Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Reinforced with Barium Sulfate Submicron Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Non-Isothermal Crystallization Kinetics
2.3. Crystal Morphology
2.4. Mechanical Testing
2.5. X-ray Images
3. Results
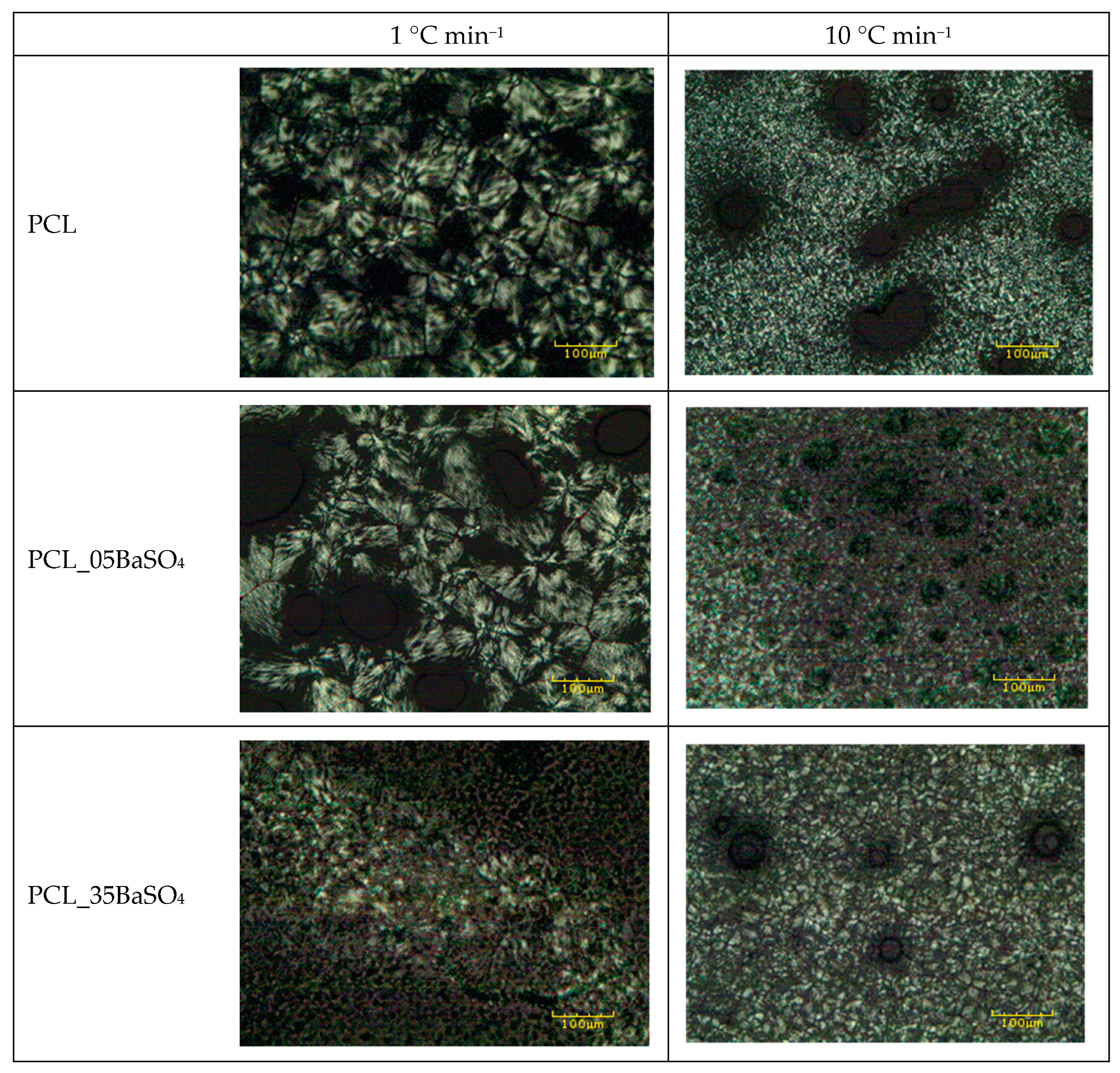
3.1. Crystallization Behavior and Crystal Morphology
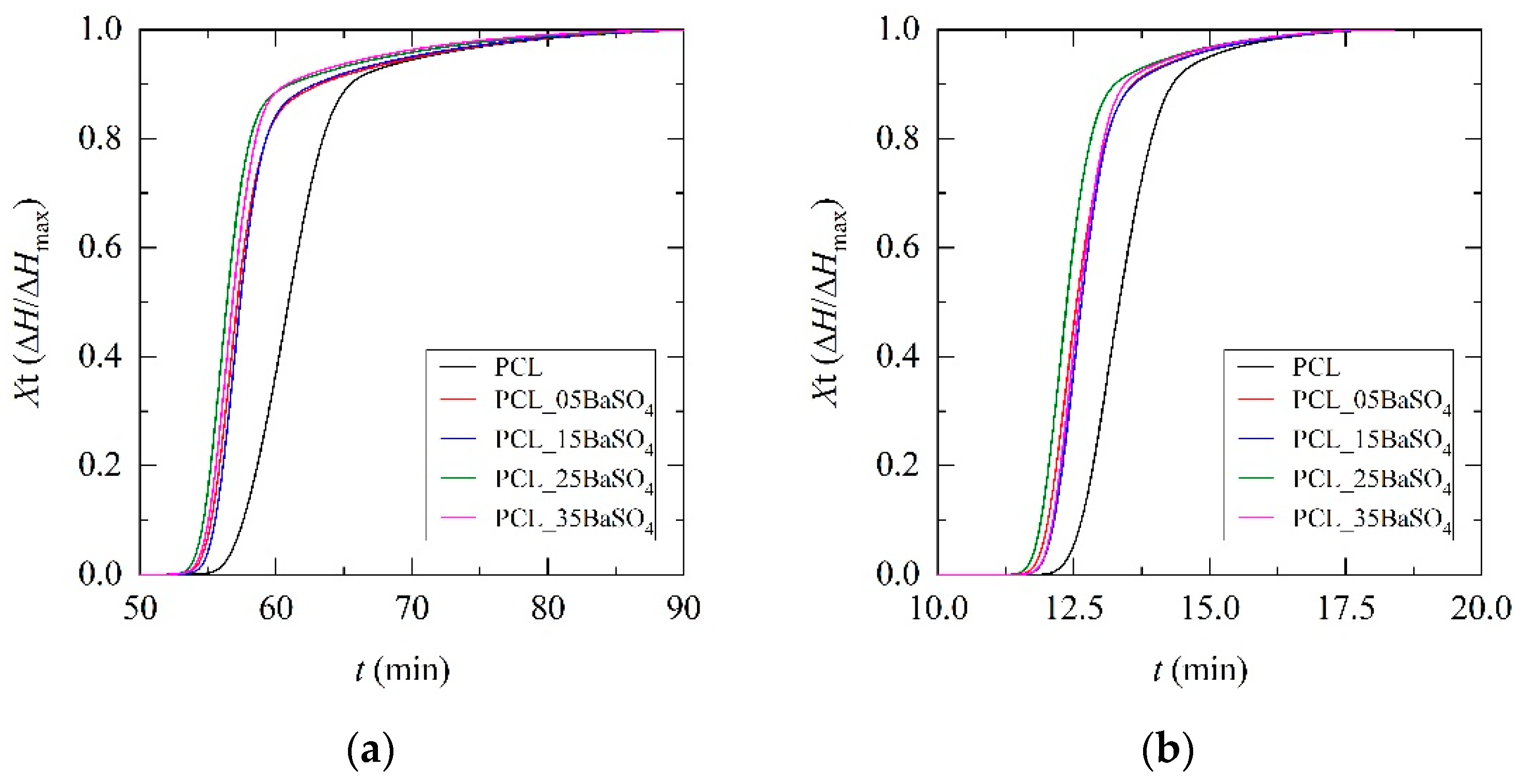
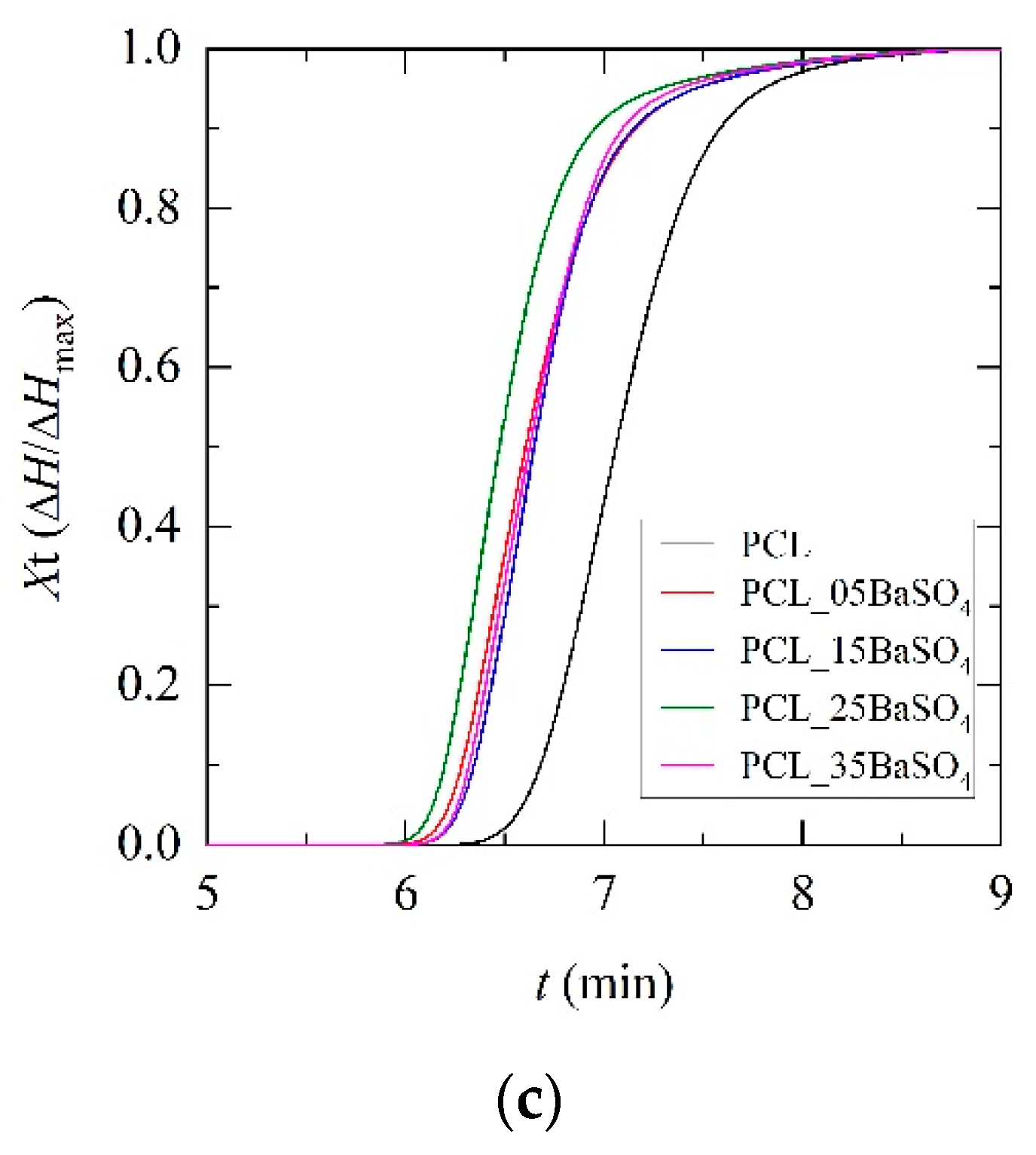
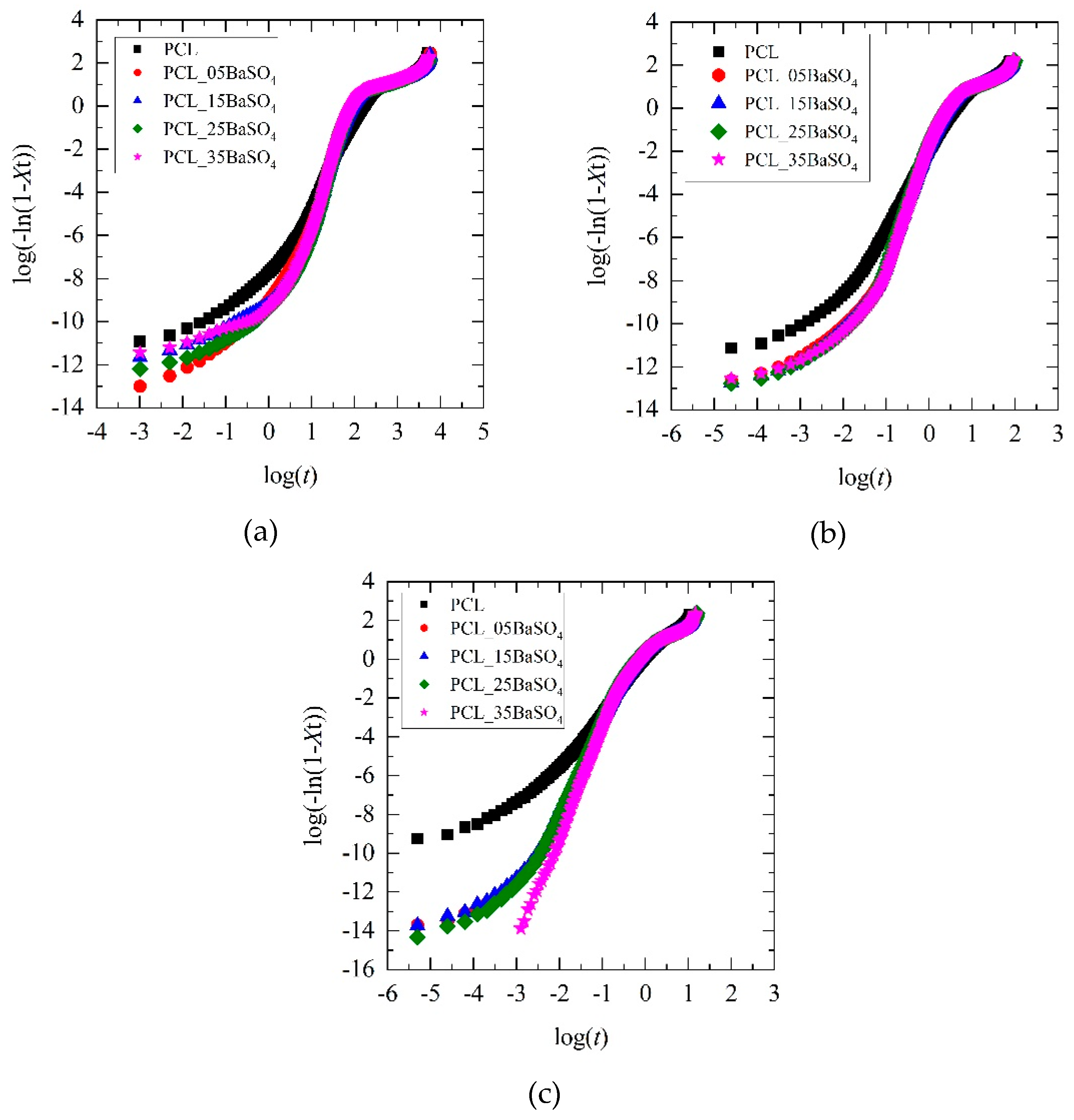
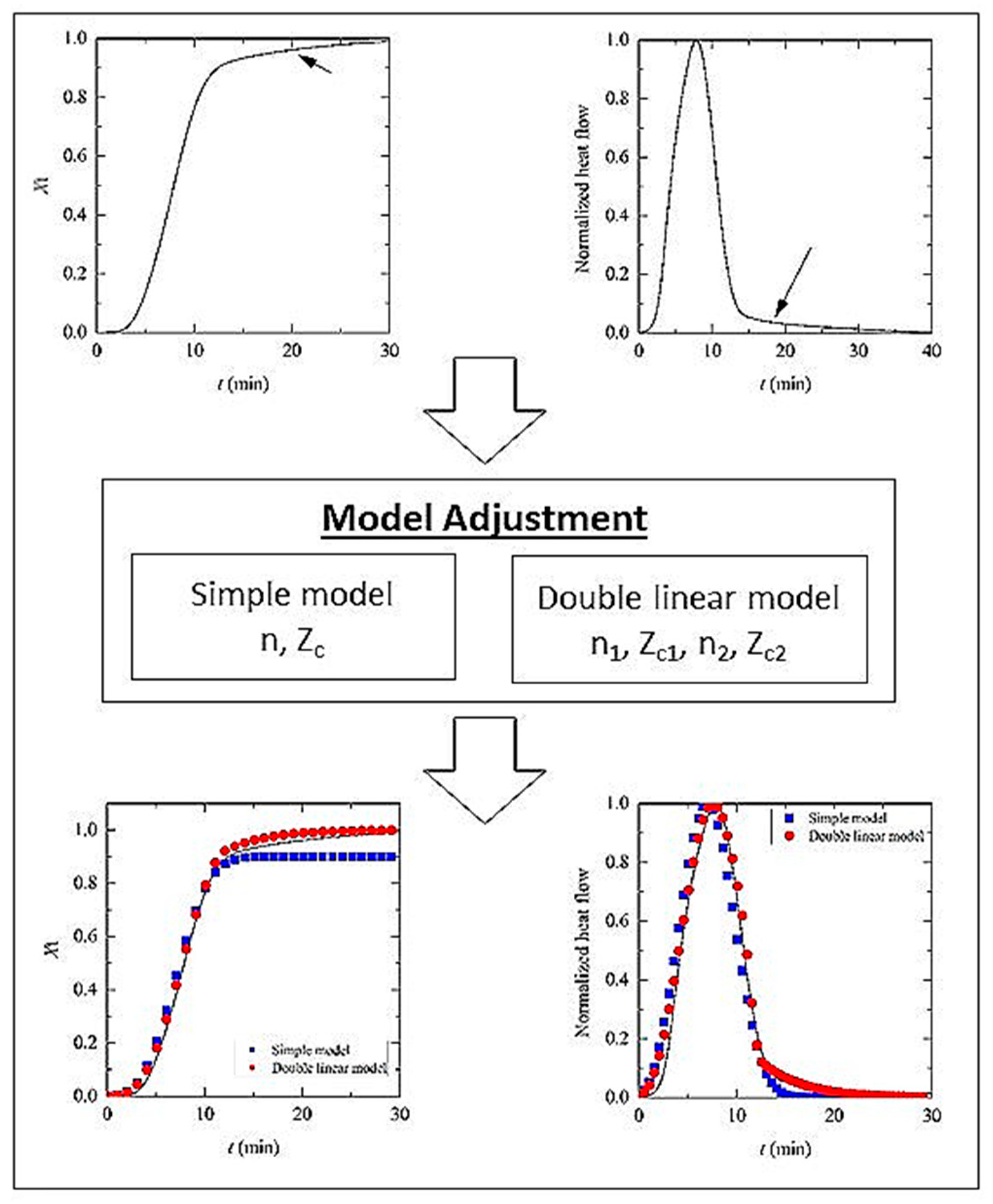
3.2. Non-Isothermal Crystallization and Kinetics Analysis
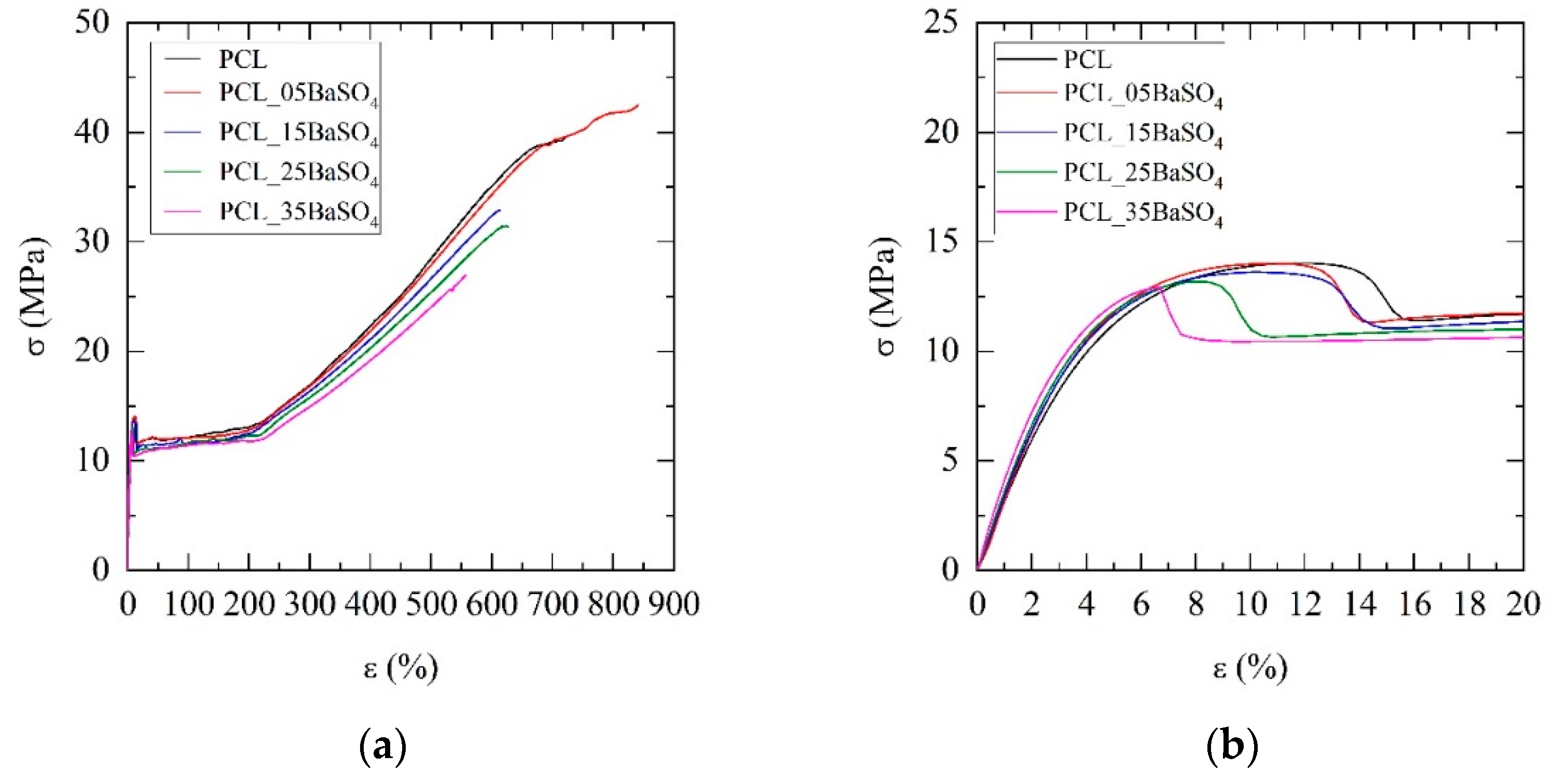
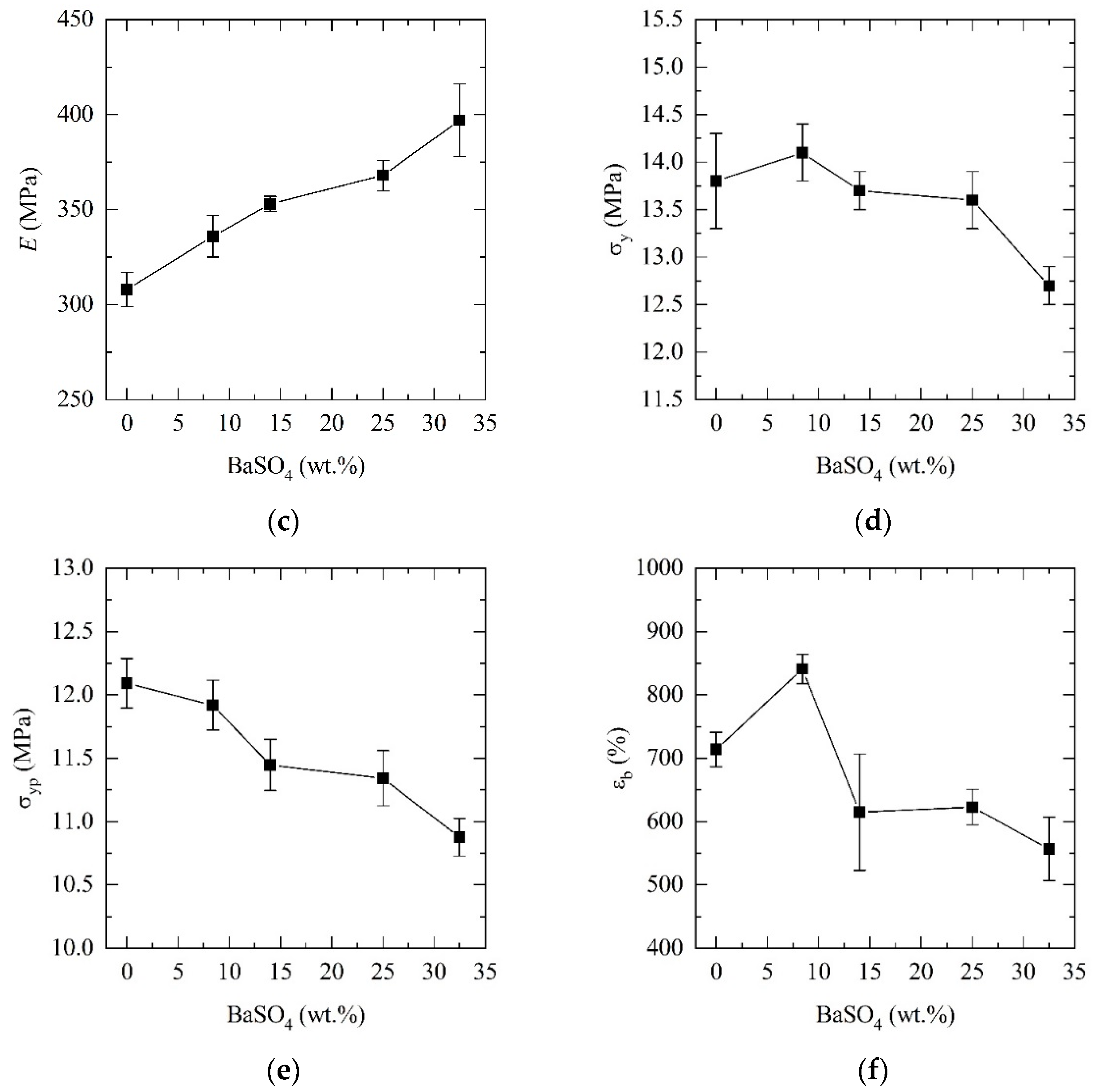
3.3. Mechanical Properties
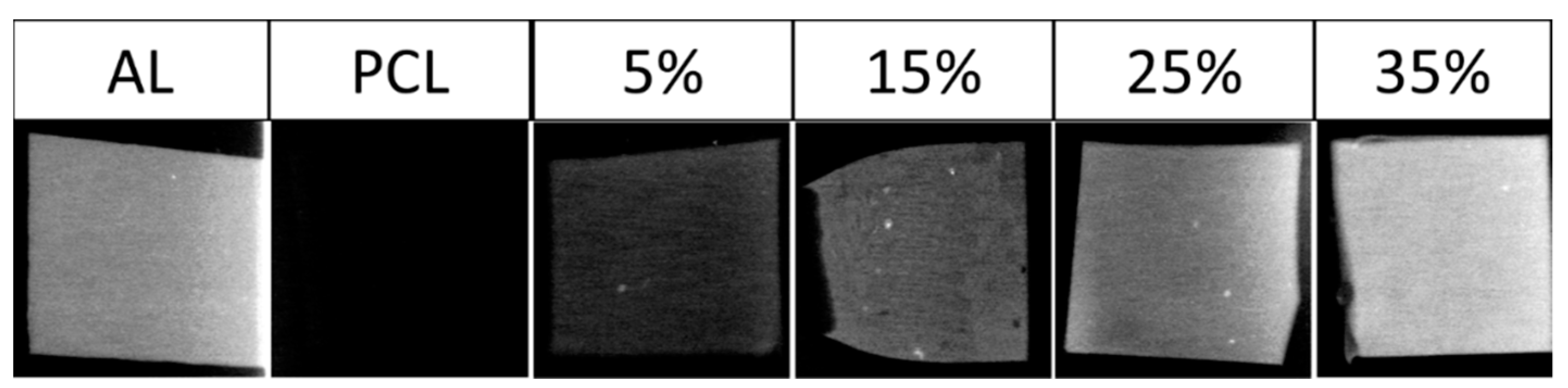
3.4. X-ray Imaging and Radiopacity Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vert, M.; Li, S.M.; Spenlehauer, G.; Guerin, P. Bioresorbability and biocompatibility of aliphatic polyesters. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1992, 3, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, A.C.; Varma, I.K. Recent developments in ring opening polymerization of lactones for biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1466–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugartemendia, J.M.; Larrañaga, A.; Amestoy, H.; Sarasua, J.R. Supramolecular evolution over an initial period of biodegradation of lactide and caprolactone based medical (co)polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Auzmendi, O.; Amestoy, H.; Diez-Torre, A.; Sarasua, J.R. Mechanical properties and fatigue analysis on poly(ε-caprolactone)-polydopamine-coated nanofibers and poly(ε-caprolactone)-carbon nanotube composite scaffolds. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañaga, A.; Aldazabal, P.; Martin, F.J.; Sarasua, J.R. Hydrolytic degradation and bioactivity of lactide and caprolactone based sponge-like scaffolds loaded with bioactive glass particles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Abdel-Hay, F.I.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Wnek, G.E. Processing of polymer nanofibers through electrospinning as drug delivery systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, J.; Ma, L.L.; Ramakrishna, S. Biocompatible nanofiber matrices for the engineering of a dermal substitute for skin regeneration. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Kratz, K.; Lendlein, A. Shape-Memory Properties of Radiopaque Micro-Composites from Amorphous Polyether Urethanes Designed for Medical Application. MRS Proceedings 2009, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rexach, E.; Iturri, J.; Fernandez, J.; Meaurio, E.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Sarasua, J.R. Novel biodegradable and non-fouling systems for controlled-release based on poly(ϵ-caprolactone)/Quercetin blends and biomimetic bacterial S-layer coatings. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 24154–24163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rexach, E.; Martínez de Arenaza, I.; Sarasua, J.R.; Meaurio, E. Antimicrobial poly(ε-caprolactone)/thymol blends: Phase behavior, interactions and drug release kinetics. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 83, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañaga, A.; Sarasua, J.R. Effect of bioactive glass particles on the thermal degradation behaviour of medical polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaba, N.; Martini, R.; Barthelat, F.; Martinez de Arenaza, I.; Larrañaga, A.; Sarasua, J.R.; Zuza, E. Understanding the toughness mechanism prompted by submicron rigid particles in polylactide/barium sulphate composites. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grémare, A.; Guduric, V.; Bareille, R.; Heroguez, V.; Latour, S.; L’heureux, N.; Fricain, J.C.; Catros, S.; Le Nihouannen, D. Characterization of printed PLA scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, J.-P.; Clerc, C.; Törmälä, P. Mechanical properties and in vitro degradation of self-reinforced radiopaque bioresorbable polylactide fibres. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2003, 14, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-J.; Pan, Y.-H.; Tzeng, J.-J.; Wu, T.-L.; Fong, T.-H.; Feng, S.-W.; Huang, H.-M. Development and Testing of X-Ray Imaging-Enhanced Poly-L-Lactide Bone Screws. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor Azman, N.Z.; Musa, N.F.L.; Nik Ab Razak, N.N.A.; Ramli, R.M.; Mustafa, I.S.; Abdul Rahman, A.; Yahaya, N.Z. Effect of Bi2O3 particle sizes and addition of starch into Bi2O3–PVA composites for X-ray shielding. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunahel, B.M.; Mustafa, I.S.; Noor Azman, N.Z. Characteristics of X-ray attenuation in nano-sized bismuth oxide/epoxy-polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) matrix composites. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämsä, T.; Jin, H.; Mikkonen, J.; Laukkarinen, J.; Sand, J.; Nordback, I. Biocompatibility of a new bioabsorbable radiopaque stent material (BaSO4 containing poly-L,D-lactide) in the rat pancreas. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkarinen, J.; Lämsä, T.; Nordback, I.; Mikkonen, J.; Sand, J. A novel biodegradable pancreatic stent for human pancreatic applications: A preclinical safety study in a large animal model. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez De Arenaza, I.; Sadaba, N.; Larrañaga, A.; Zuza, E.; Sarasua, J.R. High toughness biodegradable radiopaque composites based on polylactide and barium sulphate. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Nie, S.; Cheng, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, J. Morphological structure, impact toughness, thermal porperty and kinetic analysis on the cold crystallization of poly(lactic acid) bio-composites toughned by precipitated barium sulfate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Chen, G.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, X. Preparation of X-ray developable LDPE/SA-BaSO4 composites and their thermal and mechanical properties. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Shao, K.; Ding, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, J. Morphologies, mechanical properties and thermal stability of poly(lactic acid) toughened by precipitated barium sulfate. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 89, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Zeng, H. Microstructure and fracture behavior of polypropylene/ barium sulfate composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of barium sulfate nanoparticles on mechanical properties and crystallization behaviour of HDPE. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2010, 18, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuza, E.; Meaurio, E.; Sarasua, J.-R. Biodegradable Polylactide-Based Composites. In Composites from Renewable and Sustainable Materials; InTech: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lepoittevin, B.; Devalckenaere, M.; Pantoustier, N.; Alexandre, M.; Kubies, D.; Calberg, C.; Jérôme, R.; Dubois, P. Poly(ε-caprolactone)/clay nanocomposites prepared by melt intercalation: Mechanical, thermal and rheological properties. Polymer 2002, 43, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siaueira, G.; Bras, J.; Dufresne, A. Cellulose whiskers versus microfibrils: Influence of the nature of the nanoparticle and its surface functionalization on the thermal and mechanical properties of nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Avella, M.; Errico, M.; Laurienzo, P.; Martuscelli, E.; Raimo, M.; Rimedio, R. Preparation and characterisation of compatibilised polycaprolactone/starch composites. Polymer 2000, 41, 3875–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B. The research of crystalline morphology and breakdown characteristics of polymer/micro-nano-composites. Materials 2020, 13, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Microstructure and properties of polycaprolactone/calcium sulfate particle and whisker composites. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, C.G.; Chasalow, F.I.; Hibionada, Y.M.; Klimas, D.M.; Schindler, A. Aliphatic polyesters. I. The degradation of poly(ϵ-caprolactone) in vivo. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1981, 26, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. I: General theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. Kinetics of non-isothermal crystallization. Polymer 1971, 12, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M. Rheological properties and crystallization behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotube/poly(ɛ-caprolactone) composites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 3137–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; He, P.; Yuan, L.; Xiong, H.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of modified bamboo fiber/PCL composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorny, A. Parameters characterizing the kinetics of the non-isothermal crystallization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) determined by DSC. Polymer 1978, 19, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.S.O.; Fernandes, M.H.F.V.; de Oliveira, J.M.M. Crystallization kinetics of PCL and PCL–glass composites for additive manufacturing. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Shi, H. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of high-density polyethylene/barium sulfate nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 2342–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, M.; Wlochowicz, A. Kinetics of non-isothermal crystallization of polyethylene and polypropylene. Polymer 1983, 24, 1593–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chen, X.; Sha, J.; Peng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xie, L. Fabrication of shish-kebab-structured carbon nanotube/poly(e-caprolactone) composite nanofibers for potential tissue engineering applications. Rare Met. 2019, 38, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, L. Preparation, characterization, and properties of modified barium sulfate nanoparticles/polyethylene nanocomposites as T-shaped copper intrauterine devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Ye, L.; Zeng, H. Mechanical properties and toughening mechanisms of polypropylene/barium sulfate composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2003, 34, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample (Name Code) | BaSO4 Content
(wt.%) | Real BaSO4 Content
(wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| PCL | 0 | 0 |
| PCL_05BaSO4 | 5 | 8.4 |
| PCL_15BaSO4 | 15 | 14.2 |
| PCL_25BaSO4 | 25 | 25.0 |
| PCL_35BaSO4 | 35 | 32.5 |
| Sample (Name Code) | BaSO4 Content
(wt. %) | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
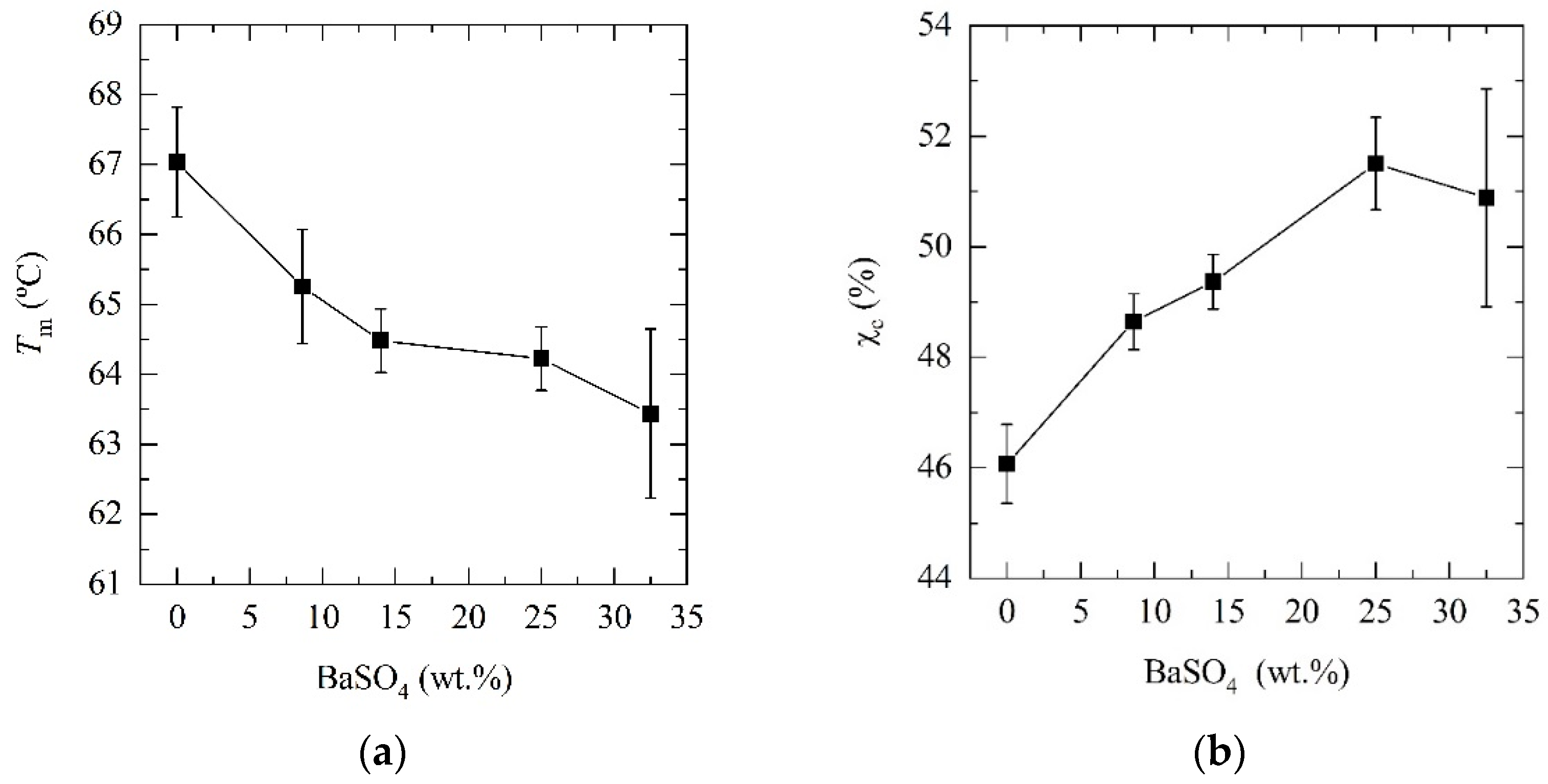
| PCL | 0 | 67.0 ± 0.8 | 70.5 ± 1.1 | 46 |
| PCL_05BaSO4 | 8.4 | 65.3 ± 0.8 | 68.2 ± 0.7 | 49 |
| PCL_15BaSO4 | 14.2 | 64.5 ± 0.5 | 64.8 ± 0.6 | 49 |
| PCL_25BaSO4 | 25.0 | 64.2 ± 0.5 | 59.1 ± 1.0 | 52 |
| PCL_35BaSO4 | 32.5 | 63.4 ± 1.2 | 52.6 ± 2.0 | 51 |
| Sample (Name Code) | Cooling Rate
(°C min−1) | Tc (°C) | ΔHc (J g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
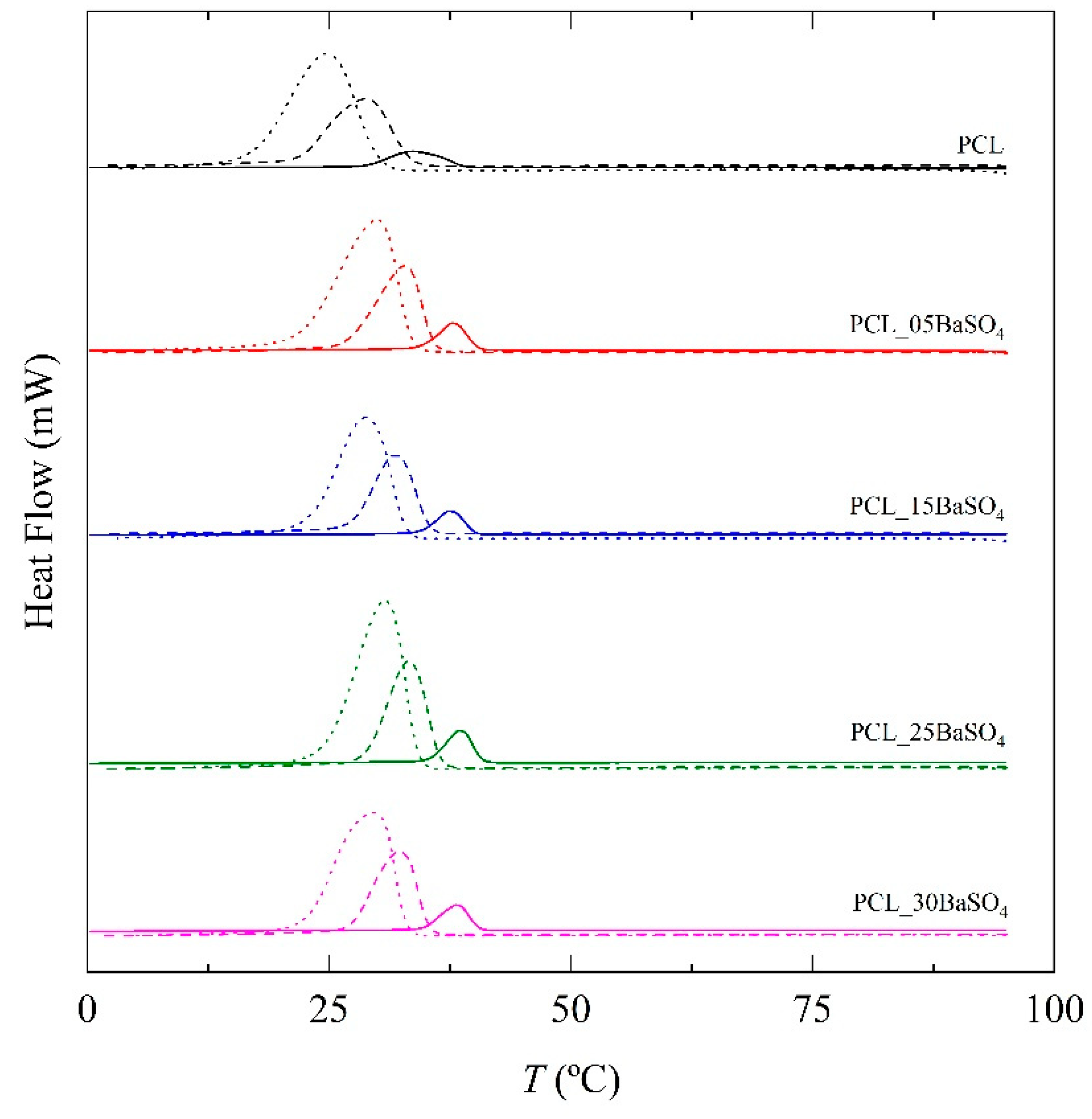
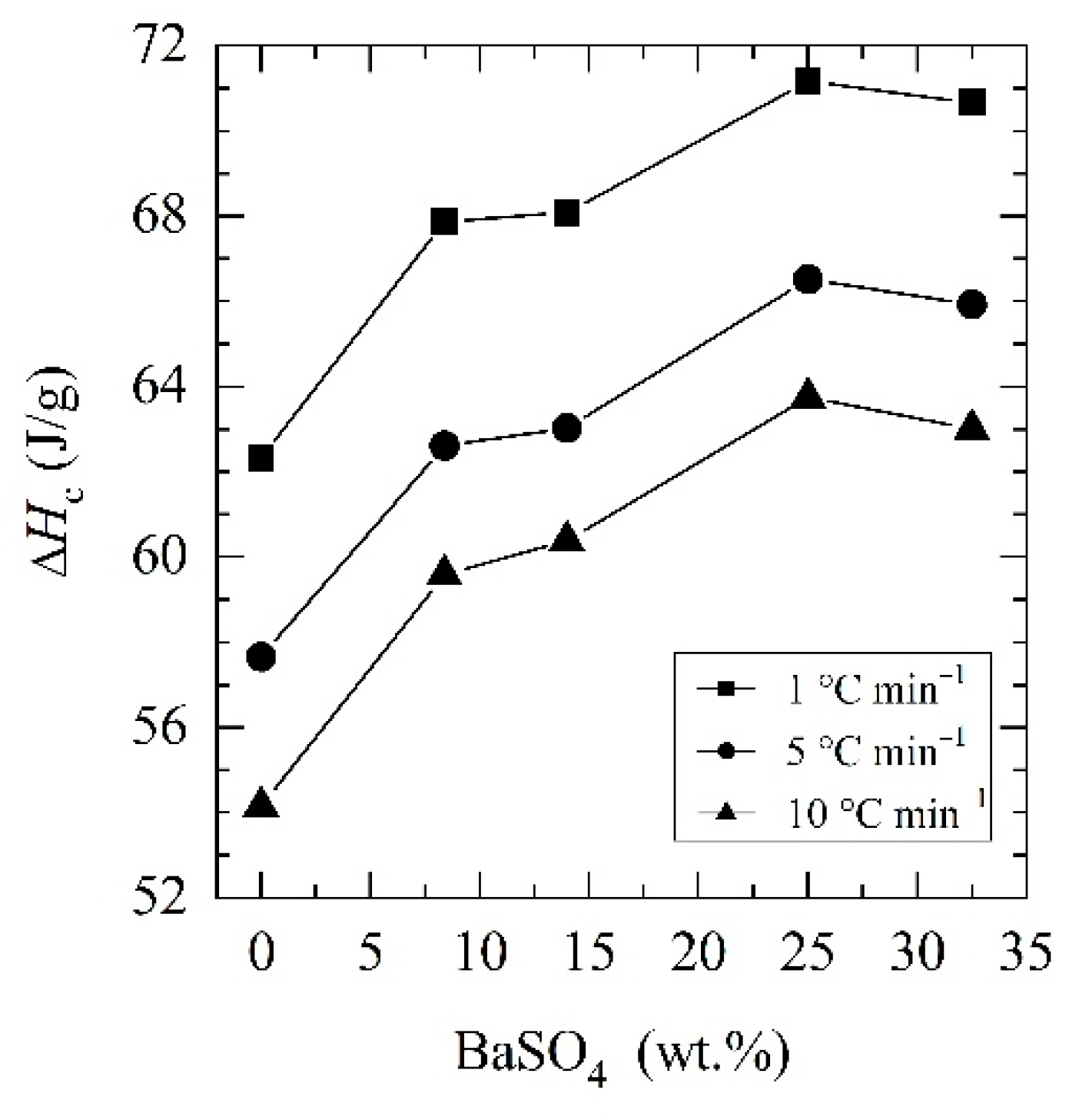
| PCL | 1 | 33.7 | 62.3 |
| 5 | 28.7 | 57.7 | |
| 10 | 24.8 | 54.1 | |
| PCL_05BaSO4 | 1 | 37.8 | 67.9 |
| 5 | 32.8 | 62.6 | |
| 10 | 29.9 | 59.6 | |
| PCL_15BaSO4 | 1 | 37.5 | 68.1 |
| 5 | 31.8 | 63.0 | |
| 10 | 28.8 | 60.4 | |
| PCL_25BaSO4 | 1 | 38.5 | 71.2 |
| 5 | 33.2 | 66.5 | |
| 10 | 30.7 | 63.7 |
| Sample (Name Code) | Φ
(°C min−1) | Zc1 × 106 | n1 | r1 | Zc2 × 106 | n2 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL | 1 | 393 | 3.06 | 0.96 | 112,010 | 1.12 | 0.90 |
| 5 | 26,661 | 3.00 | 0.97 | 134,567 | 1.24 | 0.96 | |
| 10 | 93,981 | 2.46 | 0.97 | 138,174 | 1.65 | 0.98 | |
| PCL_05BaSO4 | 1 | 311 | 3.76 | 0.94 | 156,060 | 1.01 | 0.91 |
| 5 | 22,345 | 3.68 | 0.94 | 157,177 | 1.08 | 0.95 | |
| 10 | 130,814 | 3.69 | 0.97 | 149,402 | 1.33 | 0.96 | |
| PCL_15BaSO4 | 1 | 353 | 3.68 | 0.91 | 171,962 | 0.98 | 0.92 |
| 5 | 24,246 | 3.73 | 0.95 | 159,310 | 1.09 | 0.94 | |
| 10 | 145,824 | 3.65 | 0.97 | 161,103 | 1.30 | 0.95 | |
| PCL_25BaSO4 | 1 | 266 | 3.86 | 0.91 | 173,790 | 0.99 | 0.90 |
| 5 | 25,408 | 3.79 | 0.95 | 169,341 | 1.05 | 0.94 | |
| 10 | 169,961 | 3.81 | 0.97 | 170,617 | 1.22 | 0.93 | |
| PCL_35BaSO4 | 1 | 339 | 3.70 | 0.91 | 136,477 | 1.08 | 0.89 |
| 5 | 21,298 | 3.72 | 0.95 | 144,059 | 1.17 | 0.94 | |
| 10 | 229,399 | 3.92 | 0.97 | 147,983 | 1.39 | 0.92 |
| Sample (Name Code) | E* (MPa) | σy (MPa) | εy (%) | σyp (MPa) | εb (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL | 308 ± 9 | 13.8 ± 0.5 | 10.2 ± 1.5 | 12.1 ± 0.2 | 714 ± 27 |
| PCL_05BaSO4 | 336 ± 11 | 14.1 ± 0.3 | 10.9 ± 0.8 | 11.9 ± 0.2 | 841 ± 23 |
| PCL_15BaSO4 | 353 ± 4 | 13.7 ± 0.2 | 9.9 ± 0.3 | 11.4 ± 0.2 | 615 ± 92 |
| PCL_25BaSO4 | 368 ± 8 | 13.6 ± 0.3 | 8.8 ± 0.7 | 11.3 ± 0.2 | 623 ± 28 |
| PCL_35BaSO4 | 397 ± 19 | 12.7 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 557 ± 50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amestoy, H.; Diego, P.; Meaurio, E.; Muñoz, J.; Sarasua, J.-R. Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Reinforced with Barium Sulfate Submicron Particles. Materials 2021, 14, 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092368
Amestoy H, Diego P, Meaurio E, Muñoz J, Sarasua J-R. Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Reinforced with Barium Sulfate Submicron Particles. Materials. 2021; 14(9):2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092368
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmestoy, Hegoi, Paul Diego, Emilio Meaurio, Jone Muñoz, and Jose-Ramon Sarasua. 2021. "Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Reinforced with Barium Sulfate Submicron Particles" Materials 14, no. 9: 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092368
APA StyleAmestoy, H., Diego, P., Meaurio, E., Muñoz, J., & Sarasua, J.-R. (2021). Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Reinforced with Barium Sulfate Submicron Particles. Materials, 14(9), 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092368









