Abstract
Mixtures of nematic liquid crystals (LCs) with chiral ionic liquids (CILs) may find application as active materials for electrically driven broadband mirrors. Five nematic liquid crystal hosts were mixed with twenty three ionic liquids, including chiral ones, and studied in terms of their miscibility within the nematic phase. Phase diagrams of the mixtures with CILs which exhibited twisted nematic phase were determined. Miscibility, at levels between 2 and 5 wt%, was found in six mixtures with cyanobiphenyl-based liquid crystal host—E7. On the other hand, the highest changes in the isotropization temperature was found in the mixtures with isothiocyanate-based liquid crystal host—1825. Occurrence of chemical reactions was found. A novel chiral binaphtyl-based organic salt [N11116][BNDP] was synthesized and, in reaction to the 1825 host, resulted in high helical twisting power product(s). Selectivity of the reaction with the isothiocyanate-based liquid crystal was found.
1. Introduction
Electrically induced broadening of the reflection band was presented in liquid crystal (LC) mixtures with chiral ionic liquids (CILs) [1,2]. Thus, they are candidates for application in electrically switchable mirrors and transflective displays, e.g., e-TransFlector™, developed by Kent Optronics. The LC + CIL mixtures might be advantageous with respect to the widely-studied Polymer Stabilized Cholesteric Liquid Crystals [3,4,5,6] in terms of lower energy consumption in this application.
A miscibility of CILs with LCs within the nematic phase, besides sufficiently high helical twisting power (HTP) of the chiral dopant, seems to be the most crucial parameter for these applications. Such mixtures have already been studied in the literature [1,2,7,8,9,10,11,12], mainly with respect to their electrically induced effects. In our recent paper [9], chiral ionic compounds, formed by mesogenic chiral phenylpyridine derivative and strong organic acids, were miscible, to some extent, with the nematic LC host. The papers from Akagi group [7,8] describe miscibility of nematic ionic liquid crystals with chiral dopants and, alternatively, with a salt composed of binaphtyl-based chiral counter-ions, obtaining, in both cases, twisted nematic phase with use of chiral ionic species, which makes these mixtures potentially applicable. More examples of ionic liquid crystals forming the nematic phase by themselves are described in refs. [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. However, these examples should be treated as exceptions to the rule because lamellar smectic or columnar phases are preferred in most ionic liquid crystals [20], which, in turn, are not likely to mix with nematic LCs [21].
Based on literature, the solubility of ILs increases in various environments because of such factors as: hydrophilicity of each of the ions of ILs [22,23], presence of Coulomb interactions of the IL with amino acid chains [24,25], and affinity of the IL to formation of hydrogen bonds—e.g., cellulose compounds [26]. Moreover, it is expected that enhanced miscibility of ILs with common nematic LCs could be searched by an extension of the structure of ionic compounds, using the structural fragments found commonly in nematogens, as presented in refs. [7,8], and as an analogy of design of chiral dopants with good miscibility with the host LC [27,28].
The aim of this work was to find systems with mutual miscibility between LCs and ILs, as well as related structural properties, which can influence this property. Moreover, to understand basic phenomena occurring in various systems, as e.g., reactivity between the components, which could be effect of presence of functional groups in LCs’ structures. Special attention is paid to mixtures of LCs with CILs exhibiting a twisted nematic phase because of potential application.
The article consists of three main parts. In the first part (Section 3.1), the survey studies on the miscibility of five LC hosts, with twenty three IL dopants at the level of about 5 wt%, were presented. The studies included 13 CILs: two CILs with lactate anion, nine menthoxymethyl-based CILs, and new chiral salts with the cetyltrimethylammonium (CTA)—[N11116] cation and anions based on binaphtyl phosphonic acid (BNDHP) (potentially giving high HTP [7,8,29,30]) and naproxen. In ten LC + CIL mixtures, the twisted nematic phase was induced. In these mixtures, a dependence of the phase transition temperatures, with respect to the weight fraction (xIL), was studied, to construct phase diagrams. Stability of the isotropization temperature (TNI) of these mixtures with a heating time was investigated, to search for mutual chemical reactions between the components (Section 3.2). Moreover, in these LC + CIL mixture, measurements of the helical pitch of the twisted nematic phase (p) were performed (Section 3.3). As reactivity of the isothiocyanates-based LC host 1825 with some ILs was found, the reaction progress with chosen salt with chiral binaphtyl-based anion—[N11116][BNDP], was studied in Section 3.4. The near infrared (NIR) and ultraviolet/visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy was used to determine dependence of the helical pitch of the mixture, with respect to the heating time, characterizing HTP of the reaction product(s). A variety of reference tests of the reaction were performed in order to search, e. g., for the specificity of the reaction.
Detailed experimental information is described in Section S1 in Supplementary Materials. Synthesis and properties of the chiral salts, based on binaphtyl phosphonic acid (BNDHP) and naproxen anions and [N11116] cations, are enclosed in Section S2. Supplemental results of the characterization of the LC + CIL mixtures and chemical reaction with [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt studies are reported in Section S3.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Liquid Crystals
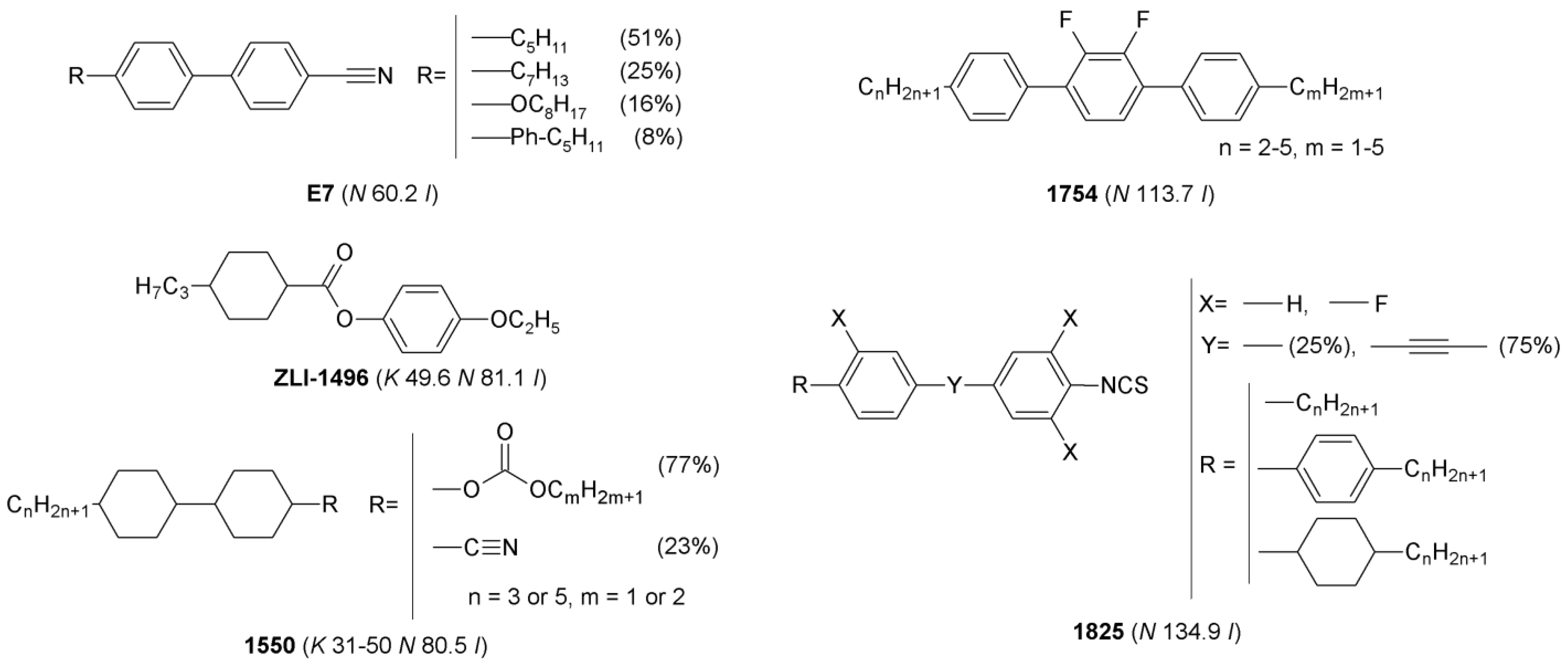
The following multicomponent LCs: 1754, E7, 1550, 1825, and single-component LC—ZLI-1496 of structures, depicted in Figure 1, were used in the studies. Phase transition temperatures determined by Polarized Optical Microscopy (POM) are also presented in the Figure 1. Physical properties of the LCs [31,32,33,34,35] are described in Section S1.1 in the Supplementary Materials.
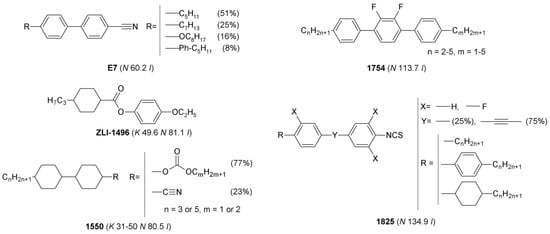
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of single- and multicomponent liquid crystals used as hosts in mixtures with ionic liquids. Phase transition temperatures, determined by POM, are given in the parentheses.
2.2. Ionic Liquids
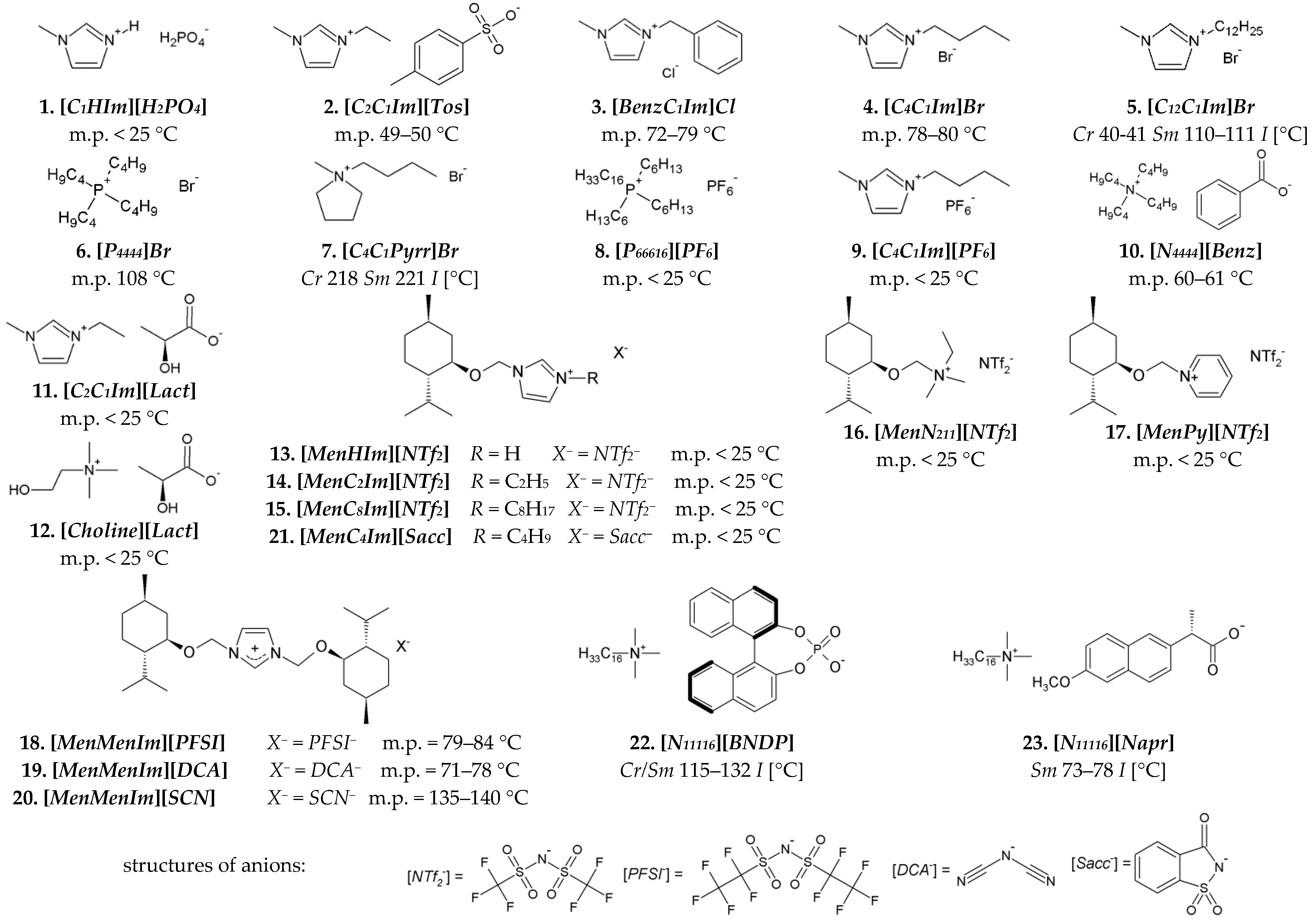
The following ILs were used for the miscibility studies with the LCs. Non-chiral ILs of nos. 1–10, and CILs of nos. 11 and 12 are presented in Figure 2. The following CILs of nos. 13–23 in Figure 2 were synthesized by our team. CILs with menthoxymethyl substituent(s) (Men) and various ammonium groups: imidazolium [36,37,38,39], pyridinium [40], and alkylammonium [41] groups (nos. 13–21 in Figure 2) were synthesized according to procedures given in the references. Cetyltrimethylammonium salts of a chiral binaphtyl-based phosphonic acid [N11116][BNDP] and with a naproxen anion [N11116][Napr] (nos. 22 and 23 in Figure 2) were synthesized, according to the procedures described in Sections S2.1 and S2.2 in the Supplementary Materials, respectively. The properties of these salts are described in Section S2.3 in the Supplementary Materials.
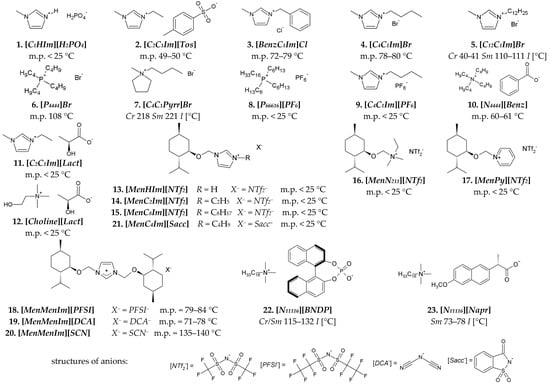
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of ionic liquids used in the studies: nonchiral (first two rows) and chiral (third and fourth rows)—including menthoxymethyl-based (Men) chiral ionic liquids and chiral organic salts, based on cetyltrimethylammonium [N11116] cation and chiral anion. The phase transition temperatures were determined by POM. Structures of more complex anions are explicated at the bottom. Legend: Cr—crystal, Sm—smectic phase, I—isotropic liquid.
For the estimation of water content in ionic liquids, the Mid-IR absorption spectra in the 4000–400 cm−1 range were recorded, with the use of ATR FT-IR accessory. Absorption at the arbitrarily chosen wavenumber 3450 cm−1 of the water absorption band was chosen. Direct values from the ATR measurements after subtraction of the background (minimal value in range 4000–3200 cm−1) were taken for rough comparison of the water content in the studied ionic liquids. Details and the Mid-IR spectra are presented in Section S3.1 in the Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Studies of Miscibility, Reactivity and Helical Pitch in Mixtures of the LCs with ILs
For the miscibility and related studies, for which results are presented in Section 3.1, Section 3.2 and Section 3.3, the LC and the IL components were weighted at proper weight fraction and mixed in a vial on a hot-plate with the temperature set above the melting and isotropization points of both components for a time of 2 min, if not stated otherwise. For mixtures of the LCs with the CILs exhibiting a twisted nematic phase, additional sets of samples were prepared for study of the phase diagrams (in range to CIL weight fraction up to about 30%). The mixtures were enclosed between two plain cover glass microscopic slides, and the textures of the mixtures were collected under the microscope with respect to the temperature. Details of the preparation of the mixtures are described in Section S1.2 in the Supplementary Materials.
For the studies of reactivity between the LC and the CIL components, the mixtures exhibiting twisted nematic phase at xIL ≈ 5 wt% were heated at the hot-plate at a similar temperature to the mixture preparation for a total time of 2, 10, and 30 min. Magnitude of the shift in the isotropization temperature with the heating time was studied. Experimental details of the reactivity studies are described in Section S1.3 in the Supplementary Materials.
The phase transition temperatures were investigated under a polarized optical microscope, equipped with a heating/cooling stage in a crossed-polarizers setup. The number of phases in the samples was also judged macroscopically by the observation of the sample through crossed polarizers. The isotropization temperature was determined as a temperature at which no anisotropic regions were observed in the field of view (assuring no homeotropic alignment). Protocol for identification of the microscopic textures, appearing dark in crossed-polarizers setup, is described in Section S1.4.1 in the Supplementary Materials. The standard uncertainty of the microscopic measurements of the phase transition temperature (u) was estimated at 1.0 °C. More experimental details of the microscopic determinations are described in Section S1.4 in the Supplementary Materials.
For study of the helical pitch of the twisted nematic phase, of the mixtures exhibiting twisted nematic phase, the fingerprint (Legarde) and wedge cell (Grandjean-Cano) methods were used alternatively, depending on the type of anchoring of the twisted nematic phase in the cells—homeotropic twisted nematic (cholesteric) and planar twisted nematic (cholesteric), respectively. The measurements by the fingerprint method were performed after cooling the mixtures from the isotropic phase before the measurement. Spectrophotometric method for helical pitch determination was used to monitor progress of the reaction of 1825 liquid crystal host with [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt, described in the Section 3.4. Experimental details of the helical pitch measurements are described in Section S1.5 in the Supplementary Materials.
2.4. Studies of the Reaction of the 1825 Liquid Crystal Host with the [N11116][BNDP] Chiral Salt
For the studies of the reaction of the 1825 LC host with the [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt, mixtures with about 10 wt% of the dopant were prepared. The reactions were performed at temperatures of the mixture equal to 150 °C and 131 °C, which was found to be above and below the isotropization temperature of the LC host, respectively. Small portions of the reaction mixture were collected after certain periods of time after the start: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 105, and 170 min (or other, if stated), and the helical pitch of the twisted nematic phase was determined, as described in the previous section. A reference sample, composed of two molecules separately containing the ions of the novel chiral salt—5 wt% of [N11116]Br and 5 wt% of BNDHP, was studied. Other reference samples were investigated, at slightly changed conditions, to study specificity of the reaction. Details are described in Section S1.6 in the Supplementary Materials.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Survey Studies of Miscibility of the Liquid Crystals with the Ionic Liquids
LCs of the structures depicted in Figure 1 were used as hosts in the mixtures with ILs (Figure 2) for a study of their mutual miscibility by POM. At this stage, each of the studied ILs was doped into each of the LCs at the xIL in a range of 4.4–5.4% (with exception of some of the mixtures with ILs nos. 11 and 12—which were doped into LC hosts at a weight fraction of 20 ± 1%; detailed conditions are described in Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials). The doping level of about 5% was chosen in order to introduce sufficient helical twisting power to observe twisted nematic phase textures under the microscope. For practical use, commercial chiral dopants as CB15 (HTP ≈ 6–8 μm−1) [21,42] and S811/R811 (HTP ≈ 11 μm−1) [42] should be doped evenly at about 32% or 20%, respectively, to form selective reflection of light in the visible range.
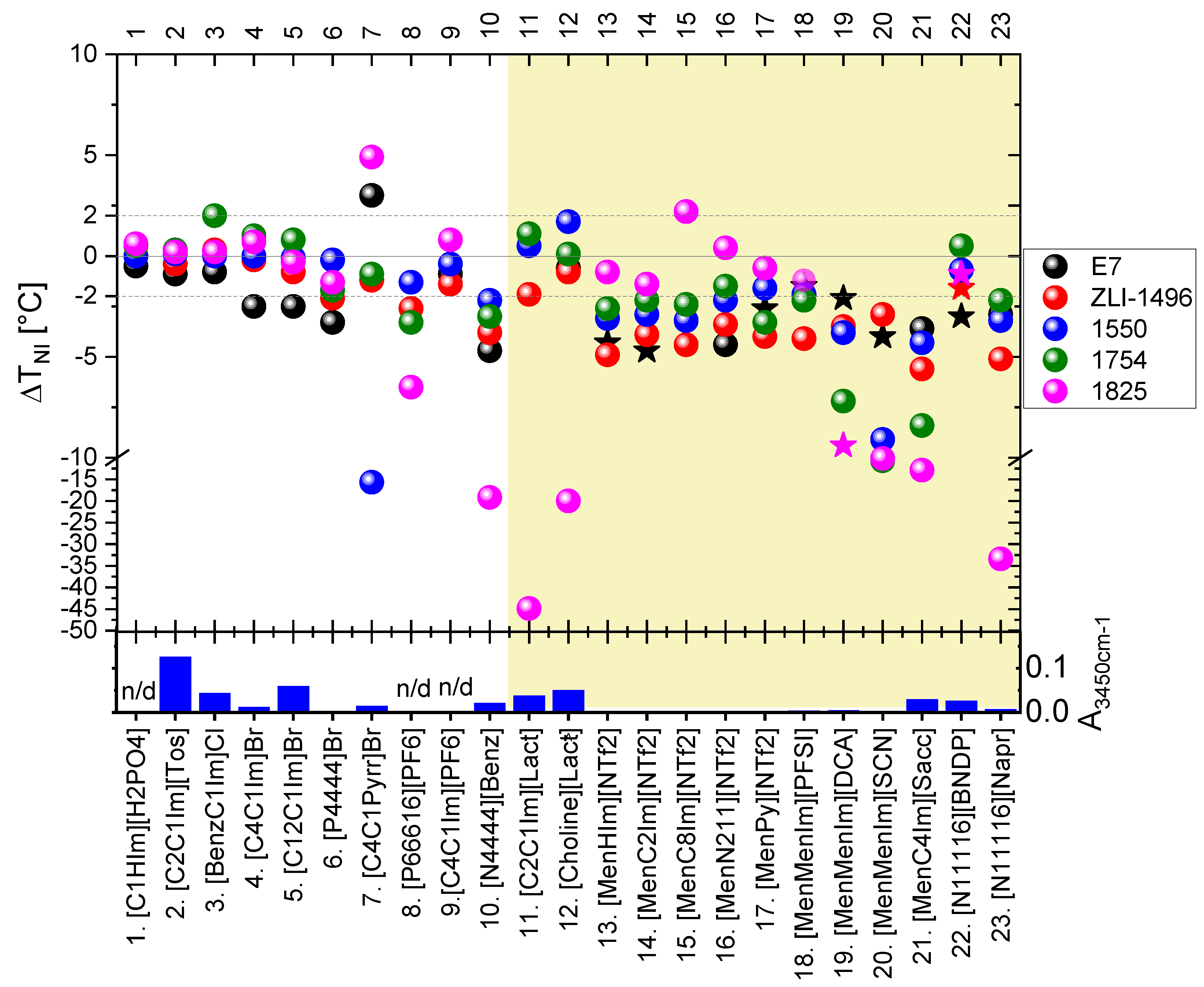
The mixtures were characterized in terms of: (a) presence of a separate phase of the IL dopant; (b) shift in the isotropization temperature of the nematic phase of LC host (nematic-isotropic phase transition temperature) (ΔTNI) of the nematic LC host; (c) presence of the twisted nematic phase (only in case of CILs). For a rough estimation of relative water content, the ILs were characterized by absorbance value at an arbitrarily chosen wavenumber of 3450 cm−1 (A3450cm−1).
All of the studied LC + IL mixtures at IL content about 5 wt%, studied by POM, were found to be biphasic. Only partial solubility of the ILs in the host nematic phase of the LC hosts were found. The isotropic or crystalline phase (depending on the IL type) co-extisted with the nematic phase of the LC hosts. Signs of miscibility of the ILs with the LC hosts were noticed: significant magnitude of the |ΔTNI| and induction of the twisted nematic phase (indicated in graph in the Figure 3 by star symbols), but the only latter in case of mixtures with some of the CILs. The results of the |ΔTNI|, with respect to LC and IL used, are presented in the Figure 3 and in the Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials. Chemical reactions between the LC and CIL components were considered to affect the results, and they could be an effect of self-reactivity of the ILs or their reactivity with the LC hosts.
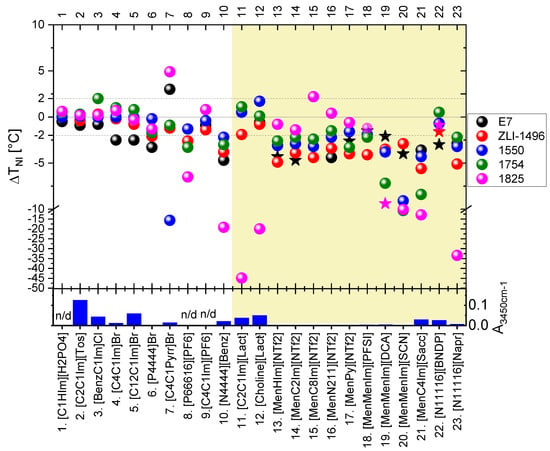
Figure 3.
Shift in the isotropization temperature of the nematic phase (ΔTNI) in the studied mixtures of LCs doped with 4.4–5.4 wt% (or 20 ± 1 wt%—in case of some mixtures with ILs nos. 11 and 12) of ILs. Dotted lines at ±2.0 °C indicate a range of double value of uncertainty of the measurement (±2u) around the TNI of the LC host. The star symbols in the graph indicate induction of the twisted nematic phase in the mixtures. The results are also presented in the Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials. The column graph below presents the parameter A3450cm−1, related to the water content of the ILs. Mixtures with CILs are highlighted by yellow background color. Details are described in the text.
Analyzing the results, with respect to the studied ILs, the mixtures of the LCs with nonchiral ILs nos. 1–6 and 9 introduced only low |ΔTNI| values. An exception to this observation was slightly higher |ΔTNI|—specifically in the case of the E7 mixtures with bromide ILs nos. 4–6. Higher |ΔTNI| were observed in the studied mixtures of the LCs with the following ILs: [C4C1Pyrr]Br (no. 7), [P66616][PF6] (no. 8) and [N4444][Benz] (no. 10). However, in the case of the [C4C1Pyrr]Br (no. 7), the results might be affected by partial evaporation of the LCs during mixing of the components at high temperature—above 230 °C. High |ΔTNI|, in case of the mixture with host 1550, might be influenced by possible reaction with a component possessing cyanide group, which was present in this multicomponent LC host at a weight fraction of 23%. Mixtures with commercial chiral lactate ILs: [C2C1Im][Lact] (IL no. 11) and [Choline][Lact] (IL no. 12), exhibited high |ΔTNI| only for the 1825 LC host, which might be an effect of a chemical reaction, manifested by the change in the color of the mixtures and formation of gaseous products.
More generally, high |ΔTNI| values in mixtures of the 1825 LC host with carboxylate ILs nos. 10–12 and 23 were expected to be caused by chemical reactions. The water contained in the ILs may have affected the mixtures with the host 1825 because of potential reactivity with isothiocyanates. However, relatively high water content, also present in ILs nos. 2, 3, and 5, did not substantially change the TNI in their mixtures with the 1825 LC host.
All of the synthesized CILs with menthoxymethyl substituent(s) (nos. 13–21) exhibited significant |ΔTNI| of the mixtures with most of the studied LC hosts. The most pronounced changes were found in the mixtures with: [MenMenIm][DCA], [MenMenIm][SCN], and [MenC4Im][Sacc]. These CIL dopants caused high |ΔTNI|, even in the mixtures with the 1754 LC host, which was considered to be non-reactive. These IL dopants might have dissolved partially in the 1754 LC host or underwent a self-reaction in the reaction environment because of: high temperature, presence of air, water, or LC host.
Despite the miscibility or reactivity of some non-chiral ILs with the 1825 host, only a low |ΔTNI| was found in the case of the mixtures doped with synthesized menthoxymethyl-based CILs composed of fluorinated anions: [NTf2] and [PFSI]. Without more extensive studies, one could only speculate that this was due to a low amount of water in these ILs, as isothiocyanate (-N=C=S) group reacts with water and alcohols. In contrast, the E7 mixtures with mentoxymethyl-based CILs often showed a relatively high |ΔTNI| and induction of the twisted nematic phase, in the case of six CILs from this group.
The synthesized chiral salts with cetyltrimethylammonium cation (ILs nos. 22 and 23) exhibited high |ΔTNI|—in case with naproxenium anion (IL no. 23) and relatively low |ΔTNI| in case of the binaphtyl-based anion (IL no. 22). However, as it will be presented below in more detailed studies, the latter chiral salt reacts with three of the studied LC hosts forming twisted nematic phase, especially with 1825 LC host, in which high HTP product(s) were formed.
With respect to the studied LC hosts, high |ΔTNI| results were the most numerously observed in the mixtures with 1825, E7, and ZLI-1496 LC hosts. The twisted nematic phase textures were observed in ten mixtures with only these three hosts, but they were the most effective in the case of the first two hosts. Figure 4 presents examples of the twisted nematic phase textures observed in the LC + CIL mixtures. The mixtures were of interest of the more detailed phase diagram and reactivity studies in the Section 3.2.
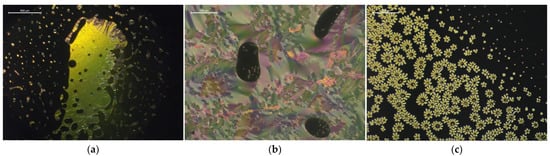
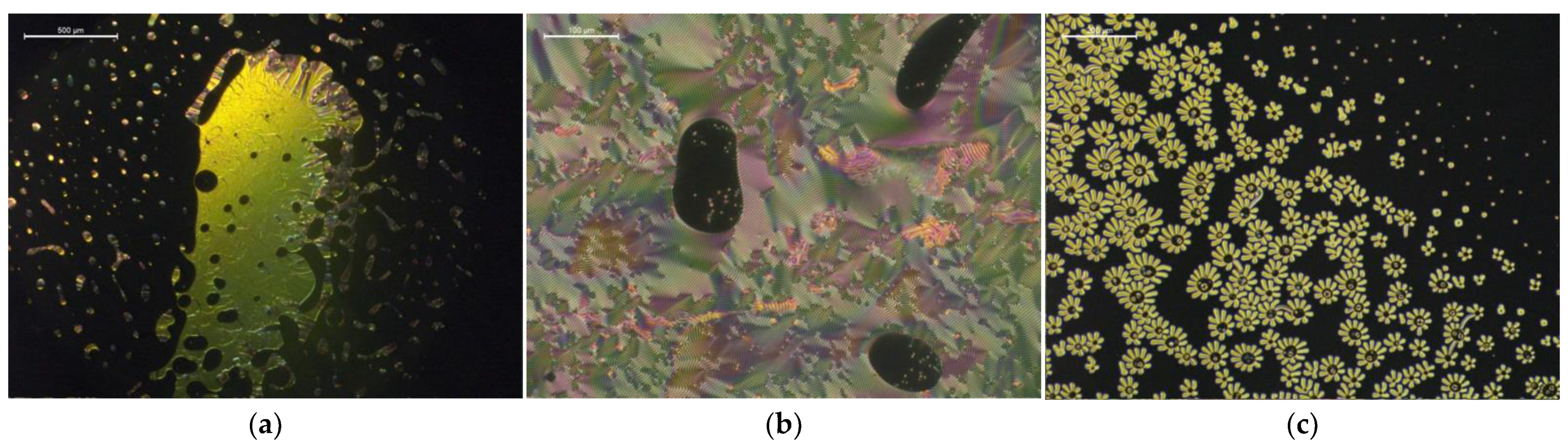
Figure 4.
Biphasic regions of isotropic and twisted nematic phases, with various textures induced in the following mixtures of the LCs with the ILs: (a) oily streaks texture in a mixture of 1825 + 19.1 wt% [MenMenIm][DCA] at 90 °C, (b) fingerprint (cholesteric gratings) texture in a mixture of E7 + 10.2 wt% [MenMenIm][DCA] at room temperature, (c) “flower-like” fingerprint texture observed during nucleation of twisted nematic phase around the domains of CIL in an overcooled mixture of E7 + 4.8% [MenMenIm][PFSI] at 40 °C, during the cooling cycle.
Moreover, the type of the anchoring of the nematic phase in the mixtures was studied in the plain glass cells, and the results are presented in the Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials. Many of the mixtures exhibited homeotropic anchoring of the nematic phase. The homeotropic anchoring studies are summarized in Section S3.3 in the Supplementary Materials.
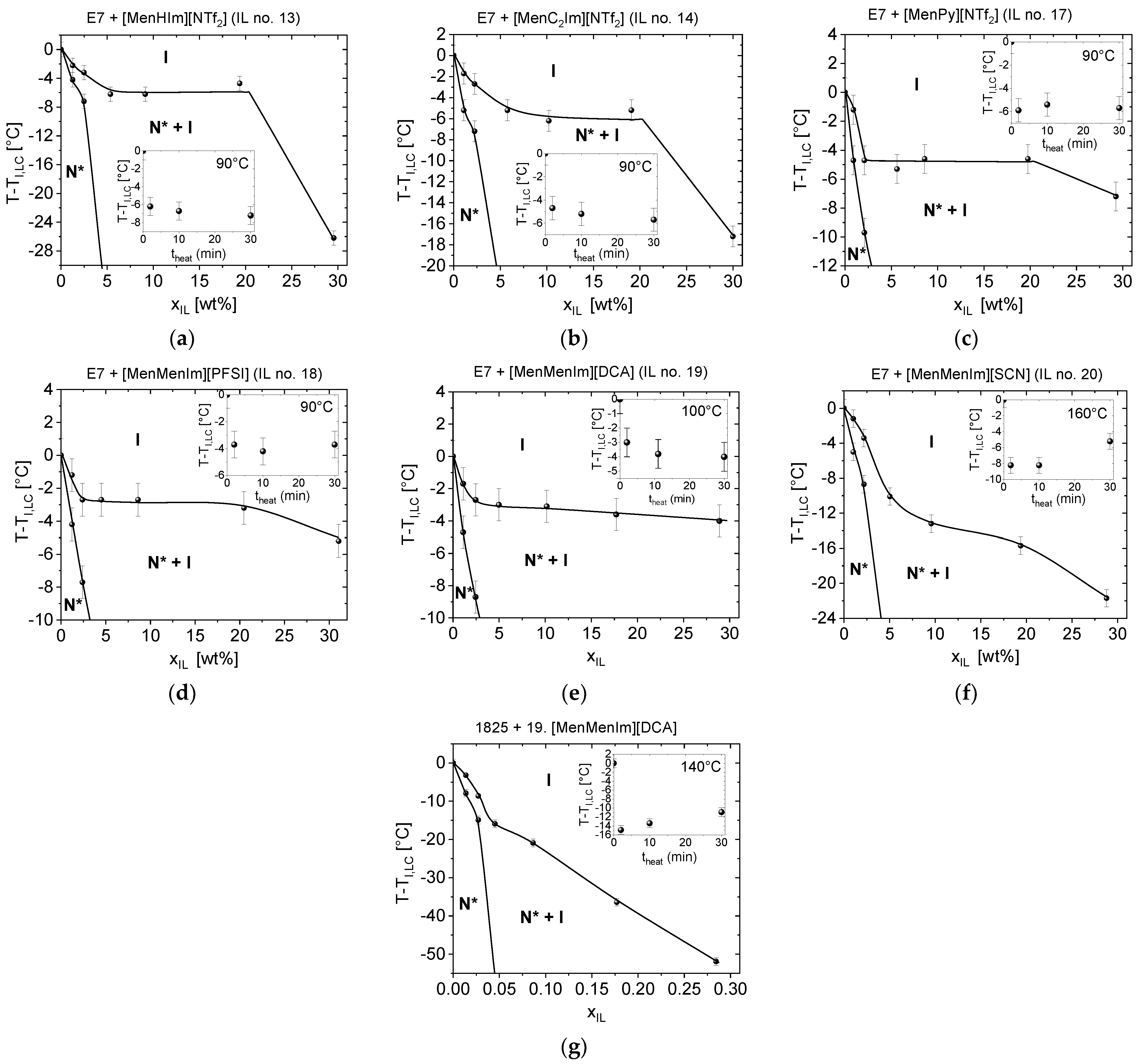
3.2. Phase Diagrams and Reactivity Studies of the Mixtures Exhibiting Twisted Nematic Phase
The LC + CIL mixtures, exhibiting a twisted nematic phase (indicated by star symbols in the Figure 3), were studied with respect to weight fraction of the CIL component in range from 0 to 30%. The phase diagrams of the LC and CIL pairs are presented in Figure 5. The CILs, which are typically crystalline at the room temperature: [MenMenIm][SCN], [MenMenIm][DCA], and [MenMenIm][PFSI] were in supercooled isotropic liquid state at the experimental conditions. The phase diagrams of the mixtures of LC hosts with the salt [N11116][BNDP] (studied in not-dried and dried state) exhibited respectively lower |ΔTNI| values with the CIL weight fraction and are presented in Figure S8 in the Supplementary Materials. The multicomponent LC hosts—1825 and E7—might be reactive with the ILs because of the presence of functional -N=C=S isothiocyanate, C≡C bonds, and cyanide group -C≡N. Another experiment was performed to check the reactivity of the selected mixtures. Progress of the |ΔTNI| of LC + CIL mixtures with heating time was studied. The results are presented as insets in graphs in the Figure 5.
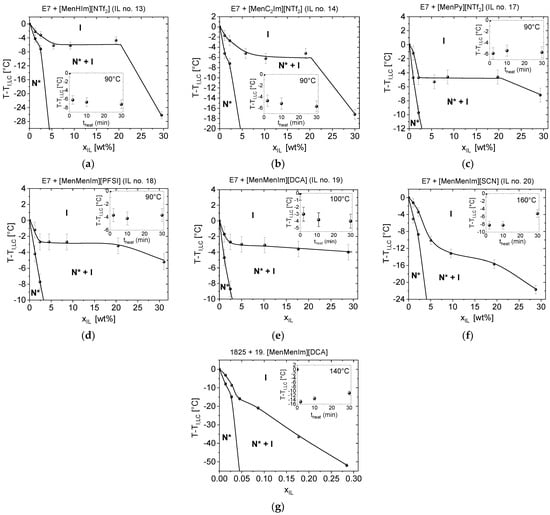
Figure 5.
Phase diagrams of chosen LCs, with CILs mixtures exhibiting twisted nematic phase, determined just after preparation of the mixtures, in a range of IL weight fraction (xIL) from 0 to 30%: (a) E7 + [MenHIm][NTf2], (b) E7 + [MenC2Im][NTf2], (c) E7 + [MenPy][NTf2], (d) E7 + [MenMenIm][PFSI], (e) E7 + [MenMenIm][DCA], (f) E7 + [MenMenIm][SCN], (g) 1825 + [MenMenIm][DCA]. Symbols: N*—twisted nematic phase, I—isotropic phase. The insets show the progress of the |ΔTNI| of the about 5 wt% mixtures with the heating time. The phase transition lines in the phase diagrams were sketched with respect to the determined points and serves for guiding an eye. Details are described in the text.
The E7 mixtures, with the CILs presented in the Figure 5, only exhibited a low change of the |ΔTNI| with heating time from 2 to 30 min, indicating no or a very slow reaction. However, it could not be excluded that an instant reaction with the LC host had occurred with no further changes in the isotropization temperature in this time range. An exception found for E7 + [MenMenIm][SCN] mixture of 3.0 °C increase in TNI might be an effect of a partial evaporation of some of the E7 host components, as the TNI of a reference sample (E7 LC host) at similar heating conditions increased by 2.0 °C. Details are described in the Section S1.3 in the Supplementary Materials.
The phase diagrams of all of the mixtures presented in the Figure 5 consisted of a region from 0 up to about 5 or 10 wt%, where the decrease in the isotropization temperature was observed. Then, the phase transition temperature stabilized at the xIL up to 20 or even 30 wt%. In case of certain mixtures (Figure 5a–d,f), the TNI decreases at the step from about 20 to 30 wt%, what might be caused by higher fraction of the isotropic phase of the IL, which, in turn, may dissolve the LC molecules at respective higher level. Miscibility of the components in the twisted nematic range was found in all of these six mixtures at a level of about 2 wt% from the room temperature up to temperature 7–10 °C below the TNI of E7 LC host. Moreover, the mixtures of E7 with [MenHIm][NTf2] and [MenMenIm][SCN] were close to be miscible at about 5 wt%, as a very low fraction of the isotropic phase was observed.
The mixtures of the 1825 LC host with the [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt (the results presented in Figure S8 in the Supplementary Materials) and with [MenMenIm][DCA] (Figure 5), presented reactivity, indicated by a decrease and an increase in the isotropization temperature with the heating time, respectively. The LC hosts E7 and ZLI-1496, doped with the [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt, only resulted in very low changes in isotropization temperature with concentration and with heating time of the 5 wt% mixtures in both cases, even without respect to the content of the water in the chiral salt (c.f. Figure S8 in the Supplementary Materials).
Slightly different shapes of the phase diagrams were observed in case of mixtures with high |ΔTNI|. A monotonic decrease in TNI with the CIL weight fraction was found in the samples: (a) 1825 with [MenMenIm][DCA], which was recognized that mutual reaction between the components have occurred and (b) E7 with [MenMenIm][SCN].
3.3. Studies of the Helical Pitch of the mixtures Exhibitingthe Twisted Nematic Phase
As highlighted by star symbols in the graph in Figure 3, the twisted nematic phase was induced in ten of the mixtures of the CILs with E7, 1825, and ZLI-1496 LC hosts, but in as many as seven mixtures with the first LC host. Helical pitch of the twisted nematic phase (p) was determined alternatively by fingerprint (Legarde) or wedge cell (Grandjean-Cano) method (compared in ref. [43]), as described in the Section S1.5 in the Supplementary Materials. The fingerprint method is not the most reliable from the known methods (according to the paper [43] and its references). However, the presence of the CILs in the mixtures caused homeotropic twisted nematic alignment in the samples, limiting the choice of the methods for the helical pitch determination. The inverse pitch was calculated for comparison purposes, as it is proportional to the weight-based HTP (βw) by relation: βw = p−1 ∙ xIL−1 (assuming enantiomeric excess of the chiral dopant to be equal unity). The results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The results of the helical pitch measurements of the LC with CIL mixtures exhibiting the twisted nematic phase. The results are related to the saturated solutions of the CILs in the LC hosts.
It must be noted that the weight fraction of the CIL was over the miscibility limit in the LC phase of the mixtures, thus the results of the pitch of the helix are related to the saturated solutions of the CILs in the LC hosts. Moreover, it should be taken into account that, for the mixtures of 1825 with [MenMenIm][DCA] and with [N11116][BNDP], the reactivity between components was found. Thus, the results are valid only for the mixture at certain heating time.
The twisting power may come from miscibility of the chiral components in the LC host or from potential chemical reaction between the components from which new chiral compounds might be formed. For the first six mixtures in the Table 1, the miscibility of the CIL in the LC according to the Figure 5 is between 2 and 5%, thus βw of these mixtures can be estimated at order of magnitude of several μm−1, which is comparable with e.g., CB15—commercial chiral dopant.
The highest determined inversed helical pitch (p−1) was found in the mixtures with [MenMenIm][DCA] IL. A high difference—about three times higher p−1 value in case of the 1825 LC host than in the case of E7—could be a result of high HTP of the chemical reaction product(s) in reaction with the 1825 LC host. The magnitude of the twisting power in mixture 1825 + [MenMenIm][DCA] is interesting for optical applications; however, the growth of the fraction of the isotropic phase with the weight fraction of the IL limits the potential applications of this dopant. A relatively low twisting power was found in case of the mixtures of the [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt with the LC hosts. However, reactivity of the salt with the 1825 mixture was found, and long-time heating of the mixture led to very high HTP (even higher than for the above-mentioned mixture—E7 + [MenMenIm][DCA]), which is studied in the next paragraph.
3.4. Studies of the Reaction of the [N11116][BNDP] Chiral Salt with the Multicomponent 1825 Liquid Crystal Host for High Helical Twisting Power Product(s)
High helical twisting power of the chiral dopants is still of interest among other liquid crystalline materials [21,44,45,46,47,48], especially those with new electro-optical functionalities, such as optical tunability [44,45], an electrically tunable reflection band [47], and blue phases, which are used in systems such as electro-optical modulators [48].
The novel chiral salt [N11116][BNDP] was chosen for further studies, because of introducing the highest HTP changes in mixtures with multicomponent isothiocyanate-based LC host—1825, pronounced by appearance of selective light reflection band within the NIR and visible light range after relatively long heating time.
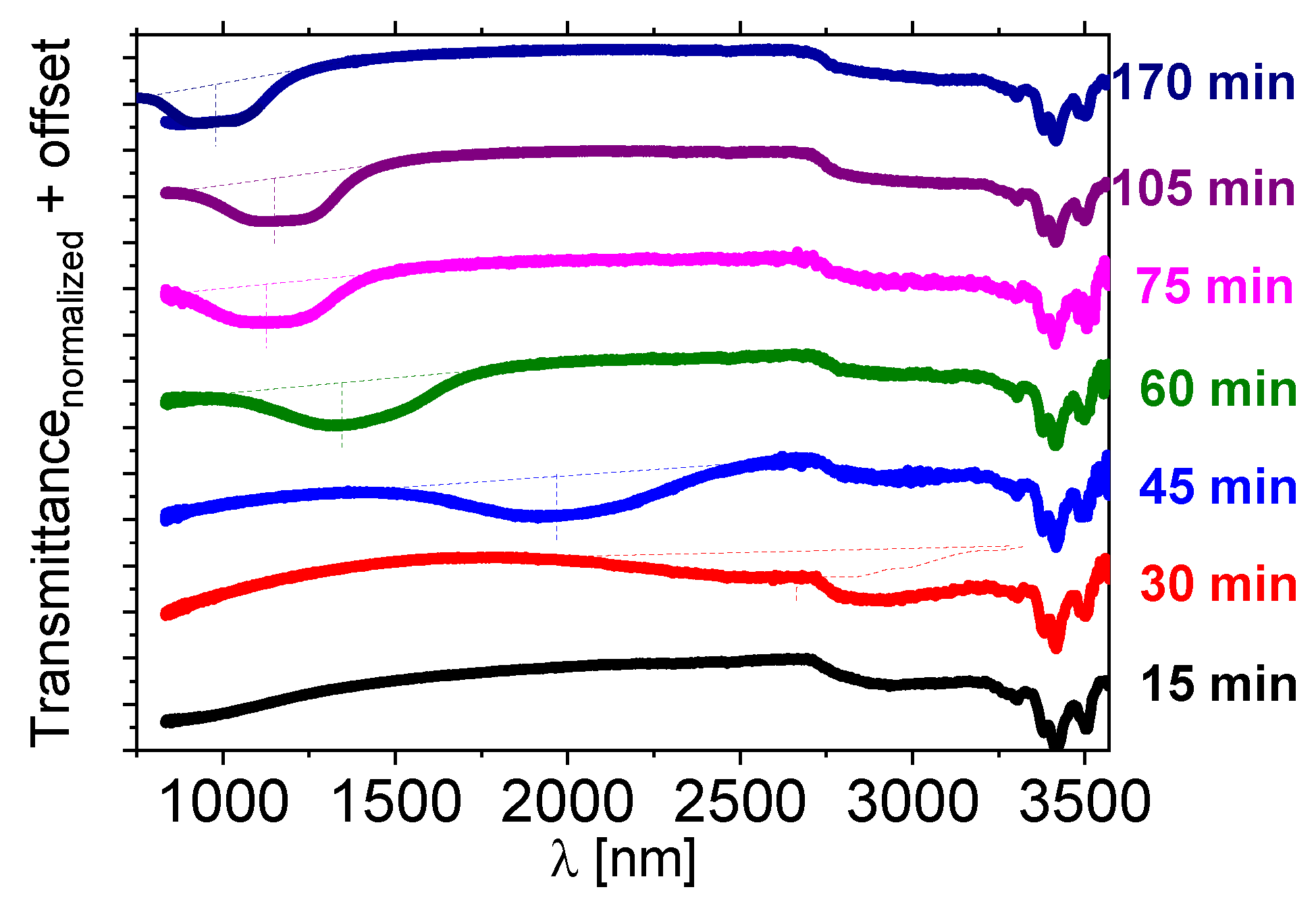
The [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt was doped to the 1825 LC host at about 10 wt%. The reaction was performed above the isotropization temperature of the liquid crystal host—at 150 °C or slightly below—at 131 °C, independently, in a presence of a small amounts of solvents. The NIR and UV-Vis transmission spectra of the mixtures, with respect to the heating time at 150 °C, are presented in Figure 6 and for heating at 131 °C—in Figure S10a in the Supplementary Materials. Details are described in the Section S1.6 in the Supplementary Materials.
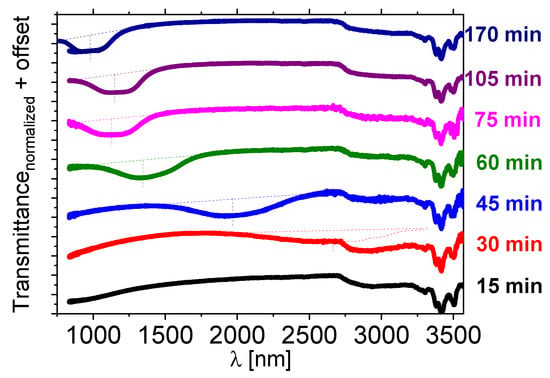
Figure 6.
Near-infrared transmission spectra of the isothiocyanate-based multicomponent LC host—1825 doped with about 10 wt% of the [N11116][BNDP] salt after various heating time at a temperature of 150 °C. For the heating time of 170 min, the result of additional measurement in a range of 750–1100 nm by another UV-Vis-NIR spectrometer is presented by individual lines of the same color. Dotted lines were sketched to indicate estimated shapes and position of the center of the reflection bands.
A selective reflection band in the NIR range appeared after 30–45 min and was shifting towards a short wavelength with the heating time. Oily streak textures were observed by the POM in the samples exhibiting reflection bands, which confirmed the planar alignment of the twisted nematic phase. The mixture heated at 131 °C behaved in a similar manner (c.f. Figure S10a in Supporting Info).
3.4.1. Reference Studies of Reactivity of the 1825 LC Host with Double Dopant Containing the [BNDP] and [N11116] Ions
In order to check the influence of a type of the dopant the reference samples consisted of LC host 1825: (a) doped with about 5 wt% chiral binaphtyl phosphonic acid BNDHP and 5 wt% of [N11116]Br salt (the molar fraction between the dopants was close to 1:1); (b) doped only with 10 wt% of BNDHP acid; (c) without doping—were prepared and the reactions were perfomed under similar conditions (150 °C).
Samples doped only with 10 wt% of BNDHP acid and those without doping did not exhibit any reflection band within the NIR range or twisted nematic texture under the microscope after heating (results not presented), which may have been caused by the poor solubility of the BNDHP compound in the 1825 host.
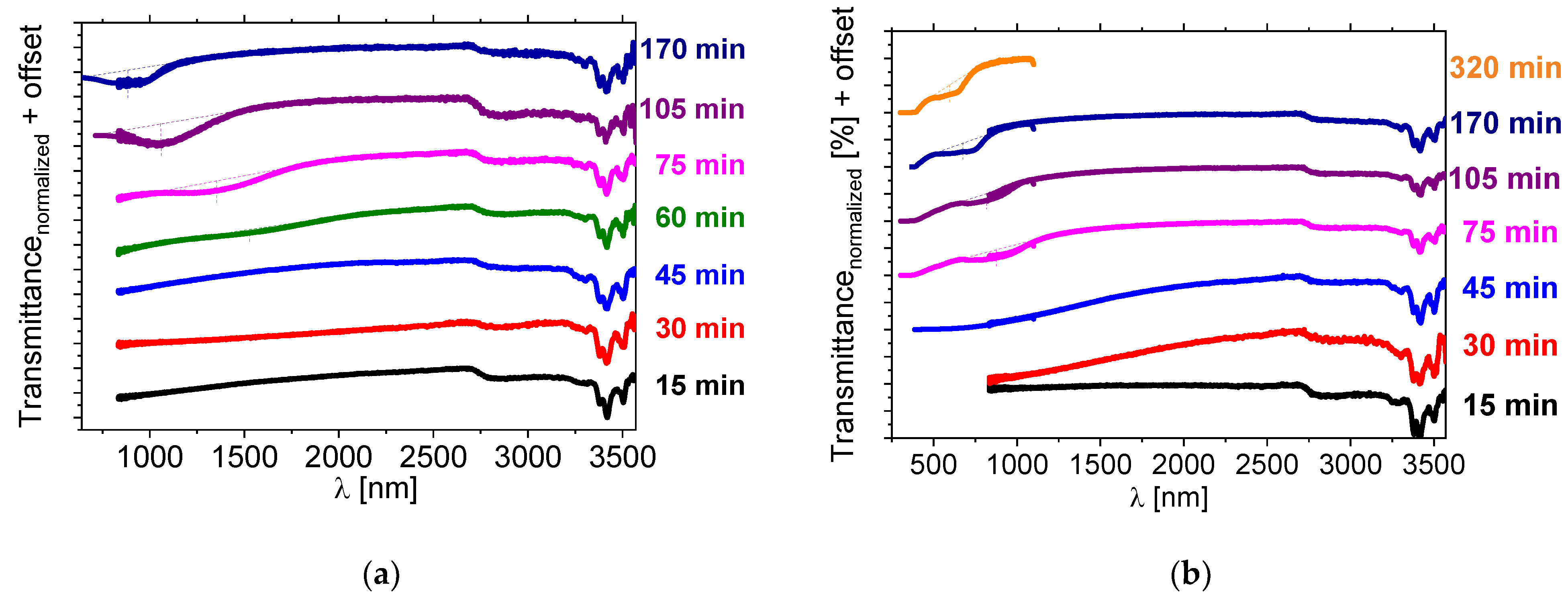
The transmission spectra of the sample doped with 5 wt% of BNDHP and 5 wt% of [N11116]Br, as a function of heating time, are presented in Figure 7a. In the case of the use of these two individual dopants, the reflection band also appeared within the NIR range and was shifting toward short wavelengths with the heating time. The reflection band did not appear when a similar reaction was performed at a hot-plate temperature of 131 °C even after 75 min (results presented in Supporting Info—Figure S10b). This finding may be related to the limited miscibility between components when the liquid crystal host 1825 was still in the nematic phase. The reaction mixture was not clear at 131 °C, which is in contrast to the result of use of the novel salt [N11116][BNDP] as the chiral dopant.
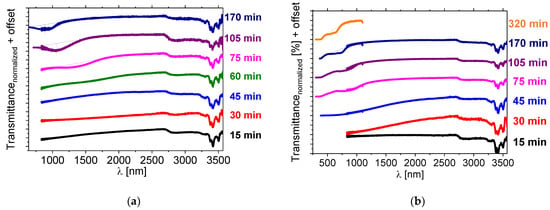
Figure 7.
Near-infrared transmission spectra of isothiocyanate-based LC mixture 1825 doped with about 5 wt% of the BNDHP acid and 5 wt% of the [N11116]Br (CTAB) salt after various heating time of the mixture at temperature 150 °C, measured: (a) directly after the preparation, (b) after one day of storing the sample at the room temperature. Results of the measurements of the samples within a range of (a) 650–1100 nm or 700–1100 nm, (b) 300–1100 nm, for the evaluation of the position of the reflection bands by another UV-Vis-NIR spectrometer are presented by the individual lines with the same color. Dotted lines were used to indicate a shape and a position of the center of the reflection bands.
During this stage of the research another intriguing feature was observed, namely a shift in the reflection band position of the samples after a couple of days, when stored at the room temperature. Mixtures of the 1825 LC host doped with about 5 wt% of BNDHP and 5 wt% of [N11116]Br were measured one day after the preparation. The transmission spectra are presented in Figure 7b. Photographs of a selected sample within the time, ranging from 2 to 45 days after preparation, are presented in Supporting Info—Figure S11 and show, visually, the progress of the reaction with aging time, as growth of the selective reflection band region on the sample.
Other reference samples, with other LC hosts—E7 and 1754—were prepared and tested for reactivity with the above single- and double-component dopants or their self-reactivity. Only low twisting power twisted nematic textures were observed by POM after 15 min of heating and remained up to 175 min, in case of E7 mixtures. The reference studies are described in more details in the Section S3.5.
3.4.2. Dynamics of the Helical Pitch of the Mixtures with the Heating Time
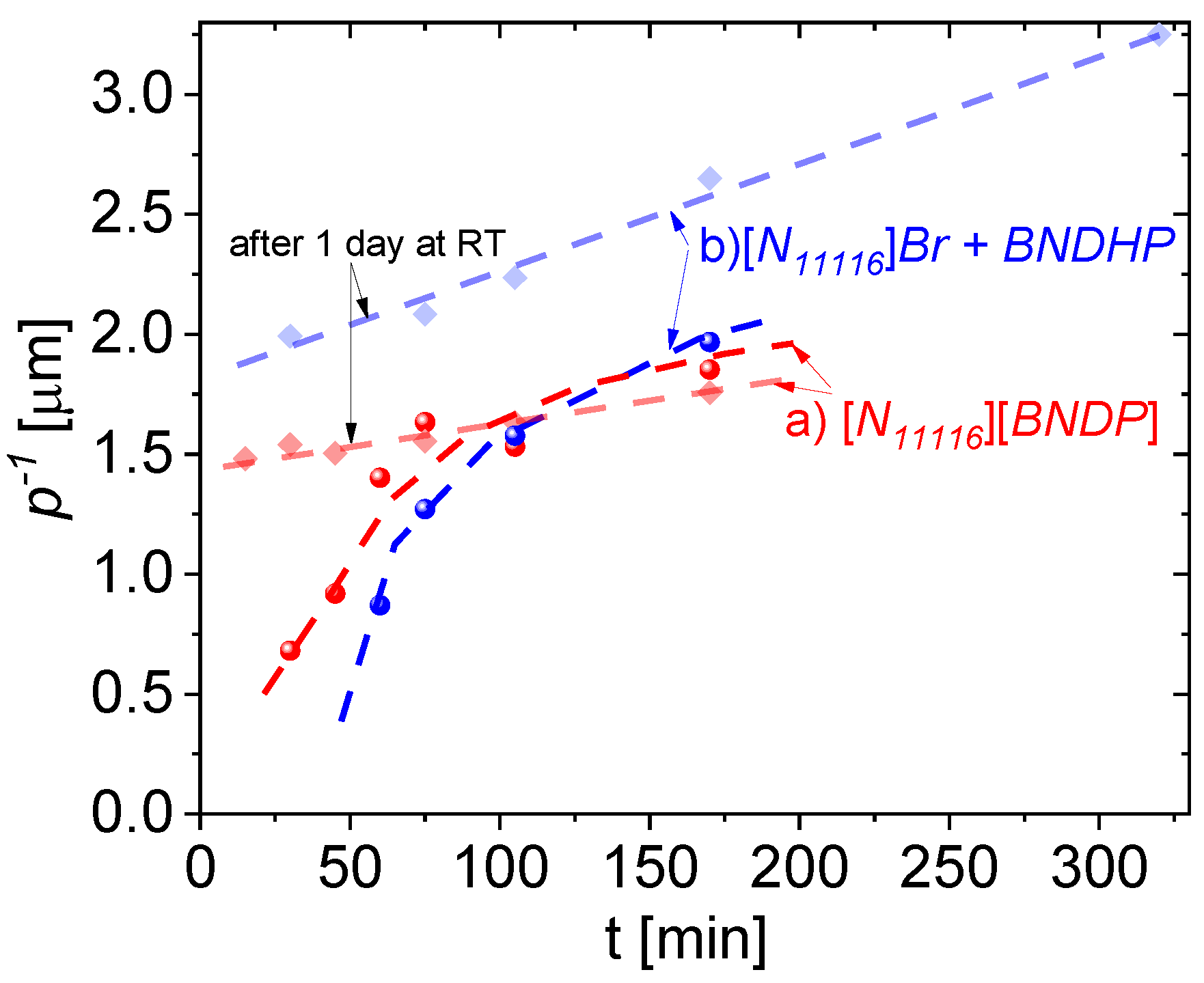
This section describes the determination of the inversed helical pitch p−1 parameter in the above-studied mixtures of the 1825 LC host with: (a) chiral salt dopant—[N11116][BNDP] or (b) double dopant—BNDHP + [N11116]Br, investigated with the increasing heating time and for aging time 0 and 1 days. The center of the selective light reflection band (λsel) was determined from the spectrophotometric results and the inversed helical pitch was calculated from relation p−1 = n · λsel−1, where: n = (no + ne)/2—average refractive index of the mixture equal (ordinary and extraordinary refractive indices of pure 1825 host mixture were assumed). The studies were performed at close weight fraction of the studied mixtures, which simplified the comparison of the results. The weight fraction equal 8.9 ± 0.8 wt% was used and was related to the content of the: (a) chiral salt dopant—[N11116][BNDP] or (b) double dopant—BNDHP + [N11116]Br (the dopants’ content was summed up). The results of the dynamics of the p−1 parameter of the studied mixtures with the heating time is presented in Figure 8.
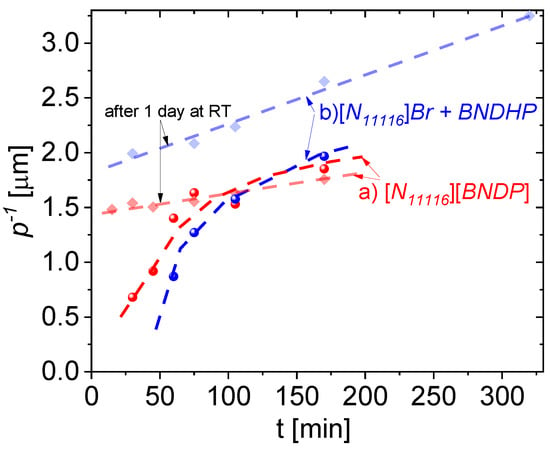
Figure 8.
Dynamics of the inversed helical pitch of the mixtures of 1825 liquid crystal host doped with: (a) 9.3 ± 0.2 wt% of [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt and (b) 4.5 ± 0.4 wt% of BNDHP acid and about 4.6 ± 0.6 wt% of the [N11116]Br (CTAB) salt, with respect to the heating time at temperature of 150 °C. Bold and light points and lines are related to the samples measured at the day of preparation and one day after preparation, respectively. Dashed curves or lines are presented for guiding an eye.
Progress of the thermal reaction at a time from several tens of minutes up to several hours is manifested by an increase in the helical twisting power of the product(s) expressed as inversed helical pitch. Increase in the p−1 after one day of aging at the room temperature, especially for the mixtures heated for relatively short time was found, confirming the observations of spontaneous progress of the reaction.
Such progress of the reaction was noticed selectively in the mixtures with the isothiocyanate-based LC host N111161825. The reaction types in the mixtures, doped with (a) [N11116][BNDP] salt and (b) two-component mixture of BNDHP and [N11116]Br, were rather similar because of a similar order of magnitude of the induced helical twisting power. Slightly delayed dynamics and higher helical twisting power were observed in the case of the double-dopant mixture. The reaction probably requires both types of ions: (a) a [N11116] (cetyltrimethyl) cation that introduces an ionic environment in the reaction mixture and long hydrocarbon chain, which may help in the solubility of the liquid crystal components; (b) a [BNDP] anion for linking with isothiocyanate compound(s) to obtain high helical twisting power product(s). Assuming the weight fraction of the dopant (or sum of the dopants) the effective helical twisting power (βw,eff) (defined as βw,eff = p−1 · xw,dopants−1) for the highest result presented in Figure 8, would be at the level of about 34 μm−1, which is quite high for chiral dopants. Potentially, separated chiral product(s) would have even higher HTP. However, a quantity and number of different chiral product(s) in the reaction mixtures were unknown.
As a joint reaction between the two components occur, high HTP of the product(s) could be expected when the chiral center was transferred and linked covalently with the LC host molecules. The reaction may occurred potentially at isothiocyanate group or triple C≡C bond of the host LC molecules. However, formation of new chiral centers in 1825 LC host molecules, also catalyzed by the chiral [BNDP] anion could not be neglected, as known that binaphtyl-based compounds can catalyze regioselective substitution [27].
4. Conclusions
The miscibility in the nematic phase was searched in mixtures of 5 various LC hosts doped with about 5 wt% of 23 various ILs. Shift in the isotropization temperature and the appearance of the twisted nematic phase in the mixtures with CILs indicated certain level of miscibility of the LC and IL components. However, the results in certain systems might have been affected by joint reaction between the components. Most of the synthesized menthoxymethyl-based CILs caused a relatively high |ΔTNI| in mixtures with various LC hosts. Twisted nematic phase was induced in some of the mixtures of E7 and 1825 LC hosts with the menthoxymethyl-based CILs and 1825, E7, and ZLI-1496 LC hosts with the novel chiral salt [N11116][BNDP]. Phase diagrams of these mixtures in range of weight fraction, up to about 30%, were determined. Six mixtures of E7 LC host with menthoxymethyl CILs exhibited miscibility at the weight fraction between about 2% and 5%. For the application purposes, the limited miscibility might be overcome by increased HTPHTP of the chiral dopant. Both of the parameters should be further balanced in the design of structures of the chiral ionic dopants.
Some of these mixtures, mainly based on isothiocyanate-based LC host—1825—exhibited reactivity with IL dopants, especially those with carboxylic anions. The highest helical twisting power was observed in mixtures of 1825 with [N11116][BNDP] chiral salt and mixtures of the 1825 and E7 LC hosts with the [MenMenIm][DCA] IL. However, in case of the first two, the results were affected by a chemical reaction between components.
The chemical reaction between 1825 LC host and novel chiral organic salt [N11116][BNDP] was indicated by the appearance and shifting of the selective reflection band of the twisted nematic phase within NIR and a visible range. Formation of high HTP chiral product(s) was found with effective HTP at level up to 34 μm−1. The reaction of the 1825 LC host, with two separate compounds with the same ions of the chiral salt, led to even slightly higher HTP product(s) and slightly different reaction dynamics. Aging of the mixtures at laboratory conditions resulted in the increase in the HTP of the mixtures. The reference samples with E7 and 1754 LC hosts were compared, but the results show that high HTP product(s) was only obtained in the mixtures with the 1825 host. Studies of the product(s) of high helical twisting power reaction are under way. The results may open up new synthetic ways for high helical twisting power and chiral dopants of high compatibility with LCs, as well as synthesis of other chiral compounds.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ma15010157/s1, Figure S1: Photomicrographs of the sample [N11116][BNDP] at various temperatures during heating cycle; Figure S2: Photomicrographs of the sample [N11116][Napr] at various temperatures during heating cycle; Figure S3: Experimental X-ray diffractogram of the synthesized salt [N11116][BNDP] and diffractogram of reference compound BNDHP; Figure S4: Experimental X-ray diffractogram of the synthesized salt [N11116][Napr]; Figure S5: Normalized Mid-IR absorption spectra of studied commercial ionic liquids; Figure S6: Normalized Mid-IR absorption spectra of studied synthesized ionic liquids; Figure S7: Absorbance at 3450 cm−1 with subtracted background of the studied ionic liquids at room temperature; Figure S8: Phase diagrams of chosen liquid crystal with [N11116][BNDP] salt (IL no. 22) mixtures exhibiting twisted nematic phase in a range of ionic liquid weight fraction (xIL) between 0 and 30%: (a) E7 + [N11116][BNDP], (b) 1825 + [N11116][BNDP], (c) ZLI-1496 + [N11116][BNDP]; Figure S9: Disturbed schlieren nematic texture with high amount of defect points in the sample of 1754 with 4.8% [MenC4Im][Sacc], observed just after preparation of the sample; Figure S10: Near-infrared transmission spectra of isocyanate-based liquid crystal host 1825 doped with (a) about 10% of [N11116][BNDP] salt, (b) about 5% of BNDHP and 5% of [N11116]Br after various heating time of the mixture at 131 °C; Figure S11: Photographs of the sample 1825 doped with about 5% of BNDHP and 5% of [N11116]Br, heated 45 min at temperature 150 °C, taken after different time (in days) after preparation: 2, 10, 31 and 45, showing changes of the area of the region of selective light reflection; Scheme S1. Synthesis route of [N11116][BNDP] salt from BNDHP; Scheme S2. Synthesis route of [N11116][Napr]; Table S1. Physical properties of the studied liquid crystals, used as hosts in mixtures with ionic liquids; Table S2. Details of the studied ionic liquids; Table S3. Shift in the isotropization temperature (ΔTNI) of the nematic phase of liquid doped with 4.4–5.4 wt% (or 20 ± 1% in case of some mixtures with ILs nos. 11 and 12) of ionic liquid; Table S4. Chosen POM microphotographs of the reference mixtures of 1754 and E7 liquid crystal hosts doped with: (a) 10% [N11116][BNDP] and (b) 5% BNDHP + 5% [N11116]Br during reaction at 150 °C; References [49,50,51] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C.; methodology, M.C. and B.P.; formal analysis, M.C.; investigation, M.C., B.P., Ł.D. and J.F.-K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C.; writing—review and editing, J.F.-K., J.C. and B.P.; visualization, M.C.; supervision, J.C.; funding acquisition, M.C. and J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by Narodowe Centrum Nauki (National Science Center), Poland, grant No. 2016/21/D/ST5/01674. The research was conducted under agreement with Łukasiewicz Research Network—PORT Polish Center for Technology Development, Wrocław.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
J.F.-K. is grateful for the financial support given by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education by subvention activity for the Faculty of Chemistry at Wrocław University of Science and Technology. M.C. is grateful for the support from R&D Department of PCC Exol SA.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hu, W.; Zhang, L.; Cao, H.H.; Song, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, H.; Guo, L. Electro-optical study of chiral nematic liquid crystal/chiral ionic liquid composites with electrically controllable selective reflection characteristics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, H.; Song, L.; Yang, Z.; Cao, H.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H. Electrically Controllable Selective Reflection of Chiral Nematic Liquid Crystal/Chiral Ionic Liquid Composites. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondiglia, V.T.; Natarajan, L.V.; Bailey, C.A.; Duning, M.M.; Sutherland, R.L.; Ke-Yang, D.; Voevodin, A.; White, T.J.; Bunning, T.J. Electrically induced bandwidth broadening in polymer stabilized cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 053109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondiglia, V.P.; Natarajan, L.V.; Bailey, C.A.; McConney, M.E.; Lee, K.M.; Bunning, T.J.; Zola, R.; Nemati, H.; Yang, D.-K.; White, T.J. Bandwidth broadening induced by ionic interactions in polymer stabilized cholesteric liquid crystals. Opt. Mater. Expr. 2014, 4, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Tondiglia, V.P.; McConney, M.E.; Natarajan, L.V.; Bunning, T.J.; White, T.J. Color-Tunable Mirrors Based on Electrically Regulated Bandwidth Broadening in Polymer-Stabilized Cholesteric Liquid Crystals. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Tondiglia, V.P.; White, T.J. Electrically Reconfigurable Liquid Crystalline Mirrors. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4453–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, S.; Wada, K.; Hidaka, M.; Hanasaki, T.; Akagi, K. Chiral Liquid-Crystalline Ionic Liquid Systems Useful for Electrochemical Polymerization that Affords Helical Conjugated Polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Yamakawa, S.; Akagi, K. Liquid crystallinity-embodied imidazolium-based ionic liquids and their chiral mesophases induced by axially chiral tetra-substituted binaphthyl derivatives. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3960–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, Ł.; Potaniec, B.; Czajkowski, M.; Fiedot-Toboła, M.; Palewicz, M.; Zdończyk, M.; Madej, A.; Cybińska, J. Studies of intermolecular proton transfer, its influence on the liquid crystal properties and electrically-driven transport of chiral ions in mixtures of chiral liquid crystalline 4-phenylpyridine derivative and organic acids of various strength. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xu, W.; Song, Z.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Hu, J.; Lv, G. Electrically switchable multi-stable cholesteric liquid crystal based on chiral ionic liquid. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 6795–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czajkowski, M.; Klajn, J.; Cybińska, J.; Feder-Kubis, J.; Komorowska, K. Cholesteric gratings induced by electric field in mixtures of liquid crystal and novel chiral ionic liquid. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, H.; Luo, D. Bistable Smart Window Based on Ionic Liquid Doped Cholesteric Liquid Crystal. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L. Branched quaternary ammonium amphiphiles: Nematic ionic liquid crystals near room temperature. Chem. Commun. 2009, 35, 5269–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, K.; Nockemann, P.; Driesen, K.; Goderis, B.; Görller-Walrand, C.; van Hecke, K.; van Meerve, L.; Pouzet, E.; Binnemans, K.; Cardinaels, T. Imidazolium ionic liquid crystals with pendant mesogenic groups. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baudoux, J.; Judeinstein, P.; Cahard, D.; Plaquevent, J.C. Design and synthesis of novel ionic liquid/liquid crystals (IL2Cs) with axial chirality. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, M.; Alcalá, R.; Barberá, J.; Romero, P.; Sánchez, C.; Serrano, J.L. Photosensitive ionic nematic liquid crystalline complexes based on dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers and a cyanoazobenzene carboxylic acid. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5209–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayón, R.; Coco, S.; Espinet, P. Gold liquid crystals displaying luminescence in the mesophase and short F···F interactions in the solid state. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; Gehringer, L.; Frey, H.; Stiriba, S.E. Supramolecular thermotropic liquid crystalline materials with nematic mesophase based on methylated hyperbranched polyethylenimine and mesogenic carboxylic acid. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2006, 27, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrat, S.; Bier, M.; Harnau, L. Phase behavior of ionic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 184901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goossens, K.; Lava, K.; Bielawski, C.W.; Binnemans, K. Ionic Liquid Crystals: Versatile Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4643–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, Ł.; Czajkowski, M.; Potaniec, B.; Vaňkátová, P. Helical twisting power and compatibility in twisted nematic phase of new chiral liquid crystalline dopants with various liquid crystalline matrices. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, J.; Othman, A.; Fan, P.; Müller, A. Explaining ionic liquid water solubility in terms of cation and anion hydrophobicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z.; Freund, H.; Sundmacher, K. An overview of mutual solubility of ionic liquids and water predicted by COSMO-RS. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6256–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindl, A.; Hagen, M.L.; Muzammal, S.; Gunasekera, H.A.D.; Croft, A.K. Proteins in ionic liquids: Reactions, applications, and futures. Front. Chem. 2019, 2019. 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schröder, C. Proteins in Ionic Liquids: Current Status of Experiments and Simulations. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohd, N.; Draman, S.F.S.; Salleh, M.S.N.; Yusof, N.B. Dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquid: A review. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1809, 020035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eelkema, R.; van Delden, R.A.; Feringa, B.L. Direct visual detection of the stereoselectivity of a catalytic reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5013–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eelkema, R.; Feringa, B.L. Amplification of chirality in liquid crystals. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3729–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Green, L.; Venkataraman, N.; Shiyanovskaya, I.; Khan, A.; Urbas, A.; Doane, J.W. Reversible photoswitchable axially chiral dopants with high helical twisting power. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12908–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Gu, W.; Wei, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, X. Novel planar chiral dopants with high helical twisting power and structure-dependent functions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9576–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, R.; Dziaduszek, J.; Stolarz, Z.; Kedzierski, J. Liquid crystalline materials with low ordinary index. J. Opt. Technol. 2005, 72, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowinowski-Kruszelnicki, E.; Kedzierski, J.; Raszewski, Z.; Jaroszewicz, L.; Dabrowski, R.; Kojdecki, M.; Piecek, W.; Perkowski, P.; Garbat, K.; Olifierczuk, M.; et al. High birefringence liquid crystal mixtures for electro-optical devices. Opt. Appl. 2012, 42, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.; Vieweg, N.; Fischer, B.M.; Mikulicz, M.; Koch, M.; Garbat, K.; Dąbrowski, R. Highly birefringent, low-loss liquid crystals for terahertz applications. APL Mater. 2013, 1, 012107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kula, P.; Spadło, A.; Dziaduszek, J.; Filipowicz, M.; Dąbrowski, R.; Czub, J.; Urban, S. Mesomorphic, dielectric, and optical properties of fluorosubstituted biphenyls, terphenyls, and quaterphenyls. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2008, 16, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestov, S.; Vill, V. Liquid Crystals. In Springer Handbook of Materials Data, 2nd ed.; Warlimont, H., Martienssen, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 959–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder-Kubis, J. Synthesis and spectroscopic properties of symmetrical ionic liquids based on (−)-menthol. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 226, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, E.; Gano, M.; Feder-Kubis, J.; Sośnicki, J. Chiral protic imidazolium salts with a (–)-menthol fragment in the cation: Synthesis, properties and use in the Diels-Alder reaction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10318–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andresová, A.; Bendová, M.; Schwarz, J.; Wagner, Z.; Feder-Kubis, J. Influence of the alkyl side chain length on the thermophysical properties of chiral ionic liquids with a (1R,2S,5R)-(–)-menthol substituent and data analysis by means of mathematical gnostics. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder-Kubis, J.; Zabielska-Matejuk, J.; Stangierska, A.; Przybylski, P.; Jacquemin, J.; Geppert-Rybczyńska, M. Toward Designing “sweet” Ionic Liquids Containing a Natural Terpene Moiety as Effective Wood Preservatives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15628–15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Feder-Kubis, J. Chiral pyridinium-based ionic liquids containing the (1R,2S,5R)-(–)-menthyl group. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2006, 17, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Feder-Kubis, J. Synthesis and properties of chiral ammonium-based ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 4441–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.-W.; Huang, S.-H.; Fuh, A.Y.-G.; Lin, T.-H. Measurement of helical twisting power based on axially symmetrical photo-aligned dye-doped liquid crystal film. Opt. Expr. 2009, 17, 15926–15931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golicha, H.S.A.; Omar, M.H.; Mbithi, N.M. Optical Techniques in the Determination of Pitch Lengths in the Cholesteric and Chiral Smectic C Phases. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 10, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Ding, Y.; Qiu, L. Tuning helical twisting power and photoisomerisation kinetics of axially chiral cyclic azobenzene dopants in cholesteric liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2019, 46, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabchun, A.; Lancia, F.; Chen, J.; Morozov, D.; Feringa, B.L.; Katsonis, N. Helix Inversion Controlled by Molecular Motors in Multistate Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.Y.; Kim, B.C.; Jeon, S.W.; Bae, J.H.; Walker, M.; Wilson, M.; Choi, S.W.; Takezoe, H. Enhancement of the helical twisting power with increasing the terminal chain length of nonchiral bent-core molecules doped in a chiral nematic liquid crystal. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1932–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Paterson, D.A.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Electrically tunable selective reflection of light from ultraviolet to visible and infrared by heliconical cholesterics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3014–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.C.; Aya, S.; Kang, S.; Araoka, F.; Ishikawa, K.; Takezoe, H. Are chiral dopants with higher twisting power advantageous to induce wider temperature range of the blue phases? Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, C.H.; Gauza, S.; Lu, R.; Wu, S.T. Refractive Indices of Liquid Crystals for Display Applications. J. Display Technol. 2005, 1, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lava, K. Ionic Liquid Crystals Based on Novel Heterocyclic Cores. Ph.D. Dissertation, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Groep Wetenschap & Technologie, Arenberg Doctoraatsschool, W. de Croylaan, Leuven, Belgium, 2012. (ISBN 978-90-8649-570-2 D/2012/10.705/87). [Google Scholar]
- Cammarata, L.; Kazarian, S.G.; Salter, P.A.; Welton, T. Molecular states of water in room temperature ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 5192–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).