Stain Susceptibility of Composite Resins: Pigment Penetration Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
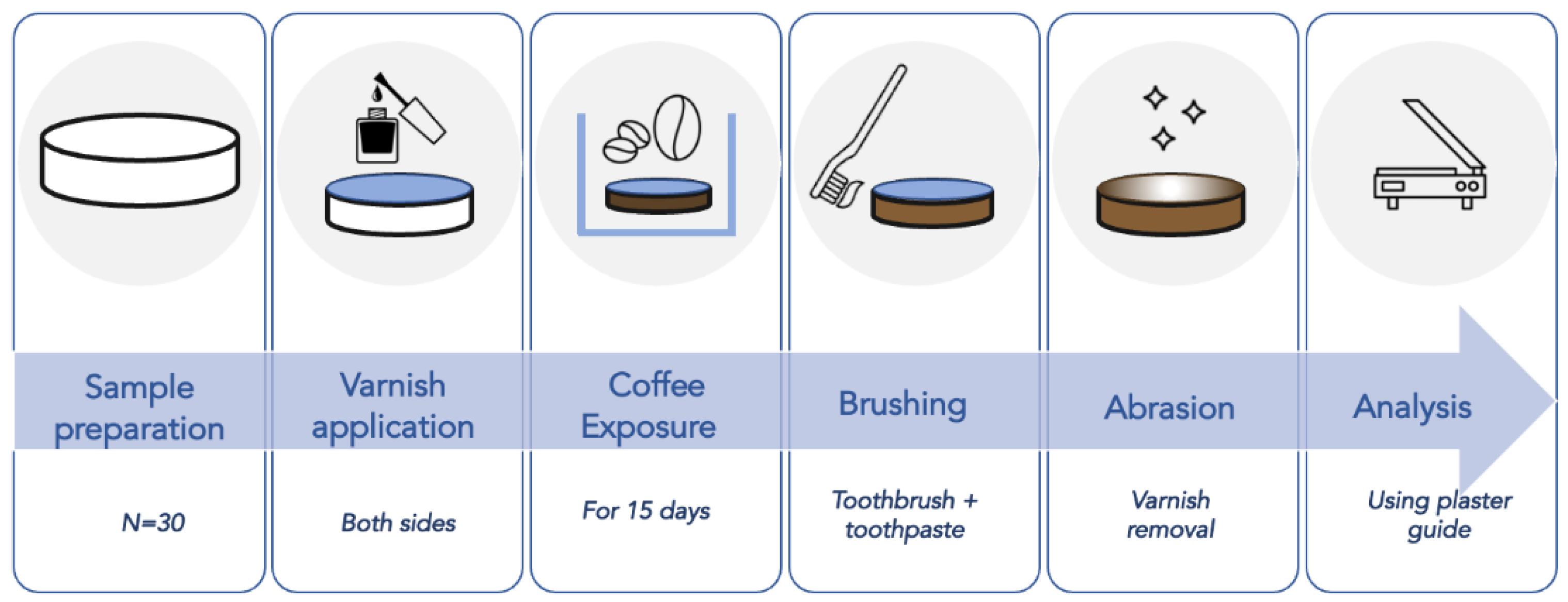
2.1. Specimen Preparation
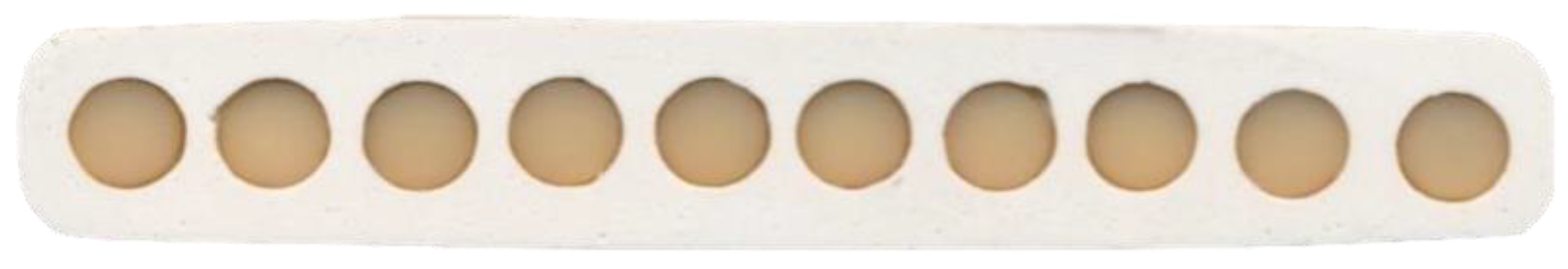
2.2. Specimen Analysis
2.3. Statistics
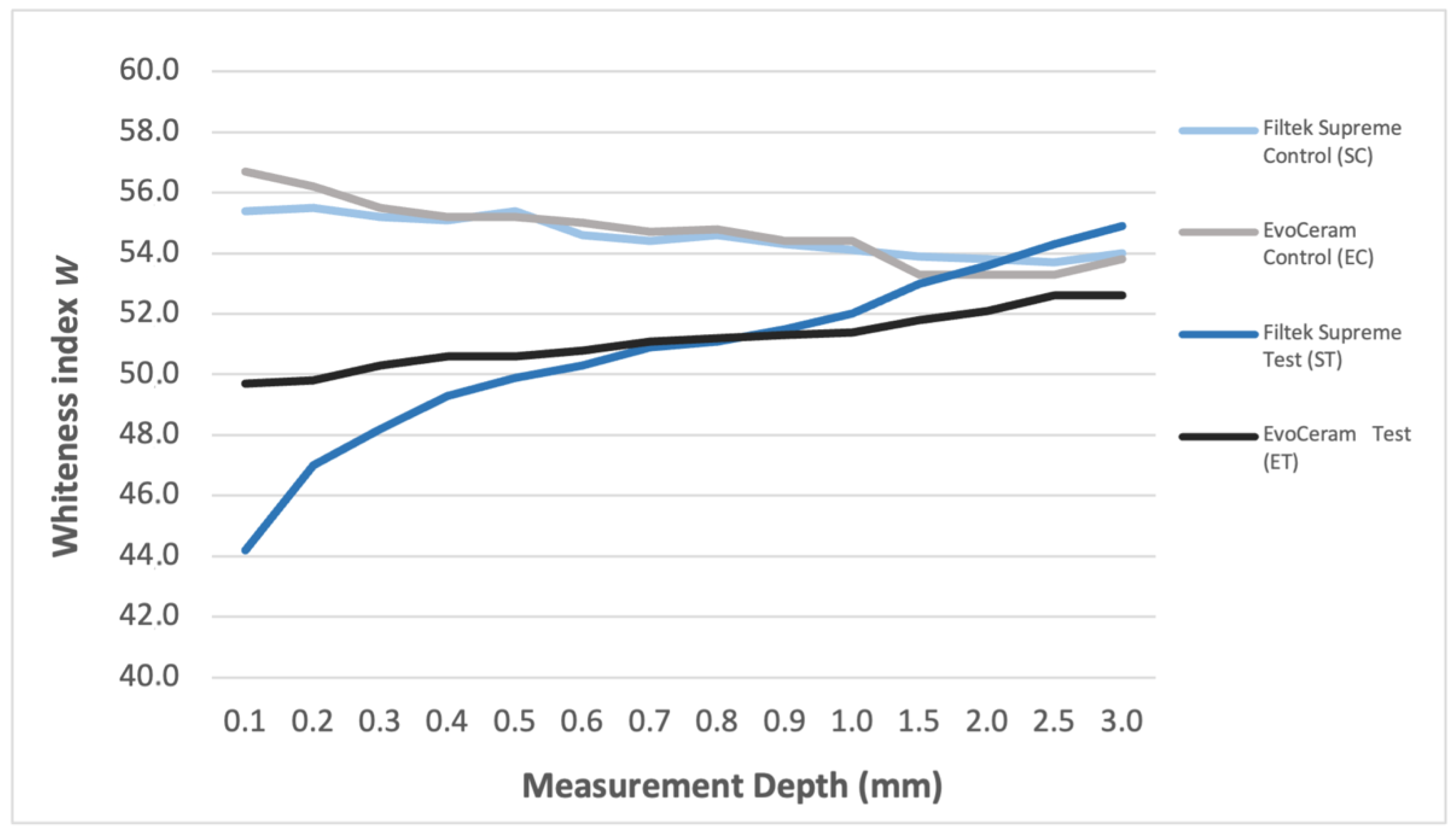
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demarco, F.F.; Collares, K.; Coelho-de-Souza, F.; Correa, M.B.; Cenci, M.S.; Moraes, R.R.; Opdam, N.J.M. Anterior composite restorations: A systematic review on long-term survival and reasons for failure. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topcu, F.T.; Sahinkesen, G.; Yamanel, K.; Erdemir, U.; Oktay, E.A.; Ersahan, S. Influence of different drinks on the colour stability of dental resin composites. Eur. J. Dent. 2009, 3, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alharbi, A.; Ardu, S.; Bortolotto, T.; Krejci, I. Stain susceptibility of composite and ceramic CAD/CAM blocks versus direct resin composites with different resinous matrices. Odontology 2017, 105, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd Elhamid, M.; Mosallam, R. Effect of bleaching versus repolishing on colour and surface topography of stained resin composite. Aust. Dent. J. 2010, 55, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raptis, C.N.; Powers, J.M.; Fan, P.L. Staining of composite resins by cigarette smoke. J. Oral. Rehabil. 1982, 9, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujjari, A.K.; Bhatnagar, V.M.; Basavaraju, R.M. Color stability and flexural strength of poly (methyl methacrylate) and bis-acrylic composite based provisional crown and bridge auto-polymerizing resins exposed to beverages and food dye: An in vitro study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2013, 24, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocha, M.A.; Mayoral, J.R.; Lefever, D.; Mercade, M.; Basilio, J.; Roig, M. Color stability of siloranes versus methacrylate-based composites after immersion in staining solutions. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2013, 17, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, A.U.; Güler, E.; Yücel, A.C.; Ertaş, E. Effects of polishing procedures on color stability of composite resins. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2009, 17, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruyter, I.E. Composites—Characterization of composite filling materials: Reactor response. Adv. Dent. Res. 1988, 2, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmussen, E.; Hansen, E.K. Surface discoloration of restorative resins in relation to surface softening and oral hygiene. Scand. J. Dent. Res. 1986, 94, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmussen, E. Factors affecting the color stability of restorative resins. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1983, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoushi, S.; Lassila, L.; Hatem, M.; Shembesh, M.; Baady, L.; Salim, Z.; Vallittu, P. Influence of staining solutions and whitening procedures on discoloration of hybrid composite resins. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergucu, Z.; Turkun, L.S.; Aladag, A. Color stability of nanocomposites polished with one-step systems. Oper. Dent. 2008, 33, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, T.; Nakanishi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Sano, H. Color differences and color changes in Vita Shade tooth-colored restorative materials. Am. J. Dent. 2003, 16, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ardu, S.; Braut, V.; Gutemberg, D.; Krejci, I.; Dietschi, D.; Feilzer, A.J. A long-term laboratory test on staining susceptibility of esthetic composite resin materials. Quintessence Int. 2010, 41, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ardu, S.; Duc, O.; Di Bella, E.; Krejci, I. Color stability of recent composite resins. Odontology 2017, 105, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, R.W.; Zhou, X.; McClanahan, S.F. Comparative response of whitening strips to a low peroxide and potassium nitrate bleaching gel. Am. J. Dent. 2002, 15, 19A–23A. [Google Scholar]
- De Camargo, E.J.; Moreschi, E.; Baseggio, W.; Cury, J.A.; Pascotto, R.C. Composite depth of cure using four polymerization techniques. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2009, 17, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.R.; Palin, W.M.; Fleming, G.J.; Shortall, A.C.; Marquis, P.M. The mechanical properties of nanofilled resin-based composites: The impact of dry and wet cyclic pre-loading on bi-axial flexure strength. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlovic, D.; Radisic, M.; Vasiljevic, T.; Zivkovic, S.; Lausevic, M.; Miletic, V. Monomer elution from nanohybrid and ormocer-based composites cured with different light sources. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, L.M.; Ferraz, L.G.; Antunes, K.B.; Garcia, I.M.; Schneider, L.F.J.; Collares, F.M. Silane content influences physicochemical properties in nanostructured model composites. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, e85–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouschlicher, M.R.; Rueggeberg, F.A. Effect of stepped light intensity on polymerization force and conversion in a photoactivated composite. J. Esthet. Dent. 2000, 12, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueggeberg, F.A.; Caughman, W.F.; Curtis, J.W.; Davis, H.C. Factors affecting cure at depths within light-activated resin composites. Am. J. Dent. 1993, 6, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duc, O.; Di Bella, E.; Krejci, I.; Betrisey, E.; Abdelaziz, M.; Ardu, S. Staining susceptibility of resin composite materials. Am. J. Dent. 2019, 32, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Um, C.M.; Ruyter, I.E. Staining of resin-based veneering materials with coffee and tea. Quintessence Int. 1991, 22, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferracane, J.L.; Moser, J.B.; Greener, E.H. Ultraviolet light-induced yellowing of dental restorative resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1985, 54, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, F.; Zhao, X.; Pan, J.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J.; Ren, Y. Effects of cigarette smoke and tobacco heating aerosol on color stability of dental enamel, dentin, and composite resin restorations. Quintessence Int. 2019, 25, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Paolone, G.; Formiga, S.; De Palma, F.; Abbruzzese, L.; Chirico, L.; Scolavino, S.; Goracci, C.; Cantatore, G.; Vichi, A. Color stability of resin-based composites: Staining procedures with liquids—A narrative review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, I.; Neelakantan, P.; Sujeer, R.; Subbarao, C. Colour stability of microfilled, microhybrid and nanocomposite resins-an in vitro study. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Westland, S.; Brunton, P.; Ellwood, R.; Pretty, I.A.; Mohan, N. Comparison of the ability of different colour indices to assess changes in tooth whiteness. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, P.; Lu, H.; Okte, Z.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Powers, J.M. Effects of staining and bleaching on color change of dental composite resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 95, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, C.; Beltrami, R.; Scribante, A.; Colombo, M.; Chiesa, M. Surface discoloration of composite resins: Effects of staining and bleaching. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Commercial Nameand Manufacturer | Filler Content (vol%) | Matrix Composition | Filler Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filtek Supreme XTE (3M ESPE) | 63 | Bis-GMA, UDMA, TEGDMA, PEGDMA, Bis-EMA. | Combination of non-agglomerated/non-aggregated 20-nm silica filler, non-agglomerated/non-aggregated 4 to 11 nm zirconia filler, and aggregated zirconia/silica cluster filler. |
| Tetric EvoCeram (Ivoclar) | 53–55 | UDMA, Bis-GMA, ethoxylated Bis-EMA. | Inorganic fillers (40 nm–3 μm): barium glass, ytterbium trifluoride, mixed oxide (SiO2/ZrO2). |
| Measurement Depth | SC (N = 10) | EC (N = 10) | ST (N = 30) | ET (N = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 mm | 55.4 (1.5) a | 56.7 (1.7) a | 44.2 (4.5) b | 49.7 (3.9) c | <0.0001 |
| 0.2 mm | 55.5 (1.1) a | 56.2 (1.5) a | 47.0 (3.0) b | 49.8 (2.7) c | <0.0001 |
| 0.3 mm | 55.2 (1.2) a | 55.5 (1.2) a | 48.2 (2.6) b | 50.3 (2.4) c | <0.0001 |
| 0.4 mm | 55.1 (1.2) a | 55.2 (0.9) a | 49.3 (2.1) b | 50.6 (2.0) b | <0.0001 |
| 0.5 mm | 55.4 (1.4) a | 55.2 (1.0) a | 49.9 (2.0) b | 50.6 (1.9) b | <0.0001 |
| 0.6 mm | 54.6 (1.5) a | 55.0 (1.1) a | 50.3 (1.5) b | 50.8 (1.7) b | <0.0001 |
| 0.7 mm | 54.4 (0.9) a | 54.7 (1.1) a | 50.9 (1.4) b | 51.1 (1.7) b | <0.0001 |
| 0.8 mm | 54.6 (1.0) a | 54.8 (1.5) a | 51.1 (1.2) b | 51.2 (1.5) b | <0.0001 |
| 0.9 mm | 54.3 (1.3) a | 54.4 (0.9) a | 51.5 (1.3) b | 51.3 (1.3) b | <0.0001 |
| 1.0 mm | 54.1 (1.1) a | 54.4 (1.0) a | 52.0 (1.2) b | 51.4 (1.2) b | <0.0001 |
| 1.5 mm | 53.9 (0.8) a | 53.3 (1.3) a | 53.0 (1.2) a | 51.8 (1.6) b | <0.0001 |
| 2.0 mm | 53.8 (1.0) a | 53.3 (1.0) a | 53.6 (1.0) a | 52.1 (1.4) b | <0.0001 |
| 2.5 mm | 53.7 (0.7) a,b | 53.3 (0.8) a,b | 54.3 (1.0) a | 52.6 (1.5) b | <0.0001 |
| 3.0 mm | 54.0 (0.7) a | 53.8 (0.8) a | 54.9 (1.0) b | 52.6 (1.3) c | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinelli, F.; Scaminaci Russo, D.; Nieri, M.; Giachetti, L. Stain Susceptibility of Composite Resins: Pigment Penetration Analysis. Materials 2022, 15, 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144874
Cinelli F, Scaminaci Russo D, Nieri M, Giachetti L. Stain Susceptibility of Composite Resins: Pigment Penetration Analysis. Materials. 2022; 15(14):4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144874
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinelli, Francesca, Daniele Scaminaci Russo, Michele Nieri, and Luca Giachetti. 2022. "Stain Susceptibility of Composite Resins: Pigment Penetration Analysis" Materials 15, no. 14: 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144874
APA StyleCinelli, F., Scaminaci Russo, D., Nieri, M., & Giachetti, L. (2022). Stain Susceptibility of Composite Resins: Pigment Penetration Analysis. Materials, 15(14), 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144874







