Investigation on the Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals under Thermal Treatment by Wide/Small-Angle X-ray Scattering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Experimental Process
3. Results and Discussion
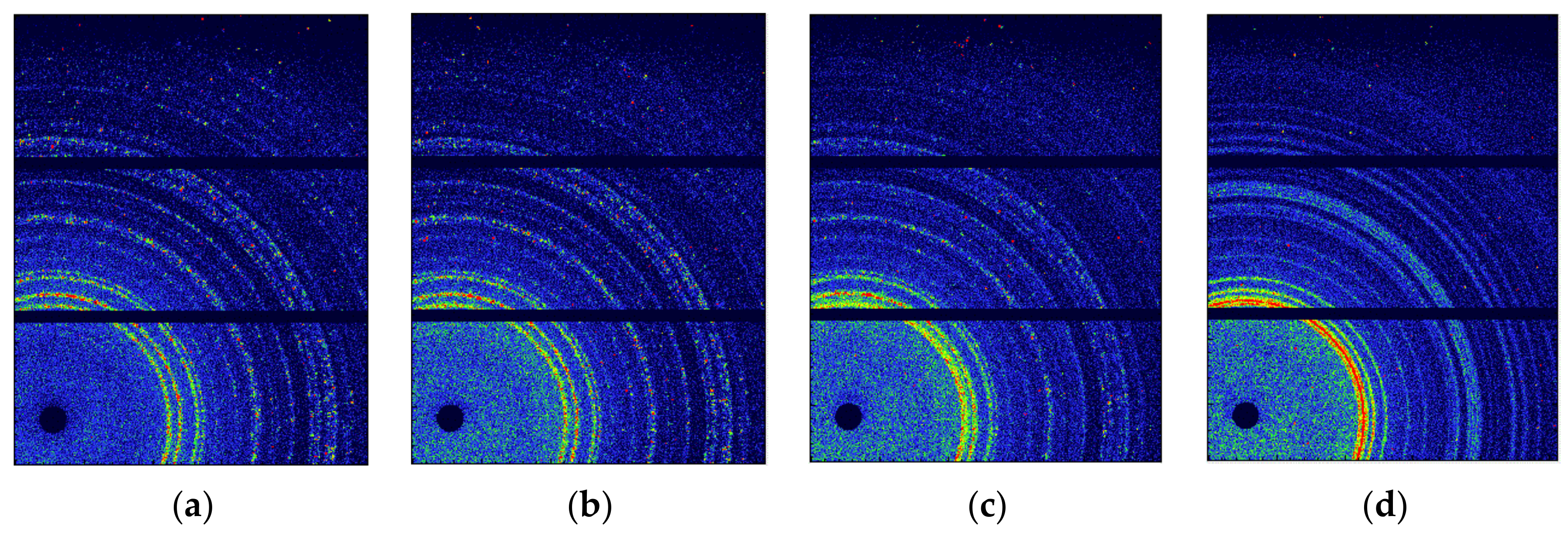
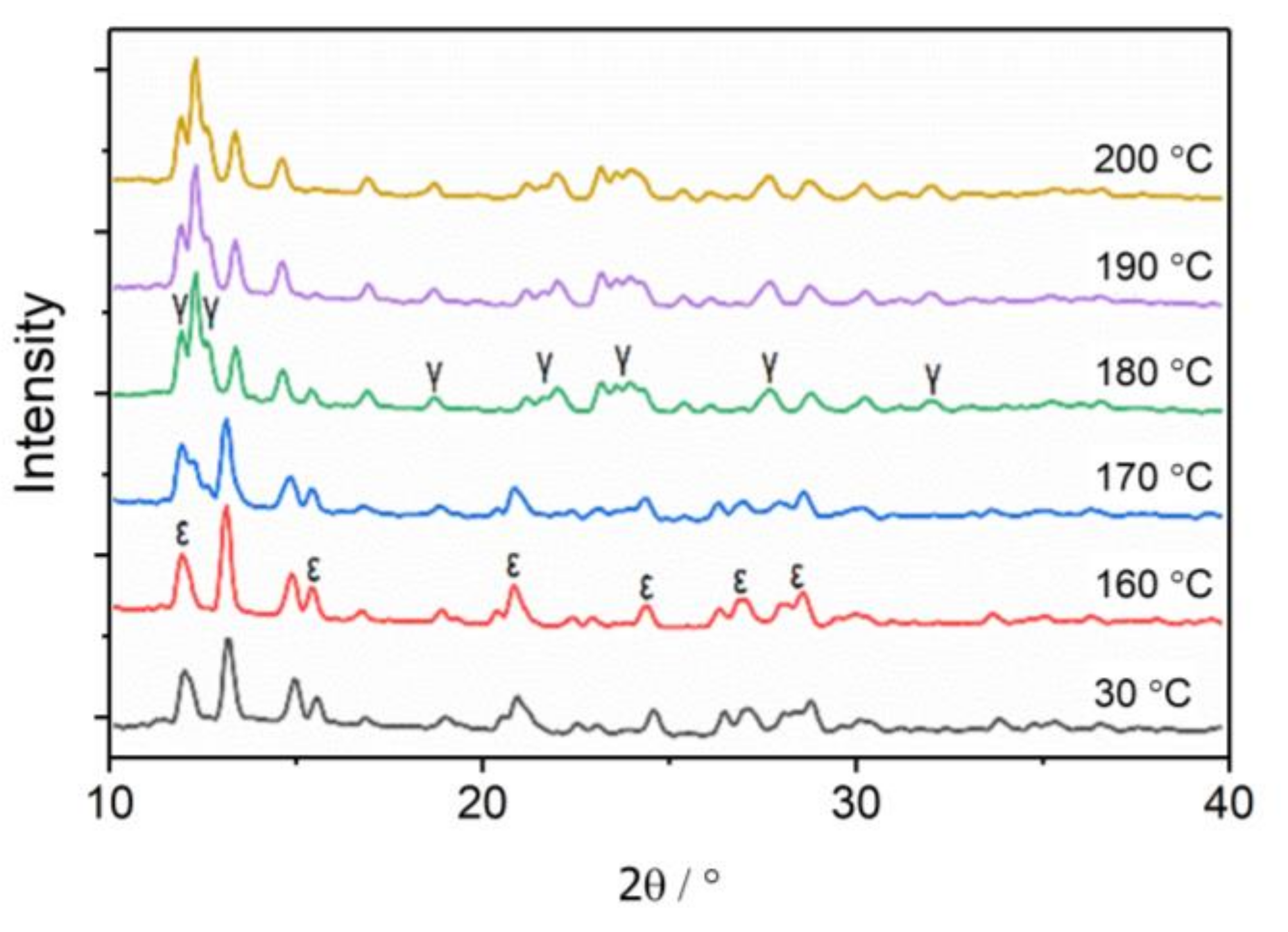
3.1. The Phase Transition of CL-20 Crystals by WAXS
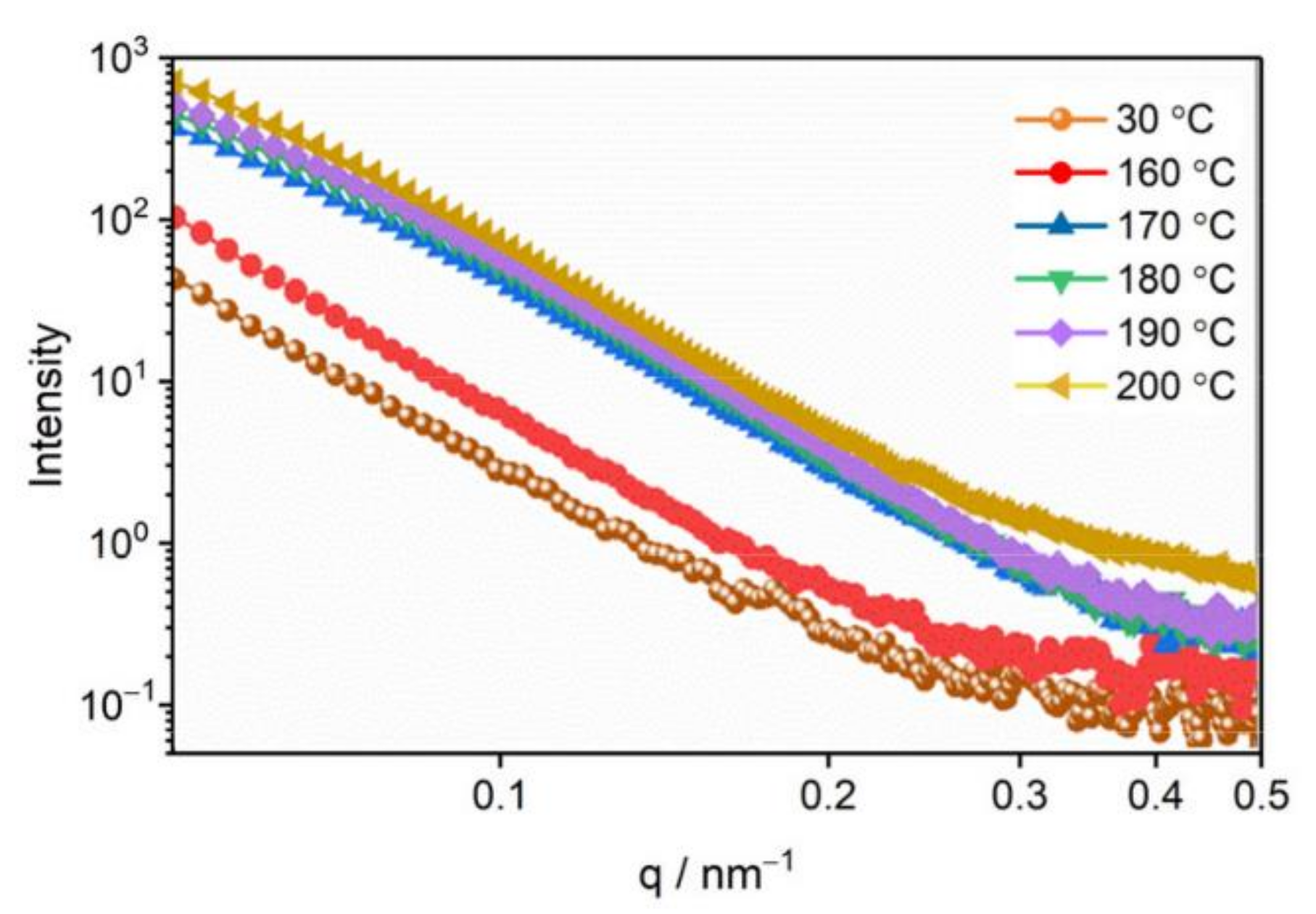
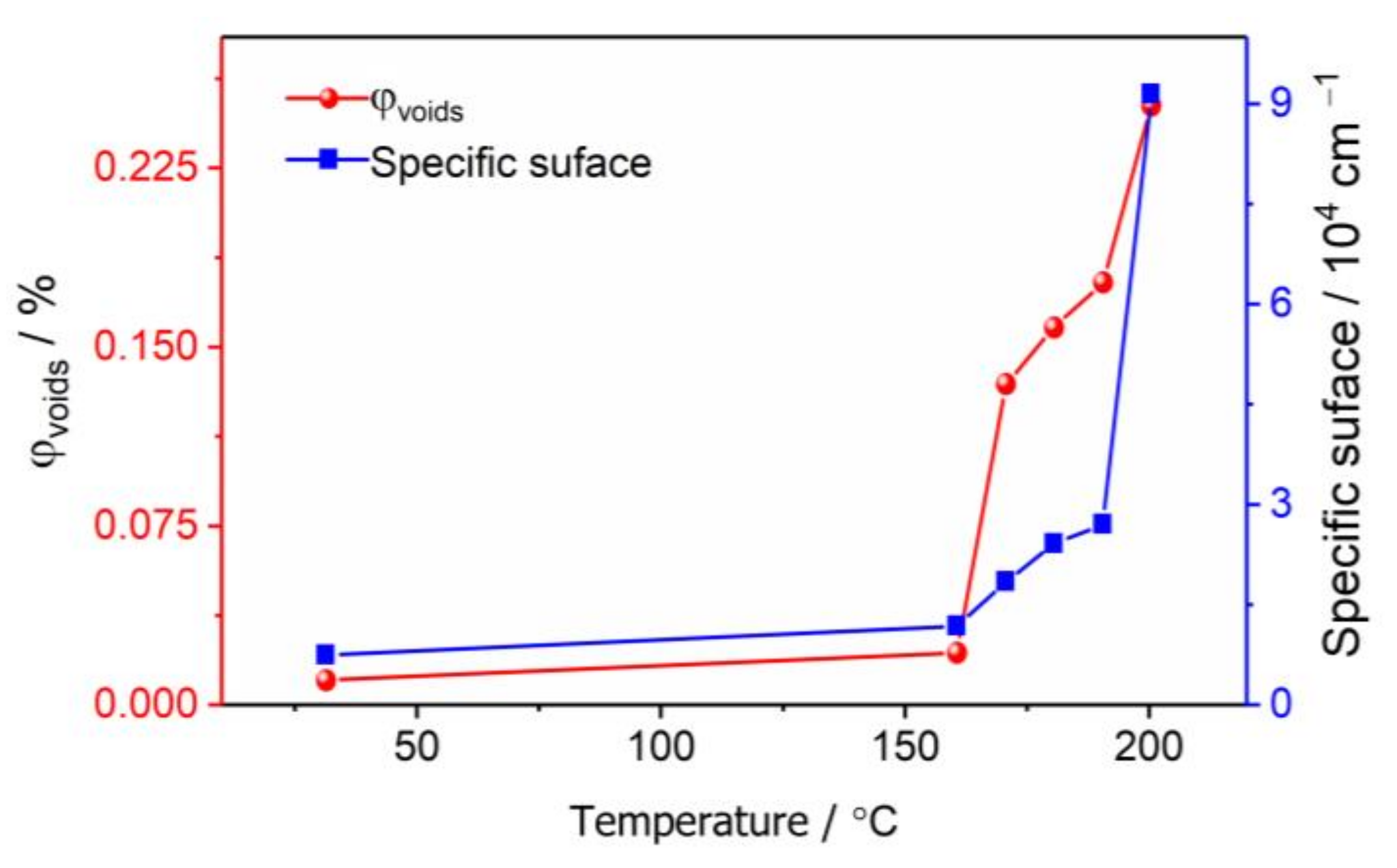
3.2. The Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals at Different Temperatures
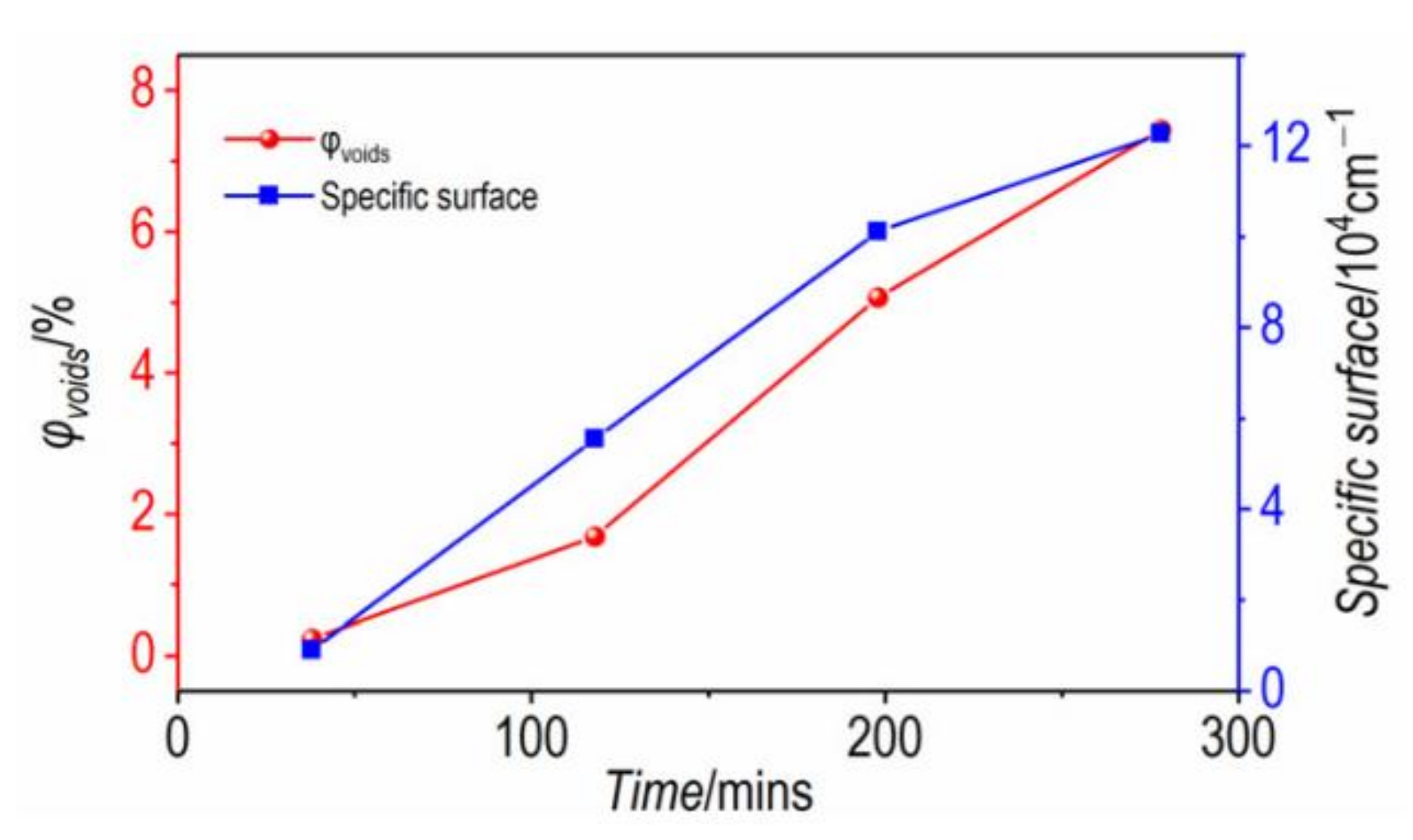
3.3. The Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals over Time at 200 °C
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Thermal expansion phase (30–160 °C): The number of pores and the specific surface area changed slightly, and the number of defects in each size increased slightly with the increase in temperature. The change of defects in the CL-20 crystals before the phase transition is mainly due to the effect of the thermal expansion of the CL-20 crystal lattice;
- (2)
- Phase transition stage (170–200 °C): The volume fraction and specific surface area of the pores of the CL-20 crystals increased significantly during the phase transition, resulting mainly in small- and medium-sized pores, but the change of large-sized pores was not obvious. From the beginning of heating to the end of the phase transition, most of the pores came from the CL-20 phase transition process, and the effect of thermal expansion effect was not significant.
- (3)
- Thermal decomposition stage (over time at 200 °C): The specific surface area and volume fraction of CL-20 pores changed over time when the temperature was fixed at 200 °C. Small-sized pores first appeared, and medium-sized and large-sized pores subsequently appeared, indicating that small-sized pores gradually grow into medium-sized and large-sized pores.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, P.; Souers, P.C.; Chidester, S.; Alvarez, J.; De Haven, M.; Garza, R.; Harwood, P.; Maienschein, J. Detonation Measurements on Damaged LX-04. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2007, 32, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urtiew, P.A.; Tarver, C.M. Shock initiation of energetic materials at different initial temperatures. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2005, 41, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, W.P.; Dlott, D.D. Shock initiation of explosives: Temperature spikes and growth spurts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 091903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Huang, M.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Nie, F.; Dai, B. Intragranular defects and shock sensitivity of RDX/HMX. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 2010, 18, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.; Field, J.E.; Huntley, J. Deformation, strengths and strains to failure of polymer bonded explosives. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1993, 440, 399–419. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Geubelle, P. The Mori–Tanaka method for composite materials with nonlinear interface debonding. Int. J. Plast. 2005, 21, 1890–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Q.; Lan, L.G.; Zhong-Hua, L.U.; Rong-Xi, H.U. Mechanical Properties and Failure Modes of PBX Explosives with Different Prefabricated Defects. Chin. J. Explos. Propellants 2015, 38, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhakar, A.R.; Mathew, S. Thermal behaviour of CuO doped phase-stabilised ammonium nitrate. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 451, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-j.; Dong, H.-s.; Shu, Y.-j.; Hao, Y.; Wang, X. The preparation of HMX crystals with defects and the influences of crystal defects on thermal sensitivity and stability. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 2003, 11, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y.; Dai, B. Characterization of RDX-Based Thermosetting Plastic-Bonded Explosive by Cone-Beam Microfocus Computed Tomography. J. Energetic Mater. 2012, 30, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.L.; Xiao, M.A.; Cheng, F.; Tao, L.I.; Hua, F.U. Coupling Properties of Crack Penetration Driven by Explosive Burning Products. Chin. J. Energetic Mater. 2019, 27, 819–823. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.A.; Kohler, R.; Koslowski, M. Dynamic fracture and frictional heating due to periodic excitation in energetic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 165109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghout, H.L.; Son, S.F.; Skidmore, C.B.; Idar, D.J.; Asay, B.W. Combustion of damaged PBX 9501 explosive. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 384, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Li, C. Applications of Small-angel Scattering (SAS) Technique in the Structure Measuring of Energetic Materials. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 2005, 13, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Yan, G.; Sun, G.; Huang, C.; Xie, L.; Chen, B.; Huang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Thermally induced damage in hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2013, 10, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Mang, J.; Skidmore, C.; Son, S.; Hjelm, R.; Rieker, T. An Optical Microscopy and Small-Angle Scattering Study of Porosity in Thermally Treated PBX 9501. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park City, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 620, pp. 833–836. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, P.D.; Mang, J.T.; Asay, B.W. Quantitative analysis of damage in an octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazonic-based composite explosive subjected to a linear thermal gradient. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 093507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, E.; Muzyrya, A.; Kostitsyn, O.; Badretdinova, L.C.; Ten, K.; Pruuel, E.; Tolochko, B.; Sharafutdinov, M.; Shmakov, A.; Kuper, K. Investigation of micro-, meso-, and macrostructure of the condensed heterogeneous explosives using synchrotron radiation. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2015, 79, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, T.M.; Hoffman, D.M.; van Buuren, T.; Lauderbach, L.; Gee, R.H.; Maiti, A.; Overturf, G.E.; Fried, L.E.; Ilavsky, J. The Microstructure of TATB-Based Explosive Formulations During Temperature Cycling Using Ultra-Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2009, 34, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, T.M.; Van Buuren, T.; Lee, J.R.; Overturf, G.E.; Kinney, J.H.; Handly, J.; Weeks, B.L.; Ilavsky, J. Changes in Pore Size Distribution upon Thermal Cycling of TATB-based Explosives Measured by Ultra-Small Angle X-Ray Scattering. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2006, 31, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, T.M.; Lauderbach, L.; Gagliardi, F.; van Buuren, T.; Glascoe, E.A.; Tringe, J.W.; Lee, J.R.; Springer, H.K.; Ilavsky, J. Mesoscale evolution of voids and microstructural changes in HMX-based explosives during heating through the β-δ phase transition. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 055901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Tian, Q.; Liu, J.; Fan, Z.; Sun, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Gong, J.; Zhou, X. The microstructural evolution in HMX based plastic-bonded explosive during heating and cooling process: An in situ small-angle scattering study. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2016, 13, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.Y.; Tian, Q.; Liu, J.H. Small-angle X-ray analysis of the effect of grain size on the thermal damage of octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7 tetrazocine-based plastic-bounded expolsives. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.Y.; Tian, Q.; Huang, C.Q.; Gu, X.M.; Sun, G.A.; Bo, C.; Ming, H.; Nie, F.D.; Yi, L.; Li, X.H. A small-angle X-ray scattering study of micro-defects in thermally treated HMX. Acta Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shu, Y.; Sun, J. Polymorphism in hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane crystallized from solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 354, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Meng, Z.; Qiu, L.; Wang, S. Thermally induced polymorphic transformation of Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane (CL-20). Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.X.; Li, X.X.; Guo, L. Chemical interplay between components in overall thermolysis of CL-20/N2O revealed by ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulations. Energetic Mater. Front. 2022, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Luo, S.N. Ignition, combustion and detonation of energetic materials: Some developments in synthesis, experiments, and modeling. Energetic Mater. Front. 2021, 2, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Characterization of crystal microstructure based on small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) Technique. Molecules 2020, 25, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Men, Y. Calibration of absolute scattering intensity in small-angle X-ray scattering. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 2016, 33, 774. [Google Scholar]
- Feigin, L.A.; Svergun, D.I. Structure Analysis by Small-Angle X-ray and Neutron Scattering; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, X. Investigation on the Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals under Thermal Treatment by Wide/Small-Angle X-ray Scattering. Materials 2022, 15, 4258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124258
Zhang H, Wang H, Xu J, Sun J, Wang X. Investigation on the Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals under Thermal Treatment by Wide/Small-Angle X-ray Scattering. Materials. 2022; 15(12):4258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124258
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haobin, Hongfan Wang, Jinjiang Xu, Jie Sun, and Xiaolin Wang. 2022. "Investigation on the Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals under Thermal Treatment by Wide/Small-Angle X-ray Scattering" Materials 15, no. 12: 4258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124258
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, H., Xu, J., Sun, J., & Wang, X. (2022). Investigation on the Evolution of Nano-Scale Defects of CL-20 Crystals under Thermal Treatment by Wide/Small-Angle X-ray Scattering. Materials, 15(12), 4258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124258





