Electropolymerized Aniline-Based Stainless Steel Fiber Coatings Modified by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electroanalysis of 4-Chlorophenol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Characterization of the CNTs
2.3. Preparation of the PANI Coated Stainless Steel Fibers
2.4. Carbon Paste Electrodes Preparation
2.5. Voltammetry
3. Results
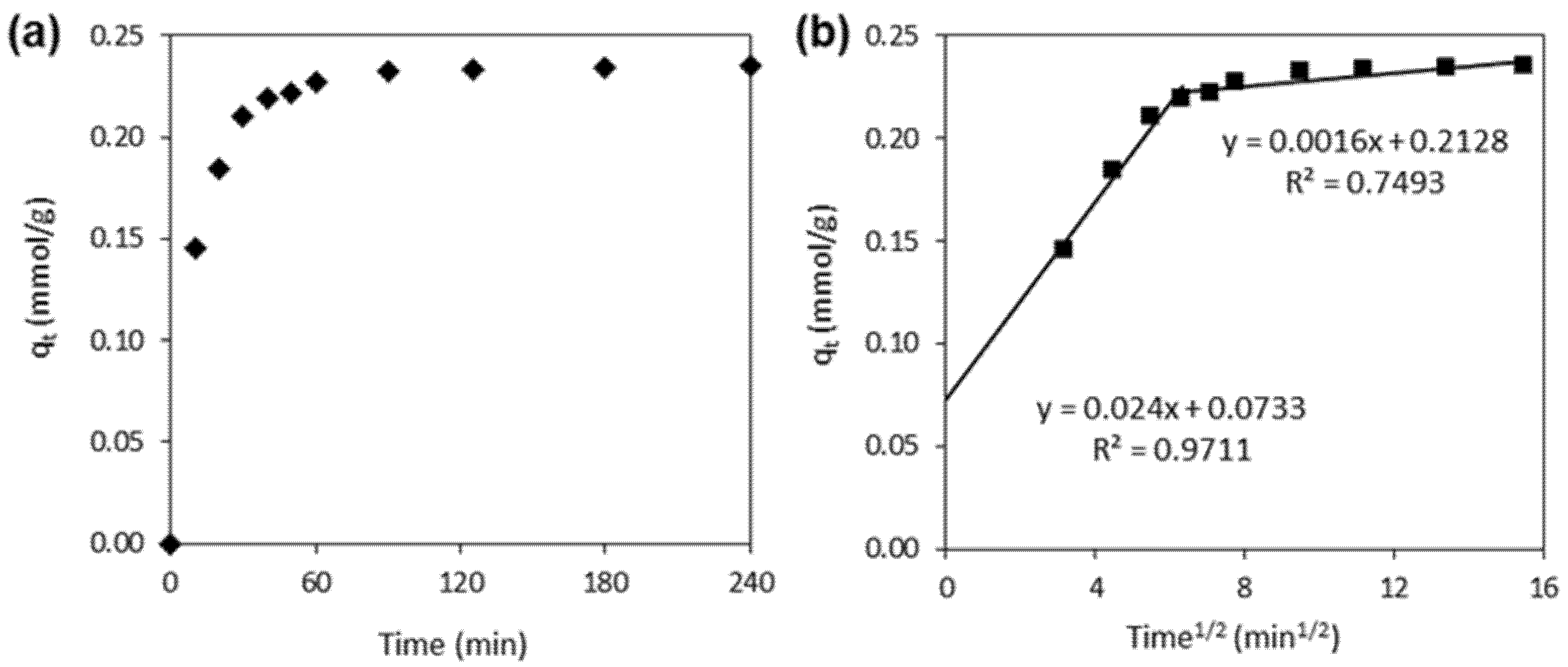
3.1. Textural and Adsorptive Properties of the CNTs
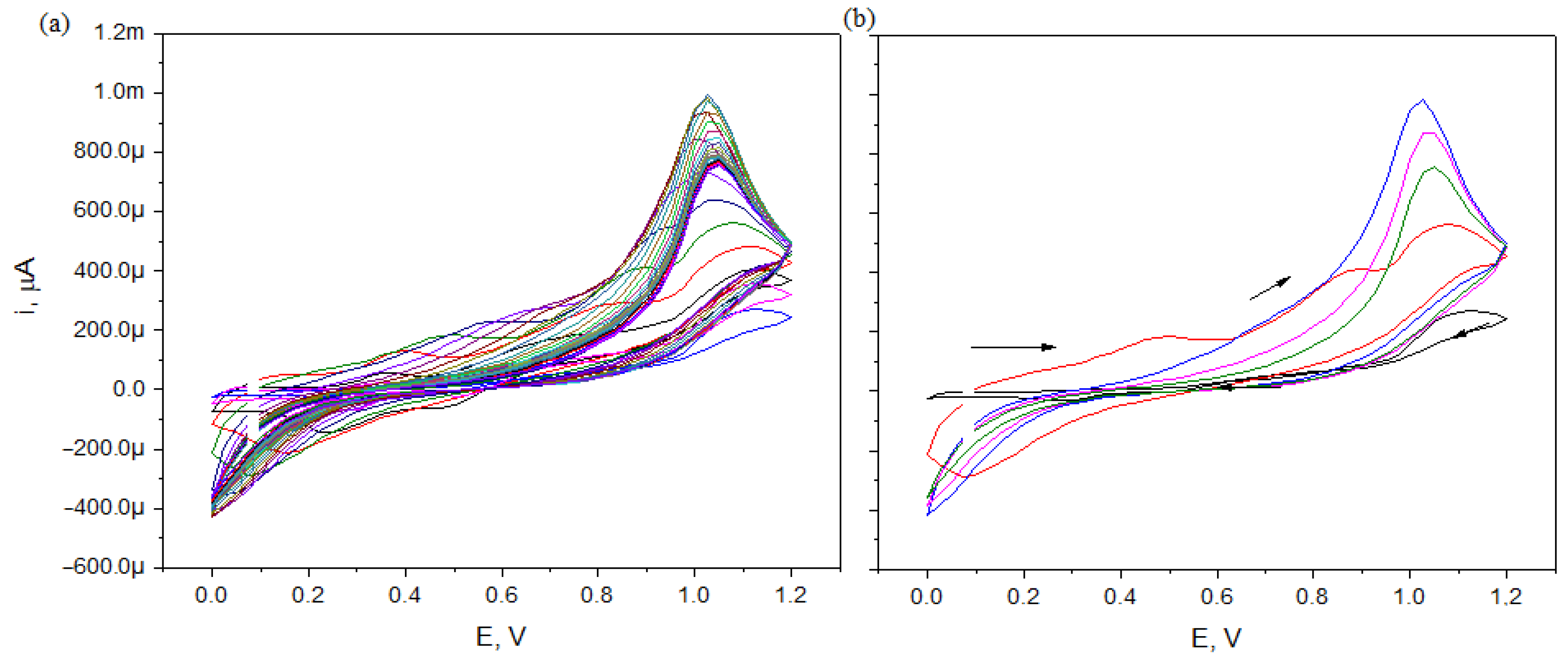
3.2. Electropolymerization of PANI Fiber Coating
3.3. Electrochemical Studies
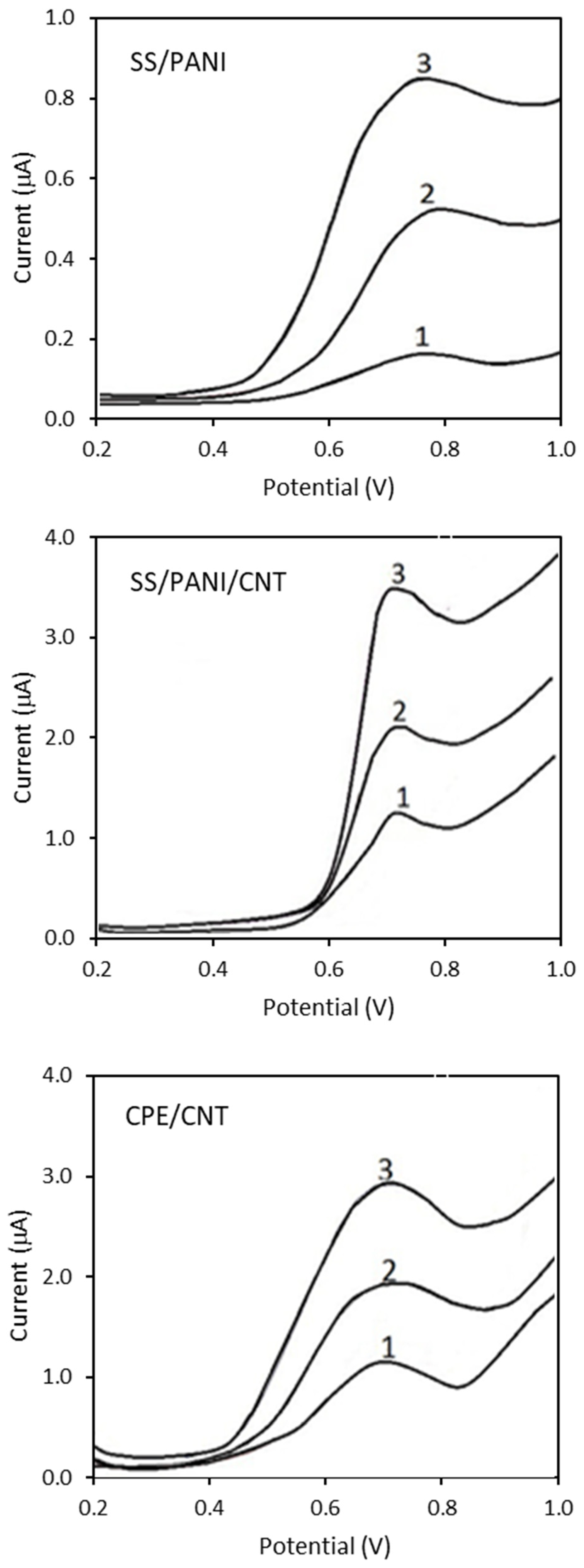
3.4. Calibration and Validation
3.5. Analytical Application of the Electrodes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.G.; Li, H.Q.; Wang, W.P.; Pan, C.Y. Preparation and characterization of polystyrene/graphite composite prepared by cationic grafting polymerization. Polymer 2004, 45, 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Li, H.Q.; Xia, Y.Y. Ordered whiskerlike polyaniline grown on the surface of mesoporous carbon and its electrochemical capacitance performance. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2619–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wei, T.; Shao, B.; Fan, Z.J.; Qian, W.Z.; Zhang, M.L.; Wei, F. Preparation of a graphene nanosheet/polyaniline composite with high specific capacitance. Carbon 2010, 48, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, X.S.; Wu, J.S. Graphene/polyaniline nanofiber composites as supercapacitor electrodes. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashat, L.; Shin, K.; Zadeh, K.K.; Plessis, J.D.; Han, S.H.; Kojima, R.W.; Kaner, R.B.; Li, D.; Gou, X.L.; Ippolito, S.J.; et al. Graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite for hydrogen sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16168–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.X.; Wan, M.X.; Lin, T.; Dai, L.M. Polyaniline nanotubes doped with sulfonated carbon nanotubes made via a self-assembly process. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, H.N.; Ding, J.F.; Xia, S.J.; Birss, V.I. Multi-technique study of the anodic degradation of polyaniline films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 459, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutić, S.; Cacan, M.; Korać, F. Electrodeposition of polyaniline films on stainless steel and their voltammetric behavior in corrosive environments. Bull. Chem. Technol. Bosn. Herz. 2017, 48, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Owais, A.A.; El-Hallag, I.S. Voltammetric and chronoamperometric studies of aniline electropolymerization in different aqueous sulfuric acid solutions. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 4571–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Application of polymer-based composites: Conductive pastes based on polymeric composite/nanocomposite. In Electrical Conductivity in Polymer-Based Composites: Experiments, Modelling and Applications; Taherian, R., Kausar, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsheer, K.; Rout, C.S. Conducting polymers: A comprehensive review on recent advances in synthesis, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 5659–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ajayan, P.M. Nanotubes from carbon. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinavel, S.; Priyadharshini, K.; Panda, D. A review on carbon nanotube: An overview of synthesis, properties, functionalization, characterization, and the application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 268, 115095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, B.; Zhou, W.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Li, H. Electrochemical capacitance of well-coated single-walled carbon nanotube with polyaniline composites. Electrochim Acta. 2004, 49, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Zhuo, S.; Cui, H. Enhanced electrochemical properties of polyaniline-coated multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Porous Mater. 2008, 15, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Fu, Q.; Su, L.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, X. Preparation and electrochemical properties of polyaniline doped with benzenesulfonic functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśmierek, K.; Sankowska, M.; Skrzypczyńska, K.; Świątkowski, A. The adsorptive properties of powdered carbon materials with a strongly differentiated porosity and their applications in electroanalysis and SPME-GC. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 446, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryło-Marczewska, A.; Zienkiewicz-Strzałka, M.; Skrzypczyńska, K.; Świątkowski, A.; Kuśmierek, K. Evaluation of the SBA-15 materials ability to accumulation of 4-chlorophenol on carbon paste electrode. Adsorption 2016, 22, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deryło-Marczewska, A.; Skrzypczyńska, K.; Kuśmierek, K.; Świątkowski, A.; Zienkiewicz-Strzałka, M. The adsorptive properties of oxidized activated carbons and their applications as carbon paste electrode modifiers. Adsorption 2019, 25, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Legocka, I.; Skrzypczyńska, K.; Świątkowski, A.; Kuśmierek, K. Halloysite as a carbon paste electrode modifier for the detection of phenol compounds. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 4114–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczyńska, K.; Kuśmierek, K.; Świątkowski, A.; Dąbek, L.; Piros, I. Nutshells as modifiers of carbon paste electrodes used in detecting chloroorganic water pollutants. BioResources 2020, 15, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Mir, A.; Babanezhad, E. An electropolymerized aniline-based fiber coating for solid phase microextraction of phenols from water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 532, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y. Polyaniline nanofibers fabricated by electrochemical polymerization: A mechanistic study. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2292–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.N. Validation of analytical methods. In Calibration and Validation of Analytical Methods—A Sampling of Current Approaches; Stauffer, M.T., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, X.; Huang, W.; Wu, K. Modification of montmorillonite with cationic surfactant and application in electrochemical determination of 4-chlorophenol. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 65, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhosana, K.E.; Shumba, M.; Nyokong, T. Electrochemical detection of 4-chlorophenol using glassy carbon electrodes modified with thulium double-decker phthalocyanine salts. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 8434–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Z. Voltammetric determination of 4-chlorophenol using multiwall carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticles nanocomposites modified glassy carbon electrodes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 34692–34698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Okoth, O.K.; Yan, K.; Zhang, J. A highly selective electrochemical sensor for 4-chlorophenoldetermination based on molecularly imprinted polymer and PDDA-functionalized graphene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolgharnein, J.; Shariatmanesh, T.; Babaei, A. Multivariate optimization of a new 4-chlorophenol sensor fabricated by modification of glassy carbon electrode using Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles-carbon nanotubes (NNH–MWCNTs). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.K.; Arruda, B.S.; de Souza, E.F.; Nogueira, A.B.; Teschke, O.; Bonugli, L.O.; Etchegaray, A. Determination of chlorophenol in environmental samples using a voltammetric biosensor based on hybrid nanocomposite. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Roostaee, M.; Tahernejad-Javazmi, F. Graphene oxide/NiO nanoparticle composite-ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode for selective sensing of 4-chlorophenol in the presence of nitrite. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 114687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, X.; Qu, J. Electrochemical sensor based on hydroxylated carbon nanotubes/platinum nanoparticles/rhodamine B composite for simultaneous determination of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol and 4-chlorophenol. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 810, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, A.; Pop, F.; Radovan, C.; Corb, I.; Burtica, G.; Malchev, P.; Picken, S.; Schoonman, J. Determination of 4-chlorophenol using two types of graphite-based composite electrodes. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2008, 53, 623–628. [Google Scholar]

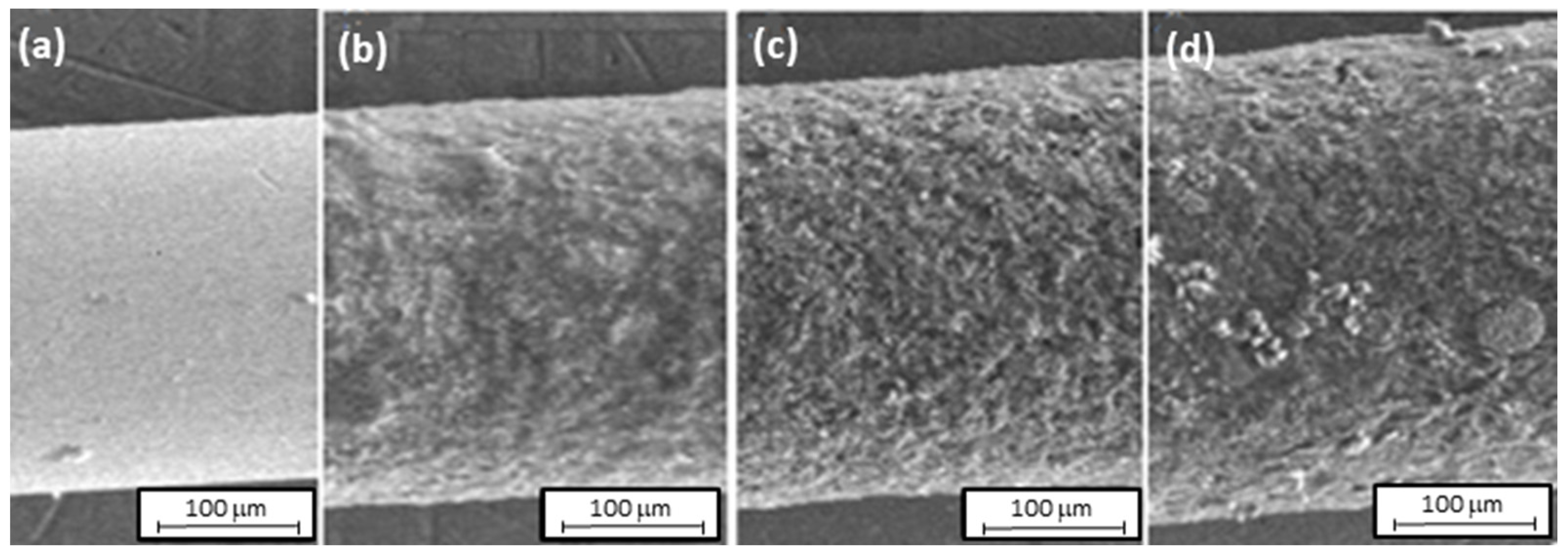



| Fiber | Diameter [µm] | Polymer Layer Thickness [µm] | Polymer Volume [mm3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS | 247 | - | - |
| SS/PANI/CNT 10 cycles | 280 | 16.5 | 0.205 |
| SS/PANI/CNT 20 cycles | 300 | 26.5 | 0.342 |
| SS/PANI/CNT 30 cycles | 313 | 33.0 | 0.435 |
| Electrode | y = ax + b | R2 | LOD | LOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µmol/L] | [µmol/L] | |||
| SS/PANI | ||||
| 10 cycles | y = 0.37x − 0.001 | 0.992 | 7.30 | 24.3 |
| 20 cycles | y = 1.18x + 0.004 | 0.998 | 2.29 | 7.43 |
| 30 cycles | y = 1.57x − 0.005 | 0.996 | 1.72 | 5.73 |
| SS/PANI/CNT | ||||
| 10 cycles | y = 2.52x − 0.014 | 0.997 | 1.07 | 3.56 |
| 20 cycles | y = 4.24x − 0.020 | 0.999 | 0.64 | 2.13 |
| 30 cycles | y = 7.01x − 0.037 | 0.994 | 0.38 | 1.26 |
| CPE/CNT | ||||
| 2.5% | y = 2.38x + 0.004 | 0.998 | 1.13 | 3.76 |
| 5% | y = 3.94x − 0.013 | 0.997 | 0.68 | 2.26 |
| 10% | y = 5.94x − 0.040 | 0.995 | 0.45 | 1.50 |
| bare/graphite electrode | y = 0.14x − 0.017 | 0.991 | 19.3 | 64.3 |
| Electrode | LOD [µmol/L] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| SS/PANI/CNT/30 | 0.38 | This study |
| CPE/CNT/10 | 0.45 | This study |
| SS/PANI/30 | 1.72 | This study |
| montmorillonite modified CPE | 0.02 | [27] |
| blue lanthanide double-decker phthalocyanines modified GCE | 0.04 | [28] |
| MWCNT/gold nanoparticles nanocomposites modified GCE | 0.11 | [29] |
| molecularly imprinted polymer with PDDA-functionalized graphene | 0.30 | [30] |
| Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles-carbon nanotubes modified GCE | 0.50 | [31] |
| CPE modified by laccase immobilized on a hybrid nanocomposite | 0.70 | [32] |
| GO/NiO nanoparticle composite-ionic liquid modified CPE | 0.70 | [33] |
| SBA-15-NH2 modified CPE | 1.40 | [19] |
| Activated carbon modified CPE | 2.38 | [20] |
| CNT/Pt nanoparticles/rhodamine B modified GCE | 3.70 | [34] |
| hazelnut shell modified CPE | 5.03 | [22] |
| green lanthanide double-decker phthalocyanines modified GCE | 6.14 | [28] |
| halloysite/gelatin modified CPE | 6.55 | [21] |
| walnut shell modified CPE | 7.90 | [22] |
| expanded graphite-epoxy electrode | 20.0 | [35] |
| halloysite modified CPE | 29.3 | [21] |
| Electrode | Added 0.1 mmol/L | Added 0.5 mmol/L | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found ± SD [mmol/L] | CV [%] | Accuracy [%] | Found ± SD mmol/L | CV [%] | Accuracy [%] | |
| Intraday | ||||||
| SS/PANI/30 | 0.102 ± 0.006 | 6.25 | 101.91 | 0.501 ± 0.007 | 1.47 | 100.21 |
| SS/PANI/CNT/30 | 0.101 ± 0.002 | 1.67 | 101.01 | 0.506 ± 0.005 | 0.59 | 101.23 |
| CPE/CNT/10 | 0.098 ± 0.005 | 5.11 | 97.96 | 0.499 ± 0.001 | 0.16 | 99.95 |
| Interday | ||||||
| SS/PANI/30 | 0.097 ± 0.010 | 9.90 | 97.22 | 0.489 ± 0.011 | 2.97 | 97.98 |
| SS/PANI/CNT/30 | 0.101 ± 0.008 | 8.33 | 100.84 | 0.508 ± 0.082 | 8.26 | 101.68 |
| CPE/CNT/10 | 0.104 ± 0.006 | 5.80 | 104.50 | 0.498 ± 0.004 | 0.82 | 99.53 |
| Electrode | Tap Water Concentration Given—0.2 mmo/L | River Water (Vistula) Concentration Given—0.2 mmo/L | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found ± SD [mmol/L] | CV [%] | Recovery [%] | Found ± SD [mmol/L] | CV [%] | Recovery [%] | |
| SS/PANI/30 | 0.195 ± 0.013 | 6.79 | 97.66 | 0.197 ± 0.013 | 6.45 | 98.61 |
| SS/PANI/CNT/30 | 0.204 ± 0.013 | 6.28 | 102.24 | 0.190 ± 0.003 | 1.53 | 95.12 |
| CPE/CNT/10 | 0.195 ± 0.004 | 1.93 | 97.72 | 0.192 ± 0.012 | 6.32 | 95.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuśmierek, K.; Skrzypczyńska, K.; Świątkowski, A.; Wierzbicka, E.; Legocka, I. Electropolymerized Aniline-Based Stainless Steel Fiber Coatings Modified by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electroanalysis of 4-Chlorophenol. Materials 2022, 15, 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103436
Kuśmierek K, Skrzypczyńska K, Świątkowski A, Wierzbicka E, Legocka I. Electropolymerized Aniline-Based Stainless Steel Fiber Coatings Modified by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electroanalysis of 4-Chlorophenol. Materials. 2022; 15(10):3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103436
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuśmierek, Krzysztof, Katarzyna Skrzypczyńska, Andrzej Świątkowski, Ewa Wierzbicka, and Izabella Legocka. 2022. "Electropolymerized Aniline-Based Stainless Steel Fiber Coatings Modified by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electroanalysis of 4-Chlorophenol" Materials 15, no. 10: 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103436
APA StyleKuśmierek, K., Skrzypczyńska, K., Świątkowski, A., Wierzbicka, E., & Legocka, I. (2022). Electropolymerized Aniline-Based Stainless Steel Fiber Coatings Modified by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electroanalysis of 4-Chlorophenol. Materials, 15(10), 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103436






