Improved Laser Ablation Method for the Production of Luminescent Carbon Particles in Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of the CNPs Colloidal Solutions
3.2. Sample Characterization
4. Results
4.1. Optical Measurements
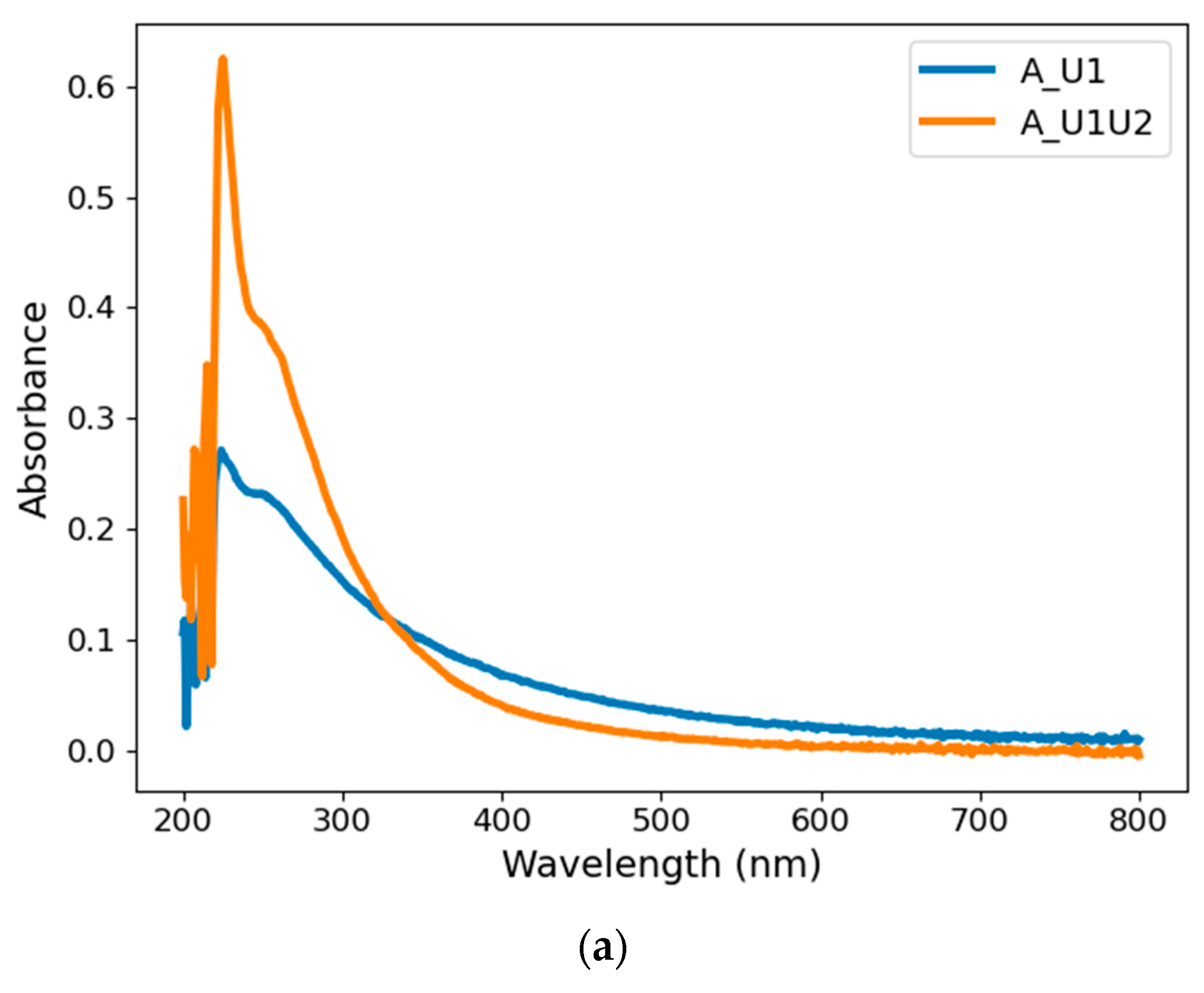
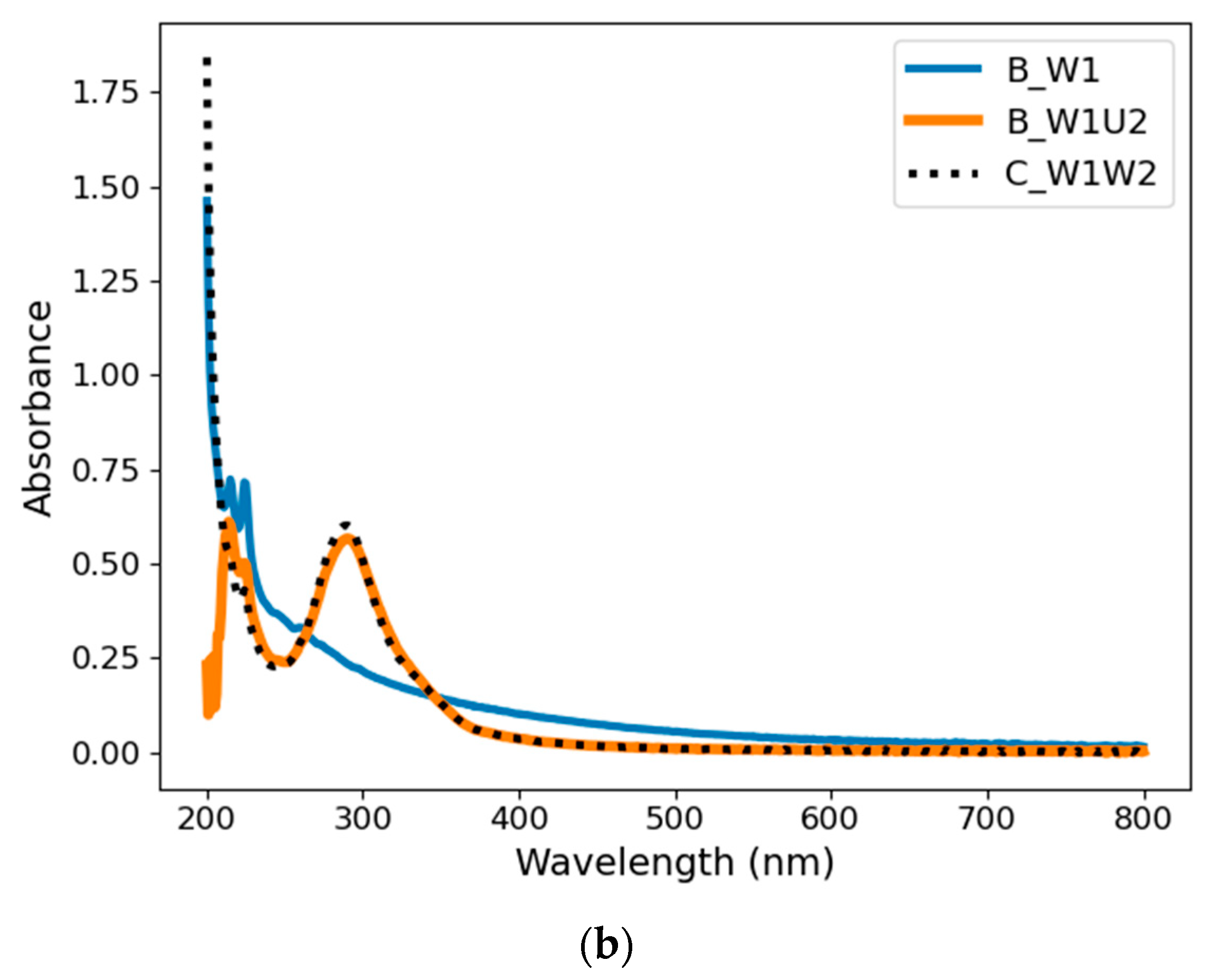
4.1.1. Absorbance
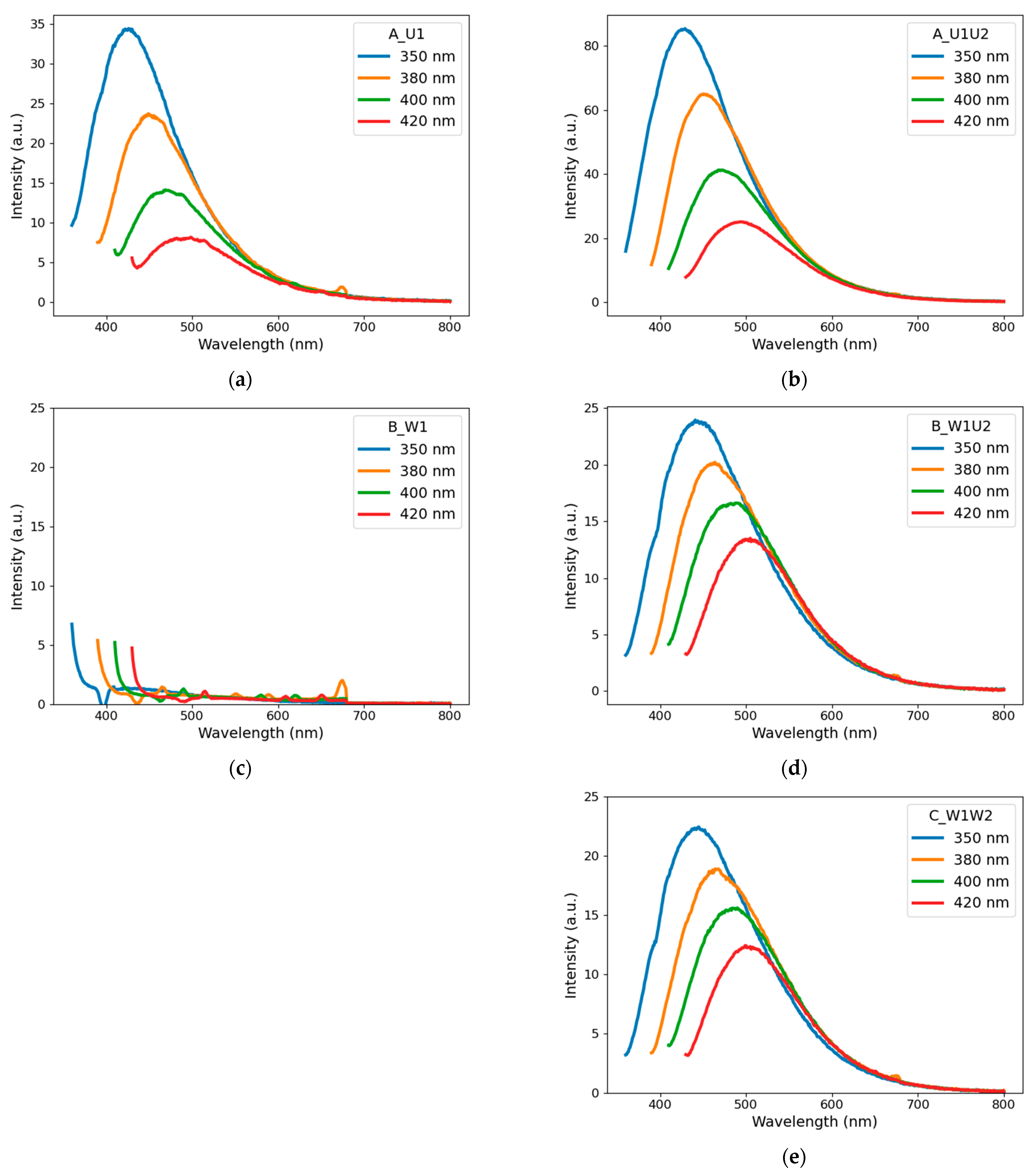
4.1.2. Photoluminescence
4.1.3. Quantum Yield Determination
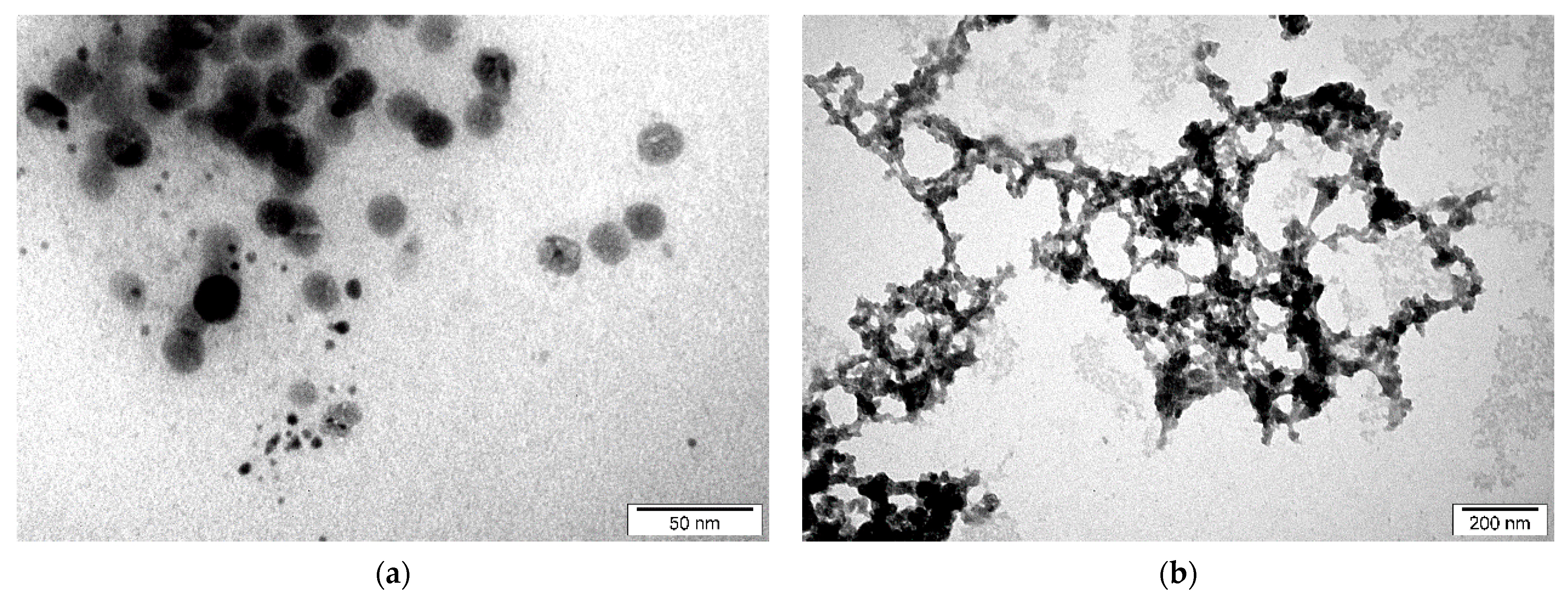
4.2. Morphology and DLS Measurements
4.3. Structural Characterization
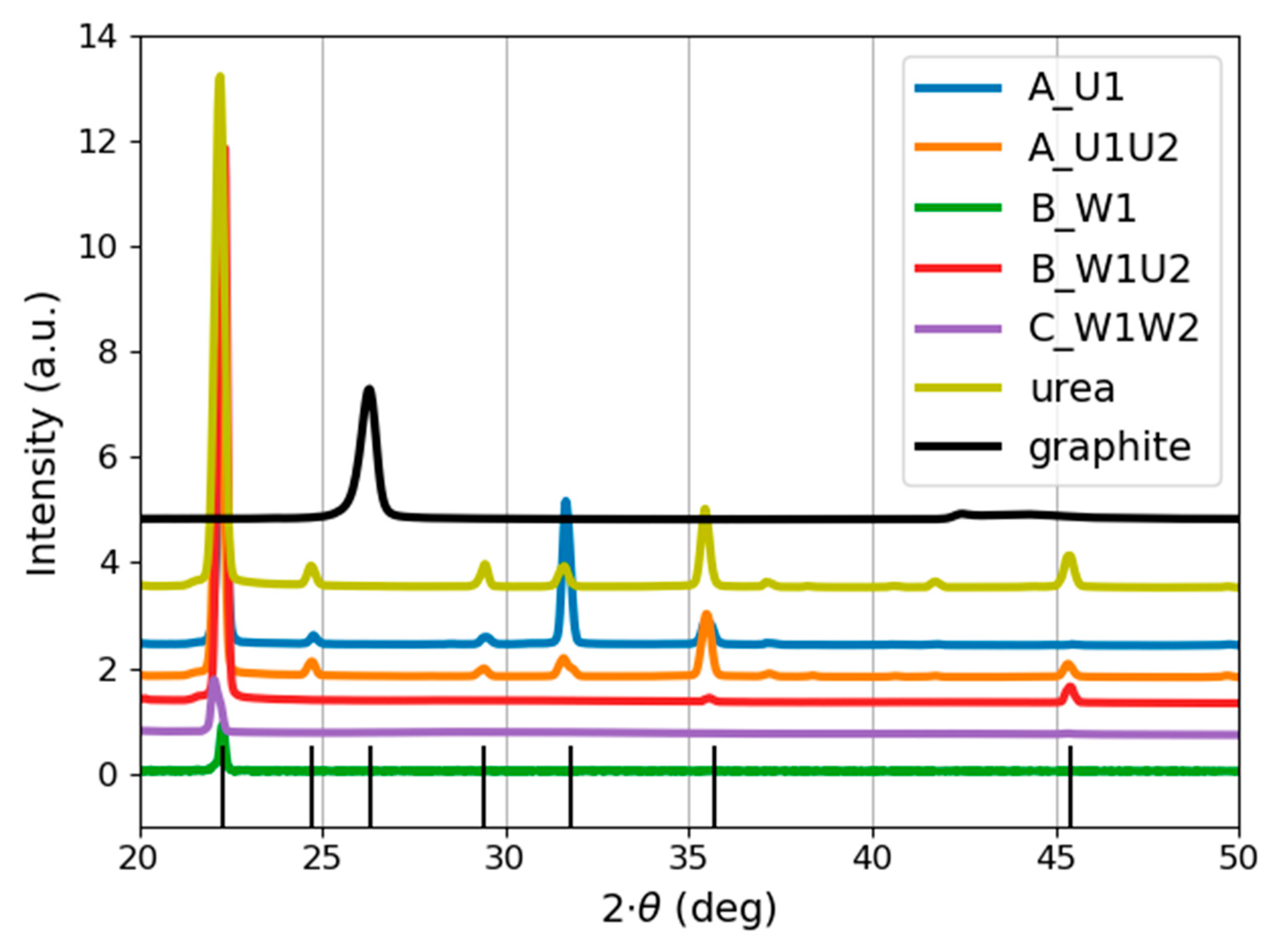
4.3.1. X-ray Diffraction
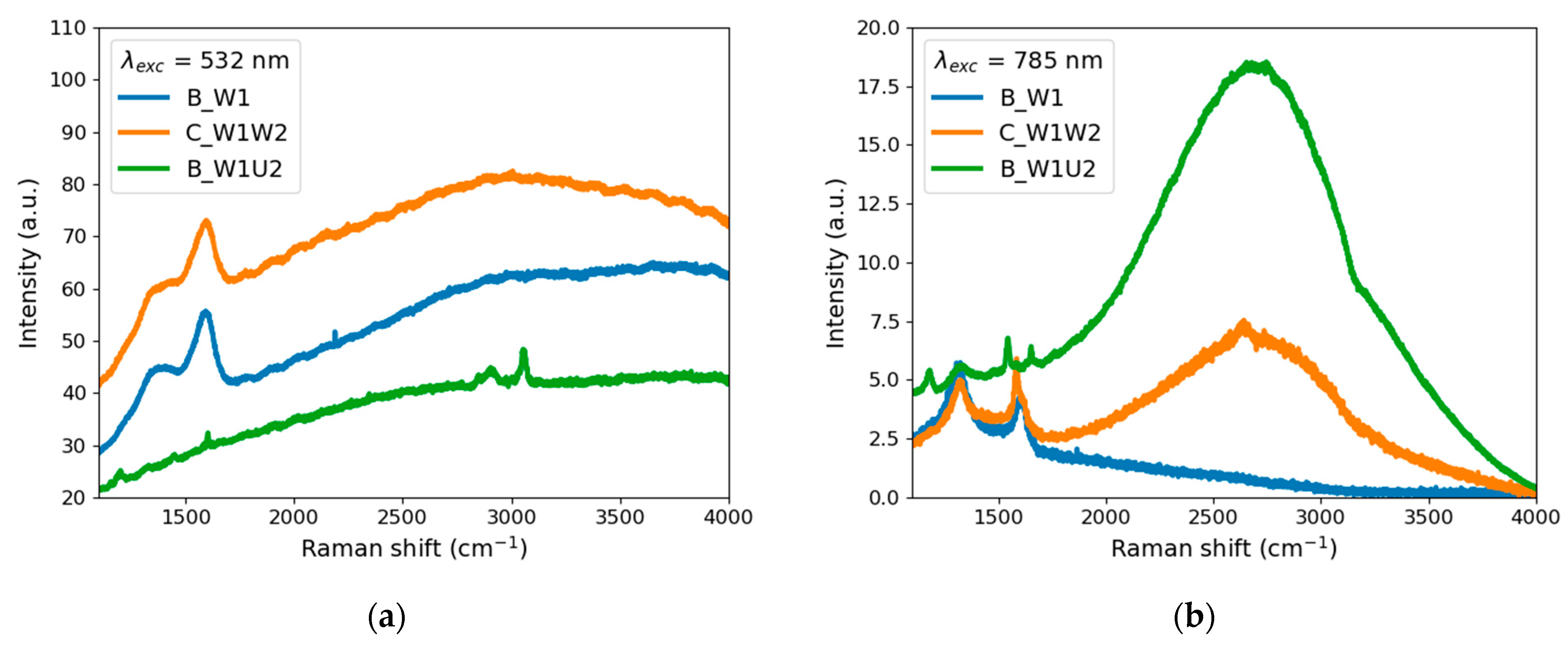
4.3.2. Raman and Infrared Emission Spectra
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Gadly, T.; Neogy, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Kumbhakar, M. Molecular origin and self-assembly of fluorescent carbon nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Ehrat, F.; Wang, Y.; Milowska, K.Z.; Reckmeier, C.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Carbon dots: A unique fluorescent cocktail of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6030–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Hoffman, J.; Morgiel, J.; Mościcki, T.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z.; Małolepszy, A. Luminescence Carbon Dots Synthesized by the Laser Ablation of Graphite in Polyethyleneimine and Ethylenediamine. Materials 2021, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.-H.; Chi, Y.; Yang, H.-H.; Yu, T. Luminescence origin of carbon-based dots obtained from citric acid and amino group containing molecules. Carbon 2017, 118, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-color light emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małolepszy, A.; Błoński, S.; Chrzanowska-Giżyńska, J.; Wojasiński, M.; Płociński, T.; Stobiński, Z.; Szymański, Z. Fluorescent carbon and graphene oxide nanoparticles synthesized by the laser ablation in liquid. App. Phys. A 2018, 124, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Dong, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, S. Simultaneous synthesis of luminescent carbon nanoparticles and carbon nanocages by laser ablation of carbon black suspension and their optical properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1957–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogesh, G.K.; Shuaib, E.P.; Sastikumar, D. Photoluminescence properties of carbon nanoparticles synthesized from activated carbon powder (4% ash) by laser ablation in solution. Mat. Res. Bull. 2017, 91, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnini, G.; Russo, P.; Tomarchio, F.; Puglisi, O.; D’Urso, L.; Scalese, S. Laser assisted green synthesis of free standing reduced graphene oxides at the water-air interface. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 505–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Contreras, D.; Camacho-Lopez, M.; Camacho-Lopez, M.A.; Camacho-Lopez, S.; Rodriguez-Beltran, R.I.; Mayorga-Rojas, M. Influence of the per pulse laser fluence on the optical properties of carbon nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation of solids in liquids. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 74, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Kalyanasundaram, D.; Kumar, S. Self-functionalized water suspension of luminescent carbon quantum dots. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2019, 225, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Synthesis and surface photochemistry of graphitized carbon quantum dots. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 356, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Pan, L.; Gao, S.; Fan, H.; Gao, B. Production of fluorescent nano-diamonds through femtosecond pulsed laser ablation. Opt. Mat. Express 2019, 9, 4734–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, P.M.; Dorranian, D. Effect of liquid medium temperature on the production rate and quality of graphene nanosheets produced by laser ablation. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2016, 48, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Solati, E.; Dorranian, D. Producing graphene nanosheets by pulsed laser ablation: Effect of liquid environment. J. Laser Appl. 2019, 31, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamaoy, A.; Chikarakara, E.; Jawad, H.; Gupta, K.; Kumar, D.; Ramachandra Rao, M.S.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Morshed, M.; Fox, E.; Brougham, D.; et al. Liquid phase-pulsed laser ablation: A route to fabricate different carbon nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 302, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novoa-De Leon, I.C.; Johny, J.; Vasquez-Rodriguez, S.; Garcia-Gomez, N.; Carranza-Bernal, S.; Mendivil, I.; Shaji, S.; Sepulveda-Guzman, S. Tuning the luminescence of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquid and their use as a selective photoluminescence on-off-on probe for ascorbic acid detection. Carbon 2019, 150, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Valcarcel, M. Semiconductor and carbon-based fluorescent nanodots: The need for consistency. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokorina, A.A.; Prikhozdenko, E.S.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Sapelkin, A.V.; Goryacheva, I.Y. Luminescent carbon nanoparticles: Synthesis, methods of investigation, applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2017, 88, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.; Chrzanowska, J.; Mościcki, T.; Radziejewska, J.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z. Plasma generated during underwater pulsed laser processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 417, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J. The effect of recoil pressure in the ablation of polycrystalline graphite by a nanosecond laser pulse. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 235201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.; Chrzanowska, J.; Kucharski, S.; Mościcki, T.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Ristoscu, C.; Szymański, Z. The effect of laser wavelength on the ablation rate of carbon. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.-L.; Niu, K.-Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, N.-Q.; Du, X.-W. One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Yan, L.; Si, J.; Hou, X. Femtosecond laser-induced size reduction of carbon nanodots in solution: Effect of laser fluence, spot size, and irradiation time. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 084304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, K.; McCann, R.; Wang, M.; Stalcup, A.; Vasquez, M.; Brabazon, D. Laser assisted synthesis of carbon nanoparticles with controlled viscosities for printing applications. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 447, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudek, M.; Rosowski, A.; Koperkiewicz, A.; Grobelny, J.; Wach, R.; Sharp, M.; French, P.; Janasz, Ł.; Kozanecki, M. Carbon nanoparticles fabricated by infrared laser ablation of graphite. Phys. Status Solidi A 2017, 216, 1600318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles, 1st ed.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; Chapter 2; p. 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakova, N.; Bulgakov, A. Pulsed laser ablation of solids: Transition from normal vaporization to phase explosion. Appl. Phys. A 2001, 73, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, A.; Guizzetti, G. Graphite. In Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids; Palik, E.D., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991; Volume 2, pp. 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles, 1st ed.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; Chapter 3; p. 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering by an Arbitrary Particle. In Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles, 1st ed.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; Chapter 4; pp. 82–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miepython-Miepython 1.3.2. Documentation. Available online: https://miepython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Wiscombe, W.J. Mie Scattering Calculations: Advances in Technique and Fast, Vector-Speed Computer Codes; No. NCAR/TN-140+STR; University Corporation for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refractive Index of H2O. Available online: https://refractiveindex.info/?shelf=main&book=H2O&page=Daimon-24.0C (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Duley, W.W. Refractive indices for amorphous carbon. Astrophys. J. 1984, 287, 694–696. Available online: http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1984ApJ...287..694D (accessed on 14 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Jeong, Y.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Son, Y.; Kim, W.R.; Lee, B.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, K.M. Pulsed laser ablation based synthetic route for nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots using graphite flakes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

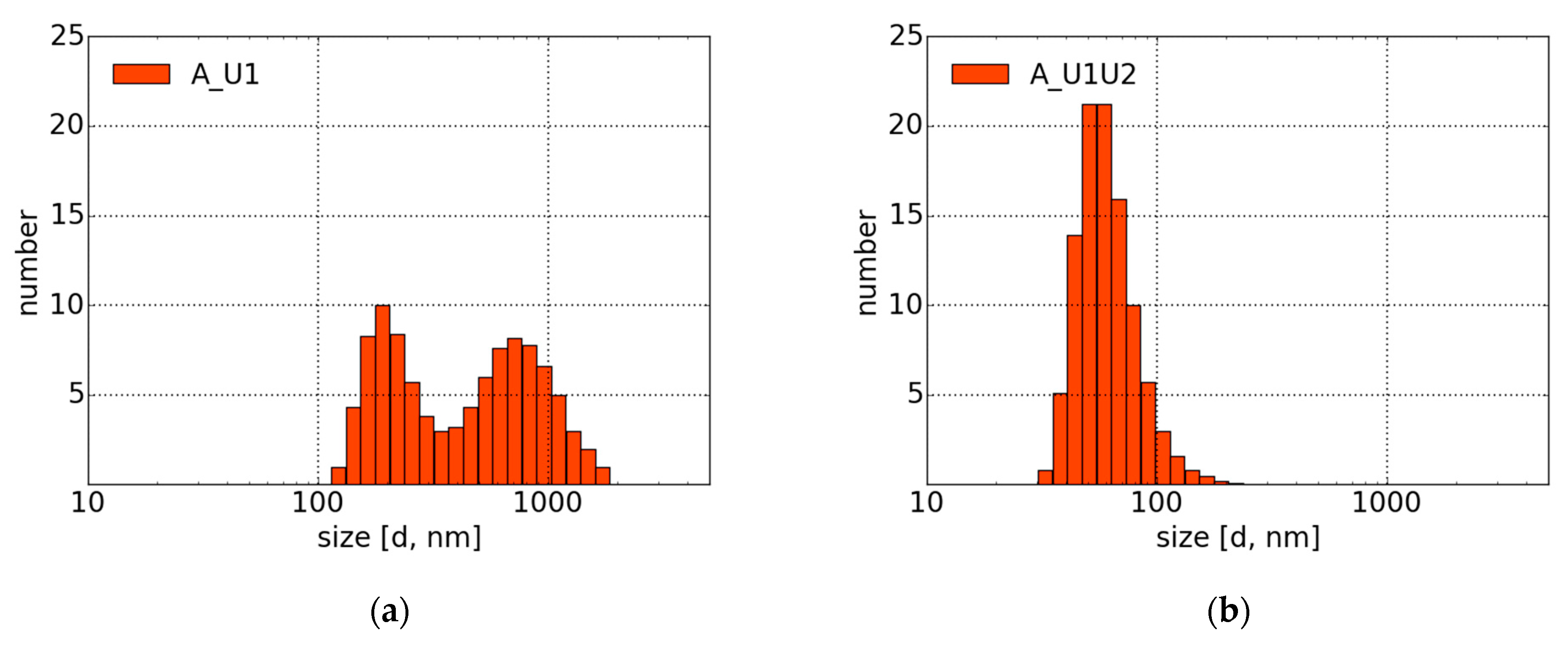
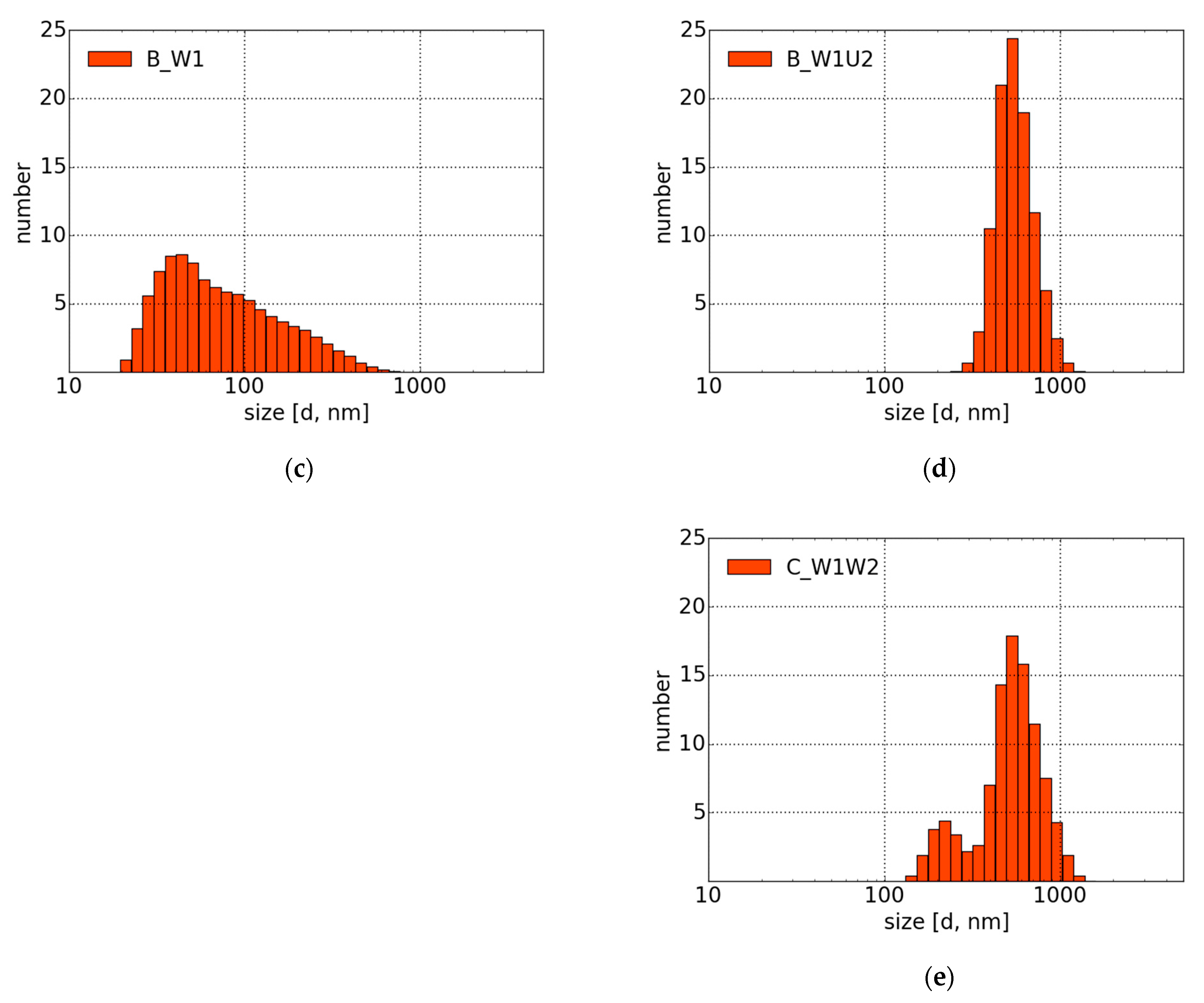

| Synthesis Approach | Laser Ablation (Step 1) Parameters | Laser Irradiation (Step 2) Parameters | Sample Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Target Unfocused laser beam 25 mL of aqueous urea solution 15 min processing time 10 W laser power | - | A_U1 |
| Target Unfocused Laser Beam 25 mL of aqueous urea solution 15 min 10 W | No target Focused laser beam 16 mL of CNPs from S1 60 min 10 W | A_U1U2 | |
| B | Target Unfocused laser beam 25 mL of water 15 min 10 W | - | B_W1 |
| Target Unfocused laser beam 25 mL of water 15 min 10 W | No target Focused laser beam 1 mL of urea solution + 16 mL of CNPs from S1 60 min 10 W | B_W1U2 | |
| C | Target Unfocused laser beam 25 mL of water 15 min 10 W | - | C_W1 = B_W1 |
| Target Unfocused laser beam 25 mL of water 15 min 10 W | No target Focused laser beam 16 mL of CNPs from S1 60 min 10 W | C_W1W2 |
| Sample Name | QY Value (%) |
|---|---|
| A_U1 | 0.46 |
| A_U1U2 | 1.46 |
| B_W1 | 0.02 |
| B_W1U2 | 0.27 |
| C_W1W2 | 0.28 |
| Peak Location (°) | Corresponding Plane | Sample Name |
|---|---|---|
| ~22 | (110) or (101) | all samples and the reference |
| 24.7 | (101) | reference, A_U1, A_U1U2 |
| 29.4 | (111) | reference, A_U1, A_U1U2 |
| 31.8 | (020) | reference, A_U1, A_U1U2 |
| 35.7 | (120) | reference, A_U1, A_U1U2 |
| 45 | (220) | reference, A_U1U2, B_W1U2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczmarek, A.; Denis, P.; Krajewski, M.; Mościcki, T.; Małolepszy, A.; Hoffman, J. Improved Laser Ablation Method for the Production of Luminescent Carbon Particles in Liquids. Materials 2021, 14, 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092365
Kaczmarek A, Denis P, Krajewski M, Mościcki T, Małolepszy A, Hoffman J. Improved Laser Ablation Method for the Production of Luminescent Carbon Particles in Liquids. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092365
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczmarek, Agata, Piotr Denis, Marcin Krajewski, Tomasz Mościcki, Artur Małolepszy, and Jacek Hoffman. 2021. "Improved Laser Ablation Method for the Production of Luminescent Carbon Particles in Liquids" Materials 14, no. 9: 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092365
APA StyleKaczmarek, A., Denis, P., Krajewski, M., Mościcki, T., Małolepszy, A., & Hoffman, J. (2021). Improved Laser Ablation Method for the Production of Luminescent Carbon Particles in Liquids. Materials, 14(9), 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092365








