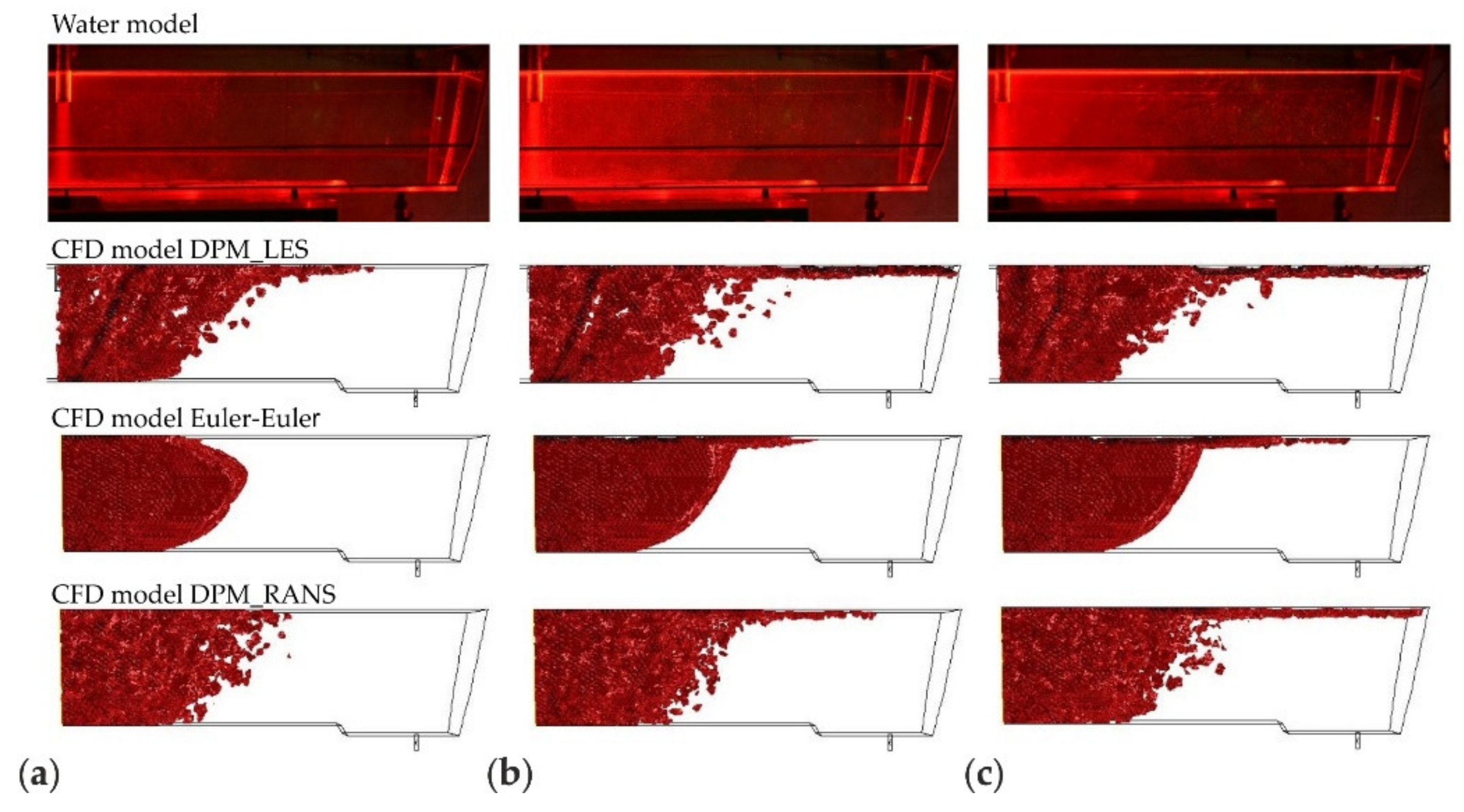
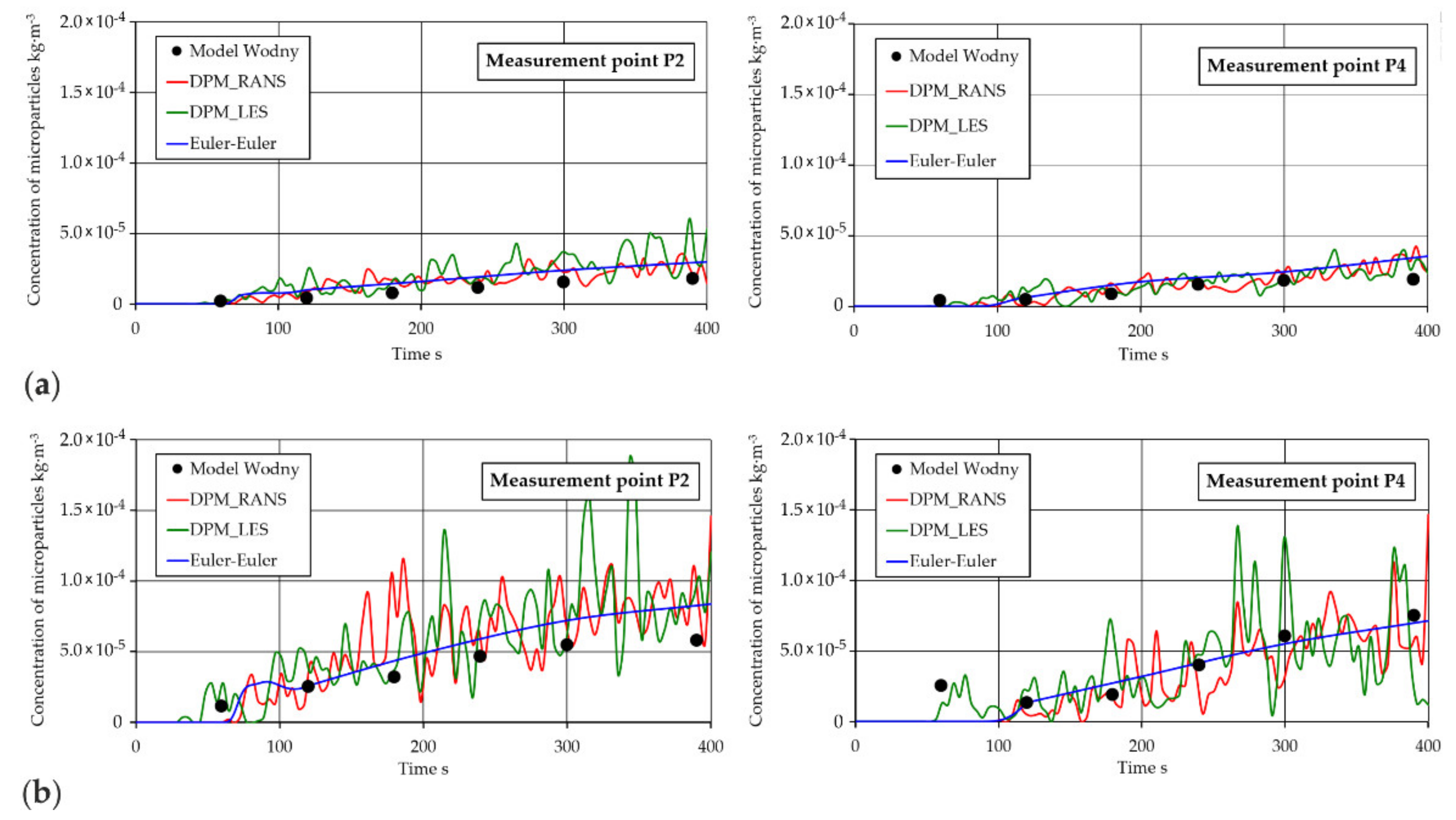
3.1. Results and Validation of Microparticles Distribution in the Tundish Model
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- the process of microparticle distribution is best described by the Euler–Lagrange method,
- distribution characteristics and local concentrations of microparticles, determined on the basis of the DPM model, reflect the empirical distribution with a high accuracy,
- the distribution of microparticles depends on the velocity of the liquid flow and thus differs for the different flow zones in the tundish,
- microparticles of a size of 20 µm generally move at the tundish bottom,
- microparticles of a size of 50 µm flow considerably slower and essentially fill the whole available working space of the tundish,
- large microparticles (with a size of 100 and 140 μm) are characterized by fast flowing up to the free surface,
- turbulent flow in the infusion zone promotes the discharge of microparticles, especially of small sizes (20 µm).
- The investigation results reported in this paper constitute the first stage of a larger research program, which envisages comprehensive studies of the distribution of nonmetallic inclusions in steel flowing though the tundish. The developed and improved model will include a modified boundary condition at the liquid-gas interface (liquid free surface), which describes whether a particle is reflected or absorbed by the surface, depending on the critical velocity of each particle that reaches the free surface. This condition will be introduced with the user-defined function UDF. We will as also modify a tool for carrying out tests for the optimization of flow in the tundish working space using flow control devices. These tests will aim to improve the hydrodynamic conditions in tundishes in terms of enhancing their liquid steel refining capabilities. The effect of this will be the obtaining of high metallurgical purity of continuously casted steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Du, L.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Hydrodynamic and mathematical simulations of flow field andtemperature profile in an asymmetrical t-type single-strand continuous casting Tundish. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Li, D.; Chattopadhyay, K. Modeling of liquid steel/slag/argon gas multiphase flow during tundish open eye formation in a two-strand tundish. Metall. Meter. Trans. B 2018, 49, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Jha, P.K.; Sharma, S.C.; Ajamani, S.K. Numerical investigation of the effect of transitory strand opening on mixing in a multistrand tundish. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2011, 18, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Ajmani, S.K. Effect of shape and flow control devices on the fluid flow characteristics in three different industrial six strand billet caster tundish. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cwudziński, A. Numerical and physical modelling of liquid steel active flow in tundish with subflux turbulence controller and dam. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, R.; Haubold, D.; Kratzsch, C. Numerical study of effects of pour box design on tundish flow characteristics. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2015, 42, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudzinski, A. Physical and mathematical modeling of bubbles plume behaviour in one strand tundish. Metall. Res. Technol. 2018, 115, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lei, H.; Bi, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.A. Fluid flow and heat transfer in a tundish with channel type induction heating. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BuIko, B.; Priesol, I.; Demeter, P.; Gasparovic, P.; Baricova, D.; Hrubovcakova, M. Geometric modification of the tundish impact point. Metals 2018, 8, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ai, X.; Han, D.; Li, S.; Zeng, H.; Li, H. Optimization of flow uniformity control device for six-stream continuous casting tundish. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wang, M.; Pan, M.; Ba, Y. Optimization of large capacity six-strand tundish with flow channelfor adapting situation of fewer strands casting. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramirez, S.; Barreto, J.J.; Palafox-Ramos, J.; Morales, R.D.; Zacharias, D. Modeling study of the influence of turbulence inhibitors on the molten steel flow, tracer dispersion, and inclusion trajectories in tundishes. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Know, Y.; Zang, J.; Lee, H.G. Water model and CFD studies of bubble dispersion and inclusion removal in continuous casting mould of steel. ISIJ Int. 2006, 46, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, R. Water modelling experiments of argon bubbling curtain in a slab continuous casting tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Banderas, A.; Morales, R.D.; Baretto, J.; Solorio- Diaz, G. Modelling study of inclusions removal by bubble flotation in the tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakata, Y.; Sung, M.G.; Sassa, K.; Asai, S. Visualization of collision behavior of participle simulating inclusions in a turbulent molten steel flow and is theoretical analysis. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, D.; Mazumdar, D.; Patil, S.P. Physical and mathematical modelling of two-phase flow in a hollow jet nozzle. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzecha, M.; Merder, T.; Warzecha, P.; Stradomski, G. Experimental and numerical investigations on non-metallic inclusions distribution in billets casted at a multi-strand continuous casting tundish. ISIJ Int. 2013, 11, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vakhrushev, A.; Wu, M.; Ludwig, A.; Nitzl, G.; Tang, Y.; Hackl, G.; Wincor, R. Water experiment benchmark to evaluate numerical models for the motion of particles in continuous casting tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, D.; Qiu, S.; Zou, Z. Effect of tunnel filters on flow characteristics in an eight trand tundish. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Cao, X.; Hsin, C.H.; Zou, Z.; Isac, M.; Guthrie, R.I.L. Removal of inclusions using micro-bubble swarms in a four-strand, full-scale, water model tundish. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeidy Pour, M.A.; Hassanpour, S. Steel cleanliness depends on inflow turbulenceintensity (in tundishes and molds). Metall. Meter. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; He, P.; Zhai, Y.C. Removal behavior of inclusions in molten steel by bubble wake flow based on water model experiment. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, C.M.; Shie, R.J.; Hwang, W.S. Studies by mathematical and physical modelling of fluid flow and inclusion removal phenomena in slab tundish for casting stainless steel using various flow control device designs. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2003, 30, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merder, T.; Warzecha, M.; Warzecha, P.; Pieprzyca, J.; Hutny, A. Modeling research technique of nonmetallic inclusions dis-tribution in liquid steel during its flow through the tundish water model. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, B.M.; Tavares, R.P. Similarity criteria for the study of removal of spherical non-metallic inclusions in physical models of continuous casting tundishes: A more fundamental approach. Metall. Meter. Trans. B 2018, 49, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, Y.; Emi, T. Tundish Technology for Clean Steel Production; World Scientific Publishing, Co. Pte. Ltd.: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, C.; Sommerfeld, M.; Tsuji, Y. Multiphase Flows with Droplets and Particles; CRC Press: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, D.Y. Mathematical modelling of multiphase flow and inclusion behavior in a single-strand tundish. Metals 2020, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkadleckova, K.; Walek, M.; Michalek, J.; Huczala, K.T. Numerical analysis of rtd curves and inclusions removal in a multi-strand asymmetric tundish with different configuration of impact pad. Metals 2020, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Jonsson, L.T.I.; Ersson, M.; Jönsson, P.G. Application of a swirling flow producer in a conventional tundish during continuous casting of steel. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar-Rodriguez, C.E.; Ramos-Banderas, J.A.; Torres-Alonso, E.; Solorio-Diaz, G.; Hernández-Bocanegra, C.A. Flow characterization and inclusions removal in a slab tundish equipped with bottom argon gas feeding. Metallurgist 2018, 61, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, X. Flow transport and inclusion motion in steel continuous casting mould under submerged entry clogging condition. Metall. Meter. Trans. B 2008, 39, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückert, A.; Warzecha, M.; Koitzsch, R.; Pawlik, M.; Pfeifer, H. Particle distribution and separation in continuous casting tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2009, 80, 568–574. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Mathematical modeling on the growth and removal of non-metallic inclusions in the molten steel in a two-strand continuous casting tundish. Metall. Meter. Trans. B 2016, 47, 2991–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkoglu, H.; Farouk, B. Numerical computations of fluid flow and heat transfer in a gas-stirred liquid bath. Metall. Meter. Trans. B 1990, 21B, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Fluent Ver. 16.0—User’s Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2015.
- Morsi, S.A.; Alexander, A.J. An investigation of participle trajectories in two-phase flow system. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 55, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD; DCW Industries, Inc.: La Canada, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Direct Modeler—User’s Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2013.
- Pope, S.B. Ten questions concerning the Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flows. New J. Phys. 2004, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merder, T. Numerical analysis of the liquid flow structure in the tundish with physical model verification. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2018, 63, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Michalek, K. The Use of Physical Modeling and Numerical Optimization for Metallurgical Processes; Publishing of the VSB: Ostrawa, Czech Republic, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Information Materials 3M_Glass-Bubbles. Available online: https://www.3m.com/3M/en_US/company-us/all-3m-products/~/3M-Glass-Bubbles-K1/ (accessed on 15 May 2016).
- Information Materials Markus Klotz GmbH—Abakus Mobil Fluid. Available online: https://www.fa-klotz.de/particlecounters/ (accessed on 20 February 2021).
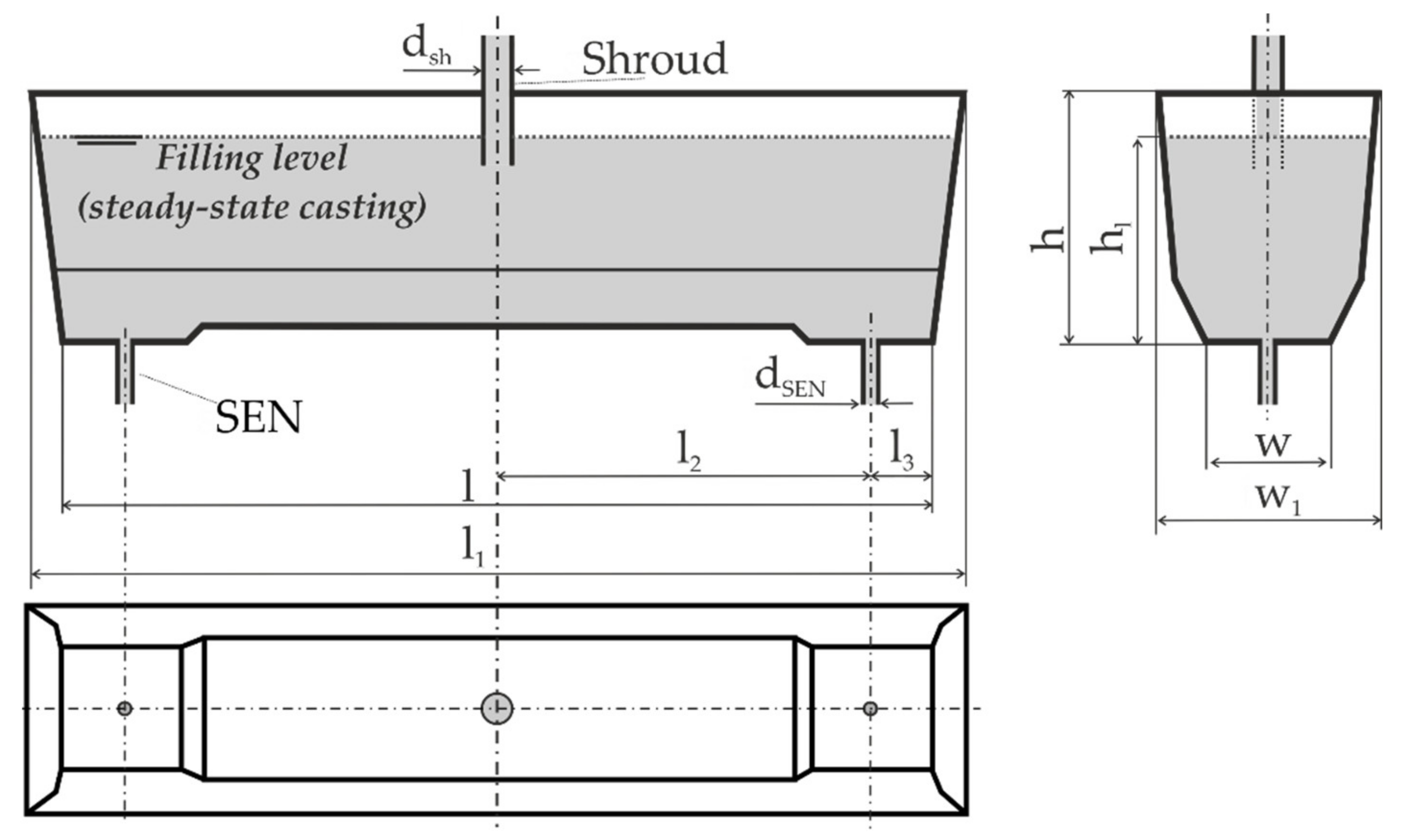
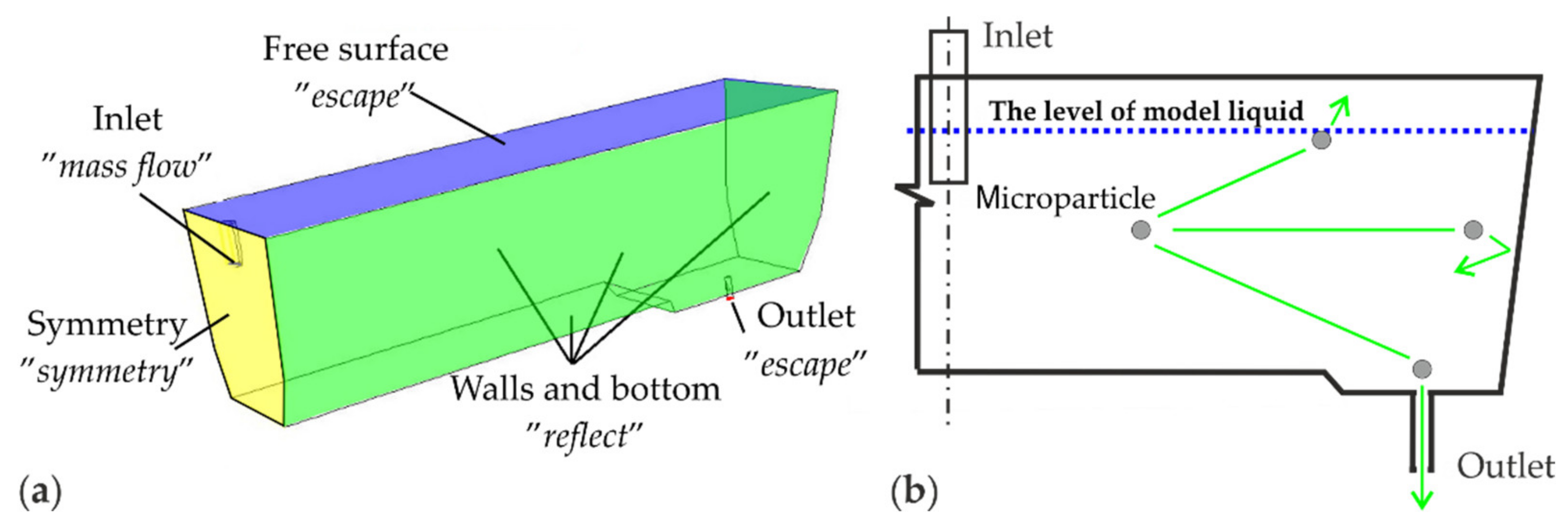
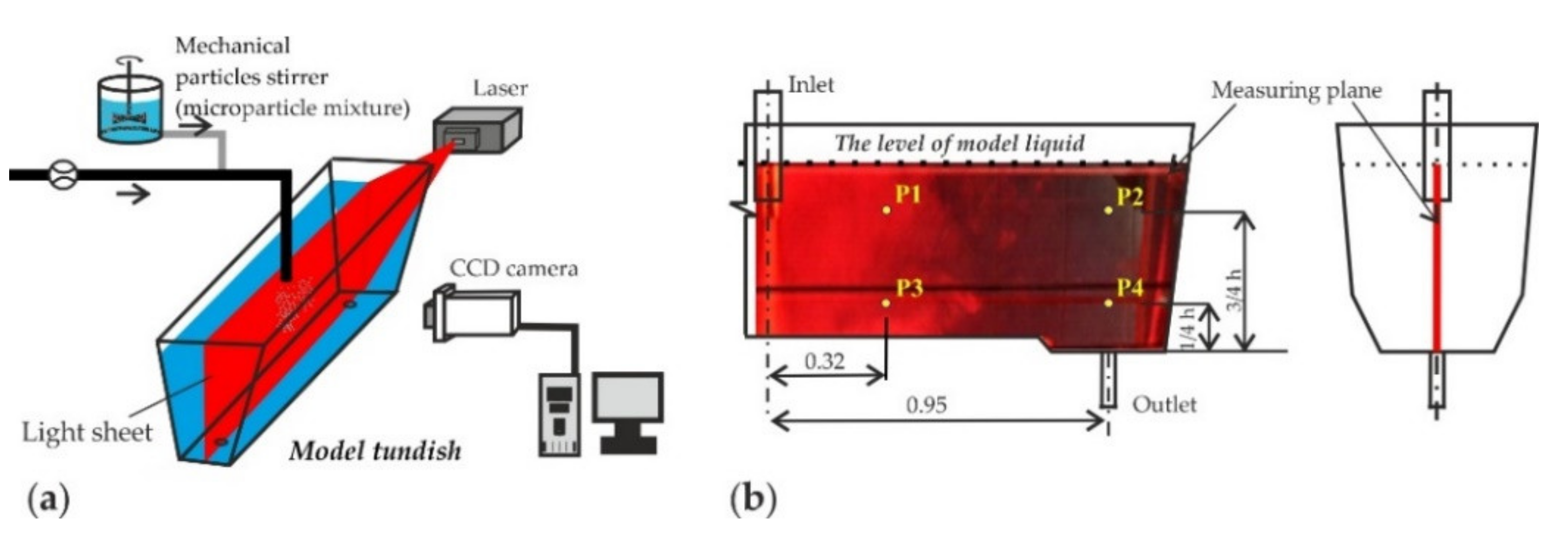

| Parameter/Unit | Symbol | Tundish | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | Model Scale 1:4 | ||
| Volume, m3 | V | 8.550 | 0.130 |
| Height (filling level), m | hl | 1.200 | 0.300 |
| Height, m | h | 1.460 | 0.365 |
| Length, m | l | 7.600 | 1.900 |
| l1 | 8.160 | 2.040 | |
| Width, m | w | 0.720 | 0.180 |
| w1 | 1.260 | 0.315 | |
| Outlet (SEN) position location, m | l2 | 3.800 | 0.950 |
| l3 | 0.400 | 0.100 | |
| Inlet (shroud) diameter, m | dsh | 0.052 | 0.013 |
| Outlets (SENs) diameter, m | dSEN | 0.090 | 0.023 |
| Parameter | CFD Simulation Variants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPM_RANS | DPM_LES | Euler–Euler | VOF | |
| Investigated object | half of the object | entire facility | half of the object | half of the object |
| Mesh Size | 282,000 | 550,400 | 282,000 | 282,000 |
| Mesh Quality criterion | QEAS = 0.5 | Mp = 0.175 | QEAS = 0.5 | QEAS = 0.5 |
| Turbulence method | RANS | LES | RANS | RANS |
| Multiphase flow method | Euler–Lagrange | Euler–Lagrange | Euler–Euler | Euler–Euler |
| Thermal boundary condition | Isothermal | |||
| Volume flow rate (water), m3·s−1 | 1.29 × 10−4 | 2.58 × 10−4 | 1.29 × 10−4 | 1.29 × 10−4 |
| Water density, kg·m−3 | 998.2 | |||
| Water kinetic viscosity, kg·m2·s−1 | 1 × 10−6 | |||
| Microparticles density, kg·m−3 | 120 | |||
| Microparticles diameter, μm | 20, 40, 100, 140 | |||
| Mass flow (microparticles), kg·s−1 | 6.25 × 10−7 | 1.25 × 10−6 | 6.25 × 10−7 | 6.25 × 10−7 |
| Time step, s | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Simulation time, s | 400 | |||
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume flow rate | Qv | m3·s−1 | 2.58 × 10−4 |
| Water density | ρw | kg·m−3 | 998.2 |
| Froude number | Fr | - | 2.10 × 10−5 |
| Microparticles density | ρpar. | kg·m−3 | 120 |
| Microparticles diameter | dpar. | μm | 10 ÷ 140 |
| Ratio density of microparticle to water density | - | - | 0.1202 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merder, T.; Pieprzyca, J.; Warzecha, M.; Warzecha, P.; Hutny, A. Evolution of the Numerical Model Describing the Distribution of Non-Metallic Inclusions in the Tundish. Materials 2021, 14, 2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092229
Merder T, Pieprzyca J, Warzecha M, Warzecha P, Hutny A. Evolution of the Numerical Model Describing the Distribution of Non-Metallic Inclusions in the Tundish. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092229
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerder, Tomasz, Jacek Pieprzyca, Marek Warzecha, Piotr Warzecha, and Artur Hutny. 2021. "Evolution of the Numerical Model Describing the Distribution of Non-Metallic Inclusions in the Tundish" Materials 14, no. 9: 2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092229
APA StyleMerder, T., Pieprzyca, J., Warzecha, M., Warzecha, P., & Hutny, A. (2021). Evolution of the Numerical Model Describing the Distribution of Non-Metallic Inclusions in the Tundish. Materials, 14(9), 2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092229








