First Principle Calculation of Accurate Electronic and Related Properties of Zinc Blende Indium Arsenide (zb-InAs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Method
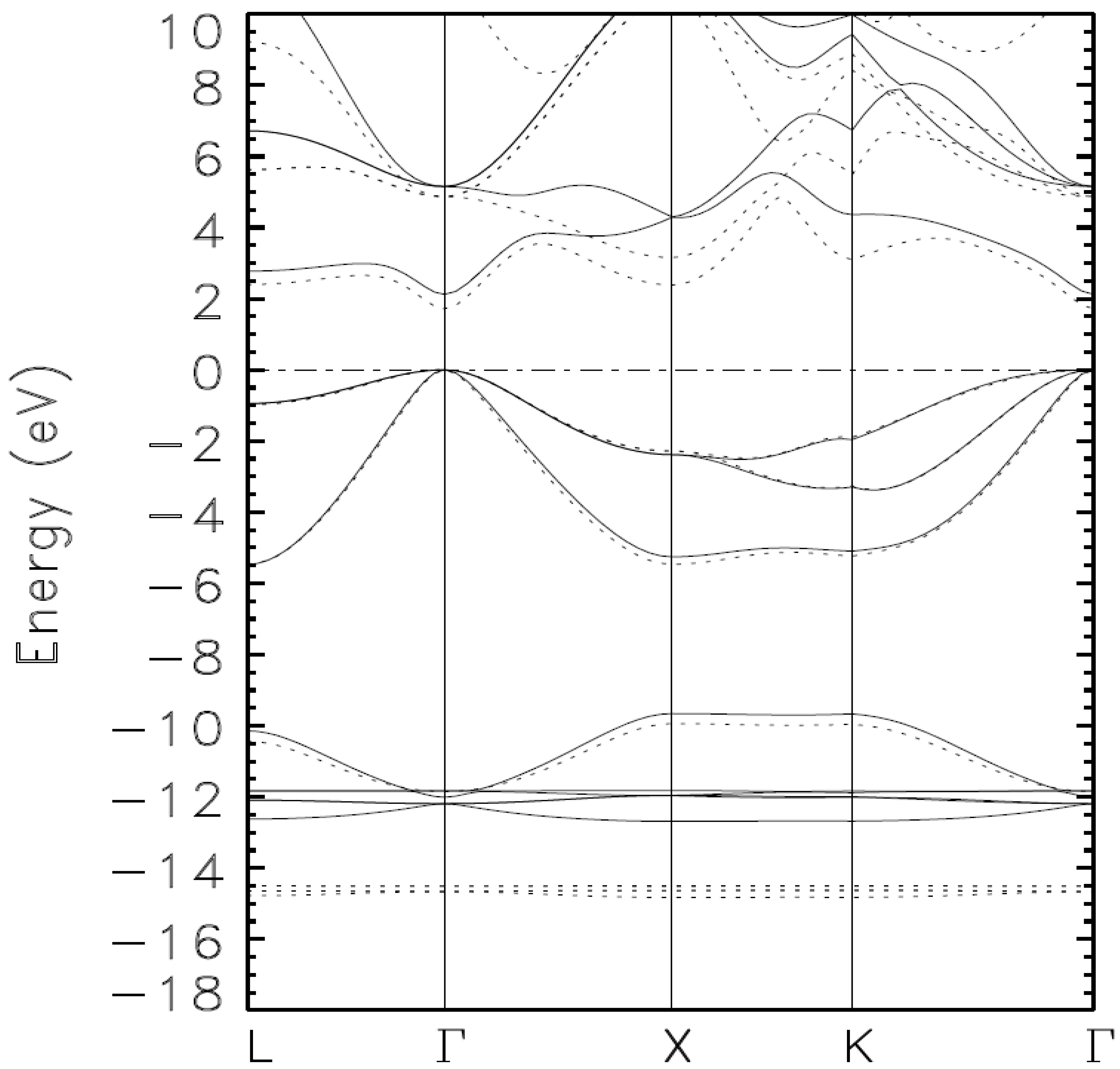
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendoza-Estrada, V.; Romero-Baños, M.; Dovale-Farelo, V.; López-Pérez, W.; González-García, Á.; González-Hernández, R. Structural, elastic, electronic and thermal properties of InAs: A study of functional density. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2017, 26, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su-Huai, W.E.I.; Zunger, A. Fingerprints of CuPt ordering in III-V semiconductor alloys:Valence-band splittings, band-gap reduction, and x-ray structure factors. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 8983. [Google Scholar]
- Massidda, S.; Continenza, A.; Freeman, A.J.; de Pascale, T.M.; Meloni, F.; Serra, M. Structural and electronic properties of narrow-band-gap semiconductors: InP, InAs, and InSb. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebegue, S.; Arnaud, B.; Alouani, M.; Bloechl, P.E. Implementation of an all-electron GW approximation based on the projector augmented wave method without plasmon pole approximation: Application to Si, SiC, AlAs, InAs, NaH, and KH. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 155208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziane, M.I.; Bensaad, Z.; Labdelli, B.; Bennacer, H. First-principles Study of Structural, Electronic and Optical Properties of III-arsenide Binary GaAs and InAs, and III-Nitrides Binary GaN and InN: Improved Density-functional-theory Study. Sens. Transducers 2014, 27, 374–384. [Google Scholar]
- Karazhanov, S.Z.; Voon, L.C.L.Y. Ab initio studies of the band parameters of III–V and II–VI zinc-blende semiconductors. Semiconductors 2005, 39, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Boufadi, F.; Touia, A.; Faudil, M.; Hachemane, D.; Boudia, K.; Slamani, A.; Aze-Eddine, A. Ab Initio Calculations Study of Structural and Electronic Properties of Ternary Alloy AlxIn1–xAs. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2012, 3, 674–683. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, R.; Hashemifar, S.J.; Akbazadeh, H.; Ahmed, M.; e-Aleem, F. Ab initio study of structural and electronic properties of III-arsenide binary compounds, Comput. Mater Sci. 2007, 39, 580–586. [Google Scholar]
- Tomic, S.; Montanari, B.; Harrison, N.M. The group III–V’s semiconductor energy gaps predicted using the B3LYP hybrid funtional. J. Phys. E 2008, 40, 2125–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remediakis, I.N.; Kaxiras, E. Band-structure calculations for semiconductors within generalized-density-functional theory. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noorafshan, M. Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure on Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of InAs: A First Principle Study. Acta. Phys. Pol. A 2020, 137, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Marshman, M.; Kresse, G.; Tran, F.; Blaha, P. Towards efficient band structure and effective mass calculations for III-V direct band-gap semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 205212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briki, M.; Abdelouhab, M.; Zaoui, A.; Ferhat, M. Relativistic effects on the structural and transport properties of III–V compounds: A first-principles study. Superlattices Microstru. 2009, 45, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hummer, K.; Kresse, G. Accurate band structures and effective masses for InP, InAs, and InSb using hybrid functionals. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemiri, O.; Ghemid, S.; Chouahda, Z.; Meradji, H.; Hassan, F.E. Structural, electronic, thermodynamic and thermal properties of zinc-blende inp, inas and their inasx p1-x ternary alloys via first principles calculations. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2013, 27, 1350166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, H.; Cui, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, C. First principles study of electronic and optical properties of InAs. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2009, 7, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, L.; Boochani, A.; Sebt, S.A.; Elahi, S.M. Structural, electronic and optical properties of InAs phases: By GGA-PBG and GGA-EV approximations. J. Chem. Res. 2017, 41, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.; Katircioglu, S.; El-Hasan, M. The electronic band structure of InN, InAs and InSb compounds. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Khan, N.; Ahmad, F.; Ali, A.; Ayaz, M. First-principles calculations of opto-electronic properties of IIIAs (III = Al, Ga, In) under influence of spin–orbit interaction effects. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Douri, Y.; Abid, H.; Zaoui, A.; Aourag, H. Correlation between the ionicity character and the heteropolar band gap in semiconductors. Phys. B 2001, 301, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechiri, A.; Bouarissa, N. Energy band gaps for the GaxIn1−xAsyP1−y alloys lattice matched to different substrates. Superlattices Microstruct. 2006, 39, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarissa, N. Optoelectronic properties of InAs1−xPx semiconducting alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2001, 86, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degheidy, A.R.; Elkenany, E.B. The response of temperature and hydrostatic pressure of zinc-blende GaxIn1−xAs semiconducting alloys. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.E.; Heyd, J.; Scuseria, G.E.; Martin, R.L. Spin-orbit splittings and energy band gaps calculated with the Heyd-Scuseria-Ernzerhof screened hybrid functional. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 073101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantis, A.N.; van Schilfgaarde, M.; Kotani, T. Ab Initio Prediction of Conduction Band Spin Splitting in Zinc Blende Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 086405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koller, D.; Tran, F.; Blaha, P. Improving the modified Becke-Johnson exchange potential. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 155109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Cao, R.; Zahid, F.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, H. Electronic structure of III-V zinc-blende semiconductors from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 235203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assali, A.; Bouslama, M.; Reshak, A.H.; Chaabane, L. Highly desirable semiconducting materials for mid-IR optoelectronics: Dilute bismide InAs1−xBix alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 95, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjab, M.; Berrah, S.; Abid, H.; Ziane, M.I.; Bennacer, H.; Yalcin, B.G. Full-potential calculations of structural and optoelectronic properties of cubic indium gallium arsenide semiconductor alloys. Optic 2016, 127, 9280–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, Y.; Tran, C.A.; Watkins, S.P.; Thewalt, M.L. Low-temperature photoluminescence of epitaxial InAs. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 80, 6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudnyi, V.N.; Kolin, N.G.; Potapov, A.I. Electrical properties of InAs irradiated with protons. Semiconductors 2003, 37, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, W.A. Electronic Structure and the Properties of Soilids; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1980; p. 157. [Google Scholar]
- Madelung, O.; Schulz, M.; Weiss, H. (Eds.) Landolt-Bornstein New Series, Group III; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Vurgafman, I.; Meyer, J.R.; Ram-Mohan, L.R. Band parameters for III–V compound semiconductors and their alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madelung, O.; Schultz, M.; Weiss, H. (Eds.) Landolt-Bornstein Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology (New Series). Group III: Crystal and Solid-State Physics, Semiconductors; subvol. A: “Physics of group IV Elements and III-V Compounds”; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1982; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Tsidilkovski, I.M. Band Structure of Semiconductors; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Madelung, O.; Rossler, U.; Schulz, M. (Eds.) Landolt-Bornstein Semiconductors; Springe: Berlin, Germany, 2002; Volume 41A1b. [Google Scholar]
- Zwerdling, S.; Lax, B.; Roth, L.M. Oscillatory Magneto-Absorption in Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 1957, 108, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagayoko, D. Understanding density functional theory (DFT) and completing it in practice. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 127104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diakite, Y.I.; Traore, S.D.; Malozovsky, Y.; Khamala, B.; Franklin, L.; Bagayoko, D. Accurate Electronic, Transport, and Bulk Properties of Zinc Blende Gallium Arsenide (Zb-GaAs). J. Mod. Phys. 2017, 8, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceperley, D.M.; Alder, B.J. Ground State of the Electron Gas by a Stochastic Method. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vosko, S.H.; Wilk, L.; Nusair, M. Accurate spin-dependent electron liquid correlation energies for local spin density calculations: A critical analysis. Can. J. Phys. 1980, 58, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmon, B.N.; Weber, W.; Hamann, D.R. Total-energy calculations for Si with a first-principles linear-combination-of-atomic-orbitals method. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 25, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. A 1965, 140, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagayoko, D.; Zhao, G.L.; Fan, J.D.; Wang, J.T. Ab initio calculations of the electronic structure and optical properties of ferroelectric tetragonal BaTiO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1998, 10, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.L.; Bagayoko, D.; Williams, T.D. Local-density-approximation prediction of electronic properties of GaN, Si, C, and RuO2. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekuma, C.E.; Jarrell, M.; Moreno, J.; Bagayoko, D. Re-examining the electronic structure of germanium: A first-principle study. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, L.; Ekuma, C.E.; Zhao, G.L.; Bagayoko, D. Density functional theory description of electronic properties of wurtzite zinc oxide. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2013, 74, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagayoko, D.; Franklin, L. Density-functional theory band gap of wurtzite InN. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 123708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakite, Y.I.; Traore, S.D.; Malozovsky, Y.; Khamala, B.; Franklin, L.; Bagayoko, D. Calculated Electronic and Related Properties of Wurtzite and Zinc Blende Gallium Nitride (GaN). Afr. Rev. Phys. 2015, 10, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Bamba, C.O.; Inakpenu, R.; Diakite, Y.I.; Franklin, L.; Malozovsky, Y.; Stewart, A.D.; Bagayoko, D. Accurate Electronic, Transport, and Related Properties of Wurtzite Beryllium Oxide (w-BeO). J. Mod. Phys. 2017, 8, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagayoko, D. Contraction of gaussian basis sets and the total energy of fcc copper. Inter. J. Quant. Chem. 1983, 17, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanolli, Z.; Fuchs, F.; Furthmüller, J.; von Barth, U.; Bechstedt, F. Model GW band structure of InAs and GaAs in the wurtzite phase. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 245121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ley, L.; Pollak, R.A.; McFeely, F.R.; Kowalczyk, S.P.; Shirley, D.A. Total valence-band densities of states of III-V and II-VI compounds from x-ray photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 9, 600–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.A.; Huckenholz, H.G.; Rybach, L.; Schmid, R.; Schopper, J.R.; Schuch, M.; Stffler, D.; Wohlenberg, J. Landolt-Borstein: Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1981; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Levenshtein, M.; Rumyantsev, S.; Shur, M. (Eds.) Handbook Series on Semiconductor Parameters; World Scientific: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Madelung, O. (Ed.) Semiconductors—Basic Data; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; ISBN 3-540-60883-4. [Google Scholar]
- Geller, C.B.; Wolf, W.; Picozzi, S.; Continenza, A.; Asahi, R.; Mannstadt, W.; Freeman, A.J.; Wimmer, E. Computational band-structure engineering of III–V semiconductor alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, S.N.F.M.; Ullah, H.; Ebadi, M.; Tahir, A.A.; Sagu, J.S.; Teridi, M.A.M. New Insights into Se/BiVO4 Heterostructure for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: A Combined Experimental and DFT Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 6218–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Tahir, A.A.; Mallick, T.K. Structural and electronic properties of oxygen defective and Se-doped p-type BiVO4(001) thin film for the applications of photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 224, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Computational Formalism | Potentials (DFT and Others) | a (Å) | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FP-LAPW | LDA | −0.64 [a] | |
| FLAPW (R, HL) | LDA | 6.058 | −0.63 [b] |
| FLAPW (SR, HL) | LDA | 6.058 | −0.51 [b] |
| FLAPW (SR, CA) | LDA | 6.058 | −0.51 [b] |
| LDA | −0.07 [c] | ||
| FLAPW (SR, CA) | LDA | 6.058 | −0.03 [b] |
| FP-LAPW | LDA | 6.0267 | 0.00 [d] |
| LDA | 6.0583 | 0.00 [e] | |
| FP-LMTO | LDA | 0.00 [f] | |
| FP-LAPW | LDA | 6.030 | 0.00 [g] |
| LSDA | 0.00 [h] | ||
| LDA | 6.04 | 0.259 [i] | |
| ab initio pseudo potential | LDA | 5.8564 | 0.4131 [e] |
| FP-LAPW | mBJ-LDA | 6.097 | 0.47 [j] |
| FP-LAPW | MBJLDA | 0.593 [d] | |
| MBJLDA | 0.61 [k] | ||
| LDA | 5.85 | 1.396 [i] | |
| GGA | −0.61[l] | ||
| GGA (PBE) | −0.30 [k] | ||
| PAW+SOC PBE | GGA | 6.194 | −0.298 [m] |
| PAW(PBE) | GGA | 6.195 | −0.188 [m] |
| FP-LAPW | GGA-WC | 6.0911 | 0.00 [d] |
| WC-GGA | 0.00 [n] | ||
| FP-LAPW+lo | GGA | 6.191 | 0.00 [o] |
| FP-LAPW | GGA | 6.195 | 0.00 [g] |
| FP-LMTO | GGA | 0.00 [f] | |
| FP-LAPW | PBE-GGA | 6.18922 | 0.00 [p] |
| EV-GGA | 0.204 [n] | ||
| FP-LAPW | GGA-EV | 0.224 [d] | |
| FP-LAPW | GGA | 6.194 | 0.277 [q] |
| FP-LAPW | GGA-EV with effect spin-orbit | 0.31533 [p] | |
| FP-LAPW+lo | EV-GGA | 0.34 [o] | |
| FP-LAPW | EV-GGA | 0.40 [g] | |
| FP-LAPW | GGA-EV | 0.42245 [p] | |
| FP-LAPW | GGA (with SOI) | 6.1 | 0.47 [r] |
| FP-LAPW | GGA (without SOI) | 6.1 | 0.56 [r] |
| mBJ | 0.568 [o] | ||
| Empirical Pseudopotential Method (EPM) | 0.499 [s] | ||
| pseudopotential | virtual crystal approximation | 0.35 [t] | |
| EPM | 0.36 [u] | ||
| EPM | 0.3637 [v] | ||
| PAW | HSE06 | 6.114 | 0.544 [m] |
| PAW | SOC HSE06 | 6.114 | 0.420 [m] |
| PAW | G0W0 + SOC(HSE06) | 0.560 [m] | |
| PAW | G0W0TC-TC + SOC(HSE06) | 0.413 [m] | |
| GTO | SOC HSE03 | 0.23 [w] | |
| LMTO | scQPGW+SOC | 0.68 [x] | |
| GW | 0.31[i] | ||
| GW | 0.46 [c] | ||
| HSE | 0.39 [h] | ||
| B3LYP | 0.55 [h] | ||
| MBJ | 0.60 [y] | ||
| TB-MBJ | 0.43 [z] | ||
| nTB-MBJ | 0.416 [z] | ||
| MBJ | 0.57 [r] | ||
| MBJ+PBE | 0.46 [r] | ||
| HSE06 | 0.42 [a’] | ||
| FP-LAPW | TB-MBJ with SOC | 0.467 [a’] | |
| TB-MBJ without SOC | 0.60 [a’] | ||
| TB-MBJ without SOC | 0.615 [b’] | ||
| Experiments | |||
| Low T | 0.417 [c’] | ||
| 0.426 [d’] | |||
| 0.42 [y, e’] | |||
| 0.418 [f’] | |||
| 0.420 [g’] | |||
| 77 K | 0.418 [h’] | ||
| Low T | 0.5 [i‘] | ||
| At 300 K | 0.354 [j’] | ||
| 0.356 [h’] | |||
| At 298 K | 0.360 ± 0.002 [k’] | ||
| Calculation Number | Trial Function for Valence States of In2+ | Trial Function for Valence States of As2− | No. of Functions | Band Gap at Γ (in eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calc I | 3d104s24p64d105s25p0 | 3s23p63d104s24p4 | 62 | 2.123 |
| Calc II | 3d104s24p64d105s25p05d0 | 3s23p63d104s24p4 | 72 | 1.715 |
| Calc III | 3d104s24p64d105s25p05d0 | 3s23p63d104s24p45s0 | 74 | 0.642 |
| Calc IV | 3d104s24p64d105s25p05d06s0 | 3s23p63d104s24p45s0 | 76 | 0.360 |
| Calc V | 3d104s24p64d105s25p0 5d06s0 | 3s23p63d104s24p45s04d0 | 86 | 0.502 |
| Calc VI | 3d104s24p64d105s25p0 5d06s06p0 | 3s23p63d104s24p45s04d0 | 92 | 0.491 |
| L-Point | Γ-Point | X-Point | K-Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.016 | 4.798 | 10.435 | 8.840 |
| 5.549 | 4.798 | 10.435 | 8.149 |
| 5.549 | 4.798 | 2.761 | 4.976 |
| 1.679 | 0.360 | 1.915 | 2.731 |
| −0.991 | 0 | −2.321 | −1.925 |
| −0.991 | 0 | −2.321 | −3.315 |
| −5.523 | 0 | −5.5283 | −5.294 |
| −10.501 | −11.890 | −10.023 | −10.036 |
| −14.552 | −14.559 | −14.548 | −14.548 |
| −14.552 | −14.559 | −14.567 | −14.559 |
| −14.694 | −14.708 | −14.680 | −14.669 |
| −14.694 | −14.708 | −14.680 | −14.678 |
| −14.848 | −14.708 | −14.884 | −14.892 |
| Our Work | Theo [a] | Theo [b] | Theo [c] | Expt [e] | Expt [f] | Expt [g] | Expt [h] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Γ-L) | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.112 | 0.028 | 0.018 | 0.026 | 0.023 average | |||
| (Γ-X) | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.094 | 0.0221 | 0.028 | 0.015 | 0.026 | 0.023 | ||
| (Γ-K) | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.017 | 0.026 | |||||
| (Γ-L) | 0.903 | 0.836 | 0.878 | 1.048 | 0.625 | 0.85 | ||||
| (Γ-X) | 0.402 | 0.343 | 0.353 | 0.4344 | 0.381 | 0.461 | 0.333 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.35 |
| (Γ-L) | 0.542 | 0.623 | 2.524 | 2.885 | 0.513 | |||||
| (Γ-L) | 0.024 | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.017 | 0.037 | |||||
| (Γ-X) | 0.023 | 0.033 | 0.046 | 0.0283 | 0.028 | 0.015 | 0.027 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.026 |
| (Γ-K) | 0.023 | 0.032 | 0.026 | 0.016 | 0.026 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diakite, Y.I.; Malozovsky, Y.; Bamba, C.O.; Franklin, L.; Bagayoko, D. First Principle Calculation of Accurate Electronic and Related Properties of Zinc Blende Indium Arsenide (zb-InAs). Materials 2022, 15, 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103690
Diakite YI, Malozovsky Y, Bamba CO, Franklin L, Bagayoko D. First Principle Calculation of Accurate Electronic and Related Properties of Zinc Blende Indium Arsenide (zb-InAs). Materials. 2022; 15(10):3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103690
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiakite, Yacouba Issa, Yuriy Malozovsky, Cheick Oumar Bamba, Lashounda Franklin, and Diola Bagayoko. 2022. "First Principle Calculation of Accurate Electronic and Related Properties of Zinc Blende Indium Arsenide (zb-InAs)" Materials 15, no. 10: 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103690
APA StyleDiakite, Y. I., Malozovsky, Y., Bamba, C. O., Franklin, L., & Bagayoko, D. (2022). First Principle Calculation of Accurate Electronic and Related Properties of Zinc Blende Indium Arsenide (zb-InAs). Materials, 15(10), 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103690






