Sustainable Epoxidized Guayule Natural Rubber, Blends and Composites with Improved Oil Resistance and Greater Stiffness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
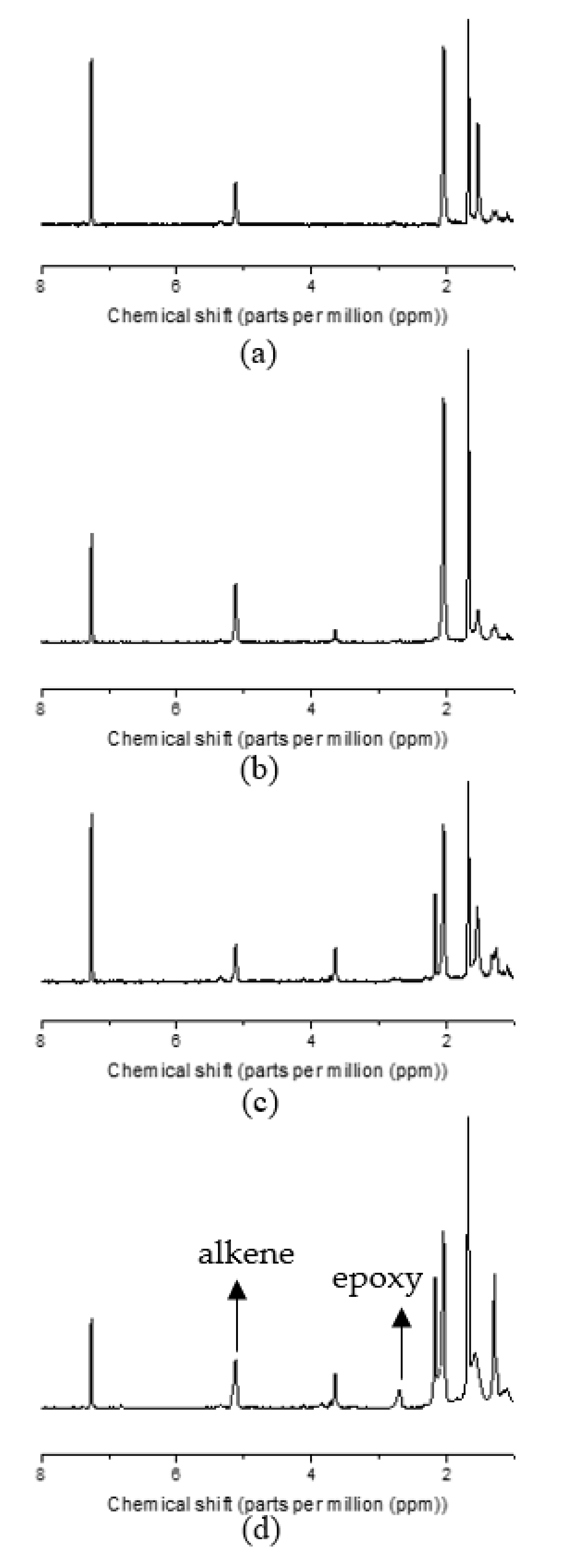
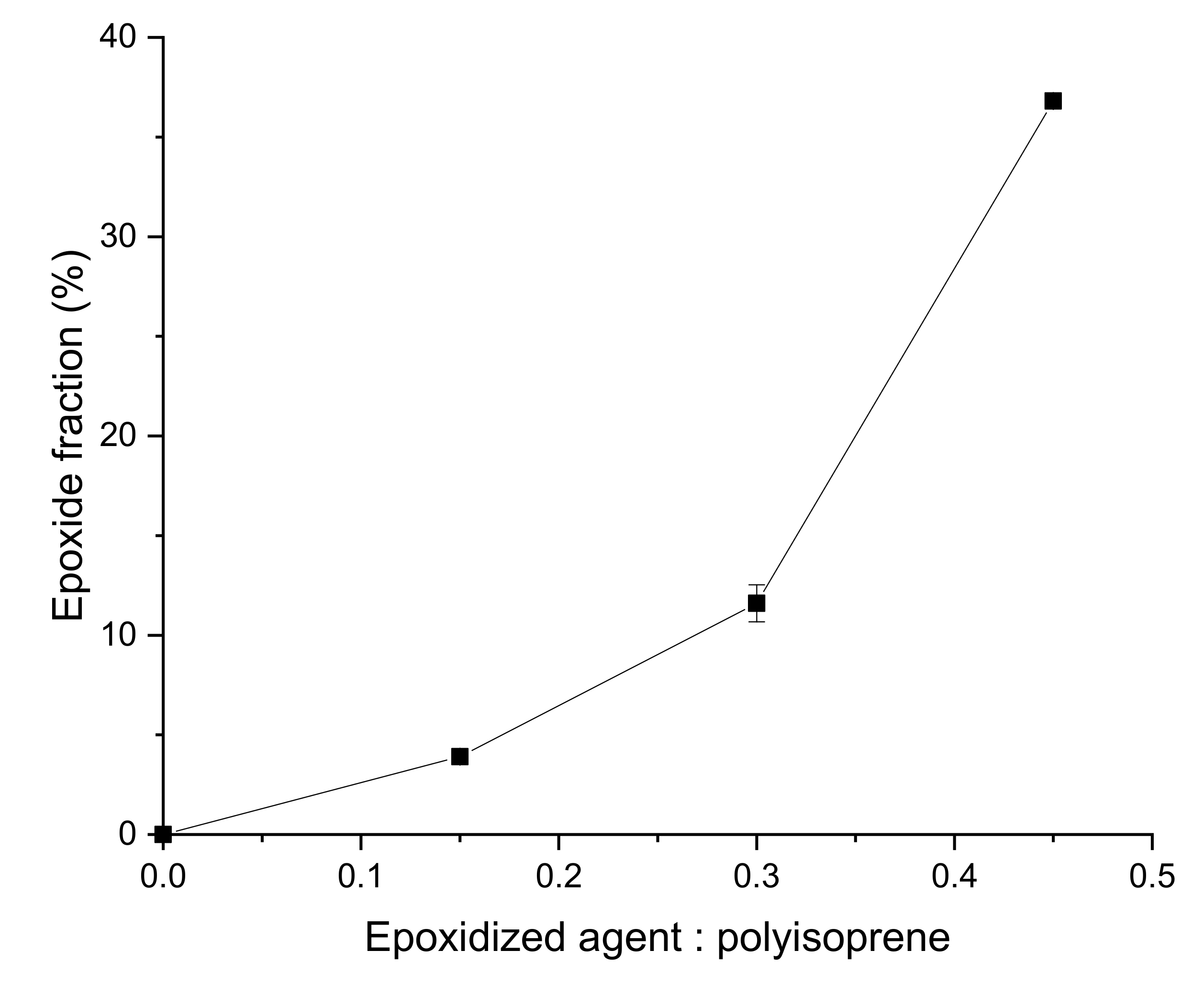
3.1. EGNR Characterization
3.2. Processability
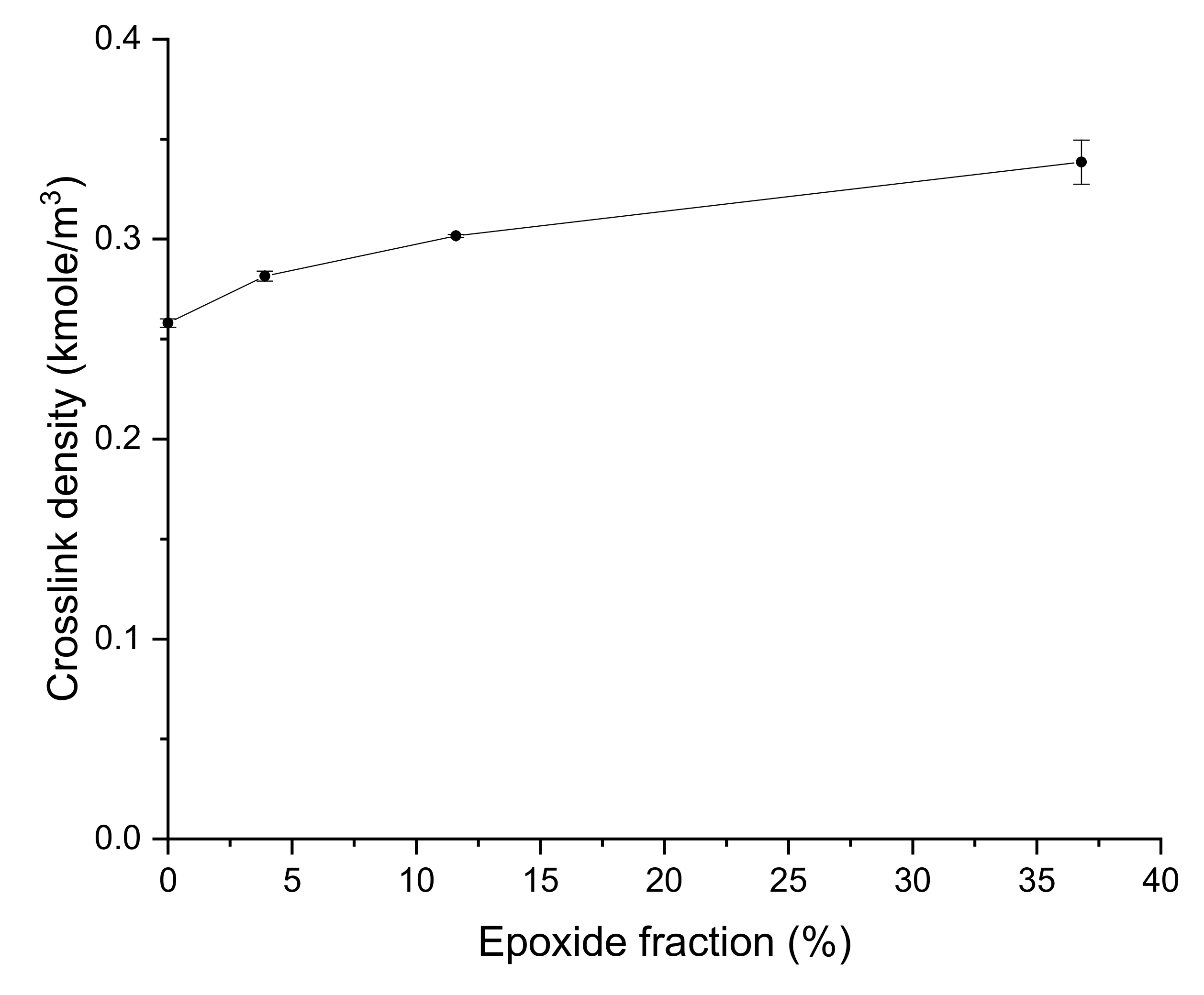
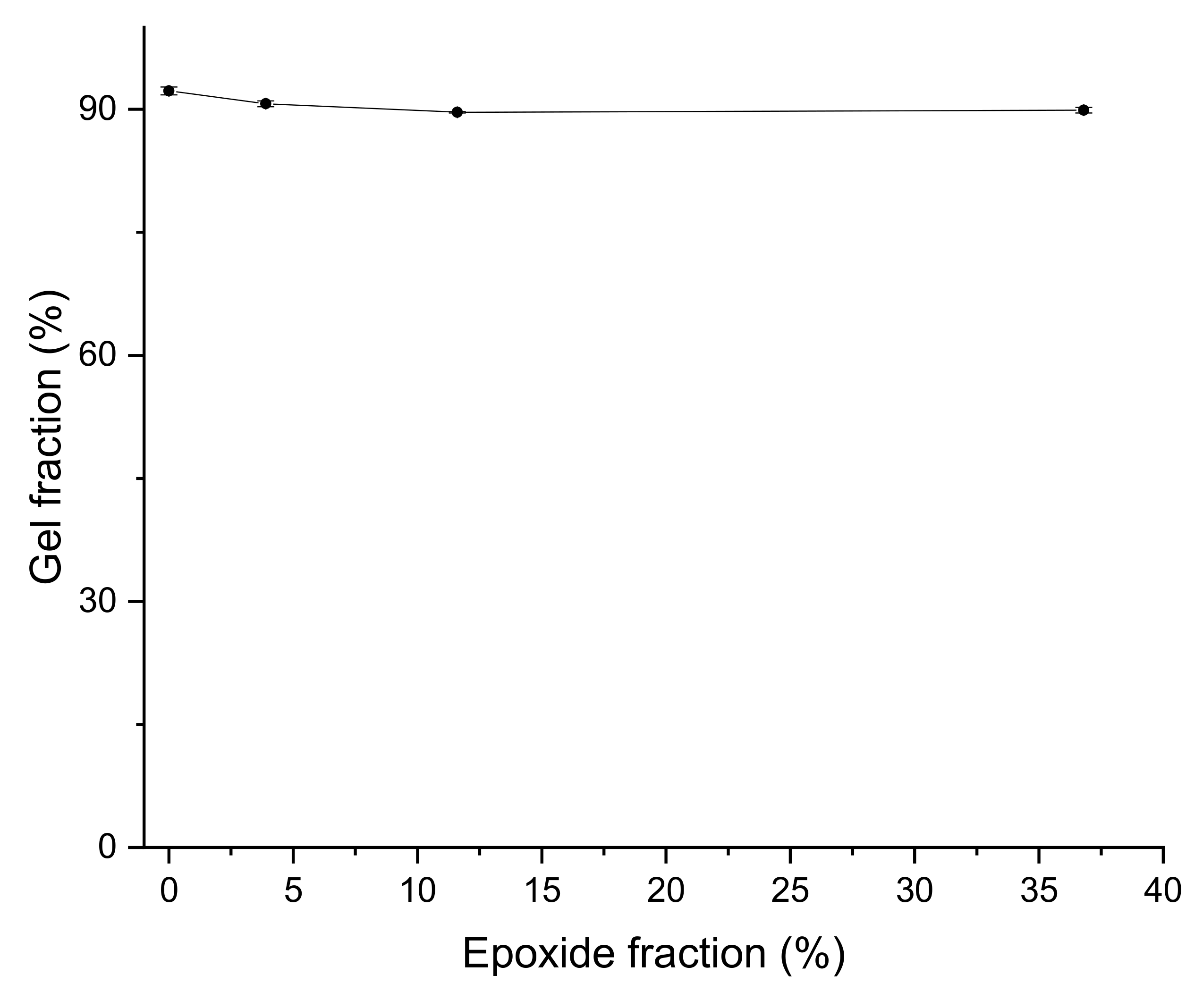
3.3. Crosslink Density and Gel Fraction
3.4. Mechanical Properties
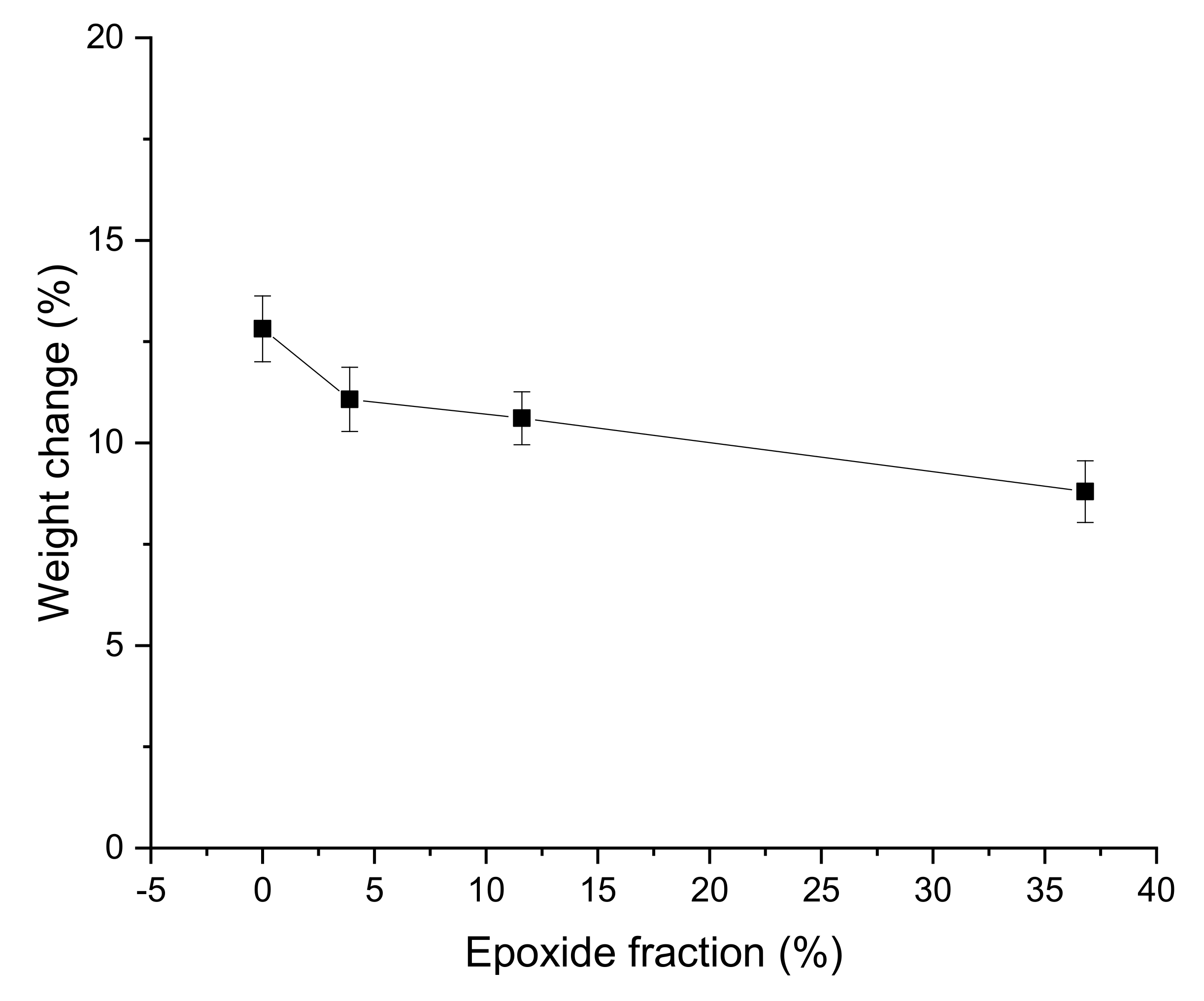
3.5. Oil Resistance
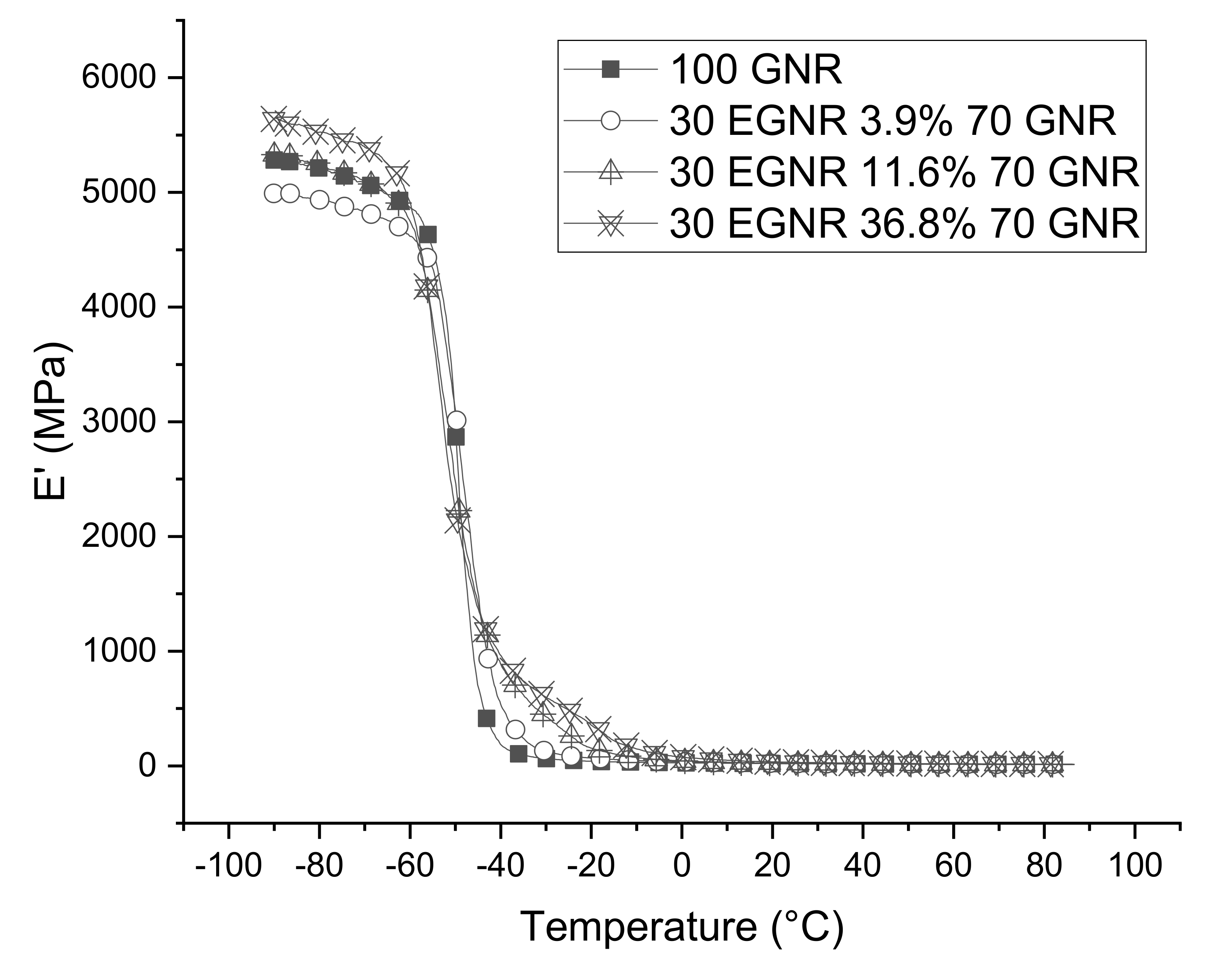
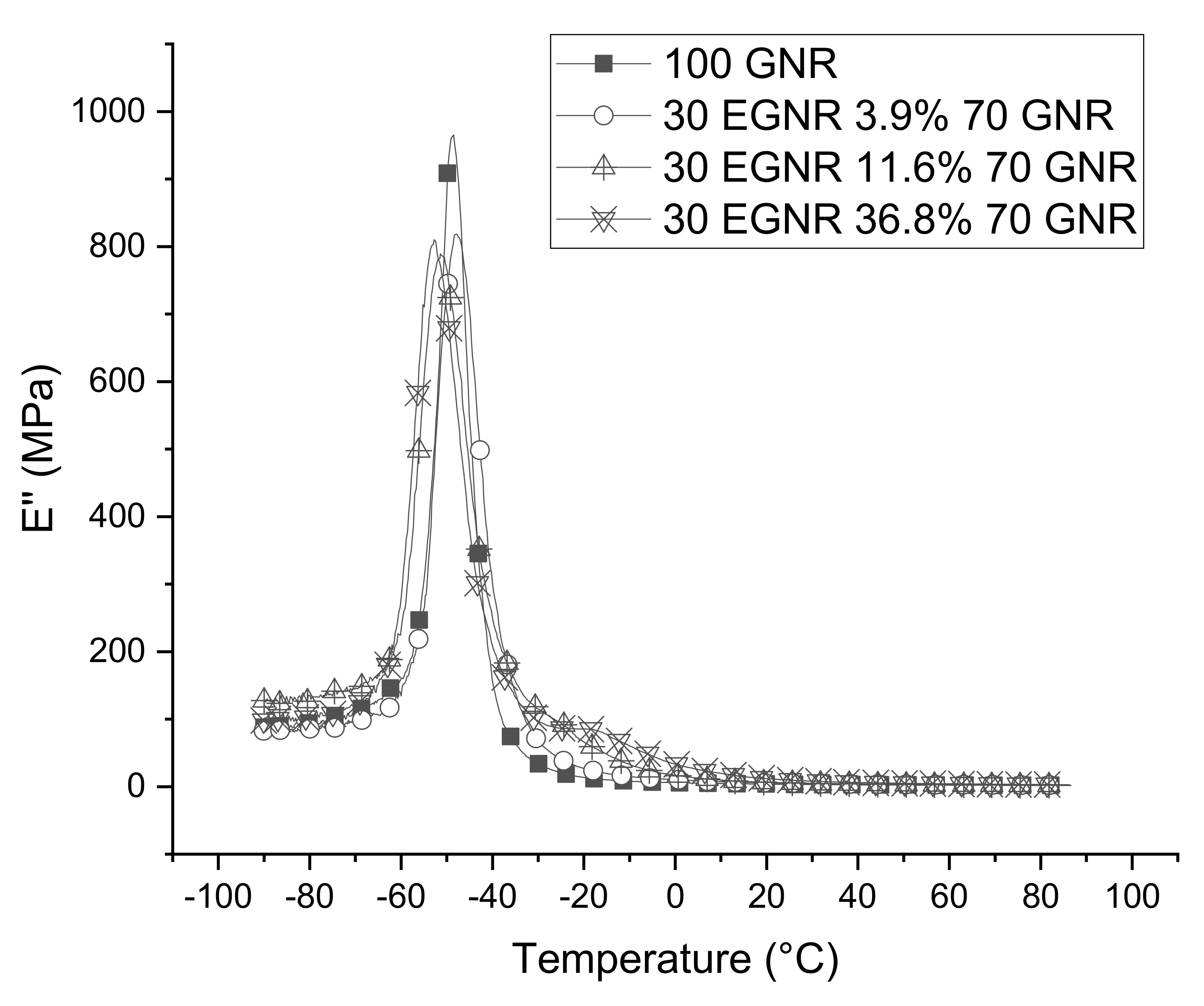
3.6. Dynamic Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natalie Aster Natural vs. Synthetic Rubber: Key Market Trends & Statistics. Available online: https://marketpublishers.com/lists/23821/news.html (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Imbernon, L.; Pauchet, R.; Pire, M.; Albouy, P.-A.; Tence-Girault, S.; Norvez, S. Strain-induced crystallization in sustainably crosslinked epoxidized natural rubber. Polymer 2016, 93, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelling, I.R.; Morrison, N.J. Sulfur vulcanization and oxidative aging of epoxidized natural rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1985, 58, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Jia, Z.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D.; Peng, Z. Interfacial interaction between the epoxidized natural rubber and silica in natural rubber/silica composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 328, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.S.L.; Gelling, I.R.; Newell, R. Epoxidized Natural Rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1985, 58, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Thomas, S. Nitrogen/oxygen permeability of natural rubber, epoxidised natural rubber and natural rubber/epoxidised natural rubber blends. Polymer 1999, 40, 3223–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Barrera, C.S.; Tardiff, J.L.; Gil, A.; Cornish, K. Liquid guayule natural rubber, a renewable and crosslinkable processing aid in natural and synthetic rubber compounds. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intharapat, P.; Kongnoo, A.; Kateungngan, K. The Potential of Chicken Eggshell Waste as a Bio-filler Filled Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) Composite and its Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloman, W.W. Low-molecular-weight guayule natural rubber as a feedstock for epoxidized natural rubber. Ind. Crops Prod. 1992, 1, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, M.; Zhai, X.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. Using epoxidized solution polymerized styrene-butadiene rubbers (ESSBRs) as coupling agents to modify silica without volatile organic compounds. Polymers 2020, 12, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, K. Hypoallergenic Natural Rubber Products from Parthenum Argentatum (Gray) and Other Non-Hevea Brasiliensis Species. U.S. Patent 5,580,942, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Saramolee, P.; Sahakaro, K.; Lopattananon, N.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Comparative properties of silica-and carbon black-reinforced natural rubber in the presence of epoxidized low molecular weight polymer. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2014, 87, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, Ł.; Colom, X.; Saeb, M.R.; Formela, K. Preparation and characterization of natural rubber composites highly filled with brewers’ spent grain/ground tire rubber hybrid reinforcement. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 145, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Effect of polymer-filler and filler-filler interactions on dynamic properties of filled vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1998, 71, 520–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, T.R.; Bhandari, V.; Chandra, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Role of calcium stearate as a dispersion promoter for new generation carbon black-organoclay based rubber nanocomposites for tyre application. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Sancaktar, E. Use of fly ash as eco-friendly filler in synthetic rubber for tire applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J. Statistical Mechanics of Cross-Linked Polymer Networks I. Rubberlike Elasticity. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.W.; Lee, D.Y. Correlation between the Crosslink Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Compound via Accelerators and Reinforcement. Polymers 2020, 12, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkhuis, K.A.J.; Noordermeer, J.W.M.; Dierkes, W.K. The relationship between crosslink system, network structure and material properties of carbon black reinforced EPDM. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 3302–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruendken, M.; Velencoso, M.M.; Hirata, K.; Blume, A. Structure-propery relationship of low molecular weight ‘ liquid ’ polymers in blends of sulfur cured SSBR-rich compounds. Polym. Test. 2020, 87, 106558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard D6814−02; Standard Test Method for Determination of Percent Devulcanization of Crumb Rubber Based on Crosslink Density. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Kulkarni, P.P.; Jafvert, C.T. Solubility of C 60 in Solvent Mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharaiya, N.; Bahadur, P.; Singh, K.; Marangoni, D.G.; Bahadur, P. Light scattering and NMR studies of Triton X-100 micelles in the presence of short chain alcohols and ethoxylates. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotman, A.H.M.; van Haeren, P.J.C.; Weber, A.J.M.; van Wijk, F.G.H.; Hofstraat, J.W.; Talma, A.G.; Steenbergen, A.; Datta, R.N. Studies on a New Antireversion Agent for Sulfur Vulcanization of Diene Rubbers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F. Preparation of Silica-Based Rubber Compounds without the Use of a Silane Coupling Agent through the Use of Epoxidized Natural Rubber. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2002, 287, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, B.T.; Tan, B.K. Mooney scorch time of epoxidized natural rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 42, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, V.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Isayev, A.I.; Massey, J.; Von Meerwall, E. Ultrasound devulcanization of sulfur vulcanized SBR: Crosslink density and molecular mobility. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burfield, D.R.; Lim, K.L.; Law, K.S. Epoxidation of natural rubber latices: Methods of preparation and properties of modified rubbers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1984, 29, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | Phr | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNR | 100 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| EGNR (mole ratio = 0.15) | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| EGNR (mole ratio = 0.3) | 0 | 0 | 30 | 0 |
| EGNR (mole ratio = 0.45) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| Carbon black N330 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Sulfur | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| TBBS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Stearic acid | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6PPD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Epoxide Fraction (%) | Average Energy Consumption, kw |
|---|---|
| 0 | 20 |
| 3.9 | 19 |
| 11.6 | 19 |
| 36.8 | 21 |
| Epoxide Fraction, (%) | TS2 (min) | T90 (min) | Curing Rate index | ML (NM) | MH(Nm) | MH-ML (Nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.93 | 4.87 | 25.38 | 0.92 | 11.21 | 10.29 |
| 3.9 | 0.98 | 4.00 | 33.11 | 0.65 | 10.69 | 10.05 |
| 11.6 | 0.87 | 3.78 | 34.36 | 0.90 | 10.96 | 10.06 |
| 36.8 | 0.79 | 4.37 | 27.93 | 1.00 | 12.51 | 11.50 |
| Epoxide Fraction, % | Volume Fraction of the Rubber, % | Crosslinks Density, kmol/m3 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25.46 | 0.26 |
| 3.9 | 26.38 | 0.28 |
| 11.6 | 27.12 | 0.30 |
| 36.8 | 28.40 | 0.34 |
| Epoxide Fraction, (%) | Tensile Strength, Mpa | Standard Deviation | Elongation at Break, % | Standard Deviation | Modulus at 100% Strain, Mpa | Standard Deviation | Hardness Number | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 22.9 | 0.4 | 301.0 | 4.3 | 6.5 | 0.1 | 74.2 | 0.4 |
| 3.9 | 22.0 | 0.1 | 273.1 | 2.2 | 7.8 | 0.1 | 75.4 | 0.5 |
| 11.6 | 19.8 | 0.5 | 219.4 | 3.8 | 9.0 | 0.1 | 78.2 | 0.8 |
| 36.8 | 18.8 | 0.4 | 197.7 | 5.4 | 9.9 | 0.1 | 80.2 | 1.1 |
| Epoxide Fraction (%) | Tan Delta at 0 °C (Wet Traction) | Tan Delta at 60 °C (Rolling Resistance) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.23 | 0.16 |
| 3.9 | 0.29 | 0.19 |
| 11.6 | 0.38 | 0.19 |
| 36.8 | 0.44 | 0.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Barrera, C.S.; Tardiff, J.L.; Cornish, K. Sustainable Epoxidized Guayule Natural Rubber, Blends and Composites with Improved Oil Resistance and Greater Stiffness. Materials 2022, 15, 3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113946
Ren X, Barrera CS, Tardiff JL, Cornish K. Sustainable Epoxidized Guayule Natural Rubber, Blends and Composites with Improved Oil Resistance and Greater Stiffness. Materials. 2022; 15(11):3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113946
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xianjie, Cindy S. Barrera, Janice L. Tardiff, and Katrina Cornish. 2022. "Sustainable Epoxidized Guayule Natural Rubber, Blends and Composites with Improved Oil Resistance and Greater Stiffness" Materials 15, no. 11: 3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113946
APA StyleRen, X., Barrera, C. S., Tardiff, J. L., & Cornish, K. (2022). Sustainable Epoxidized Guayule Natural Rubber, Blends and Composites with Improved Oil Resistance and Greater Stiffness. Materials, 15(11), 3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15113946






