Optimization of Heat Treatment for 38Si7 Spring Steel with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Controlled Decarburization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
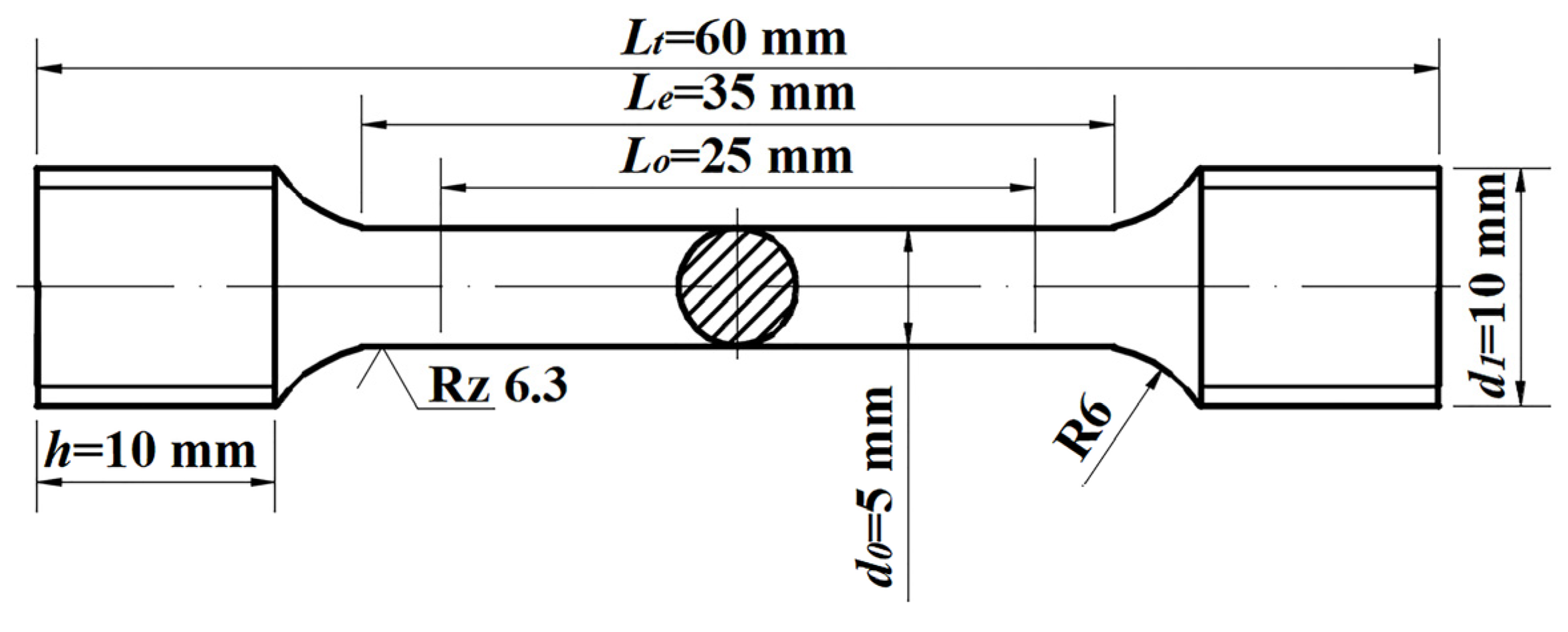
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
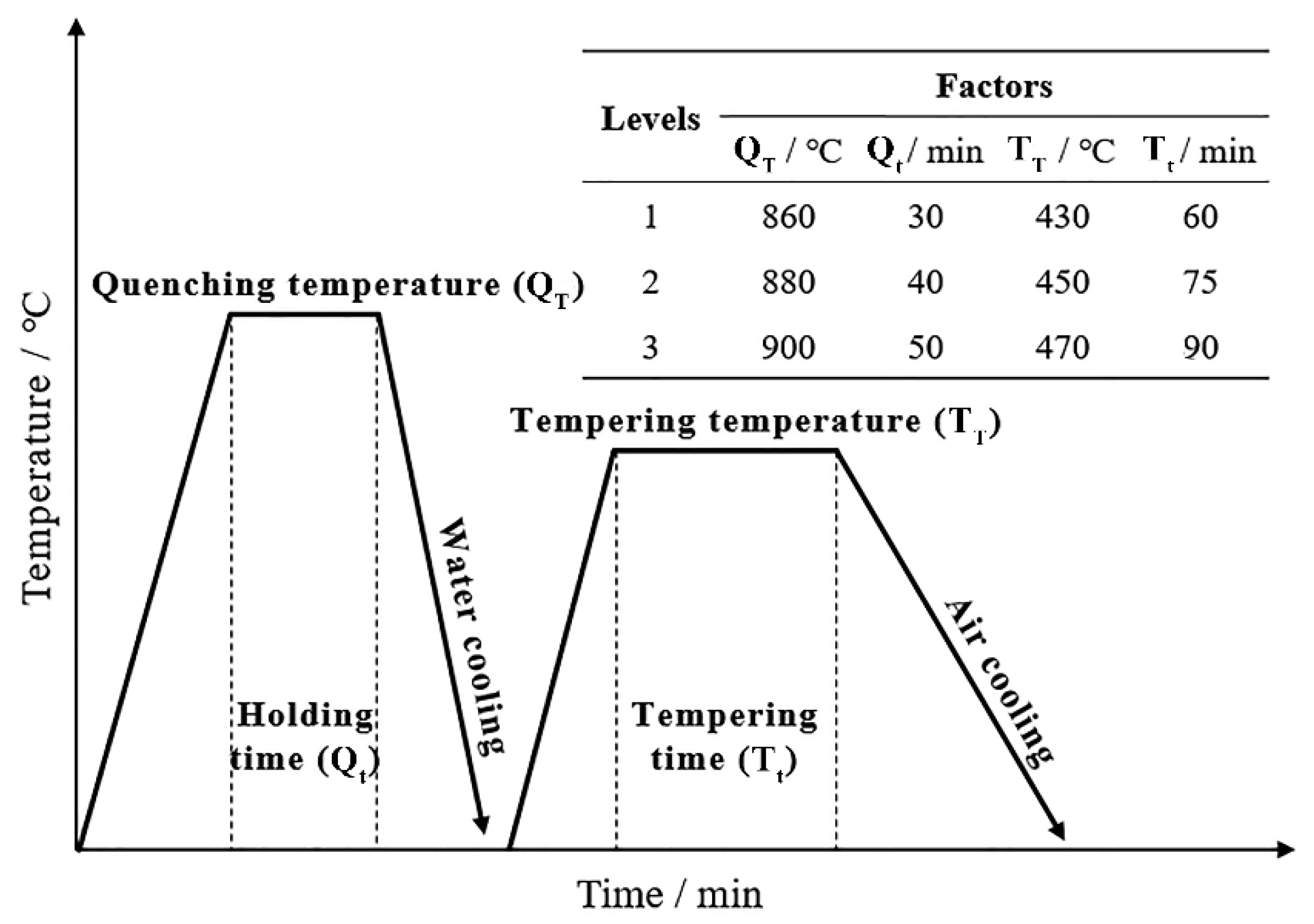
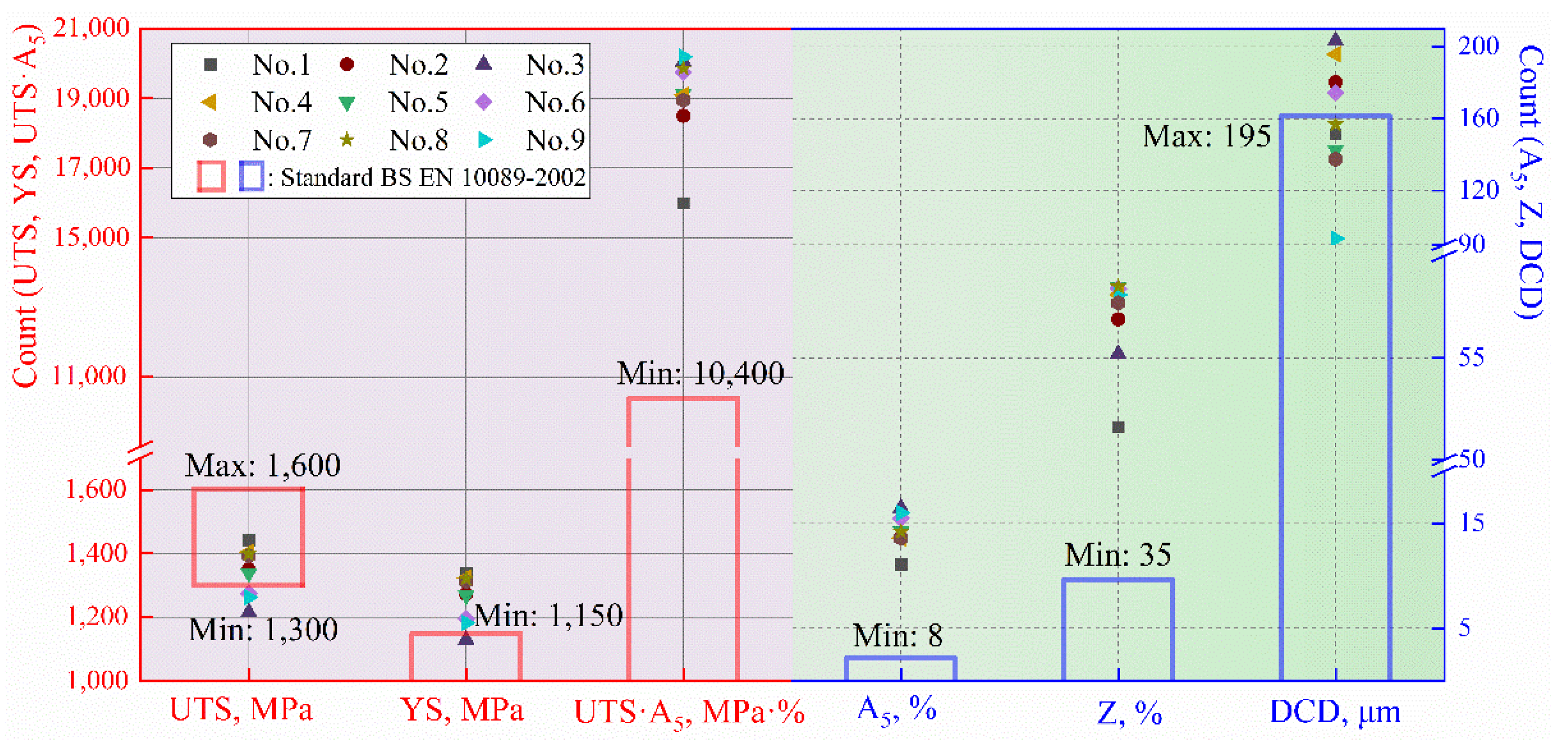
3.1. Orthogonal Experiments
3.2. Effects of Quenching on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
3.2.1. Size Evolution for Prior Austenite
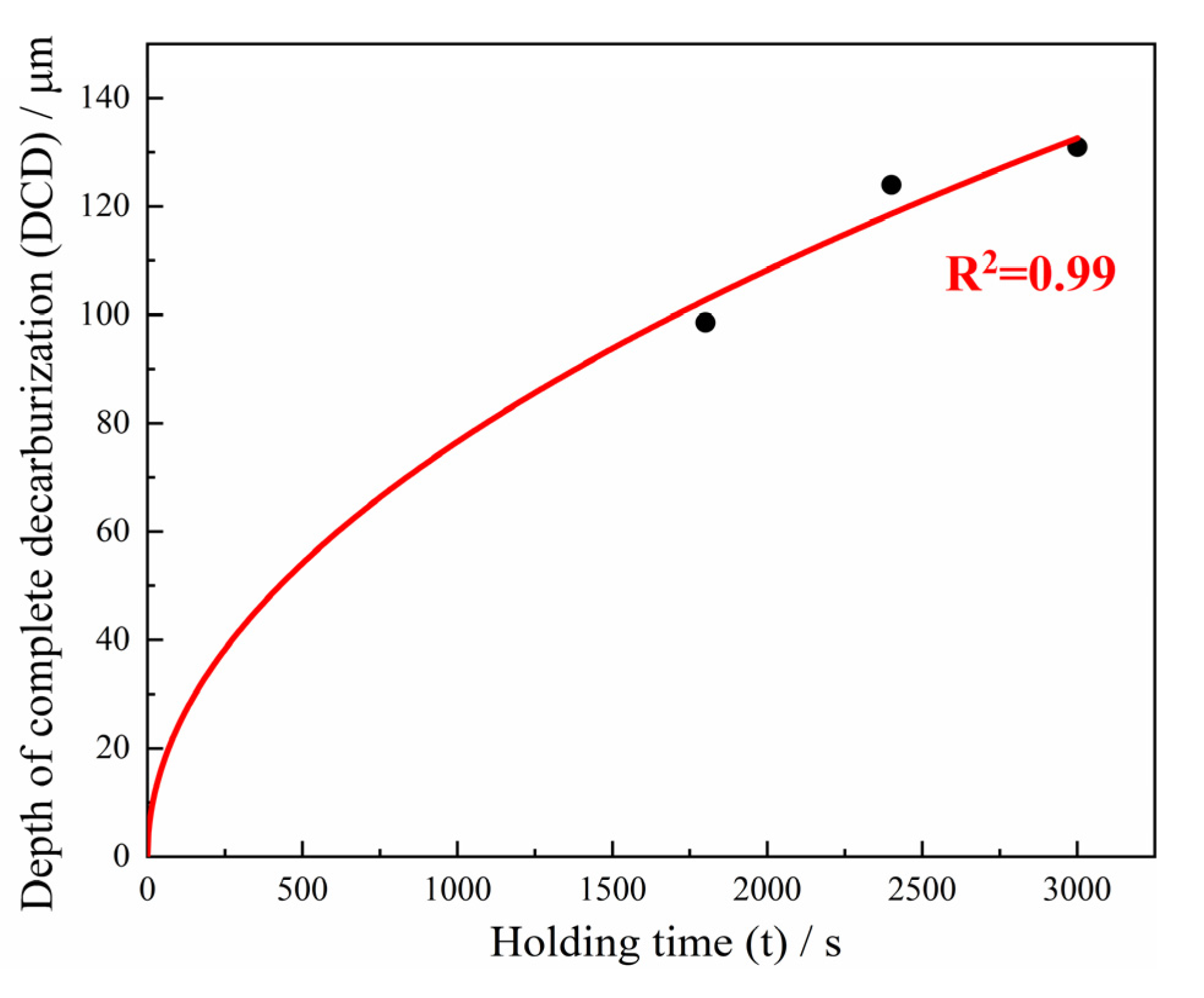
3.2.2. Surface Decarburization Behavior
3.3. Effects of Tempering Factors on Mechanical Properties and Fracture
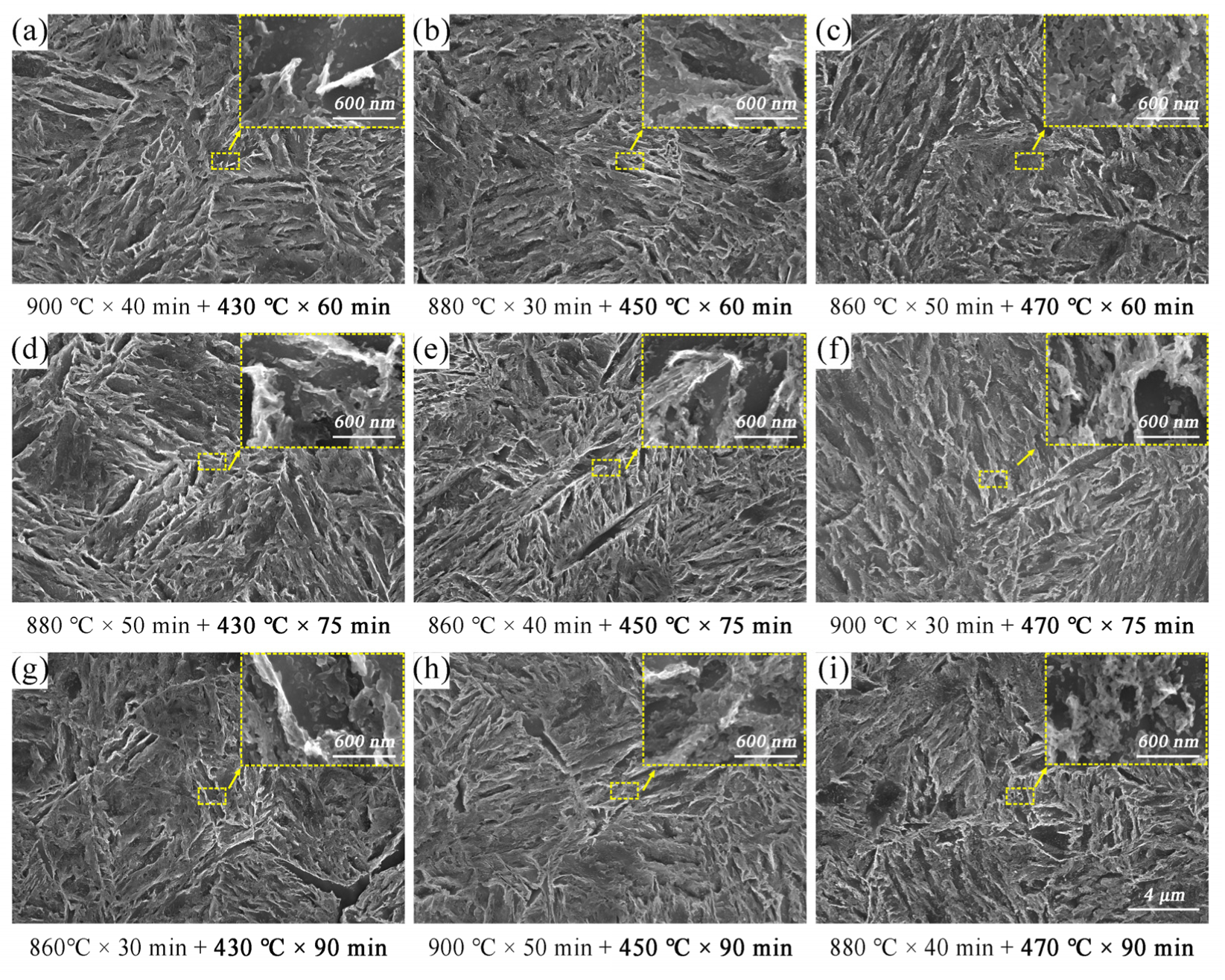
3.3.1. Mechanisms of Strength Change Caused by Tempering
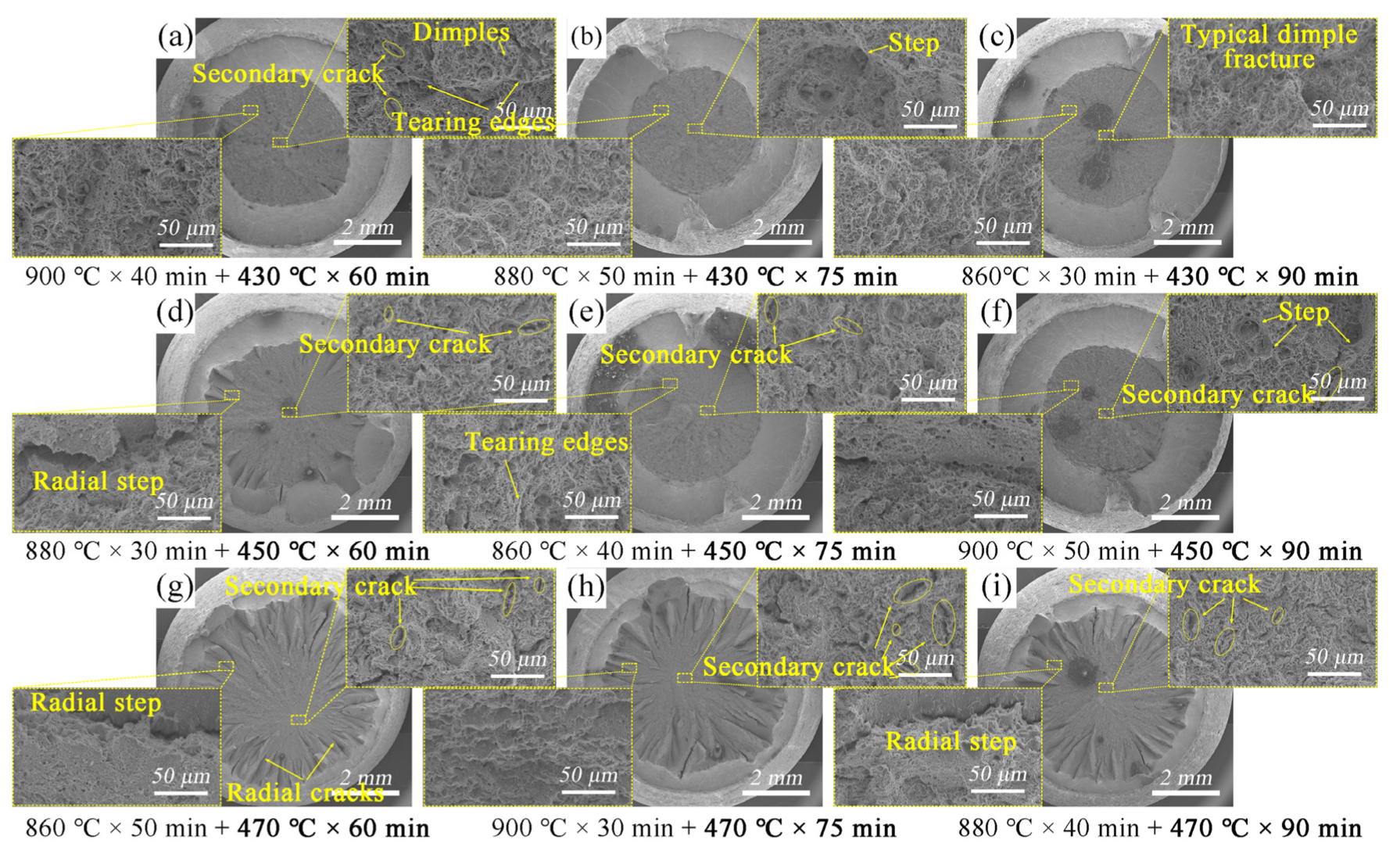
3.3.2. Fracture Characteristics
3.4. Selection of the Optimal Heat Treatment Process
4. Conclusions
- (1).
- This work proves the influence of quenching and tempering factors on the mechanical properties of Φ13 mm 38Si7 spring steel. The ultimate tensile strength and yield strength were TT > Tt > QT > Qt; elongation was TT > Tt > Qt > QT; and the reduction in area was QT > TT > Qt > Tt. This provides evidence for future, in-depth research,, as well as a research foundation for accurately regulating the steel’s overall performance.
- (2).
- When the quenching temperature exceeded 900 °C, the original austenite grains increased rapidly. The ultimate tensile strength and yield strength increased with quenching temperature. When the quenching temperature was between 860 °C and 900 °C, the depth of complete decarburization reduced monotonically as the temperature increased and the holding time decreased. The minimum depth of complete decarburization was 93.4 μm after quenching at 900 °C for 30 min.
- (3).
- The ultimate tensile strength and yield strength decreased as the tempering temperature increased between 430 °C and 470 °C, and decreased as the tempering time increased. The microstructure was simply lightly tempered martensite, and the matrix was acicular martensite. The heating process would make the carbide spheroidization obvious, and the fracture characteristics also changed from a mixed ductile–brittle fracture to a ductile fracture. The study of the fracture showed a good performance of 20.2 GPa% GPa·% after tempering at 470 °C for 75 min.
- (4).
- The optimal heat treatment scheme was determined as follows: quenching at 900 °C for 30 min and tempering at 430 °C for 60 min. This scheme aims to improve the comprehensive performance of Φ13 mm 38Si7 spring steel and promote the applicability of 38Si7 in railways.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dekker, M.M. Geographic delay characterization of railway systems. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xie, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Jia, F.; Wu, H.; Han, J.; Jiang, Z. Influence of hot compressive parameters on flow behaviour and microstructure evolution in a commercial medium carbon micro-alloyed spring steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreño, D.; Casado, J.A.; Carrascal, A.I.; Diego, S.; Ruiz, E.; Saiz, M.; Sainz-Aja, J.A.; Cimentada, A.I. Experimental and finite element fatigue assessment of the spring clip of the SKL-1 railway fastening system. Eng. Struct. 2019, 188, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhai, W.; Zhu, S.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y. Vibration-based damage detection of rail fastener using fully convolutional networks. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2021, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol-Sánchez, M.; Pirozzolo, L.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. A study into the mechanical performance of different configurations for the railway track section: A laboratory approach. Eng. Struct. 2016, 119, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q.; Yi, B. A real-time railway fastener inspection method using the lightweight depth estimation network. Measurement 2022, 189, 110613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Z. Surface decarburization characteristics and relation between decarburized types and heating temperature of spring steel 60Si2MnA. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2013, 20, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Shi, J.; Yan, Z.; Sun, L. Failure analysis of fatigue damage for fastening clips in the ballastless track of high-speed railway considering random track irregularities. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 131, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, J.; Zhao, C.; Chen, M.; Xing, M. Numerical investigation of the fatigue performance of elastic rail clips considering rail corrugation and dynamic axle load. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit. 2020, 235, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, J.; Zhao, C.; Yao, L.; Ming, X. Analysis on the Effects of Material Parameters on the Fatigue Performance of Novel Anticorrugation Elastic Rail Clips. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Chen, L.; Sun, W. Effects of soaking and tempering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of 65Si2MnWE spring steel. Vacuum 2018, 154, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, B. Continuous Cooling Kinetics Modeling for a Medium–High Carbon Spring Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Torkar, M.; Burja, J.; Godec, M.; Senčič, B. Improving properties of spring steel through nano-particles alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 638, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Leskovšek, V.; Godec, M.; Senčič, B. Microstructure refinement and its effect on properties of spring steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 599, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, M.; Yu, J.; Peng, X. Effects of the Ultrasonic Assisted Surface Rolling Process on the Fatigue Crack Initiation Position Distribution and Fatigue Life of 51CrV4 Spring Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fang, C.; Liu, J. Large size superelastic SMA bars: Heat treatment strategy, mechanical property and seismic application. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostash, O.P.; Chepil’, R.V.; Markashova, L.I.; Hrybovs’ka, V.I.; Kulyk, V.V.; Berdnikova, O.M. Influence of the Modes of Heat Treatment on the Durability of Springs Made of 65G Steel. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.J.; Lee, C.S.; Ban, D.Y. Effects of alloy additions and tempering temperature on the sag resistance of Si–Cr spring steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 289, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malikov, A.; Orishich, A.; Vitoshkin, I.; Karpov, E.; Ancharov, A. Effect of post-heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded Al-Cu-Mg alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y. Process parameter optimization for selective laser melting of Inconel 718 superalloy and the effects of subsequent heat treatment on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ye, X.; Ren, S.; Zhang, K.; Liang, X.; Liu, G. Effect of Intercritical Annealing Time on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel Subjected to Multi-Step Heat Treatment Process. Materials 2022, 15, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfa, H.; Seikh, A.H.; Soliman, M.S. Effect of Heat Treatment on Tensile Properties and Microstructure of Co-Free, Low Ni-10 Mo-1.2 Ti Maraging Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.M.; Limmer, K.R.; Hornbuckle, B.C.; Pierce, D.T.; Moore, K.E.; Sebeck, K.M. Alloy Partitioning Effect on Strength and Toughness of κ-Carbide Strengthened Steels. Materials 2022, 15, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, A.A.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D. Refinement of grain boundary carbides in a Si–Cr spring steel by thermomechanical treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 426, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Anghelina, D.; Burzic, D.; Krieger, W.; Kozeschnik, E. Investigation of decarburization in spring steel production process-part II, Simulation. Steel Res. Int. 2010, 80, 298–303. [Google Scholar]
- Prawoto, Y.; Sato, N.; Otani, I.; Ikeda, M. Carbon Restoration for Decarburized Layer in Spring Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2004, 13, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Furuya, Y.; Matsuoka, S. Gigacycle fatigue properties of 1800 MPa class spring steels. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2004, 27, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chou, K. Effect of cerium on the cleanliness of spring steel used in fastener of high-speed railway. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yanase, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Miyamoto, N.; Miyakawa, S.; Endo, M. Fatigue strength of spring steel with small scratches. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2018, 41, 1514–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, U.; Sandaiji, Y.; Tanegashima, R.; Murakami, S.; Schönbauer, B.; Fitzka, M.; Mayer, H. Inclusion initiated fracture in spring steel under axial and torsion very high cycle fatigue loading at different load ratios. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, J.-B.; Zhang, Y.-R. The fractures of e-type fastening clips used in the subway: Theory and experiment. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 81, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, E. Application of Mathematical Modelling to Hot Rolling and Controlled Cooling of Wire Rods and Bars. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Tsuzaki, K.; Tamura, I. The Morphology of Microstructure Composed of Lath Martensites in Steels. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1980, 20, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Yu, Q. The role of low angle grain boundary in deformation of titanium and its size effect. Scr. Mater. 2019, 163, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Dai, Y.; Chen, L. Evolution during hot-rolling and control by TMCP of surface decarburization on 38Si7 spring steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, in press.
- Zhao, H.; Gao, J.; Qi, J.; Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Modelling and simulation of isothermal and continuous-heating surface decarburization behaviour of Fe-0.6C-1.8Si-0.8Mn spring steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, C.; Yang, H. Enhanced bending fatigue resistance of a 50CrMnMoVNb spring steel with decarburized layer by surface spinning strengthening. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Yokoyama, N.N.; Nagata, J. Mechanism of fatigue failure in ultralong life regime. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2002, 25, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Masaki, K.; Yoshida, S. High-cycle rotating bending fatigue property in very long-life regime of high-strength steels. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2002, 25, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.-H.; Bae, C.-M.; Lee, J.S.; Suh, D.-W. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Medium-Carbon Spring Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, T.; Sun, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y. A low-alloy high-carbon martensite steel with 2.6 GPa tensile strength and good ductility. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, C.; Marques, E. Three-dimensional analysis of fracture, corrosion and wear surfaces. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2010, 17, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, B. Analysis of torsion bar failure occurring during the pre-strained manufacturing for heavy off-road tracked vehicles. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 133, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvayeh, Z.; Domitner, J.; Sommitsch, C.; Hartmann, M.; Karner, W.; Götzinger, B. Mechanical properties and fracture modes of thin butt-joined aluminum-steel blanks for automotive applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 59, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorunov, A. Investigation microstructure and fracture behavior of welded stainless steel specimens previously obtained by supersonic laser deposition. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 56, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Xie, L.-Y.; Liu, G.-L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Li, J. Surface decarburization behavior and its adverse effects of air-cooled forging steel C70S6 for fracture splitting connecting rod. Met. Mater. Int. 2016, 22, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhong, Q. Very high cycle fatigue behavior of shot-peened 3Cr13 high strength spring steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| C | Mn | Si | Ni | Cr | W | Mo | V | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60Si2MnWE | 0.65 | 0.88 | 1.80 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.96 | 0.04 | / | Bal. |
| 60Si2MnA | 0.60 | 0.75 | 1.69 | / | 0.14 | / | / | / | Bal. |
| 62Si2CrA | 0.61 | 0.70 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 0.83 | / | / | / | Bal. |
| 51CrV4 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.30 | / | 1.07 | / | / | 0.14 | Bal. |
| 38Si7 (this work) | 0.39 | 0.68 | 1.73 | 0.02 | 0.21 | / | / | / | Bal. |
| Process No. | QT/°C | Qt/min | TT/°C | Tt/min | UTS/MPa | YS/MPa | A5/% | Z/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 860 | 30 | 430 | 90 | 1440 | 1338 | 11.1 | 51.6 |
| 2 | 860 | 40 | 450 | 75 | 1350 | 1272 | 13.7 | 56.9 |
| 3 | 860 | 50 | 470 | 60 | 1215 | 1129 | 16.5 | 55.2 |
| 4 | 880 | 50 | 430 | 75 | 1404 | 1323 | 13.6 | 58.1 |
| 5 | 880 | 30 | 450 | 60 | 1338 | 1268 | 14.3 | 58.5 |
| 6 | 880 | 40 | 470 | 90 | 1274 | 1195 | 15.5 | 58.4 |
| 7 | 900 | 40 | 430 | 60 | 1393 | 1312 | 13.6 | 57.7 |
| 8 | 900 | 50 | 450 | 90 | 1398 | 1321 | 14.2 | 58.5 |
| 9 | 900 | 30 | 470 | 75 | 1262 | 1182 | 16.0 | 58.1 |
| Standard BS EN 10089-2002 | 1300~1600 | ≥1150 | ≥8 | ≥35 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.-W.; Hu, Q.-F.; Zhang, C.-L.; Chen, L.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Tao, B.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.-Z. Optimization of Heat Treatment for 38Si7 Spring Steel with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Controlled Decarburization. Materials 2022, 15, 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113763
Wang X-W, Hu Q-F, Zhang C-L, Chen L, Zhu C-Y, Tao B, Jiang B, Liu Y-Z. Optimization of Heat Treatment for 38Si7 Spring Steel with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Controlled Decarburization. Materials. 2022; 15(11):3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113763
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xian-Wen, Qing-Feng Hu, Chao-Lei Zhang, Lie Chen, Chang-Yong Zhu, Bo Tao, Bo Jiang, and Ya-Zheng Liu. 2022. "Optimization of Heat Treatment for 38Si7 Spring Steel with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Controlled Decarburization" Materials 15, no. 11: 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113763
APA StyleWang, X.-W., Hu, Q.-F., Zhang, C.-L., Chen, L., Zhu, C.-Y., Tao, B., Jiang, B., & Liu, Y.-Z. (2022). Optimization of Heat Treatment for 38Si7 Spring Steel with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Controlled Decarburization. Materials, 15(11), 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113763






