Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
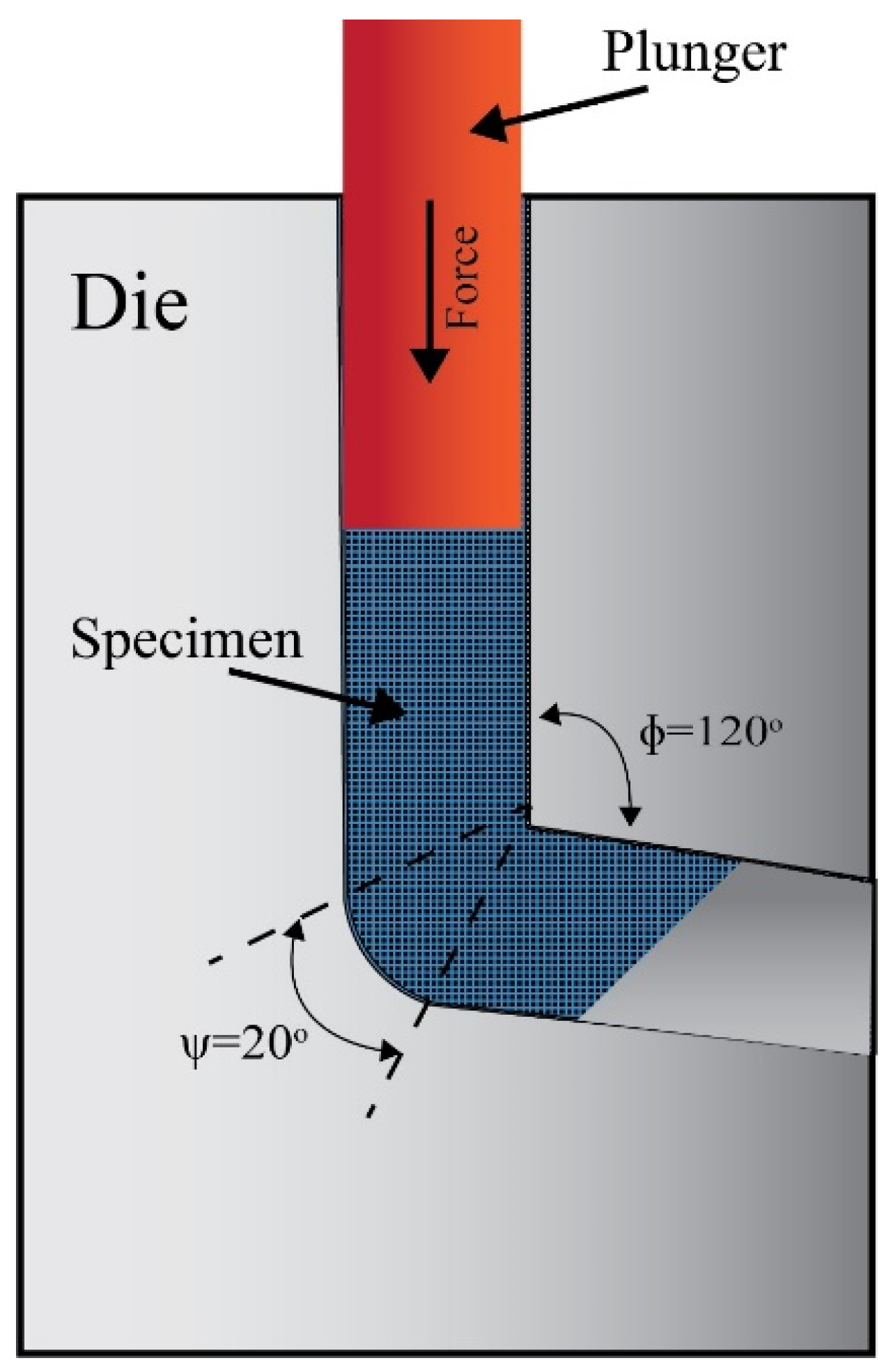
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
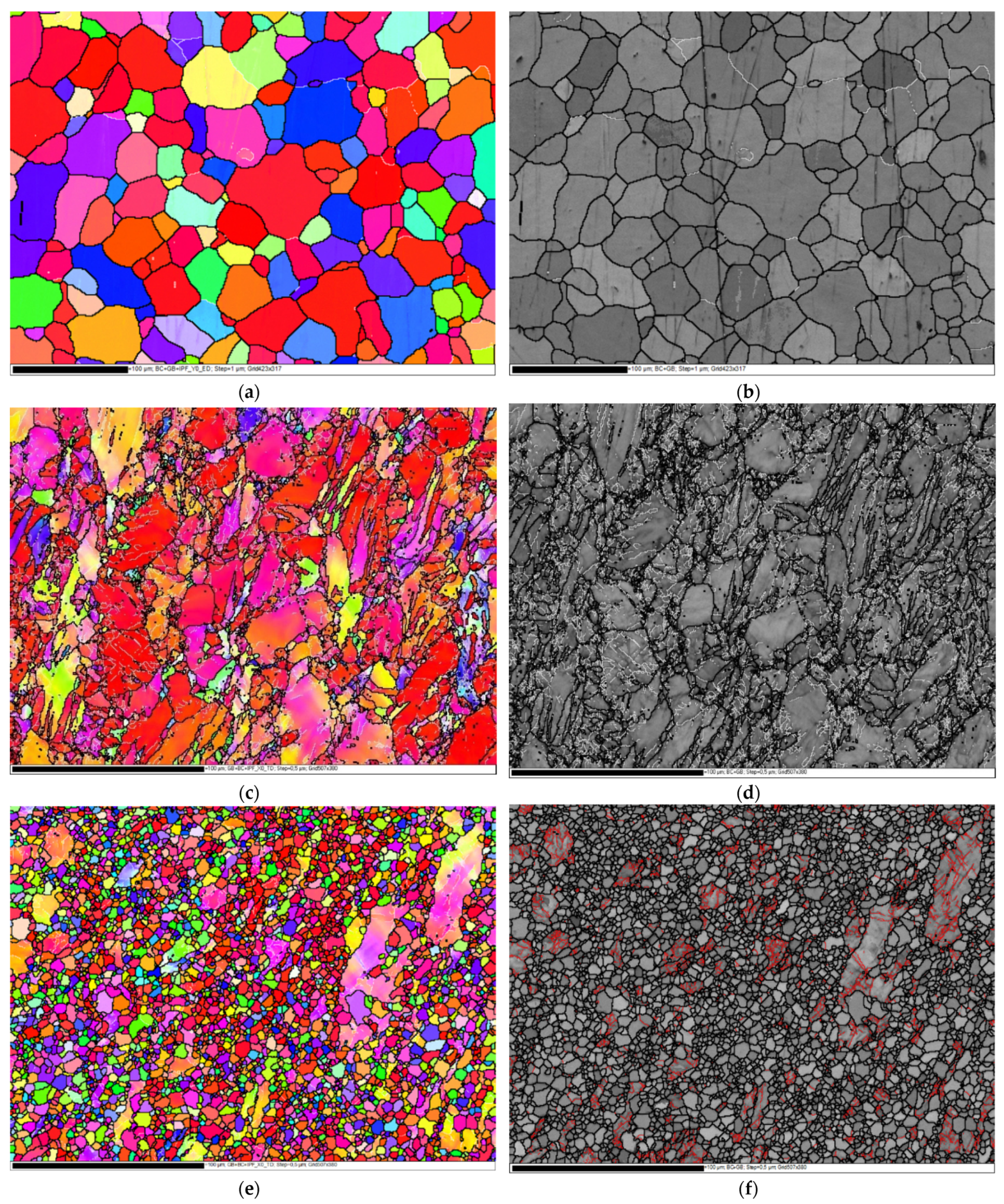
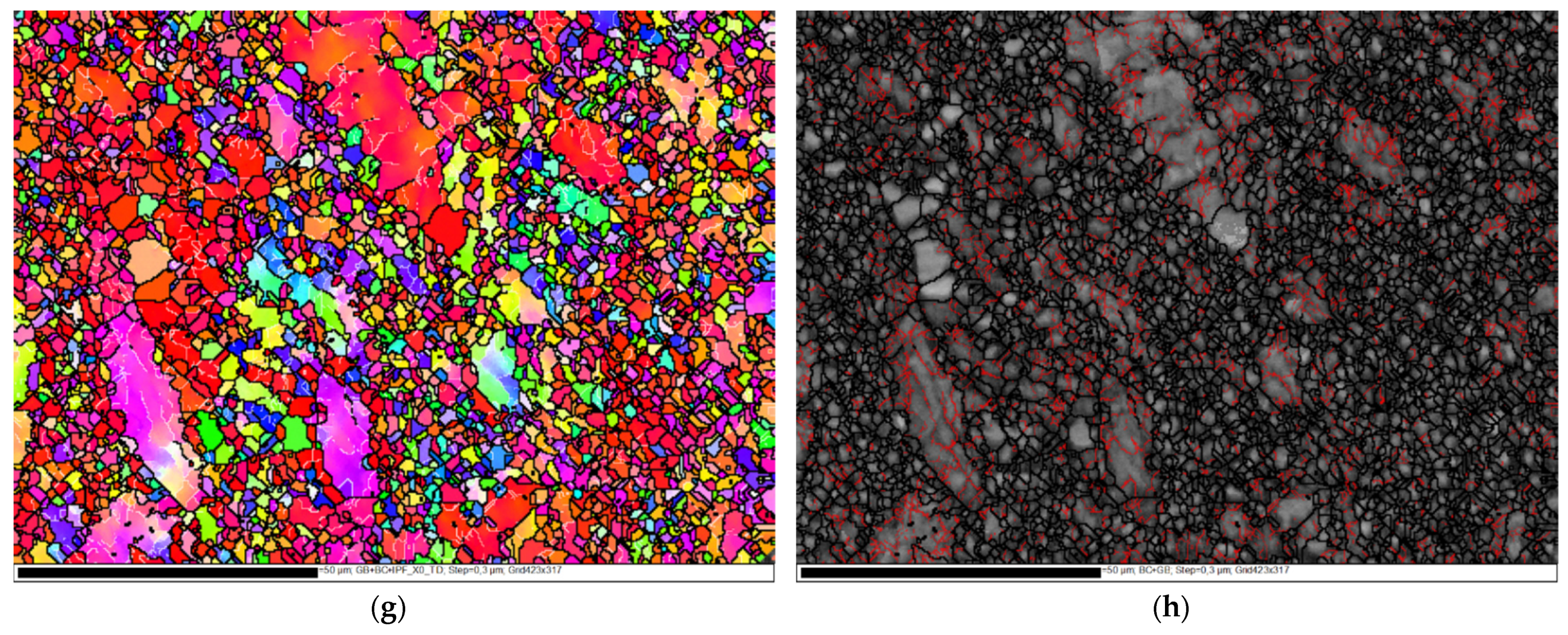
3.1. Microstructure Evolution
3.2. Crystallographic Texture
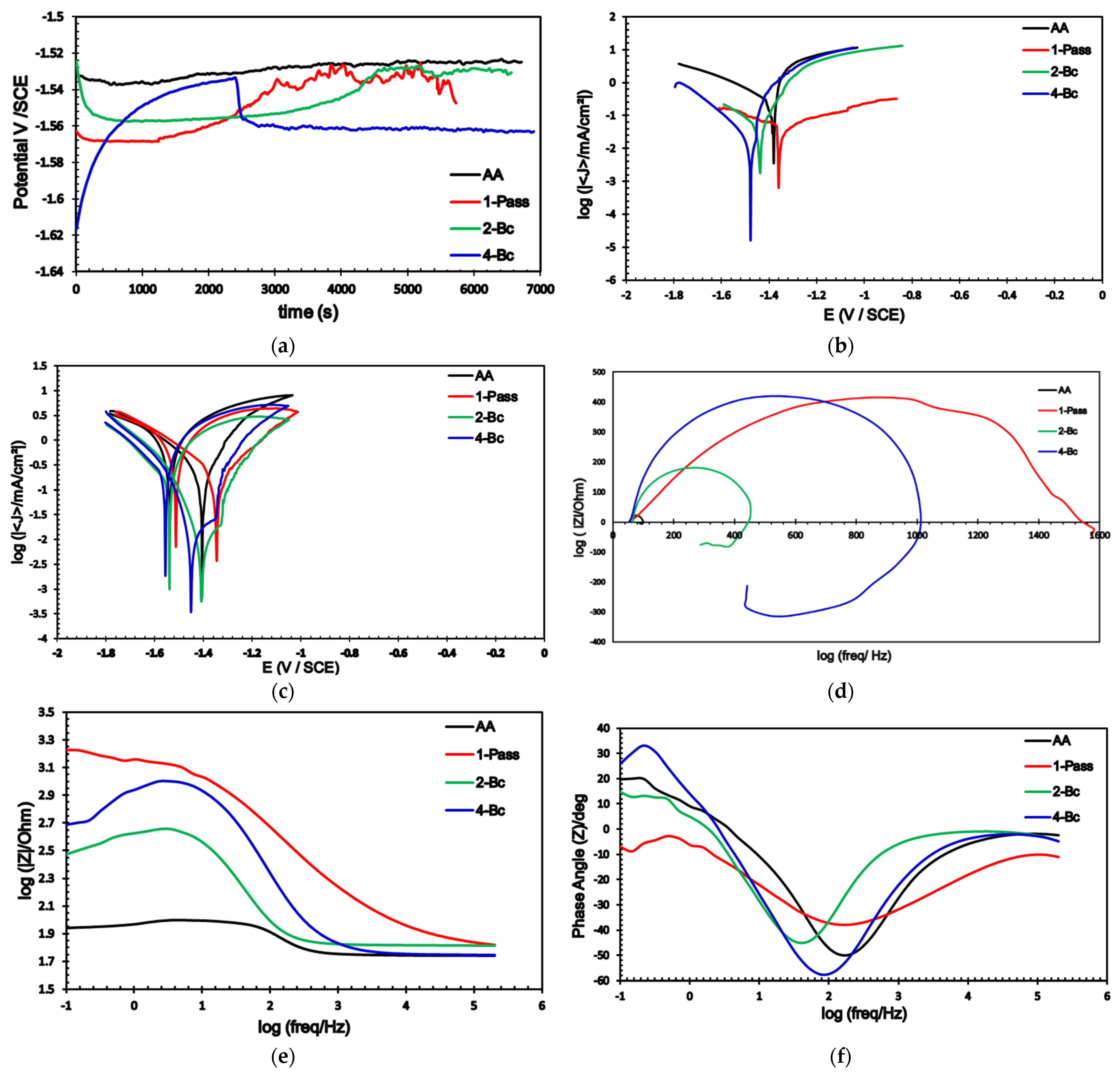
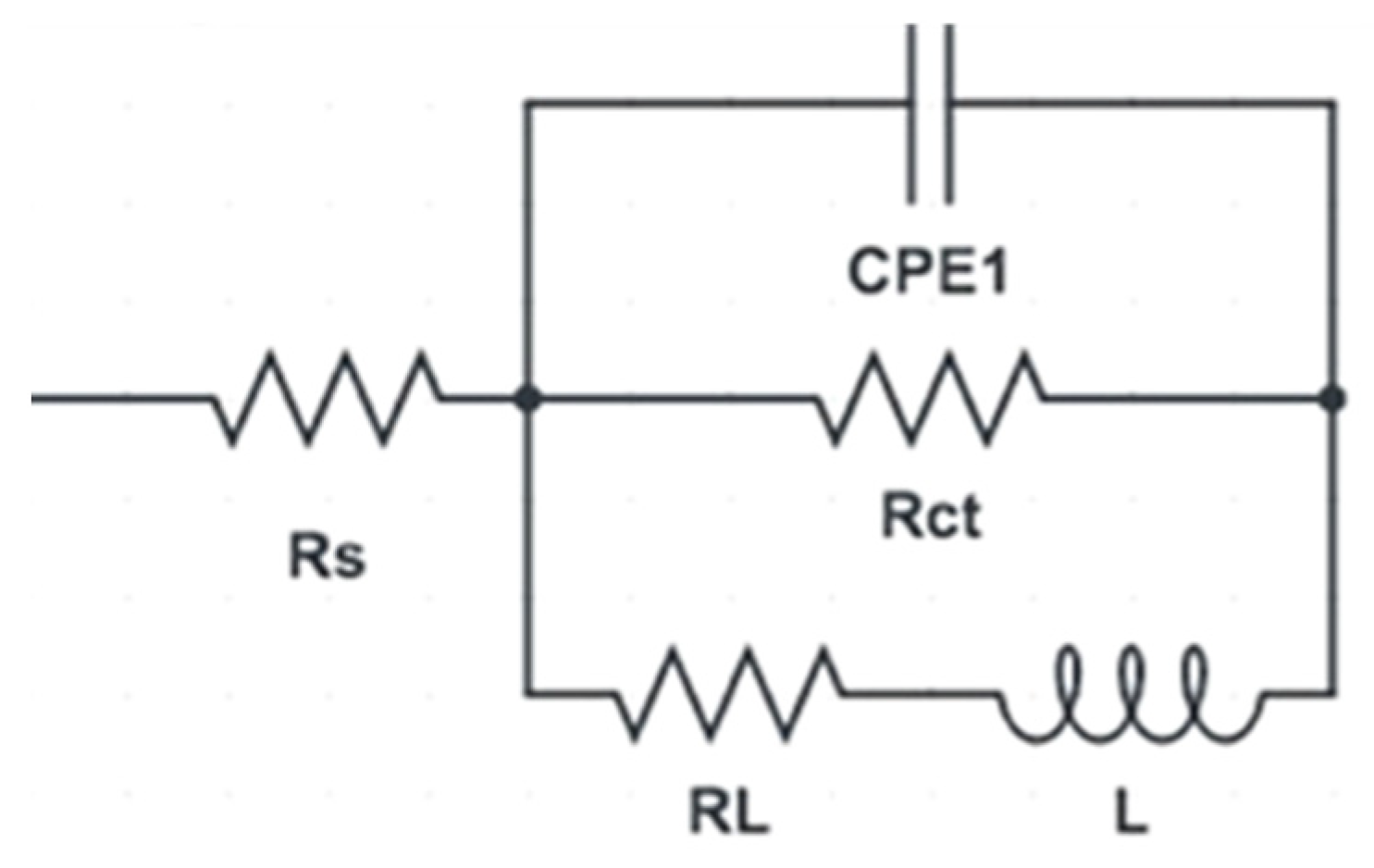
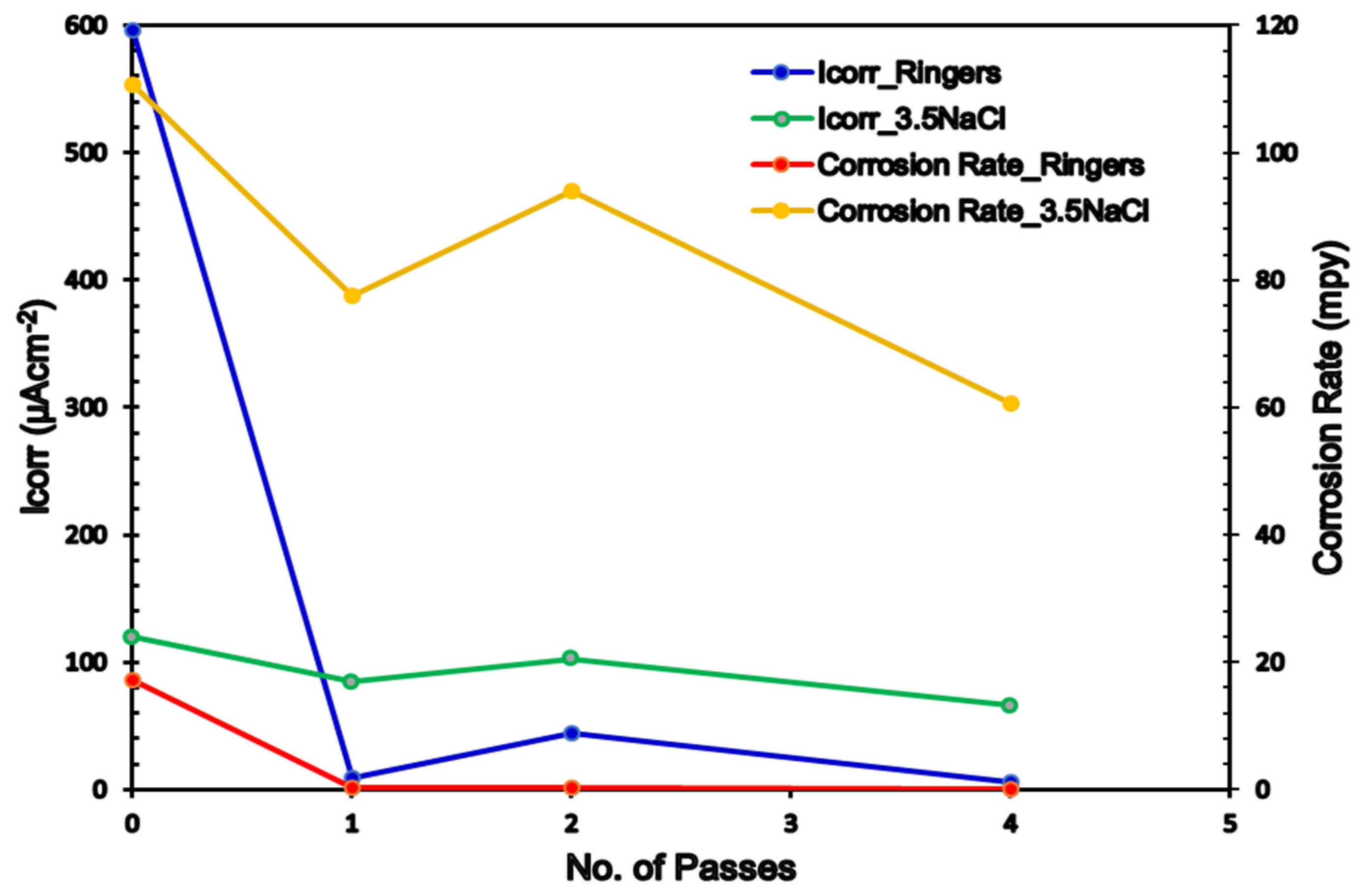
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
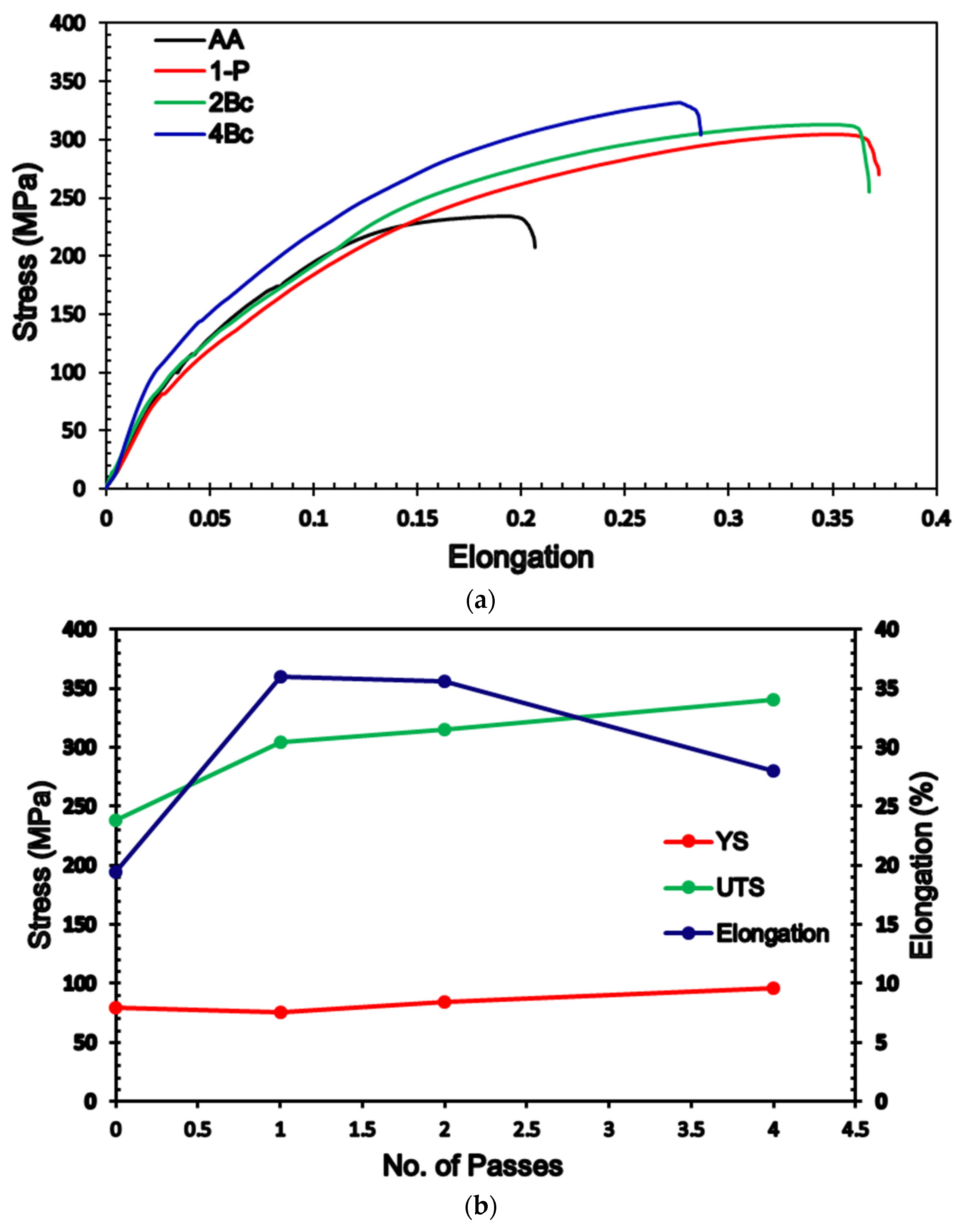
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- ECAP processing through 4-Bc resulted in a significant grain refinement of 92.8% compared with the AA counterpart.
- ECAP processing resulted in the evolution of the crystallographic texture of the ZK30 alloy to have the shear plane aligned at 45° relative to the ED.
- The maximum texture intensity was reduced from 14 times random (AA) to a maximum texture intensity of 8 times random after ECAP processing through 4-Bc.
- The corrosion rate after processing via 4-Bc was significantly reduced by 99% and 45.25% in the sample with the ringer lactate and 3.5% NaCl fluids, respectively, compared with their AA counterparts.
- The pitting corrosion resistance of ZK30 improved in ringer lactate by 471.66% and 352% during processing through 1-P and 4-Bc, respectively, compared with the NaCl findings.
- 1-P processing revealed the best improvement in pitting corrosion resistance in both ringer lactate and NaCl as it increased the pitting corrosion resistance by 3414.4% and 176.76% compared with the AA condition.
- 4-Bc resulted in improving the HV-values by 86.5% compared with the AA condition.
- ECAP processing revealed a small improvement in the YS.
- 4-Bc improved the UTS and EL by 42.8% and 37.2%, respectively, compared with the AA counterpart.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodrigues, J.D.S.; Antonini, L.M.; Bastos, A.A.C.; Zhou, J.; Malfatti, C.F. Corrosion resistance and tribological behavior of ZK30 magnesium alloy coated by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 410, 126983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Yang, K. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical and biodegradable properties of an extruded ZK60 alloy. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Zhao, M.C.; Tao, J.X.; Zhao, Y.C.; Yin, D.; Gao, C.; Shuai, C.; Atrens, A. Comparison of the biodegradation of ZK30 subjected to solid solution treating and selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almenaif, O.; Alhumaydan, Y.; Alnafisah, M.; Aldhalaan, M.; Alateyah, A.I.; El-Garaihy, W.H. A Computational Investigation into the Effect of Equal Channel Angular Processing on the Mechanical Properties of Severely Deformed ZK 60 Alloy Validated by Experiments. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 13, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Garaihy, W.H.; Alateyah, A.I.; Alawad, M.O.; Aljohani, T.A. Improving the Corrosion Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Zr Alloys Through ECAP for Usage in Biomedical Applications. In Magnesium Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Aljohani, T.A.; Alawad, M.O.; Elkatatny, S.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Improving the Corrosion Behavior of Biodegradable AM60 Alloy through Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation. Metals 2021, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liang, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, T.; Weng, Y.; Long, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, S.; et al. In vitro degradation behaviour and cytocompatibility of ZK30/bioactive glass composites fabricated by selective laser melting for biomedical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 785, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, K.; Hu, Z.; Qiu, J.; Cai, Y. The in vitro degradation process and biocompatibility of a ZK60 magnesium alloy with a forsterite-containing micro-arc oxidation coating. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8631–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamesh, M.I.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M.M.; Chu, P.K. Effects of zirconium and oxygen plasma ion implantation on the corrosion behavior of ZK60 Mg alloy in simulated body fluids. Corros. Sci. 2014, 82, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lia, Y.; Chen, J.; Zou, Z. Surface characteristics and corrosion resistance of biodegradable magnesium alloy ZK60 modified by Fe ion implantation and deposition. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2014, 24, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljihmani, L.; Alic, L.; Boudjemline, Y.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Mansoor, B.; Serpedin, E.; Qaraqe, K. Magnesium-based bioresorbable stent materials, Review of Reviews. J. Bio Tribo Corros. 2019, 5, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Geng, L.; Jiao, X. Preparation and characterization of a new biomedical Mg-Zn-Ca alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, O.; Ralston, K.D.; Birbilis, N.; Estrin, Y. Enhanced corrosion resistance of Mg alloy ZK60 after processing by integrated extrusion and equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6176–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Leala, M.; Orozco-Caballero, A.; Carreño, F.; Ruano, O.A. Superplasticity in a commercially extruded ZK30 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartsonakis, I.A.; Stanciu, S.G.; Matei, A.A.; Karaxi, E.K.; Hristu, R.; Karantonis, A.; Charitidis, C.A. Evaluation of the protective ability of typical corrosion inhibitors for magnesium alloys towards the Mg ZK30 variant. Corros. Sci. 2015, 100, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Sasikumar, Y.; Tie, D. The Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Magnesium Alloys with Different Alloying Elements for Bone Repair. Crystals 2018, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G. Recent Progress in Corrosion and Protection of Magnesium Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2005, 7, 563–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, J.; Ma, A.; Song, D.; Lu, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, D.; Chen, J. Comparative analysis for corrosion resistance of micro-arc oxidation coatings on coarse-grained and ultra-fine grained AZ91D Mg alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 216, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Aljohani, T.A.; Alawad, M.O.; Abd El-Hafez, H.; Almutairi, A.N.; Alharbi, E.S. Improved Corrosion Behavior of AZ31 Alloy through ECAP Processing. Metals 2021, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Garaihy, W.H.; Al-Rassoul, E.S.M.; Salem, H.G. Consolidation of High Performance AA6061 and AA6061-SiCp Composite Processed by High Pressure Torsion. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 783–786, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.G.; El-Garaihy, W.H.; Al-Rassoul, E.S.M. Influence of High Pressure Torsion on the Consolidation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of AA6061-SiCp Composite Powders. In Supplemental Proceedings; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubides, Y.; Karayan, A.I.; Vaughan, M.W.; Karaman, I.; Castaneda, H. Enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of a fine-grained Mg-9Al-1Zn alloy: The role of bimodal grain structure and β-Mg17Al12 precipitates. Materialia 2020, 13, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němec, M.; Jäger, A.; Tesař, K.; Gärtnerová, V. Influence of alloying element Zn on the microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of binary Mg-Zn alloys after severe plastic deformation. Mater. Charact. 2017, 134, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaed, E.; Hashempour, M.; Fabrizi, A.; Dellasega, D.; Bestetti, M.; Bonollo, F.; Vedani, M. Microstructure, texture evolution, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of ECAP processed ZK60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 37, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergueeva, A.V.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Mukherjee, A.K. Advanced mechanical properties of pure titanium with ultrafine grained structure. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Alawad, M.O.; Elkatatny, S.; Zedan, Y.; Nassef, A.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Effect of ECAP Die Angle on the Strain Homogeneity, Microstructural Evolution, Crystallographic Texture and Mechanical Properties of Pure Magnesium: Numerical Simulation and Experimental Approach. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 1491–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Zedan, Y.; El-Hafez, H.M.; Alawad, M.O.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the ECAP Processed Copper: Microstructural Evolution, Crystallographic Texture and Hardness Homogeneity. Metals 2021, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Alharbi, M.; El-Hafez, H.M.; El-Garaihy, W.H. The Effect of Equal-Channel Angular Pressing Processing on Microstructural Evolution, Hardness Homogeneity, and Mechanical Properties of Pure Aluminum. SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf. 2020, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, M.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Nassef, A.; El-Hadek, M.; Alzahrani, B.; Zedan, Y.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Effect of ECAP on the Plastic Strain Homogeneity, Microstructural Evolution, Crystallographic Texture and Mechanical Properties of AA2xxx Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2021, 1, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ma, A.; Xu, B.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J. Corrosion behavior of AZ91 Mg alloy with a heterogeneous structure produced by ECAP. Corros. Sci. 2021, 187, 109517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of equal channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 881–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Garaihy, W.H.; Rassoul, E.A.; Alateyah, A.; Alaskari, A.M.; Oraby, S. Data Manipulation Approach and Parameters Interrelationships of the High-Pressure Torsion for AA6061-15%SiCp Composite. SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf. 2018, 11, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Pu, Q.; Jia, Z.; Liu, M.; Roven, H.J.; Jia, J.; Liu, Q. Microstructure and property evolution of Al-0.4Fe-0.15Zr-0.25Er alloy processed by high pressure torsion. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 824, 153949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, W.; Kawałko, J.; Wątroba, M.; Gao, N.; Starink, M.J.; Bała, P.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a Zn-0.5Cu alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 776, 139047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Peng, P.; Tang, A.T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Mao, J.J.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Pan, F.S. Novel on-line twist extrusion process for bulk magnesium alloys. Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanlou, S.I.; Eghbali, B.; Petrov, R. Microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanisms in Al7075/graphene nano-plates/ carbon nano-tubes composite processed through accumulative roll bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 807, 140877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Garaihy, W.H.; Fouad, D.M.; Salem, H.G. Multi-channel Spiral Twist Extrusion (MCSTE): A Novel Severe Plastic Deformation Technique for Grain Refinement. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2854–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, D.M.; Moataz, A.; El-Garaihy, W.H.; Salem, H.G. Numerical and experimental analysis of multi-channel spiral twist extrusion processing of AA5083. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 764, 138216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, D.M.; El-Garaihy, W.H.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Seleman, M.M.E.; Salem, H.G. Influence of multi-channel spiral twist extrusion (MCSTE) processing on structural evolution, crystallographic texture and mechanical properties of AA1100. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 737, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, D.M.; El-Garaihy, W.H.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Albaijan, I.; Seleman, M.M.E.; Salem, H.G. Grain Structure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Channel Spiral Twist Extruded AA5083. Metals 2021, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawadhi, M.Y.; Sabbaghianrad, S.; Huang, Y.; Langdon, T.G. Evaluating the paradox of strength and ductility in ultrafine-grained oxygen-free copper processed by ECAP at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 802, 140546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minarik, P.; Jablonska, E.; Kral, R.; Lipov, J.; Ruml, T.; Blawert, C. Effect of equal channel angular pressing on in vitro degradation of LAE442 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, A.; Wen, D.; Zhu, Y. Effect of equal-channel angular pressing and aging on corrosion behaviour of ZK60 Mg alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2015, 25, 3909–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubides, Y.; Zhao, D.; Nash, L.; Yadav, D.; Xie, K.; Karaman, I.; Castaneda, H. Effects of dynamic recrystallization and strain-induced dynamic precipitation on the corrosion behavior of partially recrystallized Mg–9Al–1Zn alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 1016–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbale, A.M.; Naik, G.M.; Badiger, R.I.; Bellubbi, S.; Narendranath, S. Saltwater corrosion behaviour of equal channel angular pressed AZ80/91 Mg alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 2660–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, I.A.; Hosaka, T.; Yoshihara, S.; MacDonald, B.J. Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of AZ31 Mg Alloy Processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing and Aging. Procedia Eng. 2017, 184, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Liu, H.; Feng, N.; Bai, J.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, F. Preparation of a single-phase Mg–6Zn alloy via ECAP-stimulated solution treatment. J. Magnes. Alloys 2019, 7, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prithivirajan, S.; Narendranath, S.; Desai, V. Analyzing the combined effect of crystallographic orientation and grain refinement on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of ECAPed ZE41 Mg alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 1128–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minárik, P.; Král, R.; Janecek, M. Effect of ECAP processing on corrosion resistance of AE21 and AE42 magnesium alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 281, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, M.; Skaret, P.C.; Fabrizi, A.; Varone, A.; Montanari, R.; Roven, H.J.; Ferro, P.; Berto, F.; Torgersen, J. The effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing on the stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of AZ31 alloy in simulated body fluid. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 106, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yang, K.; Tan, L.; Ma, Z. Role of bimodal-grained structure with random texture on mechanical and corrosion properties of a Mg-Zn-Nd alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys, 2021; in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, X.; Yang, S.; Nguyen, T. Effect of equal channel angular pressing as the pretreatment on microstructure and corrosion behaviour of micro-arc oxidation (MAO) composite coating on biodegradable Mg-Zn-Ca alloy. Surf. Coat. 2020, 395, 125923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Li, C.; Liang, N.; Yang, F.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J.; Wu, G.; Ma, A.; Ma, X. Simultaneously improving corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of a magnesium alloy via equal-channel angular pressing and post water annealing. Mater. Des. 2019, 166, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, H.; Hoseini, M.; Sadrkhah, M.; Faraji, G.; Masoumi, A. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion properties of Mg-HA bionanocomposites fabricated by a novel severe plastic deformation process. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, M.W.; Karayan, A.I.; Srivastava, A.; Mansoor, B.; Seitz, J.M.; Eifler, R.; Karaman, I.; Castaneda, H.; Maier, H.J. The effects of severe plastic deformation on the mechanical and corrosion characteristics of a bioresorbable Mg-ZKQX6000 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 115, 111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xie, Q.; Qiang, M.; Ma, A.; Taylor, E.K.; Li, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, J. Stress corrosion cracking behaviours of RE-containing ME21 magnesium alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, T.; Yoshihara, S.; Amanina, I.; MacDonald, B.J. Influence of Grain Refinement and Residual Stress on Corrosion Behaviour of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Processed by ECAP in RPMI-1640 Medium. Procedia Eng. 2017, 184, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Chiu, C.; Chou, T.Y.; Rabkin, E. Effect of equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) on hydrogen storage properties of commercial magnesium alloy AZ61. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 3, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, A.; Saleh, B.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Ni, C. Enhancement of strength and ductility of SiCp/AZ91 composites by RD-ECAP processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 771, 138579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczel, A.; Akbaripanah, F.; Salevati, M.A.; Mahmudi, R.; Vida, A.; Gubicza, A. A comparative study on the microstructural evolution in AM60 alloy processed by ECAP and MDF. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, F.D.; Higuera-Cobos, O.F.; Cabrera, J.M. ZK60 alloy processed by ECAP: Microstructural, physical and mechanical characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 594, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollett, A.; Humphreys, F.; Rohrer, G.S.; Hatherly, M. Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shana, Z.; Yang, J.; Fana, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Dong, H.; Xu, B. Extraordinary mechanical properties of AZ61 alloy processed by ECAP with 160° channel angle and EPT. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.B.; Zheng, M.Y.; Hu, X.S.; Wu, K.; Xu, S.W.; Kamado, S.; Kojima, Y. Influence of ECAP routes on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 4250–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhuo, X.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Song, D.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Ma, A. Developing an industrial-scale ECAP Mg-Al-Zn alloy with multiheterostructure for synchronously high strength and good ductility. Mater. Charact. 2020, 164, 110341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of grain refinement in magnesium alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Ma, A.; Jiang, J.; Liu, H.; Saleh, B. Discharge properties of ECAP processed AZ31-Ca alloys as anodes for seawater-activated battery. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Hernández, J.V.; Letzig, D.; Golle, R.; Volk, V. Effect of processing route on texture and cold formability of AZ31 Mg alloy sheets processed by ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 669, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, K.R.; Nayaka, H.S.; Sahu, S. Microstructural Evolution and Strengthening of AM90 Magnesium Alloy Processed by ECAP. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 4635–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Han, F.Y.; Liu, C.; Li, M.Z. Microstructure, Texture Evolution, and Mechanical Properties of ECAP-Processed ZAT522 Magnesium Alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. 2020, 33, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, H.; Han, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuo, H.; et al. Microstructure and anisotropic mechanical behavior of the high-strength and ductility AZ91 Mg alloy processed by hot extrusion and multi-pass RD-ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 780, 139191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonda, R.W.; Knipling, K.E. Texture development in friction stir welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonda, R.W.; Knipling, K.E. Texture development in near-α Ti friction stir welds. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6452–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaripanah, F.; Saniee, F.F.; Mahmudi, R.; Kim, H.K. The influences of extrusion and equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) processes on the fatigue behavior of AM60 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Bai, J.; Xue, F.; Jiang, J.; Ma, A. Potential of multi-pass ECAP on improving the mechanical properties of a high-calcium-content Mg-Al-Ca-Mn alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2019, 7, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.D.; Zheng, M.Y.; Hu, X.S.; Xu, C.; Wu, K.; Golovin, I.S. Improved mechanical property and internal friction of pure Mg processed by ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; An, C.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, S.I. Mechanical properties and microstructures of an AZ61 Mg Alloy produced by equal channel angular pressing. Scr. Mater. 2002, 47, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzyl, M.; Rosochowski, A.; Boczkal, S.; Olejnik, L. The role of microstructure and texture in controlling mechanical properties of AZ31B magnesium alloy processed by I-ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 638, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.W.; Zheng, M.Y.; Kamado, S.; Wu, K. The microstructural evolution and superplastic behavior at low temperatures of Mg–5.00Zn–0.92Y–0.16Zr (wt.%) alloys after hot extrusion and ECAP process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailzadeha, S.; Aliofkhazraeia, M.; Sarlak, H. Interpretation of Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Test Results for Study of Corrosion Behavior of Metals: A Review. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyeachu, I.B.; Solomon, M.M.; Adama, K.K.; Nnadozie, C.F.; Ahanotu, C.C.; Akanazu, C.E.; Njoku, D.I. Exploration of the potentials of imidazole-based inhibitor package for heat exchanger-type stainless steel during acid cleaning operation. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, A.; Liu, X. Understanding pitting corrosion behavior of AZ91 alloy and its MAO coating in 3.5% NaCl solution by cyclic potentiodynamic polarization. J. Magnes. Alloys, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadawy, M.M.; Ghanem, M. Grain refinement of bronze alloy by equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) and its effect on corrosion behavior. Def. Technol. 2016, 12, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Ma, A.B.; Jiang, J.H.; Lin, P.H.; Yang, D.H.; Fan, J.F. Corrosion behavior of bulk ultra-fine grained AZ91D magnesium alloy fabricated by equal-channel angular pressing. Corr. Sci. 2011, 53, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.M.; Narendranath, S.; Kumar, S.S.S. Effect of ECAP Die Angles on Microstructure Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behaviour of AZ80 Mg Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 28, 2610–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, K.R.; Nayaka, H.S. Electrochemical Behaviour of ECAP-Processed AM Series Magnesium Alloy. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society. In Magnesium Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argade, G.R.; Panigrahi, S.K.; Mishra, R.S. Effects of grain size on the corrosion resistance of wrought magnesium alloys containing neodymium. Corros. Sci. 2012, 58, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ma, A.; Jiang, J.; Li, H.; Song, D.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y. Simultaneously improving mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of pure Ti by continuous ECAP plus short-duration annealing. Mater. Charact. 2018, 138, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, B.R.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Chakkingal, U.; Nandakumar, V.; Doble, M.; Prasad, V.D.; Raghunath, M. In vitro and in vivo studies of biodegradable fine grained AZ31 magnesium alloy produced by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Islamgaliev, R.K.; Tsao, C.Y.A.; Valiev, R.Z.; Lavernia, E.J.; Zhu, Y.T. Enhanced strength and ductility of AZ80 Mg alloys by spray forming and ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 670, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Zhang, H. Analysis of microstructural evolution and compressive properties for pure Mg after room-temperature ECAP. Mater. Lett. 2020, 271, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Tian, L.; Ma, S.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H. Influence of Equal Channel Angular Pressing Passes on the Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Mg-8Sn-6Zn-2Al Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, J.A.; Carreño, F.; Ruano, O.A. Influence of texture and grain size on work hardening and ductility in magnesium-based alloys processed by ECAP and rolling. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, F.; Ma, E. High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal. Nature 2002, 419, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lin, D.L.; Mao, D.L.; Zen, X.Q.; Ding, W.J. Mechanical properties and microstructure of AZ31 Mg alloy processed by two-step equal channel angular extrusion. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.W.; Hockauf, M.; Zillmann, B.; Schneider, I. Strength, ductility and impact toughness of the magnesium alloy az31b after equal-channel angular pressing. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2009, 2, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, S.R.; Horton, J.A.; Lillo, T.M. 0.; Brown, D.W. Enhanced ductility in strongly textured magnesium produced by equal channel angular processing. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; El-Garaihy, W.H.; Alawad, M.O.; Sanabary, S.E.; Elkatatny, S.; Dahish, H.A.; Kouta, H. The Effect of ECAP Processing Conditions on Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Pure Magnesium—Experimental, Mathematical Empirical and Response Surface Approach. Materials 2022, 15, 5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


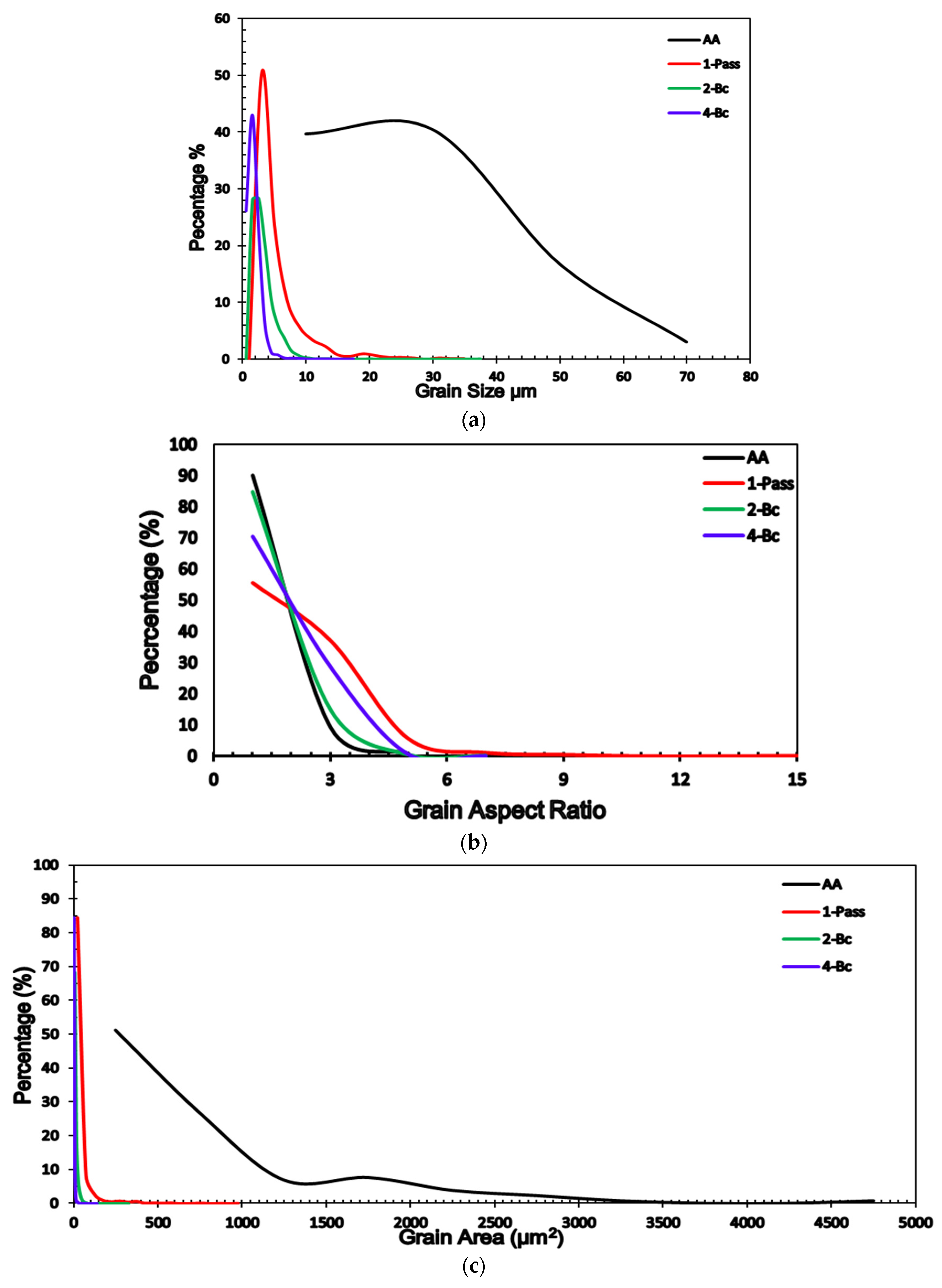
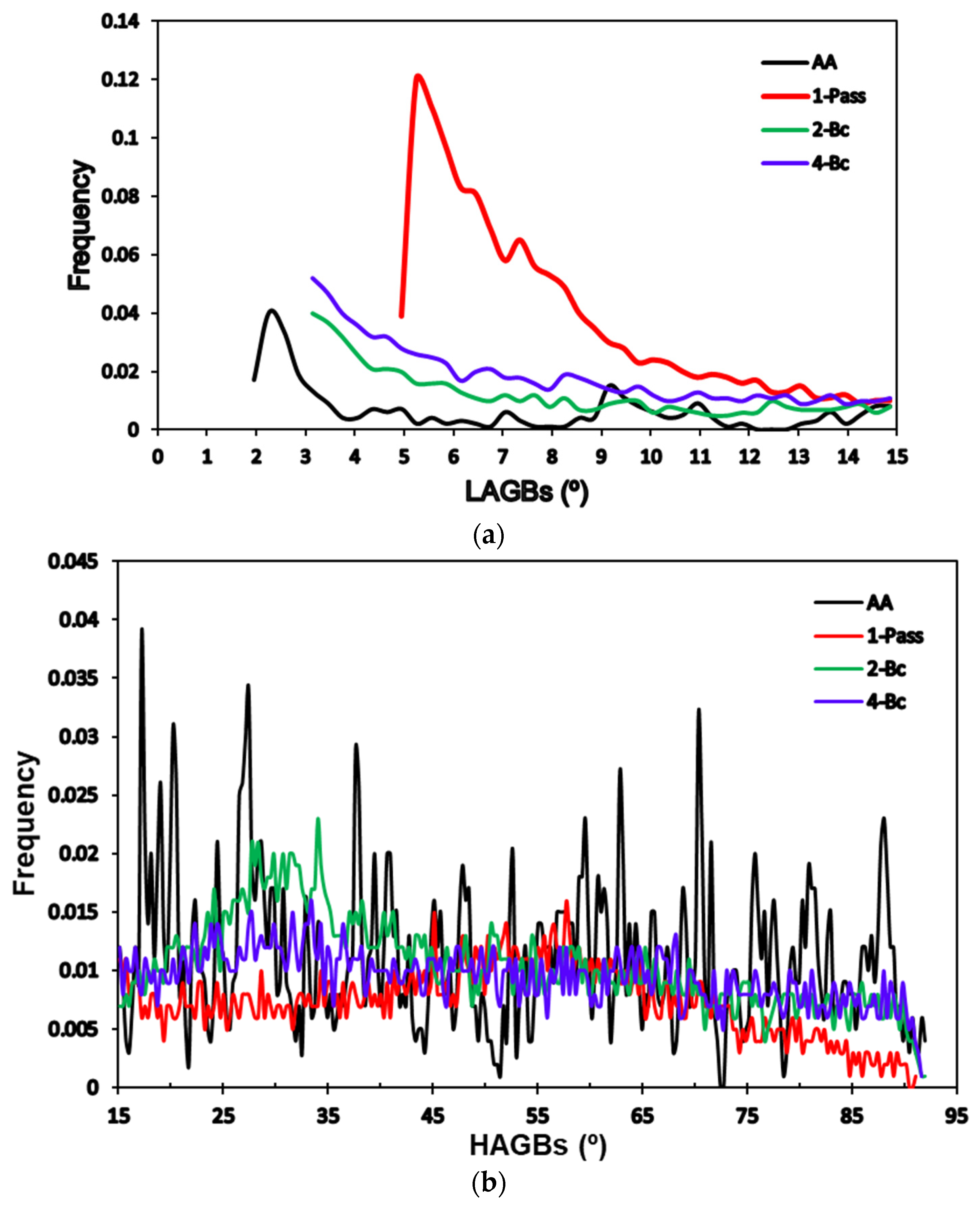
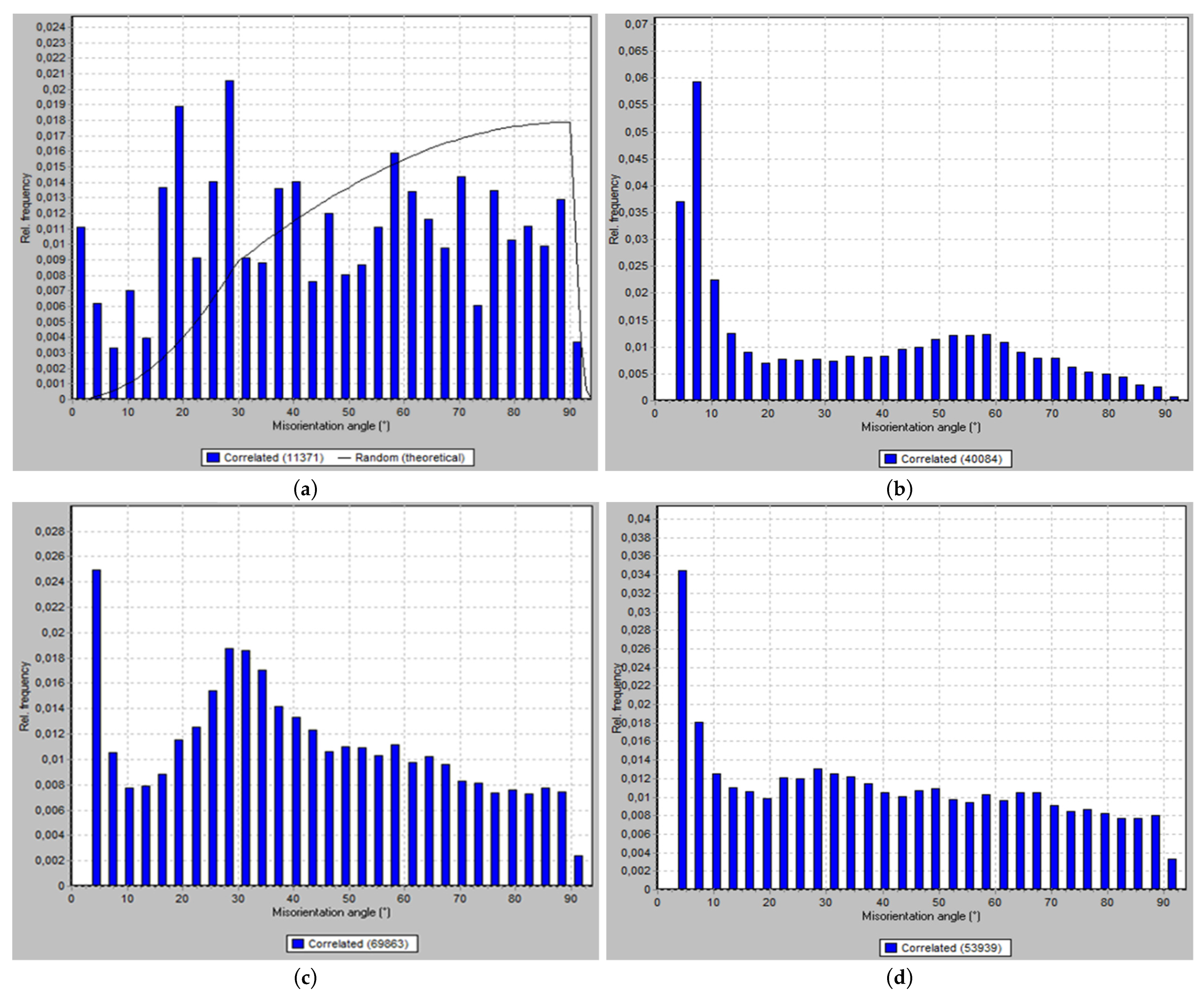
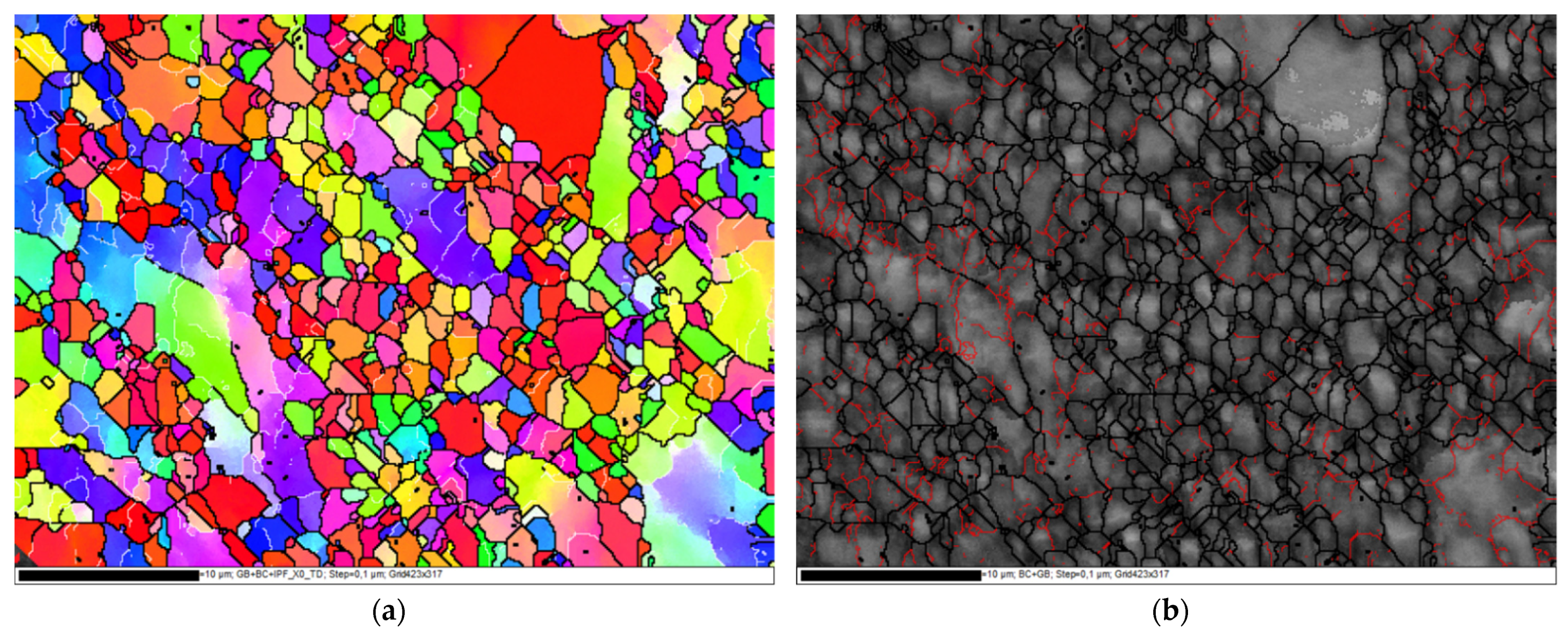




| Grain Size µm | Grain Aspect Ratio | Grain Area µm2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | 1-P | 2-Bc | 4-Bc | AA | 1-P | 2-Bc | 4-Bc | AA | 1-P | 2-Bc | 4-Bc | |
| Min | 3.39 | 2.24 | 1.13 | 0.76 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 4.25 | 1 | 0.09 |
| Max | 76.73 | 35.22 | 37.33 | 17.86 | 4.77 | 15.13 | 6.36 | 7.5 | 4624 | 974 | 1090 | 250 |
| Average | 26.69 | 5.43 | 3.17 | 1.92 | 0.46 | 2.09 | 1.55 | 1.69 | 729 | 37.14 | 10.80 | 3.25 |
| St. Deviation | 14.74 | 4.22 | 1.92 | 1.09 | 1.44 | 1.39 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 785 | 84.12 | 28.13 | 7.78 |
| Ringer | NaCl | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| βa (mV.dec−1) | -βc (mV.dec−1) | Ecorr (V/SCE) | Icorr (µAcm−2) | Corrosion Rate (mpy) | βa (mV.dec−1) | -βc (mV.dec−1) | Ecorr (V/SCE) | Icorr (µAcm−2) | Corrosion Rate (mpy) | |
| AA | 75.5 | 137.8 | −1.381 | 596 | 17.272 | 76.9 | 176.6 | −1.540 | 120.40 | 110.7 |
| 1-P | 72.8 | 16.6 | −1.361 | 9.096 | 0.2654 | 31.0 | 145.3 | −1.460 | 84.46 | 77.6 |
| 2-Bc | 73.1 | 220.5 | −1.429 | 44.02 | 0.404 | 60.0 | 169.9 | −1.561 | 102.68 | 94.1 |
| 4-Bc | 28.9 | 82.7 | −1.477 | 5.503 | 0.1605 | 76.8 | 139.9 | −1.552 | 66.03 | 60.6 |
| Ringer | NaCl | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ω. cm2) | CPE1 (Ω−1. sn. cm−2) | RL (Ω. cm2) | Rct (Ω. cm2) | L (H. cm−2) | Rs (Ω. cm2) | CPE1 (Ω−1. sn. cm−2) | RL (Ω. cm2) | Rct (Ω. cm2) | L (H. cm−2) | |
| AA | 75.5 | 137.8 | −1.381 | 596 | 17.272 | 76.9 | 176.6 | −1.540 | 120.40 | 110.7 |
| 1-P | 72.8 | 16.6 | −1.361 | 9.096 | 0.2654 | 31.0 | 145.3 | −1.460 | 84.46 | 77.6 |
| 2-Bc | 73.1 | 220.5 | −1.429 | 44.02 | 0.404 | 60.0 | 169.9 | −1.561 | 102.68 | 94.1 |
| 4-Bc | 28.9 | 82.7 | −1.477 | 5.503 | 0.1605 | 76.8 | 139.9 | −1.552 | 66.03 | 60.6 |
| HV | Yield Stress (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Elongation (EL%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS | TS | ||||||
| CR | PR | CR | PR | ||||
| AA | 52 ± 1 | 52 ± 1 | 80 ± 1 | 238 ± 1 | 20.4 ± 0.25 | ||
| 1-P | 72 ± 1 | 83 ± 0.5 | 76 ± 1 | 82 ± 1.5 | 86 ± 1 | 304 ± 3 | 37 ± 2 |
| 2-Bc | 81 ± 1 | 86 ± 1 | 80 ± 1 | 84 ± 0.5 | 88 ± 2 | 315 ± 2 | 36.6 ± 1.5 |
| 4-Bc | 90 ± 0.5 | 97 ± 0.5 | 87 ± 0.5 | 93 ± 1 | 96 ± 2 | 340 ± 2 | 28 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alateyah, A.I.; Alawad, M.O.; Aljohani, T.A.; El-Garaihy, W.H. Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents. Materials 2022, 15, 5515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165515
Alateyah AI, Alawad MO, Aljohani TA, El-Garaihy WH. Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents. Materials. 2022; 15(16):5515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165515
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlateyah, Abdulrahman I., Majed O. Alawad, Talal A. Aljohani, and Waleed H. El-Garaihy. 2022. "Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents" Materials 15, no. 16: 5515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165515
APA StyleAlateyah, A. I., Alawad, M. O., Aljohani, T. A., & El-Garaihy, W. H. (2022). Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents. Materials, 15(16), 5515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165515







