Recycled Aggregate: A Viable Solution for Sustainable Concrete Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Current Application of C&DW in Construction Materials
2.1. Application in Concrete
2.2. Application in Other Construction Materials
3. Environmental Benefits of Using RA from C&DW
4. Challenges and Outlook
- (i)
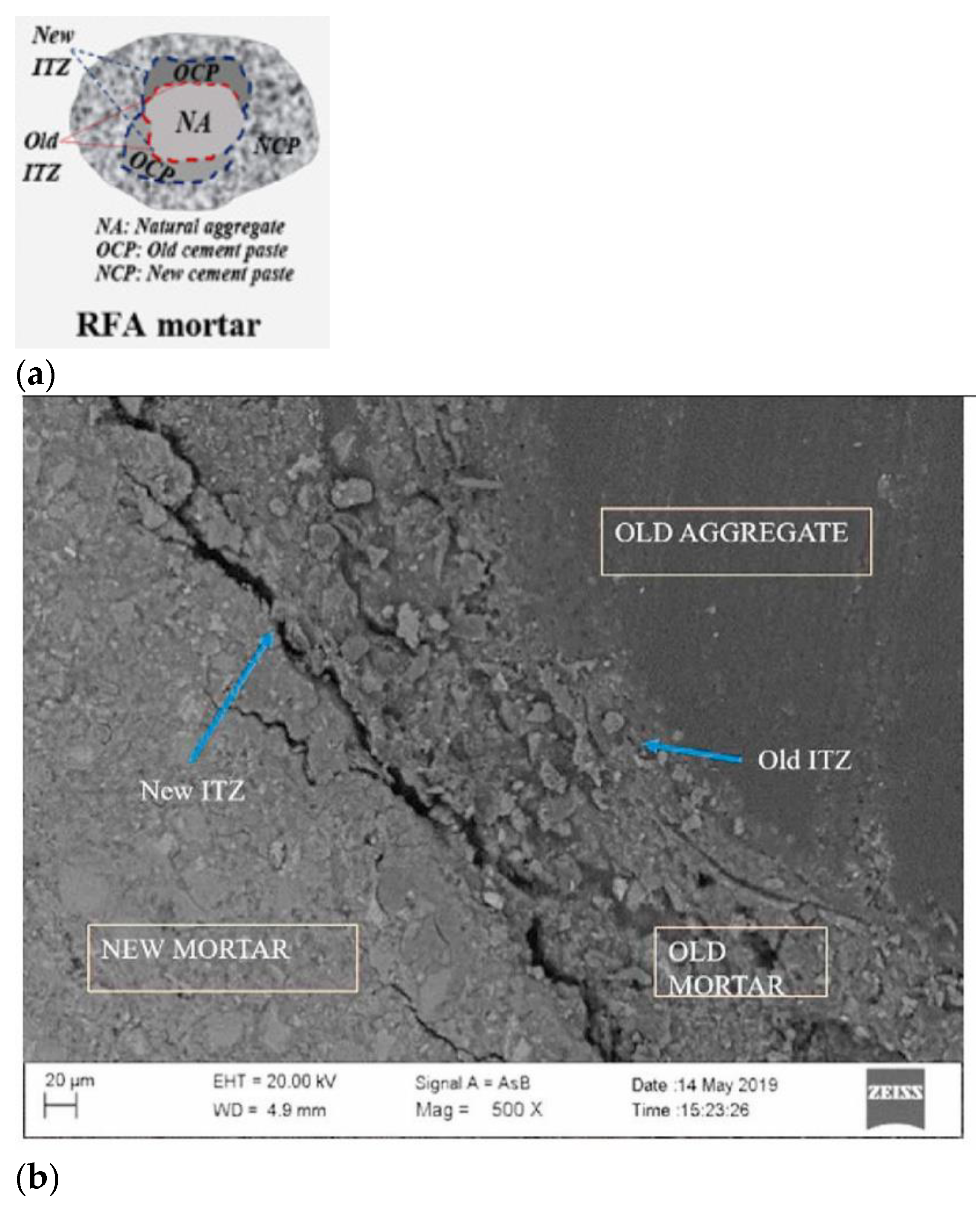
- Reducing the content of old mortar in RA: Saravanakumar et al. [54] pre-treated RA with sulfuric, nitric, and hydrochloric acids, achieving better mechanical performance in concrete than untreated RA. Thermal treatment was also used for this purpose [55], but high energy intake may be required to reach the desired decomposition temperatures (around 800 °C).
- (ii)
- Surface-treating RA before its application in concrete: He et al. [56] found that the density, water absorption, and crushing index of RA were improved with previous treatment using pozzolan slurry combined with sodium silicate and silicon-based additives, improving its performance in concrete. Li et al. [57] pre-treated RA with nanosilica suspension (spraying and soaking), observing that the micro-hardness of both the old mortar and the new mortar near the ITZ was enhanced after treatment, improving the compressive strength, water absorption, and chloride penetration resistance of RA-containing concrete. Zhang et al. [58,59] observed that pre-treating RA with a sulfoaluminate cement slurry led to a denser RA surface (with higher micro-hardness), leading to improved mechanical strength and durability.
- (iii)
- Compensating concrete performance loss using fibers: Zong et al. [60] observed that 1.2% steel fiber incorporation evened or increased the 28-day flexural strength of concretes containing 50–100% RA compared to 100% NA concrete without fibers. Similarly, Paluri et al. [61] observed 28-day compressive and flexural strength reductions of up to 23 and 18%, respectively, when NA was replaced with 50–100% RA. However, when adding 1% steel fiber, the 50% RA concrete had comparable (5% lower) compressive strength and 31% higher flexural strength than 100% NA concrete. It is worth mentioning that synthetic fibers can be advantageous from a technological point of view; however, in countries with an abundance of natural fibers like Brazil and India, these can be a better solution for the destination of agro-industrial waste [62].
5. RA from Other Wastes
5.1. Glass Waste as RA
5.2. Slag Waste as RA
5.3. Ceramic Waste as RA
5.4. PET Waste as RA
5.5. Other Waste as RA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential Economically Viable Solutions for a Low-CO2 Cement-Based Materials Industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Shukla, A.; Sahani, R.K.; Shekhar, A.R.; Singh, R. Structural Application of Concrete Made of Recycled Aggregate Sourced from Construction and Demolition Waste. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management, New Your, NY, USA, 12–15 May 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 171, ISBN 9783030803117. [Google Scholar]
- Colangelo, F.; Petrillo, A.; Farina, I. Comparative Environmental Evaluation of Recycled Aggregates from Construction and Demolition Wastes in Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Fu, Q.; Kasal, B. A Comprehensive Review on Recycled Aggregate and Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ruiz, L.A.; Roca Ramón, X.; Gassó Domingo, S. The Circular Economy in the Construction and Demolition Waste Sector—A Review and an Integrative Model Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegaki, M.; Damigos, D. A Review on Current Situation and Challenges of Construction and Demolition Waste Management. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 13, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Martínez-García, R.; de-Prado-Gil, J.; Irshad, K.; El-Shorbagy, M.A.; Fediuk, R.; Vatin, N.I. Concrete with Partial Substitution of Waste Glass and Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Materials 2022, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanhão, A.F.; Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; da Silva, T.R.; Fediuk, R.; Vatin, N. Recycled PET Sand for Cementitious Mortar. Materials 2021, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Yang, E.I. Comparison of Drying Shrinkage of Concrete Specimens Recycled Heavyweight Waste Glass and Steel Slag as Aggregate. Materials 2020, 13, 5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Barreto, E.; Stafanato, K.V.; Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Ali, M.; Pereira, R.M.L.; Monteiro, S.N. Clay Ceramic Waste as Pozzolan Constituent in Cement for Structural Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddika, A.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Mamun, M.A.A.; Alyousef, R.; Ferdous, W. Waste Glass in Cement and Geopolymer Concretes: A Review on Durability and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, W.; Manalo, A.; Siddique, R.; Mendis, P.; Zhuge, Y.; Wong, H.S.; Lokuge, W.; Aravinthan, T.; Schubel, P. Recycling of Landfill Wastes (Tyres, Plastics and Glass) in Construction—A Review on Global Waste Generation, Performance, Application and Future Opportunities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, J.; Kurda, R. The Past and Future of Sustainable Concrete: A Critical Review and New Strategies on Cement-Based Materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 123558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robalo, K.; Costa, H.; do Carmo, R.; Júlio, E. Experimental Development of Low Cement Content and Recycled Construction and Demolition Waste Aggregates Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.; Rehman, M.U.; de Brito, J.; Ghafoor, H. Multi-Criteria Optimization of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Mixes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Su, S.; Zeng, W. Use of Fine Recycled Aggregates from Ceramic Waste in Masonry Mortar Manufacturing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Singh, A.; Xiao, J.; Hou, S. Combined Use of Recycled Powder and Recycled Coarse Aggregate Derived from Construction and Demolition Waste in Self-Compacting Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Singh, B. Punching Shear Capacity of Recycled-Aggregate Concrete Slab-Column Connections. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 102430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, B.; Bravo, M.; de Brito, J.; Sáez del Bosque, I.F.; Medina, C. Mechanical Behaviour of Structural Concrete with Ground Recycled Concrete Cement and Mixed Recycled Aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez del Bosque, I.F.; Van den Heede, P.; De Belie, N.; Sánchez de Rojas, M.I.; Medina, C. Carbonation of Concrete with Construction and Demolition Waste Based Recycled Aggregates and Cement with Recycled Content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yu, L. Recycling of the End-of-Life Lightweight Aggregate Concrete (LWAC) with a Novel Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.-J.; Wei, J.-J.; Ma, H.; Xing, F. Dynamic Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Reinforced Cement Composites. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswal, U.S.; Dinakar, P. A mix design procedure for fly ash and ground granulated blast furnace slag based treated recycled aggregate concrete. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.R.G.; Cecchin, D.; Carmo, D.F.; Silva, F.C.; Campos, C.M.O.; Shtrucka, T.G.; Marvila, M.T.; Monteiro, S.N. Analysis of the Compactness and Properties of the Hardened State of Mortars with Recycling of Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW). J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5942–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, P.; Ncube, A.; D’Ambrosio, G.; Passaro, R.; Ulgiati, S. Potential Energy Savings from Circular Economy Scenarios Based on Construction and Agri-Food Waste in Italy. Energies 2021, 14, 8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos, P.R.; Sakata, R.D.; Onghero, L.; Uliano, V.G.; de Brito, J.; Campos, C.E.M.; Gleize, P.J.P. Utilization of Ceramic Tile Demolition Waste as Supplementary Cementitious Material: An Early-Age Investigation. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; de la Villa, R.V.; Fernández-Carrasco, L.; García, R. Reactivity in Cement Pastes Bearing Fine Fraction Concrete and Glass from Construction and Demolition Waste: Microstructural Analysis of Viability. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 148, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skocek, J.; Zajac, M.; Ben Haha, M. Carbon Capture and Utilization by Mineralization of Cement Pastes Derived from Recycled Concrete. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, M.; Skocek, J.; Durdzinski, P.; Bullerjahn, F.; Skibsted, J.; Ben Haha, M. Effect of Carbonated Cement Paste on Composite Cement Hydration and Performance. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 134, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Shi, C.; Cao, Z.; Guo, M.; Zheng, J. Effect of Carbonated Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregate on the Properties and Microstructure of Recycled Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhan, P. A Novel Development of Green UHPC Containing Waste Concrete Powder Derived from Construction and Demolition Waste. Powder Technol. 2021, 398, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Qian, Z.; Huang, Q.; Liu, P. Investigation on High-Temperature Stability of Recycled Aggregate Asphalt Mixture Based on Microstructural Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, P.; Huang, Q.; Qian, Z.; Luo, S. Research on Interfacial Zone Failure of Asphalt Mixture Mixed with Recycled Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, D.; Giri, J.P.; Panda, M.; Chattaraj, U. Investigations on Stone Matrix Asphalt Mixes Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregate Treated with Nanosilica. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tao, W.; Gao, J.; Yu, D.; Zhou, J.; He, L.; Yao, Y. Measurement of Particle Agglomeration and Aggregate Breakdown of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, W.; Ji, Y. Mechanical Behavior Investigation of Reclaimed Asphalt Aggregate Concrete in a Cold Region. Materials 2021, 14, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittencourt, S.V.; da Silva Magalhães, M.; da Nóbrega Tavares, M.E. Mechanical Behavior and Water Infiltration of Pervious Concrete Incorporating Recycled Asphalt Pavement Aggregate. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 14, e00473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A.; Das, S. Sustainable Utilization of Recycled Asphalt as Aggregates in Engineered Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Chen, S.; Xie, F.; Feng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Chen, C.; Gong, H.; Tang, B. Influence of Coarse Aggregate Morphological Properties on the Performances of Warm-Mix Asphalt Containing Recycled Asphalt Pavement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabonski, P.; Stankiewicz, B.; Beben, D. Influence of a Rejuvenator on Homogenization of an Asphalt Mixture with Increased Content of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in Lowered Technological Temperatures. Materials 2021, 14, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, T.; Cheng, H.; Li, T.; Fu, J. Mechanical Properties of High-Modulus Asphalt Concrete Containing Recycled Asphalt Pavement: A Parametric Study. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefa, L.; Bianco, I.; Blengini, G.A.; Bassani, M. Integrated and Comparative Structural-LCA Analysis of Unbound and Cement-Stabilized Construction and Demolition Waste Aggregate for Subbase Road Pavement Layers Formation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 352, 131599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, A.; Cerni, G.; Porceddu, P.R. Comparative Study on Resilient Modulus of Natural and Post-Quake Recycled Aggregates in Bound and Unbound Pavement Subbase Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.-B.; Bui, Q.-B.; Tang, L. Geopolymer Recycled Aggregate Concrete: From Experiments to Empirical Models. Materials 2021, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, M.; Assaad, J.J. Effect of Recycled Fine Aggregates on Performance of Geopolymer Masonry Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.S.; Khattak, M.J. Roller Compacted Geopolymer Concrete Using Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, C.; Yuan, B.; Wu, Y. Impact Behaviour of Fly Ash and Slag-Based Geopolymeric Concrete: The Effects of Recycled Aggregate Content, Water-Binder Ratio and Curing Age. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, R.M.; Butt, F.; Danish, A.; Alqurashi, M.; Mosaberpanah, M.A.; Masood, B.; Hussein, E.E. Influence of Bentonite on Mechanical and Durability Properties of High-Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete with Natural and Recycled Aggregates. Materials 2021, 14, 7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluczuk, E.; Kalinowska-Wichrowska, K.; Jiménez, J.R.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; Suescum-Morales, D. Geopolymer Concrete with Treated Recycled Aggregates: Macro and Microstructural Behavior. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; Azevedo, A.R.G.; Delaqua, G.C.G.; Mendes, B.C.; Pedroti, L.G.; Vieira, C.M.F. Performance of Geopolymer Tiles in High Temperature and Saturation Conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, A.R.G.; Teixeira Marvila, M.; Barbosa de Oliveira, L.; Macario Ferreira, W.; Colorado, H.; Rainho Teixeira, S.; Mauricio Fontes Vieira, C. Circular Economy and Durability in Geopolymers Ceramics Pieces Obtained from Glass Polishing Waste. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2021, 18, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; de Matos, P.R.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F. Rheological and the Fresh State Properties of Alkali-Activated Mortars by Blast Furnace Slag. Materials 2021, 14, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante Gomes, R.; Brazão Farinha, C.; Veiga, R.; de Brito, J.; Faria, P.; Bastos, D. CO2 Sequestration by Construction and Demolition Waste Aggregates and Effect on Mortars and Concrete Performance—An Overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, P.; Abhiram, K.; Manoj, B. Properties of Treated Recycled Aggregates and Its Influence on Concrete Strength Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbi, J.A.; Heijnen, W.M.M.; Brouwer, J.P.; Mulder, E. Preliminary Laboratory Investigation of Thermally Treated Recycled Concrete Aggregate for General Use in Concrete. Waste Manag. Ser. 2000, 1, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shen, A.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y. Properties and Mechanisms of Brick-Concrete Recycled Aggregate Strengthened by Compound Modification Treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 315, 125678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xuan, D.; Sojobi, A.O.; Liu, S.; Chu, S.H.; Poon, C.S. Development of Nano-Silica Treatment Methods to Enhance Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 118, 103963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, T.; Liu, H.; Su, S. Improving the Sulfate Resistance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) by Using Surface-Treated Aggregate with Sulfoaluminate Cement (SAC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, T.; Liu, H.; Su, S. Modifying Recycled Aggregate Concrete by Aggregate Surface Treatment Using Sulphoaluminate Cement and Basalt Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, A. Stress-Strain Behaviour of Steel-Fibre-Reinforced Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Axial Tension. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluri, Y.; Mogili, S.; Mudavath, H.; Noolu, V. Effect of Fibres on the Strength and Toughness Characteristics of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 38, 2537–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Souza, F.S.; Mendes, J.C.; Morais, L.J.B.; Silva, J.S.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Mapping and Recycling Proposal for the Construction and Demolition Waste Generated in the Brazilian Amazon. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galderisi, A.; Iezzi, G.; Bianchini, G.; Paris, E.; de Brito, J. Petrography of Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW) from Abruzzo Region (Central Italy). Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Babu, V.S.; Arunachalam, S. Characterization of Recycled Aggregate by the Combined Method: Acid Soaking and Mechanical Grinding Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 49, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 206; Concrete: Specification, Performance, Production and Conformity. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2013.
- ABNT NBR 7211; Aggregates for Concrete—Specification. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2005. (In Portuguese)
- Xiao, Y.; Pham, B.T.; Guo, M.-Z.; Ling, T.-C. Use of Luminescent-Glass Aggregates for the Production of Decorative Architectural Mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, P.; Parashar, A.K. Use of Waste Glass and Demolished Brick as Coarse Aggregate in Production of Sustainable Concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 4030–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Zhuge, Y.; Pham, P.N.; Liu, Y.; Kitipornchai, S. A Ternary Blended Binder Incorporating Alum Sludge to Efficiently Resist Alkali-Silica Reaction of Recycled Glass Aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Zhang, X.; He, Z.; Shi, J.; Gencel, O.; Hai Yen, N.T.; Wang, G. Strength, Microstructure and Nanomechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Containing Waste Glass Powder and Steel Slag Powder. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mo, K.H.; Du, H.; Ling, T.-C. Effects of CO2 Curing Treatment on Alkali-Silica Reaction of Mortars Containing Glass Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alducin-Ochoa, J.M.; Martín-del-Río, J.J.; Torres-González, M.; Flores-Alés, V.; Hernández-Cruz, D. Performance of Mortars Based on Recycled Glass as Aggregate by Accelerated Decay Tests (ADT). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, A. The Study of the Feasibility of Using Recycled Steel Slag Aggregate in Hot Mix Asphalt. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandru, P.; Karthikeyan, J. Models to Predict the Mechanical Properties of Blended SCC Containing Recycled Steel Slag and Crushed Granite Stone as Coarse Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Qi, A.; Chen, Y. Study on the Hysteretic Behavior of Recycled Aggregate Concrete-Filled Steel Tube Columns Containing Ferronickel Slag. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrounias, P.; Rogkala, A.; Giannakopoulou, P.P.; Christogerou, A.; Lampropoulou, P.; Liogris, S.; Koutsovitis, P.; Koukouzas, N. Utilization of Industrial Ferronickel Slags as Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, J.; Singh, A. Utilization Potential of Aerated Concrete Block Powder and Clay Brick Powder from C&D Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, M.; Ma, Z. Properties of the Foam Concrete Containing Waste Brick Powder Derived from Construction and Demolition Waste. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldemir, A.; Akduman, S.; Kocaer, O.; Aktepe, R.; Sahmaran, M.; Yildirim, G.; Almahmood, H.; Ashour, A. Shear Behaviour of Reinforced Construction and Demolition Waste-Based Geopolymer Concrete Beams. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 47, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.R.; Cecchin, D.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Valadão, I.; Alexandre, J.; da Silva, F.C.; Marvila, M.T.; Gunasekaran, M.; Garcia Filho, F.; Monteiro, S.N. Technological Characterization of PET—Polyethylene Terephthalate—Added Soil-Cement Bricks. Materials 2021, 14, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.; Arulrajah, A.; Wong, Y.C.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Maghool, F. Utilizing Recycled PET Blends with Demolition Wastes as Construction Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfahdawi, I.H.; Osman, S.A.; Hamid, R.; AL-Hadithi, A.I. Influence of PET Wastes on the Environment and High Strength Concrete Properties Exposed to High Temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.; You, I.; Banthia, N.; Zi, G. Utilization of Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Glass Waste in Concrete: A Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 130, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, A.Y.; Bolatova, Z.; Nikitin, D.S.; Korchagina, A.P.; Kalinina, N.A.; Ivashutenko, A.S. Glass Waste Derived Silicon Carbide Synthesis via Direct Current Atmospheric Arc Plasma. Waste Manag. 2022, 144, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.R.G.; Marvila, M.T.; Rocha, H.A.; Cruz, L.R.; Vieira, C.M.F. Use of Glass Polishing Waste in the Development of Ecological Ceramic Roof Tiles by the Geopolymerization Process. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2020, 17, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; de Oliveira, L.B.; de Castro Xavier, G.; Vieira, C.M.F. Mechanical, Physical and Durability Properties of Activated Alkali Cement Based on Blast Furnace Slag as a Function of %Na2O. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; de Matos, P.R.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F. Materials for Production of High and Ultra-High Performance Concrete: Review and Perspective of Possible Novel Materials. Materials 2021, 14, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.R.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Cecchin, D.; Marvila, M.T.; Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Vatin, N.; Karelina, M.; Klyuev, S.; Szelag, M. Application of Plastic Wastes in Construction Materials: A Review Using the Concept of Life-Cycle Assessment in the Context of Recent Research for Future Perspectives. Materials 2021, 14, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, A.R.G.; Alexandre, J.; Marvila, M.T.; Xavier, G.; Monteiro, S.N.; Pedroti, L.G. Technological and Environmental Comparative of the Processing of Primary Sludge Waste from Paper Industry for Mortar. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 249, 119336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; Alexandre, J.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Zanelato, E.B. Evaluation of the Use of Marble Waste in Hydrated Lime Cement Mortar Based. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.F.; Girondi Delaqua, G.C.; Nicolite, M.; Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Alexandre, J.; Fontes Vieira, C.M.; Monteiro, S.N. Eco-Friendly Mortars with Addition of Ornamental Stone Waste—A Mathematical Model Approach for Granulometric Optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-Y.; Qian, L.-P.; Huang, B.-T.; Dai, J.-G. Development of Artificial One-Part Geopolymer Lightweight Aggregates by Crushing Technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-Y.; Huang, B.-T.; Li, V.C.; Dai, J.-G. High-Strength High-Ductility Engineered/Strain-Hardening Cementitious Composites (ECC/SHCC) Incorporating Geopolymer Fine Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.-P.; Wang, Y.-S.; Alrefaei, Y.; Dai, J.-G. Experimental Study on Full-Volume Fly Ash Geopolymer Mortars: Sintered Fly Ash versus Sand as Fine Aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Construction Materials | Reference | Aggregate Type | Max % Used | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt pavement | [32] | Coarse | 100 | Hu et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [33] | Coarse | 100 | Hu et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [34] | Coarse | 100 | Kar et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [35] | Coarse | 50 | Yang et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [36] | Coarse and Fine | 50 | Xu et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [37] | Coarse | 100 | Bittencourt et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [38] | Fine | 100 | Adesina and Das |
| Asphalt pavement | [39] | Coarse | 100 | Guo et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [40] | Fine and Coarse | 100 | Slabonsi et al. |
| Asphalt pavement | [41] | Coarse | 100 | Zhu et al. |
| Pavement subbase | [42] | Coarse | 100 | Tefa et al. |
| Pavement subbase | [43] | Coarse | 100 | Corradini et al. |
| Geopolymer | [44] | Coarse | 30 | Haoi-Bao et al. |
| Geopolymer | [45] | Fine | 60 | Saba and Assaad |
| Geopolymer | [46] | Fine | 100 | Rahman et al. |
| Geopolymer | [47] | Coarse | 100 | Xiet et al. |
| Geopolymer | [48] | Coarse | 100 | Was et al. |
| Geopolymer | [49] | Coarse | 100 | Pawluczuk et al. |
| Waste | Reference | Aggregate Type | Max % Used | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | [67] | Fine and Coarse | 100 | Xiao et al. |
| Glass | [68] | Coarse | 100 | Sharma et al. |
| Glass | [69] | Coarse | 100 | Duan et al. |
| Glass | [70] | Fine | 30 | Zhan et al. |
| Glass | [71] | Fine | 100 | Wang et al. |
| Glass | [72] | Fine | 25 | Alducin-Ochoa et al. |
| Slag | [73] | Coarse | 75 | Goli |
| Slag | [74] | Coarse | 60 | Chandru and Karthikeyan |
| Slag | [75] | Fine | 100 | Luo et al. |
| Slag | [76] | Fine | 54 | Petrounias et al. |
| Ceramic | [77] | Filler | 30 | Liu et al. |
| Ceramic | [78] | Coarse and Fine | 30 | Yang et al. |
| Ceramic | [79] | Coarse and Fine | 100 | Aldemir et al. |
| PET | [8] | Fine | 30 | Campanhão et al. |
| PET | [80] | Fine | 30 | Silva et al. |
| PET | [81] | Fine | 5 | Perera et al. |
| PET | [82] | Fine | 2.5 | Alfahdawi et al. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marvila, M.; de Matos, P.; Rodríguez, E.; Monteiro, S.N.; de Azevedo, A.R.G. Recycled Aggregate: A Viable Solution for Sustainable Concrete Production. Materials 2022, 15, 5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155276
Marvila M, de Matos P, Rodríguez E, Monteiro SN, de Azevedo ARG. Recycled Aggregate: A Viable Solution for Sustainable Concrete Production. Materials. 2022; 15(15):5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155276
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarvila, Markssuel, Paulo de Matos, Erich Rodríguez, Sergio Neves Monteiro, and Afonso R. G. de Azevedo. 2022. "Recycled Aggregate: A Viable Solution for Sustainable Concrete Production" Materials 15, no. 15: 5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155276
APA StyleMarvila, M., de Matos, P., Rodríguez, E., Monteiro, S. N., & de Azevedo, A. R. G. (2022). Recycled Aggregate: A Viable Solution for Sustainable Concrete Production. Materials, 15(15), 5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155276








